All Exams >
NEET >
NCERT Based Tests for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Locomotion and Movement for NEET Exam
Read the following statements carefully and select the correct ones.
(i) Cardiac fibres are branched with one or more nuclei.
(ii) Smooth muscles are unbranched and cylindrical.
(iii) Skeletal muscles can be branched or unbranched.
(iv) Smooth muscles are non-striated.- a)only (iv)
- b)(ii) and (iii)
- c)(iii) and (iv)
- d)only (iii)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements carefully and select the correct ones.
(i) Cardiac fibres are branched with one or more nuclei.
(ii) Smooth muscles are unbranched and cylindrical.
(iii) Skeletal muscles can be branched or unbranched.
(iv) Smooth muscles are non-striated.
(i) Cardiac fibres are branched with one or more nuclei.
(ii) Smooth muscles are unbranched and cylindrical.
(iii) Skeletal muscles can be branched or unbranched.
(iv) Smooth muscles are non-striated.
a)
only (iv)
b)
(ii) and (iii)
c)
(iii) and (iv)
d)
only (iii)
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Smooth muscles are non-striated, unbranched and spindle shaped. Skeletal muscles are unbranched. Cardiac muscles fibres are uni-nucleated.
Which of the following is not a function of vertebral column?- a)Protects spinal cord and supports the head
- b)Serves as the point of attachment for ribs and musculature of the back
- c)Supports tarsals and metacarpals
- d)Both (b) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a function of vertebral column?
a)
Protects spinal cord and supports the head
b)
Serves as the point of attachment for ribs and musculature of the back
c)
Supports tarsals and metacarpals
d)
Both (b) and (c)
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Tarsals and metacarpals are the bones of the limb, therefore, they are the part of appendicular skeleton and not the axial skeleton which consists of vertebral column.
निम्नलिखित में से कौन भारत का पहला स्वदेशी रूप से डिजाइन और विकसित लड़ाकू विमान है?- a)तेजस
- b)गुस्सा
- c)हंसा
- d)सरस
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
निम्नलिखित में से कौन भारत का पहला स्वदेशी रूप से डिजाइन और विकसित लड़ाकू विमान है?
a)
तेजस
b)
गुस्सा
c)
हंसा
d)
सरस
|
|
Meera Kapoor answered |
भारत के 72 वें गणतंत्र दिवस के अवसर पर, आगंतुकों के लिए, लॉकडाउन अवधि के दौरान बहाल किए गए रेल लोकोमोटिव के अपने कलाकृतियों को नेहरू विज्ञान केंद्र, मुंबई ने फिर से समर्पित किया।
- भारत का पहला स्वदेशी रूप से डिजाइन और विकसित लड़ाकू विमान मारुत अब जनता के देखने के लिए उपलब्ध होगा।
- डीसी इलेक्ट्रिक लोको नं 20024 एन वी सी पी 2 को 1938 में ग्रेट इंडियन पेनिनसुलर रेलवे में कमीशन किया गया था और 40 साल तक कल्याण-पुणे सेक्शन पर पैसेंजर ट्रेनों को चलाने के लिए इस्तेमाल किया गया था।
- इसमें मुंबई से पुणे तक प्रतिष्ठित डेक्कन क्वीन के शासन का गौरव है।
- डीसी इलेक्ट्रिक लोको नं 20024 एन वी सी पी 2 भारतीय उप-महाद्वीप में इलेक्ट्रिक ट्रैक्शन की शुरूआत के बाद सेवा में शामिल किए गए पहले इलेक्ट्रिक इंजनों में से एक है
- मारुत को शुरू में सुपरसोनिक गति को पार करने के लिए विकसित किया गया था, लेकिन कभी भी मच 1 को छू नहीं सकता था, इसलिए अब यह रिकॉर्ड तेजस एलसीए के साथ है। कुल 147 मारुत का निर्माण किया गया, और भारतीय वायुसेना ने 1967 में पहली इकाई को शामिल किया। एचएफ -24 मारुत ने 1961 में अपनी पहली उड़ान का संचालन किया। जबकि मारुत ने 1971 के भारत-पाक युद्ध के दौरान लोंगेवाला सीमा पर 1980 के दशक में एक बड़ी भूमिका निभाई। अप्रचलित हो गया और 1990 तक चरणबद्ध हो गया।
Which of the following is/are not correctly matched pairs?
(i) Ball and socket joint — Between humerus and pectoral girdle
(ii) Pivot joint — Between carpal and metacarpal
(iii) Saddle joint — Between atlas and axis
(iv) Gliding joint — Between the carpals
(v) Fibrous joint — In flat skull bones
- a)(ii) and (iii)
- b)(i) and (iv)
- c)(v) only
- d)(ii) only
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is/are not correctly matched pairs?
(i) Ball and socket joint — Between humerus and pectoral girdle
(ii) Pivot joint — Between carpal and metacarpal
(iii) Saddle joint — Between atlas and axis
(iv) Gliding joint — Between the carpals
(v) Fibrous joint — In flat skull bones
(i) Ball and socket joint — Between humerus and pectoral girdle
(ii) Pivot joint — Between carpal and metacarpal
(iii) Saddle joint — Between atlas and axis
(iv) Gliding joint — Between the carpals
(v) Fibrous joint — In flat skull bones
a)
(ii) and (iii)
b)
(i) and (iv)
c)
(v) only
d)
(ii) only
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
Pivot joint — between atlas and axis.
Saddle joint — between carpal and metacarpal.
Saddle joint — between carpal and metacarpal.
Which of the following bones form a link between axial and appendicular skeleton?- a)First rib
- b)Clavicle
- c)Scapula
- d)Both (a) and (b)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following bones form a link between axial and appendicular skeleton?
a)
First rib
b)
Clavicle
c)
Scapula
d)
Both (a) and (b)
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
Clavicle is a bone that forms part of the pectoral girdle (part of appendicular skeleton) linking the scapula to the sternum (part of axial skeleton).
Actin binding sites are located on- a)troponin
- b)tropomyosin
- c)meromyosin
- d)both (b) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Actin binding sites are located on
a)
troponin
b)
tropomyosin
c)
meromyosin
d)
both (b) and (c)
|
|
Sanchita Nair answered |
Meromyosin
- Actin binding sites are primarily located on the meromyosin portion of myosin.
- Meromyosin is a fragment of myosin that consists of the myosin head region.
- The myosin head contains the actin-binding site, which allows myosin to interact with actin during muscle contraction.
Interaction with Actin
- When muscle contraction is initiated, the myosin heads bind to specific sites on actin filaments.
- This binding triggers the movement of myosin along actin, leading to muscle contraction.
- The actin-binding sites on meromyosin play a crucial role in this process by allowing myosin to interact with actin and generate the force necessary for muscle contraction.
Importance of Actin Binding Sites
- The actin binding sites on meromyosin are essential for the functioning of the muscle contraction process.
- Without these binding sites, myosin would not be able to interact with actin and generate the force required for muscle movement.
- Therefore, the actin binding sites on meromyosin are critical for proper muscle function and overall movement in the body.
- Actin binding sites are primarily located on the meromyosin portion of myosin.
- Meromyosin is a fragment of myosin that consists of the myosin head region.
- The myosin head contains the actin-binding site, which allows myosin to interact with actin during muscle contraction.
Interaction with Actin
- When muscle contraction is initiated, the myosin heads bind to specific sites on actin filaments.
- This binding triggers the movement of myosin along actin, leading to muscle contraction.
- The actin-binding sites on meromyosin play a crucial role in this process by allowing myosin to interact with actin and generate the force necessary for muscle contraction.
Importance of Actin Binding Sites
- The actin binding sites on meromyosin are essential for the functioning of the muscle contraction process.
- Without these binding sites, myosin would not be able to interact with actin and generate the force required for muscle movement.
- Therefore, the actin binding sites on meromyosin are critical for proper muscle function and overall movement in the body.
The figures given here represent three different conditions of sarcomeres. Identify these conditions and select the correct option.
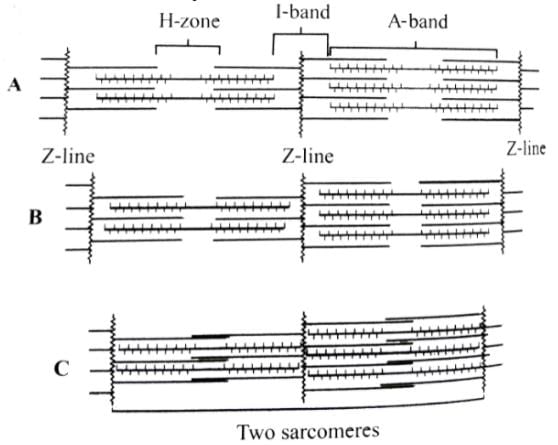
- a)A - Contracting B - Relax C - Maximally contacted
- b)A - Relax B - Contracting C - Maximally contacted
- c)A - Maximally contacted B - Contracting C - Relax
- d)A - Relax B - Contracting C - Contacting
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The figures given here represent three different conditions of sarcomeres. Identify these conditions and select the correct option.


a)
A - Contracting B - Relax C - Maximally contacted
b)
A - Relax B - Contracting C - Maximally contacted
c)
A - Maximally contacted B - Contracting C - Relax
d)
A - Relax B - Contracting C - Contacting
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
In the given figure A, the length of the two sarcomeres is normal i.e., the muscle is in relaxed state. In figure B. the length of sarcomeres, shortens, H-zone narrows and size of l-band decreases i.e., the muscle is contracting. In figure C, the length of sarcomere further shortens and H-zone disappears and l-band further decreases i.e., the muscle is maximally contracted.
Which of the following statements about the molecular arrangement of actin and myosin in myofibrils is/are incorrect?
(i) Each actin (thin filament) is made of 2F (filamentous) actins.
(ii) F-actin is the polymer of G (globular) actin.
(iii) 2F-actins are twisted into a helix.
(iv) Two strands of tropomyosin (protein) lie in the grooves of F-actin.
(v) Troponin molecules (complex proteins) are distributed at regular intervals on the tropomyosin.
(vi) Troponin forms the head of the myosin molecule.
(vii) The myosin is a polymerised protein.- a)(i), (iii) and (vii)
- b)(ii), (iv) and (v)
- c)Only (vi)
- d)Only (iii)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements about the molecular arrangement of actin and myosin in myofibrils is/are incorrect?
(i) Each actin (thin filament) is made of 2F (filamentous) actins.
(ii) F-actin is the polymer of G (globular) actin.
(iii) 2F-actins are twisted into a helix.
(iv) Two strands of tropomyosin (protein) lie in the grooves of F-actin.
(v) Troponin molecules (complex proteins) are distributed at regular intervals on the tropomyosin.
(vi) Troponin forms the head of the myosin molecule.
(vii) The myosin is a polymerised protein.
(i) Each actin (thin filament) is made of 2F (filamentous) actins.
(ii) F-actin is the polymer of G (globular) actin.
(iii) 2F-actins are twisted into a helix.
(iv) Two strands of tropomyosin (protein) lie in the grooves of F-actin.
(v) Troponin molecules (complex proteins) are distributed at regular intervals on the tropomyosin.
(vi) Troponin forms the head of the myosin molecule.
(vii) The myosin is a polymerised protein.
a)
(i), (iii) and (vii)
b)
(ii), (iv) and (v)
c)
Only (vi)
d)
Only (iii)
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
A complex troponin protein of three globular peptides (Troponin T - Binding to tropomyosin as well as to the other two troponin components; Troponin I - inhibiting the F-actin - myosin interaction, also binding to other components of troponin; Troponin C - calcium binding polypeptide) is distributed at regular intervals on the tropomyosin. In the resting stage of muscle fibre, a sub - unit of troponin masks the active sites for myosin on the actin filaments.
The functional unit of contractile system in a striated muscle is- a)sarcomere
- b)Z-band
- c)cross bridges
- d)myofibril
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The functional unit of contractile system in a striated muscle is
a)
sarcomere
b)
Z-band
c)
cross bridges
d)
myofibril
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Sarcomere is the functional unit of myofibril. It contains two types of protein filaments called actin and myosin. These filaments slide upon each other to bring about the contraction of the muscles.
Appendicular skeleton includes- a)girdles and their limbs
- b)vertebrae
- c)skull and vertebral column
- d)ribs and sternum
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Appendicular skeleton includes
a)
girdles and their limbs
b)
vertebrae
c)
skull and vertebral column
d)
ribs and sternum
|
|
Gitanjali Dasgupta answered |
Appendicular skeleton includes
The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the limbs and their associated girdles. It is one of the two main divisions of the human skeleton, with the other being the axial skeleton. The appendicular skeleton provides support and enables movement of the limbs.
1. Girdles
The appendicular skeleton includes two girdles: the pectoral girdle and the pelvic girdle.
- Pectoral Girdle: The pectoral girdle, also known as the shoulder girdle, consists of the clavicle (collarbone) and the scapula (shoulder blade). It connects the upper limbs to the axial skeleton, allowing for the movement of the arms and shoulders.
- Pelvic Girdle: The pelvic girdle, also known as the hip girdle, consists of two hip bones, also called coxal bones or innominate bones. The pelvic girdle connects the lower limbs to the axial skeleton and supports the weight of the body.
2. Limbs
The appendicular skeleton also includes the bones of the limbs, including the upper limbs (arms) and the lower limbs (legs).
- Upper Limbs: The upper limbs consist of the humerus (upper arm bone), radius and ulna (forearm bones), carpals (wrist bones), metacarpals (hand bones), and phalanges (finger bones). These bones provide support and allow for various movements of the arms, hands, and fingers.
- Lower Limbs: The lower limbs consist of the femur (thigh bone), tibia and fibula (leg bones), tarsals (ankle bones), metatarsals (foot bones), and phalanges (toe bones). These bones provide support and enable movements such as walking, running, and jumping.
3. Function
The appendicular skeleton plays a crucial role in maintaining posture, supporting the body's weight, and facilitating movement. The girdles connect the limbs to the axial skeleton and provide a stable base for the movement of the arms and legs. The bones of the limbs allow for various movements and actions, such as reaching, grasping, walking, running, and performing fine motor skills.
4. Conclusion
In conclusion, the appendicular skeleton includes the girdles and the bones of the limbs. It provides support, stability, and enables movement of the limbs, allowing for a wide range of activities and functions.
The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the limbs and their associated girdles. It is one of the two main divisions of the human skeleton, with the other being the axial skeleton. The appendicular skeleton provides support and enables movement of the limbs.
1. Girdles
The appendicular skeleton includes two girdles: the pectoral girdle and the pelvic girdle.
- Pectoral Girdle: The pectoral girdle, also known as the shoulder girdle, consists of the clavicle (collarbone) and the scapula (shoulder blade). It connects the upper limbs to the axial skeleton, allowing for the movement of the arms and shoulders.
- Pelvic Girdle: The pelvic girdle, also known as the hip girdle, consists of two hip bones, also called coxal bones or innominate bones. The pelvic girdle connects the lower limbs to the axial skeleton and supports the weight of the body.
2. Limbs
The appendicular skeleton also includes the bones of the limbs, including the upper limbs (arms) and the lower limbs (legs).
