All Exams >
NEET >
Chemistry CUET UG Mock Test Series 2026 >
All Questions
All questions of Coordination Compounds for NEET Exam
The correct IUPAC name of the complex Fe(C5H5)2 is _- a)Cyclopentadienyl iron (II)
- b)Bis (cyclopentadienyl) iron (II)
- c)Dicyclopentadiency ferrate (II)
- d)Ferrocene
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct IUPAC name of the complex Fe(C5H5)2 is _
a)
Cyclopentadienyl iron (II)
b)
Bis (cyclopentadienyl) iron (II)
c)
Dicyclopentadiency ferrate (II)
d)
Ferrocene
|
|
Alok Mehta answered |
The iron complex may be treated as cationic part, and C5H5- is a bidentate ligand therefore name can be assigned as follows “dicyclopentadienyl Iron (II) cation”.
The magnetic moment of [Ru(H2O)6]2+ corresponds to the presence of ...... unpaired electrons.
Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?
The magnetic moment of [Ru(H2O)6]2+ corresponds to the presence of ...... unpaired electrons.

|
Anuj Iyer answered |
Ru2+ =[Kr] 4d6. This forms outer complex. Hence, unpaired electrons are 4.
The IUPAC name of [Ni(PPh3)2CI2]2+ is- a)bis dichloro(triphenylphosphine) nickel (II) ion
- b)dichloro bis (triphenylphosphine) nickel (ll)ion
- c)dichloro triphenylphosphine nickel (II) ion
- d)triphenylphosphine nickel (ll)dichloride
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The IUPAC name of [Ni(PPh3)2CI2]2+ is
a)
bis dichloro(triphenylphosphine) nickel (II) ion
b)
dichloro bis (triphenylphosphine) nickel (ll)ion
c)
dichloro triphenylphosphine nickel (II) ion
d)
triphenylphosphine nickel (ll)dichloride
|
|
Aravind Rane answered |
The IUPAC name of [Ni(PPh3)CI2]2+ is dichlo ro bis (triphenylphosphine) nickel (II) ion.
A magnetic moment of 1.73 BM will be shown by one among the following- a)[Cu(NH3)4]2+
- b)[Ni(CN)4]2–
- c)TiCl4
- d)[CoCl6]4–
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A magnetic moment of 1.73 BM will be shown by one among the following
a)
[Cu(NH3)4]2+
b)
[Ni(CN)4]2–
c)
TiCl4
d)
[CoCl6]4–
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
The correct answer is Option A.
Electronic configuration of Cu2+ ion in [Cu(NH3)4]2+.
Cu2+ ion =[Ar]3d94s0.
∴Cu2+ ion has one unpaired electron.
Magnetic moment of [Cu(NH3)4]2+ (μ) =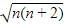 BM
BM
where, n = no. of unpaired electrons
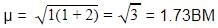
Whereas Ni2+ in [Ni(CN)4]2− , Ti4+ in TiCl4 and Co2+ ion [COCl6]4− has 2,0 and 3 unpaired electrons respectively.
Electronic configuration of Cu2+ ion in [Cu(NH3)4]2+.
Cu2+ ion =[Ar]3d94s0.
∴Cu2+ ion has one unpaired electron.
Magnetic moment of [Cu(NH3)4]2+ (μ) =
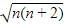 BM
BMwhere, n = no. of unpaired electrons
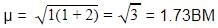
Whereas Ni2+ in [Ni(CN)4]2− , Ti4+ in TiCl4 and Co2+ ion [COCl6]4− has 2,0 and 3 unpaired electrons respectively.
The IUPAC name of the complex [(CO)5Mn - Mn(CO)5] is- a)bis (pentacarbonyl dimanganese)
- b)bis (pentacarbonyldimanganate(ll)
- c)decacarbonyldimanganate (0).
- d)bis (pentacarbonyldimanganese(O)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The IUPAC name of the complex [(CO)5Mn - Mn(CO)5] is
a)
bis (pentacarbonyl dimanganese)
b)
bis (pentacarbonyldimanganate(ll)
c)
decacarbonyldimanganate (0).
d)
bis (pentacarbonyldimanganese(O)
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Decacarbonyldimanganese (0), Mn2(CO)10, is made up of two square pyramidal Mn(CO)5 units joined by a Mn-Mn bond.
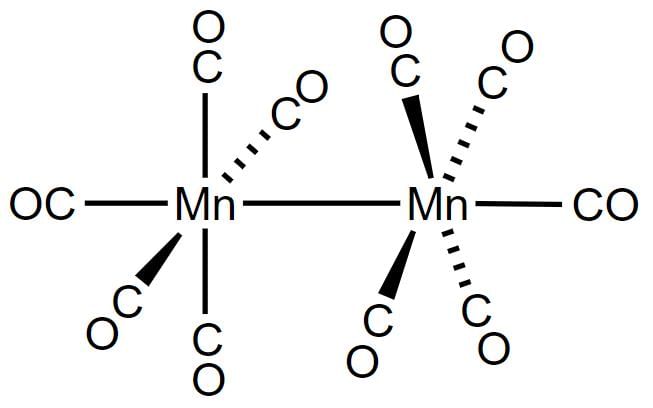
One or More than One Options Correct TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 11-15) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.Q. Which of the following complexes have correct name?- a)K [Pt(NH3)CI5] = potassiumamminepentachloridoplatinate (IV)
- b)[Ag(CN)2]- = dicyanidoargentate(l) ion
- c)K3[Cr(C2O4)3] = tripotassium trioxalatochromate(lll)
- d)Na2[Ni(EDTA)] = sodium ethylenediaminetetraacetatonickel(ll)
Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
One or More than One Options Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-15) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
Which of the following complexes have correct name?
a)
K [Pt(NH3)CI5] = potassiumamminepentachloridoplatinate (IV)
b)
[Ag(CN)2]- = dicyanidoargentate(l) ion
c)
K3[Cr(C2O4)3] = tripotassium trioxalatochromate(lll)
d)
Na2[Ni(EDTA)] = sodium ethylenediaminetetraacetatonickel(ll)
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Complexes K[Pt(NH3)Cl5] and [Ag(CN)2]- have been given their respective IUPAC names.
Tollen’s reagent contains- a)AgOH
- b)AgNO3
- c)[Ag(NO3)2]+
- d)[Ag(NH3)2]+
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Tollen’s reagent contains
a)
AgOH
b)
AgNO3
c)
[Ag(NO3)2]+
d)
[Ag(NH3)2]+

|
Akash Shah answered |
Toilen’s reagent is ammoniacal silver nitrate solution. It is used to distinguish aldehydes and ketones, reducing and non-reducing sugars.
The formula of the complex hexamminecobalt (III) chloride sulphate is- a)[Co(NH3)6]CISO4
- b)[Co(NH3)6CI]SO4
- c)[Co(NH3)6CISO4]
- d)None of these
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The formula of the complex hexamminecobalt (III) chloride sulphate is
a)
[Co(NH3)6]CISO4
b)
[Co(NH3)6CI]SO4
c)
[Co(NH3)6CISO4]
d)
None of these
|
|
Anshika Menon answered |
Formula of Complex Hexamminecobalt (III) Chloride Sulphate
The correct answer is 'A' which represents the formula [Co(NH3)6]ClSO4. Let's break down the answer into the following headings:
I. Understanding the Formula
II. Explanation of the Formula
III. Conclusion
I. Understanding the Formula
Before we dive into the formula, let's understand some key terms:
- Complex: A molecule or ion formed by the combination of a metal ion with a ligand (a molecule or ion that can donate a pair of electrons to the metal ion)
- Hexamminecobalt (III) chloride: A complex formed by the combination of cobalt (III) ion with six ammonia molecules and one chloride ion
- Sulphate: A compound containing the sulphate ion (SO4 2-)
II. Explanation of the Formula
The given complex contains cobalt (III) ion, six ammonia molecules (NH3), one chloride ion (Cl-), and one sulphate ion (SO4 2-). The cobalt (III) ion is coordinated by six ammonia molecules forming an octahedral complex. The chloride ion and sulphate ion occupy the remaining two positions of the octahedral complex. Therefore, the formula of the complex is [Co(NH3)6]ClSO4.
III. Conclusion
In conclusion, the formula of the complex hexamminecobalt (III) chloride sulphate is [Co(NH3)6]ClSO4. The complex contains cobalt (III) ion coordinated by six ammonia molecules, one chloride ion, and one sulphate ion.
The correct answer is 'A' which represents the formula [Co(NH3)6]ClSO4. Let's break down the answer into the following headings:
I. Understanding the Formula
II. Explanation of the Formula
III. Conclusion
I. Understanding the Formula
Before we dive into the formula, let's understand some key terms:
- Complex: A molecule or ion formed by the combination of a metal ion with a ligand (a molecule or ion that can donate a pair of electrons to the metal ion)
- Hexamminecobalt (III) chloride: A complex formed by the combination of cobalt (III) ion with six ammonia molecules and one chloride ion
- Sulphate: A compound containing the sulphate ion (SO4 2-)
II. Explanation of the Formula
The given complex contains cobalt (III) ion, six ammonia molecules (NH3), one chloride ion (Cl-), and one sulphate ion (SO4 2-). The cobalt (III) ion is coordinated by six ammonia molecules forming an octahedral complex. The chloride ion and sulphate ion occupy the remaining two positions of the octahedral complex. Therefore, the formula of the complex is [Co(NH3)6]ClSO4.
III. Conclusion
In conclusion, the formula of the complex hexamminecobalt (III) chloride sulphate is [Co(NH3)6]ClSO4. The complex contains cobalt (III) ion coordinated by six ammonia molecules, one chloride ion, and one sulphate ion.
IUPAC name of [Pt(NH3)2Cl(NO2)] is - a)Platinum diamminechloronitrite
- b)Chloronitrito-N-ammineplatinum (II)
- c)Diamminechloridonitrito-N-platinum (II)
- d)Diamminechloronitrito-N-plantinate (II)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
IUPAC name of [Pt(NH3)2Cl(NO2)] is
a)
Platinum diamminechloronitrite
b)
Chloronitrito-N-ammineplatinum (II)
c)
Diamminechloridonitrito-N-platinum (II)
d)
Diamminechloronitrito-N-plantinate (II)
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Ans: c
Explanation:Pt(NH3)2Cl(NO2)
m − 2 = 0
m = +2
(NH3)2 ⇒ Diammine
Cl ⇒ Chlorido
NO2 ⇒ Nitrito-N.
So, IUPAC NAME: diamminechloridonitrito-N-platinum(II)
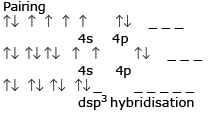
The hybrisation of Co in [Co(H2O)6]3+ is :
- a)d2sp3
- b)dsp2
- c)dsp3
- d)spd3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The hybrisation of Co in [Co(H2O)6]3+ is :
a)
d2sp3
b)
dsp2
c)
dsp3
d)
spd3
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
In this complex compound the total charge is +3 as H2O is a neutral compound so the oxidation state of cobalt is +3 and the electronic configuration of Co is 3d7 4s2. So, Co(+3)=4d6 and H2O is a weak ligand so there is no pairing of electron. So,4s 4p3 and 4d2 orbital make hybrid orbital to have a hybridization of d2sp3.
The IUPAC name of the compound [Cr(NH3)5(NCS)][ZnCI4] is- a)pentammine isothiocyanatochromium (III) tetrachlorozincate (II)
- b)pentaammine thiocyanatochromium (III) tetrachlorozincate (II)
- c)pentammine isothiocyanatochromium (0) tetrachlorozincate (IV)
- d)pentammine thiocyanatochromium (0) tetrachlorozincate (IV
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The IUPAC name of the compound [Cr(NH3)5(NCS)][ZnCI4] is
a)
pentammine isothiocyanatochromium (III) tetrachlorozincate (II)
b)
pentaammine thiocyanatochromium (III) tetrachlorozincate (II)
c)
pentammine isothiocyanatochromium (0) tetrachlorozincate (IV)
d)
pentammine thiocyanatochromium (0) tetrachlorozincate (IV

|
Avantika Joshi answered |
The lUPAC name of [Cr(NH3)5(NCS)][ZnCI4] is pentammine isothiocyanatochromium (III) tetrachlorozincate (II).
What is the IUPAC name of compound NaBH4?- a)Sodium boronhydride
- b)Sodium tetrahydridoboron (III)
- c)Sodium tetrahydridoborate (III)
- d)Sodium tetrahydridoborate (I)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the IUPAC name of compound NaBH4?
a)
Sodium boronhydride
b)
Sodium tetrahydridoboron (III)
c)
Sodium tetrahydridoborate (III)
d)
Sodium tetrahydridoborate (I)
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Common name of NaBH4 is sodium borohydride
IUPAC name of NaBH4is sodium tetrahydridoborate{III}
In the complex PtCl4.3NH3 the number of ionisable chlorines is- a)1
- b)3
- c)2
- d)0
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the complex PtCl4.3NH3 the number of ionisable chlorines is
a)
1
b)
3
c)
2
d)
0

|
Srishti Kaur answered |
Pt has coordination number of 4 so 3 chlorine will come outside the coordination sphere.
The complex potassium dicyanodioxalatonickelate (II) in solution produce....... ions.
Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?
The complex potassium dicyanodioxalatonickelate (II) in solution produce....... ions.
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
The structure of potassium dicyanodio xalatonickelate (II) is
K4[Ni(CN)2(ox)2].
K4[Ni(CN)2(ox)2] → 4K+ + [Ni(CN)2(ox)2]-
This produce 5 ions in solution.
K4[Ni(CN)2(ox)2].
K4[Ni(CN)2(ox)2] → 4K+ + [Ni(CN)2(ox)2]-
This produce 5 ions in solution.
Number of EDTA molecules required to form an octahedral complex.
Correct answer is '1'. Can you explain this answer?
Number of EDTA molecules required to form an octahedral complex.
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
One EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) molecule is required to make an octahedral complex with Ca^2+ ion
In the estimation of hardness of water, the reagent used is- a)hypo solution
- b)KMnO4
- c)EDTA solution
- d)K2Cr2O7
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the estimation of hardness of water, the reagent used is
a)
hypo solution
b)
KMnO4
c)
EDTA solution
d)
K2Cr2O7
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The EDTA solution can then be used to determine the hardness of an unknown water sample. Since both EDTA and Ca2+ are colorless, it is necessary to use a special indicator to detect the end point of the titration.
The number of ligands which have strong crystal field splitting thanH2O among SCN-, NCS-, EDTA4- , 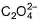 ,
, 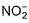 , Br-, PPh3, F-
, Br-, PPh3, F-
Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of ligands which have strong crystal field splitting than
H2O among SCN-, NCS-, EDTA4- , 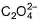 ,
, 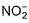 , Br-, PPh3, F-
, Br-, PPh3, F-

|
Learners Habitat answered |
NCS- edta4- , 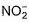 and PPh3 are strong field ligand than H2O.
and PPh3 are strong field ligand than H2O.
KCl.MgCl2.6H2O is a- a)Double salt
- b)Mixed salt
- c)Basic salt
- d)Complex salt
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
KCl.MgCl2.6H2O is a
a)
Double salt
b)
Mixed salt
c)
Basic salt
d)
Complex salt

|
Srestha Choudhury answered |
KCl.MgCl2.6H2O is double salt
From the stability constant (hypothetical values), given below, predict which is the strongest ligand:- a)Cu2+ + 4NH3
 [Cu(NH3)4]2+, K = 4.5 × 1011
[Cu(NH3)4]2+, K = 4.5 × 1011 - b)Cu2+ + 4CN-
 [Cu(CN)4]2- , K = 2.0 × 1027
[Cu(CN)4]2- , K = 2.0 × 1027 - c)Cu2+ + 2en
 [Cu(en)2]2+, K = 3.0 × 1015
[Cu(en)2]2+, K = 3.0 × 1015 - d)Cu2+ + 4H2O
 [Cu(H2O)4]2+, K = 9.5 × 108
[Cu(H2O)4]2+, K = 9.5 × 108
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
From the stability constant (hypothetical values), given below, predict which is the strongest ligand:
a)
Cu2+ + 4NH3  [Cu(NH3)4]2+, K = 4.5 × 1011
[Cu(NH3)4]2+, K = 4.5 × 1011
b)
Cu2+ + 4CN-  [Cu(CN)4]2- , K = 2.0 × 1027
[Cu(CN)4]2- , K = 2.0 × 1027
c)
Cu2+ + 2en  [Cu(en)2]2+, K = 3.0 × 1015
[Cu(en)2]2+, K = 3.0 × 1015
d)
Cu2+ + 4H2O  [Cu(H2O)4]2+, K = 9.5 × 108
[Cu(H2O)4]2+, K = 9.5 × 108

|
Raghav Yadav answered |
Higher the value of K higher will be strength of ligand & more will be thermodynamic stability of complex produced.
In the formation of complex entity, the central atom/ion acts as- a)Bronsted acid
- b)Lewis base
- c)Lewis acid
- d)Bronsted base
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the formation of complex entity, the central atom/ion acts as
a)
Bronsted acid
b)
Lewis base
c)
Lewis acid
d)
Bronsted base
|
|
Arka Das answered |
Explanation:
In the formation of a complex entity, a central atom/ion acts as a Lewis acid. This can be explained as follows:
Lewis Acid and Lewis Base:
According to Lewis acid-base theory, a Lewis acid is a species that accepts a pair of electrons to form a coordinate covalent bond, while a Lewis base is a species that donates a pair of electrons to form a coordinate covalent bond.
Formation of Complex Entity:
A complex entity is formed by the coordination of a central atom/ion with one or more ligands. Ligands are molecules or ions that donate a pair of electrons to the central atom/ion to form a coordinate covalent bond.
Role of Central Atom/Ion:
In the formation of a complex entity, the central atom/ion acts as a Lewis acid because it accepts a pair of electrons from the ligands to form a coordinate covalent bond. The central atom/ion has an incomplete outer shell, which makes it electron deficient and thus able to accept electrons from other species.
Examples:
Some examples of complex entities and their central atom/ion are as follows:
- In [Fe(CN)6]4-, Fe2+ acts as the central ion, which accepts electrons from the CN- ligands.
- In [Cu(NH3)4]2+, Cu2+ acts as the central ion, which accepts electrons from the NH3 ligands.
- In [Ag(NH3)2]+, Ag+ acts as the central ion, which accepts electrons from the NH3 ligands.
Conclusion:
Thus, we can conclude that in the formation of a complex entity, the central atom/ion acts as a Lewis acid because it accepts a pair of electrons from the ligands to form a coordinate covalent bond.
In the formation of a complex entity, a central atom/ion acts as a Lewis acid. This can be explained as follows:
Lewis Acid and Lewis Base:
According to Lewis acid-base theory, a Lewis acid is a species that accepts a pair of electrons to form a coordinate covalent bond, while a Lewis base is a species that donates a pair of electrons to form a coordinate covalent bond.
Formation of Complex Entity:
A complex entity is formed by the coordination of a central atom/ion with one or more ligands. Ligands are molecules or ions that donate a pair of electrons to the central atom/ion to form a coordinate covalent bond.
Role of Central Atom/Ion:
In the formation of a complex entity, the central atom/ion acts as a Lewis acid because it accepts a pair of electrons from the ligands to form a coordinate covalent bond. The central atom/ion has an incomplete outer shell, which makes it electron deficient and thus able to accept electrons from other species.
Examples:
Some examples of complex entities and their central atom/ion are as follows:
- In [Fe(CN)6]4-, Fe2+ acts as the central ion, which accepts electrons from the CN- ligands.
- In [Cu(NH3)4]2+, Cu2+ acts as the central ion, which accepts electrons from the NH3 ligands.
- In [Ag(NH3)2]+, Ag+ acts as the central ion, which accepts electrons from the NH3 ligands.
Conclusion:
Thus, we can conclude that in the formation of a complex entity, the central atom/ion acts as a Lewis acid because it accepts a pair of electrons from the ligands to form a coordinate covalent bond.
Which is the diamagnetic?
- a)[CoF6]3-
- b)[Ni(CN)4]2-
- c)[NiCI3]2-
- d)[Fe(CN)6]3-
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the diamagnetic?
a)
[CoF6]3-
b)
[Ni(CN)4]2-
c)
[NiCI3]2-
d)
[Fe(CN)6]3-
|
|
Niti Mishra answered |
Explanation:
Diamagnetic substances are those which do not have any unpaired electrons and are not attracted by a magnetic field. On the other hand, paramagnetic substances have unpaired electrons and are attracted by a magnetic field.
Let's examine the given options to determine which one is diamagnetic.
[CoF6]3-
Cobalt has 27 electrons. In this complex, cobalt is in the +3 oxidation state. The six fluoride ions act as ligands and each donate one pair of electrons to the cobalt ion. The complex has a total of 33 electrons, and there are three unpaired electrons in the d-orbitals of the cobalt ion. Therefore, [CoF6]3- is a paramagnetic complex.
[Ni(CN)4]2-
Nickel has 28 electrons. In this complex, nickel is in the +2 oxidation state. The four cyanide ions act as ligands and each donate one pair of electrons to the nickel ion. The complex has a total of 34 electrons, and all the electrons are paired. Therefore, [Ni(CN)4]2- is a diamagnetic complex.
[NiCl4]2-
Similar to the above complex, nickel has 28 electrons and is in the +2 oxidation state. The four chloride ions act as ligands and each donate one pair of electrons to the nickel ion. The complex has a total of 32 electrons, and all the electrons are paired. Therefore, [NiCl4]2- is a diamagnetic complex.
[Fe(CN)6]3-
Iron has 26 electrons. In this complex, iron is in the +3 oxidation state. The six cyanide ions act as ligands and each donate one pair of electrons to the iron ion. The complex has a total of 32 electrons, and there are five unpaired electrons in the d-orbitals of the iron ion. Therefore, [Fe(CN)6]3- is a paramagnetic complex.
Therefore, the diamagnetic complex among the given options is [Ni(CN)4]2-.
Diamagnetic substances are those which do not have any unpaired electrons and are not attracted by a magnetic field. On the other hand, paramagnetic substances have unpaired electrons and are attracted by a magnetic field.
Let's examine the given options to determine which one is diamagnetic.
[CoF6]3-
Cobalt has 27 electrons. In this complex, cobalt is in the +3 oxidation state. The six fluoride ions act as ligands and each donate one pair of electrons to the cobalt ion. The complex has a total of 33 electrons, and there are three unpaired electrons in the d-orbitals of the cobalt ion. Therefore, [CoF6]3- is a paramagnetic complex.
[Ni(CN)4]2-
Nickel has 28 electrons. In this complex, nickel is in the +2 oxidation state. The four cyanide ions act as ligands and each donate one pair of electrons to the nickel ion. The complex has a total of 34 electrons, and all the electrons are paired. Therefore, [Ni(CN)4]2- is a diamagnetic complex.
[NiCl4]2-
Similar to the above complex, nickel has 28 electrons and is in the +2 oxidation state. The four chloride ions act as ligands and each donate one pair of electrons to the nickel ion. The complex has a total of 32 electrons, and all the electrons are paired. Therefore, [NiCl4]2- is a diamagnetic complex.
[Fe(CN)6]3-
Iron has 26 electrons. In this complex, iron is in the +3 oxidation state. The six cyanide ions act as ligands and each donate one pair of electrons to the iron ion. The complex has a total of 32 electrons, and there are five unpaired electrons in the d-orbitals of the iron ion. Therefore, [Fe(CN)6]3- is a paramagnetic complex.
Therefore, the diamagnetic complex among the given options is [Ni(CN)4]2-.
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q. According to IUPAC nomenclature, sodium nitroprusside is named as
- a)sodium nitroferricyanide
- b)sodium nitroferrocyanide
- c)sodium pentacyanonitrosyliumferrate (II)
- d)sodium pentacyanonitrosylferrate (III)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q. According to IUPAC nomenclature, sodium nitroprusside is named as
a)
sodium nitroferricyanide
b)
sodium nitroferrocyanide
c)
sodium pentacyanonitrosyliumferrate (II)
d)
sodium pentacyanonitrosylferrate (III)
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
IUPAC name of sodium nitroprusside Na2[Fe(CN)5NO] is sodium pentacyanonitrosyl ferrate (III) because in it NO is neutral ligand and the oxidation number of Fe is +3. Which is calculated as Na2[Fe(CN)5NO]
2 × (+1) + x +5×(−1)+1×0 = 0
2 + x - 5 = 0
x - 3 = 0
x = + 3
2 × (+1) + x +5×(−1)+1×0 = 0
2 + x - 5 = 0
x - 3 = 0
x = + 3
Can you explain the answer of this question below:sp3-hybridisation is found in
- A:
[ZnCI4]2-
- B:
[Cu(NH3)4]2+
- C:
[CuCI4]2-
- D:
[Ni(CO)4]
The answer is A,C,D.
sp3-hybridisation is found in
[ZnCI4]2-
[Cu(NH3)4]2+
[CuCI4]2-
[Ni(CO)4]
|
|
Dipika Rane answered |
Explanation:
SP3 hybridization is a type of hybridization where one s orbital and three p orbitals of the same shell of an atom mix to form four sp3 hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals are arranged in a tetrahedral shape around the central atom.
The given options are:
a) [ZnCl4]2-
b) [Cu(NH3)4]2
c) [CuCl4]2-
d) [Ni(CO)4]
a) [ZnCl4]2-: In this complex ion, the central zinc atom is sp3 hybridized. The zinc ion has an electronic configuration of [Ar]3d104s0. The hybridization of the zinc ion takes place by mixing one 4s orbital and three 4p orbitals to form four sp3 hybrid orbitals.
b) [Cu(NH3)4]2: In this complex ion, the central copper atom is dsp2 hybridized. The copper ion has an electronic configuration of [Ar]3d104s1. The hybridization of the copper ion takes place by mixing one 4s orbital, two 4p orbitals, and one 3d orbital to form five dsp2 hybrid orbitals.
c) [CuCl4]2-: In this complex ion, the central copper atom is sp3 hybridized. The copper ion has an electronic configuration of [Ar]3d104s1. The hybridization of the copper ion takes place by mixing one 4s orbital and three 4p orbitals to form four sp3 hybrid orbitals.
d) [Ni(CO)4]: In this complex ion, the central nickel atom is sp3 hybridized. The nickel ion has an electronic configuration of [Ar]3d84s2. The hybridization of the nickel ion takes place by mixing one 4s orbital and three 4p orbitals to form four sp3 hybrid orbitals.
Conclusion:
Thus, the correct options are A, C, and D, as all these complex ions have a central atom that is sp3 hybridized. The complex ion in option B has a central copper atom that is dsp2 hybridized.
SP3 hybridization is a type of hybridization where one s orbital and three p orbitals of the same shell of an atom mix to form four sp3 hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals are arranged in a tetrahedral shape around the central atom.
The given options are:
a) [ZnCl4]2-
b) [Cu(NH3)4]2
c) [CuCl4]2-
d) [Ni(CO)4]
a) [ZnCl4]2-: In this complex ion, the central zinc atom is sp3 hybridized. The zinc ion has an electronic configuration of [Ar]3d104s0. The hybridization of the zinc ion takes place by mixing one 4s orbital and three 4p orbitals to form four sp3 hybrid orbitals.
b) [Cu(NH3)4]2: In this complex ion, the central copper atom is dsp2 hybridized. The copper ion has an electronic configuration of [Ar]3d104s1. The hybridization of the copper ion takes place by mixing one 4s orbital, two 4p orbitals, and one 3d orbital to form five dsp2 hybrid orbitals.
c) [CuCl4]2-: In this complex ion, the central copper atom is sp3 hybridized. The copper ion has an electronic configuration of [Ar]3d104s1. The hybridization of the copper ion takes place by mixing one 4s orbital and three 4p orbitals to form four sp3 hybrid orbitals.
d) [Ni(CO)4]: In this complex ion, the central nickel atom is sp3 hybridized. The nickel ion has an electronic configuration of [Ar]3d84s2. The hybridization of the nickel ion takes place by mixing one 4s orbital and three 4p orbitals to form four sp3 hybrid orbitals.
Conclusion:
Thus, the correct options are A, C, and D, as all these complex ions have a central atom that is sp3 hybridized. The complex ion in option B has a central copper atom that is dsp2 hybridized.
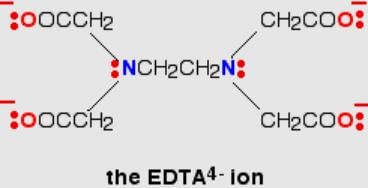
One Integer Value Correct TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 20-24) This section contains 5 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).Q. Ethylenediamminetetraacetate ion is a polydentate ligand and negatively charged. The magnitude of negative charge is
Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?
One Integer Value Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 20-24) This section contains 5 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q. Ethylenediamminetetraacetate ion is a polydentate ligand and negatively charged. The magnitude of negative charge is
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
The correct answer is 4.

In the complex Fe(CO)x, the value of x is
- a)3
- b)2
- c)4
- d)5
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the complex Fe(CO)x, the value of x is
a)
3
b)
2
c)
4
d)
5

|
Maitri Sharma answered |
Complex carbonyls follow Sidwick's EAN rule i.e compound with EAN 36 will be relatively more stable than other metal carbonyls. Iron pentacarbonyl has EAN number of 36 = Z−X+Y = (26−0+2x)
[Z = atomic number, X = oxidation state of metal, Y= total electrons donated by ligand]
∴x = 5. So, the formula will be Fe(CO)5.
[Z = atomic number, X = oxidation state of metal, Y= total electrons donated by ligand]
∴x = 5. So, the formula will be Fe(CO)5.
For the complex ion dichlorido bis (ethylene diamine) cobalt (III), select the correct statement.- a)It has three isomers, two of them are optically active and one is optically inactive.
- b)It has three isomers, all of them are optically active.
- c)It has three isomers, all of them are optically inactive.
- d)It has one optically active isomer and two geometrical isomers.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For the complex ion dichlorido bis (ethylene diamine) cobalt (III), select the correct statement.
a)
It has three isomers, two of them are optically active and one is optically inactive.
b)
It has three isomers, all of them are optically active.
c)
It has three isomers, all of them are optically inactive.
d)
It has one optically active isomer and two geometrical isomers.

|
Nidhi Nambiar answered |
In the complex Fe(CO)x, the value of x is :- a)3
- b)4
- c)5
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the complex Fe(CO)x, the value of x is :
a)
3
b)
4
c)
5
d)
6

|
Aarya Dasgupta answered |
[Fe(CO)x]0
EAN = 26 + 2x = 36
x = 5
EAN = 26 + 2x = 36
x = 5
Which of the following is π complex :- a)Trimethyl aluminium
- b)Ferrocene
- c)Diethyl zinc
- d)Nickel tetra carbonyl
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is π complex :
a)
Trimethyl aluminium
b)
Ferrocene
c)
Diethyl zinc
d)
Nickel tetra carbonyl

|
Nidhi Nambiar answered |
Al(C2H5)3 σ - complex
Fe(C5H5)2 π - complex
Zn(C2H5)2 σ - complex
[Ni(CO)4] σ - complex
Fe(C5H5)2 π - complex
Zn(C2H5)2 σ - complex
[Ni(CO)4] σ - complex
The structure of iron pentacarbonyl is :- a)Square pyramidal
- b)Trigonal bipyramidal
- c)Squrare planar
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The structure of iron pentacarbonyl is :
a)
Square pyramidal
b)
Trigonal bipyramidal
c)
Squrare planar
d)
None of these
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
[Fe(CO)5] TBP
CO is strong field ligand
Fe - 3d64s2
CO is strong field ligand
Fe - 3d64s2
The IUPAC name [CoCl(NO2)(en)2]Cl is- a)Chloridonitrobis (ethylenediamine) cobalt(II) chloride
- b)Chloridobis (ethylenediamine) nitrito-N-cobalt(III) chloride
- c)Bis(ethylenediamine) chloronitrocobalt(III) chloride
- d)Chloridonitrobis (ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chloride
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The IUPAC name [CoCl(NO2)(en)2]Cl is
a)
Chloridonitrobis (ethylenediamine) cobalt(II) chloride
b)
Chloridobis (ethylenediamine) nitrito-N-cobalt(III) chloride
c)
Bis(ethylenediamine) chloronitrocobalt(III) chloride
d)
Chloridonitrobis (ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chloride

|
Baishali Chakraborty answered |
Name of ligands name first in alphabetical order followed by anme of central ion.
Which is/are the correct statements?
- a)CFSE of [Co(NH3)6]3+ < [Rh(NH3)6]3+ < [lr(NH3)6]3+
- b)CFSE of [Co(NH3)6]3+ < [Co(en)3]3+
- c)Δo < P low spin state is more stable
- d)[Ni(H2O)6]2+ complex is green while [Ni(en)3]2+ is blue
Correct answer is option 'A,B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is/are the correct statements?
a)
CFSE of [Co(NH3)6]3+ < [Rh(NH3)6]3+ < [lr(NH3)6]3+
b)
CFSE of [Co(NH3)6]3+ < [Co(en)3]3+
c)
Δo < P low spin state is more stable
d)
[Ni(H2O)6]2+ complex is green while [Ni(en)3]2+ is blue

|
Charvi Ahuja answered |
If Δo < P high spin complexes are favoured.
Which among the following has square pyramidal geometry?- a)Tetracarbonylnickel(0)
- b)Hexaamminecobalt(II) nitrate
- c)Pentacarbonyliron(0)
- d)Bis(acetylacetonato)oxovanadium(IV)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following has square pyramidal geometry?
a)
Tetracarbonylnickel(0)
b)
Hexaamminecobalt(II) nitrate
c)
Pentacarbonyliron(0)
d)
Bis(acetylacetonato)oxovanadium(IV)

|
Malavika Shah answered |
Bis(acetylacetonato)oxovanadium(IV) has square pyramidal geometry.
The pair of compounds having the same hybridisation for the central atom is- a)[Cu(NH3)4]2+ and [Ni(NH3)4]2+
- b)[NiCI4]2- and [PtCI4]2-
- c)(Cu(NH3)4]2+ and [Zn(NH3)4]2+
- d)[Co(NH3)6]3+ and [Co(H2O)6]3+
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The pair of compounds having the same hybridisation for the central atom is
a)
[Cu(NH3)4]2+ and [Ni(NH3)4]2+
b)
[NiCI4]2- and [PtCI4]2-
c)
(Cu(NH3)4]2+ and [Zn(NH3)4]2+
d)
[Co(NH3)6]3+ and [Co(H2O)6]3+

|
Vaishnavi Dasgupta answered |
[Cu(NH3)4]2+ and [Ni(NH3)4]2+ the central atoms have dsp2 hybridisation.
The IUPAC name of the compound K[SbCl5Ph] is
- a)Potassium chlorophenylantimonate (V)
- b)Potassium pentachloro(phenyl) antimonate (V)
- c)Potassium pentachlorobenzylantimonate (V)
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The IUPAC name of the compound K[SbCl5Ph] is
a)
Potassium chlorophenylantimonate (V)
b)
Potassium pentachloro(phenyl) antimonate (V)
c)
Potassium pentachlorobenzylantimonate (V)
d)
None of the above
|
|
Rutuja Ahuja answered |
The correct option is B Potassium pentachloro(phenyl) antimonate(V)
IUPAC naming of coordination compound:
The names of coordination compounds are derived by the following principles of nomenclature,
1. The cation is named first in both positively and negatively charged coordination entities.
2. The ligands are named in an alphabetical order before the name of the central atom/ion.
3. When coordination entity is anionic, the name of central metal atom end with 'ate' followed by its oxidation number in roman numericals.
In given compound, the charge on coordination entity is -1.
Cl− and phenyl are monodentate anionic ligand.
Thus, the oxidation state of Sb is +5.
Hence, the IUPAC name of the compound K[SbCl5Ph] is Potassium pentachloro(phenyl)antimonate(V)
IUPAC naming of coordination compound:
The names of coordination compounds are derived by the following principles of nomenclature,
1. The cation is named first in both positively and negatively charged coordination entities.
2. The ligands are named in an alphabetical order before the name of the central atom/ion.
3. When coordination entity is anionic, the name of central metal atom end with 'ate' followed by its oxidation number in roman numericals.
In given compound, the charge on coordination entity is -1.
Cl− and phenyl are monodentate anionic ligand.
Thus, the oxidation state of Sb is +5.
Hence, the IUPAC name of the compound K[SbCl5Ph] is Potassium pentachloro(phenyl)antimonate(V)
In which of the following porphyrin acts as ligand?- a)Haemoglobin
- b)Chlorophyll
- c)Vitamin B-12
- d)Insulin
Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following porphyrin acts as ligand?
a)
Haemoglobin
b)
Chlorophyll
c)
Vitamin B-12
d)
Insulin
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
The Heme Porphyrin. Although the hemoglobin and myoglobin molecules are very large, complex proteins, the active site is actually a non-protein group called heme. The heme consists of a flat organic ring surrounding an iron atom.
Chlorophylls are numerous in types, but all are defined by the presence of a fifth ring beyond the four pyrrole-like rings. Most chlorophylls are classified as chlorins, which are reduced relatives to porphyrins (found in hemoglobin). They share a common biosynthetic pathway as porphyrins, including the precursor uroporphyrinogen III. Unlike hemes, which feature iron at the center of the tetrapyrrole ring, chlorophylls bind magnesium. For the structures depicted in this article, some of the ligands attached to the Mg2+ center are omitted for clarity. The chlorin ring can have various side chains, usually including a long phytol chain. The most widely distributed form in terrestrial plants is chlorophyll a.
The correct IUPAC name of Mn3(C0)12 is- a)Dodecacarbonylmanganate(0)
- b)Manganicdodecacarbonyl(0)
- c)Dodecacarbonylmanganese(0)
- d)Dodecacarbonylmaganic(II)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct IUPAC name of Mn3(C0)12 is
a)
Dodecacarbonylmanganate(0)
b)
Manganicdodecacarbonyl(0)
c)
Dodecacarbonylmanganese(0)
d)
Dodecacarbonylmaganic(II)

|
Kunal Pillai answered |
Ligands are named 1st followed by the name of central metal ion.
The EAN of platinum in potassium hexachloroplatinate (IV) is :- a)46
- b)86
- c)36
- d)84
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The EAN of platinum in potassium hexachloroplatinate (IV) is :
a)
46
b)
86
c)
36
d)
84

|
Dishani Kulkarni answered |
K2+4[PtCl6]
At No. Pt = 78
EAN = 78 – 4 + 6 × 2 = 86
At No. Pt = 78
EAN = 78 – 4 + 6 × 2 = 86
In which of the following complexes the nickel metal is in highest oxidation state.- a)Ni(CO)4
- b)[Cr(NH3)6]2[NiF 6]3
- c)[Ni(NH3)6](BF4) 2
- d)K4[Ni(CN)6]
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following complexes the nickel metal is in highest oxidation state.
a)
Ni(CO)4
b)
[Cr(NH3)6]2[NiF 6]3
c)
[Ni(NH3)6](BF4) 2
d)
K4[Ni(CN)6]

|
Milan Datta answered |
Introduction:
In coordination chemistry, the oxidation state of a metal ion refers to the charge that the metal ion would have if all the ligands were removed along with the electron pairs that were shared with the ligands. The oxidation state of a metal ion can range from positive to negative depending on the number of electrons it has gained or lost.
Explanation:
To determine the oxidation state of nickel in each complex, we need to consider the oxidation states of the other elements and the overall charge of the complex.
a) Ni(CO)4:
In this complex, each carbon monoxide (CO) ligand is considered neutral because carbon has an oxidation state of +2 and oxygen has an oxidation state of -2. Therefore, the overall charge of the complex is 0. Since there are no other ligands present, the oxidation state of nickel must be 0.
b) [Cr(NH3)6]2[NiF6]3:
In this complex, the oxidation state of chromium is +3 since each ammonia (NH3) ligand is neutral and the overall charge of the complex is 2+. The oxidation state of fluorine is -1. Therefore, to balance the charges, the oxidation state of nickel must be +3.
c) [Ni(NH3)6](BF4)2:
In this complex, the oxidation state of boron in the tetrafluoroborate (BF4) ion is +3, and the oxidation state of fluorine is -1. Since the overall charge of the complex is 0, the oxidation state of nickel must be +2 to balance the charges.
d) K4[Ni(CN)6]:
In this complex, the oxidation state of potassium is +1. The cyanide (CN) ligand is considered neutral, with carbon having an oxidation state of +2 and nitrogen having an oxidation state of -3. Therefore, to balance the charges, the oxidation state of nickel must be +2.
Conclusion:
Among the given complexes, the complex [Cr(NH3)6]2[NiF6]3 has the highest oxidation state of nickel, which is +3.
In coordination chemistry, the oxidation state of a metal ion refers to the charge that the metal ion would have if all the ligands were removed along with the electron pairs that were shared with the ligands. The oxidation state of a metal ion can range from positive to negative depending on the number of electrons it has gained or lost.
Explanation:
To determine the oxidation state of nickel in each complex, we need to consider the oxidation states of the other elements and the overall charge of the complex.
a) Ni(CO)4:
In this complex, each carbon monoxide (CO) ligand is considered neutral because carbon has an oxidation state of +2 and oxygen has an oxidation state of -2. Therefore, the overall charge of the complex is 0. Since there are no other ligands present, the oxidation state of nickel must be 0.
b) [Cr(NH3)6]2[NiF6]3:
In this complex, the oxidation state of chromium is +3 since each ammonia (NH3) ligand is neutral and the overall charge of the complex is 2+. The oxidation state of fluorine is -1. Therefore, to balance the charges, the oxidation state of nickel must be +3.
c) [Ni(NH3)6](BF4)2:
In this complex, the oxidation state of boron in the tetrafluoroborate (BF4) ion is +3, and the oxidation state of fluorine is -1. Since the overall charge of the complex is 0, the oxidation state of nickel must be +2 to balance the charges.
d) K4[Ni(CN)6]:
In this complex, the oxidation state of potassium is +1. The cyanide (CN) ligand is considered neutral, with carbon having an oxidation state of +2 and nitrogen having an oxidation state of -3. Therefore, to balance the charges, the oxidation state of nickel must be +2.
Conclusion:
Among the given complexes, the complex [Cr(NH3)6]2[NiF6]3 has the highest oxidation state of nickel, which is +3.
Which of the following species is not expected to be a ligand?- a)NO
- b)NH4+
- c)NH2CH2CH2NH2
- d)CO
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following species is not expected to be a ligand?
a)
NO
b)
NH4+
c)
NH2CH2CH2NH2
d)
CO
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
The correct answer is option B
Complexes are formed when ligands donate a pair of electrons to metals. In ammonia, N atom has one lone pair of electrons. Nitrogen donates this lone pair of electrons to protons to form ammonium ion. So NH4+ ion does not have a lone pair of electrons which it can donate to central metal ions. Hence it cannot behave as a ligand.
Complexes are formed when ligands donate a pair of electrons to metals. In ammonia, N atom has one lone pair of electrons. Nitrogen donates this lone pair of electrons to protons to form ammonium ion. So NH4+ ion does not have a lone pair of electrons which it can donate to central metal ions. Hence it cannot behave as a ligand.
The oxidation state of Mo in its oxo-complex species [Mo2O4(C2H4 )2(H2O)2]2- is :- a)+2
- b)+3
- c)+4
- d)+5
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The oxidation state of Mo in its oxo-complex species [Mo2O4(C2H4 )2(H2O)2]2- is :
a)
+2
b)
+3
c)
+4
d)
+5

|
Charvi Ahuja answered |
Let the O. N. of Mo in the complex is x
2x + (–2) × 2 + 0 × 2 + 0 × 2 = – 2
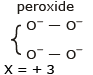
2x + (–2) × 2 + 0 × 2 + 0 × 2 = – 2
The increasing order of wavelength of absorption for the complex ions
I. [Cr(NH3)6]3+
II. [CrCI6]3-
III. [Cr(H2O)6]3+
IV. [Cr(CN)6]3-
is :
a)IV < I < III < IIb)IV < III < II < Ic)IV < II < III < Id)II < III < I < IVCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
IV. [Cr(CN)6]3-

|
Mrinalini Chopra answered |
Weak field ligand have minimum wavelength of absorption.
Chapter doubts & questions for Coordination Compounds - Chemistry CUET UG Mock Test Series 2026 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Coordination Compounds - Chemistry CUET UG Mock Test Series 2026 in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup


















