All Exams >
EmSAT Achieve >
Physics for EmSAT Achieve >
All Questions
All questions of Refraction for EmSAT Achieve Exam
When light undergoes refraction, its frequency- a)Increases
- b)Remains same
- c)Decreases
- d)Increases exponentially
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When light undergoes refraction, its frequency
a)
Increases
b)
Remains same
c)
Decreases
d)
Increases exponentially
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Light refracts as it passes through a material. It's direction changes, but it still passes through. Light travels at a maximum speed -- the speed of light in a vacuum, but when traveling in anything else it slows down. Different materials slow the speed of passing light at different rates. This property of matter is called the refractive index. When refracting, light doesn't change it's frequency, but since it changes it's speed, it must also change it's wavelength (it gets squished or elongated). Frequency, wavelength, and speed are all related, so if one property changes, another must as well.
When light undergoes refraction, the wavelength- a)Increases in rarer medium
- b)Decreases in rarer medium
- c)Increases in denser medium
- d)Decreases in denser medium
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When light undergoes refraction, the wavelength
a)
Increases in rarer medium
b)
Decreases in rarer medium
c)
Increases in denser medium
d)
Decreases in denser medium
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
When light undergoes refraction at the surface of separation of two media, wavelength decreases on entering a denser medium and wavelength increases on entering a rarer medium.
Just before setting, the sun may appear to be elliptical. This happens due to:
- a)Refraction
- b)Dispersion
- c)Reflection
- d)Diffraction
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Just before setting, the sun may appear to be elliptical. This happens due to:
a)
Refraction
b)
Dispersion
c)
Reflection
d)
Diffraction
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Refraction of light ray through the atmosphere may cause different magnification in mutually perpendicular directions.
Sunlight enters the Earth's atmosphere from the vacuum of space. The refractive index of air with respect to vacuum is 1.0029. This means that the speed of light in air is 1.0029 times slower than the speed of light in vacuum. This causes the light rays to bend towards the normal (refraction).
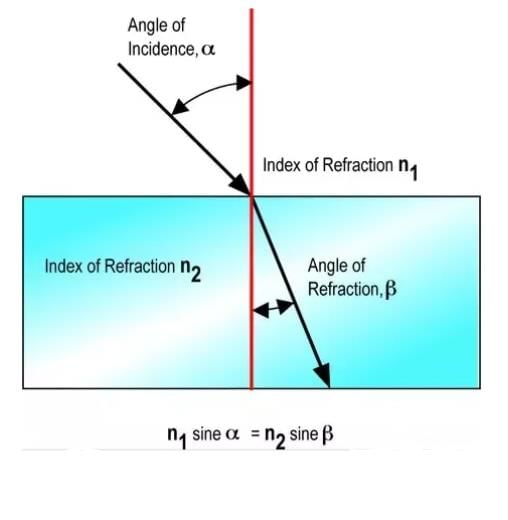
Sunlight enters the Earth's atmosphere from the vacuum of space. The refractive index of air with respect to vacuum is 1.0029. This means that the speed of light in air is 1.0029 times slower than the speed of light in vacuum. This causes the light rays to bend towards the normal (refraction).

Due to _______ the depth of an optically denser medium appears to be _______ than its real depth.- a)Refraction , more
- b)Reflection , less
- c)Reflection , more
- d)Refraction , less
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Due to _______ the depth of an optically denser medium appears to be _______ than its real depth.
a)
Refraction , more
b)
Reflection , less
c)
Reflection , more
d)
Refraction , less
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
When light moves from 1 medium to another, refraction takes place. And when light enters a denser medium, the ray bends away from normal and meets at a point above the actual point where they would have met, if the medium was absent. So, apparent depth decreases.
A thick plano convex lens made of crown glass (refractive index 1.5) has a thickness of 3cm at its centre. The radius of curvature of its curved face is 5cm. An ink mark made at the centre of its plane face, when viewed normally through the curved face, appears to be at a distance ‘x’ from the curved face. Then, x is equal to: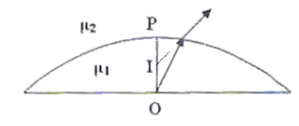
- a)2.5cm
- b)2.3cm
- c)2cm
- d)2.1cm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A thick plano convex lens made of crown glass (refractive index 1.5) has a thickness of 3cm at its centre. The radius of curvature of its curved face is 5cm. An ink mark made at the centre of its plane face, when viewed normally through the curved face, appears to be at a distance ‘x’ from the curved face. Then, x is equal to:
a)
2.5cm
b)
2.3cm
c)
2cm
d)
2.1cm

|
EduRev Humanities answered |
A thick Plano convex lens made of crown glass (refractive index 1.5) has a thickness of 3cm at its centre. The radius of curvature of its curved face is 5cm. An ink mark made at the centre of its plane face, when viewed normally through the curved face, appears to be at a distance ‘x’ from the curved face, and we have to determine the value of ' x'
According to the picture, the ray of light gets refracted at the interface between the air and the lens from the object 'p' and 'I' is the refracted image of 'p'
object distance 'u'= BO
Image distance 'v'/'x' = BI
we know
n2/v - n1/u = (n2- n1) / R
or 1/v - 1.5/(-3 )= (1-1.5)/ (-5) [where n2= 1, n1= 1.5 ,u= -3 ,R= -5]
so, 1/v = -6/15
or, v = -2.5
so, x is equal to 2.5 cm
According to the picture, the ray of light gets refracted at the interface between the air and the lens from the object 'p' and 'I' is the refracted image of 'p'
object distance 'u'= BO
Image distance 'v'/'x' = BI
we know
n2/v - n1/u = (n2- n1) / R
or 1/v - 1.5/(-3 )= (1-1.5)/ (-5) [where n2= 1, n1= 1.5 ,u= -3 ,R= -5]
so, 1/v = -6/15
or, v = -2.5
so, x is equal to 2.5 cm
Bending effect of light as it passes from one transparent material into other is known as- a)refraction
- b)deflection
- c)reflection
- d)diffraction
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Bending effect of light as it passes from one transparent material into other is known as
a)
refraction
b)
deflection
c)
reflection
d)
diffraction
|
|
Leelu Bhai answered |
Its refraction yrr.. This is a common definition of refraction that u r asking 🤦🏻♂️
An air bubble inside a glass slab (μ = 1.5) appears at 6 cm when viewed from the opposite side. The thickness of the slab is:- a)10 cm
- b)6.67 cm
- c)15 cm
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An air bubble inside a glass slab (μ = 1.5) appears at 6 cm when viewed from the opposite side. The thickness of the slab is:
a)
10 cm
b)
6.67 cm
c)
15 cm
d)
None of the above
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
We know that μ=(apparent depth/real depth)
Let the thickness of the slab be t and real depth of the bubble from one side be x. Then
μ=(x/6)=(t−x)/4 or 1.5=x/6 = (t−x)/4
This gives x=9 and 1.5=(t−9)/4 or t=15cm
A prism of refractive index √2 and refractive angle A produces minimum deviation δm of a ray on one face at an angle of incidence 45°. The values of A and δm are respectively- a)45°, 45°
- b)60°, 30°
- c)60°, 45°
- d)45°, 60°
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A prism of refractive index √2 and refractive angle A produces minimum deviation δm of a ray on one face at an angle of incidence 45°. The values of A and δm are respectively
a)
45°, 45°
b)
60°, 30°
c)
60°, 45°
d)
45°, 60°

|
Bs Academy answered |
μ=sinisinr
Again for minimum deviation
μ=sin(A+δmin2)sinA2
∴μ=sinisinA2
⇒sinA2=siniμ
⇒sinA2=sin45∘√2=12
⇒A2=30∘
⇒A=60∘
Again i+e=A+δmin
For minimum deviation i=e
∴2i=A+δmin
⇒δmin=2i−A
⇒δmin=2×45∘−60∘=30∘
A ray of light going from denser to rarer medium suffers refraction at a concave surface. Which of the following relations is correct?- a)
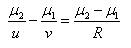
- b)
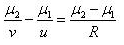
- c)
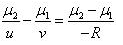
- d)
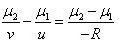
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A ray of light going from denser to rarer medium suffers refraction at a concave surface. Which of the following relations is correct?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
EduRev JEE answered |
Solution :
The correct option is Option A.
Laws of refraction;-
The incident ray,the refracted ray and the normal to the refracting surface at the point of incidence lie in the same plane.
For a given pair of media and for a given colour of light the ration between the sine of angle of incidence to the sine of refraction is a constant.This constant is known as refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first medium.
When a ray of light passes through a glass slab, ∠i,∠r and the normal all lie in the same plane.
When a ray of light passes from one medium to another, here from air to glass or glass to air, the ratio sini / sinr = constant.
A microscope is focused on an ink mark on the top of a table. If we place a glass slab 3cm thick on it, how should the microscope be moved to focus the ink spot again? The refractive index of glass slab is 1.5 cm.- a)2 cm downward
- b)1 cm upwards
- c)1 cm downwards
- d)2 cm upwards
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A microscope is focused on an ink mark on the top of a table. If we place a glass slab 3cm thick on it, how should the microscope be moved to focus the ink spot again? The refractive index of glass slab is 1.5 cm.
a)
2 cm downward
b)
1 cm upwards
c)
1 cm downwards
d)
2 cm upwards
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
The image of the ink spot moves up by 1cm.
Refractive index = Real depth/ apparent depth
1.5 = 3/ apparent depth
Apparent depth = 3/1.5 = 2 cm
Distance through which the microscope is moved is 3 cm -2 cm = 1 cm upwards
A ray of light passes through a plane glass slab of thickness t and refractive index μ = 1.5. The angle between the incident ray and emergent ray will be:- a)30°
- b)45°
- c)60°
- d)0°
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A ray of light passes through a plane glass slab of thickness t and refractive index μ = 1.5. The angle between the incident ray and emergent ray will be:
a)
30°
b)
45°
c)
60°
d)
0°

|
Ayush Joshi answered |
The incident ray and emergent ray are parallel to each other but latteray displaced due to reflaction at two surfaces . So, the angle between them is Zero.
Can absolute value of refractive index be less than unity?- a)No
- b)Refractive index is always unity
- c)Depends on situation
- d)Yes
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Can absolute value of refractive index be less than unity?
a)
No
b)
Refractive index is always unity
c)
Depends on situation
d)
Yes
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Absolute refractive index of a medium = speed of light in vacuum / speed of light in in that medium.
Since the speed of light is maximum in vacuum, the refractive index cannot be less than unity.
A thin prism P1 with angle 4° and made from glass of refractive index 1.54 is combined with another thin prism P2 made from glass of refractive index 1.72 to produce dispersion without deviation . The angle of prism P2 is:- a)5.33°
- b)2.6°
- c)3°
- d)4°
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A thin prism P1 with angle 4° and made from glass of refractive index 1.54 is combined with another thin prism P2 made from glass of refractive index 1.72 to produce dispersion without deviation . The angle of prism P2 is:
a)
5.33°
b)
2.6°
c)
3°
d)
4°
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |

Which is the position of minimum deviation in prism?- a)When the angle of incidence is such that the refracted ray inside the prism is perpendicular to the base of the prism.
- b)When the angle of incidence is such that the refracted ray inside the prism is parallel to the base of the prism.
- c)When the angle of incidence is such that the refracted ray inside the prism reflects back from the base of the prism.
- d)When the angle of incidence is such that the refracted ray inside the prism is at 45 degrees to the base of the prism.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the position of minimum deviation in prism?
a)
When the angle of incidence is such that the refracted ray inside the prism is perpendicular to the base of the prism.
b)
When the angle of incidence is such that the refracted ray inside the prism is parallel to the base of the prism.
c)
When the angle of incidence is such that the refracted ray inside the prism reflects back from the base of the prism.
d)
When the angle of incidence is such that the refracted ray inside the prism is at 45 degrees to the base of the prism.
|
|
Priyanshu Pandey answered |
A prism is said to be in the position of minimum deviation when the angle of incidence of the light ray at the first prism surface is equal to the angle of emergence at the second surface of prism. In this condition, the refracted ray inside the prism is parallel to the base of the prism.
The ratio of angular dispersion of to the angle of deviation for the mean wavelength is called Dispersive Power. Represented by
- a)
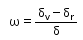
- b)
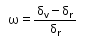
- c)
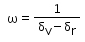
- d)
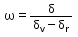
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The ratio of angular dispersion of to the angle of deviation for the mean wavelength is called Dispersive Power. Represented by
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Om Desai answered |
The dispersive power(ω)Of a prism is defined as the ratio of angular dispersion to the mean deviation produced by the prism,
Mean deviation=��
Angular dispersion= ��v- ��y
Dispersive power=angular dispersion/mean deviation
Dispersive power= ��v- ��y/ ��
Mean deviation=��
Angular dispersion= ��v- ��y
Dispersive power=angular dispersion/mean deviation
Dispersive power= ��v- ��y/ ��
Dispersive power is dependent on- a)Material of prism
- b)Angle of prism
- c)Length of prism
- d)Angle of emergence of the ray of light
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Dispersive power is dependent on
a)
Material of prism
b)
Angle of prism
c)
Length of prism
d)
Angle of emergence of the ray of light
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
Dispersive power of a prism depends only on the nature of material of the prism.However angular dispersion and mean deviation, both depend on angle of prism.
What is the Principle of Reversibility?- a)If the final path of a ray of light is reversed after any number of reflections and refractions, then the ray retraces its entire path.
- b)If the final path of a ray of light is reversed after any number of refractions only, then the ray retraces its entire path.
- c)If the final path of a ray of light is reversed after any number of reflections and refractions, then the ray retraces half of its path.
- d)If the initial path of a ray of light is reversed after any number of reflections only, then the ray retraces its entire path.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the Principle of Reversibility?
a)
If the final path of a ray of light is reversed after any number of reflections and refractions, then the ray retraces its entire path.
b)
If the final path of a ray of light is reversed after any number of refractions only, then the ray retraces its entire path.
c)
If the final path of a ray of light is reversed after any number of reflections and refractions, then the ray retraces half of its path.
d)
If the initial path of a ray of light is reversed after any number of reflections only, then the ray retraces its entire path.
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The principle of reversibility of light :-
If the path of light is reversed after a number for reflections and refraction then it retraces it's path.

Note the directions of the arrow.
The beam of light travels back on the same path as it was traveling before the refraction and after the refraction after being encountered by the obstacle in the water.
What is dispersive power?- a)The ratio of angular dispersion to the angle of deviation for the mean wavelength.
- b)The ratio of angular dispersion to the angle of refraction for the mean wavelength.
- c)The ratio of angular dispersion to the angle of reflection for the mean wavelength.
- d)The ratio of angular dispersion to the angle of deviation for the total wavelength.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is dispersive power?
a)
The ratio of angular dispersion to the angle of deviation for the mean wavelength.
b)
The ratio of angular dispersion to the angle of refraction for the mean wavelength.
c)
The ratio of angular dispersion to the angle of reflection for the mean wavelength.
d)
The ratio of angular dispersion to the angle of deviation for the total wavelength.
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
Dispersive power of a prism is defined as the ratio between angular dispersion to mean deviation produced by the prism.
If dμ denotes the difference between the refractive indices of material of prism for violet and red light,
ω = δμ / μ – 1
Here ‘μ’ is the refractive index of prism for a mean colour. A mean colour is that colour whose wavelength lies in between that of violet and red. For white light, yellow colour is, generally, taken to be the mean colour.
Since μv is always greater than μr, the dispersive power of a prism is always positive. It depends upon the type of glass used. It is different for crown glass and for flint glass.
Waves on top of spectrum are- a)infrared waves
- b)gamma rays
- c)x-rays
- d)ultraviolet rays
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Waves on top of spectrum are
a)
infrared waves
b)
gamma rays
c)
x-rays
d)
ultraviolet rays
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
The correct answer is b.
Infrared: Night vision goggles pick up the infrared light emitted by our skin and objects with heat. In space, infrared light helps us map the dust between stars.
Infrared: Night vision goggles pick up the infrared light emitted by our skin and objects with heat. In space, infrared light helps us map the dust between stars.
Visible: Our eyes detect visible light. Fireflies, light bulbs, and stars all emit visible light.
Ultraviolet: Ultraviolet radiation is emitted by the Sun and are the reason skin tans and burns. "Hot" objects in space emit UV radiation as well.
X-ray: A dentist uses X-rays to image your teeth, and airport security uses them to see through your bag. Hot gases in the Universe also emit X-rays.
Gamma ray: Doctors use gamma-ray imaging to see inside your body. The biggest gamma-ray generator of all is the Universe.


Consider a curved surface between two different media with refractive indices n1 = 1 and n2 = 2. The relation between radius of curvature, image distance and object distance is given by- a)
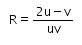
- b)
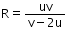
- c)
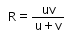
- d)
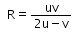
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider a curved surface between two different media with refractive indices n1 = 1 and n2 = 2. The relation between radius of curvature, image distance and object distance is given by
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
The relation between radius of curvature, image distance and object distance is given by
n2/v-n1/u=n2-n1
un2-vn2/vu=n2-n1/R
R=vu(n2-n2)/un2-vn2
=uv(2)/u(2)-v(1)
=[uv/2u-v)
n2/v-n1/u=n2-n1
un2-vn2/vu=n2-n1/R
R=vu(n2-n2)/un2-vn2
=uv(2)/u(2)-v(1)
=[uv/2u-v)
In the adjoining figure, SS is a spherical surface separating two media of refractive indices n1 and n2 where n1 > n2. C is the centre of curvature of the spherical surface. An observer, keeping his eye beyond C in the medium of refractive index n2 views the refracted image of an object AB placed as shown in the medium of refractive index n1. The image will be: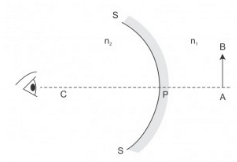
- a)real, upright and diminished
- b)virtual, upright and magnified
- c)real, inverted and magnified
- d)virtual, upright and diminished
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the adjoining figure, SS is a spherical surface separating two media of refractive indices n1 and n2 where n1 > n2. C is the centre of curvature of the spherical surface. An observer, keeping his eye beyond C in the medium of refractive index n2 views the refracted image of an object AB placed as shown in the medium of refractive index n1. The image will be:
a)
real, upright and diminished
b)
virtual, upright and magnified
c)
real, inverted and magnified
d)
virtual, upright and diminished

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |

The image will be virtual, upright and diminished.
Angle of dispersion depends on- a)Angle of Prism
- b)Material of Prism
- c)Medium in which prism is kept
- d)Both a and b
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Angle of dispersion depends on
a)
Angle of Prism
b)
Material of Prism
c)
Medium in which prism is kept
d)
Both a and b

|
Guru Randhawa answered |
Simple just see the formula ref index and A angle of prism is there
A mark on the bottom of the liquid appears to rise by 0.1 m. The depth of the liquid is 1 m. The refractive index of the liquid is- a)0.9
- b)1.33
- c)1.1
- d)1.5
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A mark on the bottom of the liquid appears to rise by 0.1 m. The depth of the liquid is 1 m. The refractive index of the liquid is
a)
0.9
b)
1.33
c)
1.1
d)
1.5
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
Real depth = 1m Apparent depth = 1−0.1=0.9m Refractive index μ=
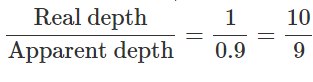
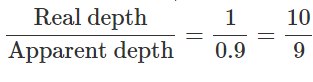
Just before setting, the sun may appear to be elliptical. This happens due to:- a)Refraction
- b)Dispersion
- c)Reflection
- d)Diffraction
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Just before setting, the sun may appear to be elliptical. This happens due to:
a)
Refraction
b)
Dispersion
c)
Reflection
d)
Diffraction
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Refraction, in physics, the change in direction of a wave passing from one medium to another caused by its change in speed. For example, waves in deep water travel faster than in shallow. If an ocean wave approaches a beach obliquely, the part of the wave farther from the beach will move faster than that closer in, and so the wave will swing around until it moves in a direction perpendicular to the shoreline. The speed of sound waves is greater in warm air than in cold. At night, air is cooled at the surface of a lake, and any sound that travels upward is refracted down by the higher layers of air that still remain warm. Thus, sounds, such as voices and music, can be heard much farther across water at night than in the daytime.
Chapter doubts & questions for Refraction - Physics for EmSAT Achieve 2025 is part of EmSAT Achieve exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the EmSAT Achieve exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for EmSAT Achieve 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Refraction - Physics for EmSAT Achieve in English & Hindi are available as part of EmSAT Achieve exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for EmSAT Achieve Exam by signing up for free.
Physics for EmSAT Achieve
208 videos|329 docs|212 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