- Upper Limbs: The upper limbs consist of the humerus (upper arm bone), radius and ulna (forearm bones), carpals (wrist bones), metacarpals (hand bones), and phalanges (finger bones). These bones provide support and allow for various movements of the arms, hands, and fingers.
- Lower Limbs: The lower limbs consist of the femur (thigh bone), tibia and fibula (leg bones), tarsals (ankle bones), metatarsals (foot bones), and phalanges (toe bones). These bones provide support and enable movements such as walking, running, and jumping.
3. Function
The appendicular skeleton plays a crucial role in maintaining posture, supporting the body's weight, and facilitating movement. The girdles connect the limbs to the axial skeleton and provide a stable base for the movement of the arms and legs. The bones of the limbs allow for various movements and actions, such as reaching, grasping, walking, running, and performing fine motor skills.
4. Conclusion
In conclusion, the appendicular skeleton includes the girdles and the bones of the limbs. It provides support, stability, and enables movement of the limbs, allowing for a wide range of activities and functions.
A cricket player is fast chasing a ball in the field. Which one of the following groups of bones are directly contributing in this movement?- a)Femur, malleus, tibia, metatarsals
- b)Pelvis, ulna, patella, tarsals
- c)Sternum, femur, tibia, fibula
- d)Tarsals, femur, metatarsals, tibia
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A cricket player is fast chasing a ball in the field. Which one of the following groups of bones are directly contributing in this movement?
a)
Femur, malleus, tibia, metatarsals
b)
Pelvis, ulna, patella, tarsals
c)
Sternum, femur, tibia, fibula
d)
Tarsals, femur, metatarsals, tibia
|
|
Kabir Verma answered |
Trasals, femur, metatarsals and tibia are bones of the legs which are involved in running during chasing the ball by a cricket player.
Smallest bone in human system is- a)stapes
- b)patella
- c)malleus
- d)incus
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Smallest bone in human system is
a)
stapes
b)
patella
c)
malleus
d)
incus
|
|
Yash Shah answered |
Smallest Bone in Human System - Stapes
The smallest bone in the human body is called the stapes. It is located in the middle ear and is one of the three tiny bones known as the ossicles. The stapes is also commonly referred to as the stirrup bone due to its stirrup-like shape.
Function of Stapes
The primary function of the stapes is to transmit sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear. It plays a crucial role in the process of hearing by amplifying and transferring sound waves through the middle ear.
Size and Structure
Despite its small size, the stapes is a significant component of the auditory system. It measures approximately 3 millimeters in length and resembles a stirrup, with a head, neck, and two branches known as the crura.
Importance in Hearing
The stapes is vital for the process of hearing as it helps convert sound waves into mechanical vibrations that can be interpreted by the brain. Any damage or abnormalities in the stapes can lead to hearing loss or other auditory problems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the stapes is the smallest bone in the human body and plays a crucial role in the auditory system. Its small size belies its importance in the process of hearing, making it an essential component of the middle ear.
The smallest bone in the human body is called the stapes. It is located in the middle ear and is one of the three tiny bones known as the ossicles. The stapes is also commonly referred to as the stirrup bone due to its stirrup-like shape.
Function of Stapes
The primary function of the stapes is to transmit sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear. It plays a crucial role in the process of hearing by amplifying and transferring sound waves through the middle ear.
Size and Structure
Despite its small size, the stapes is a significant component of the auditory system. It measures approximately 3 millimeters in length and resembles a stirrup, with a head, neck, and two branches known as the crura.
Importance in Hearing
The stapes is vital for the process of hearing as it helps convert sound waves into mechanical vibrations that can be interpreted by the brain. Any damage or abnormalities in the stapes can lead to hearing loss or other auditory problems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the stapes is the smallest bone in the human body and plays a crucial role in the auditory system. Its small size belies its importance in the process of hearing, making it an essential component of the middle ear.
Out of the following pairs of the human skeletal parts, identify the wrongly matched pair- a)Sternum and ribs - Axial skeleton
- b)Clavicle and glenoid cavity - Pelvic girdle
- c)Humerus and ulna - Appendicular skeleton
- d)Malleus and stapes - Ear ossicles
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Out of the following pairs of the human skeletal parts, identify the wrongly matched pair
a)
Sternum and ribs - Axial skeleton
b)
Clavicle and glenoid cavity - Pelvic girdle
c)
Humerus and ulna - Appendicular skeleton
d)
Malleus and stapes - Ear ossicles
|
|
Kabir Verma answered |
Clavicle and glenoid cavity are skeletal parts pelvic girdle.
The joints between the carpal bones are- a)gliding joints
- b)hinge joints
- c)saddle joints
- d)pivot joints
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The joints between the carpal bones are
a)
gliding joints
b)
hinge joints
c)
saddle joints
d)
pivot joints
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Joints between carpal bones are gliding joints. A gliding joint is a type of synovial joint whose articular surface is usually flat, permitting only back-and-forth and side-to-side movements.
During muscular contraction, which of the following events occur?
(I) H-zoned is appears
(ii) A band widens
(iii) I band reduces in width
(iv) Width of A band is unaffected
(v) M line and Z line come closer.- a)(i), (iii), (iv) and (v)
- b)(i), (ii) and (v)
- c)(ii), (iv) and (v)
- d)(i), (ii) and (iii)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
During muscular contraction, which of the following events occur?
(I) H-zoned is appears
(ii) A band widens
(iii) I band reduces in width
(iv) Width of A band is unaffected
(v) M line and Z line come closer.
(I) H-zoned is appears
(ii) A band widens
(iii) I band reduces in width
(iv) Width of A band is unaffected
(v) M line and Z line come closer.
a)
(i), (iii), (iv) and (v)
b)
(i), (ii) and (v)
c)
(ii), (iv) and (v)
d)
(i), (ii) and (iii)
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
Muscle contraction is brought about by sliding movement of actin filaments over myosin filaments. When a muscle fibril contracts, ita A band remain constant and I band shortens. H zone also disappears as the actin filaments of both sides in each sarcomere overlap each other at M-line. M-line and Z-line also come closer.
Which of the following is incorrect regarding muscle contraction?- a)Actin and myosin make actomyosin.
- b)Phosphate reserve comes from phosphocreatine.
- c)Chemical energy is converted into mechanical energy.
- d)Mechanical energy is converted into chemical energy.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is incorrect regarding muscle contraction?
a)
Actin and myosin make actomyosin.
b)
Phosphate reserve comes from phosphocreatine.
c)
Chemical energy is converted into mechanical energy.
d)
Mechanical energy is converted into chemical energy.
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
During muscle contraction, chemical energy is converted into mechanical energy.
The type of muscle fibre present in the wall of alimentary canal is- a)smooth muscle fibre
- b)striped muscle fibre
- c)cardiac muscle fibre
- d)both (a) and (b)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The type of muscle fibre present in the wall of alimentary canal is
a)
smooth muscle fibre
b)
striped muscle fibre
c)
cardiac muscle fibre
d)
both (a) and (b)
|
|
Sameer Roy answered |
Understanding Muscle Fibres in the Alimentary Canal
The alimentary canal, also known as the digestive tract, plays a crucial role in the digestion and absorption of food. The type of muscle fibres present in its walls is primarily smooth muscle fibres.
Characteristics of Smooth Muscle Fibres:
- Involuntary Control: Smooth muscle operates without conscious control, making it essential for the automatic functioning of the digestive system.
- Non-Striated Appearance: Unlike skeletal muscle, smooth muscle fibres lack the striations that are characteristic of striped (skeletal) muscle, giving them a uniform appearance.
- Location: Smooth muscle is found in various organs, including the stomach, intestines, and blood vessels, where it facilitates involuntary movements.
Functions in the Alimentary Canal:
- Peristalsis: Smooth muscle fibres contract rhythmically to propel food through the digestive tract in a process called peristalsis.
- Regulation of Digestive Processes: These muscles help regulate the movement of food, controlling the rate at which it passes through different sections of the alimentary canal.
Other Muscle Types:
- Striped Muscle Fibres: Found in skeletal muscles, these are under voluntary control and are not present in the alimentary canal.
- Cardiac Muscle Fibres: These are specific to the heart and are also involuntary, but they do not play a role in the alimentary canal.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 'A' because the wall of the alimentary canal is predominantly made up of smooth muscle fibres, which are essential for the digestive processes. Understanding the types of muscle fibres helps in comprehending their roles in human physiology, particularly in digestion.
The alimentary canal, also known as the digestive tract, plays a crucial role in the digestion and absorption of food. The type of muscle fibres present in its walls is primarily smooth muscle fibres.
Characteristics of Smooth Muscle Fibres:
- Involuntary Control: Smooth muscle operates without conscious control, making it essential for the automatic functioning of the digestive system.
- Non-Striated Appearance: Unlike skeletal muscle, smooth muscle fibres lack the striations that are characteristic of striped (skeletal) muscle, giving them a uniform appearance.
- Location: Smooth muscle is found in various organs, including the stomach, intestines, and blood vessels, where it facilitates involuntary movements.
Functions in the Alimentary Canal:
- Peristalsis: Smooth muscle fibres contract rhythmically to propel food through the digestive tract in a process called peristalsis.
- Regulation of Digestive Processes: These muscles help regulate the movement of food, controlling the rate at which it passes through different sections of the alimentary canal.
Other Muscle Types:
- Striped Muscle Fibres: Found in skeletal muscles, these are under voluntary control and are not present in the alimentary canal.
- Cardiac Muscle Fibres: These are specific to the heart and are also involuntary, but they do not play a role in the alimentary canal.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 'A' because the wall of the alimentary canal is predominantly made up of smooth muscle fibres, which are essential for the digestive processes. Understanding the types of muscle fibres helps in comprehending their roles in human physiology, particularly in digestion.
Acromion process is characteristically found in the __________ of mammals.- a)pectoral girdle
- b)sperm
- c)pelvic girdle
- d)skull
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Acromion process is characteristically found in the __________ of mammals.
a)
pectoral girdle
b)
sperm
c)
pelvic girdle
d)
skull
|
|
Kabir Verma answered |
Each pectoral girdle consists of two bones -1 clavicle and 1 scapula. The scapula consists of a sharp ridge, the spine and a triangular body. The end of the spine projects as a flattened and expanded process called acromion. This process articulates with the clavicle
The coxal of the pelvic girdle is formed by the fusion of- a)ilium, ischium and pubis
- b)scapula and clavicle
- c)ilium and scapula
- d)ilium, scapula and ischium
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The coxal of the pelvic girdle is formed by the fusion of
a)
ilium, ischium and pubis
b)
scapula and clavicle
c)
ilium and scapula
d)
ilium, scapula and ischium
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
The pelvic girdle is composed of two coxal (hip) bones. Each coxal bone consists of three separate parts: the ilium (short and straight bone), the ischium (lower elongated bone running parallel to vertebral column) and the pubis (inner smaller bone).
Humerus with Its rounded upper end (head) articulates into:- a)acromion process
- b)deltoid cavity
- c)glenoid cavity
- d)acetabulum
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Humerus with Its rounded upper end (head) articulates into:
a)
acromion process
b)
deltoid cavity
c)
glenoid cavity
d)
acetabulum
|
|
Sharmila Khanna answered |
The correct answer for this question is option 'C' - glenoid cavity. Let's understand why the humerus articulates with the glenoid cavity.
Head of the Humerus:
The humerus is the long bone that forms the upper arm. It consists of a rounded upper end called the head, which is located proximally.
Articulation with the Glenoid Cavity:
The glenoid cavity is a shallow, concave socket located on the lateral side of the scapula. It forms the glenohumeral joint, commonly known as the shoulder joint. The head of the humerus articulates with the glenoid cavity to form this joint.
Explanation:
When the rounded head of the humerus articulates with the glenoid cavity, it allows for a wide range of movement in the shoulder joint. The shallow nature of the glenoid cavity provides stability to the joint while allowing for flexibility and mobility.
The articulation between the humerus and the glenoid cavity is a synovial joint, which means it is surrounded by a joint capsule filled with synovial fluid. This fluid lubricates the joint, reducing friction and allowing for smooth movement.
Importance of the Glenohumeral Joint:
The glenohumeral joint is one of the most mobile joints in the human body. It allows for movements such as flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, medial and lateral rotation, and circumduction of the arm. This joint plays a crucial role in activities that involve reaching, lifting, throwing, and other arm movements.
Conclusion:
In summary, the rounded upper end (head) of the humerus articulates with the glenoid cavity of the scapula to form the glenohumeral joint. This joint provides stability and allows for a wide range of movements in the shoulder.
Head of the Humerus:
The humerus is the long bone that forms the upper arm. It consists of a rounded upper end called the head, which is located proximally.
Articulation with the Glenoid Cavity:
The glenoid cavity is a shallow, concave socket located on the lateral side of the scapula. It forms the glenohumeral joint, commonly known as the shoulder joint. The head of the humerus articulates with the glenoid cavity to form this joint.
Explanation:
When the rounded head of the humerus articulates with the glenoid cavity, it allows for a wide range of movement in the shoulder joint. The shallow nature of the glenoid cavity provides stability to the joint while allowing for flexibility and mobility.
The articulation between the humerus and the glenoid cavity is a synovial joint, which means it is surrounded by a joint capsule filled with synovial fluid. This fluid lubricates the joint, reducing friction and allowing for smooth movement.
Importance of the Glenohumeral Joint:
The glenohumeral joint is one of the most mobile joints in the human body. It allows for movements such as flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, medial and lateral rotation, and circumduction of the arm. This joint plays a crucial role in activities that involve reaching, lifting, throwing, and other arm movements.
Conclusion:
In summary, the rounded upper end (head) of the humerus articulates with the glenoid cavity of the scapula to form the glenohumeral joint. This joint provides stability and allows for a wide range of movements in the shoulder.
The shoulder blade is made of- a)clavicle
- b)humerus
- c)ilium
- d)scapula
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The shoulder blade is made of
a)
clavicle
b)
humerus
c)
ilium
d)
scapula
|
|
Kabir Verma answered |
Scapula or shoulder blade is a bone of the pectoral girdle. It is a flat triangular bone, providing anchoroge for the muscle of the forelimb and an articulation for the humerus at the glenoid cavity.
The joint in which one of the two bones is fixed in its place and bears a peg like process over which the other bone rotates is called- a)hinge joint
- b)saddle joint
- c)pivot joint
- d)angular joint
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The joint in which one of the two bones is fixed in its place and bears a peg like process over which the other bone rotates is called
a)
hinge joint
b)
saddle joint
c)
pivot joint
d)
angular joint
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
Pivot joint allows only a rotatory movement of one bone on the other, which remains stationary. A rounded end of one bone fits into a shallow pit of another bone. E.g., joint between atlas and axis vertebrae which enables the head to turn from side to side.
Which of the following is the most abundant mineral element in the skeletal muscle?- a)Sodium
- b)Calcium
- c)Potassium
- d)Phosphorous
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the most abundant mineral element in the skeletal muscle?
a)
Sodium
b)
Calcium
c)
Potassium
d)
Phosphorous
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Potassium is the most abundant mineral in muscles. It works closely with sodium in muscle function. All other minerals are present only in traces. So, the correct option is 'potassium'.
Which of the following is the contractile protein of a muscle?- a)Tropomyosin
- b)Tubulin
- c)Myosin
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the contractile protein of a muscle?
a)
Tropomyosin
b)
Tubulin
c)
Myosin
d)
All of these
|
|
Uday Dasgupta answered |
Myosin as the Contractile Protein of a Muscle:
Myosin is the contractile protein of a muscle responsible for generating the force during muscle contraction. It is a motor protein that interacts with actin to produce movement.
Structure of Myosin:
- Myosin is composed of two heavy chains and four light chains.
- The heavy chains have globular heads that interact with actin and ATP to generate movement.
Function of Myosin:
- Myosin interacts with actin filaments to form cross-bridges, which slide past each other during muscle contraction.
- This sliding of filaments is powered by the hydrolysis of ATP by myosin, leading to the shortening of the muscle fiber.
Role in Muscle Contraction:
- Myosin plays a crucial role in the process of muscle contraction by interacting with actin filaments in a cyclic manner.
- The ATPase activity of myosin hydrolyzes ATP to ADP and inorganic phosphate, providing the energy for the movement of the myosin heads along the actin filaments.
Comparison with Tropomyosin and Tubulin:
- Tropomyosin is a regulatory protein that blocks the myosin-binding sites on actin in the absence of calcium ions.
- Tubulin is a protein component of microtubules, which are involved in various cellular processes such as cell division and intracellular transport.
In conclusion, myosin is the contractile protein of a muscle that plays a central role in muscle contraction by interacting with actin filaments to generate force and movement.
Myosin is the contractile protein of a muscle responsible for generating the force during muscle contraction. It is a motor protein that interacts with actin to produce movement.
Structure of Myosin:
- Myosin is composed of two heavy chains and four light chains.
- The heavy chains have globular heads that interact with actin and ATP to generate movement.
Function of Myosin:
- Myosin interacts with actin filaments to form cross-bridges, which slide past each other during muscle contraction.
- This sliding of filaments is powered by the hydrolysis of ATP by myosin, leading to the shortening of the muscle fiber.
Role in Muscle Contraction:
- Myosin plays a crucial role in the process of muscle contraction by interacting with actin filaments in a cyclic manner.
- The ATPase activity of myosin hydrolyzes ATP to ADP and inorganic phosphate, providing the energy for the movement of the myosin heads along the actin filaments.
Comparison with Tropomyosin and Tubulin:
- Tropomyosin is a regulatory protein that blocks the myosin-binding sites on actin in the absence of calcium ions.
- Tubulin is a protein component of microtubules, which are involved in various cellular processes such as cell division and intracellular transport.
In conclusion, myosin is the contractile protein of a muscle that plays a central role in muscle contraction by interacting with actin filaments to generate force and movement.
What is sarcomere?- a)part between two H-line
- b)part between two A-line
- c)part between two I-band
- d)part between two Z-line
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is sarcomere?
a)
part between two H-line
b)
part between two A-line
c)
part between two I-band
d)
part between two Z-line
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Sarcomere is a part of myofibril between two successive Z-lines, which consists of two I-band halves, and an A-band between them. It is functional unit of myofibril.
What is the name of joint between ribs and sternum?- a)Cartilaginous joint
- b)Angular joint
- c)Gliding joint
- d)Fibrous joints
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the name of joint between ribs and sternum?
a)
Cartilaginous joint
b)
Angular joint
c)
Gliding joint
d)
Fibrous joints
|
|
Dishani Khanna answered |
The name of the joint between ribs and sternum is a cartilaginous joint.
Which one of the following pairs of structures is correctly matched with their description?- a)Tibia and fibula — Both form parts of knee joint
- b)Joint between atlas and axis — Pivot joint
- c)Shoulder joint and elbow joint — Ball and socket type of joint
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following pairs of structures is correctly matched with their description?
a)
Tibia and fibula — Both form parts of knee joint
b)
Joint between atlas and axis — Pivot joint
c)
Shoulder joint and elbow joint — Ball and socket type of joint
d)
None of these
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Only tibia connects to the femur to form the knee joint with the patella. Shoulder joint is of ball-and-socket type and elbow joint is a hinge joint.
Consider the following four statements (i) - (iv) and select the correct option.
(i) Actin is present in thin filament.
(ii) H-zone of striated muscle fibre represents both thick and thin filaments.
(iii) There are 11 pairs of ribs in man.
(iv) Sternum Is present on ventral side of the body.
- a)(i) F, (ii) F, (iii) T, (iv) F
- b)(i) F, (ii) F, (iii) F, (iv) T
- c)(i) T,, (ii) F (iii) F, (iv) T
- d)(i) T, (ii) F, (iii) T, (iv) F
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following four statements (i) - (iv) and select the correct option.
(i) Actin is present in thin filament.
(ii) H-zone of striated muscle fibre represents both thick and thin filaments.
(iii) There are 11 pairs of ribs in man.
(iv) Sternum Is present on ventral side of the body.
(i) Actin is present in thin filament.
(ii) H-zone of striated muscle fibre represents both thick and thin filaments.
(iii) There are 11 pairs of ribs in man.
(iv) Sternum Is present on ventral side of the body.
a)
(i) F, (ii) F, (iii) T, (iv) F
b)
(i) F, (ii) F, (iii) F, (iv) T
c)
(i) T,, (ii) F (iii) F, (iv) T
d)
(i) T, (ii) F, (iii) T, (iv) F
|
|
Yash Patel answered |
Actin is a globular protein present in thin filaments. There are 12 pairs of ribs in man. Sternun is a flat bone present on the ventral side of the body in the middle of the front of the chest.
Which of the following ions help in muscle contraction?- a)K+ and Mg++
- b)Na+ and K+
- c)Ca++ and Na++
- d)Ca++ and Mg++
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following ions help in muscle contraction?
a)
K+ and Mg++
b)
Na+ and K+
c)
Ca++ and Na++
d)
Ca++ and Mg++
|
|
Parth Sharma answered |
Importance of Ca++ and Mg++ in Muscle Contraction
Muscle contraction is a complex process that involves the interaction of various ions within the muscle cells. Two important ions that play a crucial role in muscle contraction are Ca++ and Mg++.
Ca++
- Calcium ions (Ca++) are essential for initiating muscle contraction.
- When a muscle cell is stimulated, Ca++ is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum within the cell.
- The binding of Ca++ to the protein troponin allows the protein tropomyosin to move away from the active binding sites on actin, enabling myosin to bind to actin and initiate muscle contraction.
Mg++
- Magnesium ions (Mg++) also play a role in muscle contraction by helping to regulate the activity of ATP, the energy source for muscle contraction.
- Mg++ is required for the ATPase activity of myosin, which allows for the breakdown of ATP to provide energy for muscle contraction.
Combined Role of Ca++ and Mg++
- While Ca++ initiates muscle contraction by allowing myosin to bind to actin, Mg++ helps in the actual energy production required for muscle contraction.
- Both ions work together to ensure that muscle contraction occurs efficiently and effectively.
Therefore, it is essential for muscle contraction that both Ca++ and Mg++ ions are present in the muscle cells.
Muscle contraction is a complex process that involves the interaction of various ions within the muscle cells. Two important ions that play a crucial role in muscle contraction are Ca++ and Mg++.
Ca++
- Calcium ions (Ca++) are essential for initiating muscle contraction.
- When a muscle cell is stimulated, Ca++ is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum within the cell.
- The binding of Ca++ to the protein troponin allows the protein tropomyosin to move away from the active binding sites on actin, enabling myosin to bind to actin and initiate muscle contraction.
Mg++
- Magnesium ions (Mg++) also play a role in muscle contraction by helping to regulate the activity of ATP, the energy source for muscle contraction.
- Mg++ is required for the ATPase activity of myosin, which allows for the breakdown of ATP to provide energy for muscle contraction.
Combined Role of Ca++ and Mg++
- While Ca++ initiates muscle contraction by allowing myosin to bind to actin, Mg++ helps in the actual energy production required for muscle contraction.
- Both ions work together to ensure that muscle contraction occurs efficiently and effectively.
Therefore, it is essential for muscle contraction that both Ca++ and Mg++ ions are present in the muscle cells.
If a stimulus, several times greater than the threshold stimulus is provided to a muscle fibre, it will- a)contract with a larger force
- b)contract with a smaller force
- c)contract with the same force
- d)undergo tetany
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If a stimulus, several times greater than the threshold stimulus is provided to a muscle fibre, it will
a)
contract with a larger force
b)
contract with a smaller force
c)
contract with the same force
d)
undergo tetany
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
A muscle fibre would contract only when it receives stimulation of certain intensity called threshold stimulus. Response of a muscle fibre to a stimulus is not proportional to its intensity. It is absent when the intensity is subliminal. Muscle fibre contracts to the maximum whether the stimulus has threshold value or supraliminal value.
Which of the following statements is incorrect?- a)Smooth muscles are found in urinary bladder, alimentary canal and genital tract
- b)A striated muscle is a syncytium i.e., a multinucleate structure
- c)The cytoplasm of striated muscle is called endoplasm
- d)The plasma membrane and ER of striated muscles are called sarcolemma and sarcoplasmic reticulum respectively
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
a)
Smooth muscles are found in urinary bladder, alimentary canal and genital tract
b)
A striated muscle is a syncytium i.e., a multinucleate structure
c)
The cytoplasm of striated muscle is called endoplasm
d)
The plasma membrane and ER of striated muscles are called sarcolemma and sarcoplasmic reticulum respectively
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The cytoplasm of striated muscle is called sarcoplasm.
In a muscle undergoes rapid contraction and relaxation, the sarcoplasmic reticulum extension- a)requires constant plugging in and out of Ca2+
- b)rapidly synthesise myosin
- c)does not require energy all of these.
- d)all of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a muscle undergoes rapid contraction and relaxation, the sarcoplasmic reticulum extension
a)
requires constant plugging in and out of Ca2+
b)
rapidly synthesise myosin
c)
does not require energy all of these.
d)
all of these
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Sarcoplasmic reticulum of muscle cells store Ca2+ ions. During contracting of muscle, Ca2+ ions are released from sarcoplasmic reticulum to sarcoplasm and vice versa occurs during relaxation. Therefore, if a muscle undergoes rapid contraction and relaxation it requires constant plugging in and out of Ca2+ ions from sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Which one of the following is the correct description of a certain part of a normal human skeleton?- a)Parietal bone and the temporal bone of the skull are joined fibrous joint
- b)First vertebra is axis which articulates with the occipital condyles
- c)The 9th and 10th pairs of ribs are called the floating ribs
- d)Glenoid cavity is a depression to which the thigh bone articulates
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is the correct description of a certain part of a normal human skeleton?
a)
Parietal bone and the temporal bone of the skull are joined fibrous joint
b)
First vertebra is axis which articulates with the occipital condyles
c)
The 9th and 10th pairs of ribs are called the floating ribs
d)
Glenoid cavity is a depression to which the thigh bone articulates
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Parietal bone and temporal bone of the skull are joined by fibrous joint (immovable joint). First cervical vertebra is atlas. The last two pairs (11th and 12th) of ribs are called flothing ribs. Glenoid cavity is a depression to which humaerus articulates.
The joint of radio-ulna with the upper arm is- a)hinge joint
- b)pivot joint
- c)socket joint
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The joint of radio-ulna with the upper arm is
a)
hinge joint
b)
pivot joint
c)
socket joint
d)
none of these
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
The joint of radio-ulna with the upper arm is a hinge joint. This joint allows the movement only in a single plane.
Which of the following statements are incorrect regarding a normal human?
(i) The skull is dicondylic.
(ii) Metacarpals are five in numbers.
(iii) Patella is a cup-shaped bone covering the knee dorsally.
(iv) Scapula is a large triangular flat bale, situated on the ventral side of the thorax.
(v) The pelvic girdle has two coxal bones.- a)(i) and (v)
- b)(i) and (ii)
- c)(ii) and (v)
- d)(iii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements are incorrect regarding a normal human?
(i) The skull is dicondylic.
(ii) Metacarpals are five in numbers.
(iii) Patella is a cup-shaped bone covering the knee dorsally.
(iv) Scapula is a large triangular flat bale, situated on the ventral side of the thorax.
(v) The pelvic girdle has two coxal bones.
(i) The skull is dicondylic.
(ii) Metacarpals are five in numbers.
(iii) Patella is a cup-shaped bone covering the knee dorsally.
(iv) Scapula is a large triangular flat bale, situated on the ventral side of the thorax.
(v) The pelvic girdle has two coxal bones.
a)
(i) and (v)
b)
(i) and (ii)
c)
(ii) and (v)
d)
(iii) and (iv)
|
|
Rishabh Choudhury answered |
Incorrect statements regarding a normal human:
(i) The skull is dicondylic - This statement is incorrect. The skull is synarthrodial and has a single condyle on each side.
(iv) Scapula is a large triangular flat bale, situated on the ventral side of the thorax - This statement is incorrect. The scapula is a large triangular flat bone, situated on the dorsal side of the thorax.
Correct statements regarding a normal human:
(ii) Metacarpals are five in numbers - This statement is correct. Metacarpals are long bones in the hand and there are five in number.
(iii) Patella is a cup-shaped bone covering the knee dorsally - This statement is correct. The patella, also known as the kneecap, is a small, flat, triangular bone in the front of the knee joint.
(v) The pelvic girdle has two coxal bones - This statement is correct. The pelvic girdle is formed by two coxal bones, also known as hip bones, which are fused to the sacrum posteriorly.
(i) The skull is dicondylic - This statement is incorrect. The skull is synarthrodial and has a single condyle on each side.
(iv) Scapula is a large triangular flat bale, situated on the ventral side of the thorax - This statement is incorrect. The scapula is a large triangular flat bone, situated on the dorsal side of the thorax.
Correct statements regarding a normal human:
(ii) Metacarpals are five in numbers - This statement is correct. Metacarpals are long bones in the hand and there are five in number.
(iii) Patella is a cup-shaped bone covering the knee dorsally - This statement is correct. The patella, also known as the kneecap, is a small, flat, triangular bone in the front of the knee joint.
(v) The pelvic girdle has two coxal bones - This statement is correct. The pelvic girdle is formed by two coxal bones, also known as hip bones, which are fused to the sacrum posteriorly.
Cranium of human contains- a)8 bones
- b)12 bones
- c)14 bones
- d)20 bones
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Cranium of human contains
a)
8 bones
b)
12 bones
c)
14 bones
d)
20 bones
|
|
Garima Joshi answered |
Cranium Overview
The human cranium is a complex structure that plays a vital role in protecting the brain and supporting the structures of the face. It is composed of a specific number of bones that are fused together in adulthood.
Composition of the Cranium
- The human cranium consists of 8 bones.
- These bones are categorized into two groups: cranial bones and facial bones.
Cranial Bones
- The eight cranial bones include:
- Frontal Bone: Forms the forehead and the upper part of the eye sockets.
- Parietal Bones (2): Located on the sides and top of the skull, these bones are responsible for protecting the brain.
- Temporal Bones (2): Situated on the sides of the skull, they house structures of the ear and protect the brain.
- Occipital Bone: Forms the back and base of the skull, allowing for the attachment of the spinal column.
- Sphenoid Bone: This complex bone contributes to the base of the skull and the side of the cranium.
- Ethmoid Bone: Located between the eyes, it forms part of the nasal cavity and the orbits.
Significance of the Cranium
- Protects the brain from physical damage.
- Supports the structures of the face and provides attachment points for muscles.
- Houses the organs of vision, hearing, and balance.
By understanding the anatomy of the cranium, one can appreciate its critical role in both protection and function within the human body.
The human cranium is a complex structure that plays a vital role in protecting the brain and supporting the structures of the face. It is composed of a specific number of bones that are fused together in adulthood.
Composition of the Cranium
- The human cranium consists of 8 bones.
- These bones are categorized into two groups: cranial bones and facial bones.
Cranial Bones
- The eight cranial bones include:
- Frontal Bone: Forms the forehead and the upper part of the eye sockets.
- Parietal Bones (2): Located on the sides and top of the skull, these bones are responsible for protecting the brain.
- Temporal Bones (2): Situated on the sides of the skull, they house structures of the ear and protect the brain.
- Occipital Bone: Forms the back and base of the skull, allowing for the attachment of the spinal column.
- Sphenoid Bone: This complex bone contributes to the base of the skull and the side of the cranium.
- Ethmoid Bone: Located between the eyes, it forms part of the nasal cavity and the orbits.
Significance of the Cranium
- Protects the brain from physical damage.
- Supports the structures of the face and provides attachment points for muscles.
- Houses the organs of vision, hearing, and balance.
By understanding the anatomy of the cranium, one can appreciate its critical role in both protection and function within the human body.
In the resting muscle fibre, tropomyosin partially covers- a)calcium binding sites on troponin
- b)actin binding sites on myosin
- c)myosin binding sites on actin
- d)calcium binding sites on actin
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the resting muscle fibre, tropomyosin partially covers
a)
calcium binding sites on troponin
b)
actin binding sites on myosin
c)
myosin binding sites on actin
d)
calcium binding sites on actin
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
When the muscle is at rest, the tropomyosin molecule covers the binding site of the actin molecule where interaction with myosin occurs. During contraction of the Tuscte the active site is uncovered, allowing the interaction of actin With myosin.
Myoglobin is present in- a)all muscle fibres
- b)white muscle fibres
- c)red muscle fibres
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Myoglobin is present in
a)
all muscle fibres
b)
white muscle fibres
c)
red muscle fibres
d)
none of these
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Myoglobin (red coloured oxygen storing pigment) is present in all muscle fibres. Red muscle fibres have abundant myoglobin while white muscle fibres have less myoglobin
Read the statements regarding muscle proteins.
(i) Actin is a thin filament and is made up of two F-actins,
(ii) The complex protein, tropomyosin is distributed at regular intervals on the troponin
(iii) Myosin is a thick filament which is also a polymerized protein
(iv) The globular head of meromyosin consists of light meromyosin (LMM)- a)(i), (ii) and (iii) are correct
- b)(i), (ii) and (iv) are correct
- c)(i) and (iii) are correct
- d)(ii) and (iv) are correct
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the statements regarding muscle proteins.
(i) Actin is a thin filament and is made up of two F-actins,
(ii) The complex protein, tropomyosin is distributed at regular intervals on the troponin
(iii) Myosin is a thick filament which is also a polymerized protein
(iv) The globular head of meromyosin consists of light meromyosin (LMM)
(i) Actin is a thin filament and is made up of two F-actins,
(ii) The complex protein, tropomyosin is distributed at regular intervals on the troponin
(iii) Myosin is a thick filament which is also a polymerized protein
(iv) The globular head of meromyosin consists of light meromyosin (LMM)
a)
(i), (ii) and (iii) are correct
b)
(i), (ii) and (iv) are correct
c)
(i) and (iii) are correct
d)
(ii) and (iv) are correct
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Each actin (thin) filament is made of two 'F' (filamentous) actin helically wound to each other. Each F actin is a polymer of monomeric 'G' (globular) actins. Myosin (thick) filament is a polymerised protein. Many monomeric proteins called meromyosins constitute one thick filament. Tropomyosin is a fibrous molecule that attaches to F actin in the groove between its filament. The globular head of meromyosin consists of heavy meromyosin.
Total number of bones in a hindlimb of a man is- a)24
- b)30
- c)14
- d)21
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Total number of bones in a hindlimb of a man is
a)
24
b)
30
c)
14
d)
21
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Each hind limb consists of 30 bones 1 femur, 1 patella, 1 tibia, 1 fibula, 7 tarsals, 5 metatarsals and 14 phalanges.
Lumbar vertebra are found in- a)neck region
- b)abdominal region
- c)hip region
- d)thorax
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Lumbar vertebra are found in
a)
neck region
b)
abdominal region
c)
hip region
d)
thorax
|
|
Arka Patel answered |
Lumbar vertebrae are found in the abdominal region.
Explanation:
The lumbar vertebrae are a set of five vertebrae located in the lower back region of the spinal column. They are the largest and strongest vertebrae in the spinal column and are responsible for supporting the weight of the upper body. The lumbar vertebrae are numbered L1 to L5, with L1 being the topmost lumbar vertebra and L5 being the bottommost.
Here is a detailed explanation of why the correct answer is option 'B' - abdominal region:
1. Structure of the lumbar vertebrae:
- The lumbar vertebrae are larger and thicker compared to the other vertebrae in the spinal column.
- They have a robust body and a wide, thick vertebral arch that protects the spinal cord.
- The spinous processes of the lumbar vertebrae are relatively short and project posteriorly.
- The transverse processes are strong and project laterally.
2. Location of the lumbar vertebrae:
- The lumbar vertebrae are situated between the thoracic vertebrae (in the thoracic region) and the sacral vertebrae (in the sacral region).
- They are located in the lower back region, just above the pelvis.
- The lumbar vertebrae are positioned below the thoracic vertebrae, which are in the thorax region.
- This makes option 'D' - thorax, incorrect.
3. Function of the lumbar vertebrae:
- The lumbar vertebrae provide support to the upper body and help maintain an upright posture.
- They play a crucial role in weight-bearing and are subjected to significant forces during activities such as lifting, bending, and twisting.
- The lumbar vertebrae also contribute to the flexibility and mobility of the lower back.
Based on the above points, it is clear that lumbar vertebrae are found in the abdominal region (option 'B'). They are located below the thoracic vertebrae and above the sacral vertebrae, playing a vital role in supporting the upper body and providing flexibility to the lower back.
Explanation:
The lumbar vertebrae are a set of five vertebrae located in the lower back region of the spinal column. They are the largest and strongest vertebrae in the spinal column and are responsible for supporting the weight of the upper body. The lumbar vertebrae are numbered L1 to L5, with L1 being the topmost lumbar vertebra and L5 being the bottommost.
Here is a detailed explanation of why the correct answer is option 'B' - abdominal region:
1. Structure of the lumbar vertebrae:
- The lumbar vertebrae are larger and thicker compared to the other vertebrae in the spinal column.
- They have a robust body and a wide, thick vertebral arch that protects the spinal cord.
- The spinous processes of the lumbar vertebrae are relatively short and project posteriorly.
- The transverse processes are strong and project laterally.
2. Location of the lumbar vertebrae:
- The lumbar vertebrae are situated between the thoracic vertebrae (in the thoracic region) and the sacral vertebrae (in the sacral region).
- They are located in the lower back region, just above the pelvis.
- The lumbar vertebrae are positioned below the thoracic vertebrae, which are in the thorax region.
- This makes option 'D' - thorax, incorrect.
3. Function of the lumbar vertebrae:
- The lumbar vertebrae provide support to the upper body and help maintain an upright posture.
- They play a crucial role in weight-bearing and are subjected to significant forces during activities such as lifting, bending, and twisting.
- The lumbar vertebrae also contribute to the flexibility and mobility of the lower back.
Based on the above points, it is clear that lumbar vertebrae are found in the abdominal region (option 'B'). They are located below the thoracic vertebrae and above the sacral vertebrae, playing a vital role in supporting the upper body and providing flexibility to the lower back.
Which of the following pairs is correctly matched?- a)Hinge joint - Between vertebrae
- b)Gliding joint - Between zygapo- physes of the successive vertebrae
- c)Cartilaginous joint - Skull bones
- d)Fibrous joint - Between phalanges.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following pairs is correctly matched?
a)
Hinge joint - Between vertebrae
b)
Gliding joint - Between zygapo- physes of the successive vertebrae
c)
Cartilaginous joint - Skull bones
d)
Fibrous joint - Between phalanges.
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The gliding joint allows sliding movements of two bones over each other. The joint between zygapophyses of successive vertebrae is of this type.
In an adult human, how many bones are present as ear ossicles?- a)4
- b)6
- c)3
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In an adult human, how many bones are present as ear ossicles?
a)
4
b)
6
c)
3
d)
None of these
|
|
Yash Patel answered |
Six ear ossicles are present, three in each ear. They are malleus, incus and stapes.
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the codes given below.
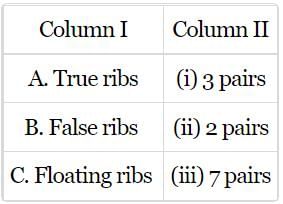
- a)A-(i), B-(ii), C-(iii)
- b)A-(iii), B-(i), C-(ii)
- c)A-(iii), B-(ii), C-(i)
- d)A-(ii), B-(i), C-(iii)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the codes given below.


a)
A-(i), B-(ii), C-(iii)
b)
A-(iii), B-(i), C-(ii)
c)
A-(iii), B-(ii), C-(i)
d)
A-(ii), B-(i), C-(iii)
|
|
Yash Patel answered |
The first 7 pairs of ribs are called true ribs as their anterior ends are attached directly to the sternum. The 8th, 9th and 10th pairs are called false ribs as they are attached indirectly to the sternum. The 11th and 12th pairs are called floating ribs as their anterior ends are not attached to sternum.
Choose the pair of characteristics and example of a synovial joint in humans.
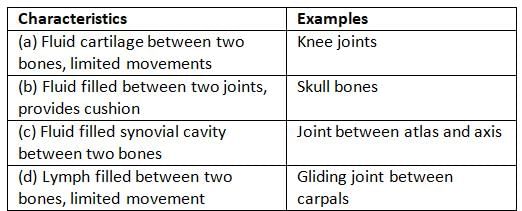
- a)(a)
- b)(b)
- c)(c)
- d)(d)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the pair of characteristics and example of a synovial joint in humans.


a)
(a)
b)
(b)
c)
(c)
d)
(d)

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Synovial joints are characterised by the presence of a fluid filled synovial cavity between the articulating surfaces of the two bones. These joints help in locomotion and many other movements. Ball and socket joint (between humerus and pectoral girdle), hinge joint (knee joint), pivot joint (between atlas and axis), gliding joint (between the carpals) and saddle joint (between carpal and metacarpal of thumb) are some examples.
Dark bands are- a)A-band
- b)B-band
- c)I-band
- d)Z-line
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Dark bands are
a)
A-band
b)
B-band
c)
I-band
d)
Z-line
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
A myofibril has dark and light bands. The dark bands are called A bands (Anisotropic bands). Light bands are called I bands (isotropic bands).
Which one of the following options shown the next stage of muscle contraction after the stage given in question?
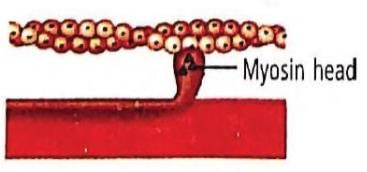
- a)
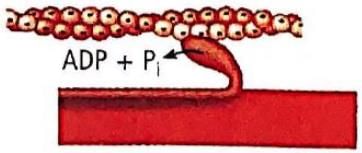
- b)
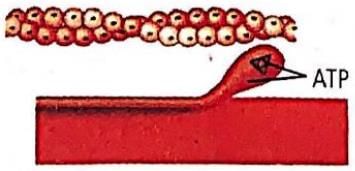
- c)
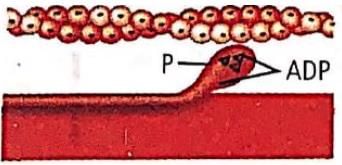
- d)
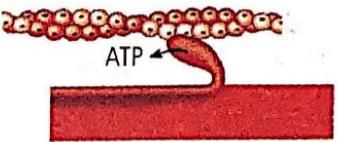
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following options shown the next stage of muscle contraction after the stage given in question?


a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The figure in the question shows formation of cross bridge between myosin head and actin filament. Next stage would be the figure showing the sliding/rotation of the head of myosin filament of the actin filament.
Fill in the blanks to complete the sequence of vertebral counts starting from the skull:
Cervical (), Thoracic (), Lumbar (), Sacral ( ), Coccygeal ( ).- a)7, 12, 5, 1, 1
- b)7, 10, 5, 2, 1
- c)5, 12, 5, 1, 1
- d)7, 12, 4, 1, 2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Cervical (), Thoracic (), Lumbar (), Sacral ( ), Coccygeal ( ).
a)
7, 12, 5, 1, 1
b)
7, 10, 5, 2, 1
c)
5, 12, 5, 1, 1
d)
7, 12, 4, 1, 2

|
Top Rankers answered |
The human vertebral column is divided into five regions with the following typical vertebrae counts:
Cervical: 7 vertebrae
Thoracic: 12 vertebrae
Lumbar: 5 vertebrae
Sacral: 1 segment formed by the fusion of 5 sacral vertebrae
Coccygeal: 1 segment formed by the fusion of 4 coccygeal vertebrae
Thus the correct sequence is 7, 12, 5, 1 (fused), 1 (fused), matching Option A.
Cervical: 7 vertebrae
Thoracic: 12 vertebrae
Lumbar: 5 vertebrae
Sacral: 1 segment formed by the fusion of 5 sacral vertebrae
Coccygeal: 1 segment formed by the fusion of 4 coccygeal vertebrae
Thus the correct sequence is 7, 12, 5, 1 (fused), 1 (fused), matching Option A.
What is a defining characteristic of synovial joints?- a) Connection via ligaments
- b) Presence of a fluid-filled synovial cavity
- c) Presence of cartilage
- d) Lack of movement
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is a defining characteristic of synovial joints?
a)
Connection via ligaments
b)
Presence of a fluid-filled synovial cavity
c)
Presence of cartilage
d)
Lack of movement

|
Bs Academy answered |
Synovial joints are characterized by the presence of a synovial cavity filled with synovial fluid, which allows for a greater range of motion.
Topic in NCERT: Joints
Line in NCERT: "synovial joints are characterised by the presence of a fluid filled synovial cavity between the articulating surfaces of the two bones."
Chapter doubts & questions for Locomotion and Movement - NCERT Based Tests for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Locomotion and Movement - NCERT Based Tests for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily










