All Exams >
UPSC >
Lucent for GK >
All Questions
All questions of Vegetation & Wildlife for UPSC CSE Exam
Which one of the following is not a tropical desert?- a) Atacama
- b) Arabia
- c) Gobi
- d) Kalahari
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is not a tropical desert?
a)
Atacama
b)
Arabia
c)
Gobi
d)
Kalahari
|
|
Siddharth Dasgupta answered |
Tropical Deserts
Tropical deserts are characterized by their hot and dry climate, with very little rainfall. These deserts are found in regions near the equator, where the atmospheric conditions create a lack of moisture in the air. Some of the well-known tropical deserts include the Sahara Desert in Africa, the Arabian Desert in the Middle East, and the Atacama Desert in South America.
Atacama Desert
The Atacama Desert is located in northern Chile, along the Pacific coast of South America. It is known as one of the driest places on Earth, receiving very little rainfall throughout the year. The desert is characterized by its vast expanse of barren landscapes, salt flats, and sand dunes. The extremely arid conditions in the Atacama Desert are a result of the cold Humboldt Current that flows off the coast, preventing the formation of rain clouds.
Arabian Desert
The Arabian Desert is located in the Arabian Peninsula and covers parts of Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Oman, and the United Arab Emirates. It is the largest continuous sand desert in the world, with vast stretches of sandy plains, dunes, and gravel plains. The desert experiences extremely high temperatures during the day and very low temperatures at night. The Arabian Desert is known for its unique sand formations, such as sand seas and sand sheets.
Gobi Desert
The Gobi Desert is located in northern China and southern Mongolia. It is a cold desert, rather than a tropical desert, as it experiences extremely cold temperatures during the winter months. The Gobi Desert is characterized by its vast expanses of gravel plains, rocky mountains, and sand dunes. It receives very little rainfall, and most of the precipitation occurs during the summer months.
Kalahari Desert
The Kalahari Desert is located in southern Africa, covering parts of Botswana, Namibia, and South Africa. It is a semi-arid desert, with a mixture of desert and savannah vegetation. The Kalahari Desert experiences a hot climate, with high temperatures during the day and cooler temperatures at night. It receives more rainfall compared to other deserts, with the majority of the precipitation occurring during the summer months.
Conclusion
Out of the given options, the Gobi Desert is not a tropical desert. It is a cold desert situated in northern China and southern Mongolia. The Gobi Desert experiences extremely cold temperatures during the winter months and is characterized by gravel plains, rocky mountains, and sand dunes.
Tropical deserts are characterized by their hot and dry climate, with very little rainfall. These deserts are found in regions near the equator, where the atmospheric conditions create a lack of moisture in the air. Some of the well-known tropical deserts include the Sahara Desert in Africa, the Arabian Desert in the Middle East, and the Atacama Desert in South America.
Atacama Desert
The Atacama Desert is located in northern Chile, along the Pacific coast of South America. It is known as one of the driest places on Earth, receiving very little rainfall throughout the year. The desert is characterized by its vast expanse of barren landscapes, salt flats, and sand dunes. The extremely arid conditions in the Atacama Desert are a result of the cold Humboldt Current that flows off the coast, preventing the formation of rain clouds.
Arabian Desert
The Arabian Desert is located in the Arabian Peninsula and covers parts of Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Oman, and the United Arab Emirates. It is the largest continuous sand desert in the world, with vast stretches of sandy plains, dunes, and gravel plains. The desert experiences extremely high temperatures during the day and very low temperatures at night. The Arabian Desert is known for its unique sand formations, such as sand seas and sand sheets.
Gobi Desert
The Gobi Desert is located in northern China and southern Mongolia. It is a cold desert, rather than a tropical desert, as it experiences extremely cold temperatures during the winter months. The Gobi Desert is characterized by its vast expanses of gravel plains, rocky mountains, and sand dunes. It receives very little rainfall, and most of the precipitation occurs during the summer months.
Kalahari Desert
The Kalahari Desert is located in southern Africa, covering parts of Botswana, Namibia, and South Africa. It is a semi-arid desert, with a mixture of desert and savannah vegetation. The Kalahari Desert experiences a hot climate, with high temperatures during the day and cooler temperatures at night. It receives more rainfall compared to other deserts, with the majority of the precipitation occurring during the summer months.
Conclusion
Out of the given options, the Gobi Desert is not a tropical desert. It is a cold desert situated in northern China and southern Mongolia. The Gobi Desert experiences extremely cold temperatures during the winter months and is characterized by gravel plains, rocky mountains, and sand dunes.
Spruce and Cedar are tree varieties of- a) Equatorial forest
- b) Temperate coniferous forest
- c) Monsoon forest
- d) Temperate deciduous forest
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Spruce and Cedar are tree varieties of
a)
Equatorial forest
b)
Temperate coniferous forest
c)
Monsoon forest
d)
Temperate deciduous forest
|
|
Rajesh Kulkarni answered |
Explanation:
Spruce and cedar are tree varieties that belong to the temperate coniferous forest.
Temperate Coniferous Forest:
The temperate coniferous forest, also known as the taiga or boreal forest, is a biome characterized by cold temperatures, moderate precipitation, and the dominance of coniferous trees. This biome is typically found in the northern hemisphere, primarily in North America, Europe, and Asia.
Spruce:
Spruce trees are a common species found in the temperate coniferous forest. They are tall evergreen trees that have needle-like leaves and bear cones. Spruce trees are adapted to the cold climate of this biome and are able to withstand harsh winter conditions. They are known for their straight trunks and dense foliage, which provide shelter and nesting sites for various bird species.
Cedar:
Cedar trees, specifically the western red cedar, are also found in the temperate coniferous forest. These trees are evergreen and have scale-like leaves. Cedar trees are known for their durability and resistance to decay, which makes them highly valued for their timber. They are commonly used for construction, furniture, and other woodworking purposes.
Characteristics of the Temperate Coniferous Forest:
- Cold temperatures: The temperate coniferous forest experiences long winters with freezing temperatures and short summers.
- Moderate precipitation: This biome receives moderate rainfall throughout the year, with snowfall in winter.
- Coniferous trees: The dominant tree species in this biome are conifers, such as spruce, cedar, fir, and pine.
- Needle-like leaves: Coniferous trees have needle-like leaves that help them conserve water and withstand cold temperatures.
- Wildlife: The temperate coniferous forest is home to a variety of wildlife, including deer, moose, bears, wolves, and various bird species.
In conclusion, spruce and cedar are tree varieties that belong to the temperate coniferous forest biome. They are well-adapted to the cold climate and play a crucial role in the ecosystem by providing habitat and resources for various organisms.
Spruce and cedar are tree varieties that belong to the temperate coniferous forest.
Temperate Coniferous Forest:
The temperate coniferous forest, also known as the taiga or boreal forest, is a biome characterized by cold temperatures, moderate precipitation, and the dominance of coniferous trees. This biome is typically found in the northern hemisphere, primarily in North America, Europe, and Asia.
Spruce:
Spruce trees are a common species found in the temperate coniferous forest. They are tall evergreen trees that have needle-like leaves and bear cones. Spruce trees are adapted to the cold climate of this biome and are able to withstand harsh winter conditions. They are known for their straight trunks and dense foliage, which provide shelter and nesting sites for various bird species.
Cedar:
Cedar trees, specifically the western red cedar, are also found in the temperate coniferous forest. These trees are evergreen and have scale-like leaves. Cedar trees are known for their durability and resistance to decay, which makes them highly valued for their timber. They are commonly used for construction, furniture, and other woodworking purposes.
Characteristics of the Temperate Coniferous Forest:
- Cold temperatures: The temperate coniferous forest experiences long winters with freezing temperatures and short summers.
- Moderate precipitation: This biome receives moderate rainfall throughout the year, with snowfall in winter.
- Coniferous trees: The dominant tree species in this biome are conifers, such as spruce, cedar, fir, and pine.
- Needle-like leaves: Coniferous trees have needle-like leaves that help them conserve water and withstand cold temperatures.
- Wildlife: The temperate coniferous forest is home to a variety of wildlife, including deer, moose, bears, wolves, and various bird species.
In conclusion, spruce and cedar are tree varieties that belong to the temperate coniferous forest biome. They are well-adapted to the cold climate and play a crucial role in the ecosystem by providing habitat and resources for various organisms.
Which one of the following states has the largest forest area to its total land area? - a) Mizoram
- b) Arunachal Pradesh
- c) Sikkim
- d) Jammu and Kashmir
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following states has the largest forest area to its total land area?
a)
Mizoram
b)
Arunachal Pradesh
c)
Sikkim
d)
Jammu and Kashmir
|
|
Academic Studio answered |
According to the 2011 Forest Survey of India. Mizoram has the third-highest total forest cover with 1,594,000 hectares and highest percentage area (90.68%) covered by forests, among the states of India.
Which of the following is not correctly matched? National Park State- a)Bandipur -Karnataka
- b)Rajaji -Uttarakhand
- c)Simlipal -Odisha
- d)Pin Valley -Jammu & Kashmir
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not correctly matched?
National Park State
a)
Bandipur -Karnataka
b)
Rajaji -Uttarakhand
c)
Simlipal -Odisha
d)
Pin Valley -Jammu & Kashmir
|
|
Varun Kapoor answered |
The correct answer is option d) Pin Valley - Jammu & Kashmir.
Pin Valley National Park is located in the Lahaul and Spiti district of Himachal Pradesh, not Jammu & Kashmir.
