All Exams >
BPSC (Bihar) >
Science & Technology for State PSC Exams >
All Questions
All questions of Biology for BPSC (Bihar) Exam
Which of the following tissues has dead cells?- a) Parenchyma
- b) Sclerenchyma
- c) Collenchyma
- d) Epithelial tissue
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following tissues has dead cells?
a)
Parenchyma
b)
Sclerenchyma
c)
Collenchyma
d)
Epithelial tissue

|
Nandita Saha answered |
Sclerenchyma → cells are the permanent tissues present in the plants. They provide hardness and stiffness to the plant and are composed of dead cells.
From which of the following part of a plant opium is obtained?- a)Dried leaves
- b)Dried latex
- c)Roots
- d)Stem bark
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
From which of the following part of a plant opium is obtained?
a)
Dried leaves
b)
Dried latex
c)
Roots
d)
Stem bark

|
Nishanth Jain answered |
Opium is the dried latex obtained from the opium poppy
Meristematic tissues are found in- a) only stems of the plants
- b)both roots and stems
- c)in all growing tips of the plant body
- d)only roots of the plants
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Meristematic tissues are found in
a)
only stems of the plants
b)
both roots and stems
c)
in all growing tips of the plant body
d)
only roots of the plants

|
Debanshi Sarkar answered |
A meristem is the tissue in most plants containing undifferentiated cells (meristematic cells), found in zones of the plant where growth can take place. Meristematic cells give rise to various organs of a plant and are responsible for growth
Various functions like photosynthesis, storage, excretion performed by _________.- a) Sclerenchyma
- b) parenchyma
- c) Collenchyma
- d) Aerenchyma
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Various functions like photosynthesis, storage, excretion performed by _________.
a)
Sclerenchyma
b)
parenchyma
c)
Collenchyma
d)
Aerenchyma

|
Dhruba Saini answered |
Parenchyma forms the bulk of plant ground tissue, where they may be specialised to function in photosynthesis, storage, or transport.
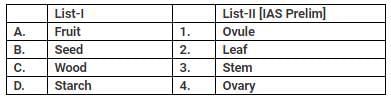
- a)A-2; B-1; C-3; D- 4
- b) A-4; B-1; C-3; D-2
- c) A-2; B-3; C-1; D-4
- d) A-4; B-3; C-1; D-2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

a)
A-2; B-1; C-3; D- 4
b)
A-4; B-1; C-3; D-2
c)
A-2; B-3; C-1; D-4
d)
A-4; B-3; C-1; D-2
|
|
Sharad Chavan answered |
1. fruits is made up of ovary
2. seed is made up of ovule
3. wood is made up of stem
4. starch is present in leaf
so the correct answer is B.
2. seed is made up of ovule
3. wood is made up of stem
4. starch is present in leaf
so the correct answer is B.
Cavity or lumen is narrow in- a) Sclerenchyma
- b) Parenchyma
- c) Collenchyma
- d) Tracheids
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Cavity or lumen is narrow in
a)
Sclerenchyma
b)
Parenchyma
c)
Collenchyma
d)
Tracheids

|
Dipika Gupta answered |
Lumen are cavities present inside the cell,cells of sclerenchyma tissue have narrow lumen because sclerenchyma are strongly lignified which lead to compressing the cell and thus only narrow cavity is left
A plant belonging to which of the following groups would show least adaptation to marine water?- a)Pteridophytes
- b)Gymnosperms
- c)Angiosperms
- d)Bryophytes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A plant belonging to which of the following groups would show least adaptation to marine water?
a)
Pteridophytes
b)
Gymnosperms
c)
Angiosperms
d)
Bryophytes

|
K.L Institute answered |
The correct option is C.
A plant belonging to the angiosperms group would show least adaptation to marine water. Angiosperms are vascular plants that have stems, roots, and leaves.
A plant belonging to the angiosperms group would show least adaptation to marine water. Angiosperms are vascular plants that have stems, roots, and leaves.
Which tissue does lack blood supply and heals slowly?- a) nervous
- b) muscle
- c) cartilage
- d) bone
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which tissue does lack blood supply and heals slowly?
a)
nervous
b)
muscle
c)
cartilage
d)
bone

|
Debanshi Sarkar answered |
Cartilage heals slowly because it has no blood supply
Presence of vessel in the wood is- a)A primitive character
- b)An advanced character
- c)A vestigeal character
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Presence of vessel in the wood is
a)
A primitive character
b)
An advanced character
c)
A vestigeal character
d)
None of the above

|
Nandita Saha answered |
Vessels are usually present in angiosperms while in other lower plants they are not present.
Nucleated part of nerve cell is called- a) axon
- b) dendrites
- c) cyton
- d) None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Nucleated part of nerve cell is called
a)
axon
b)
dendrites
c)
cyton
d)
None of the above

|
Surbhi Basu answered |
Axon is the long, thin hair like part arising from the cell body of the neuron.
Dendrites are short, branched parts arising from cell body or cyton. Dendrites are many in number.
Cyton is a part of neuron containing the nucleus. It is also called cell body. Therefore, option C is correct.
Dendrites are short, branched parts arising from cell body or cyton. Dendrites are many in number.
Cyton is a part of neuron containing the nucleus. It is also called cell body. Therefore, option C is correct.
Main function of lenticel is- a) transpiration
- b) guttation
- c) gaseous exchange
- d) both [a] & [c]
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Main function of lenticel is
a)
transpiration
b)
guttation
c)
gaseous exchange
d)
both [a] & [c]

|
Shreya Desai answered |
The lenticels functions as a pore, providing a pathway for the direct exchange of gasesbetween the internal tissues and atmosphere through the bark, which is otherwise impermeable to gases.The lenticels help in the gaseous exchange between the atmosphere and the internal tissue of the stem. The lenticels also helps in transpiration called as the lenticular transpiration.Lenticels are a portions of periderm with numerous intercellular spaces and loosely organized cells
The angle between the line (x - 2)/2 = (y + 1)/-1 = (z - 3)/2 and the plane 3x + 6y - 2z + 5 = 0 is- a)cos⁻1(4/21)
- b)sin⁻1-(4/21)
- c)sin⁻1(6/21)
- d)sin⁻1(4/21)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The angle between the line (x - 2)/2 = (y + 1)/-1 = (z - 3)/2 and the plane 3x + 6y - 2z + 5 = 0 is
a)
cos⁻1(4/21)
b)
sin⁻1-(4/21)
c)
sin⁻1(6/21)
d)
sin⁻1(4/21)
|
|
Gauri Reddy answered |
To find the angle between the given line and the plane, we can use the dot product of the direction vector of the line and the normal vector of the plane. The dot product formula is given by:
a · b = |a| |b| cos θ
Where a and b are vectors, θ is the angle between them, and |a| and |b| are the magnitudes of vectors a and b, respectively.
Let's find the direction vector of the line first. From the given equation of the line, we can write the direction vector as:
V = (2, -1, 2)
Next, let's find the normal vector of the plane. The equation of the plane is given as:
3x - 6y - 2z + 5 = 0
Rewriting it in the form of ax + by + cz + d = 0, we get:
3x - 6y - 2z + 5 = 0
So, the normal vector of the plane is (3, -6, -2).
Now, let's calculate the dot product of the direction vector of the line and the normal vector of the plane:
V · N = (2, -1, 2) · (3, -6, -2)
= 2*3 + (-1)*(-6) + 2*(-2)
= 6 + 6 - 4
= 8
Next, let's calculate the magnitudes of the direction vector and the normal vector:
|V| = √(2^2 + (-1)^2 + 2^2)
= √(4 + 1 + 4)
= √9
= 3
|N| = √(3^2 + (-6)^2 + (-2)^2)
= √(9 + 36 + 4)
= √49
= 7
Now, we can substitute the values into the dot product formula to find the cosine of the angle:
cos θ = (V · N) / (|V| |N|)
= 8 / (3 * 7)
= 8 / 21
To find the sine of the angle, we can use the trigonometric identity:
sin^2 θ + cos^2 θ = 1
sin^2 θ + (8/21)^2 = 1
sin^2 θ = 1 - (64/441)
sin^2 θ = (441 - 64) / 441
sin^2 θ = 377 / 441
Taking the square root of both sides, we get:
sin θ = √(377/441)
= √377 / √441
= √377 / 21
Therefore, the answer is option (D) sin^(-1)(4/21)
a · b = |a| |b| cos θ
Where a and b are vectors, θ is the angle between them, and |a| and |b| are the magnitudes of vectors a and b, respectively.
Let's find the direction vector of the line first. From the given equation of the line, we can write the direction vector as:
V = (2, -1, 2)
Next, let's find the normal vector of the plane. The equation of the plane is given as:
3x - 6y - 2z + 5 = 0
Rewriting it in the form of ax + by + cz + d = 0, we get:
3x - 6y - 2z + 5 = 0
So, the normal vector of the plane is (3, -6, -2).
Now, let's calculate the dot product of the direction vector of the line and the normal vector of the plane:
V · N = (2, -1, 2) · (3, -6, -2)
= 2*3 + (-1)*(-6) + 2*(-2)
= 6 + 6 - 4
= 8
Next, let's calculate the magnitudes of the direction vector and the normal vector:
|V| = √(2^2 + (-1)^2 + 2^2)
= √(4 + 1 + 4)
= √9
= 3
|N| = √(3^2 + (-6)^2 + (-2)^2)
= √(9 + 36 + 4)
= √49
= 7
Now, we can substitute the values into the dot product formula to find the cosine of the angle:
cos θ = (V · N) / (|V| |N|)
= 8 / (3 * 7)
= 8 / 21
To find the sine of the angle, we can use the trigonometric identity:
sin^2 θ + cos^2 θ = 1
sin^2 θ + (8/21)^2 = 1
sin^2 θ = 1 - (64/441)
sin^2 θ = (441 - 64) / 441
sin^2 θ = 377 / 441
Taking the square root of both sides, we get:
sin θ = √(377/441)
= √377 / √441
= √377 / 21
Therefore, the answer is option (D) sin^(-1)(4/21)
With reference to the human body, consider the following statements:
1. The production of somatropin goes up when a person exercises.
2. Men’s testes produce progesterone.
3. Women’s adrenal glands secret testosterone.
4. Stress causes the adrenal to release very less amount of cortisol than usual.Q. Which of these statements are correct?- a)1, 2, 3 and 4
- b)1, 2 and 3
- c)2, 3 and 4
- d)1 and 4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
With reference to the human body, consider the following statements:
1. The production of somatropin goes up when a person exercises.
2. Men’s testes produce progesterone.
3. Women’s adrenal glands secret testosterone.
4. Stress causes the adrenal to release very less amount of cortisol than usual.
1. The production of somatropin goes up when a person exercises.
2. Men’s testes produce progesterone.
3. Women’s adrenal glands secret testosterone.
4. Stress causes the adrenal to release very less amount of cortisol than usual.
Q. Which of these statements are correct?
a)
1, 2, 3 and 4
b)
1, 2 and 3
c)
2, 3 and 4
d)
1 and 4

|
Surbhi Basu answered |
During exercise, the level of somatotropin goes up. Testes secrete testosterone and females’ adrenal glands secrete progesterone. Stress causes the adrenal glands to release very less amount of cortisol (a steroid hormone) than usual.
A tissue is a group of cells which are- a)similar in origin, but dissimilar in form and function.
- b)dissimilar in origin, form and function.
- c)dissimilar in origin, but similar in form and function.
- d)similar in origin, form and function.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A tissue is a group of cells which are
a)
similar in origin, but dissimilar in form and function.
b)
dissimilar in origin, form and function.
c)
dissimilar in origin, but similar in form and function.
d)
similar in origin, form and function.

|
Surbhi Basu answered |
Tissue is a group of cells which act together to perform a specific task. If we talk about a single tissue then, all the cells constituting it performs similar function.
The most stable measure of central tendency is- a)mean
- b)median
- c)mode
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The most stable measure of central tendency is
a)
mean
b)
median
c)
mode
d)
none of these
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
Range is not a measure of central tendency at all. It is an absolute measure of Dispersion that is explained by the difference between the maximum and the minimum values in a series. Now, a comparison between the stability amongst Mean, Median and Mode depends on the nature of the distribution that you're working with. Let's say your data has a lot of outliers, in such a case mean will not serve the purpose well as a measure of CT, Median would be more appropriate. Remember that Mean is affected by extreme values while Median is not. Mode is more appropriate when you're more concerned about the frequency of occurences. For example if you wanted to know what size of shoes should a shoe seller keep more in stock compared to the other sizes.
Cloves, used as a spice, are derived from which of the following plant parts? - a) Seeds
- b) Fruits
- c) Flower buds
- d) Young leaves
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Cloves, used as a spice, are derived from which of the following plant parts?
a)
Seeds
b)
Fruits
c)
Flower buds
d)
Young leaves

|
Janhavi Bajaj answered |
Cloves are the rich, brown, dried, unopened flower buds of Syzygium aromaticum, an evergreen tree in the myrtle family. The name comes from the French "clou" meaning nail. Cloves come from Madagascar, Indonesia and Sri Lanka. Cloves are used in spice cookies and cakes.
Consider the following statements:
1. Human beings have 23 pairs of chromosomes.
2. Sex chromosome in human male is named XX.
3. Chromosomes are best seen in metaphase.Q. Which of the statements given above are false about chromosomes?- a)1 and 2
- b)2 only
- c)1, 2 and 3
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
1. Human beings have 23 pairs of chromosomes.
2. Sex chromosome in human male is named XX.
3. Chromosomes are best seen in metaphase.
1. Human beings have 23 pairs of chromosomes.
2. Sex chromosome in human male is named XX.
3. Chromosomes are best seen in metaphase.
Q. Which of the statements given above are false about chromosomes?
a)
1 and 2
b)
2 only
c)
1, 2 and 3
d)
None of these

|
Nitya Gupta answered |
Humans are diploid organisms by having two members or homologous chromosomes in a pair. Total 23 pairs of chromosomes exist in each somatic cell of the body. Total 46 chromosomes occur. One particular pair individually in male and female determines their respective sex. This one pair is XX in females and XY in males. All the 46 chromosomes in pairs can be seen under microscope at metaphase stage in the cells which are undergoing mitosis.
Which plant kingdom can survive both on land and in water?- a)Tracheophyta
- b)Pteridophyta
- c)Thallophyta
- d)Bryophyta
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which plant kingdom can survive both on land and in water?
a)
Tracheophyta
b)
Pteridophyta
c)
Thallophyta
d)
Bryophyta

|
Nidhi Pillai answered |
The sperm of bryophyte (antherozoids) are flagellate and need water to swim to the eggs. In other words, as these plants need water for reproduction unlike other plants, they are called as amphibians. Amphibians are those organisms which live on both land and in water.
Total number of ATP consume during Kreb's cycle is- a) 0
- b) 1
- c) 2
- d) 3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Total number of ATP consume during Kreb's cycle is
a)
0
b)
1
c)
2
d)
3

|
Saranya Basak answered |
The Krebs cycle produces two molecules of ATP for every molecule of glucose. The Krebs cycle also produces eight molecules of NADH and two molecules of FADH2 per molecule of glucose.
The dead element present in the phloem is- a) companion cells
- b) phloem fibres
- c) phloem parenchyma
- d) sieve tube
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The dead element present in the phloem is
a)
companion cells
b)
phloem fibres
c)
phloem parenchyma
d)
sieve tube

|
Athul Saini answered |
Phloem fibres are thick walled, elongated spindle shaped dead cells which possess narrow lumen. They provides mechanical support to the tissue. Phloem parenchyma are thin walled-living cells of parenchyma. They have two functions, storage and lateral food conduction
The equilibrium constant in a reversible chemical reaction at a given temperature- a)depends on the initial concentration of the reactants
- b)depends on the concentration of one of the products at equilibrium
- c)does not depend on the initial concentrations of reactants
- d)is not characteristic of the reaction
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The equilibrium constant in a reversible chemical reaction at a given temperature
a)
depends on the initial concentration of the reactants
b)
depends on the concentration of one of the products at equilibrium
c)
does not depend on the initial concentrations of reactants
d)
is not characteristic of the reaction
|
|
Swati Khanna answered |
The correct option is C.
The equilibrium constant in a reversible reaction at a given temperature. Solution : Equilibrium constant is independent of original concentration of reactant.
The equilibrium constant in a reversible reaction at a given temperature. Solution : Equilibrium constant is independent of original concentration of reactant.
Which one of the following plant nutrients is not supplemented in the soil for growing legumes?- a)Nitrogen
- b)Potassium
- c)Phosphorus
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following plant nutrients is not supplemented in the soil for growing legumes?
a)
Nitrogen
b)
Potassium
c)
Phosphorus
d)
None of these

|
Avantika Mukherjee answered |
- Growing legume cover crops is one of the most important tools for increasing soil fertility in an organic garden.
- The bacteria take gaseous nitrogen from the air in the soil and feed this nitrogen to the legumes; in exchange the plant provides carbohydrates to the bacteria.
- The bacteria take gaseous nitrogen from the air in the soil and feed this nitrogen to the legumes; in exchange the plant provides carbohydrates to the bacteria.
The chief function of vessels in the plant body is- a) to translocate food material
- b) to conduct water and mineral salts
- c) to support living cells
- d) all above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The chief function of vessels in the plant body is
a)
to translocate food material
b)
to conduct water and mineral salts
c)
to support living cells
d)
all above

|
Dipika Gupta answered |
Xylem, plant vascular tissue that conveys water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant and also provides physical support.
Consider the following statements:
1. Warm-blooded animals can remain active in cold environment in which cold-blooded animals can hardly move.
2. Cold-blooded animals require much less energy to survive than warm-blooded animals.
Q. Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- a)1 only
- b)Both 1 and 2
- c)2 only
- d)Neither 1 nor 2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
1. Warm-blooded animals can remain active in cold environment in which cold-blooded animals can hardly move.
2. Cold-blooded animals require much less energy to survive than warm-blooded animals.
1. Warm-blooded animals can remain active in cold environment in which cold-blooded animals can hardly move.
2. Cold-blooded animals require much less energy to survive than warm-blooded animals.
Q. Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a)
1 only
b)
Both 1 and 2
c)
2 only
d)
Neither 1 nor 2

|
Sagarika Menon answered |
The correct answer is:
- Both 1 and 2
Explanation:
- This statement is correct. Warm-blooded animals have the ability to regulate their internal body temperature, allowing them to remain active in cold environments where cold-blooded animals may struggle due to their reliance on external sources of heat for temperature regulation.
- This statement is also correct. Cold-blooded animals typically have lower metabolic rates and require much less energy to survive compared to warm-blooded animals, which need to maintain a constant internal body temperature through metabolic processes that require more energy.
What is the function of the petiole in a plant leaf?- a)Photosynthesis
- b)Storing water and nutrients
- c)Leaf attachment to the stem
- d)Reproduction
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Photosynthesis
b)
Storing water and nutrients
c)
Leaf attachment to the stem
d)
Reproduction

|
Master Training Institute answered |
The petiole is the stalk of a plant leaf, and its primary function is to attach the leaf to the stem. It also plays a role in positioning the leaf for maximum exposure to sunlight.
What is the main role of connective tissues in the body?- a)To facilitate muscle contraction
- b)To provide shape to the body
- c)To transmit nervous signals
- d)To bind and support other tissues and organs
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
To facilitate muscle contraction
b)
To provide shape to the body
c)
To transmit nervous signals
d)
To bind and support other tissues and organs

|
Amrita Mukherjee answered |
Main Role of Connective Tissues
Connective tissues play a fundamental role in maintaining the structure and function of the body. Here’s a detailed breakdown of their primary functions:
Binding and Supporting Other Tissues
- Connective tissues serve as the framework for the body, providing support and anchoring other tissues and organs.
- They create a network that helps maintain the integrity of organs and systems, ensuring that all parts of the body work cohesively.
Types of Connective Tissues
- Loose Connective Tissue: This type fills spaces between organs, providing cushioning and support.
- Dense Connective Tissue: Found in tendons and ligaments, it provides strength and stability to joints.
- Adipose Tissue: Stores energy and insulates the body, playing a crucial role in energy metabolism.
- Blood: A specialized connective tissue that transports nutrients, gases, and waste products throughout the body.
Protection and Defense
- Connective tissues play a protective role by surrounding and cushioning vital organs.
- They also contain immune cells that defend against pathogens, contributing to the body’s overall health and resilience.
Transport and Nutrient Supply
- Blood, a connective tissue, is essential for transporting oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products, ensuring that all cells receive what they need for proper function.
Conclusion
In summary, the primary role of connective tissues is to bind and support other tissues and organs, playing a critical part in the overall architecture and function of the body. Their diverse types and functions highlight their importance in maintaining health and homeostasis.
Connective tissues play a fundamental role in maintaining the structure and function of the body. Here’s a detailed breakdown of their primary functions:
Binding and Supporting Other Tissues
- Connective tissues serve as the framework for the body, providing support and anchoring other tissues and organs.
- They create a network that helps maintain the integrity of organs and systems, ensuring that all parts of the body work cohesively.
Types of Connective Tissues
- Loose Connective Tissue: This type fills spaces between organs, providing cushioning and support.
- Dense Connective Tissue: Found in tendons and ligaments, it provides strength and stability to joints.
- Adipose Tissue: Stores energy and insulates the body, playing a crucial role in energy metabolism.
- Blood: A specialized connective tissue that transports nutrients, gases, and waste products throughout the body.
Protection and Defense
- Connective tissues play a protective role by surrounding and cushioning vital organs.
- They also contain immune cells that defend against pathogens, contributing to the body’s overall health and resilience.
Transport and Nutrient Supply
- Blood, a connective tissue, is essential for transporting oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products, ensuring that all cells receive what they need for proper function.
Conclusion
In summary, the primary role of connective tissues is to bind and support other tissues and organs, playing a critical part in the overall architecture and function of the body. Their diverse types and functions highlight their importance in maintaining health and homeostasis.
What is the primary function of the skeletal system in the body?- a)To provide insulation
- b)To store excess fat
- c)To protect internal organs
- d)To facilitate digestion
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
To provide insulation
b)
To store excess fat
c)
To protect internal organs
d)
To facilitate digestion
|
|
Academic Studio answered |
The primary function of the skeletal system is to protect internal organs, such as the brain, spinal cord, and lungs. It provides a rigid framework that safeguards these delicate structures.
What did Watson and Crick propose about the structure of DNA in 1953?- a)DNA is a single-stranded polymer of nucleotides.
- b)DNA is a protein-based genetic material.
- c)DNA is a double-stranded polymer of nucleotides arranged as a helix.
- d)DNA is a random arrangement of nucleotides.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
DNA is a single-stranded polymer of nucleotides.
b)
DNA is a protein-based genetic material.
c)
DNA is a double-stranded polymer of nucleotides arranged as a helix.
d)
DNA is a random arrangement of nucleotides.

|
T.S Academy answered |
Watson and Crick proposed that DNA is a double-stranded polymer of nucleotides arranged as a helix, known as the double helix structure.
What term is used to describe the elimination of defective germplasm in a society through measures like sexual separation and sterilization?- a)Genetic engineering
- b)Genetic counseling
- c)Positive eugenics
- d)Negative eugenics
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Genetic engineering
b)
Genetic counseling
c)
Positive eugenics
d)
Negative eugenics

|
Future Foundation Institute answered |
Negative eugenics refers to the elimination of defective germplasm in a society through measures like sexual separation and sterilization.
What is the condition characterized by the excessive use of an organ leading to its development according to Lamarck's theory?- a)Evolution
- b)Atrophy
- c)Acquired characteristics
- d)Hypertrophy
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Evolution
b)
Atrophy
c)
Acquired characteristics
d)
Hypertrophy
|
|
Academic Studio answered |
According to Lamarck's theory, the condition characterized by the excessive use of an organ leading to its development is referred to as "acquired characteristics." Lamarck believed that such characteristics could be passed on to offspring.
What principle does homeopathy follow for treatment?- a)"Opposites cure opposites"
- b)"Likes cure likes"
- c)"Nature heals itself"
- d)"Prevention is better than cure"
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
"Opposites cure opposites"
b)
"Likes cure likes"
c)
"Nature heals itself"
d)
"Prevention is better than cure"

|
Ias Masters answered |
Homeopathy follows the principle of "likes cure likes." This means that a substance that causes symptoms in a healthy person can be used in diluted form to treat similar symptoms in a sick person.
What is the characteristic feature of malignant tumor cells in cancer?- a)They remain localized and do not spread
- b)They are benign and harmless
- c)They undergo metastasis, spreading to neighboring tissues
- d)They do not replicate
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
They remain localized and do not spread
b)
They are benign and harmless
c)
They undergo metastasis, spreading to neighboring tissues
d)
They do not replicate
|
|
Rishabh Malik answered |
Understanding Malignant Tumor Cells
Malignant tumor cells are characterized by their aggressive nature and ability to invade other tissues, a feature that distinguishes them from benign tumors. The correct answer to the question about malignant tumor cells is option 'C': they undergo metastasis, spreading to neighboring tissues.
Key Features of Malignant Tumor Cells
Conclusion
The capability of malignant tumor cells to metastasize is a significant factor in cancer severity and treatment challenges. Understanding this characteristic is crucial in cancer diagnosis and developing effective therapies. Early detection and intervention are vital to managing malignancy and preventing the spread of cancerous cells.
Malignant tumor cells are characterized by their aggressive nature and ability to invade other tissues, a feature that distinguishes them from benign tumors. The correct answer to the question about malignant tumor cells is option 'C': they undergo metastasis, spreading to neighboring tissues.
Key Features of Malignant Tumor Cells
- Invasive Growth: Malignant cells can invade surrounding tissues, unlike benign cells that remain localized.
- Metastasis: These cells can break away from the primary tumor, travel through the bloodstream or lymphatic system, and form secondary tumors in distant organs.
- Uncontrolled Division: Malignant cells replicate uncontrollably, leading to tumor growth and potential spread throughout the body.
- Altered Cell Characteristics: Malignant cells often exhibit abnormal shapes, sizes, and structures, differentiating them from normal cells.
- Resistance to Apoptosis: They can evade programmed cell death (apoptosis), allowing them to survive longer than normal cells.
Conclusion
The capability of malignant tumor cells to metastasize is a significant factor in cancer severity and treatment challenges. Understanding this characteristic is crucial in cancer diagnosis and developing effective therapies. Early detection and intervention are vital to managing malignancy and preventing the spread of cancerous cells.
What is the primary cause of AIDS?- a)Bacterial infection
- b)Overactive immune response
- c)Human T-Cell Lymphotropic Virus-III (HTLV III)
- d)Genetic mutation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Bacterial infection
b)
Overactive immune response
c)
Human T-Cell Lymphotropic Virus-III (HTLV III)
d)
Genetic mutation
|
|
Ujwal Chatterjee answered |
Primary Cause of AIDS
AIDS, or Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome, is primarily caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), specifically the strain designated as HTLV III. Understanding this virus is crucial to comprehending how AIDS develops.
What is HTLV III?
- HTLV III is an early name for HIV, which is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system.
- It primarily targets CD4+ T cells, which are vital for a robust immune response.
How HIV Causes AIDS
- The virus enters the body through blood, sexual contact, or from mother to child during childbirth or breastfeeding.
- Once inside, HIV integrates its genetic material into the host's cells. It replicates, leading to a progressive decline in the number of CD4+ T cells.
- As the immune system weakens, the body becomes increasingly susceptible to opportunistic infections and certain cancers.
Stages of HIV Infection
- Initial Infection: Flu-like symptoms may occur, but many individuals remain asymptomatic for years.
- Chronic Phase: The virus continues to replicate, and CD4+ T cell counts gradually decline.
- AIDS: Diagnosed when CD4+ T cell counts drop below a critical level or when opportunistic infections manifest.
Importance of Early Detection
- Early diagnosis and antiretroviral therapy (ART) can significantly prolong life and improve quality by maintaining immune function and preventing the progression to AIDS.
In summary, option 'C' is correct because HTLV III (HIV) is the virus responsible for the immune system's deterioration, leading to AIDS. Understanding this virus is essential for prevention, treatment, and management of the disease.
AIDS, or Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome, is primarily caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), specifically the strain designated as HTLV III. Understanding this virus is crucial to comprehending how AIDS develops.
What is HTLV III?
- HTLV III is an early name for HIV, which is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system.
- It primarily targets CD4+ T cells, which are vital for a robust immune response.
How HIV Causes AIDS
- The virus enters the body through blood, sexual contact, or from mother to child during childbirth or breastfeeding.
- Once inside, HIV integrates its genetic material into the host's cells. It replicates, leading to a progressive decline in the number of CD4+ T cells.
- As the immune system weakens, the body becomes increasingly susceptible to opportunistic infections and certain cancers.
Stages of HIV Infection
- Initial Infection: Flu-like symptoms may occur, but many individuals remain asymptomatic for years.
- Chronic Phase: The virus continues to replicate, and CD4+ T cell counts gradually decline.
- AIDS: Diagnosed when CD4+ T cell counts drop below a critical level or when opportunistic infections manifest.
Importance of Early Detection
- Early diagnosis and antiretroviral therapy (ART) can significantly prolong life and improve quality by maintaining immune function and preventing the progression to AIDS.
In summary, option 'C' is correct because HTLV III (HIV) is the virus responsible for the immune system's deterioration, leading to AIDS. Understanding this virus is essential for prevention, treatment, and management of the disease.
Consider the following statements:
Assertion(A): In humans, female sex is determined by XX-chromosomes.
Reason(R): Male sex is determined by YY-chromosomes.- a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true, but R is false.
- d)A is false, but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
Assertion(A): In humans, female sex is determined by XX-chromosomes.
Reason(R): Male sex is determined by YY-chromosomes.
Assertion(A): In humans, female sex is determined by XX-chromosomes.
Reason(R): Male sex is determined by YY-chromosomes.
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true, but R is false.
d)
A is false, but R is true.

|
Amrutha Kapoor answered |
Humans are diploid with 23 pairs of chromosomes. Of this, 22 pairs are somatic and the one pair is sex chromosomes. This particular pair exists as XX in human females and XY in males. The presence of two X chromosomes contributes to the female phenotype while presence of only one Y chromosome is responsible for the human to be male. Females produce only X-type haploid gametes and males produce two types (X and Y) of haploid gametes. Fusion of either X or Y of male gamete with the female gamete determines the sex of the offspring.
Consider the following statements:
1. Frogs can breathe by lungs as well as skin.
2. Gills are not present in any stage of lifespan of frogs.Q. Which of the statements given above is/are correct?- a)1 and 2 only
- b)1 only
- c)2 only
- d)Neither 1 nor 2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
1. Frogs can breathe by lungs as well as skin.
2. Gills are not present in any stage of lifespan of frogs.
1. Frogs can breathe by lungs as well as skin.
2. Gills are not present in any stage of lifespan of frogs.
Q. Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a)
1 and 2 only
b)
1 only
c)
2 only
d)
Neither 1 nor 2
|
|
Pragati Banerjee answered |
Explanation:
Frogs are amphibians that have adaptations to live both on land and in water. They have unique respiratory systems that allow them to breathe in both air and water. Let's take a look at the given statements.
1. Frogs can breathe by lungs as well as skin.
This statement is true. Frogs have lungs that allow them to breathe in air, just like humans. However, they also have a unique adaptation that allows them to breathe through their skin. Their skin is thin and moist, which makes it easier for oxygen to diffuse into their bloodstream. This is especially helpful when they are underwater and cannot breathe through their lungs.
2. Gills are not present in any stage of lifespan of frogs.
This statement is also true. While some amphibians, such as salamanders, have gills as larvae, frogs do not. Instead, they undergo a metamorphosis from tadpole to adult frog. During this process, their gills are replaced by lungs, and they develop the ability to breathe through their skin.
In conclusion, both statements are true, but only statement 1 is correct. Frogs can breathe by lungs as well as skin, but they do not have gills at any stage of their lifespan.
Frogs are amphibians that have adaptations to live both on land and in water. They have unique respiratory systems that allow them to breathe in both air and water. Let's take a look at the given statements.
1. Frogs can breathe by lungs as well as skin.
This statement is true. Frogs have lungs that allow them to breathe in air, just like humans. However, they also have a unique adaptation that allows them to breathe through their skin. Their skin is thin and moist, which makes it easier for oxygen to diffuse into their bloodstream. This is especially helpful when they are underwater and cannot breathe through their lungs.
2. Gills are not present in any stage of lifespan of frogs.
This statement is also true. While some amphibians, such as salamanders, have gills as larvae, frogs do not. Instead, they undergo a metamorphosis from tadpole to adult frog. During this process, their gills are replaced by lungs, and they develop the ability to breathe through their skin.
In conclusion, both statements are true, but only statement 1 is correct. Frogs can breathe by lungs as well as skin, but they do not have gills at any stage of their lifespan.
According to Weismann, which cells are responsible for passing on hereditary variations to the next generations?- a)Somatic cells
- b)Germ cells
- c)Muscle cells
- d)Nerve cells
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Somatic cells
b)
Germ cells
c)
Muscle cells
d)
Nerve cells

|
Ias Masters answered |
According to Weismann, germ cells are responsible for passing on hereditary variations to the next generations. He emphasized the distinction between germ cells and somatic cells in terms of hereditary information.
What is the term for the process of decoding mRNA for protein synthesis?- a)Translation
- b)Transcription
- c)Replication
- d)Duplication
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Translation
b)
Transcription
c)
Replication
d)
Duplication
|
|
Ananya Ahuja answered |
Understanding Translation
Translation is the essential biological process where the information encoded in messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded to synthesize proteins. This process is crucial for expressing the genetic information carried by DNA.
Key Steps in Translation:
- Initiation:
- The ribosome assembles around the mRNA molecule.
- The first transfer RNA (tRNA) brings the corresponding amino acid to the start codon (AUG) on the mRNA.
- Elongation:
- The ribosome moves along the mRNA, reading codons (three-nucleotide sequences).
- Each tRNA brings a specific amino acid that matches the codon, forming a growing polypeptide chain.
- Termination:
- When a stop codon (UAA, UAG, UGA) is reached, the process ends.
- Release factors bind to the ribosome, prompting the release of the polypeptide and the disassembly of the ribosome.
Importance of Translation:
- Protein Synthesis:
- Proteins are essential for numerous cellular functions, including structure, enzymatic activity, and regulation.
- Gene Expression:
- Translation is a key step in the central dogma of molecular biology, linking genetic information from DNA to functional proteins.
Conclusion:
In summary, translation is the process of decoding mRNA to synthesize proteins, making it a fundamental aspect of cellular biology and the flow of genetic information. Understanding this process is essential for fields like genetics, molecular biology, and biotechnology.
Translation is the essential biological process where the information encoded in messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded to synthesize proteins. This process is crucial for expressing the genetic information carried by DNA.
Key Steps in Translation:
- Initiation:
- The ribosome assembles around the mRNA molecule.
- The first transfer RNA (tRNA) brings the corresponding amino acid to the start codon (AUG) on the mRNA.
- Elongation:
- The ribosome moves along the mRNA, reading codons (three-nucleotide sequences).
- Each tRNA brings a specific amino acid that matches the codon, forming a growing polypeptide chain.
- Termination:
- When a stop codon (UAA, UAG, UGA) is reached, the process ends.
- Release factors bind to the ribosome, prompting the release of the polypeptide and the disassembly of the ribosome.
Importance of Translation:
- Protein Synthesis:
- Proteins are essential for numerous cellular functions, including structure, enzymatic activity, and regulation.
- Gene Expression:
- Translation is a key step in the central dogma of molecular biology, linking genetic information from DNA to functional proteins.
Conclusion:
In summary, translation is the process of decoding mRNA to synthesize proteins, making it a fundamental aspect of cellular biology and the flow of genetic information. Understanding this process is essential for fields like genetics, molecular biology, and biotechnology.
The phenomenon in which seeds germinate and seedlings grow while still attached to their mother plant before dropping down to establish themselves or be transported elsewhere, is most commonly found in which among the following plants?- a)Allium cepa
- b)Rhizophora
- c)Solanum tuberosum
- d)Solanum melongena
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The phenomenon in which seeds germinate and seedlings grow while still attached to their mother plant before dropping down to establish themselves or be transported elsewhere, is most commonly found in which among the following plants?
a)
Allium cepa
b)
Rhizophora
c)
Solanum tuberosum
d)
Solanum melongena

|
Samarth Gupta answered |
Allium cepa is onion. Solanum tuberosum is potato, Solanum melongena is Brinjal. The phenomenon given in this question is shown by Mangrove Plants and is known as Vivipary and Rhizophora belongs to that category.
Lignin is the important constituent in the cell wall of- a) phloem
- b) parenchyma
- c) xylem
- d) cambium
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Lignin is the important constituent in the cell wall of
a)
phloem
b)
parenchyma
c)
xylem
d)
cambium
|
|
Debanshi Chavan answered |
Lignin and Its Role in Plant Cell Walls
Lignin is a complex organic polymer found in the cell walls of many plants, particularly in woody plants. It plays a vital role in providing structural support and rigidity.
Importance of Lignin in Xylem
- Structural Integrity: Lignin reinforces the cell walls of xylem vessels, allowing them to withstand the pressure of water transport from roots to leaves.
- Water Resistance: It contributes to the hydrophobic properties of xylem, preventing water loss and protecting the plant from pathogens.
- Support for Growth: The presence of lignin enables plants to grow taller and stronger, as it allows them to develop a more robust vascular system.
Comparison with Other Plant Tissues
- Phloem: While phloem primarily facilitates the transport of nutrients, it contains less lignin compared to xylem. Its main components are living cells that need flexibility rather than rigidity.
- Parenchyma: This tissue is involved in storage and metabolic functions, lacking lignin. Parenchyma cells are generally more flexible and less supportive.
- Cambium: The cambium is a layer of actively dividing cells responsible for secondary growth. It primarily produces phloem and xylem, but itself does not contain lignin.
Conclusion
In summary, lignin is predominantly found in the xylem, where it serves essential functions for water transport and structural support. Understanding its role highlights the significance of lignin in plant physiology and growth.
Lignin is a complex organic polymer found in the cell walls of many plants, particularly in woody plants. It plays a vital role in providing structural support and rigidity.
Importance of Lignin in Xylem
- Structural Integrity: Lignin reinforces the cell walls of xylem vessels, allowing them to withstand the pressure of water transport from roots to leaves.
- Water Resistance: It contributes to the hydrophobic properties of xylem, preventing water loss and protecting the plant from pathogens.
- Support for Growth: The presence of lignin enables plants to grow taller and stronger, as it allows them to develop a more robust vascular system.
Comparison with Other Plant Tissues
- Phloem: While phloem primarily facilitates the transport of nutrients, it contains less lignin compared to xylem. Its main components are living cells that need flexibility rather than rigidity.
- Parenchyma: This tissue is involved in storage and metabolic functions, lacking lignin. Parenchyma cells are generally more flexible and less supportive.
- Cambium: The cambium is a layer of actively dividing cells responsible for secondary growth. It primarily produces phloem and xylem, but itself does not contain lignin.
Conclusion
In summary, lignin is predominantly found in the xylem, where it serves essential functions for water transport and structural support. Understanding its role highlights the significance of lignin in plant physiology and growth.
Which of the following stem modifications is specialized for climbing in plants?- a)Rhizome
- b)Thorns
- c)Phylloclade
- d)Tendril
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Rhizome
b)
Thorns
c)
Phylloclade
d)
Tendril

|
Future Foundation Institute answered |
Tendrils are specialized stem modifications in plants that are adapted for climbing. Tendrils are slender, elongated structures that plants use to attach to a support and climb upwards. They often coil around objects to provide stability and allow the plant to reach for sunlight. Examples of plants with tendrils include passionflowers and certain types of peas.
Which plant group is known for its floating roots that help in aeration and respiration?- a)Gymnosperms
- b)Angiosperms
- c)Bryophytes
- d)Pteridophytes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Gymnosperms
b)
Angiosperms
c)
Bryophytes
d)
Pteridophytes
|
|
Sahana Menon answered |
Floating Roots in Angiosperms
Angiosperms, or flowering plants, are renowned for their diverse adaptations, particularly in aquatic environments. One such adaptation is the presence of floating roots that play a crucial role in aeration and respiration.
Key Features of Floating Roots
- Adaptation to Aquatic Environments:
Floating roots are commonly found in plants like water lilies and mangroves, allowing them to thrive in waterlogged or submerged conditions.
- Aeration:
These roots are specialized structures that extend above the water surface, facilitating gas exchange. This is vital for the plant's respiration, as oxygen is absorbed directly from the air.
- Support and Stability:
Floating roots also provide stability to the plant, anchoring it while still allowing access to sunlight and air.
- Nutrient Uptake:
In addition to respiration, floating roots can absorb dissolved nutrients from the water, assisting the plant in growth and development.
Comparison with Other Plant Groups
- Gymnosperms:
Typically, gymnosperms do not possess floating roots, as they are primarily terrestrial and adapted to well-drained soils.
- Bryophytes:
While some bryophytes thrive in moist environments, they lack true roots, relying instead on rhizoids for anchorage and nutrient uptake.
- Pteridophytes:
These plants, such as ferns, also do not exhibit floating roots; they usually have more traditional root systems that anchor them in soil.
Conclusion
In summary, angiosperms are distinguished by their innovative floating roots, enabling them to adapt to aquatic habitats efficiently. This characteristic not only supports respiration but also enhances nutrient absorption and stability, underscoring the diversity and adaptability of flowering plants.
Angiosperms, or flowering plants, are renowned for their diverse adaptations, particularly in aquatic environments. One such adaptation is the presence of floating roots that play a crucial role in aeration and respiration.
Key Features of Floating Roots
- Adaptation to Aquatic Environments:
Floating roots are commonly found in plants like water lilies and mangroves, allowing them to thrive in waterlogged or submerged conditions.
- Aeration:
These roots are specialized structures that extend above the water surface, facilitating gas exchange. This is vital for the plant's respiration, as oxygen is absorbed directly from the air.
- Support and Stability:
Floating roots also provide stability to the plant, anchoring it while still allowing access to sunlight and air.
- Nutrient Uptake:
In addition to respiration, floating roots can absorb dissolved nutrients from the water, assisting the plant in growth and development.
Comparison with Other Plant Groups
- Gymnosperms:
Typically, gymnosperms do not possess floating roots, as they are primarily terrestrial and adapted to well-drained soils.
- Bryophytes:
While some bryophytes thrive in moist environments, they lack true roots, relying instead on rhizoids for anchorage and nutrient uptake.
- Pteridophytes:
These plants, such as ferns, also do not exhibit floating roots; they usually have more traditional root systems that anchor them in soil.
Conclusion
In summary, angiosperms are distinguished by their innovative floating roots, enabling them to adapt to aquatic habitats efficiently. This characteristic not only supports respiration but also enhances nutrient absorption and stability, underscoring the diversity and adaptability of flowering plants.
What is the advantage of micropropagation by plant tissue culture?- a)It produces genetically diverse plants.
- b)It requires a large amount of space.
- c)It can produce virus-free clones.
- d)It is limited to dicot plants.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
It produces genetically diverse plants.
b)
It requires a large amount of space.
c)
It can produce virus-free clones.
d)
It is limited to dicot plants.
|
|
Academic Studio answered |
Micropropagation by plant tissue culture has the advantage of producing virus-free clones by raising callus from shoot apex. This technique is useful for obtaining disease-free plants.
What is the term for the uncontrolled growth of cells that accompanies cellular transformation in cancer?- a)Metastasis
- b)Neoplasm
- c)Apoptosis
- d)Differentiation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Metastasis
b)
Neoplasm
c)
Apoptosis
d)
Differentiation

|
Valor Academy answered |
Neoplasm refers to the uncontrolled growth of cells that accompanies cellular transformation in cancer. It leads to the formation of tumors or masses of abnormal cells.
Which of the following diseases are infectious in milch animals?
1. Hand diseases
2. Anthrax
3. Black quarter
4. Cowpox
Q. Select the correct answer from the codes given below:- a)1, 2 and 3
- b)2, 3 and 4
- c)1 and 4
- d)1, 2, 3 and 4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following diseases are infectious in milch animals?
1. Hand diseases
2. Anthrax
3. Black quarter
4. Cowpox
Q. Select the correct answer from the codes given below:
1. Hand diseases
2. Anthrax
3. Black quarter
4. Cowpox
Q. Select the correct answer from the codes given below:
a)
1, 2 and 3
b)
2, 3 and 4
c)
1 and 4
d)
1, 2, 3 and 4

|
Hiral Singh answered |
Milch animals are those animals which are source of milk, e.g. cow, goat, buffalo. Foot-andmouth disease, caused by Aphthae epizooticae is an infectious disease that affects cloven-hoofed animals. Anthrax is an acute infectious disease caused by the bacterium Bacillus anthracis. Blackleg, black quarter is an infectious bacterial disease caused by Clostridium chauvoei affecting cattle, sheep and goats. Cowpox is caused by cowpox virus and is infectious.
Fungi are plants that lack:- a)Oxygen
- b)Carbon dioxide
- c)Chlorophyll
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Fungi are plants that lack:
a)
Oxygen
b)
Carbon dioxide
c)
Chlorophyll
d)
None of these
|
|
Preethi Chauhan answered |
Fungi are not plants because they lack chlorophyll, which is a key characteristic of plants. Chlorophyll is a pigment found in the chloroplasts of plant cells that is responsible for capturing sunlight and converting it into energy through the process of photosynthesis. Fungi, on the other hand, obtain their nutrients by absorbing organic matter from their environment, such as decaying plant and animal material.
Here is a detailed explanation of why fungi are not plants:
1. Absence of Chlorophyll:
Chlorophyll is essential for plants to carry out photosynthesis, the process by which they convert sunlight into energy. Fungi do not possess chlorophyll and are incapable of performing photosynthesis. Instead, they obtain their energy by breaking down organic matter through the secretion of enzymes and absorbing the resulting nutrients.
2. Mode of Nutrition:
Fungi are heterotrophic organisms, meaning they cannot produce their own food and rely on external sources for nutrients. They are decomposers, playing a crucial role in the ecosystem by breaking down dead organic matter and recycling nutrients. In contrast, plants are autotrophic organisms that can synthesize their own food through photosynthesis.
3. Cell Wall Composition:
The cell walls of fungi are primarily composed of chitin, a tough and flexible polysaccharide. In contrast, the cell walls of plants are composed of cellulose. This difference in cell wall composition is another distinguishing feature between fungi and plants.
4. Reproduction:
Fungi have a unique mode of reproduction that sets them apart from plants. While plants reproduce through seeds or spores produced within flowers or cones, fungi reproduce through the production of spores, which are released into the environment to establish new fungal colonies.
5. Taxonomic Classification:
Fungi belong to the kingdom Fungi, which is distinct from the kingdom Plantae. The kingdom Fungi includes diverse organisms such as mushrooms, yeasts, molds, and lichens. This taxonomic classification further emphasizes the biological differences between fungi and plants.
In conclusion, fungi are not plants because they lack chlorophyll, have a different mode of nutrition, possess cell walls made of chitin, reproduce differently, and are classified in a separate kingdom. These characteristics differentiate fungi from plants and highlight their unique biological features.
Here is a detailed explanation of why fungi are not plants:
1. Absence of Chlorophyll:
Chlorophyll is essential for plants to carry out photosynthesis, the process by which they convert sunlight into energy. Fungi do not possess chlorophyll and are incapable of performing photosynthesis. Instead, they obtain their energy by breaking down organic matter through the secretion of enzymes and absorbing the resulting nutrients.
2. Mode of Nutrition:
Fungi are heterotrophic organisms, meaning they cannot produce their own food and rely on external sources for nutrients. They are decomposers, playing a crucial role in the ecosystem by breaking down dead organic matter and recycling nutrients. In contrast, plants are autotrophic organisms that can synthesize their own food through photosynthesis.
3. Cell Wall Composition:
The cell walls of fungi are primarily composed of chitin, a tough and flexible polysaccharide. In contrast, the cell walls of plants are composed of cellulose. This difference in cell wall composition is another distinguishing feature between fungi and plants.
4. Reproduction:
Fungi have a unique mode of reproduction that sets them apart from plants. While plants reproduce through seeds or spores produced within flowers or cones, fungi reproduce through the production of spores, which are released into the environment to establish new fungal colonies.
5. Taxonomic Classification:
Fungi belong to the kingdom Fungi, which is distinct from the kingdom Plantae. The kingdom Fungi includes diverse organisms such as mushrooms, yeasts, molds, and lichens. This taxonomic classification further emphasizes the biological differences between fungi and plants.
In conclusion, fungi are not plants because they lack chlorophyll, have a different mode of nutrition, possess cell walls made of chitin, reproduce differently, and are classified in a separate kingdom. These characteristics differentiate fungi from plants and highlight their unique biological features.
Consider the following statements:
Assertion (A): Scientists can cut apart and paste together DNA molecules at will, regardless of the source of the molecules.
Reason (R): DNA fragments can be manipulated from restriction endonucleases and DNA ligases.- a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true, but R is false.
- d)A is false, but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
Assertion (A): Scientists can cut apart and paste together DNA molecules at will, regardless of the source of the molecules.
Reason (R): DNA fragments can be manipulated from restriction endonucleases and DNA ligases.
Assertion (A): Scientists can cut apart and paste together DNA molecules at will, regardless of the source of the molecules.
Reason (R): DNA fragments can be manipulated from restriction endonucleases and DNA ligases.
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true, but R is false.
d)
A is false, but R is true.

|
Rishabh Sen answered |
In genetic engineering, a DNA segment from any foreign source can be inserted into any other genetic material. The enzymes, called restriction endonucleases, act like scissors that cut apart a particular or specific part of the DNA. This cut out DNA piece can be inserted into other genetic material which has been cut to make space for containing the foreign DNA. The DNA once inserted can be ligated by enzymes known as ligases.
Consider the following statements and select the correct answer from the codes given below:
Assertion (A): If somebody stops taking green vegetables, he will suffer from night blindness.
Reason (R): He will suffer from vitamin A deficiency.- a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true, but R is false.
- d)A is false, but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements and select the correct answer from the codes given below:
Assertion (A): If somebody stops taking green vegetables, he will suffer from night blindness.
Reason (R): He will suffer from vitamin A deficiency.
Assertion (A): If somebody stops taking green vegetables, he will suffer from night blindness.
Reason (R): He will suffer from vitamin A deficiency.
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true, but R is false.
d)
A is false, but R is true.

|
Akanksha Ahuja answered |
Vitamin A has a major role in phototransduction. Its deficiency causes night blindness in humans. Xerophthalmia, keratomalacia can also occur with its deficiency. Green, yellow-orange-red (dark- coloured) fruits and vegetables, eggs, milk; fortified cereals are rich source of vitamin A. Their avoidance over a long period may cause the vit-A deficiency symptoms.
Consider the following statements:
1. Dengue is a protozoan disease transmitted by mosquitos.
2. Retro-orbital pain is not a symptom of dengue.
3. Skin rash and bleeding from nose and gums are some of the symptoms of the dengue.
Q. Which of the statements given above is/are correct?- a)1 and 2 only
- b)2 only
- c)3 only
- d)1 and 3 only
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
1. Dengue is a protozoan disease transmitted by mosquitos.
2. Retro-orbital pain is not a symptom of dengue.
3. Skin rash and bleeding from nose and gums are some of the symptoms of the dengue.
Q. Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
1. Dengue is a protozoan disease transmitted by mosquitos.
2. Retro-orbital pain is not a symptom of dengue.
3. Skin rash and bleeding from nose and gums are some of the symptoms of the dengue.
Q. Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a)
1 and 2 only
b)
2 only
c)
3 only
d)
1 and 3 only

|
Amrita Bose answered |
Dengue is a viral disease transmitted through mosquito. Fever, headache, pain in joints, back muscles and eyeballs, skin rash for a few days, bleeding from nose and gums are some of the symptoms of the dengue fever.
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer from the codes given below:
List-I List-II
(Bone) (Name)
A. Breast bone 1. Clavicle
B. Collar bone 2. Patella
C. Knee cap 3. Scapula
D. Shoulder blade 4. Sternum- a)A: 4, B: 1, C: 3, D: 2
- b)A:1, B: 4, C: 3, D: 2
- c)A: 1, B: 4, C: 2, D: 3
- d)A:4, B: 1, C: 2, D: 3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer from the codes given below:
List-I List-II
(Bone) (Name)
A. Breast bone 1. Clavicle
B. Collar bone 2. Patella
C. Knee cap 3. Scapula
D. Shoulder blade 4. Sternum
List-I List-II
(Bone) (Name)
A. Breast bone 1. Clavicle
B. Collar bone 2. Patella
C. Knee cap 3. Scapula
D. Shoulder blade 4. Sternum
a)
A: 4, B: 1, C: 3, D: 2
b)
A:1, B: 4, C: 3, D: 2
c)
A: 1, B: 4, C: 2, D: 3
d)
A:4, B: 1, C: 2, D: 3

|
Surbhi Basu answered |
Sternum is the breast bone. Clavicle is the collar bone. Patella is the knee cap. Scapula is the shoulder blade.
Consider the following statements and choose the correct code.
Assertion (A): A true nucleus is absent in E. coli and other prokaryotes.
Reason (R): An undifferentiated, unorganised fibrillar chromosome existsinside the prokaryotic cells.- a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is false, but R is true.
- d)Both A and R are false.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements and choose the correct code.
Assertion (A): A true nucleus is absent in E. coli and other prokaryotes.
Reason (R): An undifferentiated, unorganised fibrillar chromosome existsinside the prokaryotic cells.
Assertion (A): A true nucleus is absent in E. coli and other prokaryotes.
Reason (R): An undifferentiated, unorganised fibrillar chromosome existsinside the prokaryotic cells.
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is false, but R is true.
d)
Both A and R are false.

|
Srishti Nambiar answered |
In the prokaryotes, all the genetic materials lie inside the cell, no clear or separate nuclear wall is recognized in these cells. In fact no membranebound organelles are found in the prokaryotes. While on the other hand, one of the characteristic features of the eukaryotic cells is the presence of membrane bound organelles. Clear and distinguished nuclear membrane bounds the genetic material inside.
Chapter doubts & questions for Biology - Science & Technology for State PSC Exams 2025 is part of BPSC (Bihar) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the BPSC (Bihar) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for BPSC (Bihar) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Biology - Science & Technology for State PSC Exams in English & Hindi are available as part of BPSC (Bihar) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for BPSC (Bihar) Exam by signing up for free.
Science & Technology for State PSC Exams
113 videos|527 docs|217 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









