All Exams >
GRE >
Chemistry for GRE Paper II >
All Questions
All questions of Periodic Table for GRE Exam
Which of the following bond is strongest- a)C – C
- b)C – H
- c)C – O
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following bond is strongest
a)
C – C
b)
C – H
c)
C – O
d)
None
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
Because of small differences in electronegativities, the C−H bond is generally regarded as being non-polar. The real reason here is atomic size. The hydrogen atom is much smaller than the carbon atom. Smaller bonds lead to higher bond energy; therefore C−H bond has higher bond enthalpy than the C−C bond.
If the Aufbau principle had not been followed, Ca (Z = 20) would have been placed in the:a) s-blockb) p-blockc) d-blockd) f-blockThe correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Aditya Deshmukh answered |
Electronic configuration of Ca is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2.
Filling of 3d orbital starts after the filling of 4s orbitals. If the aufbau principle had not been followed, the filling of 3d orbital would have been prior to filling of 4s orbital and the electronic configuration of Ca would have been 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d2 and it belongs to d block.
First ionization energy is the lowest with:
- a)Lead
- b)Carbon
- c)Silicon
- d)Tin
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
First ionization energy is the lowest with:
a)
Lead
b)
Carbon
c)
Silicon
d)
Tin

|
Asf Institute answered |
Ionization energy decreases down the group. As charge density is minimum for tin so first ionization energy is lowest for tin.
The correct order of ionic size of N3–, Na+, F–, Mg2+ and O2– is:- a)Mg2+ > Na+ > F– > O2– < N3–
- b)N3– < F– > O2– > Na+ > Mg2+
- c)Mg2+ < Na+ < F– < O2– < N3–
- d)N3– > O2– > F– > Na+ < Mg2+
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct order of ionic size of N3–, Na+, F–, Mg2+ and O2– is:
a)
Mg2+ > Na+ > F– > O2– < N3–
b)
N3– < F– > O2– > Na+ > Mg2+
c)
Mg2+ < Na+ < F– < O2– < N3–
d)
N3– > O2– > F– > Na+ < Mg2+

|
Siddharth Banerjee answered |
If the ions derived from different atoms are isoelectronic species, then they all have same number of electrons in their electronic shells and will have got same electronic configuration but their nuclear charge will differ because of their difference in number of protons in the nucleus. With increase in number of protonsin the nucleus the electrons are more attracted towards nucleus thereby causing the decrease in ionic radius. On this principle our problem will be solved
The given ions are
- 7N3-→no. of proton=7 and no of electron=10
- 8O2-→no. of proton=8 and no of electron=10
- 9F-→no. of proton=9 and no of electron=10
- 11Na+→no. of proton=11 and no of electron=10
- 12Mg2+→no. of proton=12 and no of electron=10
Hence the increasing order of ionic radius is
12Mg2+< 11Na+< 9F-< 8O2-< 7N3-
For isoelectronic species lower the nuclear charge higher the radius
The third ionization energy is maximum for:
- a)Boron
- b)Phosphorus
- c)Aluminium
- d)Nitrogen
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The third ionization energy is maximum for:
a)
Boron
b)
Phosphorus
c)
Aluminium
d)
Nitrogen

|
Shivam Sharma answered |
Explanation:
Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom or ion. The third ionization energy refers to the energy needed to remove the third electron.
Looking at the electronic configurations of the given elements:
1. Boron (B): 1s² 2s² 2p¹
2. Phosphorus (P): 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p³
3. Aluminium (Al): 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p¹
4. Nitrogen (N): 1s² 2s² 2p³
For Nitrogen, the electronic configuration of the outer shell is a half-filled configuration (2s² 2p³). This configuration is considered stable, as half-filled orbitals are more stable due to their symmetric arrangement and better shielding effect.
When we try to remove the third electron from nitrogen (third ionization), we are disturbing the stable half-filled configuration, which would require more energy. Thus, the third ionization energy is maximum for nitrogen among the given elements.
Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom or ion. The third ionization energy refers to the energy needed to remove the third electron.
Looking at the electronic configurations of the given elements:
1. Boron (B): 1s² 2s² 2p¹
2. Phosphorus (P): 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p³
3. Aluminium (Al): 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p¹
4. Nitrogen (N): 1s² 2s² 2p³
For Nitrogen, the electronic configuration of the outer shell is a half-filled configuration (2s² 2p³). This configuration is considered stable, as half-filled orbitals are more stable due to their symmetric arrangement and better shielding effect.
When we try to remove the third electron from nitrogen (third ionization), we are disturbing the stable half-filled configuration, which would require more energy. Thus, the third ionization energy is maximum for nitrogen among the given elements.
Incorrect order of ionic size is:- a)La3+ > Gd3+ > Eu3+ > Lu3+
- b)V2+ > V3+ > V4+ > V5+
- c)Tl+ > In+ > Sn2+ > Sb3+
- d)K+ > Sc3+ > V5+ > Mn7+
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Incorrect order of ionic size is:
a)
La3+ > Gd3+ > Eu3+ > Lu3+
b)
V2+ > V3+ > V4+ > V5+
c)
Tl+ > In+ > Sn2+ > Sb3+
d)
K+ > Sc3+ > V5+ > Mn7+
|
|
Pooja Choudhury answered |
In a given lanthanide series , ionic radii decreases due to lanthanoid contraction . So size of Eu3+ should be larger than Gadolinium ion Gd3+
Hence option A is the answer.
An element belongs to period 2 and group 2th, then number of valence electrons in the atoms of this element is? - a)2
- b)4
- c)3
- d)1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An element belongs to period 2 and group 2th, then number of valence electrons in the atoms of this element is?
a)
2
b)
4
c)
3
d)
1

|
Abhishek Nambiar answered |
The elememt belongs to group 2 and period 2 is Be( atomic number 4)
Which of the following ions is most unlikely to exist?
- a)Li–
- b)Be–
- c)B–
- d)F–
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following ions is most unlikely to exist?
a)
Li–
b)
Be–
c)
B–
d)
F–

|
Swara Reddy answered |
Be- ions is most unlikely to exist as Be has higher tendency to loose electron and Be has full filled configuration.
If period number and group number of any representative element(s) are same then which of the following statement is incorrect regarding such type element(s) in their ground state: (Period number and group number are according to modern form of periodic table)- a)The possible value of principal quantum number is 2
- b)The possible value of azimuthal quantum number is zero
- c)The possible value of magnetic quantum number is 1
- d)The species could be paramagnetic
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If period number and group number of any representative element(s) are same then which of the following statement is incorrect regarding such type element(s) in their ground state: (Period number and group number are according to modern form of periodic table)
a)
The possible value of principal quantum number is 2
b)
The possible value of azimuthal quantum number is zero
c)
The possible value of magnetic quantum number is 1
d)
The species could be paramagnetic

|
Madhavan Iyer answered |
When period and group is same it can only be for 2s2, and for 2s2 principle quantum number (n)=2, azimuthal quantum number (l)= 0, magnetic quantum number (m)=0,spin quantum number (s)= +1/2 or -1/2.
The first ionization potential in electron volts of nitrogen and oxygen atoms are respectively given by:a)14.6, 13.6b)13.6, 14.6c)13.6, 13.6d)14.6, 14.6The correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Rashi Choudhury answered |
Nitrogen has higher ionization energy than Oxygen because it has a stable half-filled electronic configuration as shown below:
7 N - (1s)2(2s)2(2px)1(2py)1(2pz) and
7 N - (1s)2(2s)2(2px)1(2py)1(2pz) and
8 O - (1s)2(2s)2(2px)2(2py)1(2pz)1
The elements with the lowest atomic number that has a ground state electronic configuration of (n – 1) d6ns2 is located in the:- a)Fifth period
- b)Sixth period
- c)Fourth period
- d)Third period
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The elements with the lowest atomic number that has a ground state electronic configuration of (n – 1) d6ns2 is located in the:
a)
Fifth period
b)
Sixth period
c)
Fourth period
d)
Third period

|
Vaishu Navi answered |
Fourth period is begin d plock elements so the lowest atomic number of above electronic configuration is fourth period
In which of the following pair, both the species are isoelectronic but the first one is large in size than the second?- a)S2–, O2–
- b)Cl–, S2–
- c)F–, Na+
- d)N3–, P3–
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following pair, both the species are isoelectronic but the first one is large in size than the second?
a)
S2–, O2–
b)
Cl–, S2–
c)
F–, Na+
d)
N3–, P3–

|
Bhavana Dasgupta answered |
F- and Na+ both have 10 electrons .Atomic no of F is 9 and for Na it is 11.so for F-, 9 proton is pulling 10 electrons and for Na+,11 proton is pulling 10 electrons . So attractive force is more for Na+ compared to F-. So radius of F- is more than Na+.
What is the atomic number of the element with the maximum number of unpaired 4p electron:- a)33
- b)26
- c)23
- d)15
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the atomic number of the element with the maximum number of unpaired 4p electron:
a)
33
b)
26
c)
23
d)
15

|
Shivam Sharma answered |
33, because p block has 6 elements per period.
Max unpaired is halfway, so 3rd.
3rd element of 4th period p-block is 33.
Which of the following order is correct for the property ment ioned in brackets:- a)S2– > Cl– > K+ > Ca2+ (Ionization energy)
- b)C < N < F < O (2nd Ionization energy)
- c)B > Al > Ga > In > Tl (Electronegativity)
- d)Na+ > Li+ > Mg2+ > Be2+ > Al3+ (Ionicradius)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following order is correct for the property ment ioned in brackets:
a)
S2– > Cl– > K+ > Ca2+ (Ionization energy)
b)
C < N < F < O (2nd Ionization energy)
c)
B > Al > Ga > In > Tl (Electronegativity)
d)
Na+ > Li+ > Mg2+ > Be2+ > Al3+ (Ionicradius)

|
Asf Institute answered |
The answer is option (b) C<N<F<O (2nd Ionisation energy).
Consider the following statements: (I) The radius of an anion is larger than that of the parent atom. (II) The ionization energy generally increases with increasing atomic number in a period (III) The electronegativity of an element is the tendency of an isolated atom to attract an electron.Which of the above statements is/are correct:
- a)I alone
- b)II alone
- c)I and II
- d)II and III
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements: (I) The radius of an anion is larger than that of the parent atom. (II) The ionization energy generally increases with increasing atomic number in a period (III) The electronegativity of an element is the tendency of an isolated atom to attract an electron.Which of the above statements is/are correct:
a)
I alone
b)
II alone
c)
I and II
d)
II and III

|
Edurev.iitjam answered |

The correct order of increasing electron affinity of the following elements is:- a)O < S < F < Cl
- b)O < S < Cl < F
- c)S < O < F < Cl
- d)S < O < Cl < F
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct order of increasing electron affinity of the following elements is:
a)
O < S < F < Cl
b)
O < S < Cl < F
c)
S < O < F < Cl
d)
S < O < Cl < F

|
Amar Chawla answered |
Order of Increasing Electron Affinity:
Electron affinity refers to the tendency of an atom to attract an electron towards itself. The correct order of increasing electron affinity of the given elements is as follows:
a) O S F Cl
Explanation:
The correct order of increasing electron affinity can be explained as follows:
- Oxygen (O) has the least electron affinity as it has a small atomic size and a stable electronic configuration. It requires less energy to remove an electron from its outermost shell, making it less likely to attract an additional electron.
- Sulfur (S) has a slightly higher electron affinity than oxygen due to its larger atomic size and lower effective nuclear charge. This makes it easier for sulfur to attract an electron towards itself.
- Fluorine (F) has a higher electron affinity than sulfur due to its smaller atomic size and high effective nuclear charge. It has a strong attraction towards electrons and tends to form stable anions.
- Chlorine (Cl) has the highest electron affinity among the given elements due to its larger atomic size and lower effective nuclear charge. It has a stronger attraction towards electrons than fluorine and forms stable anions.
Therefore, the correct order of increasing electron affinity of the given elements is O < s="" />< f="" />< cl.="" />
Electron affinity refers to the tendency of an atom to attract an electron towards itself. The correct order of increasing electron affinity of the given elements is as follows:
a) O S F Cl
Explanation:
The correct order of increasing electron affinity can be explained as follows:
- Oxygen (O) has the least electron affinity as it has a small atomic size and a stable electronic configuration. It requires less energy to remove an electron from its outermost shell, making it less likely to attract an additional electron.
- Sulfur (S) has a slightly higher electron affinity than oxygen due to its larger atomic size and lower effective nuclear charge. This makes it easier for sulfur to attract an electron towards itself.
- Fluorine (F) has a higher electron affinity than sulfur due to its smaller atomic size and high effective nuclear charge. It has a strong attraction towards electrons and tends to form stable anions.
- Chlorine (Cl) has the highest electron affinity among the given elements due to its larger atomic size and lower effective nuclear charge. It has a stronger attraction towards electrons than fluorine and forms stable anions.
Therefore, the correct order of increasing electron affinity of the given elements is O < s="" />< f="" />< cl.="" />
The incorrect statement is:- a)The second ionization energy of Se is greater than that of second ionization energy of As
- b)The first ionizat ion energy of C2+ ion is greater than that of first ionizat ion energy of N2+ ion.
- c)The third ionizat ion energy of F is greater than that of third ionization energy of O
- d)Helogens have highest I.E. in respective period
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The incorrect statement is:
a)
The second ionization energy of Se is greater than that of second ionization energy of As
b)
The first ionizat ion energy of C2+ ion is greater than that of first ionizat ion energy of N2+ ion.
c)
The third ionizat ion energy of F is greater than that of third ionization energy of O
d)
Helogens have highest I.E. in respective period
|
|
Aditya Deshmukh answered |
Halogens are present in the group 17 in periodic table.They needs only one electron in their outermost subshell to attain noble gas configuration and becomes stable...so they try to get one electron in their outermost subshell and thus their electron gain enthylpe is high.
A, B and C are hydroxy-compounds of the elements X, Y and Z respectively. X, Y and Z are in the same period of the periodic table. A gives an aqueous solution of pH less than seven. B reacts with both strong acids alkalis. C gives an aqueous solution which is strongly alkaline.Which of the following statements is/are true?
(I) The three elements are metals.
(II) The electronegativities decrease from X to Y to Z
(III) The atomic radius decreases in the order X, Y and Z
(IV) X, Y and Z could be phosphorus aluminium and sodium respectively.- a)I, II, III only correct
- b)I, III only correct
- c)II, IV only correct
- d)II, III IV only correct
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A, B and C are hydroxy-compounds of the elements X, Y and Z respectively. X, Y and Z are in the same period of the periodic table. A gives an aqueous solution of pH less than seven. B reacts with both strong acids alkalis. C gives an aqueous solution which is strongly alkaline.
Which of the following statements is/are true?
(I) The three elements are metals.
(II) The electronegativities decrease from X to Y to Z
(III) The atomic radius decreases in the order X, Y and Z
(IV) X, Y and Z could be phosphorus aluminium and sodium respectively.
(I) The three elements are metals.
(II) The electronegativities decrease from X to Y to Z
(III) The atomic radius decreases in the order X, Y and Z
(IV) X, Y and Z could be phosphorus aluminium and sodium respectively.
a)
I, II, III only correct
b)
I, III only correct
c)
II, IV only correct
d)
II, III IV only correct
|
|
Pooja Choudhury answered |
- The electronegativities decrease from X to Y to Z.
- X, Y and Z could be phosphorus aluminium and sodium respectively.
Which one of the following statements is incorrect:
- a)Greater is the nuclear charge, greater is the electron gain enthalpy
- b)Nitrogen has almost zero electron gain enthalpy
- c)Electron gain enthalpy decreases from fluorine to iodine in the group
- d)Chlorine has highest electron gain enthalpy
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is incorrect:
a)
Greater is the nuclear charge, greater is the electron gain enthalpy
b)
Nitrogen has almost zero electron gain enthalpy
c)
Electron gain enthalpy decreases from fluorine to iodine in the group
d)
Chlorine has highest electron gain enthalpy

|
Shivam Sharma answered |
The incorrect statement is:
Electron gain enthalpy decreases from fluorine to iodine in the group.
Explanation:
Electron gain enthalpy is the energy released when an electron is added to an isolated gaseous atom. In general, electron gain enthalpy becomes more negative (i.e., more energy is released) as we move across a period from left to right and up a group from bottom to top in the periodic table. This is due to the increasing effective nuclear charge and decreasing atomic size, which makes it easier for the atom to attract and hold an additional electron.
However, statement 3 is incorrect because electron gain enthalpy actually increases (becomes less negative or more positive) as we move down a group, such as from fluorine to iodine. This is because, as we move down a group, the atomic size increases and the effective nuclear charge experienced by the incoming electron decreases. This makes it less favorable for the atom to gain an electron, resulting in a less negative (or more positive) electron gain enthalpy.
Electron gain enthalpy decreases from fluorine to iodine in the group.
Explanation:
Electron gain enthalpy is the energy released when an electron is added to an isolated gaseous atom. In general, electron gain enthalpy becomes more negative (i.e., more energy is released) as we move across a period from left to right and up a group from bottom to top in the periodic table. This is due to the increasing effective nuclear charge and decreasing atomic size, which makes it easier for the atom to attract and hold an additional electron.
However, statement 3 is incorrect because electron gain enthalpy actually increases (becomes less negative or more positive) as we move down a group, such as from fluorine to iodine. This is because, as we move down a group, the atomic size increases and the effective nuclear charge experienced by the incoming electron decreases. This makes it less favorable for the atom to gain an electron, resulting in a less negative (or more positive) electron gain enthalpy.
Consider the following changes:
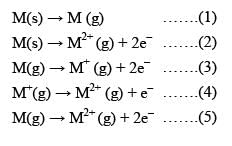 The second ionization energy of M could be calculated from the energy values associated with:
The second ionization energy of M could be calculated from the energy values associated with:
- a)1 + 3 + 4
- b)2 – 1 + 3
- c)1 + 5
- d)5 – 3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following changes:
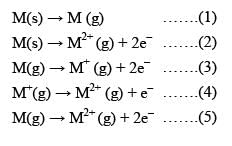
The second ionization energy of M could be calculated from the energy values associated with:
a)
1 + 3 + 4
b)
2 – 1 + 3
c)
1 + 5
d)
5 – 3
|
|
Dronacharya Institute answered |
M (s) → M (g) ........(1)
M (s) → M2+ (g) + 2e- .......(2)
M (g) → M+ (g) + 2e- .......(3)
M+ (g) → M2+ (g) + e- .......(4)
M (g) → M2+ (g) + 2e- .......(5)
As we are interested in 2nd I.E.
i.e. Energy required to form M2+ (g) from M+ (g)
∴ 4 is correct.
but this option doesn't exist.
⇒ 1 + 3 + 4 is also wrong
1 + 5 gives total energy for M(g) → M2+ (g)
∴ it is also wrong.
3rd reaction is wrong,
∴ 2 - 1 + 3 also dismised.
⇒ (d) is correct
M (s) → M2+ (g) + 2e- .......(2)
M (g) → M+ (g) + 2e- .......(3)
M+ (g) → M2+ (g) + e- .......(4)
M (g) → M2+ (g) + 2e- .......(5)
As we are interested in 2nd I.E.
i.e. Energy required to form M2+ (g) from M+ (g)
∴ 4 is correct.
but this option doesn't exist.
⇒ 1 + 3 + 4 is also wrong
1 + 5 gives total energy for M(g) → M2+ (g)
∴ it is also wrong.
3rd reaction is wrong,
∴ 2 - 1 + 3 also dismised.
⇒ (d) is correct
 Calculate the among of energy required to convert 110 mg of ‘X’ atom in gaseous state into X+ ion.
Calculate the among of energy required to convert 110 mg of ‘X’ atom in gaseous state into X+ ion.- a)10.4 kJ
- b)12.3 kJ
- c)11.3 kJ
- d)14.5 kJ
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the among of energy required to convert 110 mg of ‘X’ atom in gaseous state into X+ ion.
a)
10.4 kJ
b)
12.3 kJ
c)
11.3 kJ
d)
14.5 kJ

|
Ameya Reddy answered |
Explanation:
The melting point of a compound is dependent on several factors such as the strength of the intermolecular forces, size and charge of the ions, and lattice energy. In this case, the melting point of NaF is higher than the other three compounds due to the following reasons:
Ionic Character:
NaF has the highest ionic character among the given compounds. This is because the difference in electronegativity between Na and F is the highest among the given compounds. As a result, the bond between Na and F is highly polar covalent, and the F ion has a high negative charge. This leads to stronger electrostatic forces of attraction between the oppositely charged ions, resulting in a higher melting point.
Lattice Energy:
The lattice energy of NaF is the highest among the given compounds. This is because the F ion is the smallest among the given anions, and NaF has the highest charge density. The high charge density leads to a higher attraction between the ions, resulting in a higher lattice energy. The high lattice energy contributes to the high melting point of NaF.
Size and Charge of Ions:
The size and charge of the ions also play a role in the melting point of a compound. In this case, NaBr and NaI have larger anions, which means that the distance between the ions in the lattice is greater. This leads to weaker electrostatic forces of attraction and a lower melting point. Additionally, NaCl and NaBr have smaller charges on their anions, resulting in weaker electrostatic forces and lower lattice energies.
In conclusion, NaF has the highest melting point among the given compounds due to its high ionic character, high lattice energy, and small size of the F ion.
The melting point of a compound is dependent on several factors such as the strength of the intermolecular forces, size and charge of the ions, and lattice energy. In this case, the melting point of NaF is higher than the other three compounds due to the following reasons:
Ionic Character:
NaF has the highest ionic character among the given compounds. This is because the difference in electronegativity between Na and F is the highest among the given compounds. As a result, the bond between Na and F is highly polar covalent, and the F ion has a high negative charge. This leads to stronger electrostatic forces of attraction between the oppositely charged ions, resulting in a higher melting point.
Lattice Energy:
The lattice energy of NaF is the highest among the given compounds. This is because the F ion is the smallest among the given anions, and NaF has the highest charge density. The high charge density leads to a higher attraction between the ions, resulting in a higher lattice energy. The high lattice energy contributes to the high melting point of NaF.
Size and Charge of Ions:
The size and charge of the ions also play a role in the melting point of a compound. In this case, NaBr and NaI have larger anions, which means that the distance between the ions in the lattice is greater. This leads to weaker electrostatic forces of attraction and a lower melting point. Additionally, NaCl and NaBr have smaller charges on their anions, resulting in weaker electrostatic forces and lower lattice energies.
In conclusion, NaF has the highest melting point among the given compounds due to its high ionic character, high lattice energy, and small size of the F ion.
How does the energy gap between successive energy levels in an atom vary from low to high n values:- a)All energy gaps are the same
- b)The energy gap decreases as n increases
- c)The energy gap increases as n increases
- d)The energy gap changes unpredictably as n increases
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How does the energy gap between successive energy levels in an atom vary from low to high n values:
a)
All energy gaps are the same
b)
The energy gap decreases as n increases
c)
The energy gap increases as n increases
d)
The energy gap changes unpredictably as n increases

|
Ishani Dasgupta answered |
The further away an electron is from the nucleus, the less force it feels from the electron, so the less energy is needed to “pop it off” the atom. The value of the energy level is exactly this amount of energy so the smaller it is, the smaller the difference with neighboring levels will be.
The correct values of ionization enthalpies (in kJ mol–1) of Si, P, Cl and S respectively are:- a)786, 1012, 999, 1256
- b)1012, 786, 999, 1256
- c)786, 1012, 1256, 999
- d)786, 999, 1012, 1256
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct values of ionization enthalpies (in kJ mol–1) of Si, P, Cl and S respectively are:
a)
786, 1012, 999, 1256
b)
1012, 786, 999, 1256
c)
786, 1012, 1256, 999
d)
786, 999, 1012, 1256

|
Mihir Singh answered |
-1) for the first 20 elements are:
1. Hydrogen - 1312
2. Helium - 2372
3. Lithium - 520
4. Beryllium - 899
5. Boron - 801
6. Carbon - 1086
7. Nitrogen - 1402
8. Oxygen - 1314
9. Fluorine - 1681
10. Neon - 2081
11. Sodium - 496
12. Magnesium - 738
13. Aluminum - 578
14. Silicon - 786
15. Phosphorus - 1012
16. Sulfur - 1000
17. Chlorine - 1251
18. Argon - 1521
19. Potassium - 419
20. Calcium - 590
1. Hydrogen - 1312
2. Helium - 2372
3. Lithium - 520
4. Beryllium - 899
5. Boron - 801
6. Carbon - 1086
7. Nitrogen - 1402
8. Oxygen - 1314
9. Fluorine - 1681
10. Neon - 2081
11. Sodium - 496
12. Magnesium - 738
13. Aluminum - 578
14. Silicon - 786
15. Phosphorus - 1012
16. Sulfur - 1000
17. Chlorine - 1251
18. Argon - 1521
19. Potassium - 419
20. Calcium - 590
The most electropositive element possesses the electronic configuration:- a)[He]2s1
- b)[Ne]3s2
- c)[Xe]6s1
- d)[Xe]6s2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The most electropositive element possesses the electronic configuration:
a)
[He]2s1
b)
[Ne]3s2
c)
[Xe]6s1
d)
[Xe]6s2

|
Mrinalini Sen answered |
The electronic configuration [Xe]6s^1 is the configuration of Cs which is highly electropositive element of alkali metal family. It has the lowest ionisation potential in its family.
Which of the following species must have maximum number of electrons in ‘dxy’ orbital:- a)Cr
- b)Fe3+
- c)Cu+
- d)Both a and b
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following species must have maximum number of electrons in ‘dxy’ orbital:
a)
Cr
b)
Fe3+
c)
Cu+
d)
Both a and b

|
Sinjini Singh answered |
Explanation:
Electronic Configurations:
The maximum number of electrons in the dxy orbital is 2. To determine which of the given species has the maximum number of electrons in the dxy orbital, we need to look at their electronic configurations.
Electronic Configurations:
a) Cr: [Ar] 3d5 4s1
b) Fe3+: [Ar] 3d5
c) Cu: [Ar] 3d10 4s1
From the electronic configurations, we can see that:
- Cromium (Cr) has 5 electrons in the d orbital (d1, d2, d3, d4, d5)
- Iron (Fe3+) has 5 electrons in the d orbital (d1, d2, d3, d4, d5)
- Copper (Cu) has 10 electrons in the d orbital (d1, d2, d3, d4, d5, d6, d7, d8, d9, d10)
Therefore, the species with the maximum number of electrons in the dxy orbital is Copper (Cu) because the dxy orbital is one of the five d orbitals, and copper has a completely filled d orbital with 10 electrons.
Hence, the correct answer is option 'C'.
Which one of the following elements shows both positive and negative oxidation states:- a)Cesium
- b)Fluorine
- c)Iodine
- d)Xenon
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following elements shows both positive and negative oxidation states:
a)
Cesium
b)
Fluorine
c)
Iodine
d)
Xenon

|
Sagarika Patel answered |
All the other halogens-chlorine, bromine and iodine- exhibit positive oxidation states upto +7, apart from the most stable negative state of -1. But fluorine is more electronegative than any other element in the periodic table and so it cannot be assigned a positive oxidation number in its compounds.
Which of the following statements is/are wrong:- a)Van der Waals radius of iodine is more than its covalent radius
- b)All isoelectronic ions belong to same period of the periodic table
- c)I.E1 of N is higher than that of O while I.E2 of O is higher than that of N
- d)The electron affinity N is almost zero while that of P is 74.3 kJ mol–1
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is/are wrong:
a)
Van der Waals radius of iodine is more than its covalent radius
b)
All isoelectronic ions belong to same period of the periodic table
c)
I.E1 of N is higher than that of O while I.E2 of O is higher than that of N
d)
The electron affinity N is almost zero while that of P is 74.3 kJ mol–1
|
|
Aditya Deshmukh answered |
Well, noble gases such as Helium, Neon and Argon have an electron affinity nearly zero because they have octet configuration. Due to this reason , they find it hard to attaract electrons. However higher members of Group 18 in the periodic table such Xenon, krypton and radon, do form compound like XeO2 and XeO4 due to the presence of vacant d- orbitals.
Consider the following information about element P and Q:
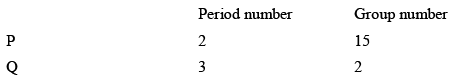 Then formula of the compound formed by P and Q element is:
Then formula of the compound formed by P and Q element is:
- a)PQ
- b)P3Q2
- c)P2Q3
- d)PQ2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following information about element P and Q:
Then formula of the compound formed by P and Q element is:
a)
PQ
b)
P3Q2
c)
P2Q3
d)
PQ2
|
|
Surendra Bind answered |
Group 15write the configuration in outer shell in 5clectron so element in vacancy 3&5but 3valancy is more stable because absence is d orbital (in case of Nitrogen) and group 2write the configuration in outer shell in 2 electron so this vacancy is 2 so the formula of the compound is formula P2Q3
The second electron gain enthalpies (in kJ mol–1) of oxygen and sulphur respectively are:- a)–780, + 590
- b)–590, + 780
- c)+590, + 780
- d)+780, +590
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The second electron gain enthalpies (in kJ mol–1) of oxygen and sulphur respectively are:
a)
–780, + 590
b)
–590, + 780
c)
+590, + 780
d)
+780, +590

|
Nandini Das answered |
The second electron gain enthalpy (electron affinity) is the energy released when a neutral atom gains an electron to form a negative ion with a 1- charge.
Explanation:
- Oxygen has 6 electrons in its valence shell and needs 2 more electrons to complete its octet.
- When it gains the first electron, it becomes a negatively charged ion, O-.
- However, when it gains the second electron, it has to overcome a repulsive force from the already existing negative charge. This makes it more difficult for oxygen to gain the second electron, hence it has a higher second electron gain enthalpy value.
- Sulphur, on the other hand, has 6 electrons in its valence shell and needs 2 more electrons to complete its octet.
- When it gains the first electron, it becomes a negatively charged ion, S-.
- When it gains the second electron, it is easier for sulphur to gain it as compared to oxygen, hence it has a lower second electron gain enthalpy value.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' where oxygen has a higher second electron gain enthalpy of 780 kJ mol-1 and sulphur has a lower second electron gain enthalpy of 590 kJ mol-1.
Explanation:
- Oxygen has 6 electrons in its valence shell and needs 2 more electrons to complete its octet.
- When it gains the first electron, it becomes a negatively charged ion, O-.
- However, when it gains the second electron, it has to overcome a repulsive force from the already existing negative charge. This makes it more difficult for oxygen to gain the second electron, hence it has a higher second electron gain enthalpy value.
- Sulphur, on the other hand, has 6 electrons in its valence shell and needs 2 more electrons to complete its octet.
- When it gains the first electron, it becomes a negatively charged ion, S-.
- When it gains the second electron, it is easier for sulphur to gain it as compared to oxygen, hence it has a lower second electron gain enthalpy value.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' where oxygen has a higher second electron gain enthalpy of 780 kJ mol-1 and sulphur has a lower second electron gain enthalpy of 590 kJ mol-1.
Which of the following statements is incorrect:- a)The second ionization energy of sulphur is greater than that of chlorine
- b)The third ionization energy of phosphorus is greater than that of aluminium
- c)The first ionization energy of aluminium is approximately the same as that of gallium
- d)The second ionization energy of boron is greater than that of carbon.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is incorrect:
a)
The second ionization energy of sulphur is greater than that of chlorine
b)
The third ionization energy of phosphorus is greater than that of aluminium
c)
The first ionization energy of aluminium is approximately the same as that of gallium
d)
The second ionization energy of boron is greater than that of carbon.

|
Baishali Bajaj answered |
In this situation, the effect of an increase in nuclear charge in aluminium is greater than the shielding of the 3p electron by the 3s electrons.
When magnesium burns, in air, compounds of magnesium formed are magnesium oxide and:- a)Mg3N2
- b)MgCO3
- c)Mg(NO3)2
- d)MgSO4
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When magnesium burns, in air, compounds of magnesium formed are magnesium oxide and:
a)
Mg3N2
b)
MgCO3
c)
Mg(NO3)2
d)
MgSO4

|
Rahul Chatterjee answered |
There’s only one product, I guess.
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
This is, of course, considering pure oxygen.
If magnesium is burnt in air (which contains 78% N2), a side-product Mg3N2
The set representing the correct order of ionic radius is:- a)Na+ > Mg2+ > Li+ > Be2+
- b)Na+ > Li+ > Mg2+ > Be2+
- c)Be2+ > Na+ > Mg2+ > Li+
- d)Na+ > Mg2+ > Li+ < Be2+
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The set representing the correct order of ionic radius is:
a)
Na+ > Mg2+ > Li+ > Be2+
b)
Na+ > Li+ > Mg2+ > Be2+
c)
Be2+ > Na+ > Mg2+ > Li+
d)
Na+ > Mg2+ > Li+ < Be2+

|
Anushka Basak answered |
Na+: 1.02 Ao
Be2+: 0.39 Ao
Mg2+: 0.72 Ao
Li+: 0.76 Ao
The correct option is B.
The size of isoelectronic species: F–, Ne and Na+ is affected by:- a)Nuclear charge (n)
- b)Valence principal quantum number(n)
- c)Electron-electron interaction in the outer orbitals
- d)None of the factor because their size is the same
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The size of isoelectronic species: F–, Ne and Na+ is affected by:
a)
Nuclear charge (n)
b)
Valence principal quantum number(n)
c)
Electron-electron interaction in the outer orbitals
d)
None of the factor because their size is the same

|
Shivam Sharma answered |
nuclear charge (Z). Isoelectronic species are the species belonging to different atoms or ions which have same number of electrons but different magnitudes of nuclear charges.
The size of an isoelectronic species increases with a decrease in the nuclear charge (Z). For example, the order of the increasing nuclear charge of F–, Ne, and Na+ is as follows:
F– < Ne < Na+
Z 9 10 11
Therefore, the order of the increasing size of F–, Ne and Na+ is as follows:
Na+ < Ne < F–
The correct order of second I. E. of C, N, O and F are in the order:- a)F > O > N > C
- b)C > N > O > F
- c)O > N > F > C
- d)O > F > N > C
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct order of second I. E. of C, N, O and F are in the order:
a)
F > O > N > C
b)
C > N > O > F
c)
O > N > F > C
d)
O > F > N > C

|
Aaron B Mathew answered |
The electronic configuration of oxygen is 1s2 2s2 2p4 on removing one electron we get a half filled configuration which is stable. So among these it will b the hardest to remove the second electron of oxygen. The size of fluorine is less than nitrogen. On removing one electron, its size will decrease again and so, its second I.E will be greater than nitrogen. carbon has the least second I.E because on removing the second electron, it will complete octet and attain stability
Consider the following electronic configuration of an element (P):[Xe] 4f145d16s2The correct statement about element ‘P’ is:- a)It belongs to 6th period and 1st group
- b)It belongs to 6th period and 2nd group
- c)It belongs to 6th period and 3rd group
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following electronic configuration of an element (P):
[Xe] 4f145d16s2
The correct statement about element ‘P’ is:
a)
It belongs to 6th period and 1st group
b)
It belongs to 6th period and 2nd group
c)
It belongs to 6th period and 3rd group
d)
None of these

|
Anirban Kapoor answered |
Electronic Configuration of Element P
The electronic configuration of element P is: [Xe] 4f14 5d1 6s2.
Determining the Period and Group of Element P
To determine the period and group of element P, we need to look at its valence shell configuration, which is 6s2.
Period: The valence shell of element P is in the sixth energy level, so it belongs to the sixth period.
Group: The valence shell of element P has two electrons in the s orbital, so it belongs to the third group (also known as group 13 or the boron group).
Therefore, the correct statement is option C: Element P belongs to the 6th period and 3rd group.
The electronic configuration of element P is: [Xe] 4f14 5d1 6s2.
Determining the Period and Group of Element P
To determine the period and group of element P, we need to look at its valence shell configuration, which is 6s2.
Period: The valence shell of element P is in the sixth energy level, so it belongs to the sixth period.
Group: The valence shell of element P has two electrons in the s orbital, so it belongs to the third group (also known as group 13 or the boron group).
Therefore, the correct statement is option C: Element P belongs to the 6th period and 3rd group.
Among NaF , NaCl , NaBr and Nal , the NaF has highest melting point because- a)It has maximum ionic character
- b)It has minimum ionic character
- c)It has associated molecules
- d)It has least molecular weight
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Among NaF , NaCl , NaBr and Nal , the NaF has highest melting point because
a)
It has maximum ionic character
b)
It has minimum ionic character
c)
It has associated molecules
d)
It has least molecular weight

|
Srishti Kulkarni answered |
Explanation:
NaF, NaCl, NaBr, and NaI are all ionic compounds, which means they are formed by the transfer of electrons from the metal to the non-metal. The melting point of these compounds is directly proportional to the strength of the ionic bond between the metal and non-metal.
Ionic Character:
The ionic character of a compound is a measure of the degree to which electrons are transferred from the metal to the non-metal. The greater the difference in electronegativity between the metal and non-metal, the greater the ionic character of the compound. NaF has the highest ionic character among the given options because fluoride ion is the most electronegative of all halide ions.
Melting Point:
The melting point is the temperature at which a solid changes to a liquid. The melting point of an ionic compound depends on the strength of the ionic bond between the metal and non-metal. The stronger the ionic bond, the higher the melting point of the compound.
NaF has the highest melting point among the given options because it has the highest ionic character due to the small size and high electronegativity of the fluoride ion, which results in a strong ionic bond between Na+ and F- ions.
Conclusion:
NaF has the highest melting point among the given options because it has the maximum ionic character due to the small size and high electronegativity of the fluoride ion.
NaF, NaCl, NaBr, and NaI are all ionic compounds, which means they are formed by the transfer of electrons from the metal to the non-metal. The melting point of these compounds is directly proportional to the strength of the ionic bond between the metal and non-metal.
Ionic Character:
The ionic character of a compound is a measure of the degree to which electrons are transferred from the metal to the non-metal. The greater the difference in electronegativity between the metal and non-metal, the greater the ionic character of the compound. NaF has the highest ionic character among the given options because fluoride ion is the most electronegative of all halide ions.
Melting Point:
The melting point is the temperature at which a solid changes to a liquid. The melting point of an ionic compound depends on the strength of the ionic bond between the metal and non-metal. The stronger the ionic bond, the higher the melting point of the compound.
NaF has the highest melting point among the given options because it has the highest ionic character due to the small size and high electronegativity of the fluoride ion, which results in a strong ionic bond between Na+ and F- ions.
Conclusion:
NaF has the highest melting point among the given options because it has the maximum ionic character due to the small size and high electronegativity of the fluoride ion.
In the fourth period of the periodic table, how many elements have one or more 4d electrons:- a)2
- b)18
- c)0
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the fourth period of the periodic table, how many elements have one or more 4d electrons:
a)
2
b)
18
c)
0
d)
6

|
Harshitha Sharma answered |
Answer:
In the fourth period of the periodic table, there are no elements that have one or more 4d electrons. This is because the fourth period corresponds to the n=4 energy level, which includes the 4s and 3d sublevels.
Explanation:
- The fourth period of the periodic table includes the elements potassium (K) through krypton (Kr).
- The 4s sublevel can hold up to 2 electrons, and the 3d sublevel can hold up to 10 electrons.
- Therefore, the elements in the fourth period can have up to 12 electrons in the n=4 energy level.
- However, none of the elements in the fourth period have any electrons in the 4d sublevel.
- The 4d sublevel comes after the 3d sublevel in energy, so it is not filled until the fifth period.
- Elements in the fifth period, such as niobium (Nb) and ruthenium (Ru), have electrons in the 4d sublevel.
- Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C', which states that there are no elements in the fourth period with 4d electrons.
In the fourth period of the periodic table, there are no elements that have one or more 4d electrons. This is because the fourth period corresponds to the n=4 energy level, which includes the 4s and 3d sublevels.
Explanation:
- The fourth period of the periodic table includes the elements potassium (K) through krypton (Kr).
- The 4s sublevel can hold up to 2 electrons, and the 3d sublevel can hold up to 10 electrons.
- Therefore, the elements in the fourth period can have up to 12 electrons in the n=4 energy level.
- However, none of the elements in the fourth period have any electrons in the 4d sublevel.
- The 4d sublevel comes after the 3d sublevel in energy, so it is not filled until the fifth period.
- Elements in the fifth period, such as niobium (Nb) and ruthenium (Ru), have electrons in the 4d sublevel.
- Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C', which states that there are no elements in the fourth period with 4d electrons.
Which of the following metal is highest electropositive (metallic) in nature:
- a)Be
- b)FR
- c)Mn
- d)Tl
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following metal is highest electropositive (metallic) in nature:
a)
Be
b)
FRc)
Mn
d)
Tl

|
Baishali Bajaj answered |
The most metallic element is francium. However, francium is a man-made element, except for one isotope, and all isotopes are so radioactive they almost instantly decay into another element.Francium 87 is the most electropositive element.
Which of these does not reflect the periodicity of the elements?a)Bonding behaviourb)Electronegativityc)Ionization energyd)Neutron/proton ratioThe correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Anagha Bajaj answered |
Neutron/proton ratio is cause of radioactivity
The atomic numbers of the metallic and non-metallic elements which are liquid at room temperature respectively are:- a)55, 87
- b)33, 87
- c)35, 80
- d)80, 35
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The atomic numbers of the metallic and non-metallic elements which are liquid at room temperature respectively are:
a)
55, 87
b)
33, 87
c)
35, 80
d)
80, 35

|
Sagarika Patel answered |
Bromine (symbol Br and atomic number 35) and mercury (symbol Hg and atomic number 80) are both liquids at room temperature. Bromine is a reddish-brown liquid, with a melting point of 265.9 K. Mercury is a toxic shiny silvery metal, with a melting point of 234.32 K.
Consider the following four elements, which are represented according to long form of periodic table.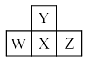 Here W, Y and Z are left, up and right elements with respect to the element ‘X’ and ‘X’ belongs to 16th group and 3rd period. Then according to given informat ion the incorrect statement regarding given elements is:
Here W, Y and Z are left, up and right elements with respect to the element ‘X’ and ‘X’ belongs to 16th group and 3rd period. Then according to given informat ion the incorrect statement regarding given elements is:- a)Maximum electronegativity: Y
- b)Maximum catenation property: X
- c)Maximum electron affinit y: Z
- d)Y exhibit s variable covalency
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following four elements, which are represented according to long form of periodic table.
Here W, Y and Z are left, up and right elements with respect to the element ‘X’ and ‘X’ belongs to 16th group and 3rd period. Then according to given informat ion the incorrect statement regarding given elements is:
a)
Maximum electronegativity: Y
b)
Maximum catenation property: X
c)
Maximum electron affinit y: Z
d)
Y exhibit s variable covalency

|
Raj Kathiriya answered |
Explain catenation properties
In which of the following arrangements, the order is not correct according to the property indicated against it:- a)Increasing size: Al3+ < Mg2+ < Na+ < F–
- b)Increasing I.E.1: B < C < N < O
- c)Increasing E.A1: I < Br < F < Cl
- d)Increasing metallic radius: Li < Na < K < Rb
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following arrangements, the order is not correct according to the property indicated against it:
a)
Increasing size: Al3+ < Mg2+ < Na+ < F–
b)
Increasing I.E.1: B < C < N < O
c)
Increasing E.A1: I < Br < F < Cl
d)
Increasing metallic radius: Li < Na < K < Rb

|
Ameya Reddy answered |
A) Increasing size: Al3+ < mg2+="" />< />
This arrangement is not correct according to the property of increasing size. The correct arrangement should be Na+ < mg2+="" />< al3+="" as="" the="" size="" of="" the="" ion="" increases="" with="" the="" addition="" of="" more="" electrons="" and="" protons.="" na+="" has="" the="" smallest="" size,="" followed="" by="" mg2+="" and="" then="" al3+.="" al3+="" as="" the="" size="" of="" the="" ion="" increases="" with="" the="" addition="" of="" more="" electrons="" and="" protons.="" na+="" has="" the="" smallest="" size,="" followed="" by="" mg2+="" and="" then="" />
This arrangement is not correct according to the property of increasing size. The correct arrangement should be Na+ < mg2+="" />< al3+="" as="" the="" size="" of="" the="" ion="" increases="" with="" the="" addition="" of="" more="" electrons="" and="" protons.="" na+="" has="" the="" smallest="" size,="" followed="" by="" mg2+="" and="" then="" al3+.="" al3+="" as="" the="" size="" of="" the="" ion="" increases="" with="" the="" addition="" of="" more="" electrons="" and="" protons.="" na+="" has="" the="" smallest="" size,="" followed="" by="" mg2+="" and="" then="" />
Which of the following arrangements shows the correct order of decreasing paramagnetism:- a)N > Al > O > Ca
- b)N > O > Al > Ca
- c)O > N > Al > Ca
- d)O > N > Ca > Al
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following arrangements shows the correct order of decreasing paramagnetism:
a)
N > Al > O > Ca
b)
N > O > Al > Ca
c)
O > N > Al > Ca
d)
O > N > Ca > Al
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
Correct Answer :- b
Explanation :
N > O > Al > Ca
First the ionization energies (in kJ/mol) of three representative elements are given below: Then incorrect option is:
Then incorrect option is:- a)Q: Alkaline earth metal
- b)P: Alkali metals
- c)R: s-block element
- d)They belong to same period
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
First the ionization energies (in kJ/mol) of three representative elements are given below:
Then incorrect option is:
a)
Q: Alkaline earth metal
b)
P: Alkali metals
c)
R: s-block element
d)
They belong to same period
|
|
Sanjeev Kumar Yadav answered |
In P difference between 1st and 2nd ionisation enthalpy is high it means it is difficult to remove 2nd electron from P it means alkali metal
similarly Q is alkaline earth metal.
similarly R is group 13 element and not sure block element
similarly Q is alkaline earth metal.
similarly R is group 13 element and not sure block element
The period number and group number of “Tantalum” (Z = 73) are respectively:- a)5, 7
- b)6, 13
- c)6, 5
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The period number and group number of “Tantalum” (Z = 73) are respectively:
a)
5, 7
b)
6, 13
c)
6, 5
d)
None of these

|
Anisha Banerjee answered |
Period and Group of Tantalum
Periodic Table of Elements
The periodic table of elements is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements based on the periodic trends in their properties. The elements are arranged in rows and columns according to their atomic number, electron configuration, and chemical properties.
Tantalum (Ta)
Tantalum is a chemical element with the symbol Ta and atomic number 73. It is a rare, hard, blue-gray, lustrous transition metal that is highly corrosion-resistant. Tantalum is used in the production of capacitors, surgical implants, and nuclear reactors.
Period Number of Tantalum
The period number of an element in the periodic table is the number of electron shells it has. Tantalum has an atomic number of 73, which means it has 73 electrons arranged in different shells. The period number of an element is equal to the number of shells it has. Therefore, the period number of tantalum is 6.
Group Number of Tantalum
The group number of an element in the periodic table is the number of valence electrons it has. Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom that are involved in chemical bonding. Tantalum belongs to group 5 of the periodic table because it has 5 valence electrons. Therefore, the group number of tantalum is 5.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option C, which states that the period number and group number of tantalum are 6 and 5, respectively.
Periodic Table of Elements
The periodic table of elements is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements based on the periodic trends in their properties. The elements are arranged in rows and columns according to their atomic number, electron configuration, and chemical properties.
Tantalum (Ta)
Tantalum is a chemical element with the symbol Ta and atomic number 73. It is a rare, hard, blue-gray, lustrous transition metal that is highly corrosion-resistant. Tantalum is used in the production of capacitors, surgical implants, and nuclear reactors.
Period Number of Tantalum
The period number of an element in the periodic table is the number of electron shells it has. Tantalum has an atomic number of 73, which means it has 73 electrons arranged in different shells. The period number of an element is equal to the number of shells it has. Therefore, the period number of tantalum is 6.
Group Number of Tantalum
The group number of an element in the periodic table is the number of valence electrons it has. Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom that are involved in chemical bonding. Tantalum belongs to group 5 of the periodic table because it has 5 valence electrons. Therefore, the group number of tantalum is 5.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option C, which states that the period number and group number of tantalum are 6 and 5, respectively.
True increasing order of acidity of the oxides of Mn is- a)MnO < MnO2 < Mn2O7
- b)Mn2O7 < MnO2 > MnO
- c)MnO2 > MnO > Mn2O7
- d)MnO2 > Mn2O7 > MnO
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
True increasing order of acidity of the oxides of Mn is
a)
MnO < MnO2 < Mn2O7
b)
Mn2O7 < MnO2 > MnO
c)
MnO2 > MnO > Mn2O7
d)
MnO2 > Mn2O7 > MnO

|
Sourav Dutta answered |
With increasing (+)ve oxidation state, acidity increases.
Which of the following represents an excited state of an atom:- a)[Ne]3s23p64s23d8
- b)[Ne]3s23p64s13d5
- c)[Ne]3s23p64s23d1
- d)1s22s22p53s1
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following represents an excited state of an atom:
a)
[Ne]3s23p64s23d8
b)
[Ne]3s23p64s13d5
c)
[Ne]3s23p64s23d1
d)
1s22s22p53s1
|
|
Rajeev Menon answered |
Example
The ground state electron configuration of sodium is
1s22s22p53s1
In its excited state, the valence electron in the 3s sublevel is promoted to the 3P
sublevel, giving the electron configuration as
.1s22s22p53s1
This is a very unstable condition and the excited electron will drop back down to the 3s
sublevel, releasing the same amount of energy that was absorbed, and producing a characteristic color of light, in this case yellow.
Chapter doubts & questions for Periodic Table - Chemistry for GRE Paper II 2025 is part of GRE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the GRE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for GRE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Periodic Table - Chemistry for GRE Paper II in English & Hindi are available as part of GRE exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for GRE Exam by signing up for free.
Chemistry for GRE Paper II
135 videos|250 docs|77 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily











