All Exams >
NEET >
Chemistry CUET UG Mock Test Series 2026 >
All Questions
All questions of Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers for NEET Exam
Identify the alcohol or phenol having a stronger acidic nature from the following.- a)CH3CH2OH
- b)C6H5OH
- c)CH3CHOHCH2CH3
- d)CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the alcohol or phenol having a stronger acidic nature from the following.
a)
CH3CH2OH
b)
C6H5OH
c)
CH3CHOHCH2CH3
d)
CH3CH2CH2CH2OH

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
- Phenol (C₆H₅OH) is more acidic than typical alcohols.
- This is due to the resonance stabilization of the phenoxide ion formed when phenol loses a hydrogen ion (H⁺).
- The negative charge on the oxygen atom in phenoxide ion is delocalized over the aromatic ring, increasing stability and acidity.
- In contrast, alcohols like ethanol (CH₃CH₂OH) do not have such resonance stabilization, making them less acidic.
- Therefore, phenol is the strongest acid among the given options.
- This is due to the resonance stabilization of the phenoxide ion formed when phenol loses a hydrogen ion (H⁺).
- The negative charge on the oxygen atom in phenoxide ion is delocalized over the aromatic ring, increasing stability and acidity.
- In contrast, alcohols like ethanol (CH₃CH₂OH) do not have such resonance stabilization, making them less acidic.
- Therefore, phenol is the strongest acid among the given options.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:The acidity of phenols is due to
- A:
Oxidation process
- B:
Resonance stabilization of its ions.
- C:
Hybridisation
- D:
Presence of O-H group
The answer is b.
The acidity of phenols is due to
Oxidation process
Resonance stabilization of its ions.
Hybridisation
Presence of O-H group
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
The acidity of phenols is due to its ability to lose hydrogen ion to form phenoxide ions. In a phenol molecule, the sp2hybridised carbon atom of benzene ring attached directly to the hydroxyl group acts as an electron withdrawing group. This sp2 hybridized carbon atom of benzene ring attached directly to the hydroxyl group has higher electronegativity in comparison to hydroxyl group. Due to the higher electronegativity of this carbon atom in comparison to the hydroxyl group attached, electron density decreases on oxygen atom. The decrease in electron density increases the polarity of O-H bond and results in the increase in ionization of phenols. Thus, the phenoxide ion is formed. The phenoxide ion formed is stabilized by the delocalization of negative charge due to the resonance in benzene ring. Phenoxide ion has greater stability than phenols, as in case of phenol charge separation takes place during resonance.The resonance structures of phenoxide ions explain the delocalization of negative charge. In case of substituted phenols, acidity of phenols increases in the presence of electron withdrawing group. This is due to the stability of the phenoxide ion generated. The acidity of phenols further increases if these groups are attached at ortho and para positions. This is due to the fact that the negative charge in phenoxide ion is mainly delocalized at ortho and para positions of the attached benzene ring. On the other hand, the acidity of phenols decreases in presence of electron donating groups as they prohibit the formation of phenoxide ion.
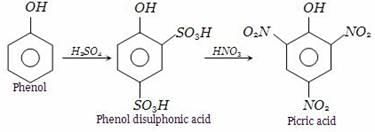
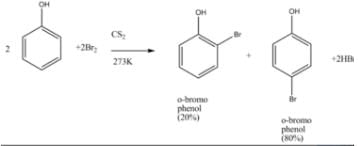
We can obtain picric acid from phenol by:- a)Sulphonation of phenol
- b)By Reimer Tiemann reaction
- c)Nitration of phenol
- d)Halogenation of phenol
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
We can obtain picric acid from phenol by:
a)
Sulphonation of phenol
b)
By Reimer Tiemann reaction
c)
Nitration of phenol
d)
Halogenation of phenol
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
Phenol heated with sulphuric acid gives phenol disulphonic acid, which further on reaction with nitric acid forms picric acid (2,4,6-trinitrophenol).
IUPAC name of m-cresol is ___________.- a)3-methylphenol
- b)3-chlorophenol
- c) 3-methoxyphenol
- d)benzene-1,3-diol
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
IUPAC name of m-cresol is ___________.
a)
3-methylphenol
b)
3-chlorophenol
c)
3-methoxyphenol
d)
benzene-1,3-diol
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Meta-Cresol, also 3-methylphenol, is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4(OH). It is a colourless, viscous liquid that is used as an intermediate in the production of other chemicals. It is a derivative of phenol and is an isomer of p-cresol and o-cresol.
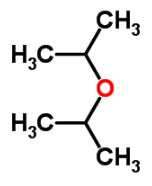
What is the IUPAC name of di-isopropyl ethera)Salicyaldehydeb)Ethyl acetatec)Iso propoxy propaned)Ethyl methyl etherCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
2-Iso propoxy propane
- Molecular Formula: C6H14O
- Average mass: 102.174797 Da
- Monoisotopic mass: 102.104462 Da

Phenols do not respond to which of these tests?- a)Schiff’s reagent test
- b)FeCl3 test
- c)Br2 water test
- d)Litmus test
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Phenols do not respond to which of these tests?
a)
Schiff’s reagent test
b)
FeCl3 test
c)
Br2 water test
d)
Litmus test
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Phenols respond to all the above mentioned tests except Schiff’s reagent test, which is shown by aldehydes.
One or More than One Options Correct TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 9-14) This section contains 6 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correctConsider the following reaction,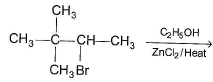 Q. The expected substitution product(s) is/are
Q. The expected substitution product(s) is/are- a)
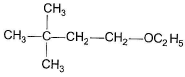
- b)
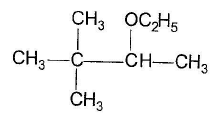
- c)
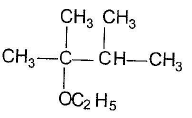
- d)
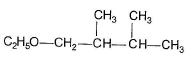
Correct answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
One or More than One Options Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 9-14) This section contains 6 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct
Consider the following reaction,
Q.
The expected substitution product(s) is/are
a)
b)

c)

d)

|
Agam Bagga answered |
No i can't explain this
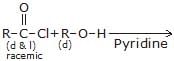 Product of above reaction is -
Product of above reaction is -- a)Enantiomer
- b)Racemic
- c)Diastereomers
- d)Meso
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Product of above reaction is -
a)
Enantiomer
b)
Racemic
c)
Diastereomers
d)
Meso
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |

HCl is formed in above reaction and react with pyridine and gives
Williamsons synthesis is an example of :- a)Electrophilic substitution
- b)Electrophilic addition
- c)Nucleophilic substitution reaction
- d)Nucleophilic addition
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Williamsons synthesis is an example of :
a)
Electrophilic substitution
b)
Electrophilic addition
c)
Nucleophilic substitution reaction
d)
Nucleophilic addition
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
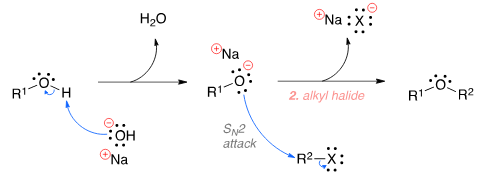
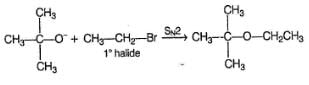
The Williamson ether synthesis is an organic reaction used to convert an alcohol and an alkyl halide to an ether using a base such as NaOH. The mechanism begins with the base abstracting the proton from the alcohol to form an alkoxide intermediate. The alkoxide then attacks the alkyl halide in a nucleophilic substi-tution reaction (SN2), which results in the formation of the final ether product and a metal halide by-product.

Which of the following compound reduces by NaBH4 ?- a)

- b)CH3–NO2
- c)
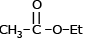
- d)
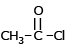
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following compound reduces by NaBH4 ?
a)
b)
CH3–NO2
c)
d)
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
NaBH4 are weak reducing agent so only acid chloride are reduced in alcohal.
Ethers may be used as solvents because they react only with which of the following reactants?- a)Acids
- b)Bases
- c)Oxidising agent
- d)Reducing agents
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Ethers may be used as solvents because they react only with which of the following reactants?
a)
Acids
b)
Bases
c)
Oxidising agent
d)
Reducing agents
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Ethers resist the attack of nucleophiles and bases. However, they are very good solvents in many organic reactions due to their ability to solvate cations by donating the electron pair from oxygen atom. Ethers are generally less reactive and react only with acids.
Phenol can be distinguished from ethanol by the reactions with _________.
- a)Br2/water
- b)Na
- c)Neutral FeCl3
- d)A and C
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Phenol can be distinguished from ethanol by the reactions with _________.
a)
Br2/water
b)
Na
c)
Neutral FeCl3
d)
A and C

|
Nisha Banerjee answered |
- Phenol can be distinguished from ethanol using Br2/water and Neutral FeCl3.
- Br2/water: Phenol reacts with bromine water to give a white precipitate of 2,4,6-tribromophenol, while ethanol does not react.
- Neutral FeCl3: Phenol forms a violet complex with neutral ferric chloride, whereas ethanol shows no color change.
- Therefore, options A and C are correct for distinguishing phenol from ethanol.
Phenol on treatment with Phthalic anhydride gives:- a)Phenolphthalein
- b)Salicylaldehyde
- c)Phthalic acid
- d)Salicylic acid
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Phenol on treatment with Phthalic anhydride gives:
a)
Phenolphthalein
b)
Salicylaldehyde
c)
Phthalic acid
d)
Salicylic acid

|
Infinity Academy answered |
The correct answer is option A
Phenolphthalein gives pink colour with alkali.
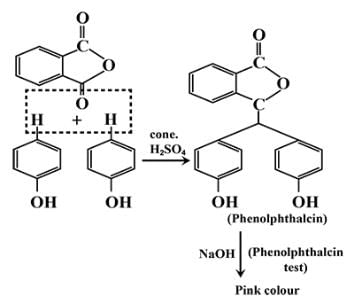
Phenolphthalein gives pink colour with alkali.

To prepare tert-butyl ethyl ether, the reagents required are: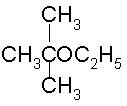
- a)Sodium ethoxide and tert-butyl bromide
- b)Sodium tert butoxide and ethyl bromide
- c)Dimethyl ketone, ethylbromide and sodium
- d)Sodium propoxide and propyl bromide
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
To prepare tert-butyl ethyl ether, the reagents required are:
a)
Sodium ethoxide and tert-butyl bromide
b)
Sodium tert butoxide and ethyl bromide
c)
Dimethyl ketone, ethylbromide and sodium
d)
Sodium propoxide and propyl bromide

|
Ayush Joshi answered |
Because 3degree haloalkanes like tert-butyl bromide (option a) give alkenes and not ethers when treated with a strong base like sodium ethoxide. So the exact answer is (b).
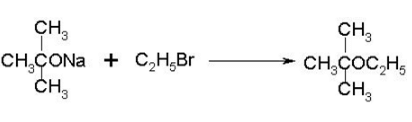
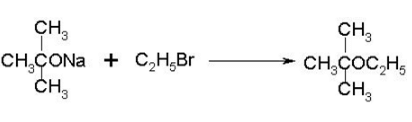
How many alcohols with molecular formula C4H10O are chiral in nature?a)2b)1c)4d)3Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Mansi Nair answered |

Here, again carbon is not chiral in nature.
So, only one alcohol is chiral in nature
So, only one alcohol is chiral in nature
Which of the following compounds will react with sodium hydroxide solution in water?- a)C6H5OH
- b)C6H5CH2OH
- c)(CH3)3COH
- d)C2H5OH
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following compounds will react with sodium hydroxide solution in water?
a)
C6H5OH
b)
C6H5CH2OH
c)
(CH3)3COH
d)
C2H5OH
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
When phenol reacts with sodium hydroxide solution it gives a colourless solution containing sodium phenoxide.
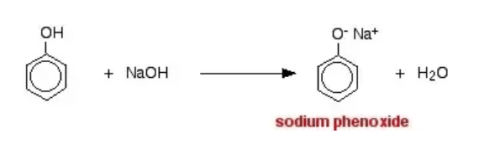
In this reaction, the hydrogen ion has been removed by the strongly basic hydroxide ion in the sodium hydroxide solution.
An organic compound X is oxidised by using acidified K2Cr2O7. The product obtained reacts with Phenyl hydrazine but does not answer silver mirror test. The possible structure of X is- a)CH3CH2OH
- b)CH3CHO
- c)(CH3)2CHOH
- d)None of the these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An organic compound X is oxidised by using acidified K2Cr2O7. The product obtained reacts with Phenyl hydrazine but does not answer silver mirror test. The possible structure of X is
a)
CH3CH2OH
b)
CH3CHO
c)
(CH3)2CHOH
d)
None of the these
|
|
Baby Ghosh answered |
Yup...it will be propan-2-ol..by oxidation it..it will convert into acetone and it reacts with phenyl hydrazine,it produces acetone phenyl hydrazone and there is no aldehyde grp in acetone. so it doesn't react in silver mirror test means with tollen's reagent..
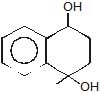
 (A)product (A) is -
(A)product (A) is -- a)
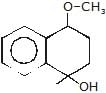
- b)
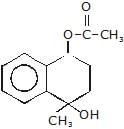
- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
product (A) is -
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Baby Ghosh answered |
According to Frice rearrangement...I think...
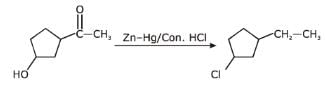
An alcohol has molecular formula C6H12O X and it gives immediate turbidity with cold, concentrated HCI even in the absence of ZnCI2. X can also be obtained by treatment of an ether with excess of CH3MgBr followed by acid hydrolysis. Hence, the correct statement regarding X is- a)It is 3-methyl-3-pentanol
- b)It is 2-methyl-3-pentanol
- c)It is 2-methyl-2-pentanol
- d)Either (b) or (c)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An alcohol has molecular formula C6H12O X and it gives immediate turbidity with cold, concentrated HCI even in the absence of ZnCI2. X can also be obtained by treatment of an ether with excess of CH3MgBr followed by acid hydrolysis. Hence, the correct statement regarding X is
a)
It is 3-methyl-3-pentanol
b)
It is 2-methyl-3-pentanol
c)
It is 2-methyl-2-pentanol
d)
Either (b) or (c)

|
Arpita Nair answered |
Only One Option Correct TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 1-8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.Q. Identify the final major product of the reaction sequence.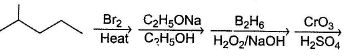
- a)

- b)

- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Only One Option Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
Identify the final major product of the reaction sequence.
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Dr Manju Sen answered |
One Integer Value Correct TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 19-22) This section contains 4 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).In the following reaction,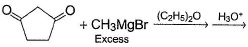 Q. How many different diols are formed as a result of nucleophilic addition reaction?
Q. How many different diols are formed as a result of nucleophilic addition reaction?
Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer?
One Integer Value Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 19-22) This section contains 4 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
In the following reaction,
Q.
How many different diols are formed as a result of nucleophilic addition reaction?
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
What is the correct structure for the major compound produced by the following reaction sequence?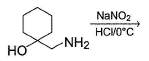
- a)

- b)

- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the correct structure for the major compound produced by the following reaction sequence?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Gunjan Lakhani answered |
Reaction involves rearrangement of carbocation
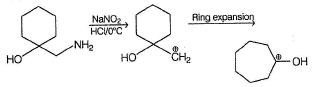
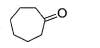
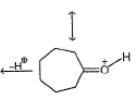


One of the following alcohol is a poison and Ingestion of even small quantities can cause blindness and large quantities causes even death.
- a)methanol
- b)propanol
- c)ethanol
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
One of the following alcohol is a poison and Ingestion of even small quantities can cause blindness and large quantities causes even death.
a)
methanol
b)
propanol
c)
ethanol
d)
None of the above

|
Rithika Mehta answered |
Explanation:
Methanol:
- Methanol is a type of alcohol that is considered poisonous to humans.
- Ingestion of even small quantities of methanol can cause severe health issues, including blindness.
- Large quantities of methanol can be lethal and result in death.
- Methanol is often found in solvents, antifreeze, and windshield washer fluid.
- When ingested, methanol is metabolized by the body into formaldehyde and formic acid, which are highly toxic.
Propanol and Ethanol:
- Propanol and ethanol are also types of alcohol, but they are not as toxic as methanol.
- Ingestion of propanol and ethanol in moderate quantities may cause intoxication, but they are not known to cause blindness or death in the same way that methanol does.
Conclusion:
- In summary, methanol is the alcohol that is considered a poison, as even small amounts can have severe consequences on human health.
- It is important to be cautious when handling products containing methanol and to seek immediate medical attention if methanol poisoning is suspected.
Which of the following compound reduces by DIBAL-H ?- a)CH3–
 –OH
–OH - b)
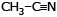
- c)CH3–
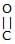 –O–Et
–O–Et - d)All
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following compound reduces by DIBAL-H ?
a)
CH3–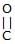 –OH
–OH
b)
c)
CH3–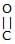 –O–Et
–O–Et
d)
All

|
Kiran Sanodiya answered |
Yes it can reduce ester ,acid n cyanide to corresponding aldehydes.
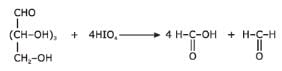
Which reaction(s) given below gives dicarbonyl?
- a)
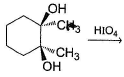
- b)
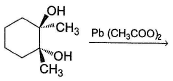
- c)

- d)
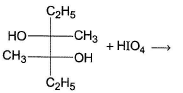
Correct answer is option 'A,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which reaction(s) given below gives dicarbonyl?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Gunjan Lakhani answered |
Syn vicinal diols undergo oxidative cleavage with HIO4 giving diols, Option (b) and option (c) are anti diol and have restricted rotation.
Ph– –O–CH3
–O–CH3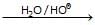 Above reaction is known as -
Above reaction is known as -- a)Esterification
- b)saponification
- c)Transesterification
- d)Acidic hydrolysis
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Ph– –O–CH3
–O–CH3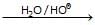
Above reaction is known as -
a)
Esterification
b)
saponification
c)
Transesterification
d)
Acidic hydrolysis
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
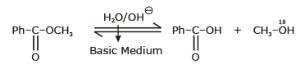
Hydrolysis of ester in basic Medium is known as saponification.
Lucas test is associated with
- a)Phenols
- b)Aldehydes
- c)Carboxylic acid
- d)Alcohols
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Lucas test is associated with
a)
Phenols
b)
Aldehydes
c)
Carboxylic acid
d)
Alcohols

|
Mihir Patel answered |
Lucas Test and Alcohols
The Lucas test is a chemical test used to distinguish between primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols. It is based on the observation of the rate at which an alcohol reacts with Lucas reagent, which is a mixture of concentrated hydrochloric acid and zinc chloride.
Principle of the Lucas Test
- Tertiary alcohols react almost immediately with Lucas reagent to form an alkyl chloride, which is seen as a cloudy solution due to the low solubility of the resulting product.
- Secondary alcohols react within a few minutes to form a cloudy solution.
- Primary alcohols do not react with Lucas reagent at room temperature and therefore do not produce a cloudy solution.
Significance of the Lucas Test
- The Lucas test is a quick and simple method to identify the type of alcohol present in a given compound.
- It is especially useful in organic chemistry labs for qualitative analysis of alcohols.
Application of the Lucas Test
- The Lucas test is commonly used in organic chemistry laboratories to differentiate between primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols.
- It helps in the identification and characterization of unknown compounds containing alcohol functional groups.
In conclusion, the Lucas test is primarily associated with alcohols as it is a specific test used to classify alcohols based on their reactivity with Lucas reagent.
The Lucas test is a chemical test used to distinguish between primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols. It is based on the observation of the rate at which an alcohol reacts with Lucas reagent, which is a mixture of concentrated hydrochloric acid and zinc chloride.
Principle of the Lucas Test
- Tertiary alcohols react almost immediately with Lucas reagent to form an alkyl chloride, which is seen as a cloudy solution due to the low solubility of the resulting product.
- Secondary alcohols react within a few minutes to form a cloudy solution.
- Primary alcohols do not react with Lucas reagent at room temperature and therefore do not produce a cloudy solution.
Significance of the Lucas Test
- The Lucas test is a quick and simple method to identify the type of alcohol present in a given compound.
- It is especially useful in organic chemistry labs for qualitative analysis of alcohols.
Application of the Lucas Test
- The Lucas test is commonly used in organic chemistry laboratories to differentiate between primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols.
- It helps in the identification and characterization of unknown compounds containing alcohol functional groups.
In conclusion, the Lucas test is primarily associated with alcohols as it is a specific test used to classify alcohols based on their reactivity with Lucas reagent.
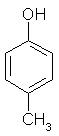
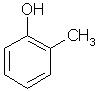
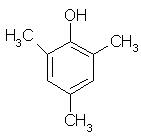
Which of the following is obtained as a major product in Friedel-Craft’s alkylation of phenol ?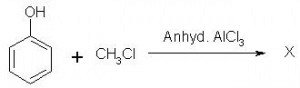
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
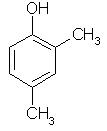
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is obtained as a major product in Friedel-Craft’s alkylation of phenol ?
a)
b)
c)

d)

|
Sushil Kumar answered |
The correct answer is option A
P-methyl phenol is the major product.
P-methyl phenol is the major product.

The correct statement regarding 3-ethyl-3-hexanol is
- a)It changes colour of CrO3/H2SO4
- b)It is oxidised on heating with copper metal, producing ketone
- c)It gives yellow precipitate with NaOH/I2
- d)It changes colour of cerric nitrate [Ce(NO3)4] from yellow to r
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct statement regarding 3-ethyl-3-hexanol is
a)
It changes colour of CrO3/H2SO4
b)
It is oxidised on heating with copper metal, producing ketone
c)
It gives yellow precipitate with NaOH/I2
d)
It changes colour of cerric nitrate [Ce(NO3)4] from yellow to r

|
Srestha Choudhury answered |
- 3-ethyl-3-hexanol is a tertiary alcohol. This characteristic influences its chemical behaviour:
- It does not oxidise easily. Therefore, it does not change the colour of CrO3/H2SO4.
- It does not produce a yellow precipitate with NaOH/I2, as this is a characteristic reaction of methyl ketones (Iodoform test).
- When heated with copper, it generally does not produce a ketone, as tertiary alcohols are resistant to oxidation.
- It changes the colour of cerric nitrate from yellow to red, which is a typical reaction for detecting alcohols in general, including tertiary alcohols.
What is the product of the reaction of methyl cyclohexene with B2H6 in THF followed by the oxidation with alkaline H2O2?

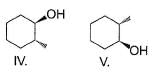
- a)Both I and IV
- b)Only II
- c)Both III and IV
- d)Both II and II
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the product of the reaction of methyl cyclohexene with B2H6 in THF followed by the oxidation with alkaline H2O2?


a)
Both I and IV
b)
Only II
c)
Both III and IV
d)
Both II and II
|
|
Shail Chawla answered |
In hydroboration oxidation reaction anti-Markownikoff addition of water takes place. Also both "H" and "OH" groups are attached from same side.
If 3, 3-dimethyl-2, 4-pentanedione is treated with a Grignard reagent consisting of mixture of CH3MgBr and C2H5MgBr and finally hydrolysing product with dilute H2SO4 results in the formation of how many different diols?
Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?
If 3, 3-dimethyl-2, 4-pentanedione is treated with a Grignard reagent consisting of mixture of CH3MgBr and C2H5MgBr and finally hydrolysing product with dilute H2SO4 results in the formation of how many different diols?
|
|
Om Desai answered |
(II) has two chiral carbon but symmetrical, hence, three stereoisomers.
(III) has only one chiral carbon hence, two stereoisomers (pair of enantiomers).
Chapter doubts & questions for Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers - Chemistry CUET UG Mock Test Series 2026 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers - Chemistry CUET UG Mock Test Series 2026 in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Chemistry CUET UG Mock Test Series 2026
3 docs|163 tests
|





 +CH3–O18H
+CH3–O18H