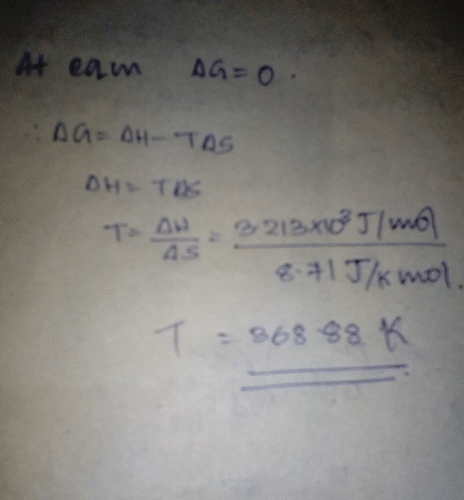All Exams >
EmSAT Achieve >
Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve >
All Questions
All questions of Entropy for EmSAT Achieve Exam
In which of the following cases, entropy of I is larger than that of II?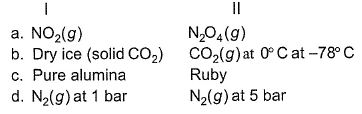
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following cases, entropy of I is larger than that of II?
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d

|
Infinity Academy answered |
a) More molar mass, more entropy. So ∆SN2O4 > ∆SNO2
b) CO2 has more entropy than dry ice at -78°C
c) Pure alumina iss crystalline solid while ruby is amorphous. And ∆Samorphous > ∆SCrystalline. So alumina has less entropy than ruby.
d) At lower pressure, entropy be higher as gas particles are far from each other. So (∆SN2)1 bar > (∆SN2)5 bar
b) CO2 has more entropy than dry ice at -78°C
c) Pure alumina iss crystalline solid while ruby is amorphous. And ∆Samorphous > ∆SCrystalline. So alumina has less entropy than ruby.
d) At lower pressure, entropy be higher as gas particles are far from each other. So (∆SN2)1 bar > (∆SN2)5 bar
3 moles of a diatomic gas are heated from 127° C to 727° C at a constant pressure of 1 atm. Entropy change is (log 2.5 = 0 .4)- a)-22.98 JK-1
- b)22.98 JK-1
- c)57.4 JK-1
- d)80.42 JK-1
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
3 moles of a diatomic gas are heated from 127° C to 727° C at a constant pressure of 1 atm. Entropy change is (log 2.5 = 0 .4)
a)
-22.98 JK-1
b)
22.98 JK-1
c)
57.4 JK-1
d)
80.42 JK-1

|
Crafty Classes answered |
∆S = nCplnT2/T1 + nRlnP1/P2
Since pressure is constant, so the second term will be zero.
Or ∆S = 3×7/2×8.314×2.303×log(1000/400)
= 80.42 JK-1
Since pressure is constant, so the second term will be zero.
Or ∆S = 3×7/2×8.314×2.303×log(1000/400)
= 80.42 JK-1
The equilibrium constant for a reaction is 10. Calculate the value of ΔG° at 300K , R = R =8.314 JK−1mol−1
- a)-5.527 kJ/mol–
- b)4.744 kJ/mol
- c)-4.744 kJ/mol–
- d)- 5.744 kJ/mol
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The equilibrium constant for a reaction is 10. Calculate the value of ΔG° at 300K , R = R =8.314 JK−1mol−1
a)
-5.527 kJ/mol–
b)
4.744 kJ/mol
c)
-4.744 kJ/mol–
d)
- 5.744 kJ/mol

|
Infinity Academy answered |
The value of equilibrium constant(k) = 10
∆G° = -2.303RTlogk
On calculating values, we will get ∆G° = -5.744kJmol-1
∆G° = -2.303RTlogk
On calculating values, we will get ∆G° = -5.744kJmol-1
Consider the following figure representing the increase in entropy of a substance from absolute zero to its gaseous state at some temperature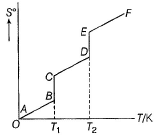 Q. ΔS° (fusion) and ΔS° (vaporisation) are respectively indicated by
Q. ΔS° (fusion) and ΔS° (vaporisation) are respectively indicated by - a)AB, BC
- b)BC,CD
- c)BC, DE
- d)CD, DE
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following figure representing the increase in entropy of a substance from absolute zero to its gaseous state at some temperature
Q. ΔS° (fusion) and ΔS° (vaporisation) are respectively indicated by
a)
AB, BC
b)
BC,CD
c)
BC, DE
d)
CD, DE
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
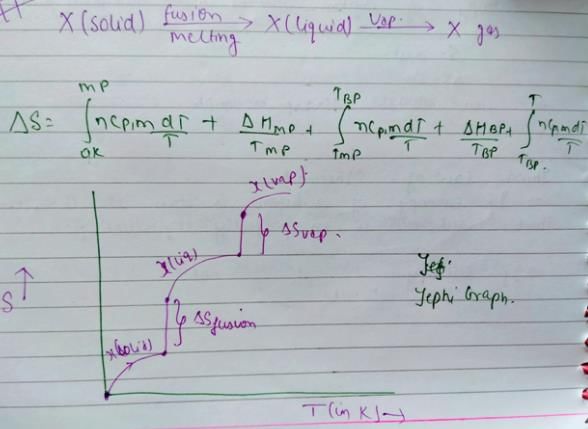
You can co-relate both graph and the result will be option c.
Standard entropies of X2, Y2 and XY3 are given below the reaction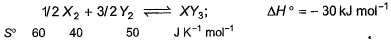 Q. At what temperature, reaction would be in equilibrium?
Q. At what temperature, reaction would be in equilibrium? - a)500 K
- b)750 K
- c)1000 K
- d)1250 K
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Standard entropies of X2, Y2 and XY3 are given below the reaction
Q. At what temperature, reaction would be in equilibrium?
a)
500 K
b)
750 K
c)
1000 K
d)
1250 K
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
1/2X2 + 3/2Y2 ⟶XY3,
ΔH= −30 kJ
ΔSreaction = ∑ΔSproduct−∑ΔSreactant
X2 + 3Y2 → 2XY3
ΔH=−60 kJ
ΔSreaction = 2×50−3×40−1×60 =100−120−60=−80 JK−1mol−1
ΔG=ΔH−TΔS=0
ΔH=TΔS
1000×(−60)=−80×T
T=750 K
ΔH= −30 kJ
ΔSreaction = ∑ΔSproduct−∑ΔSreactant
X2 + 3Y2 → 2XY3
ΔH=−60 kJ
ΔSreaction = 2×50−3×40−1×60 =100−120−60=−80 JK−1mol−1
ΔG=ΔH−TΔS=0
ΔH=TΔS
1000×(−60)=−80×T
T=750 K
For the process,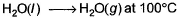 and 1 atmosphere pressure, the correct choice is[JEE Advanced 2014]
and 1 atmosphere pressure, the correct choice is[JEE Advanced 2014]- a)ΔS(System) > 0, ΔS(surrounding) > 0
- b)ΔS(System) > 0, ΔS(surrounding) < 0
- c)ΔS(System) < 0, ΔS(surrounding) > 0
- d)ΔS(System) < 0, ΔS(surrounding) < 0
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For the process,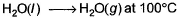 and 1 atmosphere pressure, the correct choice is
and 1 atmosphere pressure, the correct choice is
[JEE Advanced 2014]
a)
ΔS(System) > 0, ΔS(surrounding) > 0
b)
ΔS(System) > 0, ΔS(surrounding) < 0
c)
ΔS(System) < 0, ΔS(surrounding) > 0
d)
ΔS(System) < 0, ΔS(surrounding) < 0
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
At 100°C and 1 atmosphere pressure H2O (l) ⇋ H2O(g) is at equilibrium. For equilibrium


GivenI. C (diamond) + O2(g) → CO2(g) ; ΔH° = - 91.0 kcdl mol-1
II. C(graphite) + O2(g) → CO2(g) ; ΔH° = - 94.0 kcal mol-1Q. At 298 K, 2.4 kg of carbon (diamond) is converted into graphite form. Thus, entropy change is- a)10.07 cal K-1
- b)2.013 kcal K-1
- c)305.4 cal K-1
- d)- 2.013 kcal K-1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Given
I. C (diamond) + O2(g) → CO2(g) ; ΔH° = - 91.0 kcdl mol-1
II. C(graphite) + O2(g) → CO2(g) ; ΔH° = - 94.0 kcal mol-1
II. C(graphite) + O2(g) → CO2(g) ; ΔH° = - 94.0 kcal mol-1
Q. At 298 K, 2.4 kg of carbon (diamond) is converted into graphite form. Thus, entropy change is
a)
10.07 cal K-1
b)
2.013 kcal K-1
c)
305.4 cal K-1
d)
- 2.013 kcal K-1
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
The reaction is
C(diamond) → C(graphite) ∆H = (94-91) = 3 kcal mol-1
∆S = ∆H/T
∆H = (94-91)×2.4×103/12
= 600 kcal
∆S = 600/298 = 2.013 kcal K-1
C(diamond) → C(graphite) ∆H = (94-91) = 3 kcal mol-1
∆S = ∆H/T
∆H = (94-91)×2.4×103/12
= 600 kcal
∆S = 600/298 = 2.013 kcal K-1
Which reaction, with the following values of ΔH and ΔS at 400 K is spontaneous and endothermic?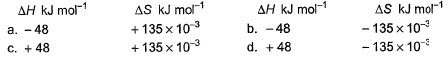
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which reaction, with the following values of ΔH and ΔS at 400 K is spontaneous and endothermic?
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Om Desai answered |
∆G = ∆H - T∆S
For opt (c), ∆G = 48000 - 400(135)
= 48000 - 54000
= -6000
∆G is -ve
Therefore reaction is spontaneous.
For opt (c), ∆G = 48000 - 400(135)
= 48000 - 54000
= -6000
∆G is -ve
Therefore reaction is spontaneous.
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.Q. Entropy change for the following reversible process is 1 mole H2O(l, 1 atm, 100°C )  1 mole H2O (g , 1 atm, 100°C)(ΔHvap = 40850 J mol-1)
1 mole H2O (g , 1 atm, 100°C)(ΔHvap = 40850 J mol-1)- a)+109.52 JK-1 mol-1
- b)-109.52 JK-1 mol-1
- c)0.00 JK-1 mol-1
- d)+6.084 JK-1 mol-1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Entropy change for the following reversible process is 1 mole H2O
(l, 1 atm, 100°C )  1 mole H2O (g , 1 atm, 100°C)(ΔHvap = 40850 J mol-1)
1 mole H2O (g , 1 atm, 100°C)(ΔHvap = 40850 J mol-1)
a)
+109.52 JK-1 mol-1
b)
-109.52 JK-1 mol-1
c)
0.00 JK-1 mol-1
d)
+6.084 JK-1 mol-1
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
∆S=Change in energy/Absolute temp =∆H/(100+273)K =40850/373 = 109.52 J/K/mol
Passage II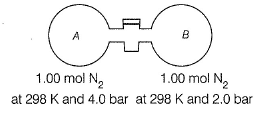 The stopcock connecting A and B is of negligible volume. Stopcock is opened and gases are allowed to mix isothermally. Q. Final pressure set up is
The stopcock connecting A and B is of negligible volume. Stopcock is opened and gases are allowed to mix isothermally. Q. Final pressure set up is- a)6.00 bar
- b)4.00 bar
- c)2.00 bar
- d)2.67 bar
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage II
The stopcock connecting A and B is of negligible volume. Stopcock is opened and gases are allowed to mix isothermally.
Q. Final pressure set up is
a)
6.00 bar
b)
4.00 bar
c)
2.00 bar
d)
2.67 bar

|
Lohit Matani answered |
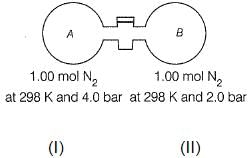
Volume in (I) = nRT/P1 = 1× 0.0821× 298/4 = 6.11 L
Volume in (II) = nRT/P2 = 1× 0.0821× 298/2 = 12.23 L
Total volume = 18.34 L
Applying PV = nRT at final condition,
P = 2× 0.0821× 298/18.34 = 2.66
Which of the following statements is correct about the process of evaporation of water from an open beaker?- a)It is a spontaneous and endothermic process.
- b)It is a non-spontaneous and endothermic process.
- c)It is a spontaneous and exothermic process.
- d)It is a non-spontaneous and exothermic process.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is correct about the process of evaporation of water from an open beaker?
a)
It is a spontaneous and endothermic process.
b)
It is a non-spontaneous and endothermic process.
c)
It is a spontaneous and exothermic process.
d)
It is a non-spontaneous and exothermic process.
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Evaporation of water from an open pot is a spontaneous process. As it starts on its own without any external agent. However it takes heat from surrounding means that it is endothermic.
The value of log10 K for a reaction, A  B is (Given, ΔH°298 = - 54.07 kJ mol-1;ΔS°298 = + 10 JK-1 mol-1; R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1 2.303 x 8.314 x 298 = 5705) [IITJEE2007]
B is (Given, ΔH°298 = - 54.07 kJ mol-1;ΔS°298 = + 10 JK-1 mol-1; R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1 2.303 x 8.314 x 298 = 5705) [IITJEE2007]- a)5
- b)10
- c)95
- d)100
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The value of log10 K for a reaction, A  B is (Given, ΔH°298 = - 54.07 kJ mol-1;
B is (Given, ΔH°298 = - 54.07 kJ mol-1;
ΔS°298 = + 10 JK-1 mol-1; R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1 2.303 x 8.314 x 298 = 5705)
[IITJEE2007]
a)
5
b)
10
c)
95
d)
100
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
∆G° = ∆H° - T∆S°
= -54070 - 298 10
= -57050
∆G° = -2.303 RT log10k
-57050 = -2.303 8.314 298 log10k
57050 = 5705 log10k
log10k = 10
= -54070 - 298 10
= -57050
∆G° = -2.303 RT log10k
-57050 = -2.303 8.314 298 log10k
57050 = 5705 log10k
log10k = 10
10 dm3 of an ideal monoatomic gas at 27° C and 1.01 x 105 Nm-2 pressure are heated at constant pressure to 127°C. Thus entropy change is- a)2.422 JK-1
- b)5.98 JK-1
- c)- 2.422 JK-1
- d)- 5.981 JK-1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
10 dm3 of an ideal monoatomic gas at 27° C and 1.01 x 105 Nm-2 pressure are heated at constant pressure to 127°C. Thus entropy change is
a)
2.422 JK-1
b)
5.98 JK-1
c)
- 2.422 JK-1
d)
- 5.981 JK-1
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
For isobaric process, we have ∆S =nCpln(T2/T1)
T2 = 273+127 = 400K and T1 = 273+227 = 300K
Applying pV = nRT at initial condition,
1×10 = n×0.0821×300
n = 0.40
Applying ∆S =nCpln(T2/T1)
∆S =0.40×5/2R×ln(400/300) = 2.38 JK-1
T2 = 273+127 = 400K and T1 = 273+227 = 300K
Applying pV = nRT at initial condition,
1×10 = n×0.0821×300
n = 0.40
Applying ∆S =nCpln(T2/T1)
∆S =0.40×5/2R×ln(400/300) = 2.38 JK-1
ΔHvap = 30 kJ mol-1 and ΔSvap = 75 J mol-1 K-1. Thus, temperature of the vapour at 1 atm is[IIT JEE 2004]- a)400 K
- b)350 K
- c)298 K
- d)250 K
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
ΔHvap = 30 kJ mol-1 and ΔSvap = 75 J mol-1 K-1. Thus, temperature of the vapour at 1 atm is
[IIT JEE 2004]
a)
400 K
b)
350 K
c)
298 K
d)
250 K
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Vapour pressure is equal to atmospheric pressure ,it means the substance is at boiling point
At boiling point, liquid and Gas are in equilibrium. Therefore dG=0
dG = H - TdS
dG = 0
⇒H = TdS
⇒T = H/dS
⇒ T = 30 103/75 = 400K
At boiling point, liquid and Gas are in equilibrium. Therefore dG=0
dG = H - TdS
dG = 0
⇒H = TdS
⇒T = H/dS
⇒ T = 30 103/75 = 400K
Passage IIFor oxidation of iron at 298 K, 4 Fe (s) + 3 O2(g) → 2 Fe2O3(s)
ΔS° = - 549.4 JK-1 mol-1 and ΔH ° = - 1648 . 0 kJ mol-1 Q. Select the correct alternate.- a)This reaction is spontaneous
- b)ΔS° (surrounding) > 0
- c)ΔS° (total) > 0
- d)All of these are correct statements
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage II
For oxidation of iron at 298 K, 4 Fe (s) + 3 O2(g) → 2 Fe2O3(s)
ΔS° = - 549.4 JK-1 mol-1 and ΔH ° = - 1648 . 0 kJ mol-1
ΔS° = - 549.4 JK-1 mol-1 and ΔH ° = - 1648 . 0 kJ mol-1
Q. Select the correct alternate.
a)
This reaction is spontaneous
b)
ΔS° (surrounding) > 0
c)
ΔS° (total) > 0
d)
All of these are correct statements

|
Deepaklal T S answered |
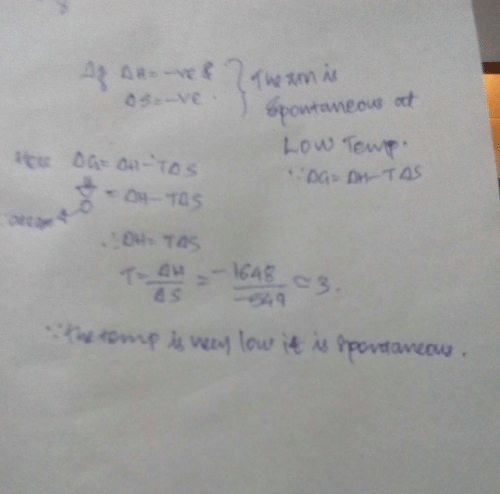
Entropy change when 2 moles of an ideal gas expands reversibly from an initial volume of 1 dm3 to a final volume of 10 dm3 at a constant temperature of 298 K is- a)5705.8 JK-1
- b)19.15 JK-1
- c)38.29 JK-1
- d)-19.15 JK-1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Entropy change when 2 moles of an ideal gas expands reversibly from an initial volume of 1 dm3 to a final volume of 10 dm3 at a constant temperature of 298 K is
a)
5705.8 JK-1
b)
19.15 JK-1
c)
38.29 JK-1
d)
-19.15 JK-1
|
|
Om Desai answered |
∆S= 2.303nR × log(V2/V1)Here n=2, R=8.314, V2= 10, V1= 1
For a spontaneous chemical process, the free energy change is- a)not measurable
- b)negative
- c)positive
- d)zero
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For a spontaneous chemical process, the free energy change is
a)
not measurable
b)
negative
c)
positive
d)
zero

|
Ameya Basu answered |
The sign of ΔG will change from positive to negative (or vice versa) where T = ΔH/ΔS. In cases where ΔG is: negative, the process is spontaneous and may proceed in the forward direction as written. positive, the process is non-spontaneous as written, but it may proceed spontaneously in the reverse direction.
Which of the following is true about a spontaneous process?- a)Spontaneity does not depend on Gibbs energy.
- b)Gibbs energy change is less than 0.
- c)Gibbs energy change is 0.
- d)Gibbs energy change is greater than 0.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is true about a spontaneous process?
a)
Spontaneity does not depend on Gibbs energy.
b)
Gibbs energy change is less than 0.
c)
Gibbs energy change is 0.
d)
Gibbs energy change is greater than 0.

|
Ameya Basu answered |
A spontaneous process is the time-evolution of a system in which it releases free energy and it moves to a lower, more thermodynamically stable energy state. For cases involving an isolated system where no energy is exchanged with the surroundings, spontaneous processes are characterized by an increase in entropy
Which of the following is extensive property?- a)Specific heat capacity
- b)Entropy
- c)Temperature
- d)Refractive index
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is extensive property?
a)
Specific heat capacity
b)
Entropy
c)
Temperature
d)
Refractive index
|
|
Tanishq Unni answered |
Extensive Property:
An extensive property is a physical property of a system that depends on the amount of substance present in the system. In other words, extensive properties are additive and scale with the size or amount of the system. The value of an extensive property changes when the size or amount of the system changes.
Explanation:
Out of the given options, the correct answer is option 'B' - Entropy.
Entropy is a measure of the disorder or randomness of a system. It is a thermodynamic property that quantifies the number of microscopic configurations that a system can have. Entropy is an extensive property because it depends on the size or amount of the system.
Comparison with Other Options:
a) Specific Heat Capacity:
Specific heat capacity is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a substance by a certain amount. It is an intensive property because it does not depend on the amount of substance present. The specific heat capacity of a substance remains the same regardless of the size or amount of the substance.
b) Entropy:
As mentioned earlier, entropy is an extensive property as it depends on the amount of substance present in the system. If the system size or amount changes, the entropy of the system will also change proportionally.
c) Temperature:
Temperature is an intensive property because it does not depend on the amount of substance present. The temperature of a substance remains the same regardless of the size or amount of the substance.
d) Refractive Index:
Refractive index is a measure of how light propagates through a medium. It is an intensive property because it does not depend on the amount of substance present. The refractive index of a substance remains the same regardless of the size or amount of the substance.
Conclusion:
Among the given options, entropy is the only extensive property. It is a thermodynamic property that depends on the amount of substance present in the system. The other options, specific heat capacity, temperature, and refractive index, are intensive properties that do not depend on the amount of substance present.
An extensive property is a physical property of a system that depends on the amount of substance present in the system. In other words, extensive properties are additive and scale with the size or amount of the system. The value of an extensive property changes when the size or amount of the system changes.
Explanation:
Out of the given options, the correct answer is option 'B' - Entropy.
Entropy is a measure of the disorder or randomness of a system. It is a thermodynamic property that quantifies the number of microscopic configurations that a system can have. Entropy is an extensive property because it depends on the size or amount of the system.
Comparison with Other Options:
a) Specific Heat Capacity:
Specific heat capacity is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a substance by a certain amount. It is an intensive property because it does not depend on the amount of substance present. The specific heat capacity of a substance remains the same regardless of the size or amount of the substance.
b) Entropy:
As mentioned earlier, entropy is an extensive property as it depends on the amount of substance present in the system. If the system size or amount changes, the entropy of the system will also change proportionally.
c) Temperature:
Temperature is an intensive property because it does not depend on the amount of substance present. The temperature of a substance remains the same regardless of the size or amount of the substance.
d) Refractive Index:
Refractive index is a measure of how light propagates through a medium. It is an intensive property because it does not depend on the amount of substance present. The refractive index of a substance remains the same regardless of the size or amount of the substance.
Conclusion:
Among the given options, entropy is the only extensive property. It is a thermodynamic property that depends on the amount of substance present in the system. The other options, specific heat capacity, temperature, and refractive index, are intensive properties that do not depend on the amount of substance present.
Direction (Q. Nos. 19 and 20) This section contains 2 questions. Each question, when worked out will result in an integer from 0 fo 9 (both inclusive).Q. Consider two Carnot engines (1) and (2)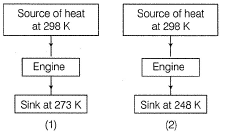 Efficiency η2
Efficiency η2
Derive the value of η2 η1
Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 19 and 20) This section contains 2 questions. Each question, when worked out will result in an integer from 0 fo 9 (both inclusive).
Q. Consider two Carnot engines (1) and (2)
Efficiency η2
Derive the value of η2 η1
Derive the value of η2 η1
|
|
Om Desai answered |
η1 = 1-273/298 = 25/298
η2 = 1-248/298 = 50/298
η2/η1 = (50/298)/25/298 = 2
η2 = 1-248/298 = 50/298
η2/η1 = (50/298)/25/298 = 2
The value of ΔS for spontaneous process is- a)ΔSTotal is constant
- b)ΔSTotal > 0
- c)ΔSTotal < 0
- d)ΔSTotal = 0
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The value of ΔS for spontaneous process is
a)
ΔSTotal is constant
b)
ΔSTotal > 0
c)
ΔSTotal < 0
d)
ΔSTotal = 0

|
Raghav Yadav answered |
The second law of thermodynamics states that for any spontaneous process, the overall ΔS must be greater than or equal to zero; yet, spontaneous chemical reactions can result in a negative change in entropy.
What is the change in the entropy of water, When ice melts into water?- a)Entropy of water increases.
- b)Entropy of water becomes zero.
- c)Entropy of water decreases.
- d)Entropy of water remains same.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the change in the entropy of water, When ice melts into water?
a)
Entropy of water increases.
b)
Entropy of water becomes zero.
c)
Entropy of water decreases.
d)
Entropy of water remains same.

|
Raghav Yadav answered |
The greater the randomness in a system, greater is its entropy. The randomness is greater in liquid state as compared to solid state so the entropy increases when ice melts into water.
Direction (Q. No. 9) This sectionis based on statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the code given below.Q. Statement I :Every endothermic reaction is spontaneous if TΔS > ΔH.Statement II : Sign of ΔG is the true criterion for deciding spontaneity of a reaction.- a)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
- b)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
- c)Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- d)Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. No. 9) This sectionis based on statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the code given below.
Q.
Statement I :Every endothermic reaction is spontaneous if TΔS > ΔH.
Statement II : Sign of ΔG is the true criterion for deciding spontaneity of a reaction.
a)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
b)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
c)
Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
d)
Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect

|
Ambition Institute answered |
Statement I: Every endothermic reaction is spontaneous if TΔS > ΔH.
Endothermic reactions have a positive ΔH (heat absorbed). For spontaneity, we use the Gibbs free energy equation:
ΔG=ΔH−TΔS\Delta G = \Delta H - T\Delta SΔG=ΔH−TΔS For a process to be spontaneous, ΔG<0\Delta G < 0ΔG<0. If TΔS>ΔHT\Delta S > \Delta HTΔS>ΔH, then ΔG\Delta GΔG becomes negative, indicating spontaneity. Hence, Statement I is correct.
ΔG=ΔH−TΔS\Delta G = \Delta H - T\Delta SΔG=ΔH−TΔS For a process to be spontaneous, ΔG<0\Delta G < 0ΔG<0. If TΔS>ΔHT\Delta S > \Delta HTΔS>ΔH, then ΔG\Delta GΔG becomes negative, indicating spontaneity. Hence, Statement I is correct.
Statement II: Sign of ΔG is the true criterion for deciding spontaneity of a reaction.
This is a fundamental thermodynamic principle. The sign of ΔG\Delta GΔG indeed determines whether a reaction is spontaneous (ΔG<0\Delta G < 0ΔG<0) or non-spontaneous (ΔG>0\Delta G > 0ΔG>0). Hence, Statement II is also correct.
Correct Answer: Since both statements are correct and the second statement explains the first, the correct option is:
A: Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I.
In the evaporation of water, the entropy- a)does not change
- b)increases
- c)decreases
- d)first increases and then decreases
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the evaporation of water, the entropy
a)
does not change
b)
increases
c)
decreases
d)
first increases and then decreases

|
Raghav Yadav answered |
The entropy of vaporization is the increase in entropy upon vaporization of a liquid. This is always positive, since the degree of disorder increases in the transition from a liquid in a relatively small volume to a vapor or gas occupying a much larger space.
For the reaction Hg (l) ———> Hg (g) , the entropy change will have the sign:
- a)Negative
- b)Positive
- c)Both positive and negative
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For the reaction Hg (l) ———> Hg (g) , the entropy change will have the sign:
a)
Negative
b)
Positive
c)
Both positive and negative
d)
None of the above
|
|
Deepak Kumar answered |
Hg(l) is the chemical formula for liquid mercury.
A cyclic heat engine operates between a source temperature of 927 oC and a sink temperature of 27 oC. What will be the maximum efficiency of the heat engine?- a)100 %
- b)80 %
- c)75 %
- d)70 %
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A cyclic heat engine operates between a source temperature of 927 oC and a sink temperature of 27 oC. What will be the maximum efficiency of the heat engine?
a)
100 %
b)
80 %
c)
75 %
d)
70 %

|
Anisha Chauhan answered |
Heat engine is operated between the temperatures
T1 = 927 0C = 927 + 273 = 1200 K and
T2 = 27 0C = 27 + 273 = 300 K
The maximum efficiency of a heat engine is given by,
ηmax = 1 – (T2/T1)
ηmax = 1 – (300/1200)
ηmax = 0.75
T1 = 927 0C = 927 + 273 = 1200 K and
T2 = 27 0C = 27 + 273 = 300 K
The maximum efficiency of a heat engine is given by,
ηmax = 1 – (T2/T1)
ηmax = 1 – (300/1200)
ηmax = 0.75
Consider a reversible isentropic expansion of 1.0 mole of an ideal monoatomic gas from 25°C to 75°C. If the initial pressure was 1.0 bar, final pressure is - a)1.474 bar
- b)0.678 bar
- c)0.796 bar
- d)1.00 bar
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider a reversible isentropic expansion of 1.0 mole of an ideal monoatomic gas from 25°C to 75°C. If the initial pressure was 1.0 bar, final pressure is
a)
1.474 bar
b)
0.678 bar
c)
0.796 bar
d)
1.00 bar
|
|
Sonal Dey answered |
Isentropic process means that entropy is constant. This is true only for reversible adiabatic process.
Applying P11-γ T1γ = P21-γ T2γ (for monatomic species, γ = 5/3)
(1/P)-⅔ = (75+273/25+273)5/3
Or (1/P)-2 = (348/298)5
Or P = 1.474 bar
Applying P11-γ T1γ = P21-γ T2γ (for monatomic species, γ = 5/3)
(1/P)-⅔ = (75+273/25+273)5/3
Or (1/P)-2 = (348/298)5
Or P = 1.474 bar
Direction (Q. Nos. 10 and 11) This section contains 2 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.Q. Which of the following statements is/are true?- a)The entropy of a substance increases on going from the liquid to the vapour state at any temperature
- b)An exothermic reaction will always be spontaneous
- c)Reactions with a positive (ΔH° and ΔS°) can never be product favoured
- d)If ΔG° for a reaction is negative, the reaction will have an equilibrium constant i greater than one
Correct answer is option 'A,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 10 and 11) This section contains 2 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
Q. Which of the following statements is/are true?
a)
The entropy of a substance increases on going from the liquid to the vapour state at any temperature
b)
An exothermic reaction will always be spontaneous
c)
Reactions with a positive (ΔH° and ΔS°) can never be product favoured
d)
If ΔG° for a reaction is negative, the reaction will have an equilibrium constant i greater than one
|
|
Pallabi Rane answered |
The entropy of a substance increases on going from the liquid to the vapour state at any temperature. It is true. As randomness increases, entropy also increases.
∆G = ∆H - T∆S. So for spontaneous reaction, all 3(T, ∆H and ∆S) are needed.
An exothermic reaction will always be spontaneous. THis is false
Reactions with a positive (ΔH° and ΔS°) can never be product favoured. False, for a larger value of T, ∆G might be negative.
If ΔG° for a reaction is negative, the reaction will have an equilibrium constant greater than one. True, for ΔG° less than 0, reaction is spontaneous and so, ith=s eqm constant will have value greater than 1.
∆G = ∆H - T∆S. So for spontaneous reaction, all 3(T, ∆H and ∆S) are needed.
An exothermic reaction will always be spontaneous. THis is false
Reactions with a positive (ΔH° and ΔS°) can never be product favoured. False, for a larger value of T, ∆G might be negative.
If ΔG° for a reaction is negative, the reaction will have an equilibrium constant greater than one. True, for ΔG° less than 0, reaction is spontaneous and so, ith=s eqm constant will have value greater than 1.
Calculate the Gibbs free energy for the reaction of conversion of ATP into ADP at 293 Kelvin the change in enthalpy is 19.07 Kcal and the change in entropy is 90 cal per Kelvin.- a)7.3 cal
- b)-5.3 Kcal
- c)7.3 Kcal
- d) -7.3 Kcal
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the Gibbs free energy for the reaction of conversion of ATP into ADP at 293 Kelvin the change in enthalpy is 19.07 Kcal and the change in entropy is 90 cal per Kelvin.
a)
7.3 cal
b)
-5.3 Kcal
c)
7.3 Kcal
d)
-7.3 Kcal
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
We have ΔG = ΔH – TΔS; by substituting ΔH = 19.07 kcal and ΔS = 90 cal/K, we get ΔG = 19.07 Kcal – 293(90 cal/K) = 19.07 Kcal – 26.37 Kcal = -7300 cal = -7.3 Kcal. The Gibbs free energy change is -7.3 Kcal.
Which of the following is NOT a state function?- a)q + w
- b)q
- c)qrev/T
- d)PV
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is NOT a state function?
a)
q + w
b)
q
c)
qrev/T
d)
PV

|
Nitin Sharma answered |
A state function is the property of the system whose value depends only on the initial and final state of the system and is independent of the path. It is a state function because it is independent of the path. Heat (q) and work (W) are not state functions being path dependent.
Exactly 100 J of heat was transferred reversibly to a block of gold at 25.00° C from a thermal reservoir at 25.01 °C, and then exactly 100 J of heat was absorbed reversibled from the block of gold by a thermal reservoir at 24.99° C. Thus entropy change of the system is- a)0.335 JK-1
- b)-0.33 JK-1
- c)0.670 JK-1
- d)0.00 JK-1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Exactly 100 J of heat was transferred reversibly to a block of gold at 25.00° C from a thermal reservoir at 25.01 °C, and then exactly 100 J of heat was absorbed reversibled from the block of gold by a thermal reservoir at 24.99° C. Thus entropy change of the system is
a)
0.335 JK-1
b)
-0.33 JK-1
c)
0.670 JK-1
d)
0.00 JK-1
|
|
Bhargavi Joshi answered |
Explanation:
To find out the entropy change of the system, we need to use the formula:
ΔS = Q/T
where ΔS is the entropy change, Q is the amount of heat transferred, and T is the temperature at which the heat is transferred.
Given that 100 J of heat was transferred from a thermal reservoir at 25.01 C to a block of gold at 25.00 C, we can calculate the entropy change as follows:
ΔS1 = Q1/T1 = 100 J/298.16 K = 0.335 JK-1
where T1 = 25.01 C + 273.15 = 298.16 K
Similarly, when 100 J of heat was absorbed from the block of gold by a thermal reservoir at 24.99 C, we can calculate the entropy change as follows:
ΔS2 = Q2/T2 = -100 J/298.14 K = -0.335 JK-1
where T2 = 24.99 C + 273.15 = 298.14 K
Note that the negative sign in front of ΔS2 indicates that the process is reversible, which is consistent with the problem statement.
Therefore, the total entropy change of the system is:
ΔS = ΔS1 + ΔS2 = 0.335 JK-1 + (-0.335 JK-1) = 0.00 JK-1
Hence, the correct option is (c) 0.670 JK-1.
To find out the entropy change of the system, we need to use the formula:
ΔS = Q/T
where ΔS is the entropy change, Q is the amount of heat transferred, and T is the temperature at which the heat is transferred.
Given that 100 J of heat was transferred from a thermal reservoir at 25.01 C to a block of gold at 25.00 C, we can calculate the entropy change as follows:
ΔS1 = Q1/T1 = 100 J/298.16 K = 0.335 JK-1
where T1 = 25.01 C + 273.15 = 298.16 K
Similarly, when 100 J of heat was absorbed from the block of gold by a thermal reservoir at 24.99 C, we can calculate the entropy change as follows:
ΔS2 = Q2/T2 = -100 J/298.14 K = -0.335 JK-1
where T2 = 24.99 C + 273.15 = 298.14 K
Note that the negative sign in front of ΔS2 indicates that the process is reversible, which is consistent with the problem statement.
Therefore, the total entropy change of the system is:
ΔS = ΔS1 + ΔS2 = 0.335 JK-1 + (-0.335 JK-1) = 0.00 JK-1
Hence, the correct option is (c) 0.670 JK-1.
ΔHvap = 30 kJ mol-1 and ΔSvap = 75 J mol-1 K-1. Thus, temperature of vapour at one atmosphere is[IIT JEE 2004]- a)400 K
- b)350 K
- c)298 K
- d)250 K
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
ΔHvap = 30 kJ mol-1 and ΔSvap = 75 J mol-1 K-1. Thus, temperature of vapour at one atmosphere is
[IIT JEE 2004]
a)
400 K
b)
350 K
c)
298 K
d)
250 K
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
∆HVap = 30kJ/mol and ∆S = 75 J/K
∆G = ∆H - T∆S
At eqm, ∆G = 0
Therefore, ∆H = T∆S
Or T = 30×103/75 = 400 K
∆G = ∆H - T∆S
At eqm, ∆G = 0
Therefore, ∆H = T∆S
Or T = 30×103/75 = 400 K
Consider the following process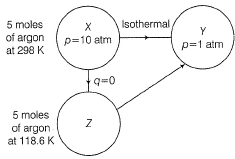 Select correct choices(s)
Select correct choices(s)- a)
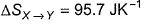
- b)
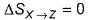
- c)
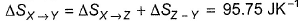
- d)
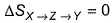
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following process
Select correct choices(s)
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Poulomi Singh answered |
∆SX→Y = ∆SX→Z + ∆SZ→Y(Entropy is a state function, so it is additive)
However, ∆SX→Z is zero. As for adiabatic process. There is no change in entropy.
∆SX→Y = ∆SZ→Y = 2.303 5 8.314 log(10/1) = 95.7 JK-1
However, ∆SX→Z is zero. As for adiabatic process. There is no change in entropy.
∆SX→Y = ∆SZ→Y = 2.303 5 8.314 log(10/1) = 95.7 JK-1
Direction (Q. Nos. 15 and 18) This section contains 2 paragraphs, each describing theory, experiments, data etc. Four questions related to the paragraphs have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d)Passage I Consider a series of isotherms and adiabates as shown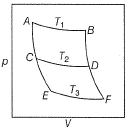 AB, CD and EF are isotherms.
AB, CD and EF are isotherms.
AC, CE, BD and D F are adiabates. Q. 
- a)
- b)
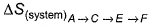
- c)
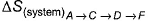
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 15 and 18) This section contains 2 paragraphs, each describing theory, experiments, data etc. Four questions related to the paragraphs have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d)
Passage I
Consider a series of isotherms and adiabates as shown
AB, CD and EF are isotherms.
AC, CE, BD and D F are adiabates.
AC, CE, BD and D F are adiabates.
Q. 
a)
b)
c)
d)
All of these
|
|
Rishika Deshpande answered |
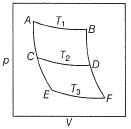
AB, CD and EF are isotherms.
AC, CE, BD and D F are adiabates.
For adiabatic process, we have change n entropy = 0
So EntropyA→B = EntropyC→D = EntropyE→F and EntropyA→C = EntropyA→C = EntropyC→E = EntropyF→D = EntropyD→B
By this, all options are correct.
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-14) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.Q. For an ideal gas, consider only (p -V) work in going from initial state X to the final state Z. The final state Z can be reached either of the two paths shown in the figure. Which of the following choice (s) is (are) correct?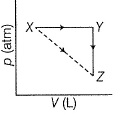 (Take ΔS as change in entropy and W as work done)[IIT JEE 2012]
(Take ΔS as change in entropy and W as work done)[IIT JEE 2012]- a)
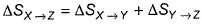
- b)
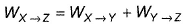
- c)
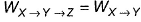
- d)
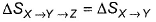
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-14) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
Q. For an ideal gas, consider only (p -V) work in going from initial state X to the final state Z. The final state Z can be reached either of the two paths shown in the figure. Which of the following choice (s) is (are) correct?
(Take ΔS as change in entropy and W as work done)
[IIT JEE 2012]
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Ananya Sarkar answered |
∆SX→Z = ∆SX→Y + ∆SY→Z(Entropy is a state function, so it is additive)
WX→Y→Z = WX→Y (work done in y→z is zero as the process is isochoric)
WX→Y→Z = WX→Y (work done in y→z is zero as the process is isochoric)
If for the cell, Zn(s) + Cu2+(ag)  Cu(s) + Zn2+ (ag)entropy change ΔS° is 96.5 JK-1 mol-1, then temperature coefficient of the emf of a cell is
Cu(s) + Zn2+ (ag)entropy change ΔS° is 96.5 JK-1 mol-1, then temperature coefficient of the emf of a cell is- a)5 x 10-4 VK-1
- b)1 x 10-3 VK-1
- c)2 x 10-3 VK-1
- d)9.65 x 104 VK-1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If for the cell, Zn(s) + Cu2+(ag)  Cu(s) + Zn2+ (ag)entropy change ΔS° is 96.5 JK-1 mol-1, then temperature coefficient of the emf of a cell is
Cu(s) + Zn2+ (ag)entropy change ΔS° is 96.5 JK-1 mol-1, then temperature coefficient of the emf of a cell is
a)
5 x 10-4 VK-1
b)
1 x 10-3 VK-1
c)
2 x 10-3 VK-1
d)
9.65 x 104 VK-1
|
|
Amrita Choudhary answered |
ΔG=ΔH−nFT(dE/dT)P
and ΔG=ΔH−TΔS
∴ΔS/nF=(dE/dT)P
or
96.5/2×96500=(dE/dT)P
∴(dEcell/dT)P
=1×10−3 / 2
=5×10−4VK−1
and ΔG=ΔH−TΔS
∴ΔS/nF=(dE/dT)P
or
96.5/2×96500=(dE/dT)P
∴(dEcell/dT)P
=1×10−3 / 2
=5×10−4VK−1
When HCI(g)and NH3(g)come in contact, they react producing a white cloud of solid NH4CI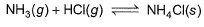 For this,
For this,- a)
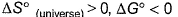
- b)
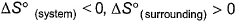
- c)
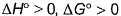
- d)

Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
When HCI(g)and NH3(g)come in contact, they react producing a white cloud of solid NH4CI
For this,
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Upasana Roy answered |
According to me, correct options are b and d.
For a reversible reaction, ∆S°(Universe) will be zero. ∆S°(Universe) is greater than zero for an irreversible reaction. SInce the randomness decreases, ∆S°(system) becomes less than zero and ∆S°(surrounding) becomes more than zero. BOth becomes equal with sign opposite and thus for reversible reaction, ∆S°(universe) = ∆S°(System) + ∆S°(surrounding) = 0
For a reversible reaction, ∆S°(Universe) will be zero. ∆S°(Universe) is greater than zero for an irreversible reaction. SInce the randomness decreases, ∆S°(system) becomes less than zero and ∆S°(surrounding) becomes more than zero. BOth becomes equal with sign opposite and thus for reversible reaction, ∆S°(universe) = ∆S°(System) + ∆S°(surrounding) = 0
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-14) This section contains 2 paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d).Passage lSulphur undergoes a phase transition between 80 and 110°C
S(rhombic)  S (monoclinic); ΔH° = 3.213 kJ mol-1; ΔS° = 8.71 JK-1 mol-1 Q. Select the correct alternate(s).
S (monoclinic); ΔH° = 3.213 kJ mol-1; ΔS° = 8.71 JK-1 mol-1 Q. Select the correct alternate(s).- a)At 80°C SR is as stable as SM
- b)At 80°C SR is less stable than SM
- c)At 110°C SR is more stable than SM
- d)At 110°C SR is less stable than SM
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-14) This section contains 2 paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d).
Passage l
Sulphur undergoes a phase transition between 80 and 110°C
S(rhombic)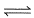 S (monoclinic); ΔH° = 3.213 kJ mol-1; ΔS° = 8.71 JK-1 mol-1
S (monoclinic); ΔH° = 3.213 kJ mol-1; ΔS° = 8.71 JK-1 mol-1
S(rhombic)
Q. Select the correct alternate(s).
a)
At 80°C SR is as stable as SM
b)
At 80°C SR is less stable than SM
c)
At 110°C SR is more stable than SM
d)
At 110°C SR is less stable than SM
|
|
Ameya Choudhury answered |
We have ∆G = ∆H - T∆S
For spontaneous reaction ∆G<0 and vice versa,
∆G at 80° C:-
3213 - (80+273)8.73 = 141.9 kJ mol-1
As it comes positive, the conversion of rhombic and monoclinic is non- spontaneous at 80° C.In other words, rhombic is more stable than monoclinic at this temperature.
∆G at 110° C:-
3213 - (110+273)8.73 = -119.1 kJ mol-1
As it comes positive, the conversion of rhombic and monoclinic is spontaneous at 110° C.In other words, rhombic is less stable than monoclinic at this temperature.
For spontaneous reaction ∆G<0 and vice versa,
∆G at 80° C:-
3213 - (80+273)8.73 = 141.9 kJ mol-1
As it comes positive, the conversion of rhombic and monoclinic is non- spontaneous at 80° C.In other words, rhombic is more stable than monoclinic at this temperature.
∆G at 110° C:-
3213 - (110+273)8.73 = -119.1 kJ mol-1
As it comes positive, the conversion of rhombic and monoclinic is spontaneous at 110° C.In other words, rhombic is less stable than monoclinic at this temperature.
Direction (Q. Nos. 1- 8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.Q. For the given reaction, 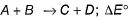 = - 1.3818 kcal at 300 K. Thus equilibrium constant is
= - 1.3818 kcal at 300 K. Thus equilibrium constant is- a)1
- b)0
- c)0.1
- d)100
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1- 8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. For the given reaction, 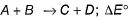 = - 1.3818 kcal at 300 K. Thus equilibrium constant is
= - 1.3818 kcal at 300 K. Thus equilibrium constant is
a)
1
b)
0
c)
0.1
d)
100
|
|
Aaryaa Sharma answered |
Since the reaction is not reversible, equilibrium constant is zero.
Passage II The stopcock connecting A and B is of negligible volume. Stopcock is opened and gases are allowed to mix isothermally. Q. Entropy change for the system is
The stopcock connecting A and B is of negligible volume. Stopcock is opened and gases are allowed to mix isothermally. Q. Entropy change for the system is - a)0.96 JK-1
- b)3.35 JK-1
- c)- 2.40 JK-1
- d)- 0.96 JK-1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage II
The stopcock connecting A and B is of negligible volume. Stopcock is opened and gases are allowed to mix isothermally.
Q. Entropy change for the system is
a)
0.96 JK-1
b)
3.35 JK-1
c)
- 2.40 JK-1
d)
- 0.96 JK-1
|
|
Elementer Dangers answered |
A is correct answer
Chapter doubts & questions for Entropy - Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve 2025 is part of EmSAT Achieve exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the EmSAT Achieve exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for EmSAT Achieve 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Entropy - Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve in English & Hindi are available as part of EmSAT Achieve exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for EmSAT Achieve Exam by signing up for free.
Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve
191 videos|265 docs|160 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup

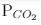 = 0.0030 atm.
= 0.0030 atm.