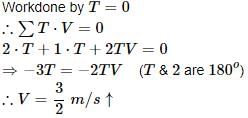All Exams >
ACT >
Science for ACT >
All Questions
All questions of Laws of Motion for ACT Exam
How is inertia used when riding a bicycle?- a)Bicycles don’t use inertia.
- b)You can stop paddling and still continue rolling forward.
- c)You must paddle harder when going up hill.
- d)You must paddle slower when going up hill.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How is inertia used when riding a bicycle?
a)
Bicycles don’t use inertia.
b)
You can stop paddling and still continue rolling forward.
c)
You must paddle harder when going up hill.
d)
You must paddle slower when going up hill.
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Due to inertia, even if we stop paddling of motion, we will continue to move forward up to a certain distance as friction will finally make us stop.
For a body to be able to loop a vertical circle of radius R, the minimum velocity required at its lowest point is:- a)
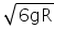
- b)
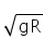
- c)
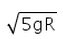
- d)
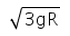
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For a body to be able to loop a vertical circle of radius R, the minimum velocity required at its lowest point is:
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
For a body to be able to loop a vertical circle of radius R. the minimum velocity required at its lowest point is √5gR
The dimensional formula for impulse is- a)[MLT-1]
- b)[ML2T-1]
- c)[M2LT]
- d)[ML-1T2]
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The dimensional formula for impulse is
a)
[MLT-1]
b)
[ML2T-1]
c)
[M2LT]
d)
[ML-1T2]
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
We know that I = P, where P is momentum
As subtracting initial momentum from the final momentum won't affect its unit, we get unit if I is the same as that of P.
As subtracting initial momentum from the final momentum won't affect its unit, we get unit if I is the same as that of P.
We slip on a rainy day due to- a)Change in momentum
- b)Inertia
- c)Decrease in friction
- d)Increase in friction
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
We slip on a rainy day due to
a)
Change in momentum
b)
Inertia
c)
Decrease in friction
d)
Increase in friction
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
On a rainy day, the rainwater forms a layer on the road.
This layer works like a lubricant which decreases the friction. Due to less friction, we slip on a rainy day.
This layer works like a lubricant which decreases the friction. Due to less friction, we slip on a rainy day.
A body of mass 2 kg is hung on a spring balance mounted vertically in a lift. If the lift moves up with an acceleration equal to the acceleration due to gravity, the reading on the spring balance will bea)5 kgb)8 kgc)7 kgd)4 kgCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
As the lift moves upwards but the spring feels itself at rest hence we need to compensate the non inertial frame by adding an appropriate pseudo force to treat it as an inertial frame. Hence the pseudo force to be applied acts on every mass in the lift which is equal to mass x acceleration (=g) downwards.
Hence the tension in the spring would be 40N (20 due to weight and 20 pseudo). Thus the reading would be 4kg.
Hence the tension in the spring would be 40N (20 due to weight and 20 pseudo). Thus the reading would be 4kg.
A block of 5 kg mass rests on a horizontal floor. The action of the block on the floor is- a)50 N vertically upward
- b)5 N vertically upward
- c)5 N vertically downward
- d)50 N vertically downward
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A block of 5 kg mass rests on a horizontal floor. The action of the block on the floor is
a)
50 N vertically upward
b)
5 N vertically upward
c)
5 N vertically downward
d)
50 N vertically downward
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Weight of the block, mg = 5kg x 10 m/s2 = 50 N.
According to Newton’s third law, the action of the block, that is the force exerted on the floor by the block is equal to 50 N in magnitude and is directly vertically downward.
Two masses are in the ratio 1:5. What is ratio of their inertia?- a)1:5
- b)5:1
- c)1:25
- d)25:1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two masses are in the ratio 1:5. What is ratio of their inertia?
a)
1:5
b)
5:1
c)
1:25
d)
25:1
|
|
Sagar Goyal answered |
Force of inertia = ma
Let the masses be 1x and 5x
Force of inertia for 1st body= 1x * a
Force of inertia for 2nd = 5x * a
Ratio= x * a / 5x * a = 1:5
Can you explain the answer of this question below:A horizontal force of 100 N pulls two masses 5 kg and 10 kg tied to each other by a light string. What is the tension in the string if the force is applied on 10 kg mass?
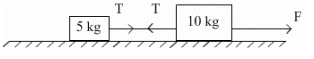
- A:
30 N
- B:
23 N
- C:
43 N
- D:
33.3 N
The answer is d.
A horizontal force of 100 N pulls two masses 5 kg and 10 kg tied to each other by a light string. What is the tension in the string if the force is applied on 10 kg mass?
30 N
23 N
43 N
33.3 N
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
At first considering both blocks as one system with only one external force F
We get common acceleration at right be a = 100/15 m/s2
Now considering 10 kg block
We get F - T = 10a
i.e. T = 100 - 10(100/15)
= 100 (1 - 2/3)
= 33.33 N
We get common acceleration at right be a = 100/15 m/s2
Now considering 10 kg block
We get F - T = 10a
i.e. T = 100 - 10(100/15)
= 100 (1 - 2/3)
= 33.33 N
A monkey of mass 40 kg climbs on a rope which can stand a maximum tension of 600 N. In which of the following cases will the rope break. When the monkey
(a) Climbs up with an acceleration of 6 ms−2.
- a)640 N
- b)632 N
- c)760 N
- d)740 N
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A monkey of mass 40 kg climbs on a rope which can stand a maximum tension of 600 N. In which of the following cases will the rope break. When the monkey
(a) Climbs up with an acceleration of 6 ms−2.
(a) Climbs up with an acceleration of 6 ms−2.
a)
640 N
b)
632 N
c)
760 N
d)
740 N
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Mass of the monkey, m = 40 kg
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 10 m/s
Maximum tension that the rope can bear, Tmax = 600 N
Acceleration of the monkey, a = 6 m/s2 upward
Using Newtons second law of motion, we can write the equation of motion as:
T mg = ma
T = m(g + a)
= 40 (10 + 6)
= 640 N
Since T > Tmax, the rope will break in this case.
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 10 m/s
Maximum tension that the rope can bear, Tmax = 600 N
Acceleration of the monkey, a = 6 m/s2 upward
Using Newtons second law of motion, we can write the equation of motion as:
T mg = ma
T = m(g + a)
= 40 (10 + 6)
= 640 N
Since T > Tmax, the rope will break in this case.
Two bodies of mass 4 kg and 6 kg are attached to the ends of a string passing over a pulley. A 4 kg mass is attached to the table top by another string. The tension in this string T1 is equal to (g = 10 m/s2) 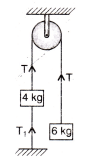
- a)20 N
- b)25 N
- c)15 N
- d)10 N
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two bodies of mass 4 kg and 6 kg are attached to the ends of a string passing over a pulley. A 4 kg mass is attached to the table top by another string. The tension in this string T1 is equal to (g = 10 m/s2)
a)
20 N
b)
25 N
c)
15 N
d)
10 N
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Find velocity of block 'B' at the instant shown in figure. 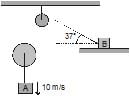
- a)25 m/s
- b)20 m/s
- c) 22 m/s
- d)30 m/s
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Find velocity of block 'B' at the instant shown in figure.
a)
25 m/s
b)
20 m/s
c)
22 m/s
d)
30 m/s
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Net Force = Force exerted by Cyclist - Frictional Force
Also, according to newton's second law
Fnet = m.a
250 N - Frictional Force = 30x4
∴ Frictional Force = 250 - 120 N
= 130 N
Also, according to newton's second law
Fnet = m.a
250 N - Frictional Force = 30x4
∴ Frictional Force = 250 - 120 N
= 130 N
A block of mass m is pushed by applying a force F at an angle θ with the horizontal surface. The normal force on the block is given as –- a)F = mg – F sin θ
- b)F = mg + F sin θ
- c)F = F sin θ
- d)F = mg
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A block of mass m is pushed by applying a force F at an angle θ with the horizontal surface. The normal force on the block is given as –
a)
F = mg – F sin θ
b)
F = mg + F sin θ
c)
F = F sin θ
d)
F = mg
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Both of them are vector quantities. And both of them can be easily simplified. If taken in the vector form then the task is even easier. Thus it is not necessary for the force or the couple to be vector only, even if the magnitude is taken, the simplification is done in the 2D.
The forces F1, F2, and F3 are acting on a particle of mass m, such that F2 and F3are mutually perpendicular and under the effect of F1, F2, and F3 , the particle remains stationary. What will be the acceleration of the particle, if the force F1 is removed?- a)
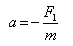
- b)
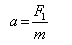
- c)
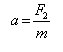
- d)
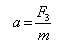
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The forces F1, F2, and F3 are acting on a particle of mass m, such that F2 and F3are mutually perpendicular and under the effect of F1, F2, and F3 , the particle remains stationary. What will be the acceleration of the particle, if the force F1 is removed?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Concept: Forces.The particle is a stationary under the effect of forces F1, F2 and F3.
This shows that force F1 is equal and opposite to the resultant of forces F2 and F3.
Hence, if the force F1 is removed the particle will move under the action of the force -ve F1 and the acceleration will the particle will be,a =-F1/m.
This shows that force F1 is equal and opposite to the resultant of forces F2 and F3.
Hence, if the force F1 is removed the particle will move under the action of the force -ve F1 and the acceleration will the particle will be,a =-F1/m.
Which law is in control of a spacecraft that cruises through space at a constant speed without using any fuel?- a)Universal law of gravitation
- b)Newton’s third law
- c)Newton’s second law
- d)Newton’s first law
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which law is in control of a spacecraft that cruises through space at a constant speed without using any fuel?
a)
Universal law of gravitation
b)
Newton’s third law
c)
Newton’s second law
d)
Newton’s first law
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
According to Newton’s first law the spacecraft will continue moving with constant speed unless an external opposite force is applied on it.
In the arrangement shown in figure, pulleys are massless and frictionless and threads are inextensible. The Block of mass m1 will remain at rest, if 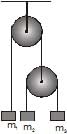
- a)
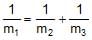
- b) m1 = m2 + m3
- c)
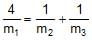
- d)
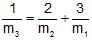
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the arrangement shown in figure, pulleys are massless and frictionless and threads are inextensible. The Block of mass m1 will remain at rest, if
a)
b)
m1 = m2 + m3
c)
d)
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
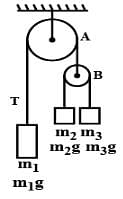
a = [(m3−m2 )/(m2+m3) ]g (m3 > m2)
T = [2m2m3g] / [m2+m3]
T′ = 2T = [4m2m3g] / [m2+m3]
m1g = 4m2m3gm / m2+m3
4/m1 = [1/m2] + [1/m3]
Adjoining figure shows a force of 40 N acting at 30° to the horizontal on a body of mass 5 kg resting on a smooth horizontal surface. Assuming that the acceleration of free-fall is 10 ms_2, which of the following statements A, B, C, D, E is (are) correct? [1] The horizontal force acting on the body is 20 N[2] The weight of the 5 kg mass acts vertically downwards[3] The net vertical force acting on the body is 30 N
[1] The horizontal force acting on the body is 20 N[2] The weight of the 5 kg mass acts vertically downwards[3] The net vertical force acting on the body is 30 N- a)1,2,3
- b)1,2
- c)2 only
- d)1 only
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Adjoining figure shows a force of 40 N acting at 30° to the horizontal on a body of mass 5 kg resting on a smooth horizontal surface. Assuming that the acceleration of free-fall is 10 ms_2, which of the following statements A, B, C, D, E is (are) correct?
[1] The horizontal force acting on the body is 20 N
[2] The weight of the 5 kg mass acts vertically downwards
[3] The net vertical force acting on the body is 30 N
a)
1,2,3
b)
1,2
c)
2 only
d)
1 only
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
(C) 2 only
[2] The weight of the 5kg mass acts vertically downwards
Concept of pseudo force is valid only in- a)inertial frame
- b)Non-inertial frame
- c)can be inertial or non-inertial frame
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Concept of pseudo force is valid only in
a)
inertial frame
b)
Non-inertial frame
c)
can be inertial or non-inertial frame
d)
None of these
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
This is because newton's laws are valid only for inertial frames. Analysis from an inertial frame isn't possible using those laws, to put it simple.
Let us assume a glass lift is going up with an acceleration 'a'. with respect to the ground. Clearly, this is a non-inertial frame as it has an acceleration. Man 'A' is inside the lift and wants to analyze the motion of the lift, but he cannot, as the newton's laws are not valid. So he takes his phone and calls Man 'B', who stands outside on the ground (in an inertial frame). This fellow watches Man 'A' go up with acceleration 'a'. Forces acting on Man 'A' are:
1. Weight, mg
2. Normal reaction offered by the lift, N
Thus, taking upward direction as positive and using Newton's Law, he writes the equation,
N - mg = ma, or
N = mg+ma
He tells "N=mg+ma" on phone to Man 'A'.
Now, Man 'A' looks around himself. According to himself, he is at rest. So, according to him, N = mg. Sadly, he knows this is not a correct analysis, as the newton's laws can't be applied!
The correct analysis, as received on phone, is N=mg+ma!
This is his eureka moment! He realizes that if he considers a "pseudo force" of magnitude 'ma' acting in opposite direction to acceleration of his frame, a correct analysis is possible!
This is why the concept of pseudo force is introduced, although it isn't necessary. You can always equate the net force in a direction equal to mass times acceleration from outside the non-inertial frame. However, if you want to do it from the non-inertial frame, the result can be interpreted in such a way, which suggests that the body is under rest, but an additional force (pseudo force) is acting.
Free body diagram of a situation is shown below. The net force is known, however, the magnitude of few of the forces is not known. The magnitude of the unknown forces C and D will be: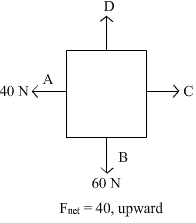
- a)C = 40 N, D = 80 N
- b)C = 40 N, D = 100 N
- c)C = 40 N, D = 80 N
- d)C = 40 N, D = 60 N
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Free body diagram of a situation is shown below. The net force is known, however, the magnitude of few of the forces is not known. The magnitude of the unknown forces C and D will be:
a)
C = 40 N, D = 80 N
b)
C = 40 N, D = 100 N
c)
C = 40 N, D = 80 N
d)
C = 40 N, D = 60 N
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
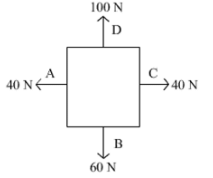
Force on A’ and B’ is 40 N and 60 N respectively. Net force of the situation is 40 N upward. So to balance the force on A’ a force of 40 N has to apply on C’. Similarly a force of 100 N is also be applied to get the net force of 40 N in upward direction.
A bomb of mass 16kg at rest, explodes into two pieces of masses 4kg and 12kg. After explosion, the velocity of the 12kg mass is 4m/s. What is the velocity of the 4kg piece?- a)-12 m/s
- b)12 m/s
- c)-4 m/s
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A bomb of mass 16kg at rest, explodes into two pieces of masses 4kg and 12kg. After explosion, the velocity of the 12kg mass is 4m/s. What is the velocity of the 4kg piece?
a)
-12 m/s
b)
12 m/s
c)
-4 m/s
d)
none of these
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Simply by conserving the momentum of the system we get that,
0 (initial momentum) = 12 x 4 + 4 x v (final momentum)
Thus we get v = -12 m/s
0 (initial momentum) = 12 x 4 + 4 x v (final momentum)
Thus we get v = -12 m/s
A mass of 100 kg is resting on a rough inclined plane of 60o. If the coefficient of friction is 0.5, then the least force acting parallel to the plane to keep the mass in equilibrium is- a)605 N
- b)100 N
- c)500 N
- d)603.7 N
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A mass of 100 kg is resting on a rough inclined plane of 60o. If the coefficient of friction is 0.5, then the least force acting parallel to the plane to keep the mass in equilibrium is
a)
605 N
b)
100 N
c)
500 N
d)
603.7 N
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
The force parallel to the plane but downwards, W = mg.sin 60 = 980 x √3/2 = 848.7N
Maximum friction force acting, f = mg.cos 60 x 0.5 = 980 x ½ x 0.5 = 245N
Thus the minimum extra force required, let say F = 848.7 - 245 = 603.3 N
Maximum friction force acting, f = mg.cos 60 x 0.5 = 980 x ½ x 0.5 = 245N
Thus the minimum extra force required, let say F = 848.7 - 245 = 603.3 N
In the arrangement shown in fig. the ends P and Q of an unstretchable string move downwards with uniform speed U. Pulleys A and B are fixed. Mass M moves upwards with a speed. 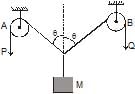
- a)2 U cos q
- b) U cos q
- c)
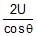
- d)
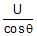
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the arrangement shown in fig. the ends P and Q of an unstretchable string move downwards with uniform speed U. Pulleys A and B are fixed. Mass M moves upwards with a speed.
a)
2 U cos q
b)
U cos q
c)
d)
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
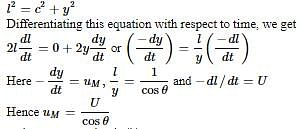
Thus option D is correct
A particle moves in the xy plane under the action of a force F such that the value of its linear momentum (P) at any time t is, Px = 2 cost, Py = 2 sint. The angle q between P and F at that time t will be -- a)0º
- b)30º
- c)90º
- d)180º
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle moves in the xy plane under the action of a force F such that the value of its linear momentum (P) at any time t is, Px = 2 cost, Py = 2 sint. The angle q between P and F at that time t will be -
a)
0º
b)
30º
c)
90º
d)
180º
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
Fx = dpx / dt = - 2sint
Fy = dpy / dt = 2cost
So angle between F and P will be 90º because we see that their dot product is zero.
Fy = dpy / dt = 2cost
So angle between F and P will be 90º because we see that their dot product is zero.
A block is placed on a rough floor and a horizontal force F is applied on it. The force of friction f by the floor on the block is measured for different values of F and a graph is plotted between them-- a) The graph is a straight line of slope 45°
- b)The graph is straight line parallel to the F axis
- c) The graph is a straight line of slope 45º for smal lF and a straight line parallel to the F-axis for large F.
- d) There is small kink on the graph
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A block is placed on a rough floor and a horizontal force F is applied on it. The force of friction f by the floor on the block is measured for different values of F and a graph is plotted between them-
a)
The graph is a straight line of slope 45°
b)
The graph is straight line parallel to the F axis
c)
The graph is a straight line of slope 45º for smal lF and a straight line parallel to the F-axis for large F.
d)
There is small kink on the graph
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
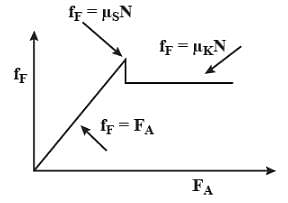
For a small value of the applied force the force of friction f increases linearly upto the limiting friction. When it crosses the maximum point of static friction then the friction force due to kinetic friction does not change any more.
If no resultant force acts on a body then the body will be in- a)rest
- b)motion
- c)earlier state (no change in state)
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If no resultant force acts on a body then the body will be in
a)
rest
b)
motion
c)
earlier state (no change in state)
d)
none of the above
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
What do you think about Newton's 1st law, he was said that " every body have nature to maintain inertia of rest or motion untill there is not net force applied on that body". means body will be earlier state (no change in state) when net force applied on that body equals zero.
I know, you thought answer is option (a). but this is not true. for better understanding, Let's take. an example. a body moves with uniform velocity then, net force applied on body = 0 because acceleration of body is zero . but here you see body is not in rest . it is in motion. it is in earlier state . its state doesn't change.
I know, you thought answer is option (a). but this is not true. for better understanding, Let's take. an example. a body moves with uniform velocity then, net force applied on body = 0 because acceleration of body is zero . but here you see body is not in rest . it is in motion. it is in earlier state . its state doesn't change.
A man weighs 70 kg. He stands on a weighing scale in a lift which is moving upwards with an acceleration of 5ms2.What would be the reading on the scale? (g=10 ms2)- a)1050 N
- b)1200 N
- c)220 N
- d)1000 N
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A man weighs 70 kg. He stands on a weighing scale in a lift which is moving upwards with an acceleration of 5ms2.What would be the reading on the scale? (g=10 ms2)
a)
1050 N
b)
1200 N
c)
220 N
d)
1000 N
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
As the moving elevator is a non inertial frame hence newton's laws can’t be applied directly to it. So to apply Newton's laws we need to add a pseudo force to the man's body equal to mass times the acceleration of lift in the opposite direction to that of acceleration. Thus the balancing normal force is equal to the weight of the man + mass times the acceleration which is,
Reading = Normal force = 700 + 70 x 5
= 700 + 350
= 1050 N
Reading = Normal force = 700 + 70 x 5
= 700 + 350
= 1050 N
Which of the following cannot be regarded as yet another kind of force?- a)centripetal force
- b)gravitational force
- c)electrostatic force
- d)magnetic force
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following cannot be regarded as yet another kind of force?
a)
centripetal force
b)
gravitational force
c)
electrostatic force
d)
magnetic force
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
if an object is moving in a horizontal circle at constant speed, the centripetal force does not do any work and cannot alter the total mechanical energy of the object. For the reason, the kinetic energy and therefore the speed of the object will remain constant.
Newton’s third law states that when two bodies interact.- a)they exert forces on each other that at each instant are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction
- b)they exert forces on each other that at each instant are equal in magnitude and same in direction
- c)they exert forces on each other that at some instants are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction
- d)they exert forces on each other that at some instants are equal in magnitude and same in direction
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Newton’s third law states that when two bodies interact.
a)
they exert forces on each other that at each instant are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction
b)
they exert forces on each other that at each instant are equal in magnitude and same in direction
c)
they exert forces on each other that at some instants are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction
d)
they exert forces on each other that at some instants are equal in magnitude and same in direction
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
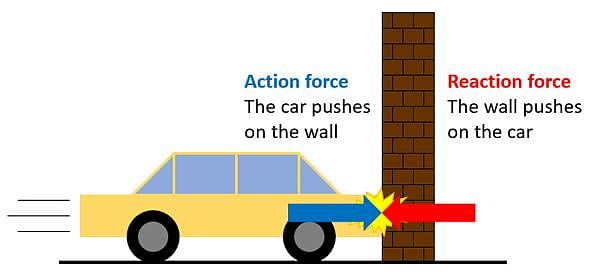
- The third law states that all forces between two objects exist in equal magnitude and opposite direction.
- If one object A exerts a force FA on a second object B, then B simultaneously exerts a force FB on A, and the two forces are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction, FA = −FB
- Newton's third Law:
What is the smallest radius of a circle at which a bicyclist can travel if his speed is 7 m/s and the coefficient of static friction between tyres and road is 0.25 - a)10 m
- b)20 m
- c)5 m
- d)15 m
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the smallest radius of a circle at which a bicyclist can travel if his speed is 7 m/s and the coefficient of static friction between tyres and road is 0.25
a)
10 m
b)
20 m
c)
5 m
d)
15 m
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Centripetal force = Frictional force
⇒ mv2/r=μmg
∴r=v2/μg
∴r=72/0.25×10
∴r=19.6 m≈20 m
⇒ mv2/r=μmg
∴r=v2/μg
∴r=72/0.25×10
∴r=19.6 m≈20 m
A man weighing 100kgf carries a load of 10kgf on his head. He jumps from tower with that load. What will be the weight of load experienced by the man.- a)0
- b)110 kgf
- c)10 kgf
- d)slightly more than 10kgf
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A man weighing 100kgf carries a load of 10kgf on his head. He jumps from tower with that load. What will be the weight of load experienced by the man.
a)
0
b)
110 kgf
c)
10 kgf
d)
slightly more than 10kgf
|
|
Jhanvi Chakraborty answered |
Weightlessness of Objects in Free Fall
Explanation:
When an object falls freely, it experiences weightlessness. This is because the object and the load on it are both accelerating towards the ground at the same rate due to gravity. Therefore, the object and the load on it will have the same weight as they would have if they were stationary on the ground.
In this case, the man is carrying a load of 10 kgf on his head and jumps from a tower. As he falls freely, both the man and the load on his head will experience weightlessness. Therefore, the weight of the load experienced by the man will be zero.
Answer:
The correct answer is option (a) 0.
Explanation:
When an object falls freely, it experiences weightlessness. This is because the object and the load on it are both accelerating towards the ground at the same rate due to gravity. Therefore, the object and the load on it will have the same weight as they would have if they were stationary on the ground.
In this case, the man is carrying a load of 10 kgf on his head and jumps from a tower. As he falls freely, both the man and the load on his head will experience weightlessness. Therefore, the weight of the load experienced by the man will be zero.
Answer:
The correct answer is option (a) 0.
A lift is moving down with the acceleration 3 m/s2. A ball is released 1.7 m above the the lift floor. How long will it take to hit the lift floor.- a)0.5s
- b)1.7s
- c)7.1s
- d)0.71s
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A lift is moving down with the acceleration 3 m/s2. A ball is released 1.7 m above the the lift floor. How long will it take to hit the lift floor.
a)
0.5s
b)
1.7s
c)
7.1s
d)
0.71s
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
Relative acceleration is,
a = 9.8 – 3 = 6.8 m/s2
Now, we have
S = ut + (1/2)at2
Here, u = 0 and S = 1.7 m
Therefore, t = 0.71 s
Find out the reading of the weighing machine in the following cases. 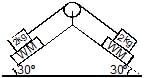
- a)
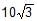
- b)
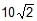
- c)
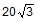
- d)
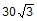
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Find out the reading of the weighing machine in the following cases.
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
N = mgcosФ
= 2 x 10 x cos30
= 2 x 10 x √3 / 2
= 10√3 N
= 2 x 10 x cos30
= 2 x 10 x √3 / 2
= 10√3 N
A block sliding along inclined plane as shown in figure. If the acceleration of chamber is ‘a’ as shown in the figure. The time required to cover a distance L along inclined plane is 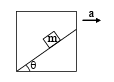
- a)
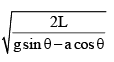
- b)
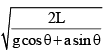
- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A block sliding along inclined plane as shown in figure. If the acceleration of chamber is ‘a’ as shown in the figure. The time required to cover a distance L along inclined plane is
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
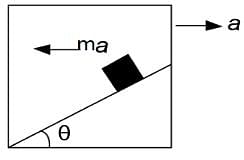
Applying pseudo force ma along the left direction of the block.
The net acceleration along the incline will be aeffective=acosθ+gsinθ
The time required will be L=0×t+½ aeffectivet2
⇒ √ 2L/ aeffective
⇒√ 2L /acosθ+gsinθ
In the above questions what is the weight of the suspended block ?- a)
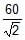 N
N - b)
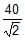 N
N - c)
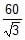 N
N - d)
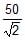 N
N
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In the above questions what is the weight of the suspended block ?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
The question is incomplete and is too vague to be found
It should be removed so as to not cause confusion.
It should be removed so as to not cause confusion.
A man of mass 70 kg stands on a weighing scale in a lift which is moving upwards with a uniform speed of 10 m s−1, what would be the reading on the scale?- a)105 kg
- b)75 kg
- c)70 kg
- d)35 kg
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A man of mass 70 kg stands on a weighing scale in a lift which is moving upwards with a uniform speed of 10 m s−1, what would be the reading on the scale?
a)
105 kg
b)
75 kg
c)
70 kg
d)
35 kg
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
Mass of the man, m = 70 kg
Acceleration, a = 0
Using Newton’s second law of motion, We can write the equation of motion as,
R – mg = ma
∴ R = mg = 70 × 10 = 700 N
∴ the weighing scale = 700 / g = 700 / 10 = 70 kg
Acceleration, a = 0
Using Newton’s second law of motion, We can write the equation of motion as,
R – mg = ma
∴ R = mg = 70 × 10 = 700 N
∴ the weighing scale = 700 / g = 700 / 10 = 70 kg
Passengers in a bus lean forward as bus suddenly stops. This is due to- a)Impulse
- b)Change in speed
- c)Inertia
- d)Change in momentum
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Passengers in a bus lean forward as bus suddenly stops. This is due to
a)
Impulse
b)
Change in speed
c)
Inertia
d)
Change in momentum
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
This is due to the presence of inertia.
When the bus moves, the passenger's body comes in the state of motion but when the bus stops the lower part of the body which is in contact with floor comes in the state of rest whereas the upper part of body still remains in the state of motion and because of this the upper part of the body falls in the forward direction.
Three blocks connected together lie on a horizontal frictionless table and pulled to the right with a force of F = 100 N. If m1 = 10 kg, m2 = 20 kg, m3 = 30kg. Then the tension T1 and T2 will be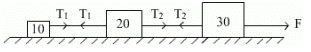
- a)T1 = 10 N, T2 = 50 N
- b)T1 = 16.66 N, T2 = 50 N
- c)T1 = 10 N, T2 = 20 N
- d)T1 = 10 N, T2 = 40 N
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Three blocks connected together lie on a horizontal frictionless table and pulled to the right with a force of F = 100 N. If m1 = 10 kg, m2 = 20 kg, m3 = 30kg. Then the tension T1 and T2 will be
a)
T1 = 10 N, T2 = 50 N
b)
T1 = 16.66 N, T2 = 50 N
c)
T1 = 10 N, T2 = 20 N
d)
T1 = 10 N, T2 = 40 N
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Considering the three block system, we have
100 = 60.a
where a is the common acceleration of all the blocks
a = 5/3 m/s2
Considering mass 1 we get,
T1 = 10 a
T1 = 50/3 N
Considering mass 1 and 2 we get,
T2 = 30 a
T2 = 50N
100 = 60.a
where a is the common acceleration of all the blocks
a = 5/3 m/s2
Considering mass 1 we get,
T1 = 10 a
T1 = 50/3 N
Considering mass 1 and 2 we get,
T2 = 30 a
T2 = 50N
A block is placed on the table. What is the angle between the action of the block on the table and reaction of the table on the block?
- a)90o
- b)300
- c)0o
- d)180o
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A block is placed on the table. What is the angle between the action of the block on the table and reaction of the table on the block?
a)
90o
b)
300
c)
0o
d)
180o
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
According to Newton's 3 rd law, every action and reaction have same magnitude and opposite direction. So the angle between them should be 180o.
Which of the following forces is not considered as a contact force in Mechanics?- a)Tensional force
- b)Gravitational force
- c)Viscous force
- d)Frictional force
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following forces is not considered as a contact force in Mechanics?
a)
Tensional force
b)
Gravitational force
c)
Viscous force
d)
Frictional force
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Gravitational force
The force exerted by the earth on a body is called gravitational force. Actually this force exists between any two bodies in the universe.This force is always of attraction. e.g. When a body is dropped from a height it moves in downward direction towards the Earth with increasing speed (with constant acceleration). This constant acceleration by which all bodies fall down is called acceleration due to gravity. Its value is 9.8 m/s' (approx 10 m/s' )on the surface of the earth. e.g. i) A fruit from tree falls down;ii) Water falls down on a ground from a tap.iii) We feel the weight of bucket full of water holding in our hand.
Force that produces an acceleration of 1 ms−2 in a body of mass of 1 kg is called- a)slow newton
- b)zero newton
- c)one newton
- d)two newton
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Force that produces an acceleration of 1 ms−2 in a body of mass of 1 kg is called
a)
slow newton
b)
zero newton
c)
one newton
d)
two newton
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
We know that F = ma, and for m = 1kg and a = 1m/s2
We get F = 1N which is one newton
We get F = 1N which is one newton
A mass M is suspended by a rope from a rigid support at A as shown in figure. Another rope is tied at the end B, and it is pulled horizontally with a force F. If the rope AB makes an angle q with the vertical in equilibrium, then the tension in the string AB is : 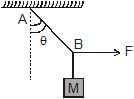
- a)F sin q
- b)F/sin q
- c)F cos q
- d)F/cos q
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A mass M is suspended by a rope from a rigid support at A as shown in figure. Another rope is tied at the end B, and it is pulled horizontally with a force F. If the rope AB makes an angle q with the vertical in equilibrium, then the tension in the string AB is :
a)
F sin q
b)
F/sin q
c)
F cos q
d)
F/cos q
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
As the block is still at the equilibrium, we get
T.cos q = mg
T.sin q = F
Thus we T = F / sin q
T.cos q = mg
T.sin q = F
Thus we T = F / sin q
A block of mass 2 kg is placed on the floor. The coefficient of static friction is 0.4. If a force of 2.8 N is applied on the block parallel to floor, the force of friction between the block and floor is (Take g = 10 m/s2) - a)2.8 N
- b)8 N
- c)2 N
- d)zero
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A block of mass 2 kg is placed on the floor. The coefficient of static friction is 0.4. If a force of 2.8 N is applied on the block parallel to floor, the force of friction between the block and floor is (Take g = 10 m/s2)
a)
2.8 N
b)
8 N
c)
2 N
d)
zero
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Weight of the block is 20N thus maximum friction that can act is 0.4 x 20 = 8N
But as the external force acting, F = 2.8N < 8N,
We get f = F = 2.8N
But as the external force acting, F = 2.8N < 8N,
We get f = F = 2.8N
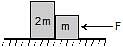
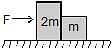
Two blocks are in contact on a frictionless table. One has mass m and the other 2m. A force F is applied on 2m as shown in the figure. Now the same force F is applied from the right on m. In the two cases respectively, the ratio force of contact between the two block will be :
- a) Same
- b)1 : 2
- c) 2 : 1
- d)1 : 3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Two blocks are in contact on a frictionless table. One has mass m and the other 2m. A force F is applied on 2m as shown in the figure. Now the same force F is applied from the right on m. In the two cases respectively, the ratio force of contact between the two block will be :
a)
Same
b)
1 : 2
c)
2 : 1
d)
1 : 3
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |


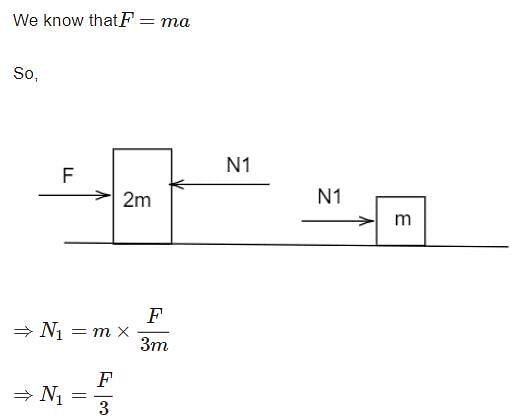
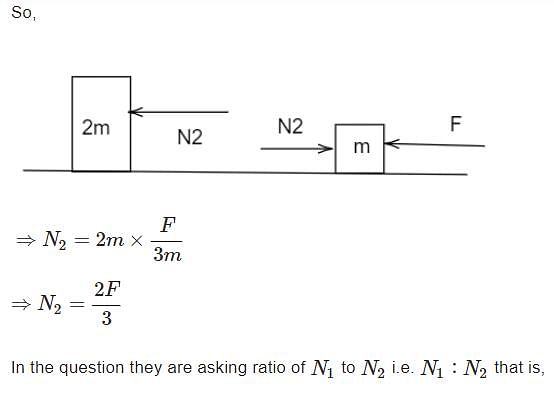

Three block are connected as shown, on a horizontal frictionless table and pulled to the right with a force T3 = 60 N. If m1 = 10 kg, m2 = 20 kg and m3 = 30 kg, the tension T2 is-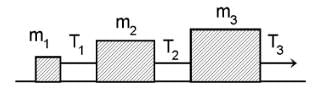
- a)10 N
- b)20 N
- c)30 N
- d)60 N
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Three block are connected as shown, on a horizontal frictionless table and pulled to the right with a force T3 = 60 N. If m1 = 10 kg, m2 = 20 kg and m3 = 30 kg, the tension T2 is-

a)
10 N
b)
20 N
c)
30 N
d)
60 N
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Let a be the acceleration of the system.
T1 = M1a .....(1)
T2 − T1 = M2a ....(2)
F − T2 = M3a ......(3)
Adding (1), (2) and (3) we get
(M1 + M2 + M3)a = F
or (10+20+30)a = 60
⇒ a = 1m/s2
Now , T2 = (M1+M2)a
⇒ (10+20)(1) = 30N
T1 = M1a .....(1)
T2 − T1 = M2a ....(2)
F − T2 = M3a ......(3)
Adding (1), (2) and (3) we get
(M1 + M2 + M3)a = F
or (10+20+30)a = 60
⇒ a = 1m/s2
Now , T2 = (M1+M2)a
⇒ (10+20)(1) = 30N
A mass of 6 kg is suspended by a rope of length 2 m from a ceiling. A force of 50 N in the horizontal direction is applied at the mid-point of the rope, as shown. What is the angle the rope makes with the vertical in equilibrium?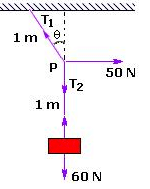
- a)60o
- b)40o
- c)50o
- d)30o
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A mass of 6 kg is suspended by a rope of length 2 m from a ceiling. A force of 50 N in the horizontal direction is applied at the mid-point of the rope, as shown. What is the angle the rope makes with the vertical in equilibrium?
a)
60o
b)
40o
c)
50o
d)
30o

|
Sushil Kumar answered |
Making the free body diagram of the body we get
T1.cosθ = T2 = mg = 60
T1.sinθ = 50N
By dividing the above two equations we get
tanθ = 5/6
Thus we get θ = 40°
T1.cosθ = T2 = mg = 60
T1.sinθ = 50N
By dividing the above two equations we get
tanθ = 5/6
Thus we get θ = 40°
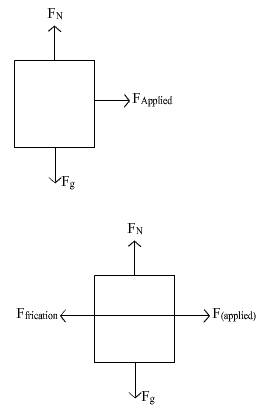
A person is sliding an iron box across the floor. Its free body diagram will be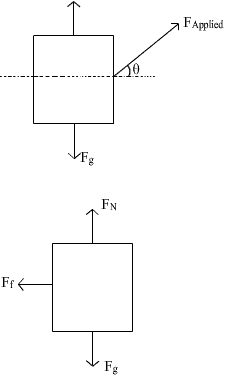
- a)A
- b)B
- c)C
- d)D
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A person is sliding an iron box across the floor. Its free body diagram will be
a)
A
b)
B
c)
C
d)
D
|
|
Om Desai answered |
In the given condition, we get that a component of applied force acts parallel to force rightwards and one is perpendicular. Also the weight, normal and friction (leftwards) would also act upon it
Hence the correct Ans is D.
Hence the correct Ans is D.
Velocity-time graph of the particle is- a)
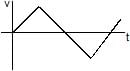
- b)

- c)
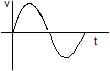
- d)

Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Velocity-time graph of the particle is
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
In the velocity time graph, the slope value should give the value of acceleration.
A particle of mass M, originally at rest is subjected to a force whose direction is constant but whose magnitude varies with the time according to the relation
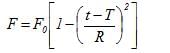
where F0 and T are constant. The force acts only for the time interval 2T. Find the velocity v of the particle after time 2T.
- a)F0/3M
- b)4F0/3M
- c)F0/2M
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle of mass M, originally at rest is subjected to a force whose direction is constant but whose magnitude varies with the time according to the relation
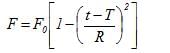
where F0 and T are constant. The force acts only for the time interval 2T. Find the velocity v of the particle after time 2T.
where F0 and T are constant. The force acts only for the time interval 2T. Find the velocity v of the particle after time 2T.
a)
F0/3M
b)
4F0/3M
c)
F0/2M
d)
none of the above

|
R L Sharma answered |
I think this statement is said by Aristotle as every body is in the natural state of rest. and it get in the state of motion ony when some external force is applied on it.
Two bodies of mass 6 kg and 4 kg are tied to a string as shown in the adjoining figure. If the table is smooth and pulley frictionless, then acceleration of mass 6 kg will be (g = 10 m/s2)
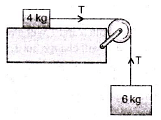
- a)60 m/s2
- b)40 m/s2
- c)6 m/s2
- d)4 m/s2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Two bodies of mass 6 kg and 4 kg are tied to a string as shown in the adjoining figure. If the table is smooth and pulley frictionless, then acceleration of mass 6 kg will be (g = 10 m/s2)
a)
60 m/s2
b)
40 m/s2
c)
6 m/s2
d)
4 m/s2
|
|
Ananya Singh answered |

Chapter doubts & questions for Laws of Motion - Science for ACT 2025 is part of ACT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Laws of Motion - Science for ACT in English & Hindi are available as part of ACT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for ACT Exam by signing up for free.
Science for ACT
486 videos|517 docs|337 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup