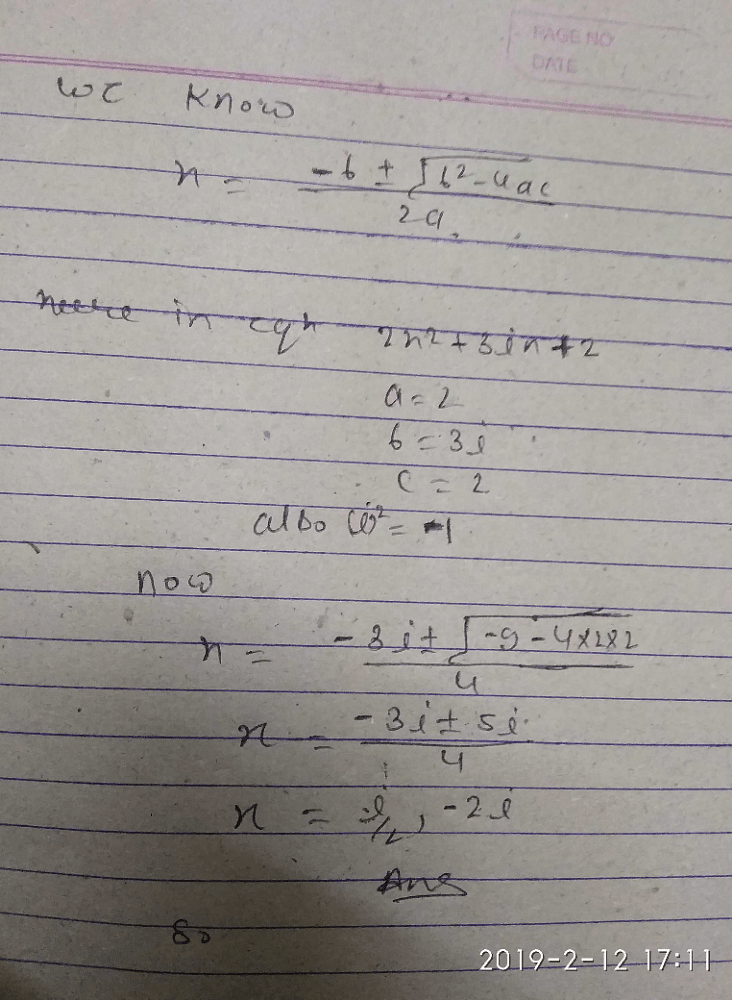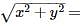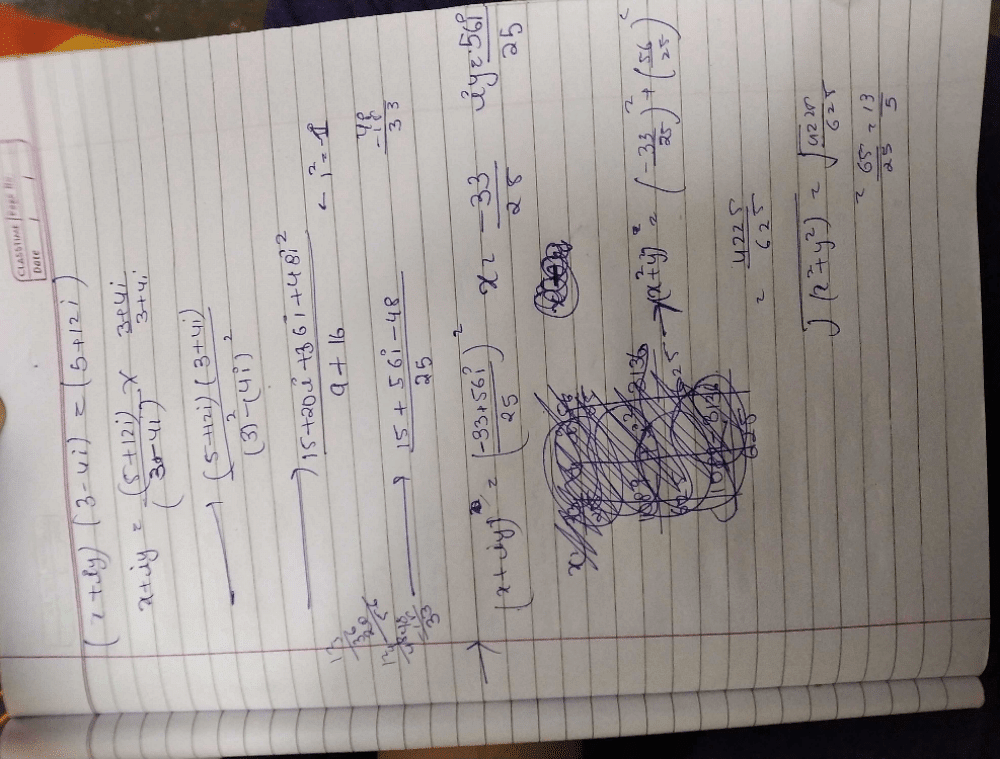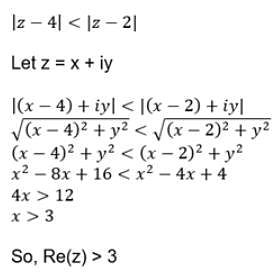All Exams >
Year 12 >
Mathematics for Year 12 >
All Questions
All questions of Complex numbers for Year 12 Exam
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Imaginary part of −i(3i + 2) isa)−2b)2c)3d)−3Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
(-i)(3i) +2(-i) =-3(i^2)-2i =-3(-1)-2i =3-2i since i=√-1 =3+(-2)i comparing with a+bi,we get b=(-2)
Write in the simplest form: (i)-997- a)-i
- b)1
- c)-1
- d)i
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Write in the simplest form: (i)-997
a)
-i
b)
1
c)
-1
d)
i

|
Muskaan Mishra answered |
I^-997= 1/i^997, 1/(i^4)^249 × i, since i^4 = 1, i^4/i= i^3= -i
For a complex number a+ib, a-ib is called its- a)opposite
- b)conjugate
- c)reciprocal
- d)additive inverse
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For a complex number a+ib, a-ib is called its
a)
opposite
b)
conjugate
c)
reciprocal
d)
additive inverse
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
This is called conjugate of complex no.
z = a+ib. conjugate of z = a-ib
- sign is put before i
z = a+ib. conjugate of z = a-ib
- sign is put before i
If z1 and z2 are non real complex numbers such that z1+z2 and z1z2 are real numbers, then- a)
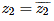
- b)
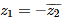
- c)
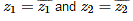
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If z1 and z2 are non real complex numbers such that z1+z2 and z1z2 are real numbers, then
a)
b)
c)
d)
none of these
|
|
Siddharth answered |
since
Z1 + Z2 & Z1Z2 are the real numbers
therefore
Z1 = conjugate of Z2
Z2 = conjugate of Z1
so
option D is correct
according to me
apke according kon sa option sahi h
Find the reciprocal (or multiplicative inverse) of -2 + 5i - a)
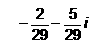
- b)
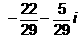
- c)
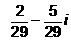
- d)
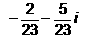
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the reciprocal (or multiplicative inverse) of -2 + 5i
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
-2 + 5i
multiplicative inverse of -2 + 5i is
1/(-2+5i)
= 1/(-2+5i) * ((-2-5i)/(-2-5i))
= -2-5i/(-2)^2 -(5i)^2
= -2-5i/4-(-25)
= -2-5i/4+25
= -2-5i/29
= -2/29 -5i/29
multiplicative inverse of -2 + 5i is
1/(-2+5i)
= 1/(-2+5i) * ((-2-5i)/(-2-5i))
= -2-5i/(-2)^2 -(5i)^2
= -2-5i/4-(-25)
= -2-5i/4+25
= -2-5i/29
= -2/29 -5i/29
Express the following in standard form : 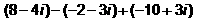
- a)3+3i
- b)2 + 2i
- c)1 + 2i
- d)0 + 2i
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Express the following in standard form : 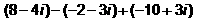
a)
3+3i
b)
2 + 2i
c)
1 + 2i
d)
0 + 2i
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
(8 - 4i) - (-2 - 3i) + (-10 + 3i)
=> 8 - 4i + 2 + 3i-10 + 3i
=> 8 + 2 - 10 - 4i + 3i + 3i =>0 + 2i
=> 8 - 4i + 2 + 3i-10 + 3i
=> 8 + 2 - 10 - 4i + 3i + 3i =>0 + 2i
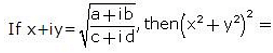
- a)
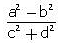
- b)
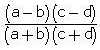
- c)
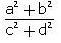
- d)
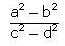
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
(x+iy)(x−iy) = (a+ib)(a−ib)/(c+id)(c−id)
⇒x2−iy2 = √[(a2−i2b2)/(c2−i2d2)]
⇒x2+y2 = √[(a2+b2)/(c2+d2)] [1i2 = -1]
(x2+y2)2 = (a2+b2)/(c2+d2)
⇒x2−iy2 = √[(a2−i2b2)/(c2−i2d2)]
⇒x2+y2 = √[(a2+b2)/(c2+d2)] [1i2 = -1]
(x2+y2)2 = (a2+b2)/(c2+d2)
Find the real numbers x and y such that : (x + iy)(3 + 2i) = 1 + i- a)
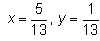
- b)
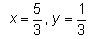
- c)
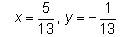
- d)
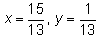
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the real numbers x and y such that : (x + iy)(3 + 2i) = 1 + i
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
(x + iy)(3 + 2i) = (1 + i)
x + iy = (1 + i)/(3 + 2i)
x + iy = [(1 + i) * (3 - 2i)] / [(3 + 2i)*(3 - 2i)]
x + iy = (3 + 3i - 2i + 2) / [(3)2 + (2)2]
x + iy = (5 + i)/[ 9 + 4]
= (5 + i) / 13
=> 13x + 13iy = 5+i
13x = 5 13y = 1
x = 5/13 y = 1/13
x + iy = (1 + i)/(3 + 2i)
x + iy = [(1 + i) * (3 - 2i)] / [(3 + 2i)*(3 - 2i)]
x + iy = (3 + 3i - 2i + 2) / [(3)2 + (2)2]
x + iy = (5 + i)/[ 9 + 4]
= (5 + i) / 13
=> 13x + 13iy = 5+i
13x = 5 13y = 1
x = 5/13 y = 1/13
Express the following in standard form : 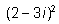
- a)5 + 2i
- b)8 + 12i
- c)-5 – 12i
- d)8 + 2i
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Express the following in standard form : 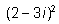
a)
5 + 2i
b)
8 + 12i
c)
-5 – 12i
d)
8 + 2i
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
(2-3i)2 = 4 + 9 (i)2 - 2.2.3i
= 4 - 9 - 12i since, i2 = -1
= - 5 - 12 i
= 4 - 9 - 12i since, i2 = -1
= - 5 - 12 i
Find the real numbers x and y such that :a)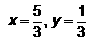 b)
b)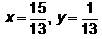 c)
c)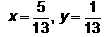 d)
d)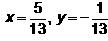 Correct answer is option 'c'. Can you explain this answer?
Correct answer is option 'c'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
(x + iy) (3 + 2i)
= 3x + 2xi + 3iy + 3i*y = 1+i
= 3x-2y + i(2x+3y) = 1+i
= 3x-2y-1 = 0 ; 2x + 3y -1 = 0
on equating real and imaginary parts on both sides
on solving two equations
x= 5/13 ; y = 1/13
= 3x + 2xi + 3iy + 3i*y = 1+i
= 3x-2y + i(2x+3y) = 1+i
= 3x-2y-1 = 0 ; 2x + 3y -1 = 0
on equating real and imaginary parts on both sides
on solving two equations
x= 5/13 ; y = 1/13
If one of the root of a quadratic equation with rational coefficients is rational, then other root must be- a)Imaginary
- b)Irrational
- c)Rational
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If one of the root of a quadratic equation with rational coefficients is rational, then other root must be
a)
Imaginary
b)
Irrational
c)
Rational
d)
None of these
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Also, αβ = r/p, which is also rational. α + β = (a+√b) + (a-√b) = 2a, a rational number and, αβ = (a+√b)(a-√b) = a² - b, a rational number. So, the other root of a quadratic equation having the one root as (a+√b) is (a-√b), where a and b are rational numbers.
Express the following in standard form: i^20 + (1-2i)^3a)-10 + 2ib)-10 + 4ic)-10 + id)-1 + 2iCorrect answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Given, i20 + (1 - 2i)3
We knoe that i = √-1
i2 = -1
Now put the values in given equation
= i20 + (1 - 2i)3
= ( i2)10 + { 1 - 8i3 - 6i + 12i2 }
= 1 +1 - 8i3 - 6i + 12i2
=1 +1 - 8i2.i1 - 6i + 12i2
=1 + 1 + 8i - 6i -12
= -10 + 2i
The multiplicative inverse of 3 – 4i is- a)(3 + 4i)/25
- b)3 + 4i
- c)-3 + 4i/5
- d)-3 + 4i
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The multiplicative inverse of 3 – 4i is
a)
(3 + 4i)/25
b)
3 + 4i
c)
-3 + 4i/5
d)
-3 + 4i
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Complete answers is in 3 steps:
1. Conjugate = 3+4i
2. Modulus = √3^2 + 4^2 =5
3. Multiplicative inverse = conjugate/square of modulus = 3+4i/5^2 = 3+4i/25
1. Conjugate = 3+4i
2. Modulus = √3^2 + 4^2 =5
3. Multiplicative inverse = conjugate/square of modulus = 3+4i/5^2 = 3+4i/25
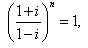 so the least integral value of n is
so the least integral value of n is- a)3
- b)-3
- c)-4
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
3
b)
-3
c)
-4
d)
4
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
{(1 + i)/(1 - i)}n = 1
multiply (1 + i) numerator as well as denominator .
{(1 + i)(1 + i)/(1 - i)(1 + i)}n = 1
{(1 + i)²/(1² - (i)²)}n = 1
{(1 + i² +2i)/2 }n = 1
{(2i)/2}n = 1
{i}n = 1
we know, i4n = 1 where , n is an integer.
so, n = 4n where n is an integers
e.g n = 4 { because least positive integer 1 }
hence, n = 4
multiply (1 + i) numerator as well as denominator .
{(1 + i)(1 + i)/(1 - i)(1 + i)}n = 1
{(1 + i)²/(1² - (i)²)}n = 1
{(1 + i² +2i)/2 }n = 1
{(2i)/2}n = 1
{i}n = 1
we know, i4n = 1 where , n is an integer.
so, n = 4n where n is an integers
e.g n = 4 { because least positive integer 1 }
hence, n = 4
Express the following in standard form :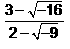
- a)
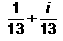
- b)
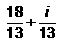
- c)
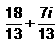
- d)
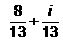
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Express the following in standard form :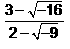
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
first write above equation in complex number format , ie using iota
(3-4i) / (2-3i)*(2+3i) / (2+3i) = (6+9i-8i+12) / 13=(18/13)+(i/13)
(3-4i) / (2-3i)*(2+3i) / (2+3i) = (6+9i-8i+12) / 13=(18/13)+(i/13)
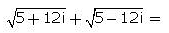
- a)10
- b)4
- c)8
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
10
b)
4
c)
8
d)
6
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Let √(5 – 12i) = x + iy
Squaring both sides, we get
5 – 12i = x2 + 2ixy +(iy)2 = x2 – y2 + 2xyi.
Comparing real and imaginary parts , we get
5 = x2 – y2 ———– (1) and xy = – 6 ———— (2)
Squaring (1), we get
25 = (x2 – y2)2 = (x2 + y2)2 – 4x2y2
⇒ 25 = (x2 + y2)2 – 4(– 6)2
⇒ (x2 + y2)2 = 169
⇒ x2 + y2 = 13 ———- (3)
Adding (1) and (3) we get
2x2 = 18
⇒ x = ± 3.
Subtracting (1) from (3) we get
2y2 = 8
⇒ y = ± 2.
Hence, square root of √(5 – 12i) is (3 – 2i)
Similarly, √(5 + 12i) is (3 + 2i)
√(5 + 12i) + √(5 – 12i)
⇒ (3 + 2i) + (3 - 2i)
⇒ 6
Squaring both sides, we get
5 – 12i = x2 + 2ixy +(iy)2 = x2 – y2 + 2xyi.
Comparing real and imaginary parts , we get
5 = x2 – y2 ———– (1) and xy = – 6 ———— (2)
Squaring (1), we get
25 = (x2 – y2)2 = (x2 + y2)2 – 4x2y2
⇒ 25 = (x2 + y2)2 – 4(– 6)2
⇒ (x2 + y2)2 = 169
⇒ x2 + y2 = 13 ———- (3)
Adding (1) and (3) we get
2x2 = 18
⇒ x = ± 3.
Subtracting (1) from (3) we get
2y2 = 8
⇒ y = ± 2.
Hence, square root of √(5 – 12i) is (3 – 2i)
Similarly, √(5 + 12i) is (3 + 2i)
√(5 + 12i) + √(5 – 12i)
⇒ (3 + 2i) + (3 - 2i)
⇒ 6

- a)
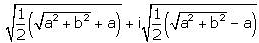
- b)
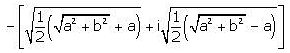
- c)
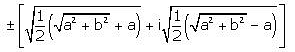
- d)
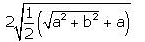
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
(a + ib)1/2 = (x + iy)
Squaring both sides,
a + ib = (x + iy)2
a + ib = x2 - y2 + 2ixy
Equating real and imaginary
a = x2 - y2 b = 2xy............(1)
Using (x2 + y2)2 = (x2 - y2)2 + 4xy
(x2 + y2)2 = a2 + b2
(x2 + y2) = (a2 + b2)1/2.......(2)
Adding (1) and (2)
2x2 = (a2 + b2)1/2 + a
x = +-{1/2(a2 + b2)1/2 + a}1/2
Subtract (2) from (1)
2y2 = (a2 + b2)1/2 - a
y = x = +-{1/2(a2 + b2)1/2 - a}1/2
Therefore, (a+ib)1/2 = x+iy
=> +-{1/2(a2 + b2)1/2 + a}1/2 + i+-{1/2(a2 + b2)1/2 - a}1/2
Squaring both sides,
a + ib = (x + iy)2
a + ib = x2 - y2 + 2ixy
Equating real and imaginary
a = x2 - y2 b = 2xy............(1)
Using (x2 + y2)2 = (x2 - y2)2 + 4xy
(x2 + y2)2 = a2 + b2
(x2 + y2) = (a2 + b2)1/2.......(2)
Adding (1) and (2)
2x2 = (a2 + b2)1/2 + a
x = +-{1/2(a2 + b2)1/2 + a}1/2
Subtract (2) from (1)
2y2 = (a2 + b2)1/2 - a
y = x = +-{1/2(a2 + b2)1/2 - a}1/2
Therefore, (a+ib)1/2 = x+iy
=> +-{1/2(a2 + b2)1/2 + a}1/2 + i+-{1/2(a2 + b2)1/2 - a}1/2
If If ω is a non real cube root of unity and (1+ω)9 = a+bω;a,b ∈ R, then a and b are respectively the numbers :- a)1, 0
- b)-1, 0
- c)0, 1
- d)0, -1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If If ω is a non real cube root of unity and (1+ω)9 = a+bω;a,b ∈ R, then a and b are respectively the numbers :
a)
1, 0
b)
-1, 0
c)
0, 1
d)
0, -1
|
|
Aryan Khanna answered |
Since w is the cube root of unity.
(1+w)9 =A+Bw
⇒(−w2)9 =A+Bw
⇒−(w3)6 = A+Bw
⇒−1=A+Bw
∴ A= -1 & B=0
(1+w)9 =A+Bw
⇒(−w2)9 =A+Bw
⇒−(w3)6 = A+Bw
⇒−1=A+Bw
∴ A= -1 & B=0
Multiplicative inverse of the non zero complex number x + iy (x,y ∈ R,)- a)
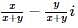
- b)
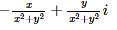
- c)
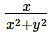 -
- 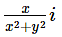
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Multiplicative inverse of the non zero complex number x + iy (x,y ∈ R,)
a)
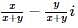
b)
c)
d)
none of these
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Let u be multiplicative inverse
zu = 1
u = 1/z
u = 1/(x+iy)
Rationalise it
[1/(x+iy)]*[(x-iy)/(x-iy)]
= (x-iy)/(x2+y2)
u = x/(x2+y2) +i(-y)/(x2+y2)
zu = 1
u = 1/z
u = 1/(x+iy)
Rationalise it
[1/(x+iy)]*[(x-iy)/(x-iy)]
= (x-iy)/(x2+y2)
u = x/(x2+y2) +i(-y)/(x2+y2)
Solve the quadratic equation x2 – ix + 6 = 0- a)1+2i, 1-2i
- b)-2, 3
- c)-2i, 3i
- d)2, -3i
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Solve the quadratic equation x2 – ix + 6 = 0
a)
1+2i, 1-2i
b)
-2, 3
c)
-2i, 3i
d)
2, -3i
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
x2 - ix + 6 = 0
x2 - 3ix + 2ix - 6i2 = 0 { i2 = -1}
x(x-3i) + 2i(x-3i) = 0
(x+2i) (x-3i) = 0
x = -2i, 3i
x2 - 3ix + 2ix - 6i2 = 0 { i2 = -1}
x(x-3i) + 2i(x-3i) = 0
(x+2i) (x-3i) = 0
x = -2i, 3i
If points corresponding to the complex numbers z1, z2, z3 and z4 are the vertices of a rhombus, taken in order, then for a non-zero real number k- a)z1 – z3 = i k( z2 –z4)
- b)z1 – z2 = i k( z3 –z4)
- c)z1 + z3 = k( z2 +z4)
- d)z1 + z2 = k( z3 +z4)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If points corresponding to the complex numbers z1, z2, z3 and z4 are the vertices of a rhombus, taken in order, then for a non-zero real number k
a)
z1 – z3 = i k( z2 –z4)
b)
z1 – z2 = i k( z3 –z4)
c)
z1 + z3 = k( z2 +z4)
d)
z1 + z2 = k( z3 +z4)
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
AC = z3 = z1 eiπ
= z1 (cosπ + i sinπ)
= z3 = z1(-1 + i(0))
= z3 = -z1
AC = z1 - z3
BC = z2 - z4
(z1 - z3)/(z2 - z4) = k
(z1 - z3) = eiπ/2(z2 - z4)
(z1 - z3) k(cosπ/2 + sinπ/2) (z2 - z4)
z1 - z3 = ki(z2 - z4)
z1 - z3 = ik(z2 - z4)
= z1 (cosπ + i sinπ)
= z3 = z1(-1 + i(0))
= z3 = -z1
AC = z1 - z3
BC = z2 - z4
(z1 - z3)/(z2 - z4) = k
(z1 - z3) = eiπ/2(z2 - z4)
(z1 - z3) k(cosπ/2 + sinπ/2) (z2 - z4)
z1 - z3 = ki(z2 - z4)
z1 - z3 = ik(z2 - z4)
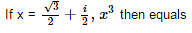
- a)- i
- b)1
- c)i
- d)-1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
- i
b)
1
c)
i
d)
-1
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
x = (√3+i)/2
x3 = 1/8(√3+i)3
Apply formula (a+b)3 = a3 + b3 + 3a2b + 3ab2
= (3√3 + i3 + 3*3*i + 3*√3*i2)/8
= (3√3 - i + 9i - 3√3)/8
= 8i/8
= i
x3 = 1/8(√3+i)3
Apply formula (a+b)3 = a3 + b3 + 3a2b + 3ab2
= (3√3 + i3 + 3*3*i + 3*√3*i2)/8
= (3√3 - i + 9i - 3√3)/8
= 8i/8
= i
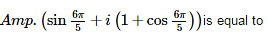
- a)9p/10
- b)5p/6
- c)6p/5
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
9p/10
b)
5p/6
c)
6p/5
d)
none of these
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
sin(6π/5) + i(1+cos(6π/5)) or −sin(π/5) + i(1−cos(π/5)) lies in the second quadrant of complex plane hence its argument is given as
arg(x+iy) = π − tan-1 |y/x| (∀ x<0,y≥0)
= π−tan-1 |1−cos(π/5)/sin(π/5)|
= π−tan-1 |2sin2(π/10)/2sin(π/10)cos(π/10)|
= π−tan-1 |sin(π/10)/cos(π/10)|
= π − tan-1 |tan(π/10)|
= π−tan-1 (tan(π/10)) (∵ tan(π/10)>0)
= π−π/10(∵−π/2≤tan−1(x)≤π/2)
= 9π/10
arg(x+iy) = π − tan-1 |y/x| (∀ x<0,y≥0)
= π−tan-1 |1−cos(π/5)/sin(π/5)|
= π−tan-1 |2sin2(π/10)/2sin(π/10)cos(π/10)|
= π−tan-1 |sin(π/10)/cos(π/10)|
= π − tan-1 |tan(π/10)|
= π−tan-1 (tan(π/10)) (∵ tan(π/10)>0)
= π−π/10(∵−π/2≤tan−1(x)≤π/2)
= 9π/10
If α is a complex a number such that α2+α+1 = 0 then α31 is- a)0
- b)1
- c)α
- d)α2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If α is a complex a number such that α2+α+1 = 0 then α31 is
a)
0
b)
1
c)
α
d)
α2
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Since α3 +1=(α+1)(α2 −α+1), using the given information, we get α3 +1 = 0
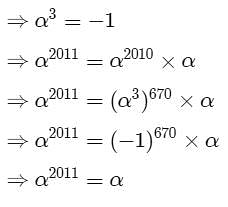
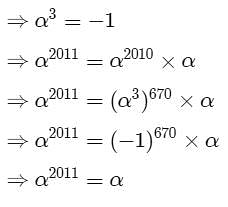
The equatiobn px = –2x2 + 6x – 9 has- a)No solution
- b) One solution
- c)Two solutions
- d)Infinite solutions
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The equatiobn px = –2x2 + 6x – 9 has
a)
No solution
b)
One solution
c)
Two solutions
d)
Infinite solutions
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
The RHS of the expression has a<0 which means the graph will lie below the x-axis and πx lies above the x-axis.Therefore,no solution.
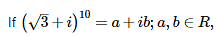 then a and b are respectively :
then a and b are respectively :- a)64 and - 64√3
- b)128 and 128√3
- c)512 and - 512√3
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
64 and - 64√3
b)
128 and 128√3
c)
512 and - 512√3
d)
none of these
|
|
Om Desai answered |
(√3 + i)10 = a + ib
Z = √3 + i = rcosθ + i rsinθ
⇒ √3 = rcosθ i = rsinθ
⇒ (√3)2 + (1)2 = r2cos2θ + r2sin2θ
⇒ 4 = r2
⇒ r = 2
tan = 1/√3
⇒ tan π/6
Therefore, Z = √3 + i = 2(cos π/6 + i sin π/6)
(Z)10 = √3 + i = (2cos π/6 + 2i sin π/6)10
= 210 (cos π/6 + i sin π/6)10
210 (cos 10π/6 + i sin 10π/6)
= 210 (cos(2π - π/3) + i sin(2π - π/3))
= 210 (cos π/3 - i sin π/3)
= 210 (1/2 - i√3/2)
29(1 - i√3)
a = 29 = 512
b = - 29(√3) = -512√3
Z = √3 + i = rcosθ + i rsinθ
⇒ √3 = rcosθ i = rsinθ
⇒ (√3)2 + (1)2 = r2cos2θ + r2sin2θ
⇒ 4 = r2
⇒ r = 2
tan = 1/√3
⇒ tan π/6
Therefore, Z = √3 + i = 2(cos π/6 + i sin π/6)
(Z)10 = √3 + i = (2cos π/6 + 2i sin π/6)10
= 210 (cos π/6 + i sin π/6)10
210 (cos 10π/6 + i sin 10π/6)
= 210 (cos(2π - π/3) + i sin(2π - π/3))
= 210 (cos π/3 - i sin π/3)
= 210 (1/2 - i√3/2)
29(1 - i√3)
a = 29 = 512
b = - 29(√3) = -512√3

- a)0
- b)-1
- c)1
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
0
b)
-1
c)
1
d)
none of these
|
|
Parth Patel answered |
If it is -1 then it is given that the w is cube root of unity
If z1 = 2 + i, z2 = 1 + 3i, then Re ( z1 - z2) =- a)ι
- b)1
- c)2 ι
- d)2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If z1 = 2 + i, z2 = 1 + 3i, then Re ( z1 - z2) =
a)
ι
b)
1
c)
2 ι
d)
2
|
|
Aditi Basu answered |
1
To find Re(z1 - z2), we first need to subtract z2 from z1:
z1 - z2 = (2i) - (1 + 3i) = 1 - i
Now, to find the real part of this complex number, we simply take the real component, which is 1. Therefore, Re(z1 - z2) = 1.
To find Re(z1 - z2), we first need to subtract z2 from z1:
z1 - z2 = (2i) - (1 + 3i) = 1 - i
Now, to find the real part of this complex number, we simply take the real component, which is 1. Therefore, Re(z1 - z2) = 1.
Amp. (z−2−3i) = π/4 then locus of z is- a)x + y = 0
- b)x – y + 1 = 0
- c)x – y = 2
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Amp. (z−2−3i) = π/4 then locus of z is
a)
x + y = 0
b)
x – y + 1 = 0
c)
x – y = 2
d)
none of these
|
|
Anirban Sharma answered |
The term "Amp.(z)" is not clear and could have multiple interpretations. It could refer to an abbreviation for "Amplifier" or "Amplitude," but without further context, it is difficult to determine the exact meaning.
If z = x + yi ; x ,y ∈ R, then locus of the equation 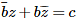 , where c ∈ R and b ∈ C, b ≠ 0 are fixed, is
, where c ∈ R and b ∈ C, b ≠ 0 are fixed, is- a)a parabola
- b)a straight line
- c)a circle
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If z = x + yi ; x ,y ∈ R, then locus of the equation 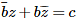 , where c ∈ R and b ∈ C, b ≠ 0 are fixed, is
, where c ∈ R and b ∈ C, b ≠ 0 are fixed, is
a)
a parabola
b)
a straight line
c)
a circle
d)
none of these
|
|
Vivek answered |
As b and c are linear constants ,independent of x and y, then by substituting them in the equation given, we get an equation linear in x and y. Thus, the given equation represents a straight line.
Express the following in standard form : (2 – √3i) (2 + √3i) + 2 – 4i- a)3 + 4i
- b)4i
- c)9 - 4i
- d)13 + 4i
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Express the following in standard form : (2 – √3i) (2 + √3i) + 2 – 4i
a)
3 + 4i
b)
4i
c)
9 - 4i
d)
13 + 4i
|
|
Arka Chavan answered |
I'm sorry, the expression provided is incomplete. Please provide the full expression.
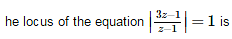
- a)none of these
- b)a circle
- c)a straight line
- d)an ellipse
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
none of these
b)
a circle
c)
a straight line
d)
an ellipse
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
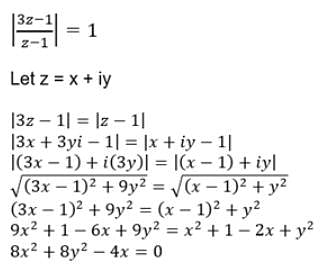 This is Equation of a Circle.
This is Equation of a Circle.Find the roots of the quadratic equation: x2 + 2x - 15 = 0?- a)-5, 3
- b)3, 5
- c)-3, 5
- d)-3, -5
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the roots of the quadratic equation: x2 + 2x - 15 = 0?
a)
-5, 3
b)
3, 5
c)
-3, 5
d)
-3, -5
|
|
Vaishnavi Iyer answered |
Solution:
The given quadratic equation is x^2 + 2x - 15 = 0.
To find the roots of the quadratic equation, we can use the quadratic formula which is given as:
x = (-b ± √(b^2 - 4ac)) / 2a
where a, b, and c are the coefficients of the quadratic equation.
By comparing the given quadratic equation with ax^2 + bx + c = 0, we can see that a = 1, b = 2, and c = -15.
Substituting these values in the quadratic formula, we get:
x = (-2 ± √(2^2 - 4(1)(-15))) / 2(1)
x = (-2 ± √(64)) / 2
x = (-2 ± 8) / 2
Therefore, the roots of the quadratic equation are:
x = (-2 + 8) / 2 = 3
x = (-2 - 8) / 2 = -5
Hence, the correct answer is option A, which is -5 and 3.
The given quadratic equation is x^2 + 2x - 15 = 0.
To find the roots of the quadratic equation, we can use the quadratic formula which is given as:
x = (-b ± √(b^2 - 4ac)) / 2a
where a, b, and c are the coefficients of the quadratic equation.
By comparing the given quadratic equation with ax^2 + bx + c = 0, we can see that a = 1, b = 2, and c = -15.
Substituting these values in the quadratic formula, we get:
x = (-2 ± √(2^2 - 4(1)(-15))) / 2(1)
x = (-2 ± √(64)) / 2
x = (-2 ± 8) / 2
Therefore, the roots of the quadratic equation are:
x = (-2 + 8) / 2 = 3
x = (-2 - 8) / 2 = -5
Hence, the correct answer is option A, which is -5 and 3.
Let x,y ∈ R, hen x + iy is a non real complex number if- a)y = 0
- b)x ≠ 0
- c)x = 0
- d)y ≠ 0
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Let x,y ∈ R, hen x + iy is a non real complex number if
a)
y = 0
b)
x ≠ 0
c)
x = 0
d)
y ≠ 0
|
|
Muskaan Chakraborty answered |
I'm sorry, but your question is incomplete. Please provide more information or specify what you would like me to do.
Chapter doubts & questions for Complex numbers - Mathematics for Year 12 2024 is part of Year 12 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Year 12 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Year 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Complex numbers - Mathematics for Year 12 in English & Hindi are available as part of Year 12 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Year 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Mathematics for Year 12
154 videos|194 docs|125 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup
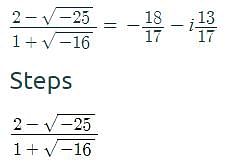
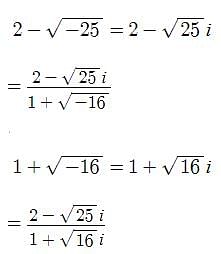
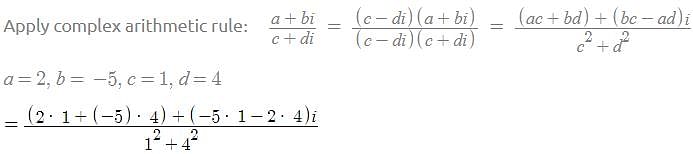
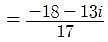
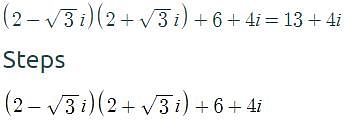
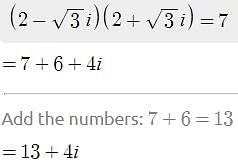
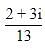
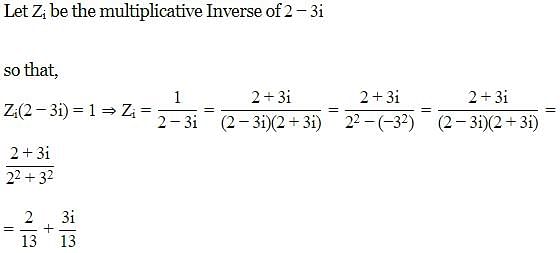
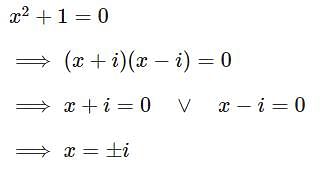
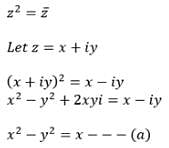
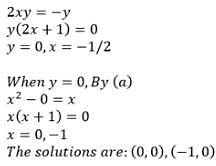
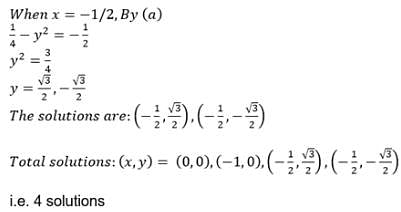
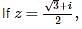 then z69 is equal to :
then z69 is equal to :