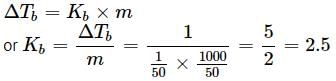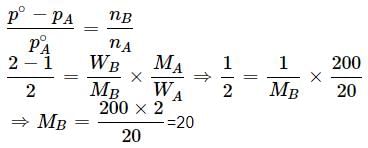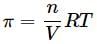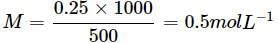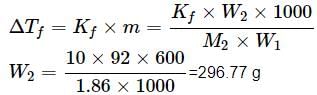All Exams >
NEET >
NCERT Based Tests for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Solutions for NEET Exam
What amount of CaCl2 (i = 2.47) is dissolved in 2 litres of water so that its osmotic pressure is 0.5atm at 27oC?- a)3.42 g
- b)9.24 g
- c)2.834 g
- d)1.820 g
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What amount of CaCl2 (i = 2.47) is dissolved in 2 litres of water so that its osmotic pressure is 0.5atm at 27oC?
a)
3.42 g
b)
9.24 g
c)
2.834 g
d)
1.820 g
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |

Amount of CaCl2 = n × M = 0.0164 × 111 = 1.820 g
The law which indicates the relationship between solubility of a gas in liquid and pressure is________.- a)Raoult’s law
- b)Henry’s law
- c)Lowering of vapour pressure
- d)Van’t Hoff law
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The law which indicates the relationship between solubility of a gas in liquid and pressure is________.
a)
Raoult’s law
b)
Henry’s law
c)
Lowering of vapour pressure
d)
Van’t Hoff law
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Henry's law states that the solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of the gas present above the surface of the liquid or solution.
p = KHX
p = KHX
A solution containing 12.5g of non-electrolyte substance in 185g of water shows boiling point elevation of 0.80K. Calculate the molar mass of the substance. (Kb = 0.52K kg mol−1)- a)53.06 g mol−1
- b)25.3 g mol−1
- c)16.08 g mol−1
- d)43.92 g mol−1
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A solution containing 12.5g of non-electrolyte substance in 185g of water shows boiling point elevation of 0.80K. Calculate the molar mass of the substance. (Kb = 0.52K kg mol−1)
a)
53.06 g mol−1
b)
25.3 g mol−1
c)
16.08 g mol−1
d)
43.92 g mol−1
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
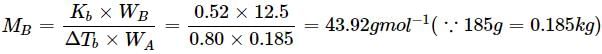
For an ideal solution with pA > pB, which of the following is true?
- a)(xA)liquid = (xB)vapour
- b)(xA)liquid > (xB)vapour
- c)(xA)liquid < (xB)vapour
- d)(xA)liquid and (xB)vapour do not bear any relationship with each other
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For an ideal solution with pA > pB, which of the following is true?
a)
(xA)liquid = (xB)vapour
b)
(xA)liquid > (xB)vapour
c)
(xA)liquid < (xB)vapour
d)
(xA)liquid and (xB)vapour do not bear any relationship with each other
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Since the vapor pressure of A is more than B so the mole fraction of A is more in vapor phase than liquid phase as A is more volatile hence vapor phase would be richer in A. Thus the correct option is (xA)liquid < (xB)Vapor
Which of the following has the highest freezing point?- a)1 m NaCl solution
- b)1 m KCl solution
- c)1 m AlCl3 solution
- d)1 m C6H12O6 solution
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following has the highest freezing point?
a)
1 m NaCl solution
b)
1 m KCl solution
c)
1 m AlCl3 solution
d)
1 m C6H12O6 solution
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
C6H12O6 is a non-electrolyte hence furnishes minimum number of particles and will have maximum freezing point.
ΔTf = iKfm or ΔTf ∝ i and ΔTf = T∘f − Tf
ΔTf = iKfm or ΔTf ∝ i and ΔTf = T∘f − Tf
How much oxygen is dissolved in 100mL water at 298K if partial pressure of oxygen is 0.5atm and KH = 1.4 × 10−3 mol / L / atm?- a)22.4 mg
- b)22.4 g
- c)2.24 g
- d)2.24 mg
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
How much oxygen is dissolved in 100mL water at 298K if partial pressure of oxygen is 0.5atm and KH = 1.4 × 10−3 mol / L / atm?
a)
22.4 mg
b)
22.4 g
c)
2.24 g
d)
2.24 mg
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
According to Henry’s law, s = KH × p, where s is concentration of O2 dissolved.
s = 1.4 × 10−3 × 0.5 = 0.7 × 10−3mol/L
s = n/V or n = 0.7×10−3 × 0.1 = 0.7 × 10−4mol
n = w/M or w = n × M
= 0.7 × 10−4 × 32 = 22.4 × 10−4g or 2.24mg
s = 1.4 × 10−3 × 0.5 = 0.7 × 10−3mol/L
s = n/V or n = 0.7×10−3 × 0.1 = 0.7 × 10−4mol
n = w/M or w = n × M
= 0.7 × 10−4 × 32 = 22.4 × 10−4g or 2.24mg
If α is the degree of dissociation of Na2SO4, the vant Hoff's factor (i) used for calculating the molecular mass is:- a)1 + α
- b)1 − α
- c)1 + 2α
- d)1 − 2α
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If α is the degree of dissociation of Na2SO4, the vant Hoff's factor (i) used for calculating the molecular mass is:
a)
1 + α
b)
1 − α
c)
1 + 2α
d)
1 − 2α
|
|
Ishan Shah answered |
You had one superpower, what would it be and why?
Osmotic pressure of a solution containing 2g dissolved protein per 300cm2 of solution is 20mm of Hg at 27oC. The molecular mass of protein is- a)6239.6 g mol−1
- b)12315.5 g mol−1
- c)3692.1 g mol−1
- d)7368.4 g mol−1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Osmotic pressure of a solution containing 2g dissolved protein per 300cm2 of solution is 20mm of Hg at 27oC. The molecular mass of protein is
a)
6239.6 g mol−1
b)
12315.5 g mol−1
c)
3692.1 g mol−1
d)
7368.4 g mol−1
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
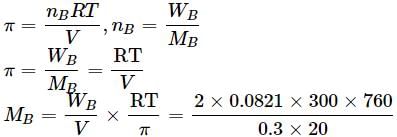
= 6239.6 g mol−1
How many grams of NaOH are present in 250 mL of 0.5 M NaOH solution?- a)7.32 g
- b)3.8 g
- c)5g
- d)0.5 g
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How many grams of NaOH are present in 250 mL of 0.5 M NaOH solution?
a)
7.32 g
b)
3.8 g
c)
5g
d)
0.5 g
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
No. of moles of NaOH
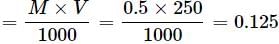
Mass of NaOH = 40 × 0.125 = 5g
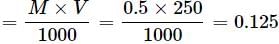
Mass of NaOH = 40 × 0.125 = 5g
Which of the following will have same value of vant's Hoff factor as that of K4[Fe(CN)6]?- a)Al2(SO4)3
- b)AlCl3
- c)Al(NO3)3
- d)Al(OH)3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following will have same value of vant's Hoff factor as that of K4[Fe(CN)6]?
a)
Al2(SO4)3
b)
AlCl3
c)
Al(NO3)3
d)
Al(OH)3
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
K4[Fe(CN)6] → 4K+ + [Fe(CN)6]4-
Al2(SO4)3 → 2Al3+ + 3SO42-
Al2(SO4)3 → 2Al3+ + 3SO42-
During dissolution when solute is added to the solvent, some solute particles separate out from the solution as a result of crystallisation. At the stage of equilibrium, the concentration of solute in the solution at given temperature and pressure- a)Increases
- b)Decreases
- c)Remains constant
- d)Keeps changing
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During dissolution when solute is added to the solvent, some solute particles separate out from the solution as a result of crystallisation. At the stage of equilibrium, the concentration of solute in the solution at given temperature and pressure
a)
Increases
b)
Decreases
c)
Remains constant
d)
Keeps changing
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
At dynamic equilibrium, number of solute particles going into the solution will be equal to solute particles separating out. Hence, the concentration of solute in the solution remains constant.
How many Na+ ions are present in 100 mL of 0.25 M of NaCl solution?- a)0.025 × 1023
- b)1.505 × 1022
- c)15 × 1022
- d)2.5 × 1023
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How many Na+ ions are present in 100 mL of 0.25 M of NaCl solution?
a)
0.025 × 1023
b)
1.505 × 1022
c)
15 × 1022
d)
2.5 × 1023
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
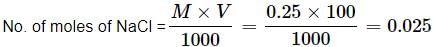
NaCl → Na+ + Cl−
No. of moles of Na+ ions = 0.025
No. of Na+ ions = 0.025 x 6.023 x 1023 = 1.505 × 1022
Sprinkling of salt helps in clearing the snow-covered roads in hills. The phenomenon involved in the process is- a)Lowering in vapour pressure of snow
- b)Depression in freezing point of snow
- c)Increase in freezing point of snow
- d)Melting of ice due to increase in temperature by putting salt
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Sprinkling of salt helps in clearing the snow-covered roads in hills. The phenomenon involved in the process is
a)
Lowering in vapour pressure of snow
b)
Depression in freezing point of snow
c)
Increase in freezing point of snow
d)
Melting of ice due to increase in temperature by putting salt
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
When salt is spread over snow covered roads, snow starts melting from the surface because of the depression in freezing point of water and it helps in clearing the roads.
What will be the mole fraction of ethanol in a sample of spirit containing 85% ethanol by mass?- a)0.69
- b)0.82
- c)0.85
- d)0.60
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What will be the mole fraction of ethanol in a sample of spirit containing 85% ethanol by mass?
a)
0.69
b)
0.82
c)
0.85
d)
0.60
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
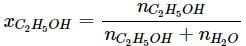
Mass of C2H5OH = 85 g
Molar mass of C2H5OH = 46 g/mol
nC2H5OH = 85/46 = 1.85 mol
Mass of water = 100 - 85 = 15 g
nH2O = 15/18 = 0.833 mol
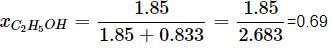
The molality of 648 g of pure water is- a)36 m
- b)55.5 m
- c)3.6 m
- d)5.55 m
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The molality of 648 g of pure water is
a)
36 m
b)
55.5 m
c)
3.6 m
d)
5.55 m
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Molality = no of moles of solute/mass of solvent in kg
Molar mass of water = 18 g
Mass of water = 648 g
No of moles of water = 648/18 = 36 mol
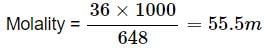
Molar mass of water = 18 g
Mass of water = 648 g
No of moles of water = 648/18 = 36 mol
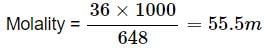
A solution containing 10.2g glycerine per litre is isotonic with a 2% solution of glucose. What is the molecular mass of glycerine?- a)91.8 g
- b)1198 g
- c)83.9 g
- d)890.3 g
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A solution containing 10.2g glycerine per litre is isotonic with a 2% solution of glucose. What is the molecular mass of glycerine?
a)
91.8 g
b)
1198 g
c)
83.9 g
d)
890.3 g
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
πglycerine = πglucose
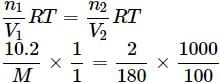
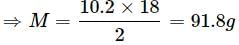
(Density of water = 1g/cm3)
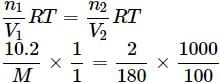
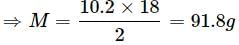
(Density of water = 1g/cm3)
A 5% solution (w/W) of cane sugar (molar mass = 342 g mol-1) has freezing point of 271 K. What will be the freezing point of a 5% glucose (molar mass = 18 g mol-1) in water if freezing point of pure water is 273.15 K?- a)273.07 K
- b)269.07 K
- c)273.15 K
- d)260.09 K
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A 5% solution (w/W) of cane sugar (molar mass = 342 g mol-1) has freezing point of 271 K. What will be the freezing point of a 5% glucose (molar mass = 18 g mol-1) in water if freezing point of pure water is 273.15 K?
a)
273.07 K
b)
269.07 K
c)
273.15 K
d)
260.09 K
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
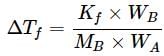
For cane sugar solution, 2.15 K =
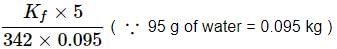
For glucose solution,
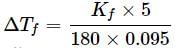
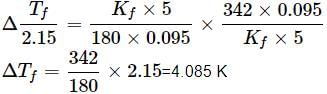
Freezing point of glucose solution = 273.15 - 4.085 = 269.07 K
Which of the following statements is correct?- a)A saturated solution will remain saturated at all temperatures
- b)A plant cell swells when placed in hypertonic solution
- c)The depression in freezing point is directly proportional to molality of the solution
- d)Lowering in vapour pressure is a colligative property
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is correct?
a)
A saturated solution will remain saturated at all temperatures
b)
A plant cell swells when placed in hypertonic solution
c)
The depression in freezing point is directly proportional to molality of the solution
d)
Lowering in vapour pressure is a colligative property
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Solubility changes with temperature. A plant cell shrinks in hypertonic solution. Relative lowering of vapour pressure is a colligative property.
Given below are few mixtures formed by mixing two components. Which of the following binary mixtures will have same composition in liquid and vapour phase?
(i) Ethanol + Chloroform
(ii) Nitric acid + Water
(iii) Benzene + Toluene
(iv) Ethyl chloride + Ethyl bromide
- a)(i) and (iii)
- b)(iii) and (iv)
- c)(i), (ii) and (iii)
- d)(i) and (ii)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Given below are few mixtures formed by mixing two components. Which of the following binary mixtures will have same composition in liquid and vapour phase?
(i) Ethanol + Chloroform
(ii) Nitric acid + Water
(iii) Benzene + Toluene
(iv) Ethyl chloride + Ethyl bromide
(i) Ethanol + Chloroform
(ii) Nitric acid + Water
(iii) Benzene + Toluene
(iv) Ethyl chloride + Ethyl bromide
a)
(i) and (iii)
b)
(iii) and (iv)
c)
(i), (ii) and (iii)
d)
(i) and (ii)
|
|
Rohit Jain answered |
(iii) and (iv) will form ideal solutions hence do not form azeotropes. Azeotropes have same composition in liquid and vapour form when distilled.
To determine which binary mixtures will have the same composition in the liquid and vapor phases, we need to identify mixtures that form ideal solutions. In an ideal solution, the composition of the liquid phase and the vapor phase is the same at equilibrium.
Here’s a brief analysis of each mixture:
-
Ethanol + Chloroform:
- This mixture does not behave ideally due to strong hydrogen bonding interactions between ethanol and chloroform, which can cause deviations from Raoult's Law.
-
Nitric Acid + Water:
- Nitric acid and water form a non-ideal solution. Nitric acid forms strong hydrogen bonds with water, resulting in significant deviations from ideal behavior. Thus, the composition in the liquid and vapor phases will not be the same.
-
Benzene + Toluene:
- Benzene and toluene form an ideal solution. The interactions between benzene and toluene are similar, and thus the composition of the liquid and vapor phases will be the same.
-
Ethyl Chloride + Ethyl Bromide:
- Ethyl chloride and ethyl bromide also form an ideal solution. The interactions between these two similar substances lead to minimal deviations from ideal behavior.
Based on the above analyses, the mixtures that will have the same composition in the liquid and vapor phases are:
2. (iii) and (iv)
So the correct answer is:
2. (iii) and (iv)
10% solution of urea is isotonic with 6% solution of a non-volatile solute X.What is the molecular mass of solute X?- a)6 g mol−1
- b)60 g mol−1
- c)36 g mol−1
- d)32 g mol−1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
10% solution of urea is isotonic with 6% solution of a non-volatile solute X.What is the molecular mass of solute X?
a)
6 g mol−1
b)
60 g mol−1
c)
36 g mol−1
d)
32 g mol−1
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
No. of moles of urea = 10/60 = 16
Weight of solute, X = 6 g
No. of moles of X = 6/M
For isotonic solutions, n1 = n2
or 1/6 = 6/M or M = 36 g mol−1
Weight of solute, X = 6 g
No. of moles of X = 6/M
For isotonic solutions, n1 = n2
or 1/6 = 6/M or M = 36 g mol−1
What will be the molarity of 30mL of 0.5M H2SO4 solution diluted to 500mL?- a)0.3 M
- b)0.03 M
- c)3 M
- d)0.103 M
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What will be the molarity of 30mL of 0.5M H2SO4 solution diluted to 500mL?
a)
0.3 M
b)
0.03 M
c)
3 M
d)
0.103 M
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
V1 = 30 mL, M1 = 0.5 M, V2 = 500 mL, M2 = ?,
M1V1 = M2V2
0.5 x 30 = M2 × 500 or M2 = 0.03 M
M1V1 = M2V2
0.5 x 30 = M2 × 500 or M2 = 0.03 M
A plant cell shrinks when it is kept in a- a)Hypotonic solution
- b)Hypertonic solution
- c)Isotonic solution
- d)Pure water
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A plant cell shrinks when it is kept in a
a)
Hypotonic solution
b)
Hypertonic solution
c)
Isotonic solution
d)
Pure water
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Hypertonic solution has high osmotic pressure. When a plant cell is placed in hypertonic solution water will diffuse out of the cell resulting in shrinking of the cell.
Which of the following solutions shows positive deviation from Raoult's law?- a)Acetone + Aniline
- b)Acetone + Ethanol
- c)Water + Nitric acid
- d)Chloroform + Benzene
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following solutions shows positive deviation from Raoult's law?
a)
Acetone + Aniline
b)
Acetone + Ethanol
c)
Water + Nitric acid
d)
Chloroform + Benzene
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Acetone + ethanol is an example of solutions showing positive deviation from Raoult's law. Since acetone-ethanol attractions are weaker than acetone - acetone and ethanol-ethanol attractions.
What is the mass percentage of carbon tetrachloride if 22g of benzene is dissolved in 122g of carbon tetrachloride?- a)84.72%
- b)15.28%
- c)50%
- d)44%
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the mass percentage of carbon tetrachloride if 22g of benzene is dissolved in 122g of carbon tetrachloride?
a)
84.72%
b)
15.28%
c)
50%
d)
44%
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Mass of solution = Mass of C6H6 + Mass of CCl4
= 22 + 122 = 144 g
Mass % of CCl4 =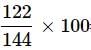 = 84.72%
= 84.72%
= 22 + 122 = 144 g
Mass % of CCl4 =
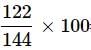 = 84.72%
= 84.72%Concentration terms like mass percentage, ppm, mole fraction and molality do not depend on temperature. However, molarity is a function of temperature because- a)Volume depends on temperature and molarity involves volume
- b)Molarity involves non-volatile solute while all other terms involve volatile solute
- c)Number of moles of solute change with change in temperature
- d)Molarity is used for polar solvents only
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Concentration terms like mass percentage, ppm, mole fraction and molality do not depend on temperature. However, molarity is a function of temperature because
a)
Volume depends on temperature and molarity involves volume
b)
Molarity involves non-volatile solute while all other terms involve volatile solute
c)
Number of moles of solute change with change in temperature
d)
Molarity is used for polar solvents only
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Molarity of a solution is defined as the number of moles of solute dissolved per litre of solution. Since volume depends on temperature and changes with change in temperature, therefore, the molarity will also change with change in temperature. On the other hand, mass does not change with change in temperature, and therefore, concentration terms such as mass percentage, mole fraction and molality which do not involve volume are independent of temperature.
Answer the following questions on the basis of given paragraph.
Osmotic pressure is widely used to determine molar masses of proteins and polymers. Two solutions having same osmotic pressure are called isotonic solutions. Water can flow in or out from substance depending on if it is kept in hypotonic or hypertonic solutions. The direction of the osmosis can be reversed if a pressure larger than osmotic pressure is applied on solution side.
Q. Sea water is desalinated to get fresh water by which of the following methods?- a)When pressure more than osmotic pressure is applied pure water is squeezed out of sea water by reverse osmosis
- b)When excess pressure is applied on sea water pure water moves in by osmosis
- c)Water moves out from sea water due to osmosis
- d)Salt is precipitated from sea water when kept undisturbed for sometime
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Answer the following questions on the basis of given paragraph.
Osmotic pressure is widely used to determine molar masses of proteins and polymers. Two solutions having same osmotic pressure are called isotonic solutions. Water can flow in or out from substance depending on if it is kept in hypotonic or hypertonic solutions. The direction of the osmosis can be reversed if a pressure larger than osmotic pressure is applied on solution side.
Q. Sea water is desalinated to get fresh water by which of the following methods?
Osmotic pressure is widely used to determine molar masses of proteins and polymers. Two solutions having same osmotic pressure are called isotonic solutions. Water can flow in or out from substance depending on if it is kept in hypotonic or hypertonic solutions. The direction of the osmosis can be reversed if a pressure larger than osmotic pressure is applied on solution side.
Q. Sea water is desalinated to get fresh water by which of the following methods?
a)
When pressure more than osmotic pressure is applied pure water is squeezed out of sea water by reverse osmosis
b)
When excess pressure is applied on sea water pure water moves in by osmosis
c)
Water moves out from sea water due to osmosis
d)
Salt is precipitated from sea water when kept undisturbed for sometime
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Reverse osmosis is used for desalination of sea water.
An aqueous solution of 2% non - volatile solute exerts a pressure of 1.004 bar at the normal boiling point of the solvent. What is the molar mass of the solute?- a)23.4 g mol-1
- b)41.35 g mol-1
- c)10 g mol-1
- d)20.8 g mol-1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An aqueous solution of 2% non - volatile solute exerts a pressure of 1.004 bar at the normal boiling point of the solvent. What is the molar mass of the solute?
a)
23.4 g mol-1
b)
41.35 g mol-1
c)
10 g mol-1
d)
20.8 g mol-1
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Vapour pressure of pure water at boiling point (P∘) = 1 atm = 1.013 bar
Vapour pressure of solution (Ps) = 1.004 bar
Let Mass of solution = 100g
Mass of solute = (w) = 2g
Mass of solvent = 100 - 2 = 98g
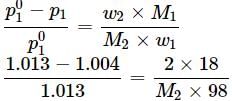
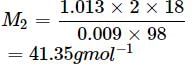
Vapour pressure of solution (Ps) = 1.004 bar
Let Mass of solution = 100g
Mass of solute = (w) = 2g
Mass of solvent = 100 - 2 = 98g
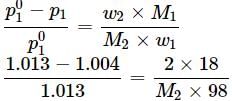
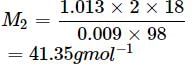
When acetone and chloroform are mixed together, hydrogen bonds are formed between them. Which of the following statements is correct about the solution made by mixing acetone and chloroform?- a)On mixing acetone and chloroform will form an ideal solution
- b)On mixing acetone and chloroform positive deviation is shown since the vapour pressure increases
- c)On mixing acetone and chloroform negative deviation is shown since there is decreae in vapour pressure
- d)At a specific composition acetone and chloroform will form minimum boiling azeotrope
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When acetone and chloroform are mixed together, hydrogen bonds are formed between them. Which of the following statements is correct about the solution made by mixing acetone and chloroform?
a)
On mixing acetone and chloroform will form an ideal solution
b)
On mixing acetone and chloroform positive deviation is shown since the vapour pressure increases
c)
On mixing acetone and chloroform negative deviation is shown since there is decreae in vapour pressure
d)
At a specific composition acetone and chloroform will form minimum boiling azeotrope
|
|
Jhanvi Bajaj answered |
Explanation:
When acetone and chloroform are mixed together, hydrogen bonds are formed between them. This interaction between the molecules affects the overall behavior of the solution.
Positive and Negative Deviation:
The behavior of a solution can be classified as either an ideal solution, positive deviation, or negative deviation based on the change in vapor pressure compared to the vapor pressure of the pure components.
- Ideal Solution: An ideal solution is formed when the vapor pressure of the solution is equal to the vapor pressure of the pure components. In an ideal solution, there are no significant interactions between the molecules, and the vapor pressure follows Raoult's law. This means that the partial vapor pressure of each component is directly proportional to its mole fraction in the solution.
- Positive Deviation: A positive deviation occurs when the vapor pressure of the solution is higher than the vapor pressure of the pure components. This indicates that there are attractive interactions between the molecules in the solution that are stronger than the attractive interactions in the pure components. As a result, the vapor pressure of each component is higher than expected based on Raoult's law.
- Negative Deviation: A negative deviation occurs when the vapor pressure of the solution is lower than the vapor pressure of the pure components. This indicates that there are attractive interactions between the molecules in the solution that are weaker than the attractive interactions in the pure components. As a result, the vapor pressure of each component is lower than expected based on Raoult's law.
Explanation of the Correct Answer:
In the case of acetone and chloroform, when they are mixed together, hydrogen bonds are formed between them. The presence of hydrogen bonds results in stronger attractive interactions between the molecules in the solution.
Since hydrogen bonding is a stronger interaction compared to the van der Waals forces present in the pure components, the attractive interactions between acetone and chloroform molecules in the solution are stronger than the attractive interactions in the pure components. This leads to a decrease in the vapor pressure of both acetone and chloroform in the solution compared to their vapor pressures in the pure state.
Therefore, when acetone and chloroform are mixed together, negative deviation is shown since there is a decrease in vapor pressure. The correct answer is option 'C'.
When acetone and chloroform are mixed together, hydrogen bonds are formed between them. This interaction between the molecules affects the overall behavior of the solution.
Positive and Negative Deviation:
The behavior of a solution can be classified as either an ideal solution, positive deviation, or negative deviation based on the change in vapor pressure compared to the vapor pressure of the pure components.
- Ideal Solution: An ideal solution is formed when the vapor pressure of the solution is equal to the vapor pressure of the pure components. In an ideal solution, there are no significant interactions between the molecules, and the vapor pressure follows Raoult's law. This means that the partial vapor pressure of each component is directly proportional to its mole fraction in the solution.
- Positive Deviation: A positive deviation occurs when the vapor pressure of the solution is higher than the vapor pressure of the pure components. This indicates that there are attractive interactions between the molecules in the solution that are stronger than the attractive interactions in the pure components. As a result, the vapor pressure of each component is higher than expected based on Raoult's law.
- Negative Deviation: A negative deviation occurs when the vapor pressure of the solution is lower than the vapor pressure of the pure components. This indicates that there are attractive interactions between the molecules in the solution that are weaker than the attractive interactions in the pure components. As a result, the vapor pressure of each component is lower than expected based on Raoult's law.
Explanation of the Correct Answer:
In the case of acetone and chloroform, when they are mixed together, hydrogen bonds are formed between them. The presence of hydrogen bonds results in stronger attractive interactions between the molecules in the solution.
Since hydrogen bonding is a stronger interaction compared to the van der Waals forces present in the pure components, the attractive interactions between acetone and chloroform molecules in the solution are stronger than the attractive interactions in the pure components. This leads to a decrease in the vapor pressure of both acetone and chloroform in the solution compared to their vapor pressures in the pure state.
Therefore, when acetone and chloroform are mixed together, negative deviation is shown since there is a decrease in vapor pressure. The correct answer is option 'C'.
Which of the following will have the highest f.pt. at one atmosphere?- a)0.1 M NaCl solution
- b)0.1 M sugar solution
- c)0.1 M BaCl2 solution
- d)0.1 M FeCl3 solution
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following will have the highest f.pt. at one atmosphere?
a)
0.1 M NaCl solution
b)
0.1 M sugar solution
c)
0.1 M BaCl2 solution
d)
0.1 M FeCl3 solution
|
|
Neha Chakraborty answered |
Explanation:
The freezing point depression is a colligative property, which depends on the number of solute particles present in a solution. The more solute particles present, the greater the freezing point depression.
Colligative properties:
Colligative properties are properties of solutions that depend solely on the number of solute particles present, regardless of their identity. These properties include freezing point depression, boiling point elevation, vapor pressure lowering, and osmotic pressure.
Freezing point depression:
Freezing point depression is the phenomenon where the freezing point of a solvent is lowered when a non-volatile solute is added to it. The magnitude of the freezing point depression is directly proportional to the concentration of the solute particles.
Comparison of solutions:
Let's compare the given solutions to determine which one will have the highest freezing point depression:
a) 0.1 M NaCl solution:
- NaCl dissociates into Na+ and Cl- ions in water.
- Therefore, it will have 1 mole of solute particles per mole of NaCl.
- The freezing point depression will be moderate.
b) 0.1 M sugar solution:
- Sugar (such as sucrose) does not dissociate into ions in water.
- Therefore, it will have only 1 mole of solute particles per mole of sugar.
- The freezing point depression will be lower than that of the 0.1 M ionic solutions.
c) 0.1 M BaCl2 solution:
- BaCl2 dissociates into Ba2+ and 2 Cl- ions in water.
- Therefore, it will have 3 moles of solute particles per mole of BaCl2.
- The freezing point depression will be greater than that of the 0.1 M NaCl solution.
d) 0.1 M FeCl3 solution:
- FeCl3 dissociates into Fe3+ and 3 Cl- ions in water.
- Therefore, it will have 4 moles of solute particles per mole of FeCl3.
- The freezing point depression will be greater than that of the 0.1 M BaCl2 solution.
Conclusion:
Among the given options, the 0.1 M sugar solution will have the highest freezing point at one atmosphere because it has the least number of solute particles, resulting in the lowest freezing point depression.
The freezing point depression is a colligative property, which depends on the number of solute particles present in a solution. The more solute particles present, the greater the freezing point depression.
Colligative properties:
Colligative properties are properties of solutions that depend solely on the number of solute particles present, regardless of their identity. These properties include freezing point depression, boiling point elevation, vapor pressure lowering, and osmotic pressure.
Freezing point depression:
Freezing point depression is the phenomenon where the freezing point of a solvent is lowered when a non-volatile solute is added to it. The magnitude of the freezing point depression is directly proportional to the concentration of the solute particles.
Comparison of solutions:
Let's compare the given solutions to determine which one will have the highest freezing point depression:
a) 0.1 M NaCl solution:
- NaCl dissociates into Na+ and Cl- ions in water.
- Therefore, it will have 1 mole of solute particles per mole of NaCl.
- The freezing point depression will be moderate.
b) 0.1 M sugar solution:
- Sugar (such as sucrose) does not dissociate into ions in water.
- Therefore, it will have only 1 mole of solute particles per mole of sugar.
- The freezing point depression will be lower than that of the 0.1 M ionic solutions.
c) 0.1 M BaCl2 solution:
- BaCl2 dissociates into Ba2+ and 2 Cl- ions in water.
- Therefore, it will have 3 moles of solute particles per mole of BaCl2.
- The freezing point depression will be greater than that of the 0.1 M NaCl solution.
d) 0.1 M FeCl3 solution:
- FeCl3 dissociates into Fe3+ and 3 Cl- ions in water.
- Therefore, it will have 4 moles of solute particles per mole of FeCl3.
- The freezing point depression will be greater than that of the 0.1 M BaCl2 solution.
Conclusion:
Among the given options, the 0.1 M sugar solution will have the highest freezing point at one atmosphere because it has the least number of solute particles, resulting in the lowest freezing point depression.
Arrange the following aqueous solutions in the order of their increasing boiling points
(i) 10−4M NaCl
(ii) 10−4M Urea
(iii) 10−3M MgCl2
(iv) 10−2M NaCl- a)(i) < (ii) < (iv) < (iii)
- b)(ii) < (i) = (iii) < (iv)
- c)(ii) < (i) < (iii) < (iv)
- d)(iv) < (iii) < (i) = (ii)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Arrange the following aqueous solutions in the order of their increasing boiling points
(i) 10−4M NaCl
(ii) 10−4M Urea
(iii) 10−3M MgCl2
(iv) 10−2M NaCl
(i) 10−4M NaCl
(ii) 10−4M Urea
(iii) 10−3M MgCl2
(iv) 10−2M NaCl
a)
(i) < (ii) < (iv) < (iii)
b)
(ii) < (i) = (iii) < (iv)
c)
(ii) < (i) < (iii) < (iv)
d)
(iv) < (iii) < (i) = (ii)
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
10−4M NaCl i = 2
10−4M Urea i = 1
10−3M MgCl2 i = 3
10−2M NaCl i = 2
More the value of i, C, more will be the elevation in boiling point hence increasing order of boding point is 10−4M Urea < 10−4M NaCl < 10−3M MgCl2 < 10−2M NaCl
10−4M Urea i = 1
10−3M MgCl2 i = 3
10−2M NaCl i = 2
More the value of i, C, more will be the elevation in boiling point hence increasing order of boding point is 10−4M Urea < 10−4M NaCl < 10−3M MgCl2 < 10−2M NaCl
What will be the molality of a solution of glucose in water which is 10% w/W?- a)0.01 m
- b)0.617 m
- c)0.668 m
- d)1.623 m
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What will be the molality of a solution of glucose in water which is 10% w/W?
a)
0.01 m
b)
0.617 m
c)
0.668 m
d)
1.623 m
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
Mass of the solution = 100g
Mass of glucose = 10g, Mass of water = 90 g
No. of moles of glucose = 10/180 = 0.0555mol
No. of moles of water = 90/18 = 5 mol
Molality = No. of moles of solute/Mass of solvent in kg
= 0.0555mol/0.0090kg = 0.617m
Mass of glucose = 10g, Mass of water = 90 g
No. of moles of glucose = 10/180 = 0.0555mol
No. of moles of water = 90/18 = 5 mol
Molality = No. of moles of solute/Mass of solvent in kg
= 0.0555mol/0.0090kg = 0.617m
The value of Henry's law constant for some gases at 293K is given below. Arrange the gases in the increasing order of their solubility.
He = 144.97kbar; H2 = 69.16kbar
N2 = 76.48kbar; O2 = 34.86kbar- a)He < N2 < H2 < O2
- b)O2 < H2 < N2 < He
- c)H2 < N2 < O2 < He
- d)He < O2 < N2 < H2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The value of Henry's law constant for some gases at 293K is given below. Arrange the gases in the increasing order of their solubility.
He = 144.97kbar; H2 = 69.16kbar
N2 = 76.48kbar; O2 = 34.86kbar
He = 144.97kbar; H2 = 69.16kbar
N2 = 76.48kbar; O2 = 34.86kbar
a)
He < N2 < H2 < O2
b)
O2 < H2 < N2 < He
c)
H2 < N2 < O2 < He
d)
He < O2 < N2 < H2
|
|
Prisha Bajaj answered |
Explanation:
Henry's Law:
Henry's Law states that the solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of that gas above the liquid. Mathematically, it can be represented as:
\[ C = k \times P \]
Where:
C = concentration of the gas in the liquid
k = Henry's Law constant
P = partial pressure of the gas
Given Henry's Law constants:
- He = 144.97 kbar
- H2 = 69.16 kbar
- N2 = 76.48 kbar
- O2 = 34.86 kbar
Increasing order of solubility:
To determine the increasing order of solubility, we need to look at the values of the Henry's Law constants. The higher the value of the constant, the more soluble the gas is in the liquid.
- He (144.97 kbar) has the highest Henry's Law constant, indicating it is the most soluble gas.
- O2 (34.86 kbar) has the lowest Henry's Law constant, indicating it is the least soluble gas.
- H2 (69.16 kbar) and N2 (76.48 kbar) have intermediate values of the Henry's Law constants.
Therefore, the correct increasing order of solubility is:
He < N2 < H2 < O2
Henry's Law:
Henry's Law states that the solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of that gas above the liquid. Mathematically, it can be represented as:
\[ C = k \times P \]
Where:
C = concentration of the gas in the liquid
k = Henry's Law constant
P = partial pressure of the gas
Given Henry's Law constants:
- He = 144.97 kbar
- H2 = 69.16 kbar
- N2 = 76.48 kbar
- O2 = 34.86 kbar
Increasing order of solubility:
To determine the increasing order of solubility, we need to look at the values of the Henry's Law constants. The higher the value of the constant, the more soluble the gas is in the liquid.
- He (144.97 kbar) has the highest Henry's Law constant, indicating it is the most soluble gas.
- O2 (34.86 kbar) has the lowest Henry's Law constant, indicating it is the least soluble gas.
- H2 (69.16 kbar) and N2 (76.48 kbar) have intermediate values of the Henry's Law constants.
Therefore, the correct increasing order of solubility is:
He < N2 < H2 < O2
H2S is a toxic gas used in qualitative analysis. If solubility of H2S in water at STPSTP is 0.195m, what is the value of KH?- a)0.0263 bar
- b)69.16 bar
- c)192 bar
- d)282 bar
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
H2S is a toxic gas used in qualitative analysis. If solubility of H2S in water at STPSTP is 0.195m, what is the value of KH?
a)
0.0263 bar
b)
69.16 bar
c)
192 bar
d)
282 bar
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
No. of moles of H2S = 0.195
No. of moles of H2O = 1000/18 = 55.55mol
Mole fraction of H2S =
Pressure at STP = 0.987 bar
According to Henry’s law, p = KHx
or KH = pH2S/xH2S = 0.98/70.0035
= 282 bar
No. of moles of H2O = 1000/18 = 55.55mol
Mole fraction of H2S =

Pressure at STP = 0.987 bar
According to Henry’s law, p = KHx
or KH = pH2S/xH2S = 0.98/70.0035
= 282 bar
2 g of sugar is added to one litre of water to give sugar solution. What is the effect of addition of sugar on the boiling point and freezing point of water?- a)Both boiling point and freezing point increase
- b)Both boiling point and freezing point decrease
- c)Boiling point increases and freezing point decreases
- d)Boiling point decreases and freezing point increases
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
2 g of sugar is added to one litre of water to give sugar solution. What is the effect of addition of sugar on the boiling point and freezing point of water?
a)
Both boiling point and freezing point increase
b)
Both boiling point and freezing point decrease
c)
Boiling point increases and freezing point decreases
d)
Boiling point decreases and freezing point increases
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
When a non-volatile solute is added to water there is elevation in boiling point and depression is freezing point.
When a gas is bubbled through water at 298K, a very dilute solution of gas is obtained. Henry’s law constant for the gas is 100kbar. If gas exerts a pressure of 1bar1bar, the number of moles of gas dissolved in 11 litre of water is- a)0.555
- b)55.55 × 10−5
- c)55.55 × 10−3
- d)5.55 × 10−5
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When a gas is bubbled through water at 298K, a very dilute solution of gas is obtained. Henry’s law constant for the gas is 100kbar. If gas exerts a pressure of 1bar1bar, the number of moles of gas dissolved in 11 litre of water is
a)
0.555
b)
55.55 × 10−5
c)
55.55 × 10−3
d)
5.55 × 10−5
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
p = KH × x
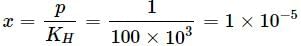
Mole fraction = Moles of gas/Total moles
Moles of H2O = 1000/18 = 55.55 (∵ 1L = 1000 g)
Mole fraction =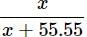 (55.55 >>> x)
(55.55 >>> x)
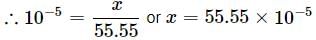
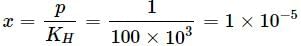
Mole fraction = Moles of gas/Total moles
Moles of H2O = 1000/18 = 55.55 (∵ 1L = 1000 g)
Mole fraction =
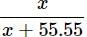 (55.55 >>> x)
(55.55 >>> x)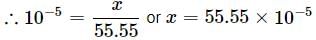
What are the conditions for an ideal solution which obeys Raoult's law over the entire range of concentration?- a)ΔmixH = 0, ΔmixV = 0, PTotal = pAoxA + pBoxB
- b)ΔmixH = +ve, ΔmixV = 0, PTotal = pAoxA + pBoxB
- c)ΔmixH = 0, ΔmixV = +ve, PTotal = pAoxA + pBoxB
- d)ΔmixH = 0, ΔmixV = 0, PTotal = pBoxB
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What are the conditions for an ideal solution which obeys Raoult's law over the entire range of concentration?
a)
ΔmixH = 0, ΔmixV = 0, PTotal = pAoxA + pBoxB
b)
ΔmixH = +ve, ΔmixV = 0, PTotal = pAoxA + pBoxB
c)
ΔmixH = 0, ΔmixV = +ve, PTotal = pAoxA + pBoxB
d)
ΔmixH = 0, ΔmixV = 0, PTotal = pBoxB
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
For an ideal solution, ΔH and Delta ΔV for mixing should be zero. PTotal = pA + pB and A − A, B − B and A − B interactions are nearly same.
Answer the following questions on the basis of given paragraph.
Osmotic pressure is widely used to determine molar masses of proteins and polymers. Two solutions having same osmotic pressure are called isotonic solutions. Water can flow in or out from substance depending on if it is kept in hypotonic or hypertonic solutions. The direction of the osmosis can be reversed if a pressure larger than osmotic pressure is applied on solution side.Q. The preservation of meat by salting and of fruits by adding sugar protects them from bacterial action because- a)Bacteria die of eating sugar or salt
- b)Due to osmosis bacteria lose water on salted meat or candid fruit and die
- c)Due to osmosis bacteria gain water on salted meat or candid fruit and die
- d)Bacteria get stuck to the salt and sugar layers and die
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Answer the following questions on the basis of given paragraph.
Osmotic pressure is widely used to determine molar masses of proteins and polymers. Two solutions having same osmotic pressure are called isotonic solutions. Water can flow in or out from substance depending on if it is kept in hypotonic or hypertonic solutions. The direction of the osmosis can be reversed if a pressure larger than osmotic pressure is applied on solution side.
Osmotic pressure is widely used to determine molar masses of proteins and polymers. Two solutions having same osmotic pressure are called isotonic solutions. Water can flow in or out from substance depending on if it is kept in hypotonic or hypertonic solutions. The direction of the osmosis can be reversed if a pressure larger than osmotic pressure is applied on solution side.
Q. The preservation of meat by salting and of fruits by adding sugar protects them from bacterial action because
a)
Bacteria die of eating sugar or salt
b)
Due to osmosis bacteria lose water on salted meat or candid fruit and die
c)
Due to osmosis bacteria gain water on salted meat or candid fruit and die
d)
Bacteria get stuck to the salt and sugar layers and die
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
The bacteria on salted meat or candid fruit loss water through osmosis, shrink and die.
Answer the following questions on the basis of given paragraph.
Osmotic pressure is widely used to determine molar masses of proteins and polymers. Two solutions having same osmotic pressure are called isotonic solutions. Water can flow in or out from substance depending on if it is kept in hypotonic or hypertonic solutions. The direction of the osmosis can be reversed if a pressure larger than osmotic pressure is applied on solution side.Q. People taking lot of salt experience puffiness or swelling of the body due to- a)Water retention in tissue cells and intercellular spaces because of osmosis
- b)Water loss from the cells through skin tissues
- c)Capillary action of water through skin pores
- d)Excessive thirst and drinking more water
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Answer the following questions on the basis of given paragraph.
Osmotic pressure is widely used to determine molar masses of proteins and polymers. Two solutions having same osmotic pressure are called isotonic solutions. Water can flow in or out from substance depending on if it is kept in hypotonic or hypertonic solutions. The direction of the osmosis can be reversed if a pressure larger than osmotic pressure is applied on solution side.
Osmotic pressure is widely used to determine molar masses of proteins and polymers. Two solutions having same osmotic pressure are called isotonic solutions. Water can flow in or out from substance depending on if it is kept in hypotonic or hypertonic solutions. The direction of the osmosis can be reversed if a pressure larger than osmotic pressure is applied on solution side.
Q. People taking lot of salt experience puffiness or swelling of the body due to
a)
Water retention in tissue cells and intercellular spaces because of osmosis
b)
Water loss from the cells through skin tissues
c)
Capillary action of water through skin pores
d)
Excessive thirst and drinking more water
|
|
Varun Desai answered |
Answer:
Water retention in tissue cells and intercellular spaces because of osmosis
Water retention in tissue cells and intercellular spaces because of osmosis is the correct answer. Let's understand why this is the case in detail.
Osmotic pressure and isotonic solutions:
- Osmotic pressure is commonly used to determine the molar masses of proteins and polymers.
- Two solutions that have the same osmotic pressure are called isotonic solutions.
- In an isotonic solution, the concentration of solute particles is the same inside and outside the cells.
Osmosis and water movement:
- Osmosis is the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration.
- In the context of the human body, osmosis plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of fluids inside and outside the cells.
- When a solution is hypertonic (higher solute concentration) compared to the fluid inside the cells, water moves out of the cells, leading to cell shrinkage.
- On the other hand, when a solution is hypotonic (lower solute concentration) compared to the fluid inside the cells, water moves into the cells, causing them to swell.
Effects of excess salt intake:
- Excessive salt intake can lead to an increase in the concentration of solute particles in the extracellular fluid.
- This increased solute concentration in the extracellular fluid creates a hypertonic solution compared to the fluid inside the cells.
- As a result, water moves out of the cells through osmosis, leading to water retention in the tissue cells and intercellular spaces.
- This water retention causes puffiness or swelling of the body.
Other options:
- Option B: Water loss from the cells through skin tissues does not explain the puffiness or swelling experienced by people taking a lot of salt.
- Option C: Capillary action of water through skin pores does not directly relate to the water retention in tissue cells and intercellular spaces.
- Option D: Excessive thirst and drinking more water may help in diluting the extracellular fluid but does not directly explain the water retention and swelling.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A - Water retention in tissue cells and intercellular spaces because of osmosis.
Water retention in tissue cells and intercellular spaces because of osmosis
Water retention in tissue cells and intercellular spaces because of osmosis is the correct answer. Let's understand why this is the case in detail.
Osmotic pressure and isotonic solutions:
- Osmotic pressure is commonly used to determine the molar masses of proteins and polymers.
- Two solutions that have the same osmotic pressure are called isotonic solutions.
- In an isotonic solution, the concentration of solute particles is the same inside and outside the cells.
Osmosis and water movement:
- Osmosis is the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration.
- In the context of the human body, osmosis plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of fluids inside and outside the cells.
- When a solution is hypertonic (higher solute concentration) compared to the fluid inside the cells, water moves out of the cells, leading to cell shrinkage.
- On the other hand, when a solution is hypotonic (lower solute concentration) compared to the fluid inside the cells, water moves into the cells, causing them to swell.
Effects of excess salt intake:
- Excessive salt intake can lead to an increase in the concentration of solute particles in the extracellular fluid.
- This increased solute concentration in the extracellular fluid creates a hypertonic solution compared to the fluid inside the cells.
- As a result, water moves out of the cells through osmosis, leading to water retention in the tissue cells and intercellular spaces.
- This water retention causes puffiness or swelling of the body.
Other options:
- Option B: Water loss from the cells through skin tissues does not explain the puffiness or swelling experienced by people taking a lot of salt.
- Option C: Capillary action of water through skin pores does not directly relate to the water retention in tissue cells and intercellular spaces.
- Option D: Excessive thirst and drinking more water may help in diluting the extracellular fluid but does not directly explain the water retention and swelling.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A - Water retention in tissue cells and intercellular spaces because of osmosis.
Why is the molecular mass determined by measuring colligative property in case of some solutes is abnormal?- a)Due to association or dissociation of solute molecules
- b)Due to insolubility of solute molecules
- c)Due to decomposition of solute molecules
- d)Due to large size of solute molecules
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Why is the molecular mass determined by measuring colligative property in case of some solutes is abnormal?
a)
Due to association or dissociation of solute molecules
b)
Due to insolubility of solute molecules
c)
Due to decomposition of solute molecules
d)
Due to large size of solute molecules
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
Due to association or dissociation of solute molecules there is a change in number of particles. Since colligative properties depend on number of particles there is a change in molecular mass.
The system that forms maximum boiling azeotrope is- a)Acetone - chloroform
- b)Ethanol - acetone
- c)n-hexane - n- heptane
- d)Carbon disulphide - acetone
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The system that forms maximum boiling azeotrope is
a)
Acetone - chloroform
b)
Ethanol - acetone
c)
n-hexane - n- heptane
d)
Carbon disulphide - acetone
|
|
Muskaan Iyer answered |
Understanding Maximum Boiling Azeotropes
Azeotropes are mixtures of two or more liquids that boil at a constant temperature and maintain the same composition in both liquid and vapor phases. They can be classified into maximum boiling and minimum boiling azeotropes.
Maximum Boiling Azeotropes
- A maximum boiling azeotrope is formed when the boiling point of the mixture is higher than that of any of its components.
- This phenomenon occurs due to strong intermolecular forces between the components, leading to a higher boiling point.
Acetone - Chloroform Azeotrope
- The acetone-chloroform mixture exhibits a maximum boiling azeotropic behavior.
- In this system, strong hydrogen bonding and dipole-dipole interactions create a stable structure that elevates the boiling point.
- The azeotropic mixture has a boiling point higher than either pure acetone or chloroform, making it a classic example of a maximum boiling azeotrope.
Comparison with Other Options
- Ethanol - Acetone: This combination forms a minimum boiling azeotrope due to weaker interactions.
- n-Hexane - n-Heptane: These are non-polar hydrocarbons that do not exhibit azeotropic behavior.
- Carbon Disulphide - Acetone: This mixture also does not form a maximum boiling azeotrope.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option 'A' (Acetone - Chloroform) as it exemplifies the characteristics of a maximum boiling azeotrope with a significantly elevated boiling point compared to its components. Understanding such systems is crucial in distillation and separation processes in chemistry.
Azeotropes are mixtures of two or more liquids that boil at a constant temperature and maintain the same composition in both liquid and vapor phases. They can be classified into maximum boiling and minimum boiling azeotropes.
Maximum Boiling Azeotropes
- A maximum boiling azeotrope is formed when the boiling point of the mixture is higher than that of any of its components.
- This phenomenon occurs due to strong intermolecular forces between the components, leading to a higher boiling point.
Acetone - Chloroform Azeotrope
- The acetone-chloroform mixture exhibits a maximum boiling azeotropic behavior.
- In this system, strong hydrogen bonding and dipole-dipole interactions create a stable structure that elevates the boiling point.
- The azeotropic mixture has a boiling point higher than either pure acetone or chloroform, making it a classic example of a maximum boiling azeotrope.
Comparison with Other Options
- Ethanol - Acetone: This combination forms a minimum boiling azeotrope due to weaker interactions.
- n-Hexane - n-Heptane: These are non-polar hydrocarbons that do not exhibit azeotropic behavior.
- Carbon Disulphide - Acetone: This mixture also does not form a maximum boiling azeotrope.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option 'A' (Acetone - Chloroform) as it exemplifies the characteristics of a maximum boiling azeotrope with a significantly elevated boiling point compared to its components. Understanding such systems is crucial in distillation and separation processes in chemistry.
At high altitudes the partial pressure of oxygen is less than that at the ground level. This leads to- a)Low concentrations of oxygen in the blood and tissues
- b)High concentrations of oxygen in the blood and tissues
- c)Release of dissolved gases and formation of bubbles of nitrogen in the blood
- d)Thickening of blood and tissues
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
At high altitudes the partial pressure of oxygen is less than that at the ground level. This leads to
a)
Low concentrations of oxygen in the blood and tissues
b)
High concentrations of oxygen in the blood and tissues
c)
Release of dissolved gases and formation of bubbles of nitrogen in the blood
d)
Thickening of blood and tissues
|
|
Disha Basu answered |
Understanding Partial Pressure of Oxygen at High Altitudes
At high altitudes, the atmosphere is thinner, leading to a decrease in the partial pressure of oxygen. This phenomenon has significant physiological implications.
Effects of Reduced Partial Pressure
- At lower altitudes, the partial pressure of oxygen is higher, allowing for efficient oxygen diffusion into the bloodstream.
- As altitude increases, the air pressure drops, resulting in a lower partial pressure of oxygen. This means there are fewer oxygen molecules available for inhalation.
Consequences on Oxygen Concentration
- Low Oxygen Availability: The reduced partial pressure leads to lower concentrations of oxygen in the blood and tissues.
- Hypoxia: This condition, known as hypoxia, can cause symptoms like dizziness, shortness of breath, and fatigue due to insufficient oxygen supply to body tissues.
Physiological Adaptations
- In response to low oxygen levels, the body may attempt to compensate by increasing heart rate and breathing rate.
- Over time, acclimatization can occur, where the body adapts to lower oxygen levels, but this process can take days to weeks.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct answer is option 'A'—low concentrations of oxygen in the blood and tissues. The decrease in partial pressure at high altitudes directly impacts oxygen availability, leading to potential health challenges for individuals who ascend rapidly without proper acclimatization.
At high altitudes, the atmosphere is thinner, leading to a decrease in the partial pressure of oxygen. This phenomenon has significant physiological implications.
Effects of Reduced Partial Pressure
- At lower altitudes, the partial pressure of oxygen is higher, allowing for efficient oxygen diffusion into the bloodstream.
- As altitude increases, the air pressure drops, resulting in a lower partial pressure of oxygen. This means there are fewer oxygen molecules available for inhalation.
Consequences on Oxygen Concentration
- Low Oxygen Availability: The reduced partial pressure leads to lower concentrations of oxygen in the blood and tissues.
- Hypoxia: This condition, known as hypoxia, can cause symptoms like dizziness, shortness of breath, and fatigue due to insufficient oxygen supply to body tissues.
Physiological Adaptations
- In response to low oxygen levels, the body may attempt to compensate by increasing heart rate and breathing rate.
- Over time, acclimatization can occur, where the body adapts to lower oxygen levels, but this process can take days to weeks.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct answer is option 'A'—low concentrations of oxygen in the blood and tissues. The decrease in partial pressure at high altitudes directly impacts oxygen availability, leading to potential health challenges for individuals who ascend rapidly without proper acclimatization.
Henry's law constant for the molality of methane in benzene at 298 K is 4.27 × 105 mm Hg. The mole fraction of methane in benzene at 298 K under 760 mm Hg is- a)1.78 x 10-3
- b)17.43
- c)0.114
- d)2.814
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Henry's law constant for the molality of methane in benzene at 298 K is 4.27 × 105 mm Hg. The mole fraction of methane in benzene at 298 K under 760 mm Hg is
a)
1.78 x 10-3
b)
17.43
c)
0.114
d)
2.814
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
According to Henry's law, p = KHx
x = p/KH
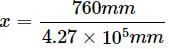 = 1.78 x 10-3
= 1.78 x 10-3
x = p/KH
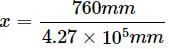 = 1.78 x 10-3
= 1.78 x 10-3What is the mass of urea required for making 2.5 kg of 0.25 molal aqueous solution?- a)37 g
- b)25 g
- c)125 g
- d)27.5 g
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the mass of urea required for making 2.5 kg of 0.25 molal aqueous solution?
a)
37 g
b)
25 g
c)
125 g
d)
27.5 g
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Mass of solvent = 1000 g
Molar mass of urea (NH2CONH2) = 60gmol−1
0.25 mole of urea = 0.25 × 60 = 15g
Total mass of solution = 100 + 15 = 1.015kg
1.015 kg of solution contain urea = 15g
2.5 kg of solution =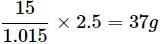
Molar mass of urea (NH2CONH2) = 60gmol−1
0.25 mole of urea = 0.25 × 60 = 15g
Total mass of solution = 100 + 15 = 1.015kg
1.015 kg of solution contain urea = 15g
2.5 kg of solution =
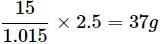
Chapter doubts & questions for Solutions - NCERT Based Tests for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Solutions - NCERT Based Tests for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily