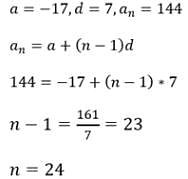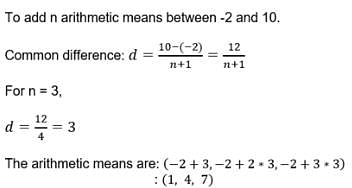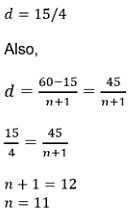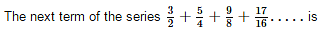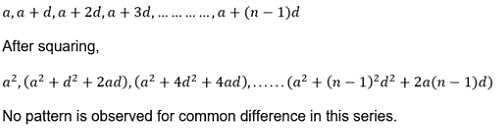All Exams >
Year 12 >
Mathematics for Year 12 >
All Questions
All questions of Sequence and series for Year 12 Exam
What is the 50th term of the sequence √3, 3, 3√3, 9, ......- a)(√3)49
- b)(√3)50
- c)349
- d)350
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the 50th term of the sequence √3, 3, 3√3, 9, ......
a)
(√3)49
b)
(√3)50
c)
349
d)
350
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
an = ar(n-1)
Given, a = √3, r = 3/√3
r = √3
a50 = ar(n-1)
= (√3)(√3)(50-1)
= (√3)(√3)49
= (√3)50
Given, a = √3, r = 3/√3
r = √3
a50 = ar(n-1)
= (√3)(√3)(50-1)
= (√3)(√3)49
= (√3)50
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The 10th term of the sequence an = 2(n -1)(2n - 1) is- a)192
- b)132
- c)212
- d)342
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The 10th term of the sequence an = 2(n -1)(2n - 1) is
a)
192
b)
132
c)
212
d)
342
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
an = 2(n -1)(2n - 1)
a10 = 2(10-1)(2(10)-1))
= 2(9)(19)
= 342
a10 = 2(10-1)(2(10)-1))
= 2(9)(19)
= 342
Find the missing number. 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, (....)- a)64
- b)54
- c)56
- d)81
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the missing number. 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, (....)
a)
64
b)
54
c)
56
d)
81
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
The given number series as follow as 1^2, 2^2, 3^2, 4^2, 5^2, 6^2, 7^2, 8^2, ...
So the next number is 8^2 = 64.
The terms of an A.P. are doubled, then the resulting sequence is- a)An A.P. with common difference equal to the common difference of the original A.P
- b)An A.P. with common difference thrice the common difference of the original A.P.
- c)An A.P. with common difference double the common difference of the original A.P.
- d)An A.P. with common difference half the common difference of the original A.P.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The terms of an A.P. are doubled, then the resulting sequence is
a)
An A.P. with common difference equal to the common difference of the original A.P
b)
An A.P. with common difference thrice the common difference of the original A.P.
c)
An A.P. with common difference double the common difference of the original A.P.
d)
An A.P. with common difference half the common difference of the original A.P.
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The general form of an AP is a, a+d, a+2d,.....
where a is the first term and d is the common difference
If we double the terms, the new sequence would be
A , a+2d, a+4d,......
We can observe that this sequence is also an AP
First term is a
Common difference is 2d nth term= 2a+(n-1)2d
= 2[a+(n-1)d]
where a is the first term and d is the common difference
If we double the terms, the new sequence would be
A , a+2d, a+4d,......
We can observe that this sequence is also an AP
First term is a
Common difference is 2d nth term= 2a+(n-1)2d
= 2[a+(n-1)d]
The sum of the first hundred even natural numbers divisible by 5 is- a)55005
- b)55000
- c)50000
- d)50500
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The sum of the first hundred even natural numbers divisible by 5 is
a)
55005
b)
55000
c)
50000
d)
50500
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
first even no. divisible by 5= 10
d=10
Sn = n/2(2a + (n-1) d)
S100= 100/2 (2(10) + (100-1)10)
S100=50(20 + 990)
S100= 50(1010)
S100 = 50500
The first negative term of the A.P.62,57,52…. is the- a)10th term
- b)14th term
- c)12th term
- d)18th term
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The first negative term of the A.P.62,57,52…. is the
a)
10th term
b)
14th term
c)
12th term
d)
18th term
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
a = 62 d = 57 - 62 = -5
tn = a + (n-1)d
= 62 + (n-1)(-5)
= 62 - 5n + 5
= 67 - 5n
From the options, we take '14'
= 67 - 5(14)
= 67 - 70
= -3 (The first negative term will be at the 14th term)
tn = a + (n-1)d
= 62 + (n-1)(-5)
= 62 - 5n + 5
= 67 - 5n
From the options, we take '14'
= 67 - 5(14)
= 67 - 70
= -3 (The first negative term will be at the 14th term)
The next term of the sequence 1, 2, 4, 7,11,…. Is- a)18
- b)17
- c)16
- d)15
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The next term of the sequence 1, 2, 4, 7,11,…. Is
a)
18
b)
17
c)
16
d)
15
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
The given series is: 1,2,4,7,11,...
Difference between second and first term = 2 - 1 = 1
Difference between third and second term = 4 - 2 = 2
Difference between fourth and third term = 7 - 4 = 3
Difference between fifth and fourth term = 11 - 7 = 4
Difference between sixth and fifth term = 16 - 11 = 5
Difference between second and first term = 2 - 1 = 1
Difference between third and second term = 4 - 2 = 2
Difference between fourth and third term = 7 - 4 = 3
Difference between fifth and fourth term = 11 - 7 = 4
Difference between sixth and fifth term = 16 - 11 = 5
What is the 10th term of the sequence defined by an = (n-1)(2-n)(3+n)?
a) 792
b) -936
c) -924
d) -792
The answer is b.
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
an = (n-1)(2-n)(3+n)
Put n = 10
an = 9×(-8)×13
= - 936
Put n = 10
an = 9×(-8)×13
= - 936
Three terms in A.P. are such that their sum is 45. What is the middle term?- a)25
- b)30
- c)15
- d)10
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Three terms in A.P. are such that their sum is 45. What is the middle term?
a)
25
b)
30
c)
15
d)
10
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
Let the three numbers be a-d, a, a+d
ATQ,
a - d + a + a + 2d = 45
3a = 45
a = 15
Middle term is 15
ATQ,
a - d + a + a + 2d = 45
3a = 45
a = 15
Middle term is 15
How many terms of the series
24,20,16,…are required so that their sum is 72?- a)8 or 6
- b)12
- c)9 or 4
- d)11
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How many terms of the series
24,20,16,…are required so that their sum is 72?
24,20,16,…are required so that their sum is 72?
a)
8 or 6
b)
12
c)
9 or 4
d)
11
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
As given above we can clearly see that the given series forms an AP. So we can use the sum formula to calculate it.
= Sn = n / 2 [ 2a + ( n-1 ) d ]
So the values are :
a = 24
d = -4
n = ?
Sn = 72
So substitute in the formula to get the answer:
= 72 = n / 2 [ 2 ( 24 ) + ( n - 1 ) -4 ]
= 72 = n / 2 [ 48 - 4n + 4 ]
= 72 * 2 = n [ 52 - 4n ]
= 144 = 52n - 4n^2
= 4n^2 - 52n + 144 = 0 ------ Dividing by 4 throughout the equation we get,
= n^2 - 13n + 36
Factorizing the above quadratic equation we get,
= n^2 - 9n - 4n + 36 = 0
= n ( n - 9 ) -4 ( n - 9 ) = 0
= ( n - 4 ) ( n - 9 ) = 0
= n = 4 , 9
So the number of terms can be both 4 terms and 9 terms. This is because since the AP is decreasing.
Hope it helps !!
The 5th term of the sequence 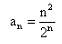 is
is- a)1
- b)5/16
- c)25/16
- d)25/32
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The 5th term of the sequence 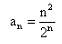 is
is
a)
1
b)
5/16
c)
25/16
d)
25/32
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
an = (n2)/2n
⇒ a5 = [(5)2]/2(5)
⇒ a5 = 25/32
⇒ a5 = [(5)2]/2(5)
⇒ a5 = 25/32
The first 4 terms of the sequence 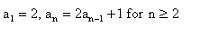 are
are- a)2, 6, 13, 27
- b)2, 5, 11, 23
- c)2, 6, 11, 24
- d)2, 5, 12, 37
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The first 4 terms of the sequence 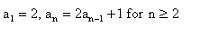 are
are
a)
2, 6, 13, 27
b)
2, 5, 11, 23
c)
2, 6, 11, 24
d)
2, 5, 12, 37
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
a1 = 2
a2 = 2a1 + 1
=> 2(2) + 1 = 5
a3 = 2a2 + 1
=> 2(5) + 1 = 11
a4 = 2a3 + 1
=> 2(11) + 1 = 23
Hence, the required series is : 2,5,11,23………
a2 = 2a1 + 1
=> 2(2) + 1 = 5
a3 = 2a2 + 1
=> 2(5) + 1 = 11
a4 = 2a3 + 1
=> 2(11) + 1 = 23
Hence, the required series is : 2,5,11,23………
Sum to 20 terms of the series (1.3)2 + (2.5)2 + (3.7)2 +… is:
- a)168090
- b)198090
- c)178090
- d)188090
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Sum to 20 terms of the series (1.3)2 + (2.5)2 + (3.7)2 +… is:
a)
168090
b)
198090
c)
178090
d)
188090
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Given that (1.3)2, (2.5)2 , (3.7)2 .....................20 terms
Here 1,2,3,.................are in A.P.
a = 1, d = 1
tn = a + (n-1) d = 1 + (n -1)1 = n
3,5,7 ............. are in A.P
a = 3, d = 2
tn = a + (n-1) d = 3 + (n -1)2 = 2n + 1
∴ nth term = n(2n + 1)2 = 4n3 + 4n2 + n
Sum of n terms Sn = ∑ ( 4n3 + 4n2 + n ) = 4 { n2(n+1)2}/4 + 4 {n (n+1)(2n+1)} / 6 + n(n+1)/2
= { n2(n+1)2} + 2 {n (n+1)(2n+1)} / 3 + n(n+1)/2
Sum of 20 terms S20 = 400 × 441 + 40 × 41 × 7 + 10 ×21 = 176400 + 11480 + 210
= 188090.
Here 1,2,3,.................are in A.P.
a = 1, d = 1
tn = a + (n-1) d = 1 + (n -1)1 = n
3,5,7 ............. are in A.P
a = 3, d = 2
tn = a + (n-1) d = 3 + (n -1)2 = 2n + 1
∴ nth term = n(2n + 1)2 = 4n3 + 4n2 + n
Sum of n terms Sn = ∑ ( 4n3 + 4n2 + n ) = 4 { n2(n+1)2}/4 + 4 {n (n+1)(2n+1)} / 6 + n(n+1)/2
= { n2(n+1)2} + 2 {n (n+1)(2n+1)} / 3 + n(n+1)/2
Sum of 20 terms S20 = 400 × 441 + 40 × 41 × 7 + 10 ×21 = 176400 + 11480 + 210
= 188090.
A man saved Rs 21700 in 14 years. In each year after the first he saved Rs 100 more than he did in the preceding year. How much did he save in the first year?- a)Rs 2100
- b)Rs 1300
- c)Rs 900
- d)Rs 600
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A man saved Rs 21700 in 14 years. In each year after the first he saved Rs 100 more than he did in the preceding year. How much did he save in the first year?
a)
Rs 2100
b)
Rs 1300
c)
Rs 900
d)
Rs 600
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
d = 100
Sn = 21700
n = 14
Sn = n/2[2a + (n-1)d]
21700 = 14/2[2a + (14-1)100]
= 21700 = 7[2a + 1300]
= 3100 = 2a + 1300
⇒ 3100 - 1300 = 2a
⇒ 1800 = 2a
⇒ a = 900
Sn = 21700
n = 14
Sn = n/2[2a + (n-1)d]
21700 = 14/2[2a + (14-1)100]
= 21700 = 7[2a + 1300]
= 3100 = 2a + 1300
⇒ 3100 - 1300 = 2a
⇒ 1800 = 2a
⇒ a = 900
If a, b, c, d are in H.P., then ab + bc + cd is- a)3 b d
- b)(a + b) (c + d)
- c)3 a d
- d)3 a c
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If a, b, c, d are in H.P., then ab + bc + cd is
a)
3 b d
b)
(a + b) (c + d)
c)
3 a d
d)
3 a c
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Since a,b,c are in H.P, so b = 2ac/(a+c).
Also, b,c,d are in H.P, so c = 2bd/(b+d).
Therefore, (a+c)(b+d) = 2ac/b × 2bd/c
⇒ab+cb+ad+cd = 4ad
⇒ab+bc+cd = 3ad
Also, b,c,d are in H.P, so c = 2bd/(b+d).
Therefore, (a+c)(b+d) = 2ac/b × 2bd/c
⇒ab+cb+ad+cd = 4ad
⇒ab+bc+cd = 3ad
If A1, A2, A3,…., An are n numbers between a and b, such that a, A1, A2, A3,…, An, b are in A.P., then nth term from beginning is:- a)b
- b)An-1
- c)An
- d)A1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If A1, A2, A3,…., An are n numbers between a and b, such that a, A1, A2, A3,…, An, b are in A.P., then nth term from beginning is:
a)
b
b)
An-1
c)
An
d)
A1
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
A1,A2,......, An are inserted between a and b then the series will become
a, A1,A2,A3,......, An,b. Now a becomes the first term, A1 will be second, A2 will become third term
An will become A(n+1)th term
therefore A(n-1) will become nth term.
a, A1,A2,A3,......, An,b. Now a becomes the first term, A1 will be second, A2 will become third term
An will become A(n+1)th term
therefore A(n-1) will become nth term.
The sum of all 2-digited numbers which leave remainder 1 when divided by 3 is- a)1605
- b)1616
- c)1604
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The sum of all 2-digited numbers which leave remainder 1 when divided by 3 is
a)
1605
b)
1616
c)
1604
d)
none of these
|
|
Maheshwar Unni answered |
Problem:
The sum of all 2-digit numbers which leave a remainder of 1 when divided by 3 is:
a) 1605
b) 1616
c) 1604
d) none of these
Solution:
To find the sum of all 2-digit numbers that leave a remainder of 1 when divided by 3, we can follow these steps:
Step 1: Determine the range of 2-digit numbers:
The range of 2-digit numbers is from 10 to 99.
Step 2: Identify the numbers that satisfy the given condition:
To find the numbers that leave a remainder of 1 when divided by 3, we can use the modulo operation. If a number leaves a remainder of 1 when divided by 3, then it can be written as 3k + 1, where k is an integer.
We need to find all values of k such that 3k + 1 is a 2-digit number. This condition is satisfied when k = 3, 4, ..., 33.
Step 3: Calculate the sum:
To find the sum of these numbers, we can use the formula for the sum of an arithmetic series:
Sum = (n/2)(first term + last term)
In this case, the first term is 3 * 3 + 1 = 10 and the last term is 3 * 33 + 1 = 100. The number of terms, n, is 33 - 3 + 1 = 31.
Using the formula, the sum of these numbers is:
Sum = (31/2)(10 + 100) = 31 * 55 = 1705
Conclusion:
Therefore, the sum of all 2-digit numbers that leave a remainder of 1 when divided by 3 is 1705. However, none of the given answer choices match this result, so the correct answer is none of these.
The sum of all 2-digit numbers which leave a remainder of 1 when divided by 3 is:
a) 1605
b) 1616
c) 1604
d) none of these
Solution:
To find the sum of all 2-digit numbers that leave a remainder of 1 when divided by 3, we can follow these steps:
Step 1: Determine the range of 2-digit numbers:
The range of 2-digit numbers is from 10 to 99.
Step 2: Identify the numbers that satisfy the given condition:
To find the numbers that leave a remainder of 1 when divided by 3, we can use the modulo operation. If a number leaves a remainder of 1 when divided by 3, then it can be written as 3k + 1, where k is an integer.
We need to find all values of k such that 3k + 1 is a 2-digit number. This condition is satisfied when k = 3, 4, ..., 33.
Step 3: Calculate the sum:
To find the sum of these numbers, we can use the formula for the sum of an arithmetic series:
Sum = (n/2)(first term + last term)
In this case, the first term is 3 * 3 + 1 = 10 and the last term is 3 * 33 + 1 = 100. The number of terms, n, is 33 - 3 + 1 = 31.
Using the formula, the sum of these numbers is:
Sum = (31/2)(10 + 100) = 31 * 55 = 1705
Conclusion:
Therefore, the sum of all 2-digit numbers that leave a remainder of 1 when divided by 3 is 1705. However, none of the given answer choices match this result, so the correct answer is none of these.
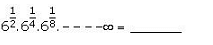
- a)4
- b)6
- c)8
- d)2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
4
b)
6
c)
8
d)
2
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
6 + 6 + 6.........∞
61/2 * 61/4 * 61/8………..∞
= 61/2 + 1/(2*2) + 1/(2*2*2) (sum of infinte G.P.= a/(1−r))
= (1/2)/(6(1-½))
= (1/2)/(61/2)
= 6
61/2 * 61/4 * 61/8………..∞
= 61/2 + 1/(2*2) + 1/(2*2*2) (sum of infinte G.P.= a/(1−r))
= (1/2)/(6(1-½))
= (1/2)/(61/2)
= 6
Which term of the following sequence is 64?2 , 2√2, 4, .....- a)12
- b)10
- c)11
- d)8
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which term of the following sequence is 64?
2 , 2√2, 4, .....
a)
12
b)
10
c)
11
d)
8
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Given sequence : 2, 2√2, 4….
First term a1 = a = 2 and 2nd term a2 = 2√2, then
Common ratio r = a2/a = (2√2)/2
Let an = 64
∴ ar(n-1) = 64
⇒ 2.(√2)(n-1) = 32
⇒ (2)(n-1)/2 = 32
∴ (2)(n-1)/2 = (2)5
⇒ (n − 1)/2 = 5,
⇒ n = 11
First term a1 = a = 2 and 2nd term a2 = 2√2, then
Common ratio r = a2/a = (2√2)/2
Let an = 64
∴ ar(n-1) = 64
⇒ 2.(√2)(n-1) = 32
⇒ (2)(n-1)/2 = 32
∴ (2)(n-1)/2 = (2)5
⇒ (n − 1)/2 = 5,
⇒ n = 11
What is the 10th A.M between 2 and 57 if 10 A.M s are inserted between these numbers?
- a)54
- b)53
- c)52
- d)55
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the 10th A.M between 2 and 57 if 10 A.M s are inserted between these numbers?
a)
54
b)
53
c)
52
d)
55
|
|
Aryan Khanna answered |
2 and 57 have 10 terms between them so including them there would be 12 terms
an = 57, a = 2, n = 12
an = a + (n-1)d
=> 57 = 2 + (12 - 1)d
=> 55 = 11d
d = 5
T10 = a + 10d
=> 2 + 10(5)
= 52
an = 57, a = 2, n = 12
an = a + (n-1)d
=> 57 = 2 + (12 - 1)d
=> 55 = 11d
d = 5
T10 = a + 10d
=> 2 + 10(5)
= 52
How many terms of the G.P. 4 + 16 + 64 + … will make the sum 5460?- a)9
- b)7
- c)8
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
How many terms of the G.P. 4 + 16 + 64 + … will make the sum 5460?
a)
9
b)
7
c)
8
d)
6
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
Sum (Sn) = a x (rn -1)/(r-1)
5460 = 4 x (4n -1)/3
16380 = 4n+1 - 4
5460 = 4 x (4n -1)/3
16380 = 4n+1 - 4
16384 = 4n+1
47 = 4n+1
7 = n + 1
n = 6
The eleventh term of the sequence 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, ….. is- a)89
- b)66
- c)72
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The eleventh term of the sequence 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, ….. is
a)
89
b)
66
c)
72
d)
none of these
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
The sequence is the Fibonacci series
1+1 = 0
1+2 = 3
2+3 = 5
3+5 = 8
5+8 = 13
8+13 = 21
13+21 = 34
21+34 = 55
34+55 = 89
The 11th term will be 89.
1+1 = 0
1+2 = 3
2+3 = 5
3+5 = 8
5+8 = 13
8+13 = 21
13+21 = 34
21+34 = 55
34+55 = 89
The 11th term will be 89.
The next term of the sequence 1, 5, 14, 30, 55, …… is
- a)95
- b)91
- c)90
- d)80
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The next term of the sequence 1, 5, 14, 30, 55, …… is
a)
95
b)
91
c)
90
d)
80
|
|
Mihir Chaudhary answered |
The sequence is obtained by adding consecutive odd numbers, starting with 1.
1 + 0 = 1
1 + 3 = 4
4 + 5 = 9
9 + 7 = 16
16 + 9 = 25
So the next term in the sequence is 25.
Therefore, the complete sequence is:
1, 5, 14, 30, 55, 25
1 + 0 = 1
1 + 3 = 4
4 + 5 = 9
9 + 7 = 16
16 + 9 = 25
So the next term in the sequence is 25.
Therefore, the complete sequence is:
1, 5, 14, 30, 55, 25
The arithmetic mean between 6 and – 12 is:- a)6
- b)-3
- c)-6
- d)9
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The arithmetic mean between 6 and – 12 is:
a)
6
b)
-3
c)
-6
d)
9
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
6, x, -12
x = (6-12)/2
x = -6/2
x = -3
x = (6-12)/2
x = -6/2
x = -3
Three geometric means between the numbers 1/4 and 64 are:- a)1/2, 8, 32
- b)4, 16, 32
- c)1, 8, 32
- d)1, 4, 16
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Three geometric means between the numbers 1/4 and 64 are:
a)
1/2, 8, 32
b)
4, 16, 32
c)
1, 8, 32
d)
1, 4, 16
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
nth G.M. between a and b is
Gn = arn
Where common ratio is r = (b/a)(1/(n+1))
So, to insert 3 geometric means between 1/4 and 64
r = (b/a)(1/(n+1))
r = (64/(¼)(1/(3+1))
r = (256)1/4
r = (4)(4)1/4
r = 4
Gn = 1 * (4)n
G0 = 1 * (4)0 = 1
G1 = 1 * (4)1 = 4
G2 = 1 * (4)2 = 16
The terms are 1, 4, 16
Gn = arn
Where common ratio is r = (b/a)(1/(n+1))
So, to insert 3 geometric means between 1/4 and 64
r = (b/a)(1/(n+1))
r = (64/(¼)(1/(3+1))
r = (256)1/4
r = (4)(4)1/4
r = 4
Gn = 1 * (4)n
G0 = 1 * (4)0 = 1
G1 = 1 * (4)1 = 4
G2 = 1 * (4)2 = 16
The terms are 1, 4, 16
Can you explain the answer of this question below:A sequence is a function whose domain is the set of- A:Natural Numbers
- B:Real numbers
- C:Whole numbers
- D:Integers
The answer is a.
A sequence is a function whose domain is the set of
A:
Natural Numbers
B:
Real numbers
C:
Whole numbers
D:
Integers
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
A sequence is a function whose domain is the set of natural numbers or a subset of the natural numbers. We usually use the symbol an to represent a sequence, where n is a natural number and an is the value of the function on n.
Which term of the sequence 8 – 6i, 7 – 4i, 6 – 2i, ….is a real number ?- a)7th
- b)6th
- c)5th
- d)4th
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which term of the sequence 8 – 6i, 7 – 4i, 6 – 2i, ….is a real number ?
a)
7th
b)
6th
c)
5th
d)
4th
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
a = 8−6i
d = 7−4i−8+6i
= −1+2i
an = a+(n−1)d
a+ib = 8−6i+(n−1)(−1+2i)
a+ib = 8−6i+(−1)(n−1)+(n−1)2i
= − 6+2(n−1)=0
= 2(n−1) = 6
n = 4
an = 8−6i+(4−1)(−1+2i)
= 8−6i−3+6i = 5
4th term = 5
d = 7−4i−8+6i
= −1+2i
an = a+(n−1)d
a+ib = 8−6i+(n−1)(−1+2i)
a+ib = 8−6i+(−1)(n−1)+(n−1)2i
= − 6+2(n−1)=0
= 2(n−1) = 6
n = 4
an = 8−6i+(4−1)(−1+2i)
= 8−6i−3+6i = 5
4th term = 5
The A.M. between two numbers is 34 and their G.M. is 16.The numbers are- a)32 and 8
- b)64 and 4
- c)62 and 6
- d)60 and 18
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The A.M. between two numbers is 34 and their G.M. is 16.The numbers are
a)
32 and 8
b)
64 and 4
c)
62 and 6
d)
60 and 18

|
Shashank Dubey answered |
A.M = (x+y/2)
G.M. = √(x*y)
64+4/2 = 34
64*4 = √256 = 16
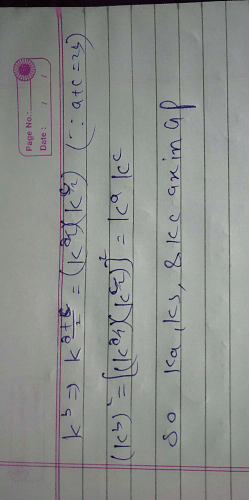
The three numbers between 1 and 256 such that the sequence is in GP are- a)4,16,64
- b)2,8,32
- c)8,16,32
- d)8,16,64
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The three numbers between 1 and 256 such that the sequence is in GP are
a)
4,16,64
b)
2,8,32
c)
8,16,32
d)
8,16,64
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
nth G.M. between a and b is
Gn = arn
Where common ratio is r = (b/a)(1/(n+1))
So, to insert 3 geometric means between 1 and 256
r = (b/a)(1/(n+1))
r = (256/(1)(1/(3+1))
r = (256)1/4
r = (4)(4)1/4
r = 4
Gn = 1 * (4)n
G1 = 1 * (4)1 = 4
G2 = 1 * (4)2 = 16
G3 = 1 * (4)3 = 64
The terms are 4, 16, 64
Gn = arn
Where common ratio is r = (b/a)(1/(n+1))
So, to insert 3 geometric means between 1 and 256
r = (b/a)(1/(n+1))
r = (256/(1)(1/(3+1))
r = (256)1/4
r = (4)(4)1/4
r = 4
Gn = 1 * (4)n
G1 = 1 * (4)1 = 4
G2 = 1 * (4)2 = 16
G3 = 1 * (4)3 = 64
The terms are 4, 16, 64
The sequence whose terms follow the certain pattern is called a- a)progression
- b)finite sequence
- c)series
- d)real sequence
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The sequence whose terms follow the certain pattern is called a
a)
progression
b)
finite sequence
c)
series
d)
real sequence
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
Progression : It is not necessary that the terms of a sequence always follow a certain pattern or they are described by some explicit formula of the nth term. Those sequences whose terms follow certain patterns are called progressions.
If the 10 times of the 10th term of an AP is equal to 15 times to the 15th term, then the 25th term is:- a)25 times of 25th term
- b)zero
- c)1
- d)2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If the 10 times of the 10th term of an AP is equal to 15 times to the 15th term, then the 25th term is:
a)
25 times of 25th term
b)
zero
c)
1
d)
2
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
According to question ,
10 x 10th term =15 x 15th term
let a is the first term and d is the common difference .
10 (a+9d)=15 (a+14d)
5a+120d=0
a +24d=0
now ,
25th term =a+(25-1) d=a+24d=0
hence 25th term=0
The digits of a positive integer having three digits are in AP and sum of their digits is 21. The number obtained by reversing the digits is 396 less than the original number. Find the original number.- a)876
- b)579
- c)975
- d)678
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The digits of a positive integer having three digits are in AP and sum of their digits is 21. The number obtained by reversing the digits is 396 less than the original number. Find the original number.
a)
876
b)
579
c)
975
d)
678
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Let the digits at ones, tens and hundreds place be (a−d)a and (a+d) respectively. The, the number is
(a+d)×100+a×10+(a−d) = 111a+99d
The number obtained by reversing the digits is
(a−d)×+a×10+(a+d) = 111a−99d
It is given that the sum of the digits is 21.
(a−d)+a+(a+d) = 21 ...(i)
Also it is given that the number obtained by reversing the digits is 594 less than the original number.
∴111a−99d = 111a+99d−396 ...(ii)
⟹ 3a = 21 and 198d = 396
⟹ a = 7 and d = -2
Original number = (a−d)×+a×10+(a+d)
= 100(9) + 10(7) + 5
= 975
(a+d)×100+a×10+(a−d) = 111a+99d
The number obtained by reversing the digits is
(a−d)×+a×10+(a+d) = 111a−99d
It is given that the sum of the digits is 21.
(a−d)+a+(a+d) = 21 ...(i)
Also it is given that the number obtained by reversing the digits is 594 less than the original number.
∴111a−99d = 111a+99d−396 ...(ii)
⟹ 3a = 21 and 198d = 396
⟹ a = 7 and d = -2
Original number = (a−d)×+a×10+(a+d)
= 100(9) + 10(7) + 5
= 975
If we want to insert 8 numbers between the numbers 4 and 31 such that the resulting sequence is an AP.The difference between the consecutive numbers will be- a)4
- b)3
- c)2
- d)5
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If we want to insert 8 numbers between the numbers 4 and 31 such that the resulting sequence is an AP.The difference between the consecutive numbers will be
a)
4
b)
3
c)
2
d)
5
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
a = 4, l = 31, n = 8
(l-a)/(n+1) = (31-4)/(8+1)
= 27/9
= 3
(l-a)/(n+1) = (31-4)/(8+1)
= 27/9
= 3
The sum of the series 2 + 6 + 18 + ….+ 4374 is:- a)6560
- b)6876
- c)8748
- d)8798
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The sum of the series 2 + 6 + 18 + ….+ 4374 is:
a)
6560
b)
6876
c)
8748
d)
8798
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
Above sequence is a gp with common ratio=3
last term = 4374 = ar^n-1
sum = a(rn-1)/(r-1)
= (arn-a)/2
= (arn-1.r-a)/2
= (4374.3-2)/2
= 6560
A sequence a1, a2, a3,…, an is called ______ progression, if each term is non-zero and 
- a)geometric, k ≥ 1
- b)arithmetic, k > 1
- c)geometric, k > 1
- d)arithmetic, k ≥ 1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A sequence a1, a2, a3,…, an is called ______ progression, if each term is non-zero
and 
a)
geometric, k ≥ 1
b)
arithmetic, k > 1
c)
geometric, k > 1
d)
arithmetic, k ≥ 1
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
The expression depicts the ratio of two numbers, if the ratio between the numbers is constant, then it will definately form a GP.
The G.M. between the numbers: 56 and 14 is:- a)14
- b)28
- c)35
- d)70
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The G.M. between the numbers: 56 and 14 is:
a)
14
b)
28
c)
35
d)
70
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Geometric mean of two numbers a and b is √ab
As two numbers are 14 and 56
Geometric mean is √14×56
= ± √2×7×2×2×2×7
= ±(2×2×7)
= ±28
As two numbers are 14 and 56
Geometric mean is √14×56
= ± √2×7×2×2×2×7
= ±(2×2×7)
= ±28
If A and G are A.M. and G.M. of two real numbers a and b, then- a)A ≤ G
- b)A > G
- c)A < G
- d)A ≥ G
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If A and G are A.M. and G.M. of two real numbers a and b, then
a)
A ≤ G
b)
A > G
c)
A < G
d)
A ≥ G

|
Siya Arora answered |
A=a+b/2. ,G=√ab
A-G=(a+b/2)-√ab
=(a+b-2√ab)/2
=(√a-√b)^2/2 is greater than or equal to zero
A-G is greater than or equal to zero so
so A is greater than equal to zero
A-G=(a+b/2)-√ab
=(a+b-2√ab)/2
=(√a-√b)^2/2 is greater than or equal to zero
A-G is greater than or equal to zero so
so A is greater than equal to zero
Chapter doubts & questions for Sequence and series - Mathematics for Year 12 2024 is part of Year 12 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Year 12 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Year 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Sequence and series - Mathematics for Year 12 in English & Hindi are available as part of Year 12 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Year 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Mathematics for Year 12
154 videos|194 docs|125 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup