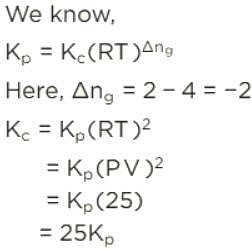All Exams >
ACT >
Chemistry for ACT >
All Questions
All questions of Equilibrium for ACT Exam
Ca(HCO3)2 is strongly heated and after equilibrium is attained, temperature changed to 25° C.
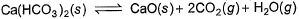
Kp = 36 (pressure taken in atm)
Thus, pressure set up due to CO2 is- a)36 atm
- b)18 atm
- c)12 atm
- d)6 atm
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Ca(HCO3)2 is strongly heated and after equilibrium is attained, temperature changed to 25° C.
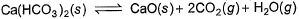
Kp = 36 (pressure taken in atm)
Thus, pressure set up due to CO2 is
Kp = 36 (pressure taken in atm)
Thus, pressure set up due to CO2 is
a)
36 atm
b)
18 atm
c)
12 atm
d)
6 atm
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
The reaction is as follow:-
Ca(HCO3)2(s)⇌CaO(s) + 2CO2 (g) + H2O(g)
At 25° C H2O goes in liquid state
Kp = (PCaO)1×(PCO2)2
(PCa(HCO3)2)
Since, Ca(HCO3)2, CaO and H2O are not in gaseous state, so their partial pressure is taken 1.
Putting all values, we have
36 = (PCO2)2
Or PCO2 = 6 atm
Ca(HCO3)2(s)⇌CaO(s) + 2CO2 (g) + H2O(g)
At 25° C H2O goes in liquid state
Kp = (PCaO)1×(PCO2)2
(PCa(HCO3)2)
Since, Ca(HCO3)2, CaO and H2O are not in gaseous state, so their partial pressure is taken 1.
Putting all values, we have
36 = (PCO2)2
Or PCO2 = 6 atm
Rate of reaction is proportional to product of molar concentration of reactants with each concentration term raised to power its stoichiometric coefficient. This is the law of- a)Equilibrium
- b)Mass action
- c)Constant proportion
- d)Reciprocal proportions
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Rate of reaction is proportional to product of molar concentration of reactants with each concentration term raised to power its stoichiometric coefficient. This is the law of
a)
Equilibrium
b)
Mass action
c)
Constant proportion
d)
Reciprocal proportions
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Law of mass action states that the rate of reaction is proportional to the product of molar concentration of reactant with each concentration term raised to power its stoichiometric coefficient.
Graphite is added to a vessel that contains CO2(g) at a pressure of 0.830 atm at a certain high temperature. The pressure rises due to a reaction that produces CO (g). The total pressure reaches an equilibrium value of 1.366 atm. Calculate the equilibrium constant of the following reaction.
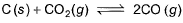
- a)2.909 atm
- b)6.909 atm
- c)4.909 atm
- d)3.909 atm
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Graphite is added to a vessel that contains CO2(g) at a pressure of 0.830 atm at a certain high temperature. The pressure rises due to a reaction that produces CO (g). The total pressure reaches an equilibrium value of 1.366 atm. Calculate the equilibrium constant of the following reaction.
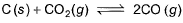
a)
2.909 atm
b)
6.909 atm
c)
4.909 atm
d)
3.909 atm
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |

Which of the following is not a general characteristic of equilibria involving physical processes?- a)Equilibrium is possible only in a closed system at a given temperature.
- b)All measurable properties of the system remain constant.
- c)All the physical processes stop at equilibrium.
- d)The opposing processes occur at the same rate and there is dynamic but stable condition.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a general characteristic of equilibria involving physical processes?
a)
Equilibrium is possible only in a closed system at a given temperature.
b)
All measurable properties of the system remain constant.
c)
All the physical processes stop at equilibrium.
d)
The opposing processes occur at the same rate and there is dynamic but stable condition.
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
All the physical processes like melting of ice and freezing of water, etc., do not stop at equilibrium.
Assume following equilibria when total pressure set up in each are equal to 1 atm, and equilibrium constant (Kp) as K1; K2 and K3
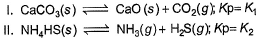
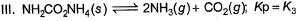
Thus,- a) K1 = K2 = K3
- b)K1 < K2 < K3
- c)K3 < K2 < K1
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assume following equilibria when total pressure set up in each are equal to 1 atm, and equilibrium constant (Kp) as K1; K2 and K3
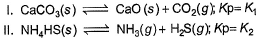
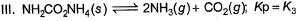
Thus,
Thus,
a)
K1 = K2 = K3
b)
K1 < K2 < K3
c)
K3 < K2 < K1
d)
None of these
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
The correct answer is option C
CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
Kp = k1 = Pco2
total pressure of container P
k1 = p
NH4HS → NH3 + H2S
PNH3 = PH2S = P0
P0 + P0 = p (total pressure)
P0 = p/2
k2 = kp = [PNH3][PH2s] p24
NH2CoNH2 → 2NH3 + CO2
PNH3 = 2P0 PCO2 = P0
2P0 + P0 = P
CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
Kp = k1 = Pco2
total pressure of container P
k1 = p
NH4HS → NH3 + H2S
PNH3 = PH2S = P0
P0 + P0 = p (total pressure)
P0 = p/2
k2 = kp = [PNH3][PH2s] p24
NH2CoNH2 → 2NH3 + CO2
PNH3 = 2P0 PCO2 = P0
2P0 + P0 = P
Following equilibrium is set up at 1000 K and 1 bar in a 5 L flask,
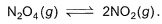
At equilibrium, NO2 is 50% o f the total volume. Thus, equilibrium constant Kc is - a)0.133
- b)0.266
- c)0.200
- d)0.400
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Following equilibrium is set up at 1000 K and 1 bar in a 5 L flask,
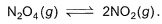
At equilibrium, NO2 is 50% o f the total volume. Thus, equilibrium constant Kc is
At equilibrium, NO2 is 50% o f the total volume. Thus, equilibrium constant Kc is
a)
0.133
b)
0.266
c)
0.200
d)
0.400
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
The correct answer is Option A.
N2O4 ⇌ 2NO2
Initial 1 0
Equilibrium 1−x 2x
N2O4 ⇌ 2NO2
Initial 1 0
Equilibrium 1−x 2x
Total moles = 1 - x + 2x
NO2 is 50% of the total volume when equilibrium is set up.
Thus, the volume fraction (at equilibrium) of NO2 = 50/100 = 0.5 = ½
So, 2x / (1+x) = ½
=> x = ⅓
Thus, the volume fraction (at equilibrium) of NO2 = 50/100 = 0.5 = ½
So, 2x / (1+x) = ½
=> x = ⅓
For 1 litre;
Kc = [NO2] / [N2O4]
= [4*(1/9)] / [⅔]
= 0.66;
Kc = [NO2] / [N2O4]
= [4*(1/9)] / [⅔]
= 0.66;
For 5 litres;
Kc = 0.66 / 5
= 0.133
Thus, option A is correct.
Kc = 0.66 / 5
= 0.133
Thus, option A is correct.
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.Q. Vapour pressure of NH4HS (s)is 20 mm at 25°C, for
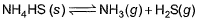
Total pressure when NH4HS (s) dissociates at 25°Cin a vessel which already contains H2S (g)at a pressure of 15 mm, is- a)25 mm
- b)50 mm
- c)5 mm
- d)10 mm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Vapour pressure of NH4HS (s)is 20 mm at 25°C, for
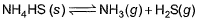
Total pressure when NH4HS (s) dissociates at 25°Cin a vessel which already contains H2S (g)at a pressure of 15 mm, is
Total pressure when NH4HS (s) dissociates at 25°Cin a vessel which already contains H2S (g)at a pressure of 15 mm, is
a)
25 mm
b)
50 mm
c)
5 mm
d)
10 mm
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The correct answer is Option A.
NH4HS -------> NH3 + H2S
Let P be the pressure at eq. of NH3 and H2S.
Therefore, Kp = P2
= (20 / 2)2
= 100 mm
= 100
Also, Kp = (15 + P) (P)
100 = 15 P + P2
P2 + 15 P – 100 = 0
P = 5
Total pressure = 15 + 2(P)
= 15 + 2(5)
= 25 mm
NH4HS -------> NH3 + H2S
Let P be the pressure at eq. of NH3 and H2S.
Therefore, Kp = P2
= (20 / 2)2
= 100 mm
= 100
Also, Kp = (15 + P) (P)
100 = 15 P + P2
P2 + 15 P – 100 = 0
P = 5
Total pressure = 15 + 2(P)
= 15 + 2(5)
= 25 mm
Passage IIThe complex ion of Fe2+ with the chelating agent dipyridyl (abbreviated dipy) has been studied kinetically in both the forward and backward directions. For the complexion reaction,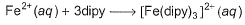
the rate of the formation of the complex at 298 K is given by rate = (1. 45 x 1013 L3mol -3s-1) [Fe 2+] [dipy]3 and for the reverse reaction , the rate of disapperance of the complex is
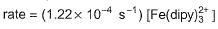 Q. What is equilibrium constant for the equilibrium ?
Q. What is equilibrium constant for the equilibrium ? 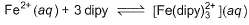
- a)8.4138x 10-18
- b)2.3770x 1017
- c)1.1885x 1017
- d)5.9426x 106
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage II
The complex ion of Fe2+ with the chelating agent dipyridyl (abbreviated dipy) has been studied kinetically in both the forward and backward directions. For the complexion reaction,
the rate of the formation of the complex at 298 K is given by rate = (1. 45 x 1013 L3mol -3s-1) [Fe 2+] [dipy]3 and for the reverse reaction , the rate of disapperance of the complex is
Q. What is equilibrium constant for the equilibrium ?
a)
8.4138x 10-18
b)
2.3770x 1017
c)
1.1885x 1017
d)
5.9426x 106
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
The correct answer is Option C.
Fe2+ + 3 dipy -----> Fe(dipy)32+
Rf = Kf [Fe2+] [dipy]3
Rb = Kb [Fe(dipy)32+]
Keq = Kb [Fe(dipy)32+] / Kf [Fe2+] [dipy]3
Rf = Rb
Keq = Kf / Kb
= 1. 45 x 1013 / 1.24 x 10-4
= 1.885 x 1017
Fe2+ + 3 dipy -----> Fe(dipy)32+
Rf = Kf [Fe2+] [dipy]3
Rb = Kb [Fe(dipy)32+]
Keq = Kb [Fe(dipy)32+] / Kf [Fe2+] [dipy]3
Rf = Rb
Keq = Kf / Kb
= 1. 45 x 1013 / 1.24 x 10-4
= 1.885 x 1017
Following equilibrium is set up at 298 K in a 1 L flask.
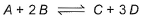
If one starts with 2 moles of A and 1 mole of B, it is found that moles of B and D are equal.Thus Kc is - a)9.0
- b)15.0
- c)3.0
- d)0.0667
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Following equilibrium is set up at 298 K in a 1 L flask.
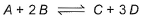
If one starts with 2 moles of A and 1 mole of B, it is found that moles of B and D are equal.Thus Kc is
If one starts with 2 moles of A and 1 mole of B, it is found that moles of B and D are equal.Thus Kc is
a)
9.0
b)
15.0
c)
3.0
d)
0.0667
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
For the equilibrium reaction:
A+2B ⇌ 2C+D
volume of flask = 1L
Initial moles of A = 2 mol
initial concentration of A=[A]i = 2 M
initial mole of B = 1 mol
[B]i = 1 M
[A]eq = 2-x, [B]eq = 1-2x, [C]eq = x, [D]eq = 3x
Given [D]eq = 1 * 1L
= 1 M
Thus x = 1M
[A]eq = 1, [B]eq = -1, [C]eq = 1, [D] = 3
Kc = {([D]eq)3 * ([C]eq)}/{[A]eq * ([B]eq)2}
= Kc = {(3)3*1}/{1*(-1)2}
= 27/1
= 27
A+2B ⇌ 2C+D
volume of flask = 1L
Initial moles of A = 2 mol
initial concentration of A=[A]i = 2 M
initial mole of B = 1 mol
[B]i = 1 M
[A]eq = 2-x, [B]eq = 1-2x, [C]eq = x, [D]eq = 3x
Given [D]eq = 1 * 1L
= 1 M
Thus x = 1M
[A]eq = 1, [B]eq = -1, [C]eq = 1, [D] = 3
Kc = {([D]eq)3 * ([C]eq)}/{[A]eq * ([B]eq)2}
= Kc = {(3)3*1}/{1*(-1)2}
= 27/1
= 27
In which of the following reaction can equilibrium be attained- a)Reversible reaction
- b)Cyclic reaction
- c)Decomposition reaction
- d)Irreversible reaction
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following reaction can equilibrium be attained
a)
Reversible reaction
b)
Cyclic reaction
c)
Decomposition reaction
d)
Irreversible reaction
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Reversible Reaction
The common observation for any reactions when they are reacted in closed containers would not go to completion, for some given conditions like temperature and pressure.
For all those cases, only the reactants are found to be present in the intial stages, but with the progress of reaction, the reactants concentration decreases and to that of the products increases. A stage is finally reached where there is no more change of reactants and products concentration is observed. The state where the reactants and products concentrations do not show any visible change within a given period of time is better known as the state of chemical equilibrium.
The reactant amount that remains unused depends upon the experimental conditions like concentration of components, temperature of the system, pressure of the system and the reaction nature.
At 1000 K, pressure of CO2 in equilibrium with CaCO3 and CaO is equal to 2.105 atm. The equilibrium constant for the reaction,
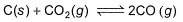
is 1.9 at the same temperature when pressure are in atm. Solid C, CaO, and CaCO3 are mixed and allowed to come to equilibrium at 1000 K in a closed vessel.Q. What is the pressure of CO (g)at equilibrium (in atm)?
Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?
At 1000 K, pressure of CO2 in equilibrium with CaCO3 and CaO is equal to 2.105 atm. The equilibrium constant for the reaction,
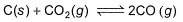
is 1.9 at the same temperature when pressure are in atm. Solid C, CaO, and CaCO3 are mixed and allowed to come to equilibrium at 1000 K in a closed vessel.
is 1.9 at the same temperature when pressure are in atm. Solid C, CaO, and CaCO3 are mixed and allowed to come to equilibrium at 1000 K in a closed vessel.
Q. What is the pressure of CO (g)at equilibrium (in atm)?
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
K= (partial pressure of co2/(partial pressure of co2)
since k =1.9
So 1.9 = (partial pressure of co)2/2.105
(partial pressure of co)2 =2.105×1.9
= 3.99 = 4
(partial pressure of co) =2
since k =1.9
So 1.9 = (partial pressure of co)2/2.105
(partial pressure of co)2 =2.105×1.9
= 3.99 = 4
(partial pressure of co) =2
Ca(HCO3)2 decomposes as,
Ca (HCO3)2(s) ⇌ CaCO3(s) + H2O(g) + CO2(g)
Equilibrium pressure is found to be 0.12 bar. What is pco2 if the reaction mixture also contains H2O(g)at 0.20 bar?
- a) 0.20 bar
- b) 0.017 ba
- c)0.040 bar
- d)0.10 bar
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Ca(HCO3)2 decomposes as,
Ca (HCO3)2(s) ⇌ CaCO3(s) + H2O(g) + CO2(g)
Equilibrium pressure is found to be 0.12 bar. What is pco2 if the reaction mixture also contains H2O(g)at 0.20 bar?
Equilibrium pressure is found to be 0.12 bar. What is pco2 if the reaction mixture also contains H2O(g)at 0.20 bar?
a)
0.20 bar
b)
0.017 ba
c)
0.040 bar
d)
0.10 bar
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |

For the following gaseous phase equilibrium,
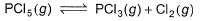
Kp is found to be equal to Kx (Kx is equilibrium constant when concentration are taken in terms of mole fraction. This is attained when pressure is - a)1 atm
- b)0.5 atm
- c)2 atm
- d)4 atm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For the following gaseous phase equilibrium,
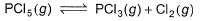
Kp is found to be equal to Kx (Kx is equilibrium constant when concentration are taken in terms of mole fraction. This is attained when pressure is
Kp is found to be equal to Kx (Kx is equilibrium constant when concentration are taken in terms of mole fraction. This is attained when pressure is
a)
1 atm
b)
0.5 atm
c)
2 atm
d)
4 atm
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The correct answer is Option A.
Kp = Equilibrium constant in terms of partial pressure
Kc = Equilibrium constant in terms of concentration
Kx = Equilibrium constant in terms of mole fraction
Kp = KcRTΔn ---(1)
Kp = K * (Pt)Δn ---(2)
a) 1 atm
Given PCl5 (g) ---> PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g)
Δn = 2 – 1
Given Kp = Kx
From (2)
Kp = Kx when PT = 1
Kp = Equilibrium constant in terms of partial pressure
Kc = Equilibrium constant in terms of concentration
Kx = Equilibrium constant in terms of mole fraction
Kp = KcRTΔn ---(1)
Kp = K * (Pt)Δn ---(2)
a) 1 atm
Given PCl5 (g) ---> PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g)
Δn = 2 – 1
Given Kp = Kx
From (2)
Kp = Kx when PT = 1
Variation of log Kp with temperature. 1/T is given by for the equilibrium.
NH4HS (s)  NH3(g) + H2S
NH3(g) + H2S
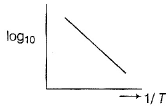 Q. The equilibrium is displaced in forward side on
Q. The equilibrium is displaced in forward side on- a)increasing temperature and decreasing pressure
- b)increasing temperature and pressure both
- c)decreasing temperature and pressure both
- d)decreasing temperature and increasing pressure
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Variation of log Kp with temperature. 1/T is given by for the equilibrium.
NH4HS (s)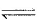 NH3(g) + H2S
NH3(g) + H2S

NH4HS (s)
Q. The equilibrium is displaced in forward side on
a)
increasing temperature and decreasing pressure
b)
increasing temperature and pressure both
c)
decreasing temperature and pressure both
d)
decreasing temperature and increasing pressure

|
Vinod Kumar answered |
This graph indicates option A is correct answer
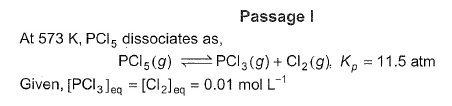 Q. What is [PCI5] eq?
Q. What is [PCI5] eq?- a)4.09 x 10-4 mol L-1
- b)2.444 x 103 mol L-1
- c)4.09 x 10-6 mol L-1
- d)2.444 x 105 mol L-1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Q. What is [PCI5] eq?
a)
4.09 x 10-4 mol L-1
b)
2.444 x 103 mol L-1
c)
4.09 x 10-6 mol L-1
d)
2.444 x 105 mol L-1
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
The correct answer is Option A.
PPCl3 = [PCl3]RT
PCl2 = [Cl2]RT

PPCl3 = [PCl3]RT
PCl2 = [Cl2]RT

We know that the relationship between Kc and Kp is Kp = Kc (RT)Δn
What would be the value of Δn for the reaction NH4Cl (s) ⇔ NH3 (g) + HCl (g)
a)1b)0.5c)1.5d)2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
The answer is d.
The relationship between Kp and Kc is
The relationship between Kp and Kc is
Kp = Kc (RT) ∆n
Where ∆n = (number of moles of gaseous products) – (number of moles of gaseous reactants)
For the reaction,
NH4C1(s) ⇆ NH3(g) + HCl(g)
∆n = 2 – 0 = 2
H2O (l) 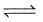 H2O(s) ; ΔH = -qApplication of pressure on this equilibrium
H2O(s) ; ΔH = -qApplication of pressure on this equilibrium- a)cause formation of more ice
- b)cause fusion of ice
- c)has no effect
- d)lower the melting point
Correct answer is option 'B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
H2O (l) 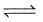 H2O(s) ; ΔH = -q
H2O(s) ; ΔH = -q
 H2O(s) ; ΔH = -q
H2O(s) ; ΔH = -qApplication of pressure on this equilibrium
a)
cause formation of more ice
b)
cause fusion of ice
c)
has no effect
d)
lower the melting point
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The correct answers are Options B and D.
As we know that reaction is exothermic it means heat is released in the reaction so, if we apply pressure then reaction will proceed in backward direction but if there is gas phase equilibrium the reaction will shift in that direction in which less number of moles are present. If pressure increases then the ice will melt and ice gets more energy at low temp. To melt ,so it’s melting point decreases.
As we know that reaction is exothermic it means heat is released in the reaction so, if we apply pressure then reaction will proceed in backward direction but if there is gas phase equilibrium the reaction will shift in that direction in which less number of moles are present. If pressure increases then the ice will melt and ice gets more energy at low temp. To melt ,so it’s melting point decreases.
For the reversible reaction, 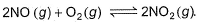
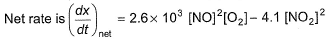
In a reaction vessel, [NO]= [O2]= 0.01 mol L-1 and [NO2]= 0.1 mol L-1 then above reaction is - a)shifted in forward direction
- b)shifted in backward direction
- c)in equilibrium
- d)not predictable in the absence of required data
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For the reversible reaction, 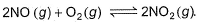
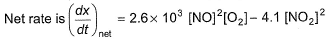
In a reaction vessel, [NO]= [O2]= 0.01 mol L-1 and [NO2]= 0.1 mol L-1 then above reaction is
In a reaction vessel, [NO]= [O2]= 0.01 mol L-1 and [NO2]= 0.1 mol L-1 then above reaction is
a)
shifted in forward direction
b)
shifted in backward direction
c)
in equilibrium
d)
not predictable in the absence of required data
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
On substituting the values of conc. of NO, O2 and NO2 in given rate equation, we get a +ve (positive) value indicating that the reaction takes place in forward direction.
Passage ISolid ammonium chloride is in equilibrium with ammonia and hydrogen chloride gases
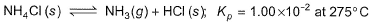
0.980 g of solid NH4CI is taken in a closed vessel of 1 L capacity and heated to 275° C.Q. Percentage decomposition of the original sample is- a)24.81%
- b)6.24%
- c)3.12%
- d)12.13%
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage I
Solid ammonium chloride is in equilibrium with ammonia and hydrogen chloride gases
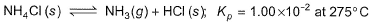
0.980 g of solid NH4CI is taken in a closed vessel of 1 L capacity and heated to 275° C.
0.980 g of solid NH4CI is taken in a closed vessel of 1 L capacity and heated to 275° C.
Q. Percentage decomposition of the original sample is
a)
24.81%
b)
6.24%
c)
3.12%
d)
12.13%

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
The state of HCl is given wrong. It will be in gaseous state.
So, the reaction be like;-
NH4Cl(s) ⇌ NH3(g) + HCl(g) kp = 1.00×10-2 at 275° C
Kp = kc(RT)2
1.00×10-2 = kc(0.0821×548)2
Or kc = 4.94×10-6
NH4Cl(s) ⇌ NH3(g) + HCl(g)
Initial 1 - -
At eqm 1-x x x
Kc = x2
x = √(4.94×10-6)
= 2.22×10-3
Therefore, NH4Cl dissociated at eqm = 2.22×10-3 × 53.5 = 0.118
%age decomposition = 0.118/0.980×100 = 12.13%
So, the reaction be like;-
NH4Cl(s) ⇌ NH3(g) + HCl(g) kp = 1.00×10-2 at 275° C
Kp = kc(RT)2
1.00×10-2 = kc(0.0821×548)2
Or kc = 4.94×10-6
NH4Cl(s) ⇌ NH3(g) + HCl(g)
Initial 1 - -
At eqm 1-x x x
Kc = x2
x = √(4.94×10-6)
= 2.22×10-3
Therefore, NH4Cl dissociated at eqm = 2.22×10-3 × 53.5 = 0.118
%age decomposition = 0.118/0.980×100 = 12.13%
For the following electrochemical cell reaction at 298 K,
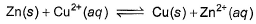
E°cell = 1.10 V
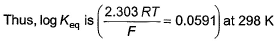
- a)0.027
- b)37.22
- c)0.012
- d)85.73
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For the following electrochemical cell reaction at 298 K,
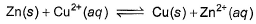
E°cell = 1.10 V
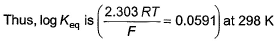
E°cell = 1.10 V
a)
0.027
b)
37.22
c)
0.012
d)
85.73
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) ⇌ Cu(s) + Zn2+(aq),
Eo = +1.10V
∴ Eo = 0.0591/n log10Keq
Eo = +1.10V
∴ Eo = 0.0591/n log10Keq
because at equilibrium,
Ecell = 0
(n = number of electrons exchanged = 2)
1.10 = 0.0591/2 log10Keq
2.20/0.0591 = log10Keq
(n = number of electrons exchanged = 2)
1.10 = 0.0591/2 log10Keq
2.20/0.0591 = log10Keq
Keq = antilog37.225
Kc forthe decomposition of NH4HS(s) is 1.8x 10-4 at 25°C.
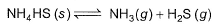
If the system already contains [NH3] = 0.020 M, then when equilibrium is reached, molar concentration are
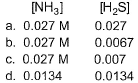
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Kc forthe decomposition of NH4HS(s) is 1.8x 10-4 at 25°C.
If the system already contains [NH3] = 0.020 M, then when equilibrium is reached, molar concentration are

If the system already contains [NH3] = 0.020 M, then when equilibrium is reached, molar concentration are
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
NH4HS (s) ⇋ NH3 (g) + H2S (g)
Initial 1 - -
At eqm 1-x x+0.02 x
Kc = [NH3][H2S] (Since NH4HS is solid, we ignore it.)
1.8×10-4 = (x+0.02)(x)
x2+0.02x-1.8×10-4 = 0
Applying quadratic formula; x = -0.02+√{(0.02)2-4×1.8×10-4}
= 0.033-0.020/2 = 0.0065
Therefore, concn of NH3 at equilibrium = x+0.020 = 0.0265
concn of H2S at equilibrium = x = 0.0065
So, option b is correct
Initial 1 - -
At eqm 1-x x+0.02 x
Kc = [NH3][H2S] (Since NH4HS is solid, we ignore it.)
1.8×10-4 = (x+0.02)(x)
x2+0.02x-1.8×10-4 = 0
Applying quadratic formula; x = -0.02+√{(0.02)2-4×1.8×10-4}
= 0.033-0.020/2 = 0.0065
Therefore, concn of NH3 at equilibrium = x+0.020 = 0.0265
concn of H2S at equilibrium = x = 0.0065
So, option b is correct
Ag+(aq)+NH3(aq)  [Ag(NH3)(aq)]+ ; K, = 3.5x 10-3
[Ag(NH3)(aq)]+ ; K, = 3.5x 10-3
[Ag(NH3)]+ (aq)+NH3(aq)  [Ag(NH3)2]2+(aq); K2 = 1.7x 10-3
[Ag(NH3)2]2+(aq); K2 = 1.7x 10-3
Formation constant of [Ag(NH3)2]+(aq) is- a)2.06
- b)5.2 x 10-3
- c)5.95 x 10-6
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Ag+(aq)+NH3(aq) 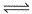 [Ag(NH3)(aq)]+ ; K, = 3.5x 10-3
[Ag(NH3)(aq)]+ ; K, = 3.5x 10-3
[Ag(NH3)]+ (aq)+NH3(aq)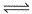 [Ag(NH3)2]2+(aq); K2 = 1.7x 10-3
[Ag(NH3)2]2+(aq); K2 = 1.7x 10-3
Formation constant of [Ag(NH3)2]+(aq) is
[Ag(NH3)]+ (aq)+NH3(aq)
Formation constant of [Ag(NH3)2]+(aq) is
a)
2.06
b)
5.2 x 10-3
c)
5.95 x 10-6
d)
None of these
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The correct answer is Option C.
To get the formation constant add both reactions-
So the resultant K = K1 × K2
= 3.5×1.7×10−3
= 5.95×10−6
To get the formation constant add both reactions-
So the resultant K = K1 × K2
= 3.5×1.7×10−3
= 5.95×10−6
Consider the following equilibrium in a closed container
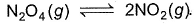 At a fixed temperature, the volume of a reaction container is halved. For this change, which of the following statements holds true regarding the equilibrium constant (Kp) and degree of dissociation (α) ?
At a fixed temperature, the volume of a reaction container is halved. For this change, which of the following statements holds true regarding the equilibrium constant (Kp) and degree of dissociation (α) ?- a)Neither Kp nor α change
- b)Both Kp and α change
- c)Kp changes but α does not change
- d)Kp does not change but α changes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following equilibrium in a closed container
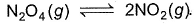
At a fixed temperature, the volume of a reaction container is halved. For this change, which of the following statements holds true regarding the equilibrium constant (Kp) and degree of dissociation (α) ?
a)
Neither Kp nor α change
b)
Both Kp and α change
c)
Kp changes but α does not change
d)
Kp does not change but α changes
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
We know that Kp depends only on Temperature. As the temp. remains constant , Kp also remains constant.
α depends on the concentration of the reactant
So as the volume of the reaction container is halved, α also changes
So option d is correct.
α depends on the concentration of the reactant
So as the volume of the reaction container is halved, α also changes
So option d is correct.
The equilibrium constant for the following reaction, is 1.6 x 105 at 1024 K.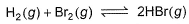
HBr (g)at 10.0 bar is introduced into a sealed container at 1024 K. Thus, partial pressure of H2(g)and Br2(g), together is- a)10 bar
- b)0.05 bar
- c)0.025 bar
- d)0.10 bar
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The equilibrium constant for the following reaction, is 1.6 x 105 at 1024 K.
HBr (g)at 10.0 bar is introduced into a sealed container at 1024 K. Thus, partial pressure of H2(g)and Br2(g), together is
a)
10 bar
b)
0.05 bar
c)
0.025 bar
d)
0.10 bar
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
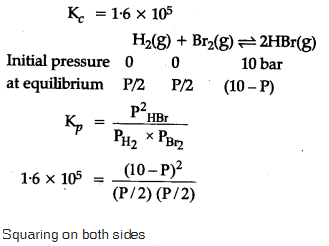
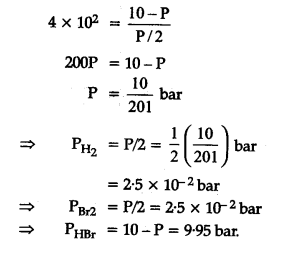
=> 10 bar approximately
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.Q. The equilibrium which is not affected by volume change at constant temperature is- a)
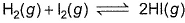
- b)
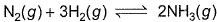
- c)N2O4(g)
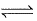 2NO2(g)
2NO2(g) - d)
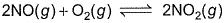
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. The equilibrium which is not affected by volume change at constant temperature is
a)
b)
c)
N2O4(g) 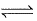 2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)
d)
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
As the number of moles of reactants and products is the same. Hence, they both will occupy equal volume at the same temperature.
Therefore, the reaction A i.e., H2 (g) +I2 (g) ⇌ 2HI (g) is not affected by change in pressure and volume.
Therefore, the reaction A i.e., H2 (g) +I2 (g) ⇌ 2HI (g) is not affected by change in pressure and volume.
A sample of N2O4(g)with a pressure of 1.00 atm is placed in a flask. When equilibrium is reached, 20% of N2O4(g)has been converted to NO2(g)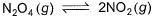 If the original pressure is made 10% of the earlier pressure, then per cent dissociation will be
If the original pressure is made 10% of the earlier pressure, then per cent dissociation will be- a)20%
- b)42%
- c)54%
- d)62%
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A sample of N2O4(g)with a pressure of 1.00 atm is placed in a flask. When equilibrium is reached, 20% of N2O4(g)has been converted to NO2(g)
If the original pressure is made 10% of the earlier pressure, then per cent dissociation will be
a)
20%
b)
42%
c)
54%
d)
62%
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Correct answer is A.

Equilibrium constant for the reaction PCL5⇋PCL3+CL2 is 0.0205 at 230°C and 1 atmospheric pressure if at equilibrium concentration of PCL5 is 0.235 moles liter−1liter-1and that of CL2= 0.028 moleslit−1lit-1 then conc. of PCL3 at equilibrium is- a)0.0174
- b)0.174
- c)0.0348
- d)1.74
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Equilibrium constant for the reaction PCL5⇋PCL3+CL2 is 0.0205 at 230°C and 1 atmospheric pressure if at equilibrium concentration of PCL5 is 0.235 moles liter−1liter-1and that of CL2= 0.028 moleslit−1lit-1 then conc. of PCL3 at equilibrium is
a)
0.0174
b)
0.174
c)
0.0348
d)
1.74
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |

In which of the following solvents is silver chloride most soluble?- a)0.1 mol dm–3 AgNO3 solution
- b)0.1 mol dm–3 HCl solution
- c)H2O
- d)Aqueous ammonia
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following solvents is silver chloride most soluble?
a)
0.1 mol dm–3 AgNO3 solution
b)
0.1 mol dm–3 HCl solution
c)
H2O
d)
Aqueous ammonia
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
Silver chloride forms a soluble complex with aqueous ammonia.
AgCl + 2NH3→ [Ag(NH3)2]Cl
For the reaction, 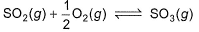
if Kp = Kc (RT)X, when the symbols have usual meaning, the value of x is (assuming ideality)[jee Main 2014]- a)-1
- b)-1/2
- c)+1/2
- d)+1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For the reaction, 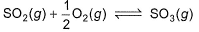
if Kp = Kc (RT)X, when the symbols have usual meaning, the value of x is (assuming ideality)
if Kp = Kc (RT)X, when the symbols have usual meaning, the value of x is (assuming ideality)
[jee Main 2014]
a)
-1
b)
-1/2
c)
+1/2
d)
+1
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
The correct answer is Option B.
SO2(g) + 1/2O2(g) ⇌ SO3(g)
KP = KC(RT)Δn
SO2(g) + 1/2O2(g) ⇌ SO3(g)
KP = KC(RT)Δn
Δn= no. of gaseous moles of product minus no. of gaseous moles of reactant
Δn = 1−1−1/2
∴Δn = −1/2
Δn = 1−1−1/2
∴Δn = −1/2
At 273 K and 1 atm, 1 L of N2O4 (g) decomposes to NO2(g)a s given,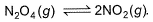 At equilibrium, original volume is 25% less than the existing volume. Percentage decomposition of N2O4 (g) is thus,
At equilibrium, original volume is 25% less than the existing volume. Percentage decomposition of N2O4 (g) is thus, - a)25%
- b)50%
- c)66.66%
- d)33.33%
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
At 273 K and 1 atm, 1 L of N2O4 (g) decomposes to NO2(g)a s given,
At equilibrium, original volume is 25% less than the existing volume. Percentage decomposition of N2O4 (g) is thus,
a)
25%
b)
50%
c)
66.66%
d)
33.33%
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
Let the initial volume of N2O4 be x and initial volume of NO2 is 0
If the degree of dissociation is a, then the final volume of N2O4 is x(1−a) and NO2 is 2ax.
Initial
It equilibrium
N2O4 ⟶ 2NO2
x 0
x(1−a) 2ax
Total initial volume =x+0=x
Final volume =x(1−a)+2ax=x+ax=x(1+a)
It is given that the initial volume is 25% less than the final volume
x=0.75×(1+a)
1+a=1.33
a=0.33
So %age dissociation = 33.33%
If the degree of dissociation is a, then the final volume of N2O4 is x(1−a) and NO2 is 2ax.
Initial
It equilibrium
N2O4 ⟶ 2NO2
x 0
x(1−a) 2ax
Total initial volume =x+0=x
Final volume =x(1−a)+2ax=x+ax=x(1+a)
It is given that the initial volume is 25% less than the final volume
x=0.75×(1+a)
1+a=1.33
a=0.33
So %age dissociation = 33.33%
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.Q. For the following equilibrium,
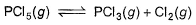
Vapour density is found to be 100 when 1 mole of PCI5 is taken in 10 dm3 flask at 300 K. Thus, equilibrium pressure is- a)1.00 atm
- b)4.92 atm
- c)2.46 atm
- d)2.57 atm
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. For the following equilibrium,
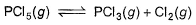
Vapour density is found to be 100 when 1 mole of PCI5 is taken in 10 dm3 flask at 300 K. Thus, equilibrium pressure is
Vapour density is found to be 100 when 1 mole of PCI5 is taken in 10 dm3 flask at 300 K. Thus, equilibrium pressure is
a)
1.00 atm
b)
4.92 atm
c)
2.46 atm
d)
2.57 atm
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
Given, vapour pressure = 100
So, molecular weight = 200
Degree of dissociation;α = 1/(n-1)[Mtheo-Mobs/Mobs]

α = 1/(2-1)×[208.5-200/208.5]
α = 0.0425
PCl5(s) ⇌ PCl3(g) + Cl2(g)
At start 1 - - -
At eqm. (1-0.0428) (0.0428) (0.0428)
Total moles at eqm. = 1.0428
Total pressure at equilibrium; pV = nRT
p = 1.0428×0.0821×300/10
p = 2.5676 atm
So, molecular weight = 200
Degree of dissociation;α = 1/(n-1)[Mtheo-Mobs/Mobs]

α = 1/(2-1)×[208.5-200/208.5]
α = 0.0425
PCl5(s) ⇌ PCl3(g) + Cl2(g)
At start 1 - - -
At eqm. (1-0.0428) (0.0428) (0.0428)
Total moles at eqm. = 1.0428
Total pressure at equilibrium; pV = nRT
p = 1.0428×0.0821×300/10
p = 2.5676 atm
For the following equilibrium, N2O4 (g) 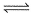 2NO2(g)Kp = KC. This is attained when
2NO2(g)Kp = KC. This is attained when- a)T = 1.0K
- b)T = 12.18 K
- c)T = 27.3 K
- d)T = 273 K
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For the following equilibrium, N2O4 (g) 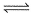 2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)
Kp = KC. This is attained when
a)
T = 1.0K
b)
T = 12.18 K
c)
T = 27.3 K
d)
T = 273 K
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
The correct answer is option B
KP=KC(RT)Δn
Δn=1
KP=KC(RT)
RT=1
T=1/R=1/0.0821=12.18
KP=KC(RT)Δn
Δn=1
KP=KC(RT)
RT=1
T=1/R=1/0.0821=12.18
The concentration of the oxides of nitrogen are monitored in air-pollution reports. At 25°C, the equilibrium constant for the reaction,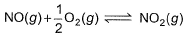
is 1.3 x 106 and that for 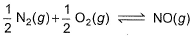
is 6.5 x 10-16 (when each species is expressed in terms of partial pressure).
For the reaction,
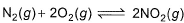
equilibrium constant is- a)
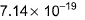
- b)
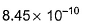
- c)

- d)
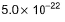
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The concentration of the oxides of nitrogen are monitored in air-pollution reports. At 25°C, the equilibrium constant for the reaction,
is 1.3 x 106 and that for
is 6.5 x 10-16 (when each species is expressed in terms of partial pressure).
For the reaction,
equilibrium constant is
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Given equations are
NO (g) + ½ O2 (g) ⇌ NO2 (g) ----------(i) k1 = 1.3×106
And ½ N2 (g) + ½ O2 (g) ⇌ NO(g) ----------(ii) k2 = 6.5×10-16
To get the reaction, N2(g) + 2O2(g) ⇌ 2NO2(g) ----------(iii) k3
We multiply eqn (i) and eqn (ii) by 2 and adding both reaction, we get eqn (iii)
k3 = k12×k22
= (1.3×106)2×(6.5×10-16)2
= 1.69×1012×42.25×10-32
= 7.14×10-19
NO (g) + ½ O2 (g) ⇌ NO2 (g) ----------(i) k1 = 1.3×106
And ½ N2 (g) + ½ O2 (g) ⇌ NO(g) ----------(ii) k2 = 6.5×10-16
To get the reaction, N2(g) + 2O2(g) ⇌ 2NO2(g) ----------(iii) k3
We multiply eqn (i) and eqn (ii) by 2 and adding both reaction, we get eqn (iii)
k3 = k12×k22
= (1.3×106)2×(6.5×10-16)2
= 1.69×1012×42.25×10-32
= 7.14×10-19
When hydrochloric acid is added to cobalt (II) nitrate solution at room temperature, the following reaction takes place
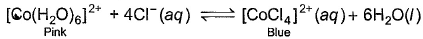 Q. The solution is blue at room temperature. However, it turns pink when cooled in a freezing mixture. Based upon this information, which of the following expression is correct for the forward reaction?
Q. The solution is blue at room temperature. However, it turns pink when cooled in a freezing mixture. Based upon this information, which of the following expression is correct for the forward reaction?- a)ΔH > 0
- b)ΔH < 0
- c)ΔH = 0
- d)The sign of ΔH can’t be predicted based on the given information
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When hydrochloric acid is added to cobalt (II) nitrate solution at room temperature, the following reaction takes place
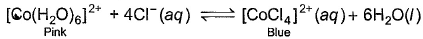
Q. The solution is blue at room temperature. However, it turns pink when cooled in a freezing mixture. Based upon this information, which of the following expression is correct for the forward reaction?
a)
ΔH > 0
b)
ΔH < 0
c)
ΔH = 0
d)
The sign of ΔH can’t be predicted based on the given information
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
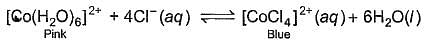
According to the given information, the solution turns pink when cooled in freezing mixture. So, the equilibrium has shifted in backward direction. So we can say that the reaction is endothermic and ∆H for the reaction is greater than zero. This is because, endothermic reactions have ∆H > 0 and they proceed in reverse direction.
Equilibrium can be attained i- a)all types of system
- b)closed system
- c)open system
- d)isolated system
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Equilibrium can be attained i
a)
all types of system
b)
closed system
c)
open system
d)
isolated system
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The equilibrium state can only be reached if the chemical reaction takes place in a closed system. Otherwise, some of the products may escape, leading to the absence of a reverse reaction. (Note that in the diagrams under "Characteristics of Chemical Equilibrium," all reactions are in closed systems.)
A gaseous phase reaction taking place in 1L flask at 400 K is given,

Starting with 1 mole N2 and 3 moles H2, equilibrium mixture required 250 mL of 1M H2SO4 . Thus, Kc is - a)0.006
- b)0.08
- c)0.029
- d)2.05
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A gaseous phase reaction taking place in 1L flask at 400 K is given,

Starting with 1 mole N2 and 3 moles H2, equilibrium mixture required 250 mL of 1M H2SO4 . Thus, Kc is
Starting with 1 mole N2 and 3 moles H2, equilibrium mixture required 250 mL of 1M H2SO4 . Thus, Kc is
a)
0.006
b)
0.08
c)
0.029
d)
2.05

|
Vivek Jyoshi answered |
The correct answer to this question is option c
Combustion of CO(g)can be increased in the following reaction by
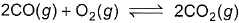
- a)decreasing volume at constant temperature
- b)adding argon gas
- c)adding O2 gas
- d)decreasing pressure at constant temperature
Correct answer is 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Combustion of CO(g)can be increased in the following reaction by
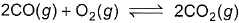
a)
decreasing volume at constant temperature
b)
adding argon gas
c)
adding O2 gas
d)
decreasing pressure at constant temperature
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
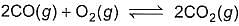
For option a; with decrease in volume or with increase in pressure, reaction shifts towards less no. of moles. So, here combustion of CO will increase.
For option b; adding argon at constant volume doesn’t make any effect on equilibrium. Also, if we add argon at constant pressure, the reaction will shift towards more no. of moles and so the combustion of CO will decrease.
For option c; adding O2 will shift the reaction in forward direction (according to Le Chatelier principle), so combustion of CO will increase.
For option d; with decrease in pressure or increases in volume, reaction shifts towards more no. of moles and so combustion of CO will decrease.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Equilibrium reactions are found in large scale in production of
- A:
ammonia
- B:
sulfuric acid
- C:
lactic acid
- D:
both A and B
The answer is d.
Equilibrium reactions are found in large scale in production of
ammonia
sulfuric acid
lactic acid
both A and B
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
An understanding of equilibrium is important in the chemical industry. Equilibrium reactions are involved in some of the stages in the large-scale production of ammonia, sulfuric acid and many other chemicals.
Direction (Q. Nos. 16-19) This section contains a paragraph, each describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d)Passage I
The equilibrium reaction 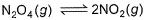 has been thoroughly studied Kp = 0.148 at 298 KIf the total pressure in a flask containing NO2 and N2O4 gas at 25°C is 1.50 atm, what fraction of the N2O4 has dissociated to NO2 ?
has been thoroughly studied Kp = 0.148 at 298 KIf the total pressure in a flask containing NO2 and N2O4 gas at 25°C is 1.50 atm, what fraction of the N2O4 has dissociated to NO2 ? - a)0.156
- b)0.844
- c)0.024
- d)0.076
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 16-19) This section contains a paragraph, each describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d)
Passage I
The equilibrium reaction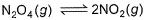 has been thoroughly studied Kp = 0.148 at 298 K
has been thoroughly studied Kp = 0.148 at 298 K
The equilibrium reaction
If the total pressure in a flask containing NO2 and N2O4 gas at 25°C is 1.50 atm, what fraction of the N2O4 has dissociated to NO2 ?
a)
0.156
b)
0.844
c)
0.024
d)
0.076
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
The correct answer is Option A.
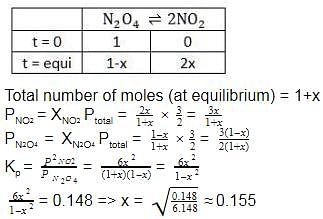
Fraction of N2O4 dissociated = x = 0.155 (x = mole fraction)
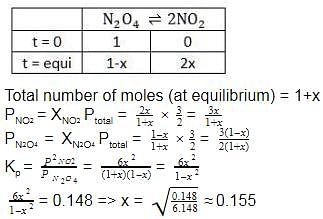
Fraction of N2O4 dissociated = x = 0.155 (x = mole fraction)
Direction (Q. Nos. 21) This section contains 2 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)Q. For the equilibrium in gaseous phase in 2 L flask we start with 2 moles of SO2 and 1 mole of O2 at 3 atm, 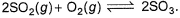
When equilibrium is attained, pressure changes to 2.5 atm. Hence, equilibrium constant Kc is
Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 21) This section contains 2 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
Q. For the equilibrium in gaseous phase in 2 L flask we start with 2 moles of SO2 and 1 mole of O2 at 3 atm, 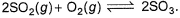
When equilibrium is attained, pressure changes to 2.5 atm. Hence, equilibrium constant Kc is
When equilibrium is attained, pressure changes to 2.5 atm. Hence, equilibrium constant Kc is
|
|
Om Desai answered |
The correct answer is 4
2SO2(g) + O2(g) ⇋ 2SO3
Initial moles 2 1
At equilibrium 2 - 2x 1 - x 2x
Net moles at equilibrium = 2 - 2x + 1 - x + 2x
=(3 - x)moles
Initial:
moles = 3,
Pressure = 3 atm,
Volume = 2L,
PV = nRT
3 x 2 = 3RT -------- 1
At equilibrium
Moles = 3 - x,
Pressure = 2.5 atm
Volume = 2L
P‘V = n’RT ---------- 2
Divide eqn 2 by 1
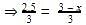
⇒2.5 = 3 - x
⇒x = 0.5
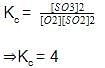
2SO2(g) + O2(g) ⇋ 2SO3
Initial moles 2 1
At equilibrium 2 - 2x 1 - x 2x
Net moles at equilibrium = 2 - 2x + 1 - x + 2x
=(3 - x)moles
Initial:
moles = 3,
Pressure = 3 atm,
Volume = 2L,
PV = nRT
3 x 2 = 3RT -------- 1
At equilibrium
Moles = 3 - x,
Pressure = 2.5 atm
Volume = 2L
P‘V = n’RT ---------- 2
Divide eqn 2 by 1
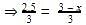
⇒2.5 = 3 - x
⇒x = 0.5
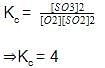
H2S (g) initially at a pressure of 10.0 atm and a temperature of 800 K, dissociates as
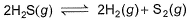 At equilibrium, the partial pressure of S2 vapour is 0.020 atm . Thus, Kp is
At equilibrium, the partial pressure of S2 vapour is 0.020 atm . Thus, Kp is - a)3.23x 10-7
- b)6.45x 10-7
- c)1.55x 106
- d)6.20x 107
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
H2S (g) initially at a pressure of 10.0 atm and a temperature of 800 K, dissociates as
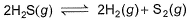
At equilibrium, the partial pressure of S2 vapour is 0.020 atm . Thus, Kp is
a)
3.23x 10-7
b)
6.45x 10-7
c)
1.55x 106
d)
6.20x 107
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
The correct answer is Option A.
2H2S(g) ⇌ 2H2(g) + S2(g)
Pressure
at t=0 Pi − −
at eqm Pi−P 2P P
2H2S(g) ⇌ 2H2(g) + S2(g)
Pressure
at t=0 Pi − −
at eqm Pi−P 2P P
as P=0.02 thus Pi−P=10−0.02
Pi=10 2P=0.04
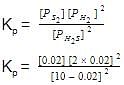
Kp = 3.23×10−7 atm.
Pi=10 2P=0.04
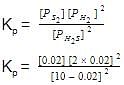
Kp = 3.23×10−7 atm.
Passage lIOne of the reactions that takes place in producing steel from iron ore is the reduction of iron (II) oxide by carbon monoxide to give iron metal and carbon dioxide.
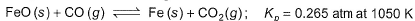
Initial partial pressure
CO(g) = 1.40 atm
CO2(g) = 0.80 atmQ. Under the given partial pressure, reaction is- a)displaced in forward side
- b)displaced in backward side
- c)in equilibrium
- d)incomplete in the absence of total pressure
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage lI
One of the reactions that takes place in producing steel from iron ore is the reduction of iron (II) oxide by carbon monoxide to give iron metal and carbon dioxide.
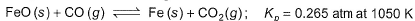
Initial partial pressure
CO(g) = 1.40 atm
CO2(g) = 0.80 atm
Initial partial pressure
CO(g) = 1.40 atm
CO2(g) = 0.80 atm
Q. Under the given partial pressure, reaction is
a)
displaced in forward side
b)
displaced in backward side
c)
in equilibrium
d)
incomplete in the absence of total pressure
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
We know that with increase in pressure on one side, reaction shifts to that side which has less no. of moles(of gaseous species). However the no. of moles are same on both sides. So the REACTION WILL REMAIN IN EQUILIBRIUM.
Select the correct statement (s) about the following equilibrium.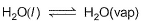
- a)At constant vapour pressure, number of molecules leaving the liquid equals the number returning to liquid from vapour
- b)This does not represent the static equilibrium
- c)This represents dynamic equilibrium and the rate of the forward and backward reactions become equal
- d)This represents dynamic as well as static equilibrium
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct statement (s) about the following equilibrium.
a)
At constant vapour pressure, number of molecules leaving the liquid equals the number returning to liquid from vapour
b)
This does not represent the static equilibrium
c)
This represents dynamic equilibrium and the rate of the forward and backward reactions become equal
d)
This represents dynamic as well as static equilibrium
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The correct answers are Options A, B and C.
During constant vapor pressure the no of molecules of H2O leaving the surface = the no of H2O molecules coming to the surface from the atmosphere. This process is dynamic as there is continuous movement of molecules.
During constant vapor pressure the no of molecules of H2O leaving the surface = the no of H2O molecules coming to the surface from the atmosphere. This process is dynamic as there is continuous movement of molecules.
For the reaction,2SO2 (g) + O2 (g)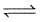 2SO3 (g) + 188.3 KJ
2SO3 (g) + 188.3 KJ
the number of moles of SO3 formed is increased if- a)temperature is increased at constant V
- b)inert gas is added to the mixture
- c)O2 is removed from the mixture
- d)volume of the reaction flask is decreased
Correct answer is option 'B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
For the reaction,
2SO2 (g) + O2 (g)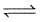 2SO3 (g) + 188.3 KJ
2SO3 (g) + 188.3 KJ
the number of moles of SO3 formed is increased if
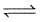 2SO3 (g) + 188.3 KJ
2SO3 (g) + 188.3 KJthe number of moles of SO3 formed is increased if
a)
temperature is increased at constant V
b)
inert gas is added to the mixture
c)
O2 is removed from the mixture
d)
volume of the reaction flask is decreased
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Volume decreased
i.e p increased
no.of moles reactant more
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-12) This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q.Conversion factor for converting partial pressures (in Kp) to active masses (in Kc) is- a)nRT
- b)1/RT
- c)(RT)2
- d)1/RT2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-12) This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q.Conversion factor for converting partial pressures (in Kp) to active masses (in Kc) is
a)
nRT
b)
1/RT
c)
(RT)2
d)
1/RT2
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Kp = kc(RT)∆ng
So to convert kp to kc we have, kc = kp(1/RT)∆ng.
So, the converting factor is 1/RT
So to convert kp to kc we have, kc = kp(1/RT)∆ng.
So, the converting factor is 1/RT
For the equilibrium,
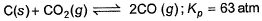
at 1000 K. If at equilibrium pCO = 10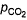 then total pressure at equilibrium is
then total pressure at equilibrium is - a)6.30 atm
- b)0.63 atm
- c)6.93 atm
- d)69.3 atm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For the equilibrium,
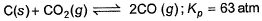
at 1000 K. If at equilibrium pCO = 10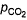 then total pressure at equilibrium is
then total pressure at equilibrium is
at 1000 K. If at equilibrium pCO = 10
a)
6.30 atm
b)
0.63 atm
c)
6.93 atm
d)
69.3 atm
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
C(s) + CO2(g) <=========> 2CO(g)
Kp = pCO2/pCO2
GIven Kp = 63 and pCO = 10pCO2
Putting the value of pCO in above equation,
63 = 100(pCO2)2/pCO2
Or pCO2 = 0.63
pCO = 6.3
Therefore, total pressure = 6.3+0.63 = 6.93 atm
Kp = pCO2/pCO2
GIven Kp = 63 and pCO = 10pCO2
Putting the value of pCO in above equation,
63 = 100(pCO2)2/pCO2
Or pCO2 = 0.63
pCO = 6.3
Therefore, total pressure = 6.3+0.63 = 6.93 atm
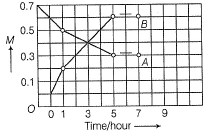
Direction (Q. Nos. 21) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.The progress of the reaction 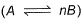 with time t is shown below.
with time t is shown below.
Match the parameters in Column l with their respective values in Column II.

Codes
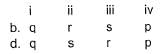
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 21) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.
The progress of the reaction 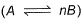 with time t is shown below.
with time t is shown below.

Match the parameters in Column l with their respective values in Column II.

Codes
Match the parameters in Column l with their respective values in Column II.
Codes

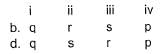
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
The correct answer is Option A.
Loss in concentration of A in I hour = 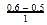 = 0.1
= 0.1
Gain in concentration of B in I hour =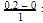 0.2
0.2
(i) ∵0.1 mole of A changes to 0.2 mole of B in a given time and thus, n=2
(ii) Equilibrium constant,
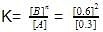 = 1.2mollitre−1
= 1.2mollitre−1
(iii) Initial rate of conversion of A = changes in conc. of A during I hour =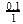
= 0.1 mol litre−1hour−1
(iv) ∵ Equilibrium is attained after 5 hr, where [B]=0.6 and [A]=0.3
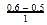 = 0.1
= 0.1Gain in concentration of B in I hour =
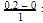 0.2
0.2(i) ∵0.1 mole of A changes to 0.2 mole of B in a given time and thus, n=2
(ii) Equilibrium constant,
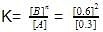 = 1.2mollitre−1
= 1.2mollitre−1(iii) Initial rate of conversion of A = changes in conc. of A during I hour =
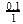
= 0.1 mol litre−1hour−1
(iv) ∵ Equilibrium is attained after 5 hr, where [B]=0.6 and [A]=0.3
In the following equilibrium AB 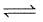 A+ + B-
A+ + B-
AB is 10% dissociated, when [AB] = 1MQ. What is per cent dissociation if 1 M AB is dissociated in the presence of 1 M A+? - a)5.2%
- b)6.0%
- c)1.1%
- d)10.0%
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following equilibrium AB 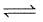 A+ + B-
A+ + B-
AB is 10% dissociated, when [AB] = 1M
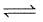 A+ + B-
A+ + B-AB is 10% dissociated, when [AB] = 1M
Q. What is per cent dissociation if 1 M AB is dissociated in the presence of 1 M A+?
a)
5.2%
b)
6.0%
c)
1.1%
d)
10.0%
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The correct answer is option C
Let initially
AB = 1M
AB = A+ + B-
⇒1 - 0.1
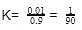
K should remain same
AB ⇌ A+ + B-
1-x
Let initially
AB = 1M
AB = A+ + B-
⇒1 - 0.1
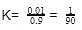
K should remain same
AB ⇌ A+ + B-
1-x
Chapter doubts & questions for Equilibrium - Chemistry for ACT 2025 is part of ACT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Equilibrium - Chemistry for ACT in English & Hindi are available as part of ACT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for ACT Exam by signing up for free.
Chemistry for ACT
110 videos|124 docs|114 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup