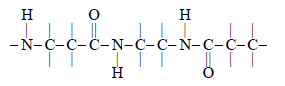All Exams >
NEET >
Organic Chemistry for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Biomolecules for NEET Exam
Synthesis of protein is controlled by:- a)Nucleotide
- b)RNA
- c)DNA
- d)Nucleoside
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Synthesis of protein is controlled by:
a)
Nucleotide
b)
RNA
c)
DNA
d)
Nucleoside
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
RNA can directly control the synthesis of proteins, hence can easily express the characters. DNA, however, is dependent on RNA for synthesis of proteins. The protein synthesising machinery has evolved around RNA.
Proteins can be classified into two types on the basis of their molecular shape i.e., fibrous proteins and globular proteins. Examples of globular proteins are :
(Multiple Answer Correct)
- a)Insulin & Albumin
- b)Myosin
- c)Keratin
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Proteins can be classified into two types on the basis of their molecular shape i.e., fibrous proteins and globular proteins. Examples of globular proteins are :
(Multiple Answer Correct)
(Multiple Answer Correct)
a)
Insulin & Albumin
b)
Myosin
c)
Keratin
d)
None of these

|
Divey Sethi answered |
The correct answer is A and C.
The structure of protein which results when the chain of polypeptides coil around to give a spherical shape are known as globular protein. These proteins are soluble in water, e.g., insulin and albumin are globular protein.
The structure of protein which results when the chain of polypeptides coil around to give a spherical shape are known as globular protein. These proteins are soluble in water, e.g., insulin and albumin are globular protein.
The compound which gives red colour with Fehling’s solution?- a)Cellulose
- b)Benzaldehyde
- c)Cane sugar
- d)Glucose
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The compound which gives red colour with Fehling’s solution?
a)
Cellulose
b)
Benzaldehyde
c)
Cane sugar
d)
Glucose

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
Fehling's solution to make difference between carbohydrate and ketone functional grp and also used for differentiate reducing and non reducing sugar and as u know glucose is a reducing sugar so it will give red colour with fehling's solution (all monosachharides are reducing sugar).
The essential amino acid is:- a)Serine
- b)Arginine
- c)Alanine
- d)Glycine
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The essential amino acid is:
a)
Serine
b)
Arginine
c)
Alanine
d)
Glycine
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
In humans, arginine is classified as a semiessential or conditionally essential amino acid, depending on the developmental stage and health status of the individual. Preterm infants are unable to synthesize or create arginine internally, making the amino acid nutritionally essential for them.
Deficiency of vitamin A results in:- a)Scurvy
- b)Night blindness
- c)Beri-beri
- d)Rickets
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Deficiency of vitamin A results in:
a)
Scurvy
b)
Night blindness
c)
Beri-beri
d)
Rickets
|
|
Mr.perfect answered |
Yup... causes hardening of cornea.
The enzyme pepsin hydrolyses:- a)polysaccharides to monosaccharides
- b)glucose to ethyl alcohol
- c)proteins to amino acids
- d)fats to fatty acids
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The enzyme pepsin hydrolyses:
a)
polysaccharides to monosaccharides
b)
glucose to ethyl alcohol
c)
proteins to amino acids
d)
fats to fatty acids

|
Nidhi Yadav answered |
Pepsin is an enzyme that is primarily found in the stomach and plays a crucial role in the digestion of proteins. It is secreted by the gastric chief cells in an inactive form called pepsinogen, which is then activated by the acidic environment of the stomach. Once activated, pepsin breaks down proteins into smaller peptide fragments and eventually into individual amino acids, which can be absorbed by the body.
Pepsin acts through a process called hydrolysis, which involves the addition of a water molecule to break the peptide bonds that hold the amino acids together in a protein. This process is essential for the body to obtain the necessary amino acids for various physiological functions, such as the synthesis of new proteins, enzyme activity, and hormone production.
To better understand why the correct answer is option 'C' (proteins to amino acids), let's break down the other options and eliminate them:
a) Polysaccharides to monosaccharides: This process is actually carried out by enzymes called amylases, not pepsin. Amylases are found in saliva and pancreatic secretions and are responsible for breaking down complex carbohydrates (polysaccharides) into simpler sugars (monosaccharides) such as glucose.
b) Glucose to ethyl alcohol: This process is not mediated by pepsin but rather by a different enzyme called yeast. Yeast is able to convert glucose into ethyl alcohol through a process called fermentation.
d) Fats to fatty acids: The digestion of fats involves the action of enzymes called lipases, not pepsin. Lipases break down fats (triglycerides) into fatty acids and glycerol, which can then be absorbed by the body.
In summary, pepsin is specifically responsible for hydrolyzing proteins into amino acids. This process is crucial for the body to obtain the necessary building blocks for protein synthesis and various other physiological functions.
Pepsin acts through a process called hydrolysis, which involves the addition of a water molecule to break the peptide bonds that hold the amino acids together in a protein. This process is essential for the body to obtain the necessary amino acids for various physiological functions, such as the synthesis of new proteins, enzyme activity, and hormone production.
To better understand why the correct answer is option 'C' (proteins to amino acids), let's break down the other options and eliminate them:
a) Polysaccharides to monosaccharides: This process is actually carried out by enzymes called amylases, not pepsin. Amylases are found in saliva and pancreatic secretions and are responsible for breaking down complex carbohydrates (polysaccharides) into simpler sugars (monosaccharides) such as glucose.
b) Glucose to ethyl alcohol: This process is not mediated by pepsin but rather by a different enzyme called yeast. Yeast is able to convert glucose into ethyl alcohol through a process called fermentation.
d) Fats to fatty acids: The digestion of fats involves the action of enzymes called lipases, not pepsin. Lipases break down fats (triglycerides) into fatty acids and glycerol, which can then be absorbed by the body.
In summary, pepsin is specifically responsible for hydrolyzing proteins into amino acids. This process is crucial for the body to obtain the necessary building blocks for protein synthesis and various other physiological functions.
Alpha helix is found in- a)RNA
- b)Lipid
- c)Carbohydrates
- d)secondary proteins
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Alpha helix is found in
a)
RNA
b)
Lipid
c)
Carbohydrates
d)
secondary proteins
|
|
Ræjû Bhæï answered |
The alpha helix (α-helix) is a common motif in the secondary structure of proteins and is a right hand-helix conformation in which every backbone N−H group hydrogen bonds to the backbone C=O. group of the amino acid located three or four residues earlier along the protein sequence.
Haemoglobin is an example of:- a)Quaternary Structure of protein
- b)Tertiary Structure of protein
- c)Primary Structure of protein
- d)Seconary Structure of protein
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Haemoglobin is an example of:
a)
Quaternary Structure of protein
b)
Tertiary Structure of protein
c)
Primary Structure of protein
d)
Seconary Structure of protein
|
|
Om Desai answered |
The correct answer is A
Haemoglobin is a Quaternary protein because it has 4 polypeptide structures - 2alpha and 2 beta.
Haemoglobin is a Quaternary protein because it has 4 polypeptide structures - 2alpha and 2 beta.
Which base is present in RNA but not in DNA ? [AIEEE-2004] - a)Uracil
- b)Cytosine
- c)Guanine
- d)Thymine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which base is present in RNA but not in DNA ?
[AIEEE-2004]
a)
Uracil
b)
Cytosine
c)
Guanine
d)
Thymine
|
|
Shreya Singh answered |
It's Uracil....Uracil is present in RNA. but not in DNA ....whereas Thymine is present in DNA and not in RNA ..
The active form of vitamin D is:- a)Calcidiol
- b)Calcitriol
- c)Cholecalciferol
- d)Any of the above
- e)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The active form of vitamin D is:
a)
Calcidiol
b)
Calcitriol
c)
Cholecalciferol
d)
Any of the above
e)
None of the above

|
Rajdeep Saini answered |
The active form of vitamin D is calcitriol.
Calcitriol, also known as 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, is the active form of vitamin D in the body. It is the biologically active metabolite that is synthesized from calcidiol, also known as 25-hydroxyvitamin D3, which is the storage form of vitamin D.
Explanation:
1. Vitamin D and its forms:
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in maintaining bone health and calcium homeostasis. It exists in several forms, including vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol), which are obtained from dietary sources or synthesized in the skin upon exposure to sunlight.
2. Conversion of vitamin D to its active form:
When vitamin D2 or D3 is ingested or synthesized, it undergoes a series of metabolic conversions in the liver and kidneys to become the active form of vitamin D. The first step involves hydroxylation in the liver, where vitamin D is converted to calcidiol (25-hydroxyvitamin D3) through the action of the enzyme 25-hydroxylase.
3. Activation of calcidiol to calcitriol:
The second and final step in the activation of vitamin D occurs in the kidneys. Calcidiol undergoes further hydroxylation by the enzyme 1-alpha-hydroxylase, resulting in the formation of calcitriol (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3). This conversion is tightly regulated by various factors, including parathyroid hormone (PTH), calcium levels, and phosphate levels.
4. Biological functions of calcitriol:
Calcitriol acts as a hormone and binds to the vitamin D receptor (VDR) in target tissues, such as the intestines, bones, and kidneys. It regulates the absorption of calcium and phosphate in the intestines, promotes bone mineralization by increasing calcium and phosphate uptake, and helps maintain normal blood calcium levels. Calcitriol also has non-skeletal functions, including modulation of immune responses and cell growth.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the active form of vitamin D is calcitriol, which is synthesized from calcidiol through the action of 1-alpha-hydroxylase in the kidneys. Calcitriol plays a crucial role in maintaining calcium homeostasis and bone health, as well as other physiological processes in the body.
Calcitriol, also known as 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, is the active form of vitamin D in the body. It is the biologically active metabolite that is synthesized from calcidiol, also known as 25-hydroxyvitamin D3, which is the storage form of vitamin D.
Explanation:
1. Vitamin D and its forms:
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in maintaining bone health and calcium homeostasis. It exists in several forms, including vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol), which are obtained from dietary sources or synthesized in the skin upon exposure to sunlight.
2. Conversion of vitamin D to its active form:
When vitamin D2 or D3 is ingested or synthesized, it undergoes a series of metabolic conversions in the liver and kidneys to become the active form of vitamin D. The first step involves hydroxylation in the liver, where vitamin D is converted to calcidiol (25-hydroxyvitamin D3) through the action of the enzyme 25-hydroxylase.
3. Activation of calcidiol to calcitriol:
The second and final step in the activation of vitamin D occurs in the kidneys. Calcidiol undergoes further hydroxylation by the enzyme 1-alpha-hydroxylase, resulting in the formation of calcitriol (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3). This conversion is tightly regulated by various factors, including parathyroid hormone (PTH), calcium levels, and phosphate levels.
4. Biological functions of calcitriol:
Calcitriol acts as a hormone and binds to the vitamin D receptor (VDR) in target tissues, such as the intestines, bones, and kidneys. It regulates the absorption of calcium and phosphate in the intestines, promotes bone mineralization by increasing calcium and phosphate uptake, and helps maintain normal blood calcium levels. Calcitriol also has non-skeletal functions, including modulation of immune responses and cell growth.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the active form of vitamin D is calcitriol, which is synthesized from calcidiol through the action of 1-alpha-hydroxylase in the kidneys. Calcitriol plays a crucial role in maintaining calcium homeostasis and bone health, as well as other physiological processes in the body.
Buna-N synthetic rubber is a copolymer of - [AIEEE 2009]- a)
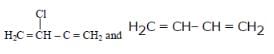
- b)H2C=CH – CH = CH2 and H5C6 – CH = CH2
- c)H2C = CH – CN and H2C = CH – CH = CH2
- d)
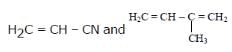
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Buna-N synthetic rubber is a copolymer of -
[AIEEE 2009]
a)
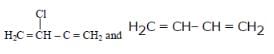
b)
H2C=CH – CH = CH2 and H5C6 – CH = CH2
c)
H2C = CH – CN and H2C = CH – CH = CH2
d)
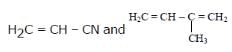
|
|
Vivek Rana answered |
The correct answer is option C
Buna - N is a copolymer of acrylonitrile (H2C= CH– CN ) and buta-1,3-diene(H2C= CH – CH=CH2).
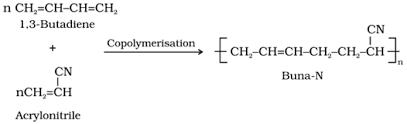
Buna - N is a copolymer of acrylonitrile (H2C= CH– CN ) and buta-1,3-diene(H2C= CH – CH=CH2).
Process which leads to the synthesis of RNA is called- a)Termination
- b)Replication
- c)Transcription
- d)Translation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Process which leads to the synthesis of RNA is called
a)
Termination
b)
Replication
c)
Transcription
d)
Translation

|
Srishti Raghuwanshi answered |
DNA TO DNA - replication
DNA TO RNA-transcription
RNA TO PROTEIN-translation
DNA TO RNA-transcription
RNA TO PROTEIN-translation
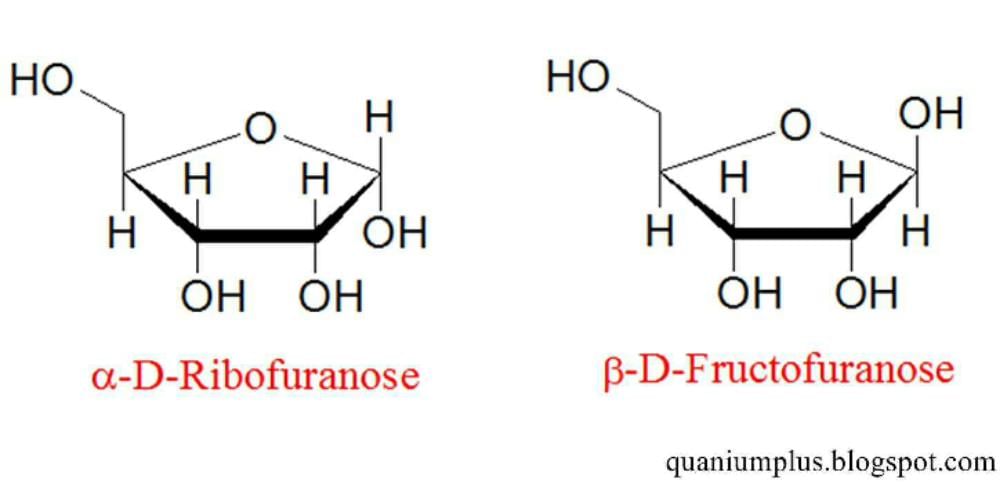
Glucose and fructose are:- a)Position isomers
- b)Functional isomers
- c)Chain isomers
- d)Optical isomers
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Glucose and fructose are:
a)
Position isomers
b)
Functional isomers
c)
Chain isomers
d)
Optical isomers
|
|
Tanvi Bose answered |
Glucose and fructose are functional isomers of each other Because they have same molecular formula that is C6H12O6 But different functional group in their chemical formula. Glucose has aldehyde group while fructose has ketone as functional group.
Purine derivative among the following bases is:- a)Uracil
- b)Cytosine
- c)Guanine
- d)Thymine
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Purine derivative among the following bases is:
a)
Uracil
b)
Cytosine
c)
Guanine
d)
Thymine
|
|
Shail Chawla answered |
Purine is a type of nitrogenous base found in DNA and RNA molecules. The purine bases are adenine and guanine. Among the given options, the purine derivative is:
c) Guanine
Explanation:
- Purine and pyrimidine are two types of nitrogenous bases found in DNA and RNA molecules.
- Purine bases are larger and have a double-ring structure, while pyrimidine bases are smaller and have a single-ring structure.
- Adenine and guanine are purine bases, while cytosine, thymine, and uracil are pyrimidine bases.
- Therefore, among the given options, the purine derivative is guanine.
c) Guanine
Explanation:
- Purine and pyrimidine are two types of nitrogenous bases found in DNA and RNA molecules.
- Purine bases are larger and have a double-ring structure, while pyrimidine bases are smaller and have a single-ring structure.
- Adenine and guanine are purine bases, while cytosine, thymine, and uracil are pyrimidine bases.
- Therefore, among the given options, the purine derivative is guanine.
Name the RNA molecules which is used to carry genetic information copied from DNA?- a)tRNA
- b)mRNA
- c)rRNA
- d)snRNA
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Name the RNA molecules which is used to carry genetic information copied from DNA?
a)
tRNA
b)
mRNA
c)
rRNA
d)
snRNA
|
|
Raushani Praween answered |
Because mRNA is called messanger RNA, which carries the information from DNA to synthesis of protein and other essential products in cell.
Which of the following terms are correct about enzyme?
- a)Proteins
- b)Dinucleotides
- c)carbohydrates
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following terms are correct about enzyme?
a)
Proteins
b)
Dinucleotides
c)
carbohydrates
d)
None of these
|
|
Suresh Kumar answered |
Enzymes are made up of proteins...but Ribozyme is an exception to this as its made up of 23 sr RNA which is a nucleic acid...
And enzymes acts as biocatalyst...
so; more accurately option d comes out to be the answer.
And enzymes acts as biocatalyst...
so; more accurately option d comes out to be the answer.
Which of the following carbohydrate is an example of an oligosaccharide?- a)Cellulose
- b)Lactose
- c)Mannose
- d)Glucose
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following carbohydrate is an example of an oligosaccharide?
a)
Cellulose
b)
Lactose
c)
Mannose
d)
Glucose
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Lactose intolerance is the inability to break down a type of natural sugar called lactose. Lactose is commonly found in dairy products, such as milk and yogurt. A person becomes lactose intolerant when his or her small intestine stops making enough of the enzyme lactase to digest and break down the lactose.
Nucleoside differs from nucleotide with the absence of:- a)Pentose sugar and Nitrogenous base
- b)Nitrogenous base
- c)Phosphoric acid
- d)Pentose sugar
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Nucleoside differs from nucleotide with the absence of:
a)
Pentose sugar and Nitrogenous base
b)
Nitrogenous base
c)
Phosphoric acid
d)
Pentose sugar
|
|
Arun Khanna answered |
The structure of nucleotide and nucleoside units are distinguished primarily by the presence (or lack thereof) of this phosphate group. Deoxyribose in DNA differs from the ribose found in RNA in that it has only a hydrogen atom in the same position that ribose has a hydroxyl (-OH) group.
In DNA, the complimentary bases are: [2008]- a)Adenine and thymine; guanine andcytosine
- b)Adenine and thymine ; guanine and uracil
- c)Adenine and guanine; thymine andcytosine
- d)Uracil and adenine; cytosine and guanine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In DNA, the complimentary bases are: [2008]
a)
Adenine and thymine; guanine andcytosine
b)
Adenine and thymine ; guanine and uracil
c)
Adenine and guanine; thymine andcytosine
d)
Uracil and adenine; cytosine and guanine

|
Prashanth Dasgupta answered |
In DNA the complimentary base are
Adenine and thymine.
Guanine and cytosine
The genetic information for cell is contained
in the sequence of bases A, T, G and C in
DNA molecule.
Adenine and thymine.
Guanine and cytosine
The genetic information for cell is contained
in the sequence of bases A, T, G and C in
DNA molecule.
Hydrolysis of sucrose is called:- a)Hydration
- b)Inversion
- c)Esterification
- d)Saponification
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Hydrolysis of sucrose is called:
a)
Hydration
b)
Inversion
c)
Esterification
d)
Saponification

|
Sahana Savalagi answered |
Hydrolysis of sucrose is inversion because the angle of specific rotation of the plane polarized light changes from positive to negative value due to the presence of optical isomers of mixture of glucose and fructose sugar...
On hydrolysis, proteins give:- a)Amides
- b)Amino acids
- c)Nucleotides
- d)Nucleosides
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
On hydrolysis, proteins give:
a)
Amides
b)
Amino acids
c)
Nucleotides
d)
Nucleosides

|
Aiims answered |
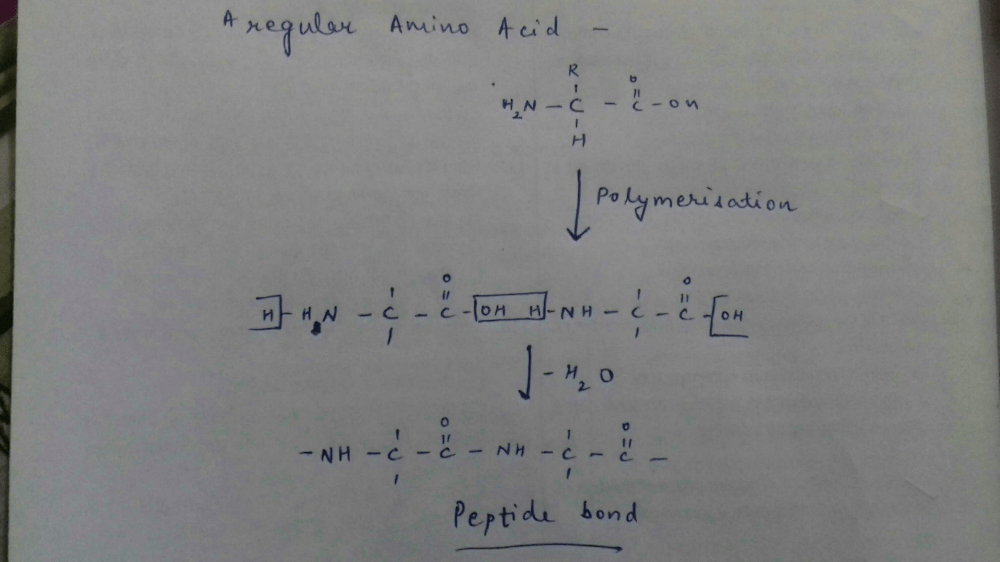
Proteins are polymers of amino acids therefore their hydrolysis gives amino acids
Coordination compounds have great importance in biological systems, In this context which of the following
statements is incorrect ? [AIEEE-2004]- a)Chlorophylls are green pigments in plants and contain calcium
- b)haemoglobin is the red pigment of blood and contains iron
- c)Cyanocobalamin is B12 and contains cobalt
- d)Carboxypeptidase–A is an enzyme and contains zinc
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Coordination compounds have great importance in biological systems, In this context which of the following
statements is incorrect ?
statements is incorrect ?
[AIEEE-2004]
a)
Chlorophylls are green pigments in plants and contain calcium
b)
haemoglobin is the red pigment of blood and contains iron
c)
Cyanocobalamin is B12 and contains cobalt
d)
Carboxypeptidase–A is an enzyme and contains zinc

|
Wrong Click answered |
Bcox chlorophyll is a coordination compound of Magnesium not calcium
Carbohydrates are classified on the basis of their behaviour on hydrolysis and also as reducing or non-reducing sugar. Sucrose is a __________.
- a)monosaccharide
- b)disaccharide
- c)non-reducing sugar
- d)Both b and c
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Carbohydrates are classified on the basis of their behaviour on hydrolysis and also as reducing or non-reducing sugar. Sucrose is a __________.
a)
monosaccharide
b)
disaccharide
c)
non-reducing sugar
d)
Both b and c

|
Divey Sethi answered |
The correct answer is option B & D.
One of the common disaccharides is sucrose which on hydrolysis gives an equimolar mixture of D−(+)− glucose and D−(−) fructose. These two monosaccharides are held together by a glycosidic linkage between Cl of α- glucose and C2 of β- fructose. Since the reducing groups of glucose and fructose are involved in glycosidic bond formation, sucrose is a non-reducing sugar.
One of the common disaccharides is sucrose which on hydrolysis gives an equimolar mixture of D−(+)− glucose and D−(−) fructose. These two monosaccharides are held together by a glycosidic linkage between Cl of α- glucose and C2 of β- fructose. Since the reducing groups of glucose and fructose are involved in glycosidic bond formation, sucrose is a non-reducing sugar.
RNA is different from DNA because RNA contains:
- a)Ribose sugar and thymine
- b)Deoxyribose sugar and thymine
- c)Ribose sugar and uracil
- d)Deoxyribose sugar and uracil
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
RNA is different from DNA because RNA contains:
a)
Ribose sugar and thymine
b)
Deoxyribose sugar and thymine
c)
Ribose sugar and uracil
d)
Deoxyribose sugar and uracil

|
Farhin Saheer answered |
There are two types of pentose sugars- ribose and deoxyribose.The former is present in rna and the latter in dna. In the case of nitrogenous bases uracil is present in rna instead of thymine
The presence or absence of hydroxy group on which carbon atom of sugar differentiates RNA and DNA ?- a)1st
- b)2nd
- c)3rd
- d)4th
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The presence or absence of hydroxy group on which carbon atom of sugar differentiates RNA and DNA ?
a)
1st
b)
2nd
c)
3rd
d)
4th
|
|
Shreya Singh answered |
It's on 2nd carbon ....it is absent in DNA ...whereas it is present in RNA ..
Which of the following base is not found in DNA?- a)Uracil
- b)Guanine
- c)Cytosine
- d)Adenine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following base is not found in DNA?
a)
Uracil
b)
Guanine
c)
Cytosine
d)
Adenine
|
|
Ritu Pal answered |
Uracil is not found in DNA , as it Uracil has more base pair affinity to adenine , guanine and cytosine. Instead thymine is present in DNA.
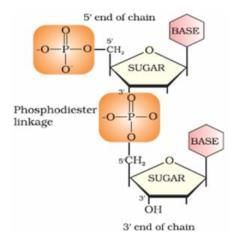
Nucleotides are joined together by 5′ and 3′ carbon atoms of pentose sugar. The linkage is known as:
- a)Glycosidic
- b)Peptide
- c)Hydrogen
- d)Phoshodiester
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Nucleotides are joined together by 5′ and 3′ carbon atoms of pentose sugar. The linkage is known as:

a)
Glycosidic
b)
Peptide
c)
Hydrogen
d)
Phoshodiester
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Nucleotides are joined together by phosphodiester linkage between 5′ and 3′ carbon atoms of pentose sugar.
Three structures are given below in which two glucose units are linked. Which of these linkages between glucose units are between C1 and C4 and which linkages are between C1 and C6?
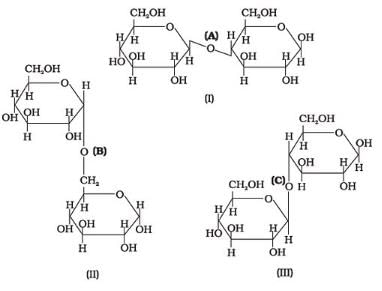
- a)(A) is between C1 and C4, (B) and (C) are between C1 and C6
- b)(A) and (B) are between C1 and C4, (C) is between C1 and C6
- c)(A) and (C) are between C1 and C4, (B) is between C1 and C6
- d)(A) and (C) are between C1 and C6, (B) is between C1 and C4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Three structures are given below in which two glucose units are linked. Which of these linkages between glucose units are between C1 and C4 and which linkages are between C1 and C6?


a)
(A) is between C1 and C4, (B) and (C) are between C1 and C6
b)
(A) and (B) are between C1 and C4, (C) is between C1 and C6
c)
(A) and (C) are between C1 and C4, (B) is between C1 and C6
d)
(A) and (C) are between C1 and C6, (B) is between C1 and C4
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The correct answer is Option C.
(i) The first structure is lactose, the linkage is (A) C1−C4 glycosidic linkage.
(ii) The 2nd structure has C1−C6 linkages.
(iii) The 3rd structure has C1−C4 linkages.
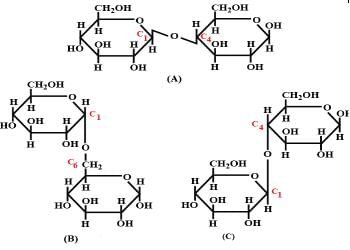
(ii) The 2nd structure has C1−C6 linkages.
(iii) The 3rd structure has C1−C4 linkages.

The oxide linkage formed by the loss of a water molecule when two monosaccharides are joined together through oxygen atom is called:- a)Carboxylic linkage
- b)Carbonyl linkage
- c)Peptide linkage
- d)Glycosidic linkage
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The oxide linkage formed by the loss of a water molecule when two monosaccharides are joined together through oxygen atom is called:
a)
Carboxylic linkage
b)
Carbonyl linkage
c)
Peptide linkage
d)
Glycosidic linkage

|
Aleena Mathew answered |
All sacchrides /carbohydrates form glycosidic bond by eliminating water molecule
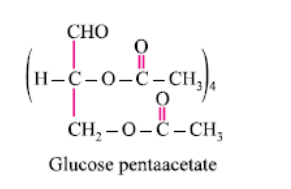
Glucose reacts with acetic anhydride to form:- a)Monoacetate
- b)Diacetate
- c)Pentaacetate
- d) Hexaacetate
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Glucose reacts with acetic anhydride to form:
a)
Monoacetate
b)
Diacetate
c)
Pentaacetate
d)
Hexaacetate
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
It forms glucose pentaacetate. The acetic anhydride esterifies with all the alcohol groups on the glucose ring.

Which of the following statements is correct about Enzymes?- a)Enzymes have optimum activity at body temperature.
- b)Enzymes are carbohydrates.
- c)Enzymes have all these properties.
- d)Enzymes consist of nucleic acid.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is correct about Enzymes?
a)
Enzymes have optimum activity at body temperature.
b)
Enzymes are carbohydrates.
c)
Enzymes have all these properties.
d)
Enzymes consist of nucleic acid.

|
Honey answered |
Yes. option a is correct as enzymes are proteins and contain amino acids and the correct option is only they have optimum activity at body temperature... hope you got it...
Which one of the following does not exhibit thephenomenon of mutarotation ? [2010]- a)(+) – Sucrose
- b)(+) – Lactose
- c)(+) – Maltose
- d)(–) – Fructose
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following does not exhibit thephenomenon of mutarotation ? [2010]
a)
(+) – Sucrose
b)
(+) – Lactose
c)
(+) – Maltose
d)
(–) – Fructose

|
Rajesh Datta answered |
Sucrose does not have free — CHO or
CO group, hence it does not undergo
mutarotation.
CO group, hence it does not undergo
mutarotation.
In which structure of protein, the polypeptide chain forms all possible hydrogen bonds by twisting into right handed screw?- a)Primary structure
- b)Tertiary structure
- c)β-pleated sheet structure
- d)α-helix structure
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In which structure of protein, the polypeptide chain forms all possible hydrogen bonds by twisting into right handed screw?
a)
Primary structure
b)
Tertiary structure
c)
β-pleated sheet structure
d)
α-helix structure
|
|
Swara Sharma answered |
Alpha helix in secondary structure.
The term anomers of glucose refers to – [AIEEE 2006]- a)a mixture of (D)-glucose and (L)-glucose
- b)enantiomers of glucose
- c)isomers of glucose that differ in configuration at carbon one (C-1)
- d)isomers of glucose that differ in configurations at carbons one and four (C-1 and C-4)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The term anomers of glucose refers to –
[AIEEE 2006]
a)
a mixture of (D)-glucose and (L)-glucose
b)
enantiomers of glucose
c)
isomers of glucose that differ in configuration at carbon one (C-1)
d)
isomers of glucose that differ in configurations at carbons one and four (C-1 and C-4)
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
The correct answer is option C
Anomers of glucose are cyclic diastereomers (epimers) differing in configuration at C-l, existing in two forms α and β respectively.

Anomers of glucose are cyclic diastereomers (epimers) differing in configuration at C-l, existing in two forms α and β respectively.

The pyrimidine bases present in DNA are – [AIEEE 2006]- a)cytosine and guanine
- b)cytosine and thymine
- c)cytosine and uracil
- d)cytosine and adenine
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The pyrimidine bases present in DNA are –
[AIEEE 2006]
a)
cytosine and guanine
b)
cytosine and thymine
c)
cytosine and uracil
d)
cytosine and adenine

|
Manoj Sengupta answered |
Thus, in DNA, the purines adenine (A) and guanine (G) pair up with the pyrimidines thymine (T) and cytosine (C), respectively. In RNA, the complement of adenine (A) is uracil (U) instead of thymine (T), so the pairs that form are adenine:uracil and guanine:cytosine.
Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar because:- a)The -CHO group of glucose is not involved in glycosidic bond formation.
- b)Two monosaccharide units are held together by a glycosidic linkage between C1 of α-glucose and C2 of β-fructose.
- c)On hydrolysis, sucrose gives dextrorotatory and laevorotatory and the mixture is laevorotatory.
- d)Sucrose is dextrorotatory.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar because:
a)
The -CHO group of glucose is not involved in glycosidic bond formation.
b)
Two monosaccharide units are held together by a glycosidic linkage between C1 of α-glucose and C2 of β-fructose.
c)
On hydrolysis, sucrose gives dextrorotatory and laevorotatory and the mixture is laevorotatory.
d)
Sucrose is dextrorotatory.
|
|
Gowri Menon answered |
Glucose and C2 of fructose, which does not have a free aldehyde or ketone group to undergo oxidation and reduction reactions.
c)Sucrose does not react with Benedict's reagent, which is used to detect the presence of reducing sugars.
d)Sucrose cannot be hydrolyzed by acid or enzyme into its constituent monosaccharides.
c)Sucrose does not react with Benedict's reagent, which is used to detect the presence of reducing sugars.
d)Sucrose cannot be hydrolyzed by acid or enzyme into its constituent monosaccharides.
Chapter doubts & questions for Biomolecules - Organic Chemistry for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Biomolecules - Organic Chemistry for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup