All Exams >
EmSAT Achieve >
Biology for EmSAT Achieve >
All Questions
All questions of Neural Control and Coordination for EmSAT Achieve Exam
If the corpus callosum is removed in mammalian brain then what will be affected :-- a)Coordination of Cerebrum
- b)Involuntary activity of brain
- c)Coordination of Cerebellum
- d)Behaviour and emotional disturbances
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If the corpus callosum is removed in mammalian brain then what will be affected :-
a)
Coordination of Cerebrum
b)
Involuntary activity of brain
c)
Coordination of Cerebellum
d)
Behaviour and emotional disturbances
|
|
Kadambala Hemalatha answered |
Option A is correct becose, corpus callosam is trancverce connection between two cerebral hemisphears.. it helps in coordination between the two cerebral hemisphears..
Brain stem is the support system of brain and is the collective name for :
- a)Medulla, Pons,and Midbrain
- b)Hypothalamus, Diencephalon, Cerebellum, and Pons
- c)Cerebrum, Mesencephalon, Diencephalon, and Medulla
- d)Prosencephalon, Mesencephalon, Pons, and Medulla
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Brain stem is the support system of brain and is the collective name for :
a)
Medulla, Pons,and Midbrain
b)
Hypothalamus, Diencephalon, Cerebellum, and Pons
c)
Cerebrum, Mesencephalon, Diencephalon, and Medulla
d)
Prosencephalon, Mesencephalon, Pons, and Medulla
|
|
Pritam Choudhary answered |
Brainstem: The Support System of Brain
The brainstem is the lower part of the brain that connects the brain to the spinal cord. It is responsible for regulating important functions such as breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, and consciousness. The brainstem consists of three main parts, which are:
Medulla
The medulla oblongata, or simply the medulla, is the lowest part of the brainstem. It controls involuntary functions such as breathing, heartbeat, and digestion. The medulla also contains reflex centers for coughing, sneezing, and vomiting.
Pons
The pons is the middle part of the brainstem, located above the medulla and below the midbrain. It is involved in the regulation of sleep, respiration, and posture. The pons also helps to relay messages between different parts of the brain.
Midbrain
The midbrain, also known as the mesencephalon, is the uppermost part of the brainstem. It is involved in the regulation of vision, hearing, and movement. The midbrain contains several important structures, including the substantia nigra, which produces dopamine and is involved in the control of movement.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the brainstem is the support system of the brain and is responsible for regulating vital functions. It consists of three main parts, which are the medulla, pons, and midbrain. The medulla controls involuntary functions such as breathing and heartbeat, the pons is involved in the regulation of sleep and posture, and the midbrain is responsible for vision, hearing, and movement.
The brainstem is the lower part of the brain that connects the brain to the spinal cord. It is responsible for regulating important functions such as breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, and consciousness. The brainstem consists of three main parts, which are:
Medulla
The medulla oblongata, or simply the medulla, is the lowest part of the brainstem. It controls involuntary functions such as breathing, heartbeat, and digestion. The medulla also contains reflex centers for coughing, sneezing, and vomiting.
Pons
The pons is the middle part of the brainstem, located above the medulla and below the midbrain. It is involved in the regulation of sleep, respiration, and posture. The pons also helps to relay messages between different parts of the brain.
Midbrain
The midbrain, also known as the mesencephalon, is the uppermost part of the brainstem. It is involved in the regulation of vision, hearing, and movement. The midbrain contains several important structures, including the substantia nigra, which produces dopamine and is involved in the control of movement.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the brainstem is the support system of the brain and is responsible for regulating vital functions. It consists of three main parts, which are the medulla, pons, and midbrain. The medulla controls involuntary functions such as breathing and heartbeat, the pons is involved in the regulation of sleep and posture, and the midbrain is responsible for vision, hearing, and movement.
Injury localised to the hypothalamus would most likely disrupt- a)short term memory
- b)coordination during locomotion
- c)executive function, such as decision making
- d)regulation of body temperature
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Injury localised to the hypothalamus would most likely disrupt
a)
short term memory
b)
coordination during locomotion
c)
executive function, such as decision making
d)
regulation of body temperature

|
Aman Sharma answered |
The primary function of the hypothalamus is homoeostasis, which is to maintain the body's normal temperature and body's status. So, if there is an injury to the hypothalamus, the thermoregulatory centre is disturbed resulting in a deregulation of body temperature. So, the correct answer is option D.
What is meant by coordination?- a)Only two organs interact
- b)Two or more organs interact
- c)Only two organs systems interact
- d)Only three organs interact
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is meant by coordination?
a)
Only two organs interact
b)
Two or more organs interact
c)
Only two organs systems interact
d)
Only three organs interact
|
|
Disha Basu answered |
Understanding Coordination
Coordination is a fundamental concept in biology, particularly in the context of how different organs and systems within an organism interact and work together to maintain homeostasis and overall function.
Key Aspects of Coordination:
- Definition: Coordination refers to the process by which two or more organs or organ systems interact to perform a specific function or response. It ensures that various physiological processes are synchronized for optimal functioning of the body.
- Complex Interactions: Unlike the options suggesting only two or three organs, coordination often involves multiple organs and systems working in harmony. For instance, the respiratory and circulatory systems coordinate to deliver oxygen to tissues and remove carbon dioxide.
- Examples:
- The digestive system coordinates with the nervous system to regulate hunger and satiety.
- The endocrine system interacts with various organs to maintain metabolic balance through hormone signaling.
- Importance: Effective coordination is vital for survival. It allows organisms to respond to environmental changes, regulate internal processes, and maintain overall health.
Conclusion:
Hence, the correct answer is option 'B', as coordination inherently involves the interaction of two or more organs. This collective effort ensures that the body can function efficiently and respond to various stimuli, highlighting the complexity and interdependence of biological systems.
Coordination is a fundamental concept in biology, particularly in the context of how different organs and systems within an organism interact and work together to maintain homeostasis and overall function.
Key Aspects of Coordination:
- Definition: Coordination refers to the process by which two or more organs or organ systems interact to perform a specific function or response. It ensures that various physiological processes are synchronized for optimal functioning of the body.
- Complex Interactions: Unlike the options suggesting only two or three organs, coordination often involves multiple organs and systems working in harmony. For instance, the respiratory and circulatory systems coordinate to deliver oxygen to tissues and remove carbon dioxide.
- Examples:
- The digestive system coordinates with the nervous system to regulate hunger and satiety.
- The endocrine system interacts with various organs to maintain metabolic balance through hormone signaling.
- Importance: Effective coordination is vital for survival. It allows organisms to respond to environmental changes, regulate internal processes, and maintain overall health.
Conclusion:
Hence, the correct answer is option 'B', as coordination inherently involves the interaction of two or more organs. This collective effort ensures that the body can function efficiently and respond to various stimuli, highlighting the complexity and interdependence of biological systems.
The function of an axon is :-- a)Transformation of nerve impulse
- b)Reception of stimuli from neurons
- c)Reception of external stimuli
- d)Conduction of nerve impulse
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The function of an axon is :-
a)
Transformation of nerve impulse
b)
Reception of stimuli from neurons
c)
Reception of external stimuli
d)
Conduction of nerve impulse
|
|
Sethulakshmi E.d Dinesan answered |
Axon transmit impulses away from cellbody to a synapse or to a neuro muscular junction.(11th ncert page no 317 .5th line)
The Schwann sheath is :-- a)A non myelinated nerve fibres
- b)Associated with myelin sheath
- c)A connective tissue cell
- d)Associated with myelinated & non myelinated nerve fibre
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The Schwann sheath is :-
a)
A non myelinated nerve fibres
b)
Associated with myelin sheath
c)
A connective tissue cell
d)
Associated with myelinated & non myelinated nerve fibre
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Neurilemma (also known as neurolemma, sheath of Schwann, or Schwann's sheath) is the outermost nucleated cytoplasmic layer of Schwann cells (also called neurilemmocytes) that surrounds the axon of the neuron. It forms the outermost layer of the nerve fiber in the peripheral nervous system.
The membrane which cover the brain and the spinal cord is :-
- a)White matter
- b)Grey matter
- c)Peritonium
- d)Meninges
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The membrane which cover the brain and the spinal cord is :-
a)
White matter
b)
Grey matter
c)
Peritonium
d)
Meninges

|
Ruchi Chakraborty answered |
Meninges are the membranes that cover and protect the brain and spinal cord. There are three layers of meanings: dura mater (closest to the bone), arachnoid (loosely around the brain), pia mater (closely attached to the brain and spinal cord surface).
Which of the following is a richly vascular layer with lots of blood capillaries :-- a)Duramater
- b)Piamater
- c)Epidermis of skin
- d)Both (1) & (2)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a richly vascular layer with lots of blood capillaries :-
a)
Duramater
b)
Piamater
c)
Epidermis of skin
d)
Both (1) & (2)
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
The pia mater of the brain is the innermost of the three membranes, that cover it. It is the vascular membrane of the brain. It carries the minute branches of the two internal carotids and the two vertebral arteries. It also returns the blood to the heart. The dura mater is the most external membrane of the brain. It forms the internal periosteum of the skull. The dura mater is a dense, tough, inelastic fibrous membrane. The epidermis contains no blood vessels, and cells in the deepest layers are nourished by diffusion from blood capillaries extending to the upper layers of the dermis. So, the correct answer is option B.
Corpus callosum connects :-- a)Two cerebral hemisphere
- b)Two optic lobes
- c)Two olfactory lobes
- d)Optic chiasma
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Corpus callosum connects :-
a)
Two cerebral hemisphere
b)
Two optic lobes
c)
Two olfactory lobes
d)
Optic chiasma
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
The part of the brain that connects the two hemispheres of the brain is called the corpus callosum. It contains a bundle of neuronal fibers found in humans and other higher order mammals that allow the two hemispheres to talk to one another.
During the propagation of a nerve impulse, the action potential results from the movement of- a)K+ ions from intracellular fluid to extracellular fluid
- b)Na+ ions from extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid
- c)K+ ions from extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid
- d)Na+ ions from intracellular fluid to extracellular fluid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
During the propagation of a nerve impulse, the action potential results from the movement of
a)
K+ ions from intracellular fluid to extracellular fluid
b)
Na+ ions from extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid
c)
K+ ions from extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid
d)
Na+ ions from intracellular fluid to extracellular fluid
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
Action potential is a change in electrical potential that occurs across a plasma membrane during the passage of a nerve impulse. During this period, there is a localized and translent switch in electric potential across the membrane from -70 mV to +45 mV. It is due to the fact that the sodium channels open and the potassium channels remain closed. As a result, sodium channels permit the influx of Na+ by diffusion from extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid.
Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding electrical synapses?- a)Transmission of signals is faster than chemical synapses
- b)Pre and postsynaptic membranes are in very close proximity
- c) Electrical synapse can flow directly from one neuron to another
- d)They are very common in our system
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding electrical synapses?
a)
Transmission of signals is faster than chemical synapses
b)
Pre and postsynaptic membranes are in very close proximity
c)
Electrical synapse can flow directly from one neuron to another
d)
They are very common in our system

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
Electrical synapses are very rare in our system. At electrical synapses, the membranes of pre and post synaptic neurons are in very close proximity. Impulse transmission across an electrical synapse is always faster than chemical synapse.
Topic in NCERT: Transmission of ImpulsesLine in NCERT: "Electrical synapses are rare in our system."
Where are the myelinated neurons found?- a)In Spinal cord and cranial nerves
- b)Only in the embryonic condition
- c)In peripheral nerve
- d)In motor neurons
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Where are the myelinated neurons found?
a)
In Spinal cord and cranial nerves
b)
Only in the embryonic condition
c)
In peripheral nerve
d)
In motor neurons

|
Ambition Institute answered |
Myelinated nerve fibres are found in spinal and cranial nerves. Unmyelinated nerve fibres are enclosed by a Schwann cell that does not form a myelin sheath around the axon and is commonly found in autonomous and the somatic neural system.
The rise in stimulus-induced permeability to
a. Potassium ions
b. Sodium ions
c. Restoring RMP
d. Diffusion of potassium ionsArrange them in order.- a)b-a-c-d
- b)a-b-c-d
- c)b-a-d-c
- d)c-a-d-b
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The rise in stimulus-induced permeability to
a. Potassium ions
b. Sodium ions
c. Restoring RMP
d. Diffusion of potassium ions
a. Potassium ions
b. Sodium ions
c. Restoring RMP
d. Diffusion of potassium ions
Arrange them in order.
a)
b-a-c-d
b)
a-b-c-d
c)
b-a-d-c
d)
c-a-d-b
|
|
Ameya Khanna answered |
Understanding the Sequence of Events
In the context of neuronal action potentials and membrane permeability, the sequence of events following a stimulus is crucial. Here's the breakdown of the correct order:
1. Rise in Stimulus-Induced Permeability
- The initial step involves a rise in membrane permeability to specific ions.
- This permeability change is often triggered by a stimulus, such as neurotransmitter release or mechanical stimulation.
2. Diffusion of Potassium Ions
- After the permeability to sodium ions increases, potassium ion channels may also open.
- Potassium ions will begin to diffuse out of the cell, contributing to the repolarization phase of the action potential.
3. Restoring Resting Membrane Potential (RMP)
- As potassium ions exit the neuron, the membrane potential begins to return to its resting state.
- This restoration occurs as the cell becomes less positive inside, eventually stabilizing at the RMP.
4. Rise in Permeability to Sodium Ions
- Initially, the permeability rises for sodium ions, allowing them to enter the neuron.
- This influx of sodium causes depolarization, leading to the action potential spike.
Conclusion
- Therefore, the correct order of events is: Rise in stimulus-induced permeability (to sodium), diffusion of potassium ions, restoring RMP, and finally, the impact of sodium ion permeability.
- Hence, the correct sequence is option 'c': b-a-d-c.
Understanding this sequence is key in grasping how neurons communicate and respond to stimuli, especially during action potentials.
In the context of neuronal action potentials and membrane permeability, the sequence of events following a stimulus is crucial. Here's the breakdown of the correct order:
1. Rise in Stimulus-Induced Permeability
- The initial step involves a rise in membrane permeability to specific ions.
- This permeability change is often triggered by a stimulus, such as neurotransmitter release or mechanical stimulation.
2. Diffusion of Potassium Ions
- After the permeability to sodium ions increases, potassium ion channels may also open.
- Potassium ions will begin to diffuse out of the cell, contributing to the repolarization phase of the action potential.
3. Restoring Resting Membrane Potential (RMP)
- As potassium ions exit the neuron, the membrane potential begins to return to its resting state.
- This restoration occurs as the cell becomes less positive inside, eventually stabilizing at the RMP.
4. Rise in Permeability to Sodium Ions
- Initially, the permeability rises for sodium ions, allowing them to enter the neuron.
- This influx of sodium causes depolarization, leading to the action potential spike.
Conclusion
- Therefore, the correct order of events is: Rise in stimulus-induced permeability (to sodium), diffusion of potassium ions, restoring RMP, and finally, the impact of sodium ion permeability.
- Hence, the correct sequence is option 'c': b-a-d-c.
Understanding this sequence is key in grasping how neurons communicate and respond to stimuli, especially during action potentials.
Assertion: The somatic neural system regulates involuntary functions of the body.
Reason: The somatic neural system is divided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems.- a)Both Assertion and Reason are correct, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
- b)Both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
- c)Assertion is correct, but Reason is incorrect.
- d)Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion: The somatic neural system regulates involuntary functions of the body.
Reason: The somatic neural system is divided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems.
Reason: The somatic neural system is divided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems.
a)
Both Assertion and Reason are correct, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
b)
Both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
c)
Assertion is correct, but Reason is incorrect.
d)
Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect
|
|
Maitri Deshpande answered |
Understanding the Somatic Neural System
The assertion and reason provided in the question relate to the functions of the somatic and autonomic nervous systems.
Assertion Explained
- The somatic neural system primarily controls voluntary functions.
- It is responsible for movements of skeletal muscles, allowing conscious control over these actions.
Reason Clarification
- The somatic neural system is not divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic systems.
- Instead, these divisions belong to the autonomic nervous system, which regulates involuntary functions such as heart rate, digestion, and respiratory rate.
Correctness of Assertion and Reason
- The assertion is incorrect because it states that the somatic neural system regulates involuntary functions, which is not true.
- The reason is also incorrect because it misidentifies the components of the nervous system.
Conclusion
Given that both the assertion and reason are incorrect, the answer to the question is option 'D':
- Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
This understanding is crucial for students preparing for exams like NEET, as it highlights the distinctions between the somatic and autonomic nervous systems.
The assertion and reason provided in the question relate to the functions of the somatic and autonomic nervous systems.
Assertion Explained
- The somatic neural system primarily controls voluntary functions.
- It is responsible for movements of skeletal muscles, allowing conscious control over these actions.
Reason Clarification
- The somatic neural system is not divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic systems.
- Instead, these divisions belong to the autonomic nervous system, which regulates involuntary functions such as heart rate, digestion, and respiratory rate.
Correctness of Assertion and Reason
- The assertion is incorrect because it states that the somatic neural system regulates involuntary functions, which is not true.
- The reason is also incorrect because it misidentifies the components of the nervous system.
Conclusion
Given that both the assertion and reason are incorrect, the answer to the question is option 'D':
- Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
This understanding is crucial for students preparing for exams like NEET, as it highlights the distinctions between the somatic and autonomic nervous systems.
Read the following statements and mark the correct option which is suitable. - The neural system of animals is composed of specialized cells called neurons.
- The central neural system (CNS) consists of the brain and spinal cord.
- The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is involved in transmitting impulses only from the CNS to muscles.
- The autonomic neural system controls voluntary actions like skeletal muscle movement.
- a)Statements 1, 2, and 4 are correct.
- b)Statements 1, 2, and 3 are correct.
- c) Statements 1 and 2 are correct, while 3 and 4 are incorrect.
- d)All statements are correct.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements and mark the correct option which is suitable.
- The neural system of animals is composed of specialized cells called neurons.
- The central neural system (CNS) consists of the brain and spinal cord.
- The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is involved in transmitting impulses only from the CNS to muscles.
- The autonomic neural system controls voluntary actions like skeletal muscle movement.
a)
Statements 1, 2, and 4 are correct.
b)
Statements 1, 2, and 3 are correct.
c)
Statements 1 and 2 are correct, while 3 and 4 are incorrect.
d)
All statements are correct.
|
|
Jhanvi Sen answered |
Understanding the Neural System of Animals
The statements presented about the neural system of animals can be analyzed for accuracy:
Statement 1: Neurons
- Correct.
- The neural system is indeed composed of specialized cells called neurons, which are responsible for transmitting signals throughout the body.
Statement 2: Central Neural System (CNS)
- Correct.
- The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord, functioning as the main control center for processing information.
Statement 3: Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- Incorrect.
- The PNS is responsible for transmitting impulses both from the CNS to muscles and from sensory organs to the CNS. It includes both afferent (sensory) and efferent (motor) pathways.
Statement 4: Autonomic Neural System
- Incorrect.
- The autonomic nervous system regulates involuntary actions, such as heart rate and digestion, not voluntary actions like skeletal muscle movement, which is controlled by the somatic nervous system.
Conclusion
- Therefore, the correct option is c): Statements 1 and 2 are correct, while 3 and 4 are incorrect. This highlights the importance of understanding the roles of different components of the nervous system in animal physiology.
The statements presented about the neural system of animals can be analyzed for accuracy:
Statement 1: Neurons
- Correct.
- The neural system is indeed composed of specialized cells called neurons, which are responsible for transmitting signals throughout the body.
Statement 2: Central Neural System (CNS)
- Correct.
- The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord, functioning as the main control center for processing information.
Statement 3: Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- Incorrect.
- The PNS is responsible for transmitting impulses both from the CNS to muscles and from sensory organs to the CNS. It includes both afferent (sensory) and efferent (motor) pathways.
Statement 4: Autonomic Neural System
- Incorrect.
- The autonomic nervous system regulates involuntary actions, such as heart rate and digestion, not voluntary actions like skeletal muscle movement, which is controlled by the somatic nervous system.
Conclusion
- Therefore, the correct option is c): Statements 1 and 2 are correct, while 3 and 4 are incorrect. This highlights the importance of understanding the roles of different components of the nervous system in animal physiology.
In the human neural system, the coordination between different organ systems is essential for maintaining homeostasis during physical activities.
Which of the following statements best explains the roles of the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS) during intense physical exercise?- a)The PNS coordinates all involuntary actions during physical exercise, including the regulation of skeletal muscles, heart rate, and respiration, while the CNS only provides feedback through the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems without direct control of the muscles
- b)The CNS exclusively controls the skeletal muscles through the somatic neural system, while the PNS regulates the automatic functions of the heart and lungs through the autonomic system, without requiring feedback to the CNS.
- c)The CNS coordinates the entire response to exercise by transmitting efferent signals to skeletal muscles through the somatic system and to involuntary organs through the autonomic system, while the PNS transmits feedback only from the muscles, excluding heart and lung responses.
- d) The CNS processes sensory information from the muscles and organs, and sends efferent impulses via the PNS to regulate heart rate and muscle contraction, while the PNS carries afferent impulses from the lungs and heart to the CNS for feedback.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the human neural system, the coordination between different organ systems is essential for maintaining homeostasis during physical activities.
Which of the following statements best explains the roles of the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS) during intense physical exercise?
Which of the following statements best explains the roles of the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS) during intense physical exercise?
a)
The PNS coordinates all involuntary actions during physical exercise, including the regulation of skeletal muscles, heart rate, and respiration, while the CNS only provides feedback through the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems without direct control of the muscles
b)
The CNS exclusively controls the skeletal muscles through the somatic neural system, while the PNS regulates the automatic functions of the heart and lungs through the autonomic system, without requiring feedback to the CNS.
c)
The CNS coordinates the entire response to exercise by transmitting efferent signals to skeletal muscles through the somatic system and to involuntary organs through the autonomic system, while the PNS transmits feedback only from the muscles, excluding heart and lung responses.
d)
The CNS processes sensory information from the muscles and organs, and sends efferent impulses via the PNS to regulate heart rate and muscle contraction, while the PNS carries afferent impulses from the lungs and heart to the CNS for feedback.

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
During intense physical exercise, the CNS processes sensory information from muscles and organs, sending efferent impulses through the PNS to regulate actions like muscle contraction and heart rate. Simultaneously, the PNS sends afferent impulses back to the CNS from the lungs and heart, providing feedback, which is crucial for coordinating the response to the increased demand for oxygen and energy.
Topic in NCERT: PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
Line in NCERT: "The afferent nerve fibres transmit impulses from tissues/organs to the CNS and the efferent fibres transmit regulatory impulses from the CNS to the concerned peripheral tissues/organs."
Topic in NCERT: PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
Line in NCERT: "The afferent nerve fibres transmit impulses from tissues/organs to the CNS and the efferent fibres transmit regulatory impulses from the CNS to the concerned peripheral tissues/organs."
Where is the midbrain located?- a)Between hypothalamus and pons
- b)Between cerebrum and hypothalamus
- c)Between cerebellum and medulla
- d)Between pons and medulla
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Where is the midbrain located?
a)
Between hypothalamus and pons
b)
Between cerebrum and hypothalamus
c)
Between cerebellum and medulla
d)
Between pons and medulla

|
Top Rankers answered |
The midbrain is located between the hypothalamus of the forebrain and the pons of the hindbrain. The midbrain is also known as the mesencephalon and controls several motor movements.
The………. difference across the resting membrane is called as Resting potential.- a)Electrochemical potential
- b)Electrical potential
- c)Chemical
- d)Chemiosmotic
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The………. difference across the resting membrane is called as Resting potential.
a)
Electrochemical potential
b)
Electrical potential
c)
Chemical
d)
Chemiosmotic
|
|
Harshitha Chakraborty answered |
Understanding Resting Potential
The resting potential refers to the electrical charge difference across the neuronal membrane when a neuron is not actively firing an action potential. This potential is crucial for the transmission of signals in the nervous system.
Key Concepts of Resting Potential
- Electrochemical Gradient:
- The difference in concentration of ions (like Na+ and K+) across the membrane creates an electrochemical gradient.
- This gradient is essential for maintaining the resting potential.
- Electrical Potential:
- The term "electrical potential" specifically refers to the voltage difference across a membrane.
- In a resting neuron, this electrical potential typically ranges from -70 to -90 mV.
- Importance of Ions:
- Potassium ions (K+) are more concentrated inside the cell, while sodium ions (Na+) are more concentrated outside.
- The selective permeability of the membrane to K+ contributes significantly to the resting potential.
- Membrane Channels:
- Ion channels, particularly potassium channels, allow K+ to exit the cell more freely, leading to a negative charge inside the cell compared to the outside.
Conclusion
The correct answer is "B) Electrical potential" as it directly describes the voltage difference across the neuronal membrane during the resting state. Understanding this concept is pivotal for grasping how neurons communicate and respond to stimuli, forming the basis for further studies in neurobiology and physiology.
The resting potential refers to the electrical charge difference across the neuronal membrane when a neuron is not actively firing an action potential. This potential is crucial for the transmission of signals in the nervous system.
Key Concepts of Resting Potential
- Electrochemical Gradient:
- The difference in concentration of ions (like Na+ and K+) across the membrane creates an electrochemical gradient.
- This gradient is essential for maintaining the resting potential.
- Electrical Potential:
- The term "electrical potential" specifically refers to the voltage difference across a membrane.
- In a resting neuron, this electrical potential typically ranges from -70 to -90 mV.
- Importance of Ions:
- Potassium ions (K+) are more concentrated inside the cell, while sodium ions (Na+) are more concentrated outside.
- The selective permeability of the membrane to K+ contributes significantly to the resting potential.
- Membrane Channels:
- Ion channels, particularly potassium channels, allow K+ to exit the cell more freely, leading to a negative charge inside the cell compared to the outside.
Conclusion
The correct answer is "B) Electrical potential" as it directly describes the voltage difference across the neuronal membrane during the resting state. Understanding this concept is pivotal for grasping how neurons communicate and respond to stimuli, forming the basis for further studies in neurobiology and physiology.
Where are the specific receptors of neurotransmitters present?- a)Synaptic cleft
- b)Post-synaptic membrane
- c)Pre-synaptic membrane
- d)Synaptic vesicle
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Where are the specific receptors of neurotransmitters present?
a)
Synaptic cleft
b)
Post-synaptic membrane
c)
Pre-synaptic membrane
d)
Synaptic vesicle

|
Lead Academy answered |
The released neurotransmitters bind to their specific receptors which are present on the post-synaptic membrane. The new potential developed may be either excitatory or inhibitory.
Read the given statements and select the correct ones.
(i) Autonomic neural system transmits impulses from the CNS to the voluntary organs and striated muscles of the body.
(ii) Unmyelinated nerve fibres do not have Schwann cells which form the myelin sheath.
(iii) Axonal membrane of a neuron while not conducting any impulse is comparatively more permeable to potassium ions (K+) than to sodium ions (Na+).
(iv) A synapse is formed by the membranes of a presynaptic neuron and a post synaptic neuron.- a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(ii) and (iii)
- c)(iii) and (iv)
- d)(i) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given statements and select the correct ones.
(i) Autonomic neural system transmits impulses from the CNS to the voluntary organs and striated muscles of the body.
(ii) Unmyelinated nerve fibres do not have Schwann cells which form the myelin sheath.
(iii) Axonal membrane of a neuron while not conducting any impulse is comparatively more permeable to potassium ions (K+) than to sodium ions (Na+).
(iv) A synapse is formed by the membranes of a presynaptic neuron and a post synaptic neuron.
(i) Autonomic neural system transmits impulses from the CNS to the voluntary organs and striated muscles of the body.
(ii) Unmyelinated nerve fibres do not have Schwann cells which form the myelin sheath.
(iii) Axonal membrane of a neuron while not conducting any impulse is comparatively more permeable to potassium ions (K+) than to sodium ions (Na+).
(iv) A synapse is formed by the membranes of a presynaptic neuron and a post synaptic neuron.
a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(ii) and (iii)
c)
(iii) and (iv)
d)
(i) and (iv)
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Autonomic neural system controls and coordinates such organs which are under involuntary control and unstriated muscles of the body. Unmyelinated nerve fibres have Schwann cells which do not form myelin sheath.
Which of the following statements is/are incorrect about the electrical synapse?
(i) At electrical synapses, the membranes of pre and post synaptic neurons are in very close proximity.
(ii) Electrical current can flow directly from one neuron into the other across the synapses
(iii) Transmission of an impulse across electrical synapses is very similar to impulse conduction along single axon
(iv) Electrica synapses pass electrical signal between cells with the use of Ach.
(v) Electrical synapses are fast.
(vi) Electrical synapses are rare in our system.- a)(ii), (iv) and (v)
- b)(i) and (iii)
- c)(iv) only
- d)(i), (v) and (vi)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is/are incorrect about the electrical synapse?
(i) At electrical synapses, the membranes of pre and post synaptic neurons are in very close proximity.
(ii) Electrical current can flow directly from one neuron into the other across the synapses
(iii) Transmission of an impulse across electrical synapses is very similar to impulse conduction along single axon
(iv) Electrica synapses pass electrical signal between cells with the use of Ach.
(v) Electrical synapses are fast.
(vi) Electrical synapses are rare in our system.
(i) At electrical synapses, the membranes of pre and post synaptic neurons are in very close proximity.
(ii) Electrical current can flow directly from one neuron into the other across the synapses
(iii) Transmission of an impulse across electrical synapses is very similar to impulse conduction along single axon
(iv) Electrica synapses pass electrical signal between cells with the use of Ach.
(v) Electrical synapses are fast.
(vi) Electrical synapses are rare in our system.
a)
(ii), (iv) and (v)
b)
(i) and (iii)
c)
(iv) only
d)
(i), (v) and (vi)
|
|
Soumya Kulkarni answered |
Incorrect Statements about Electrical Synapse:
Membranes Proximity:
- Statement (i) is incorrect because at electrical synapses, the membranes of pre and post synaptic neurons are in direct contact, not just in close proximity.
Direct Current Flow:
- Statement (ii) is correct as electrical current can flow directly from one neuron into the other across the synapses.
Impulse Transmission:
- Statement (iii) is incorrect as the transmission of an impulse across electrical synapses is not similar to impulse conduction along a single axon. It is faster and more direct.
Use of Ach:
- Statement (iv) is incorrect because electrical synapses do not pass electrical signals between cells using acetylcholine (Ach) or any other neurotransmitter.
Speed of Transmission:
- Statement (v) is correct as electrical synapses are known for their fast transmission of signals between neurons.
Prevalence of Electrical Synapses:
- Statement (vi) is incorrect as electrical synapses are actually quite common in the nervous system, especially in regions where rapid signaling is essential.
Therefore, the incorrect statements about electrical synapses are (i), (iii), and (iv), making option (c) the correct choice.
Membranes Proximity:
- Statement (i) is incorrect because at electrical synapses, the membranes of pre and post synaptic neurons are in direct contact, not just in close proximity.
Direct Current Flow:
- Statement (ii) is correct as electrical current can flow directly from one neuron into the other across the synapses.
Impulse Transmission:
- Statement (iii) is incorrect as the transmission of an impulse across electrical synapses is not similar to impulse conduction along a single axon. It is faster and more direct.
Use of Ach:
- Statement (iv) is incorrect because electrical synapses do not pass electrical signals between cells using acetylcholine (Ach) or any other neurotransmitter.
Speed of Transmission:
- Statement (v) is correct as electrical synapses are known for their fast transmission of signals between neurons.
Prevalence of Electrical Synapses:
- Statement (vi) is incorrect as electrical synapses are actually quite common in the nervous system, especially in regions where rapid signaling is essential.
Therefore, the incorrect statements about electrical synapses are (i), (iii), and (iv), making option (c) the correct choice.
Which of the following correctly describes the role of the central nervous system (CNS)?- a) It is responsible for transmitting impulses from the organs to the brain.
- b) It processes information and controls bodily functions.
- c) It includes all the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
- d) It consists only of the spinal cord.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following correctly describes the role of the central nervous system (CNS)?
a)
It is responsible for transmitting impulses from the organs to the brain.
b)
It processes information and controls bodily functions.
c)
It includes all the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
d)
It consists only of the spinal cord.

|
Ambition Institute answered |
The central nervous system (CNS) is primarily responsible for processing information and regulating bodily functions. It encompasses the brain and spinal cord, serving as the main control center for all activities in the body. The CNS interprets sensory information received from the peripheral nervous system (PNS) and coordinates responses. An interesting fact is that the brain alone contains approximately 86 billion neurons, which play a crucial role in cognitive functions, movement, and sensory perception.
Which part of the neuron is present in a high concentration in the grey matter?- a)Cell body
- b)Axon
- c)Dendrites
- d)Synaptic knobs
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which part of the neuron is present in a high concentration in the grey matter?
a)
Cell body
b)
Axon
c)
Dendrites
d)
Synaptic knobs
|
|
Gayatri Desai answered |
Grey Matter and Neurons
Grey matter is a type of neural tissue found in the brain and spinal cord. It consists of cell bodies, dendrites, and synapses, and appears grey due to the presence of unmyelinated axons and glial cells. Neurons are the functional units of the nervous system and they transmit information through electrical impulses.
Concentration of Cell Bodies in Grey Matter
The grey matter contains a high concentration of cell bodies compared to other parts of the neuron. The cell body, also known as the soma or perikaryon, is the main part of the neuron that contains the nucleus and various organelles necessary for cellular functions. It is responsible for maintaining the metabolic and structural integrity of the neuron.
Functions of Cell Bodies
The cell body plays several important roles in the neuron:
1. Protein synthesis: The cell body contains ribosomes and other organelles involved in protein synthesis. It produces proteins that are essential for the survival and functioning of the neuron.
2. Metabolism: The cell body generates energy and metabolizes various substances required for neuronal processes. It produces ATP through cellular respiration to fuel the neuron's activities.
3. Integration of information: The cell body receives signals from dendrites and processes them. It integrates these signals and determines whether to transmit or inhibit the electrical impulse.
4. Structural support: The cell body provides structural support to the neuron by giving it its shape and stability. It also connects to other neurons through synapses.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the cell body is present in a high concentration in the grey matter. It is responsible for various vital functions such as protein synthesis, metabolism, integration of information, and structural support. Understanding the distribution and functions of different parts of the neuron, including the cell body, is essential in comprehending the complexity of the nervous system and its role in various physiological processes.
Grey matter is a type of neural tissue found in the brain and spinal cord. It consists of cell bodies, dendrites, and synapses, and appears grey due to the presence of unmyelinated axons and glial cells. Neurons are the functional units of the nervous system and they transmit information through electrical impulses.
Concentration of Cell Bodies in Grey Matter
The grey matter contains a high concentration of cell bodies compared to other parts of the neuron. The cell body, also known as the soma or perikaryon, is the main part of the neuron that contains the nucleus and various organelles necessary for cellular functions. It is responsible for maintaining the metabolic and structural integrity of the neuron.
Functions of Cell Bodies
The cell body plays several important roles in the neuron:
1. Protein synthesis: The cell body contains ribosomes and other organelles involved in protein synthesis. It produces proteins that are essential for the survival and functioning of the neuron.
2. Metabolism: The cell body generates energy and metabolizes various substances required for neuronal processes. It produces ATP through cellular respiration to fuel the neuron's activities.
3. Integration of information: The cell body receives signals from dendrites and processes them. It integrates these signals and determines whether to transmit or inhibit the electrical impulse.
4. Structural support: The cell body provides structural support to the neuron by giving it its shape and stability. It also connects to other neurons through synapses.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the cell body is present in a high concentration in the grey matter. It is responsible for various vital functions such as protein synthesis, metabolism, integration of information, and structural support. Understanding the distribution and functions of different parts of the neuron, including the cell body, is essential in comprehending the complexity of the nervous system and its role in various physiological processes.
During refractory period :-- a)Nerve transmits impulse very slowly
- b)Nerve can not transmit impulse
- c)Nerve transmits impulses very rapidly
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
During refractory period :-
a)
Nerve transmits impulse very slowly
b)
Nerve can not transmit impulse
c)
Nerve transmits impulses very rapidly
d)
None of the above
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
This is the time during which another stimulus given to the neuron (no matter how strong) will not lead to a second action potential. Thus, because Na+ channels are inactivated during this time, additional depolarizing stimuli do not lead to new action potentials. The absolute refractory period takes about 1-2 ms. refractory period is a period of time during which an organ or cell is incapable of repeating a particular action, or (more precisely) the amount of time it takes for an excitable membrane to be ready for a second stimulus once it returns to its resting state following an excitation. It most commonly refers to electrically excitable muscle cells or neurons. Absolute refractory period corresponds to depolarization and repolarization, whereas relative refractory period corresponds to hyperpolarization.
The box like bony structure which encloses the brain is called :-- a)Cranium
- b)Pericardium
- c)Peritoneum
- d)Periosteum
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The box like bony structure which encloses the brain is called :-
a)
Cranium
b)
Pericardium
c)
Peritoneum
d)
Periosteum

|
Ramesh Chand answered |
The box enclosing and protecting the brain is called as the cranium . The cranium is the part of the skull, that encloses the brain. Therefore option A is the correct answer.
Cerebellum is concerned with :-- a)Co-ordination of muscular movement
- b)Memory
- c)Vision
- d)Reflex action
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Cerebellum is concerned with :-
a)
Co-ordination of muscular movement
b)
Memory
c)
Vision
d)
Reflex action
|
|
Sanjana Singh answered |
Cerebellum is a part of the brain and is responsible for motor control which includes muscle movement , equilibrium and balance as it relates to movement .
So 'a' is correct.
So 'a' is correct.
Which structure connects the two hemispheres of the cerebrum?- a)Thalamus
- b)Hypothalamus
- c)Limbic system
- d) Corpus callosum
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which structure connects the two hemispheres of the cerebrum?
a)
Thalamus
b)
Hypothalamus
c)
Limbic system
d)
Corpus callosum
|
|
Debanshi Pillai answered |
Connection Between Hemispheres
The structure that connects the two hemispheres of the cerebrum is the Corpus Callosum. This large bundle of nerve fibers plays a crucial role in interhemispheric communication.
Function of the Corpus Callosum
- Communication: It facilitates communication between the left and right hemispheres, allowing for the integration of sensory information and coordination of motor functions.
- Transfer of Information: It enables the transfer of information from one hemisphere to the other, aiding in tasks that require cooperation between both sides of the brain.
Structure of the Corpus Callosum
- Anatomy: The corpus callosum is a C-shaped structure located beneath the cerebral cortex. It consists of over 200 million axons that connect corresponding regions of the two hemispheres.
- Regions: It can be divided into four parts: the rostrum, genu, body, and splenium, each connecting different areas of the brain.
Importance in Brain Function
- Cognitive Functions: The corpus callosum is essential for higher cognitive functions such as problem-solving, language, and spatial awareness.
- Motor Coordination: It plays a vital role in coordinating movements that involve both sides of the body, ensuring they work together seamlessly.
In summary, the corpus callosum is essential for integrating the functions of the left and right hemispheres, making it a critical structure for overall brain function and coordination.
The structure that connects the two hemispheres of the cerebrum is the Corpus Callosum. This large bundle of nerve fibers plays a crucial role in interhemispheric communication.
Function of the Corpus Callosum
- Communication: It facilitates communication between the left and right hemispheres, allowing for the integration of sensory information and coordination of motor functions.
- Transfer of Information: It enables the transfer of information from one hemisphere to the other, aiding in tasks that require cooperation between both sides of the brain.
Structure of the Corpus Callosum
- Anatomy: The corpus callosum is a C-shaped structure located beneath the cerebral cortex. It consists of over 200 million axons that connect corresponding regions of the two hemispheres.
- Regions: It can be divided into four parts: the rostrum, genu, body, and splenium, each connecting different areas of the brain.
Importance in Brain Function
- Cognitive Functions: The corpus callosum is essential for higher cognitive functions such as problem-solving, language, and spatial awareness.
- Motor Coordination: It plays a vital role in coordinating movements that involve both sides of the body, ensuring they work together seamlessly.
In summary, the corpus callosum is essential for integrating the functions of the left and right hemispheres, making it a critical structure for overall brain function and coordination.
What are the short repeatedly branched fibres called?
- a)Axon
- b)Dendrite
- c)Neurite
- d)Cell body
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What are the short repeatedly branched fibres called?
a)
Axon
b)
Dendrite
c)
Neurite
d)
Cell body
|
|
Akash Nair answered |
Short Repeatedly Branched Fibres: Axon
An axon is a long, slender projection of a neuron that conducts electrical impulses away from the cell body, towards other neurons or target cells. It is the primary transmission line of the nervous system, responsible for transmitting and propagating action potentials.
Structure of an Axon:
- Axon Hillock: The axon hillock is the cone-shaped region of the neuron where the axon originates from the cell body. It is the site where action potentials are generated.
- Axon Proper: The axon proper is the elongated part of the axon that extends away from the cell body. It is covered by a lipid-rich insulating layer called the myelin sheath, which is produced by specialized supporting cells called Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system, and oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system.
- Axon Terminal: At the distal end of the axon, there are fine branches called axon terminals or terminal boutons. These branches form synapses with other neurons or target cells, allowing for the transmission of signals.
Function of an Axon:
- Signal Transmission: The main function of an axon is to transmit electrical signals, known as action potentials, from the cell body to other neurons or target cells. These signals travel along the axon, facilitated by the myelin sheath and nodes of Ranvier, which allow for saltatory conduction. This rapid transmission of signals enables efficient communication within the nervous system.
- Synaptic Transmission: At the axon terminals, the electrical signals are converted into chemical signals. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft, which then bind to receptors on the target cell, transmitting the signal from one neuron to another or to an effector cell (such as a muscle cell or gland).
Conclusion:
In summary, the short repeatedly branched fibers in neurons are called axons. Axons play a vital role in the transmission of electrical signals throughout the nervous system, allowing for communication between neurons and the activation of target cells.
An axon is a long, slender projection of a neuron that conducts electrical impulses away from the cell body, towards other neurons or target cells. It is the primary transmission line of the nervous system, responsible for transmitting and propagating action potentials.
Structure of an Axon:
- Axon Hillock: The axon hillock is the cone-shaped region of the neuron where the axon originates from the cell body. It is the site where action potentials are generated.
- Axon Proper: The axon proper is the elongated part of the axon that extends away from the cell body. It is covered by a lipid-rich insulating layer called the myelin sheath, which is produced by specialized supporting cells called Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system, and oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system.
- Axon Terminal: At the distal end of the axon, there are fine branches called axon terminals or terminal boutons. These branches form synapses with other neurons or target cells, allowing for the transmission of signals.
Function of an Axon:
- Signal Transmission: The main function of an axon is to transmit electrical signals, known as action potentials, from the cell body to other neurons or target cells. These signals travel along the axon, facilitated by the myelin sheath and nodes of Ranvier, which allow for saltatory conduction. This rapid transmission of signals enables efficient communication within the nervous system.
- Synaptic Transmission: At the axon terminals, the electrical signals are converted into chemical signals. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft, which then bind to receptors on the target cell, transmitting the signal from one neuron to another or to an effector cell (such as a muscle cell or gland).
Conclusion:
In summary, the short repeatedly branched fibers in neurons are called axons. Axons play a vital role in the transmission of electrical signals throughout the nervous system, allowing for communication between neurons and the activation of target cells.
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
(i) Synaptic cleft of neurons secrete adrenaline.
(ii) Myelinated nerve fibres are enveloped with Schwann cells, which from a myelin sheath around the axon.
(iii) Non-myelinated nerve fibre is enclosed by a Schwann cell that does not form a myelin sheath.
(iv) Spinal and cranial nerves are made of non-melinated nerve fibres.- a)Statements (i) and (ii) are correct but statements (iii) and (iv) are incorrect
- b)Statements (i), (ii) and (iii) are correct but statement (iv) is incorrect
- c)Statement (iii) and (iv) are correct but statement (i) and (ii) are incorrect
- d)Statement (ii) and (iii) are correct but statements (i) and (iv) are incorrect
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
(i) Synaptic cleft of neurons secrete adrenaline.
(ii) Myelinated nerve fibres are enveloped with Schwann cells, which from a myelin sheath around the axon.
(iii) Non-myelinated nerve fibre is enclosed by a Schwann cell that does not form a myelin sheath.
(iv) Spinal and cranial nerves are made of non-melinated nerve fibres.
(i) Synaptic cleft of neurons secrete adrenaline.
(ii) Myelinated nerve fibres are enveloped with Schwann cells, which from a myelin sheath around the axon.
(iii) Non-myelinated nerve fibre is enclosed by a Schwann cell that does not form a myelin sheath.
(iv) Spinal and cranial nerves are made of non-melinated nerve fibres.
a)
Statements (i) and (ii) are correct but statements (iii) and (iv) are incorrect
b)
Statements (i), (ii) and (iii) are correct but statement (iv) is incorrect
c)
Statement (iii) and (iv) are correct but statement (i) and (ii) are incorrect
d)
Statement (ii) and (iii) are correct but statements (i) and (iv) are incorrect
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Synaptic vesicles of the synaptic knob secrete neurotransmitter (e.g., adrenaline). Spinal nerves and cranial nerves are myelinated nerves.
Which of the following statements are correct?
(A) Depolarization of an axonal membrane is caused due to rise in stimulus-induced permeability to Na⁺ and its rapid influx into axoplasm.
(B) Diffusion of K⁺ outside the axonal membrane restores the resting potential of the membrane.
(C) Sodium-potassium pump maintains active transport of 2 Na⁺ outwards for 3 K⁺ into the axoplasm across the resting membrane.- a)A only
- b)A and B
- c)B and C
- d)A and C
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
(A) Depolarization of an axonal membrane is caused due to rise in stimulus-induced permeability to Na⁺ and its rapid influx into axoplasm.
(B) Diffusion of K⁺ outside the axonal membrane restores the resting potential of the membrane.
(C) Sodium-potassium pump maintains active transport of 2 Na⁺ outwards for 3 K⁺ into the axoplasm across the resting membrane.
a)
A only
b)
A and B
c)
B and C
d)
A and C

|
Bs Academy answered |
Depolarization of the axonal membrane happens due to an increase in Na⁺ permeability, which allows Na⁺ ions to rapidly enter the axoplasm, making Statement A correct. Statement B is also correct, as the diffusion of K⁺ out of the membrane restores the resting potential. Statement C is incorrect because the sodium-potassium pump moves 3 Na⁺ out for every 2 K⁺ in, not the other way around. Hence, the correct statements are A and B.Topic in NCERT: Generation and Conduction of Nerve Impulse
Line in NCERT: "The rise in the stimulus-induced permeability to Na* is extremely short-lived. It is quickly followed by a rise in permeability to K*. Within a fraction of a second, K+ diffuses outside the membrane and restores the resting potential of the membrane at the site of excitation and the fibre becomes once more responsive to further stimulation."
How do ions contribute to the resting potential of a neuron?- a)By moving randomly across the membrane
- b)By maintaining a higher concentration of sodium inside the cell
- c)By preventing any ion movement across the membrane
- d)By establishing a high concentration of potassium inside and sodium outside
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
How do ions contribute to the resting potential of a neuron?
a)
By moving randomly across the membrane
b)
By maintaining a higher concentration of sodium inside the cell
c)
By preventing any ion movement across the membrane
d)
By establishing a high concentration of potassium inside and sodium outside

|
Lead Academy answered |
The resting potential of a neuron is maintained by a high concentration of potassium ions inside and sodium ions outside the cell, facilitated by the sodium-potassium pump.
Topic in NCERT: Generation and Conduction of Nerve Impulse
Line in NCERT: "Consequently, the axoplasm inside the axon contains high concentration of K* and negatively charged proteins and low concentration of Na*. In contrast, the fluid outside the axon contains a low concentration of K*, a high concentration of Na* and thus form a concentration gradient."
Sodium-potassium pump transports- a)Na+ and K+ out of the neuron
- b)Na+ and K+ into the neuron
- c)Na+ into the neuron and K+ out of the neuron
- d)K+ into the neuron and Na+ out of the neuron
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Sodium-potassium pump transports
a)
Na+ and K+ out of the neuron
b)
Na+ and K+ into the neuron
c)
Na+ into the neuron and K+ out of the neuron
d)
K+ into the neuron and Na+ out of the neuron
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Each Na+ -K+ pump expels three Na+ ions for every two K+ ions imported.
Assertion: The functions of the organs in our body must be coordinated to maintain homeostasis.
Reason: Coordination is the process where two or more organs interact and complement each other’s functions.- a)Both Assertion and Reason are correct, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
- b)Both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
- c)Assertion is correct, but Reason is incorrect.
- d)Assertion is incorrect, but Reason is correct.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion: The functions of the organs in our body must be coordinated to maintain homeostasis.
Reason: Coordination is the process where two or more organs interact and complement each other’s functions.
Reason: Coordination is the process where two or more organs interact and complement each other’s functions.
a)
Both Assertion and Reason are correct, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
b)
Both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
c)
Assertion is correct, but Reason is incorrect.
d)
Assertion is incorrect, but Reason is correct.
|
|
Nidhi Chauhan answered |
Understanding Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the process by which living organisms maintain a stable internal environment despite external changes. This involves the regulation of various physiological parameters such as temperature, pH, and electrolyte balance.
Assertion Explanation
- The assertion states that the functions of the organs in our body must be coordinated to maintain homeostasis.
- This is correct because organs do not function in isolation. For example, the respiratory system works with the circulatory system to ensure that oxygen is delivered to tissues and carbon dioxide is removed.
Reason Explanation
- The reason provided indicates that coordination is the interaction and complementing functions of two or more organs.
- This is also a correct statement as organs often work together to perform complex tasks that no single organ could achieve alone. For example, the kidneys and the endocrine system work together to regulate blood pressure and fluid balance.
Linking Assertion and Reason
- The reason directly explains the assertion by highlighting how organs complement each other to maintain homeostasis.
- For instance, during exercise, the heart rate increases (cardiovascular system), while the lungs facilitate increased oxygen intake (respiratory system), showcasing their coordinated efforts to maintain stable conditions in the body.
Conclusion
- Since both the assertion and the reason are true, and the reason correctly explains the assertion, the correct answer is option 'A': Both Assertion and Reason are correct, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
Homeostasis is the process by which living organisms maintain a stable internal environment despite external changes. This involves the regulation of various physiological parameters such as temperature, pH, and electrolyte balance.
Assertion Explanation
- The assertion states that the functions of the organs in our body must be coordinated to maintain homeostasis.
- This is correct because organs do not function in isolation. For example, the respiratory system works with the circulatory system to ensure that oxygen is delivered to tissues and carbon dioxide is removed.
Reason Explanation
- The reason provided indicates that coordination is the interaction and complementing functions of two or more organs.
- This is also a correct statement as organs often work together to perform complex tasks that no single organ could achieve alone. For example, the kidneys and the endocrine system work together to regulate blood pressure and fluid balance.
Linking Assertion and Reason
- The reason directly explains the assertion by highlighting how organs complement each other to maintain homeostasis.
- For instance, during exercise, the heart rate increases (cardiovascular system), while the lungs facilitate increased oxygen intake (respiratory system), showcasing their coordinated efforts to maintain stable conditions in the body.
Conclusion
- Since both the assertion and the reason are true, and the reason correctly explains the assertion, the correct answer is option 'A': Both Assertion and Reason are correct, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
How does the pre-synaptic neuron transmit an impulse across the synaptic cleft to the post-synaptic neuron?- a)By electrical current flowing directly between the neurons across the synaptic cleft.
- b)By the release of neurotransmitters from synaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft.
- c)By ion flow through the synaptic cleft without the need for neurotransmitters.
- d)By a direct connection between the axon terminal and the post-synaptic membrane.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
By electrical current flowing directly between the neurons across the synaptic cleft.
b)
By the release of neurotransmitters from synaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft.
c)
By ion flow through the synaptic cleft without the need for neurotransmitters.
d)
By a direct connection between the axon terminal and the post-synaptic membrane.

|
Ambition Institute answered |
The pre-synaptic neuron transmits an impulse to the post-synaptic neuron by releasing neurotransmitters from synaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft, where they bind to specific receptors on the post-synaptic membrane.
Which of the following integrates all the activities of the organs?- a)Excretory and Respiratory system
- b)The neural and digestive system
- c)Digestive and excretory system
- d)The neural and endocrine system
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following integrates all the activities of the organs?
a)
Excretory and Respiratory system
b)
The neural and digestive system
c)
Digestive and excretory system
d)
The neural and endocrine system

|
Flembe Academy answered |
In our body, the neural and the endocrine system jointly coordinate and integrate all the activities of the organs so that they function in a synchronised fashion.
Topic in NCERT: NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATIONLine in NCERT: "The neural system and the endocrine system jointly coordinate and integrate all the activities of the organs so that they function in a synchronised fashion."
In Pavlov’s conditioned reflex experiment find the correct matches :

- a)a)-i, b)-iii, c)-iv, d)-ii
- b)a)-iv, b)-ii, c)-i, d)-iii
- c)a)-iii, b)-iv, c)-ii, d)-i
- d)a)-ii, b)-iii, c)-i, d)-iv
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In Pavlov’s conditioned reflex experiment find the correct matches :


a)
a)-i, b)-iii, c)-iv, d)-ii
b)
a)-iv, b)-ii, c)-i, d)-iii
c)
a)-iii, b)-iv, c)-ii, d)-i
d)
a)-ii, b)-iii, c)-i, d)-iv
|
|
Wahid Khan answered |
There are different kinds of stimulus that is received by different receptors in our body. Hearing of sound of bell is conditioned stimulus and salivation in response to bell is conditioned response. Food itself is conditioned stimulus and salivation in response to food is unconditioned response.
Match the following

- a)1-A, 2-B, 3-D, 4-C
- b)1-B, 2-A, 3-D, 4-C
- c) 1-A, 2-B, 3-C, 4-D
- d)1-B, 2-A, 3-C, 4-D
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the following


a)
1-A, 2-B, 3-D, 4-C
b)
1-B, 2-A, 3-D, 4-C
c)
1-A, 2-B, 3-C, 4-D
d)
1-B, 2-A, 3-C, 4-D

|
Bs Academy answered |
Afferent fibres transmit impulses to the CNS.
Efferent fibres transmit impulses from the CNS.
The autonomic neural system controls involuntary organs and smooth muscles.
The somatic neural system relays impulses to skeletal muscles.
Efferent fibres transmit impulses from the CNS.
The autonomic neural system controls involuntary organs and smooth muscles.
The somatic neural system relays impulses to skeletal muscles.
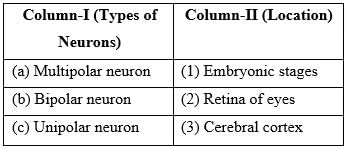
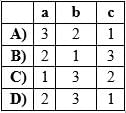
Match the following columns
- a)(A)
- b)(B)
- c)(C)
- d)(D)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the following columns




a)
(A)
b)
(B)
c)
(C)
d)
(D)

|
Infinity Academy answered |
Based on the number of axon and dendrites, the neurons are divided into three types, i.e., multipolar (with one axon and two or more dendrites; found in the cerebral cortex), bipolar (with one axon and one dendrite, found in the retina of eye) and unipolar (cell body with one axon only; found usually in the embryonic stage).
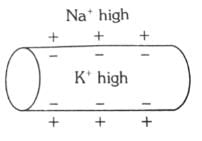
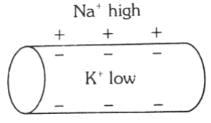
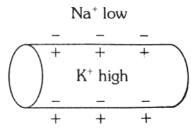
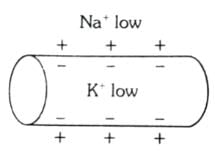
Which of the following options illustrates the distribution of Na+ and K+ ions in a section of non-myelinated axon which is at resting potential?- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following options illustrates the distribution of Na+ and K+ ions in a section of non-myelinated axon which is at resting potential?
a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
When a neuron is at resting potential i.e., not conducting any impulse; the axonal membrane is comparatively more permeable to K+ ions and nearly impermeable to Na+ ions. Consequently, the axoplasm inside the axon contains high concentration of K+ ions. In contrast, the fluid outside the axon has a high concentration of Na+ ions and thus forms a concentration gradient.
Which neural system is responsible for transmitting impulses to skeletal muscles?- a)Autonomic neural system
- b) Central neural system
- c)Somatic neural system
- d)Peripheral neural system
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which neural system is responsible for transmitting impulses to skeletal muscles?
a)
Autonomic neural system
b)
Central neural system
c)
Somatic neural system
d)
Peripheral neural system

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
The somatic neural system is the part of the nervous system that carries sensory and motor information to and from the central nervous system (CNS) to the skeletal muscles, enabling voluntary control of movements. This system is crucial for activities such as walking, writing, and any other actions that require conscious effort. An interesting fact is that the somatic nervous system can rapidly respond to stimuli, allowing for quick reflex actions, often without the need for conscious thought.
Topic in NCERT: Human Neural System
Line in NCERT: "The somatic neural system relays impulses from the CNS to skeletal muscles."
Topic in NCERT: Human Neural System
Line in NCERT: "The somatic neural system relays impulses from the CNS to skeletal muscles."
Read the given paragraph.
In the resting state, the axonal membrane is (i) with more (ii) charged ions outside than inside. This unequal distribution of ions os due to (1) the selective permeability of the membrane, which forms an almost impenetrable barrier to (iii) and (2) the action of the (iv) which pumps (v) Na+ out of the neuron for every (vi) K+ brought in.
Select the option that correctly fills the blanks in the paragraph.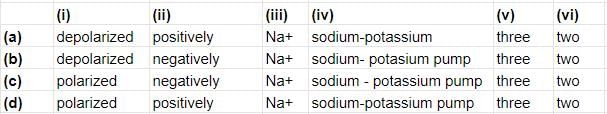
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given paragraph.
In the resting state, the axonal membrane is (i) with more (ii) charged ions outside than inside. This unequal distribution of ions os due to (1) the selective permeability of the membrane, which forms an almost impenetrable barrier to (iii) and (2) the action of the (iv) which pumps (v) Na+ out of the neuron for every (vi) K+ brought in.
Select the option that correctly fills the blanks in the paragraph.
In the resting state, the axonal membrane is (i) with more (ii) charged ions outside than inside. This unequal distribution of ions os due to (1) the selective permeability of the membrane, which forms an almost impenetrable barrier to (iii) and (2) the action of the (iv) which pumps (v) Na+ out of the neuron for every (vi) K+ brought in.
Select the option that correctly fills the blanks in the paragraph.

a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
In the resting state, the axonal membrane is polarised with more positively charged ions outside than inside, unequal distribution of ions is due to the selective permeability of the membrane, which forms impermeable barrier to sodium ion and the action of the sodium which pumps three sodium ions out of the neuron for every two potassium ions brought in.
Thus, the correct option is '(i) - polarised, (ii) - positively, (iii) - Na + , (iv) - sodium - potassium pump, (v) - three, (vi) - two.'
Thus, the correct option is '(i) - polarised, (ii) - positively, (iii) - Na + , (iv) - sodium - potassium pump, (v) - three, (vi) - two.'
What is the primary function of the visceral nervous system within the peripheral nervous system?- a) It controls voluntary movements of skeletal muscles.
- b) It relays impulses between the central nervous system and the viscera.
- c) It processes sensory information from the external environment.
- d) It regulates reflex actions in the spinal cord.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the primary function of the visceral nervous system within the peripheral nervous system?
a)
It controls voluntary movements of skeletal muscles.
b)
It relays impulses between the central nervous system and the viscera.
c)
It processes sensory information from the external environment.
d)
It regulates reflex actions in the spinal cord.

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
The visceral nervous system is responsible for transporting impulses between the central nervous system and the internal organs, or viscera. This system manages involuntary bodily functions such as digestion and heart rate, which are critical for maintaining homeostasis. Interestingly, it is often divided into two main components: the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, which have opposing effects on organ function to help regulate bodily responses to stress and relaxation.
Topic in NCERT: Visceral nervous system
Line in NCERT: "Visceral nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that comprises the whole complex of nerves, fibres, ganglia, and plexuses by which impulses travel from the central nervous system to the viscera and from the viscera to the central nervous system."
A diagram showing the axon terminal and synapse is given. Identify correctly at least two of A-D:
- a)B- Synaptic connection; D- K+
- b)A- Neurotransmitter; B- Synaptic cleft
- c)C- Neurotransmitter; D- Ca++
- d)A- Receptor; C- Synaptic vesicles
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A diagram showing the axon terminal and synapse is given. Identify correctly at least two of A-D:


a)
B- Synaptic connection; D- K+
b)
A- Neurotransmitter; B- Synaptic cleft
c)
C- Neurotransmitter; D- Ca++
d)
A- Receptor; C- Synaptic vesicles

|
Bs Academy answered |
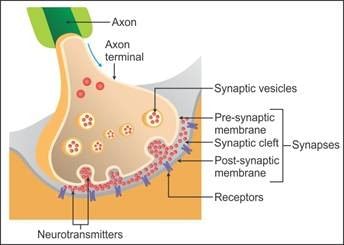
Which of the following is true about electrical synapses?- a)Electrical synapses involve the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft.
- b)Electrical synapses have a gap called the synaptic cleft that separates the neurons.
- c)Electrical synapses allow direct electrical current flow between the pre- and post-synaptic neurons.
- d)Electrical synapses are more common in the human nervous system than chemical synapses.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Electrical synapses involve the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft.
b)
Electrical synapses have a gap called the synaptic cleft that separates the neurons.
c)
Electrical synapses allow direct electrical current flow between the pre- and post-synaptic neurons.
d)
Electrical synapses are more common in the human nervous system than chemical synapses.

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
Electrical synapses allow direct electrical current flow between the pre- and post-synaptic neurons without the need for neurotransmitters or synaptic clefts. These synapses are rare in the human nervous system.
Unidirectional transmission of a nerve impulse through nerve fibre is due to the fact that- a)nerve fibre is insulated by a medullary sheath
- b)sodium pump starts operating only at the cyton and then continues into the nerve fibre
- c)neurotransmitters are released by dendrites and not by axon endings
- d)neurotransmitters are released by the axon endings and not by dendrites
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Unidirectional transmission of a nerve impulse through nerve fibre is due to the fact that
a)
nerve fibre is insulated by a medullary sheath
b)
sodium pump starts operating only at the cyton and then continues into the nerve fibre
c)
neurotransmitters are released by dendrites and not by axon endings
d)
neurotransmitters are released by the axon endings and not by dendrites
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
A nerve impulse is transmitted from one neuron to another with the help of chemicals called neurotransmitters that are released by the axon endings formed by the membrane of a pre-synaptic neuron which may or may not be separated by synaptic cleft.
Refer to the given diagram of the structure of a neuron and identify A, B and C.
- a)(A)
- b)(B)
- c)(C)
- d)(D)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Refer to the given diagram of the structure of a neuron and identify A, B and C.


a)
(A)
b)
(B)
c)
(C)
d)
(D)

|
EduRev NEET answered |
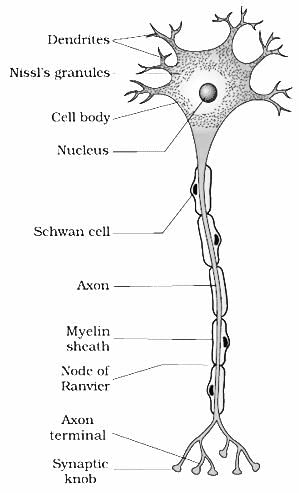
Topic in NCERT: NEURON AS STRUCTURAL AND FUNCTIONAL UNIT OF NEURAL SYSTEM
Line in NCERT: " A neuron is a microscopic structure composed of three major parts, namely, cell body, dendrites and axon."
Which of the following systems is involved in controlling involuntary actions like heart rate and digestion?- a)Somatic neural system
- b)Autonomic neural system
- c)Sympathetic neural system
- d)Peripheral nervous system
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following systems is involved in controlling involuntary actions like heart rate and digestion?
a)
Somatic neural system
b)
Autonomic neural system
c)
Sympathetic neural system
d)
Peripheral nervous system

|
Stepway Academy answered |
The autonomic neural system controls involuntary actions like heart rate, digestion, and other functions of smooth muscles and involuntary organs.
Topic in NCERT: Autonomic Neural System
Line in NCERT: "The autonomic neural system transmits impulses from the CNS to the involuntary organs and smooth muscles of the body."
Topic in NCERT: Autonomic Neural System
Line in NCERT: "The autonomic neural system transmits impulses from the CNS to the involuntary organs and smooth muscles of the body."
Chapter doubts & questions for Neural Control and Coordination - Biology for EmSAT Achieve 2025 is part of EmSAT Achieve exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the EmSAT Achieve exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for EmSAT Achieve 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Neural Control and Coordination - Biology for EmSAT Achieve in English & Hindi are available as part of EmSAT Achieve exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for EmSAT Achieve Exam by signing up for free.
Biology for EmSAT Achieve
157 videos|173 docs|136 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









