All Exams >
EmSAT Achieve >
Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve >
All Questions
All questions of Molecular Geometry for EmSAT Achieve Exam
Hybridisation of Acetylene is- a)sp
- b)sp2
- c)sp3
- d)dsp2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Hybridisation of Acetylene is
a)
sp
b)
sp2
c)
sp3
d)
dsp2
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Since acetylene is made up of triple bond. So the hybridization of carbon in acetylene is sp.
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-11) This section contains 11 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Assuming that Hund's rule is violated, the bond order and magnetic nature of the diatomic molecule B2 is
- a)1 and diamagnetic
- b)0 and diamagnetic
- c)1 and paramagnetic
- d)0 and paramagnetic
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-11) This section contains 11 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Assuming that Hund's rule is violated, the bond order and magnetic nature of the diatomic molecule B2 is
a)
1 and diamagnetic
b)
0 and diamagnetic
c)
1 and paramagnetic
d)
0 and paramagnetic
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |

A pi-bond is formed by the overlap of:- a)p-p orbitals in sidewise manner
- b)s-p orbitals
- c)s-s orbitals
- d)p-p orbitals in end to end fashion
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A pi-bond is formed by the overlap of:
a)
p-p orbitals in sidewise manner
b)
s-p orbitals
c)
s-s orbitals
d)
p-p orbitals in end to end fashion
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
pi-bond is always formed by sidewise overlapping of p – p orbitals in sidewise manner.
Which of the following is nonpolar but contains polar bonds?- a)HCI
- b)CO2
- c)NH3
- d)NO2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is nonpolar but contains polar bonds?
a)
HCI
b)
CO2
c)
NH3
d)
NO2
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
This is why molecules like carbon dioxide are nonpolar despite having the polar carbon oxygen bonds. Molecules that contain non-polar bonds are not polar unless the central atom has one or more nonbonded pairs of electrons.
Valence Bond Theory was developed in the year- a)1916
- b)1927
- c)1930
- d)1932
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Valence Bond Theory was developed in the year
a)
1916
b)
1927
c)
1930
d)
1932
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The valence bond (VB) theory of bonding was mainly developed by Walter Heitler and Fritz London in 1927, and later modified by Linus Pauling to take bond direction into account. The VB approach concentrates on forming bonds in localized orbitals between pairs of atoms, and hence retains the simple idea of Lewis structures and electron pairs.
Pick out the pair of species having identical shapes for both the molecules.- a)BF3 , PCl3
- b)PF , IF5
- c)CF4,SF4
- d)XeF2 , CO2
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Pick out the pair of species having identical shapes for both the molecules.
a)
BF3 , PCl3
b)
PF , IF5
c)
CF4,SF4
d)
XeF2 , CO2
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Both XeF2 & CO2 have linear structures. Both are actually linear Tri-atomic molecules.
Which molecule has a trigonal pyramidal shape?- a)AB4E
- b)AB2E2
- c)AB3E
- d)AB2E
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which molecule has a trigonal pyramidal shape?
a)
AB4E
b)
AB2E2
c)
AB3E
d)
AB2E
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
AB3E: trigonal pyramidal (central atom + 3 outer atoms make a pyramid)
→ start with AB4 molecule (tetrahedral) and replace a B atom w/ lone pair
→ lone pair electrons push bonding electrons away
→ bond angles are now less than 109.5°
→ start with AB4 molecule (tetrahedral) and replace a B atom w/ lone pair
→ lone pair electrons push bonding electrons away
→ bond angles are now less than 109.5°
If one of the electrons (1s2) of helium is taken in excited state then bond order of He2 is- a)0 (zero)
- b)1
- c)0.5
- d)2.0
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If one of the electrons (1s2) of helium is taken in excited state then bond order of He2 is
a)
0 (zero)
b)
1
c)
0.5
d)
2.0
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
Number of electrons in bonding orbital = 4 and in anti-bonding orbitai = 0
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-14) This section contains 14 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.Q. Assuming that Hund’s rule is violated, the bond order and magnetic nature of the diatomic molecule B2 is[IIT JEE 2010]- a)1 and diamagnetic
- b)0 and diamagnetic
- c)1 and paramagnetic
- d)0 and paramagnetic
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-14) This section contains 14 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Assuming that Hund’s rule is violated, the bond order and magnetic nature of the diatomic molecule B2 is
[IIT JEE 2010]
a)
1 and diamagnetic
b)
0 and diamagnetic
c)
1 and paramagnetic
d)
0 and paramagnetic
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
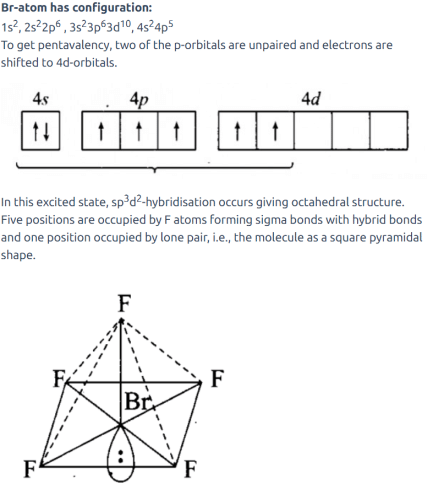
B2 (10 electrons)
MO electronic configuration is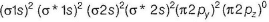
MO electronic configuration is
Bonding electrons = 6
Anti-bonding electrons = 4
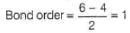
No unpaired electron-diamagnetic
Anti-bonding electrons = 4
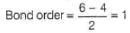
No unpaired electron-diamagnetic
Dipole moment of 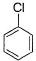 is 1.5 D. Thus, dipole moment
is 1.5 D. Thus, dipole moment 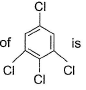
- a)0.00 D
- b)1.5 D
- c)2.0 D
- d)3.0 D
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Dipole moment of  is 1.5 D. Thus, dipole moment
is 1.5 D. Thus, dipole moment 
a)
0.00 D
b)
1.5 D
c)
2.0 D
d)
3.0 D
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
If one considers following molecule, it is
Symmetrical and thus
In the given species
Which of the following molecule doesn’t have a lone pair?- a)BeCl2
- b)XeF4
- c)NH3
- d)H2O
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following molecule doesn’t have a lone pair?
a)
BeCl2
b)
XeF4
c)
NH3
d)
H2O
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
BeCl2 has no lone pairs on the beryllium. Thus, the electrons on the chlorides willtry to stay far apart from each other, since their corresponding electrons repel each other (while experiencing no deflection from electrons on a central atom). Thus themolecule is linear in shape.
Hydrogen bonds are formed in many compounds e.g., H2O, HF, NH3 . The boiling point of such compounds depends to a large extent on the strength of hydrogen bond and the number of hydrogen bonds. The correct decreasing order of the boiling points of above compounds is :
- a)HF > H2O > NH3
- b)H2O > HF > NH3
- c)NH3 > HF > H2O
- d)NH3 > H2O > HF
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Hydrogen bonds are formed in many compounds e.g., H2O, HF, NH3 . The boiling point of such compounds depends to a large extent on the strength of hydrogen bond and the number of hydrogen bonds. The correct decreasing order of the boiling points of above compounds is :
a)
HF > H2O > NH3
b)
H2O > HF > NH3
c)
NH3 > HF > H2O
d)
NH3 > H2O > HF
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
H2O>HF>NH3
Strength of hydrogen bonding depends on the size and electronegativity of the atom.
Smaller the size of the atom, greater is the electronegativity and hence stronger is the H−bonding. Thus, the order of strength of H-bonding is H...F>H...O>H...N.
But each HF molecule is linked only to two other HF molecules while each H2O molecule is linked to four other H2O molecules through H−bonding.
Hence, the decreasing order of boiling points is H2O>HF>NH3.
Select the correct statement(s) about benzene (C6H6),- a)(C=C) bond is shorter than (C—C) bond
- b)All (C— H) bonds are equivalent
- c)C-atom is sp2-hybridised
- d)All (C=C) and (C—C) bonds are of equal stability
Correct answer is option 'B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct statement(s) about benzene (C6H6),
a)
(C=C) bond is shorter than (C—C) bond
b)
All (C— H) bonds are equivalent
c)
C-atom is sp2-hybridised
d)
All (C=C) and (C—C) bonds are of equal stability
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
Due to complete-delocalisation of π-electrons, benzene exists as resonance structures.
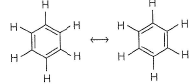
Thus, (C=C) bonds and (C —C) bonds are of equal length and stability.
All (C— H) bonds are equivalent.
C-atom is also sp2-hybridised.
Thus, (C=C) bonds and (C —C) bonds are of equal length and stability.
All (C— H) bonds are equivalent.
C-atom is also sp2-hybridised.
Among the following the maximum covalent character is shown by the compound - a)MgCl2
- b)FeCl2
- c)SnCl2
- d)AlCl3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following the maximum covalent character is shown by the compound
a)
MgCl2
b)
FeCl2
c)
SnCl2
d)
AlCl3
|
|
Sinjini Pillai answered |
Covalent character is a measure of the degree of sharing of electrons between the bonded atoms in a compound. Compounds with high covalent character have a greater degree of electron sharing between the bonded atoms.
Explanation:
MgCl2:
- Mg is a metal and Cl is a non-metal
- The electronegativity difference between Mg and Cl is large, meaning MgCl2 is an ionic compound
- Ionic compounds have low covalent character due to the complete transfer of electrons from the metal to the non-metal
FeCl2:
- Fe is a metal and Cl is a non-metal
- The electronegativity difference between Fe and Cl is moderate, meaning FeCl2 has some ionic character but also some covalent character
- However, the metal in FeCl2 is a transition metal, which can have variable oxidation states and can form complex ions. This makes it difficult to determine the exact degree of covalent character in FeCl2
SnCl2:
- Sn is a metal and Cl is a non-metal
- The electronegativity difference between Sn and Cl is small, meaning SnCl2 has a greater degree of covalent character than MgCl2 or FeCl2
- However, the metal in SnCl2 is not highly electronegative, which means it is less likely to share electrons with the non-metal Cl
AlCl3:
- Al is a metal and Cl is a non-metal
- The electronegativity difference between Al and Cl is moderate, meaning AlCl3 has some ionic character but also some covalent character
- However, AlCl3 is a Lewis acid, which means it can accept a lone pair of electrons from a Lewis base
- This Lewis acid-base interaction results in a greater degree of electron sharing between the Al and Cl atoms in AlCl3, giving it the highest covalent character among the given compounds
Therefore, the correct answer is (d) AlCl3.
Explanation:
MgCl2:
- Mg is a metal and Cl is a non-metal
- The electronegativity difference between Mg and Cl is large, meaning MgCl2 is an ionic compound
- Ionic compounds have low covalent character due to the complete transfer of electrons from the metal to the non-metal
FeCl2:
- Fe is a metal and Cl is a non-metal
- The electronegativity difference between Fe and Cl is moderate, meaning FeCl2 has some ionic character but also some covalent character
- However, the metal in FeCl2 is a transition metal, which can have variable oxidation states and can form complex ions. This makes it difficult to determine the exact degree of covalent character in FeCl2
SnCl2:
- Sn is a metal and Cl is a non-metal
- The electronegativity difference between Sn and Cl is small, meaning SnCl2 has a greater degree of covalent character than MgCl2 or FeCl2
- However, the metal in SnCl2 is not highly electronegative, which means it is less likely to share electrons with the non-metal Cl
AlCl3:
- Al is a metal and Cl is a non-metal
- The electronegativity difference between Al and Cl is moderate, meaning AlCl3 has some ionic character but also some covalent character
- However, AlCl3 is a Lewis acid, which means it can accept a lone pair of electrons from a Lewis base
- This Lewis acid-base interaction results in a greater degree of electron sharing between the Al and Cl atoms in AlCl3, giving it the highest covalent character among the given compounds
Therefore, the correct answer is (d) AlCl3.
Valence bond theory was introduced by:
- a)Gillespie
- b)Heitler
- c)Pauling
- d)Lewis
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Valence bond theory was introduced by:
a)
Gillespie
b)
Heitler
c)
Pauling
d)
Lewis
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
He then called up his associate Fritz London and they worked out the details of the theory over the course of the night. Later, Linus Pauling used the pair bonding ideas of Lewis together with Heitler–London theory to develop two other key concepts in VB theory: resonance (1928) and orbital hybridization (1930).
Direction (Q. Nos. 18 and 19) This section contains 2 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).Q. How many of the following molecules are polar?Cl2, ICI, BF3, NO, SO2
XeF4, CH2CI2, OCS, CO2- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 18 and 19) This section contains 2 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q. How many of the following molecules are polar?
Cl2, ICI, BF3, NO, SO2
XeF4, CH2CI2, OCS, CO2
XeF4, CH2CI2, OCS, CO2
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Due to electronegativity difference between the bonded atoms. ICI, NO, SO2, CH2CI2, OCS are polar compounds.
In which one of the following species the central atom has the type of hybridisation which si not the same as that present in the other three? - a)SF4
- b)I3-
- c)SbCl52-
- d)PCl5
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which one of the following species the central atom has the type of hybridisation which si not the same as that present in the other three?
a)
SF4
b)
I3-
c)
SbCl52-
d)
PCl5
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Molecules having the same number of hybrid orbitals, have same hybridisation and number of hybrid oebitals.
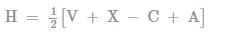
where,
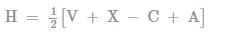
where,
V= number of valance electrons of central atom
X = number of monovalent atoms
C= charge on cation
A = charge on anion
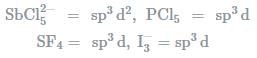
Which of the following angle corresponds to sp2 hybridisation?- a)90°
- b)120°
- c)180°
- d)109°
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following angle corresponds to sp2 hybridisation?
a)
90°
b)
120°
c)
180°
d)
109°
|
|
Arun Yadav answered |
sp2 hybridisation gives three sp2 hybrid orbitals which are planar triangular forming an angle of 120DEG with each other.
The electronic configurations of three elements A, B and C are given below.
Answer the questions from 14 to 17 on the basis of these configurations.
A ls2^2s2^2p^6
B ls2^2s2^2p63s23p^3
C ls2^2s2^2p63s^23ps
Which molecule has a bent shape?- a)CO2
- b)BeH2
- c)H2O
- d)NF3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which molecule has a bent shape?
a)
CO2
b)
BeH2
c)
H2O
d)
NF3
|
|
Shreya Singh answered |
Oxygen is sp3 hybridised in H2O molecule..... and it should have tetrahedral structure with bond angle 109•28'...but The oxygen has 6 valence electrons and thus needs 2 more electrons from 2 hydrogen atoms to complete its octet. This then leaves two lone electron pairs that are not bonded to any other atoms. ....The 2 lone electron pairs exerts a little extra repulsion on the two bonding hydrogen atoms to create a slight compression to a 104obond angle......and because of this it acquires bent/v/angular shape..
Which of the following structures is more acceptable for HNO3?- a)
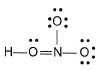
- b)
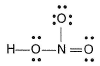
- c)Both equally
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following structures is more acceptable for HNO3?
a)
b)
c)
Both equally
d)
None of these
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
Structure is decided based on formal charge.
where, v = valence electrons
s = shared electrons
u = unshared electrons
Structure with at least one neutral atom is favoured.
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-15) This section contains 11 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.Q. For the
I. benzene (C6H6) and
II. borazine (B3N3H6)Select the correct statement.- a)C—H bond length in I is identical with N—H and B—H bond lengths
- b)The nature of double bond is perfectly identical in both
- c)Both the molecules are planar
- d)I is non-polar and II is polar
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-15) This section contains 11 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. For the
I. benzene (C6H6) and
II. borazine (B3N3H6)
I. benzene (C6H6) and
II. borazine (B3N3H6)
Select the correct statement.
a)
C—H bond length in I is identical with N—H and B—H bond lengths
b)
The nature of double bond is perfectly identical in both
c)
Both the molecules are planar
d)
I is non-polar and II is polar
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
(C—H) bond lengths are different from (B—H) and (N—H) bond lengths. Both are planar.
How many bonding MO are used in the formation of NO?
Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?
How many bonding MO are used in the formation of NO?

|
Vivek Kumar answered |
This question is wrong here its asking for bonding electron but answer is given for anti bonding .......
The common features among the species CN-, CO, NO+ and N2 are- a)isoelectronic, paramagnetic, bond order three
- b)isoelectronic, diamagnetic, bond order three
- c)isoelectronic, paramagnetic, bond order two
- d)isoelectronic, diamagnetic, bond order two
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The common features among the species CN-, CO, NO+ and N2 are
a)
isoelectronic, paramagnetic, bond order three
b)
isoelectronic, diamagnetic, bond order three
c)
isoelectronic, paramagnetic, bond order two
d)
isoelectronic, diamagnetic, bond order two

|
Arya Reddy answered |
Thus, all these are isoelectronic. MO electronic configuration is
No electron unpaired - diamagnetic
Bonding electrons = 10
Anti-bonding electrons = 4
Thus, bond- order =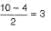
Bonding electrons = 10
Anti-bonding electrons = 4
Thus, bond- order =
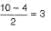
Among the following species linear shape is found in:- a)SO2
- b)O3
- c)NO2+
- d)NO2–
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following species linear shape is found in:
a)
SO2
b)
O3
c)
NO2+
d)
NO2–
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
In NO2(+) i.e. nitronium ion N-atom has sp-hybridisation ; so, it adopts linear geometry & O-N-O bond angle is 180 deg.
While, in NO2(–) i.e. nitrite ion, N–atom has sp2 hybridisation; so, it adopts bent geometry, for NO2–, actual O-N-O bond angle is 115 deg (yes, it's slightly deviated from expected 120deg because of repulsion between the interacting bond pairs and lone pair of electrons.
Two atoms are said to be bonded when:- a)System acquires minimum energy
- b)Potential energy becomes maximum
- c)Magnitude of attractive forces is greater than repulsive forces
- d)Energy becomes zero
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two atoms are said to be bonded when:
a)
System acquires minimum energy
b)
Potential energy becomes maximum
c)
Magnitude of attractive forces is greater than repulsive forces
d)
Energy becomes zero
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
Attractive forces tend to bring two atoms close to each other whereas repulsive forces tend to move them away. In hydrogen, the magnitude of the new attractive forces is greater than that of new repulsive forces. As a result, two atoms come close to each other and potential energy decreases. The atoms approach each other until the equilibrium stage is reached where the net force of attraction balances the force of repulsion and system acquires minimum energy.
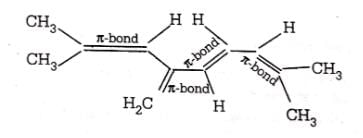
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-12) This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.Number of π bonds in the following structure is–
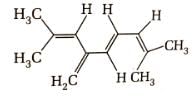
- a)4
- b)20
- c)19
- d)8
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-12) This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Number of π bonds in the following structure is–


a)
4
b)
20
c)
19
d)
8
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
In a given structure there are 4 -pi bonds.Hence, total number of pi electrons are 8.
Which of the following statement is incorrect regarding NO2 molecule?- a)It has one unpaired electron is one of the sp2-hybridised orbital
- b)It is coloured due to unpaired electron
- c)It is deeply coloured in dimeric form
- d)Paramagnetic behaviour is lost in dimeric form
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement is incorrect regarding NO2 molecule?
a)
It has one unpaired electron is one of the sp2-hybridised orbital
b)
It is coloured due to unpaired electron
c)
It is deeply coloured in dimeric form
d)
Paramagnetic behaviour is lost in dimeric form
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
NO2 molecule has unpaired electrons which are responsible for its brown colour and paramagnetic behavior.
Direction (Q. Nos. 12 and 14) This sectionis based on statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the code given below.Q. Statement I : BF3 molecule is planar but NF3 is pyramidal.Statement II : N atom is smaller than B.- a)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
- b)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
- c)Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- d)Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 12 and 14) This sectionis based on statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the code given below.
Q.
Statement I : BF3 molecule is planar but NF3 is pyramidal.
Statement II : N atom is smaller than B.
a)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
b)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
c)
Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
d)
Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect

|
Vikas Saini answered |
Nitrogen is smaller than boron.Wow what a chemistry
NH4NO3 and NH4NO2 differ is
- a) hybridisation of N of the anion
- b) hybridisation of N of the cation and anion both
- c) decomposition product
- d) structure of the anion
Correct answer is option 'B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
NH4NO3 and NH4NO2 differ is
a)
hybridisation of N of the anionb)
hybridisation of N of the cation and anion bothc)
decomposition productd)
structure of the anion

|
Kritika Bajaj answered |
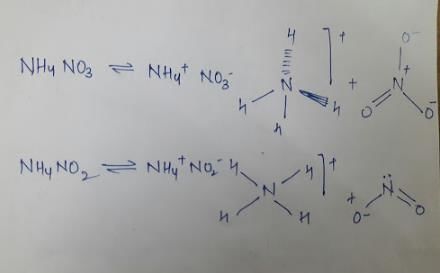
Hence we see that the two species differ in the hybridisation of Cation and anion, decomposition product and structure of anion.
Among the following molecules, the molecule with trigonal planar geometry is:- a)BF3
- b)IF3
- c)NH3
- d)PCl3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following molecules, the molecule with trigonal planar geometry is:
a)
BF3
b)
IF3
c)
NH3
d)
PCl3
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
(a) BF₃ ⇒ 3bp + 0/p ⇒ sp³ -hybridisation and triagonal planar geometry.
(b) IF₃ ⇒ 3bp + 2/p ⇒ sp³d -hybridisation and T shape.
(c) NH₃ ⇒ 3bp + 1/p ⇒ sp³ -hybridisation and pyraminal geometry.
(d) PH₃ ⇒ 3bp + 1/p ⇒ sp³ -hybridisation and pyraminal geometry.
(b) IF₃ ⇒ 3bp + 2/p ⇒ sp³d -hybridisation and T shape.
(c) NH₃ ⇒ 3bp + 1/p ⇒ sp³ -hybridisation and pyraminal geometry.
(d) PH₃ ⇒ 3bp + 1/p ⇒ sp³ -hybridisation and pyraminal geometry.
According to the VSEPR theory, the geometry and shape of the molecule depends upon:- a)Lone pair of electrons present on the central atom
- b)Bond pair of electrons present on the central atom
- c)Hybridization of the molecule
- d)Both bond pair as well as lone pair of electrons in the valence shell of the central atom
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
According to the VSEPR theory, the geometry and shape of the molecule depends upon:
a)
Lone pair of electrons present on the central atom
b)
Bond pair of electrons present on the central atom
c)
Hybridization of the molecule
d)
Both bond pair as well as lone pair of electrons in the valence shell of the central atom
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
For geometry and shape of a molecule, both bond pair and lone pair of electron in valence shell of central atom.
Which of the following equations can be constructed with x = 2?- a)3x+4=8
- b)3x−4=2
- c)3x+4=2
- d)3x−4=8
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following equations can be constructed with x = 2?
a)
3x+4=8
b)
3x−4=2
c)
3x+4=2
d)
3x−4=8
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
The correct answer is option B
Given x = 2:
Given x = 2:
3x - 4= 2
Putting x = 2;
⇒ (3 x 2) - 4 = 2
If one of the electrons in the He2 molecule is taken to the next excited state, then bond order in He2- a)increases by 1 unit
- b)decreases by 1 unit
- c)increases by 0.5 unit
- d)no change
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If one of the electrons in the He2 molecule is taken to the next excited state, then bond order in He2
a)
increases by 1 unit
b)
decreases by 1 unit
c)
increases by 0.5 unit
d)
no change
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Electron is taken to next excited state that is
Number of electrons in bonding molecular orbital = 3
and in anti-bonding molecular orbital = 1
Thus, bond order = (3 - 1) /2 =1
Thus, bond order increases by 1 unit.
Direction (Q. Nos. 18-20) This section contains a paragraph, each describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d).Fluorine nitrate, 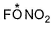 is an oxidising agent, used as a rocket propellant.
is an oxidising agent, used as a rocket propellant.
 this oxygen is different from other two)
this oxygen is different from other two)
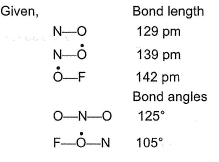
 Q. Possible structure of FONO2 is
Q. Possible structure of FONO2 is- a)
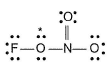
- b)
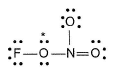
- c)Both (a) and (b)
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 18-20) This section contains a paragraph, each describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d).
Fluorine nitrate, 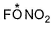 is an oxidising agent, used as a rocket propellant.
is an oxidising agent, used as a rocket propellant.
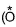 this oxygen is different from other two)
this oxygen is different from other two)
Q. Possible structure of FONO2 is
a)
b)
c)
Both (a) and (b)
d)
None of these
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
double bond single bond character character
Statement I : B atom is sp2-hybridised in B2H6.Statement II : There is no lone pair or unpaired electron in B2H6.- a)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
- b)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
- c)Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- d)Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement I : B atom is sp2-hybridised in B2H6.
Statement II : There is no lone pair or unpaired electron in B2H6.
a)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
b)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
c)
Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
d)
Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
(d) B2H6 has following types of bonding
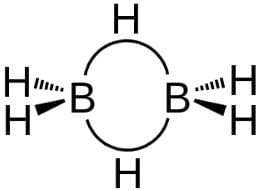
Bridging H-atoms and B-atoms are electron deficient. Each B-atom is however, joined to four H-atoms thus sp3-hybridised.
There is no lone pair or unpaired electron.
Thus, Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct.

Bridging H-atoms and B-atoms are electron deficient. Each B-atom is however, joined to four H-atoms thus sp3-hybridised.
There is no lone pair or unpaired electron.
Thus, Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct.
The statement that is true about H2O molecule is:- a)It has T-shaped geometry and two lone pair of electrons.
- b)It has V-shaped geometry and two lone pair of electrons.
- c)It has tetrahedral geometry and no lone pair of electrons.
- d)It has pyramidal geometry and one lone pair of electrons.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The statement that is true about H2O molecule is:
a)
It has T-shaped geometry and two lone pair of electrons.
b)
It has V-shaped geometry and two lone pair of electrons.
c)
It has tetrahedral geometry and no lone pair of electrons.
d)
It has pyramidal geometry and one lone pair of electrons.
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Central atom: O
At. no. = 8,
No. of valence electrons in oxygen is 6
Lewis dot structure of O atom

No. of electrons required for completing the octet = 8 - 6 =2
Atoms attached to the central atom: two H atoms
At. no. of H = 1
H atoms need one electron each for getting fully-filled K shells.
Representation of Lewis dot structures of H2O, which satisfies these conditions:
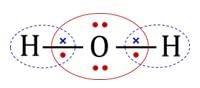
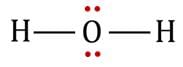
No. of valence shell electron pairs on the central atom O, after forming two covalent bonds with two H atoms = 4.
Geometry of 4 pairs, as predicted by VSEPR theory = Tetrahedral.
No. of lone pairs = Two.
Type, according to VSEPR theory:
So, geometry of pairs and geometry of atoms are different.
The geometry of atoms is derived from the geometry of pairs. At two of the four corners of the tetrahedron, there are no atoms.
Diagrams showing the geometry of 2 H atoms and two lone pairs:
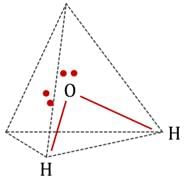
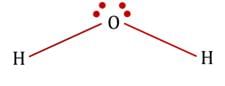
Geometry of atoms in H2O is V-shaped. i.e. H2O molecule has a bent geometry
Direction (Q. Nos. 15) This sectionis based on statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the code given below.Q. Statement I : N2 has a greater dissociation energy than 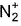 , where as O2 has lower dissociation energy than
, where as O2 has lower dissociation energy than 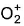 .Statement II : N2 has 14 electrons while O2 has 16 electrons .
.Statement II : N2 has 14 electrons while O2 has 16 electrons .- a)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
- b)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement
- c)Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- d)Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 15) This sectionis based on statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the code given below.
Q.
Statement I : N2 has a greater dissociation energy than 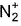 , where as O2 has lower dissociation energy than
, where as O2 has lower dissociation energy than 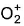 .
.
Statement II : N2 has 14 electrons while O2 has 16 electrons .
a)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
b)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement
c)
Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
d)
Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Electron from bonding molecular orbital of higher stability is lost (requires higher energy).
Electron from antibonding molecular orbital of lower stability is lost (requires lower energy).
N2 has 14 electrons and O2 has 16 electrons.
Thus, both Statements I and II are correct but Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
NO2 can be represented as 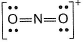 Q. Formal charge on each oxygen atom is
Q. Formal charge on each oxygen atom is- a)-2
- b)-1
- c)0
- d)+1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
NO2 can be represented as 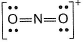
Q. Formal charge on each oxygen atom is
a)
-2
b)
-1
c)
0
d)
+1
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Formal charge (F)
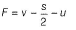
where, v = valence electrons = 6
s = shared electrons = 4
u = unshared electron = 4
s = shared electrons = 4
u = unshared electron = 4
Hydrogen bonds are formed in many compounds e.g., H2O, HF, NH3. The boiling point of such compounds depends to a large extent on the strength of hydrogen bond and the number of hydrogen bonds. The correct decreasing order of the boiling points of above compounds is :- a)HF > H2O > NH3
- b)H2O > HF > NH3
- c)NH3 > HF > H2O
- d)NH3 > H2O > HF
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Hydrogen bonds are formed in many compounds e.g., H2O, HF, NH3. The boiling point of such compounds depends to a large extent on the strength of hydrogen bond and the number of hydrogen bonds. The correct decreasing order of the boiling points of above compounds is :
a)
HF > H2O > NH3
b)
H2O > HF > NH3
c)
NH3 > HF > H2O
d)
NH3 > H2O > HF
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
Strength of H-bonding depends on the electronegativity of the atom which follows the order: F > O > N .
Strength of H-bond is in the order:
H……. F > H…….. O > H…….. N
But each H2O molecule is linked to 4 other H2O molecules through H-bonds whereas each HF molecule is linked only to two other HF molecules.
Hence, correct decreasing order of the boiling points is HzO > HF > NH3.
How many molecules out of the following have non-zero value of dipole moments?CH2CI2, CH4, CCI4, H2O, CHCI3, p-dichloro benzene, o-cresol, p-xylene, SCI2, BF3, IBr, HCHO
Correct answer is '7'. Can you explain this answer?
How many molecules out of the following have non-zero value of dipole moments?
CH2CI2, CH4, CCI4, H2O, CHCI3, p-dichloro benzene, o-cresol, p-xylene, SCI2, BF3, IBr, HCHO

|
Sarthak Verma answered |
CH2CI2,H2O,CHCI3,o-cresol, SCI2, IBr and HCHO (in all seven) have dipole moments.
CH4 is subjected to photochemical reaction and changes to CH3CI, CH2CI2, CHCI3 and CCI4.Q. One of the intermediates of the photochemical reaction is- a)methyl free radical with one unpaired electron, paramagnetic and sp2-hybridised carbon
- b)methyl carbocation with no lone pair sp2- hybridised carbon
- c)methyl carbanion with one lone pair sp3- hybridised carbon
- d)methyl free radical with one unpaired electron, paramagnetic sp3-hybridised carbon
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
CH4 is subjected to photochemical reaction and changes to CH3CI, CH2CI2, CHCI3 and CCI4.
Q. One of the intermediates of the photochemical reaction is
a)
methyl free radical with one unpaired electron, paramagnetic and sp2-hybridised carbon
b)
methyl carbocation with no lone pair sp2- hybridised carbon
c)
methyl carbanion with one lone pair sp3- hybridised carbon
d)
methyl free radical with one unpaired electron, paramagnetic sp3-hybridised carbon

|
Saptarshi Menon answered |
Thus, sp2-hybridised paramagnetic.
Chapter doubts & questions for Molecular Geometry - Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve 2025 is part of EmSAT Achieve exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the EmSAT Achieve exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for EmSAT Achieve 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Molecular Geometry - Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve in English & Hindi are available as part of EmSAT Achieve exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for EmSAT Achieve Exam by signing up for free.
Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve
191 videos|265 docs|160 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily

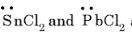 are bent shape molecule.
are bent shape molecule.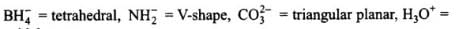 pyramidal.
pyramidal.