The other options are correctly matched:
a) Bandipur National Park is in Karnataka.
b) Rajaji National Park is in Uttarakhand.
c) Simlipal National Park is in Odisha.
Consider the following statements1. National parks are a special category of protected areas of land and sea coasts where people are an integral part of the system.2. Sanctuaries are concerned with the conservation of particular species.3. Biosphere reserves are connected with the habitat of a particular wild animal.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?- a) 1, 2 and 3
- b) Only 2
- c) 1 and 2
- d) 1 and 3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements
1. National parks are a special category of protected areas of land and sea coasts where people are an integral part of the system.
2. Sanctuaries are concerned with the conservation of particular species.
3. Biosphere reserves are connected with the habitat of a particular wild animal.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a)
1, 2 and 3
b)
Only 2
c)
1 and 2
d)
1 and 3
|
|
Anjali Rao answered |
- A national park is a park in use for conservation purposes. Often it is a reserve of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that a sovereign state declares or owns.
- Although individual nations designate their national parks differently, there is a common idea: the conservation of ‘wild nature’ for posterity and as a symbol of national pride.
- The biosphere is the global ecological system integrating all living beings and their relationships, including their interaction with the elements of the lithosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere
Which one of the following countries is devoid of Glossopteris flora?- a) India
- b) Australia
- c) Norway
- d) South Africa
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following countries is devoid of Glossopteris flora?
a)
India
b)
Australia
c)
Norway
d)
South Africa
|
|
Sanjay Rana answered |
Glossopteris flora is found in Australia, India and South Africa. They are not found in Norway.
Consider the following sentences concerning the Keibul Lamjao National Park-1. The park was initially declared as a Sanctuary in 1966, topreserve the natural refuge of the endangered Brow--antlered deer Sangai (Rucervus eldi eldi).2. The Keibul Lamjao, the only floating national park in the worldand located near Moirang in the Bishnupur district of thestate of Manipur.3. It was established as a National Park in the year of 1977.Select the correct option from the codes given below:- a) 1 and 2
- b) 1 and 3
- c) 2 and 3
- d) 1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following sentences concerning the Keibul Lamjao National Park-
1. The park was initially declared as a Sanctuary in 1966, to
preserve the natural refuge of the endangered Brow--
antlered deer Sangai (Rucervus eldi eldi).
2. The Keibul Lamjao, the only floating national park in the world
and located near Moirang in the Bishnupur district of the
state of Manipur.
3. It was established as a National Park in the year of 1977.
Select the correct option from the codes given below:
a)
1 and 2
b)
1 and 3
c)
2 and 3
d)
1, 2 and 3
|
|
Tanishq Sengupta answered |
Overview of Keibul Lamjao National Park
Keibul Lamjao National Park is a unique and significant ecological area located in Manipur, India. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the key points related to the park:
1. Sanctuary Declaration
- The park was initially declared as a Sanctuary in 1966.
- Its primary aim was to preserve the natural habitat of the endangered Brow-antlered deer, known as Sangai (Rucervus eldi eldi).
2. Unique Characteristics
- Keibul Lamjao is recognized as the only floating national park in the world.
- It is situated near Moirang in the Bishnupur district of Manipur, making it a distinctive ecological feature.
3. National Park Status
- The area was established as a National Park in 1977.
- This transition helped in better conservation efforts and enhanced protection for the local flora and fauna.
Conclusion
- All three statements about Keibul Lamjao National Park are accurate.
- The correct choice is option 'D' as it includes all three crucial facts: the sanctuary declaration in 1966, its unique floating status, and its establishment as a national park in 1977.
This park not only plays a vital role in biodiversity conservation but also contributes to the cultural heritage and ecological balance in the region.
Keibul Lamjao National Park is a unique and significant ecological area located in Manipur, India. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the key points related to the park:
1. Sanctuary Declaration
- The park was initially declared as a Sanctuary in 1966.
- Its primary aim was to preserve the natural habitat of the endangered Brow-antlered deer, known as Sangai (Rucervus eldi eldi).
2. Unique Characteristics
- Keibul Lamjao is recognized as the only floating national park in the world.
- It is situated near Moirang in the Bishnupur district of Manipur, making it a distinctive ecological feature.
3. National Park Status
- The area was established as a National Park in 1977.
- This transition helped in better conservation efforts and enhanced protection for the local flora and fauna.
Conclusion
- All three statements about Keibul Lamjao National Park are accurate.
- The correct choice is option 'D' as it includes all three crucial facts: the sanctuary declaration in 1966, its unique floating status, and its establishment as a national park in 1977.
This park not only plays a vital role in biodiversity conservation but also contributes to the cultural heritage and ecological balance in the region.
Where is the First Biosphere Reserve of India located? - a) Nilgiri
- b) Nanda Devi
- c) Sundarban
- d) Great Nicobar
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Where is the First Biosphere Reserve of India located?
a)
Nilgiri
b)
Nanda Devi
c)
Sundarban
d)
Great Nicobar
|
|
Rahul Choudhury answered |
Nilgiri is the first Biosphere Reserve formed in 1986.
The ‘Blackbuck National Park’ situated in the Indian State of - a) Karnataka
- b) Madhya Pradesh
- c) Gujarat
- d) Haryana
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The ‘Blackbuck National Park’ situated in the Indian State of
a)
Karnataka
b)
Madhya Pradesh
c)
Gujarat
d)
Haryana
|
|
Rahul Choudhury answered |
The ‘Black Buck National park’ is situated in the Indian state of GJ
Which type of forests in India are characterized by being well stratified, with trees reaching great heights, and appearing green throughout the year?- a)Tropical Deciduous forests
- b)Montane forests
- c)Tropical Evergreen and Semi Evergreen forests
- d)Tropical Thorn forests
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which type of forests in India are characterized by being well stratified, with trees reaching great heights, and appearing green throughout the year?
a)
Tropical Deciduous forests
b)
Montane forests
c)
Tropical Evergreen and Semi Evergreen forests
d)
Tropical Thorn forests

|
Goel UPSC Coaching Center answered |
Tropical Evergreen and Semi Evergreen forests found in specific regions of India are known for their stratified structure, tall trees, and evergreen appearance. These forests thrive in warm and humid areas with abundant precipitation and high temperatures. The vegetation in these forests includes a variety of trees such as rosewood, mahogany, aini, and ebony. The continuous greenery in these forests is due to the absence of a specific season for leaf shedding, flowering, and fruition, contributing to their lush appearance throughout the year.
Arrange the following tropical forest groups in the correct order of sequence based on area covered in India beginning from the largest covered area:1. Moist deciduous2. Dry deciduous3. Wet evergreen4. Semi-evergreenSelect the correct answer using the code given below :Code :- a)1-2-3-4
- b)3-4-2-1
- c)1-3-2-4
- d)4-3-2-1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Arrange the following tropical forest groups in the correct order of sequence based on area covered in India beginning from the largest covered area:
1. Moist deciduous
2. Dry deciduous
3. Wet evergreen
4. Semi-evergreen
Select the correct answer using the code given below :
Code :
a)
1-2-3-4
b)
3-4-2-1
c)
1-3-2-4
d)
4-3-2-1
|
|
Neha Verma answered |
Moist Deciduous →Dry deciduous →Wet evergreen →Semi-evergreen.
The largest reserves of sal forest is found in—
(a) Nilgiri hills
(b) Dun valley
(c) Aravallies
(d) Assam
Correct answer is 'Assam'. Can you explain this answer?
The largest reserves of sal forest is found in—
(a) Nilgiri hills
(b) Dun valley
(c) Aravallies
(d) Assam
|
|
Ojasvi Mehta answered |
The largest reserves of Sal forest is found in Assam.
A Sandy and Saline area is the natural habitat of Indian animal species. The animal is threatened due to the destruction of its habitat. Which one of the following could be that animal?- a) Indian Wild Buffalo
- b) Great Indian Bustard
- c) Indian Wild Boar
- d) Indian Gazelle
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A Sandy and Saline area is the natural habitat of Indian animal species. The animal is threatened due to the destruction of its habitat. Which one of the following could be that animal?
a)
Indian Wild Buffalo
b)
Great Indian Bustard
c)
Indian Wild Boar
d)
Indian Gazelle
|
|
Partho Goyal answered |
The Great Indian Bustard: The Threatened Indian Animal
The Great Indian Bustard (Ardeotis nigriceps) is a critically endangered bird species that is found in the sandy and saline areas of India. This magnificent bird, often referred to as the "godavan" or "ghorad" in Hindi, is one of the largest flying birds in the world and is an important part of India's biodiversity.
1. Habitat:
The Great Indian Bustard is primarily found in the sandy and saline regions of northwestern India, particularly in the states of Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Maharashtra. These areas are characterized by vast grasslands, sandy plains, and saline marshes, which provide the ideal habitat for the bird. The sandy and saline environment provides the necessary conditions for the bird to breed, forage for food, and roost.
2. Threats to Habitat:
However, the Great Indian Bustard is facing severe threats due to the destruction and degradation of its natural habitat. The conversion of grasslands into agricultural fields, rapid urbanization, industrialization, and infrastructure development have resulted in the loss of large areas of suitable habitat for the bird. Additionally, encroachment by human settlements, grazing by livestock, and invasive species have further degraded the remaining habitat.
3. Conservation Efforts:
Efforts are being made to conserve the Great Indian Bustard and its habitat. Several protected areas and wildlife sanctuaries have been established to safeguard the remaining populations of the bird. These include the Desert National Park in Rajasthan, Nannaj Bustard Sanctuary in Maharashtra, and the Kutch Bustard Sanctuary in Gujarat. These protected areas help to regulate human activities, restrict grazing, and prevent further habitat destruction.
4. Need for Further Action:
Despite these conservation efforts, the Great Indian Bustard continues to face numerous challenges. Its population has severely declined over the years, and it is estimated that there are less than 150 individuals remaining in the wild. Therefore, there is an urgent need for increased conservation measures, such as habitat restoration, captive breeding programs, and community-based initiatives to ensure the survival of this iconic species.
In conclusion, the Great Indian Bustard is the threatened Indian animal that is facing the destruction of its sandy and saline habitat. The loss of suitable habitat due to human activities poses a significant threat to the survival of this critically endangered bird. It is essential to prioritize its conservation and take immediate action to protect its habitat and ensure its long-term survival.
The Great Indian Bustard (Ardeotis nigriceps) is a critically endangered bird species that is found in the sandy and saline areas of India. This magnificent bird, often referred to as the "godavan" or "ghorad" in Hindi, is one of the largest flying birds in the world and is an important part of India's biodiversity.
1. Habitat:
The Great Indian Bustard is primarily found in the sandy and saline regions of northwestern India, particularly in the states of Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Maharashtra. These areas are characterized by vast grasslands, sandy plains, and saline marshes, which provide the ideal habitat for the bird. The sandy and saline environment provides the necessary conditions for the bird to breed, forage for food, and roost.
2. Threats to Habitat:
However, the Great Indian Bustard is facing severe threats due to the destruction and degradation of its natural habitat. The conversion of grasslands into agricultural fields, rapid urbanization, industrialization, and infrastructure development have resulted in the loss of large areas of suitable habitat for the bird. Additionally, encroachment by human settlements, grazing by livestock, and invasive species have further degraded the remaining habitat.
3. Conservation Efforts:
Efforts are being made to conserve the Great Indian Bustard and its habitat. Several protected areas and wildlife sanctuaries have been established to safeguard the remaining populations of the bird. These include the Desert National Park in Rajasthan, Nannaj Bustard Sanctuary in Maharashtra, and the Kutch Bustard Sanctuary in Gujarat. These protected areas help to regulate human activities, restrict grazing, and prevent further habitat destruction.
4. Need for Further Action:
Despite these conservation efforts, the Great Indian Bustard continues to face numerous challenges. Its population has severely declined over the years, and it is estimated that there are less than 150 individuals remaining in the wild. Therefore, there is an urgent need for increased conservation measures, such as habitat restoration, captive breeding programs, and community-based initiatives to ensure the survival of this iconic species.
In conclusion, the Great Indian Bustard is the threatened Indian animal that is facing the destruction of its sandy and saline habitat. The loss of suitable habitat due to human activities poses a significant threat to the survival of this critically endangered bird. It is essential to prioritize its conservation and take immediate action to protect its habitat and ensure its long-term survival.
Which one of the following is the correct sequence of the given tiger reserves of India from North to South?- a) Dudhwa-Kanha-Indravati-Bandipur
- b) Kanha-Bandipur-Dudhwa-Indravati
- c) Indravati-Kanha-Dudhwa-Bandipur
- d) Dudhwa-Kanha-Bandipur-Indravati
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is the correct sequence of the given tiger reserves of India from North to South?
a)
Dudhwa-Kanha-Indravati-Bandipur
b)
Kanha-Bandipur-Dudhwa-Indravati
c)
Indravati-Kanha-Dudhwa-Bandipur
d)
Dudhwa-Kanha-Bandipur-Indravati
|
|
Amit Kumar answered |
- The Dudhwa National Park is a national park in the Terai of Uttar Pradesh, India, and covers an area of 490.3 km2, with a buffer zone of 190 km2. It is part of the Dudhwa Tiger Reserve.
- Kanha National Park, also known as Kanha Tiger Reserve, is a vast expanse of grassland and forest in the central Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. Tigers, jackals and wild pigs can be spotted in Kanha Meadows.
- Indravati Tiger Reserves is a Tiger Reserve area in Chhattisgarh. Bandipur National Park, an 874-sq.-km forested reserve in the southern Indian state of Karnataka, is known for its small population of tigers.
The Himalayan range is very rich in species diversity. Which one among the following is the most appropriate reason for this phenomenon?- a) It has high rainfall that supports luxuriant vegetative growth
- b) It is a confluence of different biogeographical zones.
- c) Exotic and invasive species have not been introduced in this region.
- d) It has less human interference.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The Himalayan range is very rich in species diversity. Which one among the following is the most appropriate reason for this phenomenon?
a)
It has high rainfall that supports luxuriant vegetative growth
b)
It is a confluence of different biogeographical zones.
c)
Exotic and invasive species have not been introduced in this region.
d)
It has less human interference.
|
|
Devanshi Reddy answered |
Species Diversity in the Himalayan Range
The Himalayan range stands out as a hotspot of biodiversity due to its unique geographical and climatic characteristics. The most appropriate reason for its rich species diversity is its position as a confluence of different biogeographical zones.
Geographical Confluence
- The Himalayas connect various biogeographical realms, including the Indo-Malayan, Palearctic, and Tibetan zones.
- This convergence allows for a mix of flora and fauna that would not typically coexist in isolated regions.
Elevation Variation
- The range spans a vast altitude gradient, resulting in diverse climatic conditions.
- Different elevations host distinct ecosystems, from tropical forests at lower altitudes to alpine meadows at higher elevations.
Microclimates
- The topography creates numerous microclimates, enabling a variety of species to thrive.
- These localized conditions support unique plant and animal communities adapted to specific environmental factors.
Isolation and Endemism
- The geographical barriers formed by the mountains lead to isolation of species, fostering endemism.
- Many species have evolved uniquely in these isolated environments, adding to overall biodiversity.
Human Impact
- While human interference exists, many parts of the Himalayas remain relatively untouched, preserving natural habitats.
- Less human encroachment in certain areas allows for the survival of diverse species.
In summary, option 'B' illustrates the primary reason behind the rich biodiversity in the Himalayan range—its role as a meeting point for different biogeographical zones, which fosters a unique and diverse array of species.
The Himalayan range stands out as a hotspot of biodiversity due to its unique geographical and climatic characteristics. The most appropriate reason for its rich species diversity is its position as a confluence of different biogeographical zones.
Geographical Confluence
- The Himalayas connect various biogeographical realms, including the Indo-Malayan, Palearctic, and Tibetan zones.
- This convergence allows for a mix of flora and fauna that would not typically coexist in isolated regions.
Elevation Variation
- The range spans a vast altitude gradient, resulting in diverse climatic conditions.
- Different elevations host distinct ecosystems, from tropical forests at lower altitudes to alpine meadows at higher elevations.
Microclimates
- The topography creates numerous microclimates, enabling a variety of species to thrive.
- These localized conditions support unique plant and animal communities adapted to specific environmental factors.
Isolation and Endemism
- The geographical barriers formed by the mountains lead to isolation of species, fostering endemism.
- Many species have evolved uniquely in these isolated environments, adding to overall biodiversity.
Human Impact
- While human interference exists, many parts of the Himalayas remain relatively untouched, preserving natural habitats.
- Less human encroachment in certain areas allows for the survival of diverse species.
In summary, option 'B' illustrates the primary reason behind the rich biodiversity in the Himalayan range—its role as a meeting point for different biogeographical zones, which fosters a unique and diverse array of species.
Consider the following statements:1. Tropical Evergreen forests are characterized by trees reaching heights of up to 60 meters or above.2. Tropical Evergreen forests are found in regions with an annual precipitation of over 200 cm and mean annual temperature above 22°C.3. The British replaced oak forests in Garhwal and Kumaon with teak for railway construction.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?- a)1 Only
- b)1 and 2 Only
- c)1 and 3 Only
- d)1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
1. Tropical Evergreen forests are characterized by trees reaching heights of up to 60 meters or above.
2. Tropical Evergreen forests are found in regions with an annual precipitation of over 200 cm and mean annual temperature above 22°C.
3. The British replaced oak forests in Garhwal and Kumaon with teak for railway construction.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a)
1 Only
b)
1 and 2 Only
c)
1 and 3 Only
d)
1, 2 and 3

|
Innovative Classes answered |
1. Tropical Evergreen forests are characterized by trees reaching heights of up to 60 meters or above. This statement is correct. In the given text, it is mentioned that trees in these forests can reach great heights up to 60 meters or more.
2. Tropical Evergreen forests are found in regions with an annual precipitation of over 200 cm and mean annual temperature above 22°C. This statement is also correct. The text specifies that these forests are found in warm and humid areas with such climatic conditions.
3. The British replaced oak forests in Garhwal and Kumaon with teak for railway construction. This statement is incorrect. According to the text, the British replaced oak forests with pine (chir) for railway construction, not teak.
Thus, the correct answer is Option B: 1 and 2 Only.
Which of the following longitudes is known as “standard Meridian” in India? - a) 87° 30’ E
- b) 85° 30’ E
- c) 84° 30’ E
- d) 82° 30’ E
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following longitudes is known as “standard Meridian” in India?
a)
87° 30’ E
b)
85° 30’ E
c)
84° 30’ E
d)
82° 30’ E

|
Master Training Institute answered |
82°30’ E has been taken as the standard meridian in India.
Consider the following statements:1. Tropical Deciduous Forests in India are further classified into moist and dry deciduous based on the availability of water.2. Tropical Thorn Forests occur in regions receiving rainfall between 70-100 cm.3. Montane Forests in the northern mountain ranges show a succession of vegetation from tropical to tundra types with altitude.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?- a)1 Only
- b)1 and 3 Only
- c)2 and 3 Only
- d)1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
1. Tropical Deciduous Forests in India are further classified into moist and dry deciduous based on the availability of water.
2. Tropical Thorn Forests occur in regions receiving rainfall between 70-100 cm.
3. Montane Forests in the northern mountain ranges show a succession of vegetation from tropical to tundra types with altitude.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a)
1 Only
b)
1 and 3 Only
c)
2 and 3 Only
d)
1, 2 and 3

|
K.L Institute answered |
1. Statement 1 is correct: Tropical Deciduous Forests in India are indeed classified into moist and dry deciduous forests based on the availability of water. Moist deciduous forests are found in regions receiving rainfall between 100-200 cm, whereas dry deciduous forests are found in areas with rainfall between 70-100 cm.
2. Statement 2 is incorrect: Tropical Thorn Forests occur in areas receiving less than 50 cm of rainfall, not between 70-100 cm.
3. Statement 3 is correct: Montane Forests in the northern mountain ranges do show a succession of vegetation types, ranging from tropical to tundra, as the altitude increases. This includes deciduous forests at lower altitudes, wet temperate forests, and eventually alpine pastures and tundra vegetation at the highest altitudes.
Thus, the correct answer is Option B
The percentage of forest cover is the highest in- a) Africa
- b) Asia
- c) North America
- d) South America
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The percentage of forest cover is the highest in
a)
Africa
b)
Asia
c)
North America
d)
South America
|
|
Anita Desai answered |
The forest cover : Europe>South America>North America>Africa> Asia>Oceania
Consider the following statements:Statement-I:
Tropical evergreen forests in India are primarily found in warm and humid areas with an annual precipitation of over 200 cm and mean annual temperature above 22°C.Statement-II:
The British colonial rulers in India valued the economic potential of forests, leading to large-scale exploitation and structural changes in forest composition.Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?- a)Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I
- b)Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, but Statement-II does not explain Statement-I
- c)Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect
- d)Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement-II is correct
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
Statement-I:
Tropical evergreen forests in India are primarily found in warm and humid areas with an annual precipitation of over 200 cm and mean annual temperature above 22°C.
Tropical evergreen forests in India are primarily found in warm and humid areas with an annual precipitation of over 200 cm and mean annual temperature above 22°C.
Statement-II:
The British colonial rulers in India valued the economic potential of forests, leading to large-scale exploitation and structural changes in forest composition.
The British colonial rulers in India valued the economic potential of forests, leading to large-scale exploitation and structural changes in forest composition.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
a)
Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I
b)
Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, but Statement-II does not explain Statement-I
c)
Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect
d)
Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement-II is correct
|
|
Shail Gupta answered |
Understanding the Statements
The statements provided discuss the characteristics of tropical evergreen forests in India and the historical context of forest exploitation during British colonial rule.
Statement-I Analysis
- Tropical evergreen forests are indeed located in regions that are:
- Warm and humid
- Receive over 200 cm of annual precipitation
- Have a mean annual temperature exceeding 22°C
- These forests are primarily found in areas such as the Western Ghats, northeastern India, and parts of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Statement-II Analysis
- The British colonial rulers recognized the economic value of India's forests, which led to:
- Large-scale exploitation of timber and other forest resources
- Changes in the composition and structure of forests due to overharvesting and monoculture plantations
- This exploitation significantly impacted the biodiversity and ecological balance of forested areas in India.
Conclusion
- Both statements are accurate:
- Statement-I correctly describes the ecological conditions of tropical evergreen forests in India.
- Statement-II explains the historical context that led to the exploitation of these forests, contributing to the forest composition changes.
Thus, the correct choice is option 'A': Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I.
The statements provided discuss the characteristics of tropical evergreen forests in India and the historical context of forest exploitation during British colonial rule.
Statement-I Analysis
- Tropical evergreen forests are indeed located in regions that are:
- Warm and humid
- Receive over 200 cm of annual precipitation
- Have a mean annual temperature exceeding 22°C
- These forests are primarily found in areas such as the Western Ghats, northeastern India, and parts of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Statement-II Analysis
- The British colonial rulers recognized the economic value of India's forests, which led to:
- Large-scale exploitation of timber and other forest resources
- Changes in the composition and structure of forests due to overharvesting and monoculture plantations
- This exploitation significantly impacted the biodiversity and ecological balance of forested areas in India.
Conclusion
- Both statements are accurate:
- Statement-I correctly describes the ecological conditions of tropical evergreen forests in India.
- Statement-II explains the historical context that led to the exploitation of these forests, contributing to the forest composition changes.
Thus, the correct choice is option 'A': Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I.
The Marine National Park is located in— - a)Gulf of Kutch
- b)Sunderbans
- c)Chilka Lake
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The Marine National Park is located in—
a)
Gulf of Kutch
b)
Sunderbans
c)
Chilka Lake
d)
None of the above
|
|
Rahul Choudhury answered |
The Marine National Park is located in the Gulf of Kutch.
Over 90% of the world’s biomass is in - a) tropical rain forests
- b) freshwater wetlands
- c) top soils
- d) oceans
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Over 90% of the world’s biomass is in
a)
tropical rain forests
b)
freshwater wetlands
c)
top soils
d)
oceans
|
|
Vikram Verma answered |
Biomass is the mass of living biological organisms in a given area or ecosystem at a given time. Over 90% of the Biomass is in Oceans.
Kanha National Park belongs to which one among the following biogeographical areas in the world?- a)Tropical Sub-humid Forests
- b)Tropical Humid Forests
- c)Tropical Dry Forests
- d)Tropical Moist Forests
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Kanha National Park belongs to which one among the following biogeographical areas in the world?
a)
Tropical Sub-humid Forests
b)
Tropical Humid Forests
c)
Tropical Dry Forests
d)
Tropical Moist Forests
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
Kanha National Park belongs to tropical moist dry deciduous forest. It is a tiger reserve of India and the largest the national park of Madhya Pradesh
Where are Tropical Evergreen and Semi Evergreen forests primarily found in India?- a)Western Rajasthan
- b)Eastern Himalayas
- c)Western Ghats, northeastern hills, Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- d)Central Deccan Plateau
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Where are Tropical Evergreen and Semi Evergreen forests primarily found in India?
a)
Western Rajasthan
b)
Eastern Himalayas
c)
Western Ghats, northeastern hills, Andaman and Nicobar Islands
d)
Central Deccan Plateau

|
Future Foundation Institute answered |
Tropical Evergreen and Semi Evergreen forests are primarily found in the western slope of the Western Ghats, hills of the northeastern region, and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands in India. These forests thrive in warm and humid areas with high annual precipitation and temperatures, supporting diverse flora and fauna. The unique characteristics of these forests contribute to their ecological significance and biodiversity, making them vital components of India's natural heritage.
Which one of the following is a temperate desert?- a) Arabian desert
- b) Atacama desert
- c) Kalahari desert
- d) Patagonian desert
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is a temperate desert?
a)
Arabian desert
b)
Atacama desert
c)
Kalahari desert
d)
Patagonian desert
|
|
Siddharth Dasgupta answered |
The Patagonian desert is a temperate desert located in southern Argentina and Chile. It is the largest desert in the Americas and one of the few temperate deserts in the world. Here is a detailed explanation of why the Patagonian desert is considered a temperate desert:
1. Location and Climate:
- The Patagonian desert is situated in the southern regions of Argentina and Chile, extending from the Atlantic Ocean to the Andes Mountains.
- It lies in the temperate zone, where the climate is influenced by the cool ocean currents and the mountain ranges.
- The region experiences mild summers and cold winters, with average temperatures ranging from 8°C (46°F) in the summer to -2°C (28°F) in the winter.
- The average annual precipitation is relatively low, ranging from 100 to 400 mm (4 to 16 inches), which is a defining characteristic of deserts.
2. Vegetation:
- The vegetation in the Patagonian desert is sparse but diverse. It consists mainly of shrubs, grasses, and low-growing plants.
- Some of the common plant species found in this desert include the thorny scrub, tussock grasses, and cushions plants.
- These plants have adaptations to survive in the arid conditions, such as deep root systems to access underground water sources and thick waxy leaves to reduce water loss through evaporation.
3. Wildlife:
- Despite the harsh conditions, the Patagonian desert is home to a variety of wildlife. It is known for its unique fauna, including several endemic species.
- Some of the iconic animals found in this desert are the guanaco (a relative of the llama), the mara (a large rodent), and the Darwin's rhea (a flightless bird).
- There are also several bird species, such as the Andean condor, which inhabit the cliffs and mountains of the region.
4. Human Settlements:
- The Patagonian desert has a low population density due to its harsh climate and limited resources.
- However, there are some small towns and settlements scattered across the desert, mainly focused on agriculture and tourism.
- The region is popular among tourists for its stunning landscapes, including glaciers, fjords, and mountains.
In conclusion, the Patagonian desert is considered a temperate desert due to its location in the temperate zone, its mild climate with distinct seasons, low precipitation, and unique desert flora and fauna.
1. Location and Climate:
- The Patagonian desert is situated in the southern regions of Argentina and Chile, extending from the Atlantic Ocean to the Andes Mountains.
- It lies in the temperate zone, where the climate is influenced by the cool ocean currents and the mountain ranges.
- The region experiences mild summers and cold winters, with average temperatures ranging from 8°C (46°F) in the summer to -2°C (28°F) in the winter.
- The average annual precipitation is relatively low, ranging from 100 to 400 mm (4 to 16 inches), which is a defining characteristic of deserts.
2. Vegetation:
- The vegetation in the Patagonian desert is sparse but diverse. It consists mainly of shrubs, grasses, and low-growing plants.
- Some of the common plant species found in this desert include the thorny scrub, tussock grasses, and cushions plants.
- These plants have adaptations to survive in the arid conditions, such as deep root systems to access underground water sources and thick waxy leaves to reduce water loss through evaporation.
3. Wildlife:
- Despite the harsh conditions, the Patagonian desert is home to a variety of wildlife. It is known for its unique fauna, including several endemic species.
- Some of the iconic animals found in this desert are the guanaco (a relative of the llama), the mara (a large rodent), and the Darwin's rhea (a flightless bird).
- There are also several bird species, such as the Andean condor, which inhabit the cliffs and mountains of the region.
4. Human Settlements:
- The Patagonian desert has a low population density due to its harsh climate and limited resources.
- However, there are some small towns and settlements scattered across the desert, mainly focused on agriculture and tourism.
- The region is popular among tourists for its stunning landscapes, including glaciers, fjords, and mountains.
In conclusion, the Patagonian desert is considered a temperate desert due to its location in the temperate zone, its mild climate with distinct seasons, low precipitation, and unique desert flora and fauna.
Which of the following is/are the characteristic(s) of Tropical Deciduous Forests?(i) Trees shed their leaves in the dry season to conserve water(ii) The hardwood trees found in these forests are sal, teak and Sheesham(iii) Tigers, lions, elephants and monkeys are common animals- a) only (i)
- b) (ii) and (iii)
- c) only (iii)
- d) All of them
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is/are the characteristic(s) of Tropical Deciduous Forests?
(i) Trees shed their leaves in the dry season to conserve water
(ii) The hardwood trees found in these forests are sal, teak and Sheesham
(iii) Tigers, lions, elephants and monkeys are common animals
a)
only (i)
b)
(ii) and (iii)
c)
only (iii)
d)
All of them
|
|
Divyansh Yadav answered |
Characteristics of Tropical Deciduous Forests:
1. Trees shed their leaves in the dry season to conserve water:
Tropical deciduous forests are characterized by trees that shed their leaves during the dry season to conserve water. This adaptation helps the trees survive the prolonged periods of drought that are common in these regions.
2. The hardwood trees found in these forests are sal, teak, and Sheesham:
Tropical deciduous forests are home to a variety of hardwood trees such as sal, teak, and Sheesham. These trees are prized for their strong and durable wood, making them valuable resources for timber production.
3. Tigers, lions, elephants, and monkeys are common animals:
These forests are rich in biodiversity and are home to a wide range of animal species. Common animals found in tropical deciduous forests include tigers, lions, elephants, and monkeys. These forests provide important habitats for these animals and support a diverse ecosystem.
4. All of the above characteristics:
All the characteristics mentioned above are true for tropical deciduous forests. These forests play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance and supporting a wide range of plant and animal species.
1. Trees shed their leaves in the dry season to conserve water:
Tropical deciduous forests are characterized by trees that shed their leaves during the dry season to conserve water. This adaptation helps the trees survive the prolonged periods of drought that are common in these regions.
2. The hardwood trees found in these forests are sal, teak, and Sheesham:
Tropical deciduous forests are home to a variety of hardwood trees such as sal, teak, and Sheesham. These trees are prized for their strong and durable wood, making them valuable resources for timber production.
3. Tigers, lions, elephants, and monkeys are common animals:
These forests are rich in biodiversity and are home to a wide range of animal species. Common animals found in tropical deciduous forests include tigers, lions, elephants, and monkeys. These forests provide important habitats for these animals and support a diverse ecosystem.
4. All of the above characteristics:
All the characteristics mentioned above are true for tropical deciduous forests. These forests play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance and supporting a wide range of plant and animal species.
The valley of flowers is located in—- a) Himachal Himalaya
- b) Garhwal Himalaya
- c) Kashmir Himalaya
- d) Nepal Himalaya
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The valley of flowers is located in—
a)
Himachal Himalaya
b)
Garhwal Himalaya
c)
Kashmir Himalaya
d)
Nepal Himalaya
|
|
Chirag Chawla answered |
The Valley of Flowers
The Valley of Flowers is a stunningly beautiful national park located in the Garhwal Himalayas, making option 'B' the correct answer. Situated in the Chamoli district of Uttarakhand, India, it is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a popular tourist destination for its breathtaking natural beauty and diverse flora.
Location
The Valley of Flowers is nestled in the western Himalayas and is part of the Zanskar range. It lies in the transition zone between the Greater Himalayas and the Zanskar Himalayas. The park stretches over an area of approximately 87.5 square kilometers and is situated at an altitude ranging from 3,200 to 6,675 meters above sea level.
Accessibility
To reach the Valley of Flowers, one needs to travel to Joshimath, a small town in the Chamoli district. From Joshimath, a trek of approximately 17 kilometers leads to the entry gate of the national park. The trek takes visitors through picturesque landscapes, including dense forests, cascading waterfalls, and meandering rivers. The journey to the valley is not only physically challenging but also rewarding, offering mesmerizing views of the surrounding mountains.
Flora and Fauna
The Valley of Flowers is renowned for its rich floral diversity, which includes hundreds of species of wildflowers, alpine flowers, and rare Himalayan flowers. The park is home to numerous endemic and endangered plant species, such as the Brahma Kamal (Saussurea obvallata), Blue Poppy (Meconopsis aculeata), and Cobra Lily (Arisaema tortuosum). The blooming season, which usually occurs from July to September, transforms the valley into a vibrant carpet of colorful flowers, creating a mesmerizing spectacle.
Conservation and Protection
The Valley of Flowers was declared a national park in 1982 and was later designated as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 2005. The park is protected under various environmental laws and regulations to preserve its unique biodiversity. The area is strictly monitored to prevent any harm to the fragile ecosystem. Visitors are required to obtain permits and follow specific guidelines to ensure sustainable tourism and minimal impact on the environment.
Conclusion
The Valley of Flowers, located in the Garhwal Himalayas, is a natural paradise renowned for its breathtaking beauty and diverse floral wealth. It offers visitors a unique opportunity to immerse themselves in the lap of nature and witness the enchanting charm of the Himalayas.
The Valley of Flowers is a stunningly beautiful national park located in the Garhwal Himalayas, making option 'B' the correct answer. Situated in the Chamoli district of Uttarakhand, India, it is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a popular tourist destination for its breathtaking natural beauty and diverse flora.
Location
The Valley of Flowers is nestled in the western Himalayas and is part of the Zanskar range. It lies in the transition zone between the Greater Himalayas and the Zanskar Himalayas. The park stretches over an area of approximately 87.5 square kilometers and is situated at an altitude ranging from 3,200 to 6,675 meters above sea level.
Accessibility
To reach the Valley of Flowers, one needs to travel to Joshimath, a small town in the Chamoli district. From Joshimath, a trek of approximately 17 kilometers leads to the entry gate of the national park. The trek takes visitors through picturesque landscapes, including dense forests, cascading waterfalls, and meandering rivers. The journey to the valley is not only physically challenging but also rewarding, offering mesmerizing views of the surrounding mountains.
Flora and Fauna
The Valley of Flowers is renowned for its rich floral diversity, which includes hundreds of species of wildflowers, alpine flowers, and rare Himalayan flowers. The park is home to numerous endemic and endangered plant species, such as the Brahma Kamal (Saussurea obvallata), Blue Poppy (Meconopsis aculeata), and Cobra Lily (Arisaema tortuosum). The blooming season, which usually occurs from July to September, transforms the valley into a vibrant carpet of colorful flowers, creating a mesmerizing spectacle.
Conservation and Protection
The Valley of Flowers was declared a national park in 1982 and was later designated as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 2005. The park is protected under various environmental laws and regulations to preserve its unique biodiversity. The area is strictly monitored to prevent any harm to the fragile ecosystem. Visitors are required to obtain permits and follow specific guidelines to ensure sustainable tourism and minimal impact on the environment.
Conclusion
The Valley of Flowers, located in the Garhwal Himalayas, is a natural paradise renowned for its breathtaking beauty and diverse floral wealth. It offers visitors a unique opportunity to immerse themselves in the lap of nature and witness the enchanting charm of the Himalayas.
The wide treeless grassy plains in South America are called- a) Selvas
- b) Pampas
- c) Prairies
- d) Steppes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The wide treeless grassy plains in South America are called
a)
Selvas
b)
Pampas
c)
Prairies
d)
Steppes
|
|
Disha Roy answered |
The wide treeless grassy plains in South America are called Pampas.
The Pampas are vast grasslands that stretch across South America, primarily in Argentina and Uruguay but also extending into Brazil and Paraguay. These plains cover an area of approximately 750,000 square kilometers, making them one of the largest continuous grassland ecosystems in the world.
The Pampas are characterized by their flat and fertile landscape, ideal for extensive agricultural activities. The region is known for its rich and deep soil, which is highly suitable for farming and grazing. The grasslands support a diverse range of plant species, including perennial grasses such as buffalo grass and feather grass, as well as wildflowers and shrubs.
Climate:
The Pampas region experiences a temperate climate with distinct seasons. Summers are hot and humid, with average temperatures ranging from 25 to 30 degrees Celsius (77 to 86 degrees Fahrenheit). Winters are mild, with temperatures averaging around 10 degrees Celsius (50 degrees Fahrenheit). Precipitation is relatively evenly distributed throughout the year, ranging from 500 to 1,000 millimeters annually.
Flora and Fauna:
The Pampas are home to a diverse range of plant and animal species. The grasslands support a variety of herbaceous plants, including grasses, sedges, and rushes. Some of the dominant grass species found in the Pampas include Stipa spp., Paspalum spp., and Poa spp.
The Pampas are also home to a rich array of wildlife. The grasslands provide habitat for numerous species of mammals, such as guanacos, capybaras, and marsh deer. The region is also known for its bird diversity, with over 300 species recorded, including rheas, tinamous, and various waterfowl.
Human Activities:
The Pampas have long been utilized for agricultural purposes. The fertile soil and favorable climate make it an ideal region for farming and ranching. The grasslands are primarily used for grazing livestock, particularly cattle and sheep. Argentina, in particular, is renowned for its beef production, with the Pampas playing a significant role in the country's agricultural economy.
In addition to agriculture, the Pampas region also supports urban settlements and industrial activities. Major cities such as Buenos Aires and Montevideo are located within the Pampas, serving as economic and cultural centers.
Conservation and Challenges:
The Pampas face several challenges related to unsustainable land use practices and habitat fragmentation. Conversion of grasslands into croplands, overgrazing, and the use of agrochemicals pose threats to the ecosystem's integrity. Additionally, the expansion of urban areas and infrastructure development further fragment the grasslands, impacting wildlife populations and their migration patterns.
Efforts are being made to conserve and restore the Pampas ecosystem. Protected areas have been established to safeguard key habitats and species, and sustainable land management practices are being promoted to mitigate the negative impacts of agriculture. These conservation initiatives aim to maintain the ecological integrity of the Pampas while supporting sustainable development in the region.
The Pampas are vast grasslands that stretch across South America, primarily in Argentina and Uruguay but also extending into Brazil and Paraguay. These plains cover an area of approximately 750,000 square kilometers, making them one of the largest continuous grassland ecosystems in the world.
The Pampas are characterized by their flat and fertile landscape, ideal for extensive agricultural activities. The region is known for its rich and deep soil, which is highly suitable for farming and grazing. The grasslands support a diverse range of plant species, including perennial grasses such as buffalo grass and feather grass, as well as wildflowers and shrubs.
Climate:
The Pampas region experiences a temperate climate with distinct seasons. Summers are hot and humid, with average temperatures ranging from 25 to 30 degrees Celsius (77 to 86 degrees Fahrenheit). Winters are mild, with temperatures averaging around 10 degrees Celsius (50 degrees Fahrenheit). Precipitation is relatively evenly distributed throughout the year, ranging from 500 to 1,000 millimeters annually.
Flora and Fauna:
The Pampas are home to a diverse range of plant and animal species. The grasslands support a variety of herbaceous plants, including grasses, sedges, and rushes. Some of the dominant grass species found in the Pampas include Stipa spp., Paspalum spp., and Poa spp.
The Pampas are also home to a rich array of wildlife. The grasslands provide habitat for numerous species of mammals, such as guanacos, capybaras, and marsh deer. The region is also known for its bird diversity, with over 300 species recorded, including rheas, tinamous, and various waterfowl.
Human Activities:
The Pampas have long been utilized for agricultural purposes. The fertile soil and favorable climate make it an ideal region for farming and ranching. The grasslands are primarily used for grazing livestock, particularly cattle and sheep. Argentina, in particular, is renowned for its beef production, with the Pampas playing a significant role in the country's agricultural economy.
In addition to agriculture, the Pampas region also supports urban settlements and industrial activities. Major cities such as Buenos Aires and Montevideo are located within the Pampas, serving as economic and cultural centers.
Conservation and Challenges:
The Pampas face several challenges related to unsustainable land use practices and habitat fragmentation. Conversion of grasslands into croplands, overgrazing, and the use of agrochemicals pose threats to the ecosystem's integrity. Additionally, the expansion of urban areas and infrastructure development further fragment the grasslands, impacting wildlife populations and their migration patterns.
Efforts are being made to conserve and restore the Pampas ecosystem. Protected areas have been established to safeguard key habitats and species, and sustainable land management practices are being promoted to mitigate the negative impacts of agriculture. These conservation initiatives aim to maintain the ecological integrity of the Pampas while supporting sustainable development in the region.
Consider the following statements and select the correct answer from the codes given below:Assertion (A): The production of rubber is decreasing in the Amazon.Reason (R): Equatorial climate is favourable for rubber plantation.Codes:- a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b) Both A and R are true, but R is not a correct explanation of A.
- c) A is true, but R is false.
- d) A is false, but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements and select the correct answer from the codes given below:
Assertion (A): The production of rubber is decreasing in the Amazon.
Reason (R): Equatorial climate is favourable for rubber plantation.
Codes:
a)
Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true, but R is not a correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true, but R is false.
d)
A is false, but R is true.
|
|
Ojasvi Mehta answered |
- Cultivation of rubber in Brazil, its native habitat, was severely hindered by blight in the early 20th century.
- At present, most of the world’s natural rubber is produced by Rubber trees descended from rubber seedlings transplanted from South America to the south and south-east Asia.
- The most severe disease is the South American Leaf Blight (SALB).
- This Disease is endemic throughout the rubber growing areas in the Americas. It also poses a major global threat.
- Several fungicides can control the fungus. Some Species are not susceptible to the disease, and some strains of susceptible species are resistant.
- Crown budding or grafting of resistant plants onto productive trees can be used to control spread.
Which one of the following is not an abiotic resource?- a) Freshwater
- b) Coal
- c) Petroleum
- d) Fish
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is not an abiotic resource?
a)
Freshwater
b)
Coal
c)
Petroleum
d)
Fish
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
- The resources which are obtained from the biosphere and have life are called biotic resources. Examples of biotic resources are forests, animals, birds, fish and marine organisms.
- Mineral fuels can be regarded as biotic resources since they are derived from or products formed from decayed organic matter.
Which one of the following is the correct sequence about various levels of organization of the Biosphere?- a) Ecosystem → Biosphere → Community → Population
- b) Population → Organism → Ecosystem → Biosphere
- c) Organism → Community → Population → Biosphere
- d) Organism → Population → Ecosystem → Biosphere
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is the correct sequence about various levels of organization of the Biosphere?
a)
Ecosystem → Biosphere → Community → Population
b)
Population → Organism → Ecosystem → Biosphere
c)
Organism → Community → Population → Biosphere
d)
Organism → Population → Ecosystem → Biosphere
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
Organism → Population → Ecosystem → Biosphere
Which one of the following has evergreen forest?- a) Malwa Plateau
- b) Eastern Ghat
- c) Western Ghat
- d) Chota Nagpur Plateau
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following has evergreen forest?
a)
Malwa Plateau
b)
Eastern Ghat
c)
Western Ghat
d)
Chota Nagpur Plateau
|
|
Anita Desai answered |
Western ghats spread over parts of Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Karnataka and Maharashtra are rich in biodiversity due to presence of evergreen forests.
Which one of the following statements on biosphere reserves is not correct?- a) In 1973, UNESCO launched a worldwide programme on man and biosphere
- b) Biosphere reserves promote research on ecological conservation
- c) Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve is located in Madhya Pradesh
- d) Biosphere reserves are multipurpose protected areas to preserve the genetic diversity in ecosystems
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements on biosphere reserves is not correct?
a)
In 1973, UNESCO launched a worldwide programme on man and biosphere
b)
Biosphere reserves promote research on ecological conservation
c)
Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve is located in Madhya Pradesh
d)
Biosphere reserves are multipurpose protected areas to preserve the genetic diversity in ecosystems
|
|
Kabir Verma answered |
Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve is located in Uttarakhand. It was inscribed a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1988
Consider the following statements and select the correct answerfrom codes given below:Assertion (A): Tropical areas get more insolation than the temperate area.Reason (R): Tropical areas have a larger length of the day than the temperate areas.Codes:- a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c) A is true, but R is false.
- d) A is false, but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements and select the correct answer
from codes given below:
Assertion (A): Tropical areas get more insolation than the temperate area.
Reason (R): Tropical areas have a larger length of the day than the temperate areas.
Codes:
a)
Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true, but R is false.
d)
A is false, but R is true.
|
|
Ananya Deshmukh answered |
The solar radiation is intense and to a great extent, diffuse due to haze. It, therefore, demands generous shading devices. The haze may cause sky glare which can also be reduced by large shading devices.
Consider the following statements:1. Tropical Evergreen forests are found in areas with an annual precipitation of over 200 cm and mean annual temperature above 22°C.2. The semi evergreen forests in India are found primarily in the deltaic regions.3. The British replaced oak forests in Garhwal and Kumaon with pine (chirs) for commercial use.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?- a)1 Only
- b)1 and 2 Only
- c)1 and 3 Only
- d)1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
1. Tropical Evergreen forests are found in areas with an annual precipitation of over 200 cm and mean annual temperature above 22°C.
2. The semi evergreen forests in India are found primarily in the deltaic regions.
3. The British replaced oak forests in Garhwal and Kumaon with pine (chirs) for commercial use.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a)
1 Only
b)
1 and 2 Only
c)
1 and 3 Only
d)
1, 2 and 3

|
Divey Sethi answered |
1. Tropical Evergreen forests are found in areas with an annual precipitation of over 200 cm and mean annual temperature above 22°C.
This statement is correct. Tropical Evergreen forests thrive in warm and humid areas with high annual precipitation exceeding 200 cm and temperatures above 22°C.
This statement is correct. Tropical Evergreen forests thrive in warm and humid areas with high annual precipitation exceeding 200 cm and temperatures above 22°C.
2. The semi evergreen forests in India are found primarily in the deltaic regions.
This statement is incorrect. Semi evergreen forests are found in the less rainy parts of regions that also have tropical evergreen forests, such as the western slopes of the Western Ghats and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, not primarily in deltaic regions.
This statement is incorrect. Semi evergreen forests are found in the less rainy parts of regions that also have tropical evergreen forests, such as the western slopes of the Western Ghats and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, not primarily in deltaic regions.
3. The British replaced oak forests in Garhwal and Kumaon with pine (chirs) for commercial use.
This statement is correct. The British exploited the forests commercially and replaced oak forests with pine (chirs) to meet their needs, such as laying railway lines.
This statement is correct. The British exploited the forests commercially and replaced oak forests with pine (chirs) to meet their needs, such as laying railway lines.
Therefore, the correct answer is Option C.
The vegetation type characterized by(i) a large expanse of grassland with scattered trees and shrubs,(ii) lying between the tropical rainforest and tropical steppes and deserts and(iii) flat-topped trees is called- a) mid-latitude broad-leaf mixed forest
- b) temperate rainforest
- c) tropical savanna
- d) mid-latitude grassland
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The vegetation type characterized by
(i) a large expanse of grassland with scattered trees and shrubs,
(ii) lying between the tropical rainforest and tropical steppes and deserts and
(iii) flat-topped trees is called
a)
mid-latitude broad-leaf mixed forest
b)
temperate rainforest
c)
tropical savanna
d)
mid-latitude grassland
|
|
Vikram Verma answered |
- A Savanna is a rolling grassland scattered with shrubs and isolated trees, which can be found between a tropical rainforest and desert biome.
- Savannas are also known as tropical grasslands. These types of grassland are found in a wide band on either side of the equator on the edges of tropical rainforests.
Which of the following is the odd one out of the group?- a) Prairies
- b) Savanna
- c) Pampas
- d) Steppes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the odd one out of the group?
a)
Prairies
b)
Savanna
c)
Pampas
d)
Steppes
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
Savanna has a transitional type of climate which is bounded between equatorial rain forest and semi-arid and subtropical humid climate. Others are called mid-latitude grasslands.
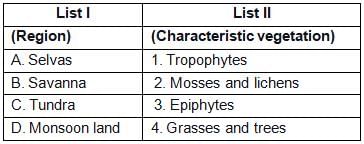
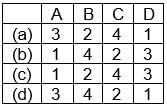
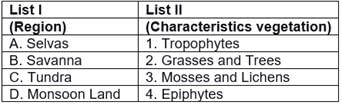
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer from the codes given below: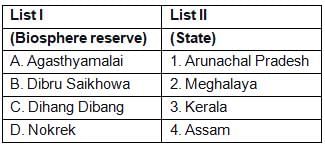 Code:A B C D(a) 1 3 4 2(b) 4 2 1 3(c) 3 1 2 4(d) 3 4 1 2
Code:A B C D(a) 1 3 4 2(b) 4 2 1 3(c) 3 1 2 4(d) 3 4 1 2- a)(a)
- b)(b)
- c)(c)
- d)(d)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer from the codes given below:

Code:
A B C D
(a) 1 3 4 2
(b) 4 2 1 3
(c) 3 1 2 4
(d) 3 4 1 2
a)
(a)
b)
(b)
c)
(c)
d)
(d)
|
|
Ananya Deshmukh answered |
- The Agasthyamalai Biosphere Reserve was established in 2001 and includes 3,500.36 km2 of which 1828 km2 is in Kerala and 1672.36 km2 is in Tamil Nadu. Agasthyamalai Biosphere Reserve became part of the World Network of Biosphere Reserves in 2016. Dibru-Saikhowa National Park is a national wildlife park in Tinsukia, Assam, India.
- Dibru-Saikhowa National Park is located about 12 km north of Tinsukia town of Assam covering an area of 350 km2. Dihang-Dibang or Dehang-Debang is a biosphere reserve established in 1998. It is in the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh. The Mouling National Park and the Dibang Wildlife Sanctuary are located fully or partly within this biosphere reserve.
- The reserve spreads over three districts: Dibang Valley, Upper Siang, and West Siang. Nokrek National Park, or Nokrek Biosphere Reserve, is a national park located approximately 2 km from Tura Peak in West Garo Hills district of Meghalaya, India. UNESCO added this National park to its list of Biosphere Reserves in May 2009.
Match the two columns and select the correct alternative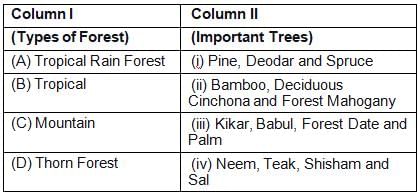
- a)A – (iv), B – (iii), C – (ii), D - (i)
- b)A – (ii), B – (iii), C – (i), D - (iv)
- c)A – (ii), B – (iv), C – (i), D - (iii)
- d)A – (i), B – (ii), C – (iii), D - (iv)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the two columns and select the correct alternative

a)
A – (iv), B – (iii), C – (ii), D - (i)
b)
A – (ii), B – (iii), C – (i), D - (iv)
c)
A – (ii), B – (iv), C – (i), D - (iii)
d)
A – (i), B – (ii), C – (iii), D - (iv)
|
|
Anjali Rao answered |
Tropical Rainforest – Bamboo, Cinchona and Forest Mahogany
Tropical Deciduous – Neem, Teak, Shisham and Sal
Mountain Forest – Pine, Deodar and spruce
Thorn Forest - Kikar, Babul, Date, Palm
Ebony and Mahogany trees are associated with- a) Coniferous forests
- b) Deciduous forests
- c) Tropical Monsoon forests
- d) Tropical Evergreen forests
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Ebony and Mahogany trees are associated with
a)
Coniferous forests
b)
Deciduous forests
c)
Tropical Monsoon forests
d)
Tropical Evergreen forests
|
|
Ojasvi Mehta answered |
- Ebony and Mahogany trees are associated with Tropical evergreen forests. Tropical evergreen forests are usually found in areas receiving more than 200 cm of rainfall and having a temperature of 15 °C to 30 °C.
- They occupy about seven per cent of the Earth’s land surface and harbour more than half of the planet’s terrestrial plants and animals.
- Tropical evergreen forests are dense, multi-layered, harbour many types of plants & animals.
Consider the following statements1. Jim Corbett National Park is the oldest national park of India.2. It was one of the nine tiger reserves created at the launch of theProject Tiger in 1973.3. Initially it was named as ‘Hailey National Park’.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?- a)1 and 2
- b)All of these
- c)2 and 3
- d)1 and 3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements
1. Jim Corbett National Park is the oldest national park of India.
2. It was one of the nine tiger reserves created at the launch of the
Project Tiger in 1973.
3. Initially it was named as ‘Hailey National Park’.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a)
1 and 2
b)
All of these
c)
2 and 3
d)
1 and 3
|
|
Kritika Roy answered |
Hailey National Park after Sir Malcolm Hailey, the then Governor of United Provinces.
4. The park is located in the state of Uttarakhand in northern India.
5. It is known for its significant population of Bengal tigers, along with other wildlife species such as leopards, elephants, and deer.
6. The park is a popular tourist destination and offers various activities such as jeep safaris, bird watching, and nature walks.
7. It is also famous for its scenic beauty, with lush forests, rivers, and waterfalls.
8. The park is named after Jim Corbett, a British-Indian hunter and conservationist, who played a key role in establishing the park and protecting its wildlife.
9. Jim Corbett National Park is spread over an area of approximately 520 square kilometers.
10. It was declared a national park in 1936 and has since been a major conservation area for endangered species.
4. The park is located in the state of Uttarakhand in northern India.
5. It is known for its significant population of Bengal tigers, along with other wildlife species such as leopards, elephants, and deer.
6. The park is a popular tourist destination and offers various activities such as jeep safaris, bird watching, and nature walks.
7. It is also famous for its scenic beauty, with lush forests, rivers, and waterfalls.
8. The park is named after Jim Corbett, a British-Indian hunter and conservationist, who played a key role in establishing the park and protecting its wildlife.
9. Jim Corbett National Park is spread over an area of approximately 520 square kilometers.
10. It was declared a national park in 1936 and has since been a major conservation area for endangered species.
Sal trees are the typical species of [NDA 2009-II]- a) Tropical rainforest
- b) Tropical monsoon forest
- c) Taiga forest
- d) Tundra forest
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Sal trees are the typical species of [NDA 2009-II]
a)
Tropical rainforest
b)
Tropical monsoon forest
c)
Taiga forest
d)
Tundra forest
|
|
Ojasvi Mehta answered |
The trees in Monsoon Forests shed their leaves for about six to eight weeks in summer on account of a long dry spell. The rainfall suited for such forests is between75 to 200 cm. Sal is of the dry deciduous variety of tropical monsoon forest.
Match column I with column II and select the correct answer using the code given below the columns:Column I Column II(Types of Forests) (Areas Associated)A. Tropical (i) Sunderbans rainforestsB. Monsoon forests (ii) Andaman and Nicobar islandsC. Thorny bushes (iii) Uttar Pradesh and BiharD. Tidal forests (iv) Rajasthan and GujaratCodes:- a) A - (ii); B - (iii); C - (iv); D - (i)
- b) A - (i); B - (ii); C - (iii); D - (iv)
- c) A - (ii); B - (iv); C - (iii); D - (i)
- d) A - (iv); B - (iii); C - (ii); D - (i)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Match column I with column II and select the correct answer using the code given below the columns:
Column I Column II
(Types of Forests) (Areas Associated)
A. Tropical (i) Sunderbans rainforests
B. Monsoon forests (ii) Andaman and Nicobar islands
C. Thorny bushes (iii) Uttar Pradesh and Bihar
D. Tidal forests (iv) Rajasthan and Gujarat
Codes:
a)
A - (ii); B - (iii); C - (iv); D - (i)
b)
A - (i); B - (ii); C - (iii); D - (iv)
c)
A - (ii); B - (iv); C - (iii); D - (i)
d)
A - (iv); B - (iii); C - (ii); D - (i)
|
|
Anjali Rao answered |
- Tropical rainforests of India are found in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, the Western Ghats, which fringe the Arabian Sea, the coastline of peninsular India, and the greater Assam region in the north-east. Small remnants of rainforest are found in Odisha state.
- Monsoon forest – Uttar Pradesh and Bihar Thorny bushes - The Thorn Forests and Scrubs are found in regions where the rainfall is less than 70cm. The vegetation in these forests is thorny trees and bushes. The Thorn Forests are found in the semi-arid areas of Gujarat & Rajasthan. Tidal forest – Sunderbans
Consider the following pairs:1. Tropical Evergreen Forests - Found in the Western slope of the Western Ghats2. Tropical Deciduous Forests - Found in the hills of the northeastern region3. Tropical Thorn Forests - Found in the deltaic regions4. Montane Forests - Found in the Himalayan heightsHow many pairs given above are correctly matched?- a)Only one pair
- b)Only two pairs
- c)Only three pairs
- d)All four pairs
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following pairs:
1. Tropical Evergreen Forests - Found in the Western slope of the Western Ghats
2. Tropical Deciduous Forests - Found in the hills of the northeastern region
3. Tropical Thorn Forests - Found in the deltaic regions
4. Montane Forests - Found in the Himalayan heights
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
a)
Only one pair
b)
Only two pairs
c)
Only three pairs
d)
All four pairs

|
Capstone Ias Learning answered |
1. Tropical Evergreen Forests - Found in the Western slope of the Western Ghats: Correct. Tropical evergreen forests are indeed found in the Western slope of the Western Ghats, as well as in the hills of the northeastern region and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. These forests thrive in warm and humid areas with high annual precipitation.
2. Tropical Deciduous Forests - Found in the hills of the northeastern region: Incorrect. Tropical deciduous forests are typically found in regions with moderate rainfall, such as the plains of the Indian subcontinent. They are not specifically characteristic of the hills of the northeastern region.
3. Tropical Thorn Forests - Found in the deltaic regions: Incorrect. Tropical thorn forests are found in arid and semi-arid regions, such as Rajasthan. They are not found in deltaic regions, which are more likely to have mangrove or tropical forests.
4. Montane Forests - Found in the Himalayan heights: Correct. Montane forests are found in the mountainous regions and are characteristic of the Himalayan heights, where the climate is cooler and supports temperate vegetation.
Thus, only pairs 1 and 4 are correctly matched.
What is the primary aim of social forestry as outlined in the National Commission on Agriculture's classification?- a)Preservation of wildlife species
- b)Promotion of urbanization
- c)Management and protection of forests
- d)Industrial development
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the primary aim of social forestry as outlined in the National Commission on Agriculture's classification?
a)
Preservation of wildlife species
b)
Promotion of urbanization
c)
Management and protection of forests
d)
Industrial development

|
Lakshya Ias answered |
Social forestry, as classified by the National Commission on Agriculture, focuses on the management and protection of forests and afforestation on barren lands to aid in environmental, social, and rural development. It encompasses activities such as urban forestry, rural forestry, and farm forestry. Urban forestry involves managing trees in urban areas, while rural forestry promotes agro-forestry and community forestry. Agro-forestry combines tree cultivation with agriculture, while community forestry engages communities in tree planting on public lands for mutual benefits.
Which one of the following has a protected mangrove region?- a)Eastern Ghats
- b)Western Ghats
- c)Goa
- d)Chandra Tal
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following has a protected mangrove region?
a)
Eastern Ghats
b)
Western Ghats
c)
Goa
d)
Chandra Tal
|
|
Sahil Khanna answered |
Protected Mangrove Region in Eastern Ghats
Mangroves are tropical trees and shrubs that grow in dense forests along sheltered coastlines, lagoons, and estuaries. They have unique adaptations to survive in harsh conditions such as saltwater, low oxygen, and strong waves. Mangroves are important ecosystems that provide numerous benefits such as carbon sequestration, coastal protection, fisheries, and tourism.
In India, mangroves are found in several regions including the Eastern Ghats. The Eastern Ghats is a mountain range that runs parallel to the Bay of Bengal in eastern India. It covers several states including Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, and Karnataka. The Eastern Ghats region has several protected areas that include mangrove forests.
One of the notable protected mangrove regions in the Eastern Ghats is the Bhitarkanika National Park in Odisha. Bhitarkanika is a unique ecosystem that consists of mangrove forests, wetlands, and estuaries. It is home to a variety of wildlife such as saltwater crocodiles, spotted deer, wild boars, and several species of birds. Bhitarkanika is also a Ramsar site, which is a wetland of international importance.
Other protected mangrove regions in the Eastern Ghats include the Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary in Andhra Pradesh and the Pichavaram Mangrove Forest in Tamil Nadu. Coringa is a coastal estuary that has a diverse mangrove ecosystem with over 35 species of mangroves. Pichavaram is a unique ecosystem that consists of a network of canals and channels that crisscross the mangrove forests. It is also a popular tourist destination for boating and birdwatching.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Eastern Ghats region has several protected areas that include mangrove forests. These ecosystems are important for their biodiversity, ecological functions, and socio-economic benefits. Protecting and conserving mangroves is crucial for sustaining these benefits and ensuring the resilience of coastal communities.
Mangroves are tropical trees and shrubs that grow in dense forests along sheltered coastlines, lagoons, and estuaries. They have unique adaptations to survive in harsh conditions such as saltwater, low oxygen, and strong waves. Mangroves are important ecosystems that provide numerous benefits such as carbon sequestration, coastal protection, fisheries, and tourism.
In India, mangroves are found in several regions including the Eastern Ghats. The Eastern Ghats is a mountain range that runs parallel to the Bay of Bengal in eastern India. It covers several states including Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, and Karnataka. The Eastern Ghats region has several protected areas that include mangrove forests.
One of the notable protected mangrove regions in the Eastern Ghats is the Bhitarkanika National Park in Odisha. Bhitarkanika is a unique ecosystem that consists of mangrove forests, wetlands, and estuaries. It is home to a variety of wildlife such as saltwater crocodiles, spotted deer, wild boars, and several species of birds. Bhitarkanika is also a Ramsar site, which is a wetland of international importance.
Other protected mangrove regions in the Eastern Ghats include the Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary in Andhra Pradesh and the Pichavaram Mangrove Forest in Tamil Nadu. Coringa is a coastal estuary that has a diverse mangrove ecosystem with over 35 species of mangroves. Pichavaram is a unique ecosystem that consists of a network of canals and channels that crisscross the mangrove forests. It is also a popular tourist destination for boating and birdwatching.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Eastern Ghats region has several protected areas that include mangrove forests. These ecosystems are important for their biodiversity, ecological functions, and socio-economic benefits. Protecting and conserving mangroves is crucial for sustaining these benefits and ensuring the resilience of coastal communities.
Match the animal with its habitat and accordingly select the correct alternative:
- a)A – (iii), B – (ii), C –(i) , D - (iv)
- b)A – (iii), B – (ii), C – (iv), D - (i)
- c)A – (ii), B – (iv), C – (i), D - (iii)
- d)A – (iii), B – (i), C – (iv), D - (ii)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

Match the animal with its habitat and accordingly select the correct alternative:
a)
A – (iii), B – (ii), C –(i) , D - (iv)
b)
A – (iii), B – (ii), C – (iv), D - (i)
c)
A – (ii), B – (iv), C – (i), D - (iii)
d)
A – (iii), B – (i), C – (iv), D - (ii)
|
|
Ananya Deshmukh answered |
Correct option is B.
The most abundant source of energy is- a) Oil
- b) Biomass
- c) Coal
- d) Sun
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The most abundant source of energy is
a)
Oil
b)
Biomass
c)
Coal
d)
Sun
|
|
Anjali Rao answered |
A most abundant source of energy is solar power energy. It is the cleanest and most abundant renewable energy source available.
Chapter doubts & questions for Vegetation & Wildlife - Lucent for GK 2025 is part of UPSC CSE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the UPSC CSE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for UPSC CSE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Vegetation & Wildlife - Lucent for GK in English & Hindi are available as part of UPSC CSE exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for UPSC CSE Exam by signing up for free.
Lucent for GK
643 videos|792 docs|420 tests
|
Related UPSC CSE Content
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup