All Exams >
Grade 10 >
Science for Grade 10 >
All Questions
All questions of Light and Reflection for Grade 10 Exam
A 10 mm long awl pin is placed vertically in front of a concave mirror. A 5 mm long image of the awl pin is formed at 30 cm in front of the mirror. The focal length of this mirror is- a)- 30 cm
- b)- 20 cm
- c)- 40 cm
- d)- 60 cm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A 10 mm long awl pin is placed vertically in front of a concave mirror. A 5 mm long image of the awl pin is formed at 30 cm in front of the mirror. The focal length of this mirror is
a)
- 30 cm
b)
- 20 cm
c)
- 40 cm
d)
- 60 cm
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
Given h0 = +10 mm - + 0.1 cm
h2 = - 5 mm = -0 .5 cm
for real image, v = - 30 cm
h2 = - 5 mm = -0 .5 cm
for real image, v = - 30 cm
Now magnification,


∴ f = -20 cm
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Speed of light in vacuum is:- a)3 x 108 m/s
- b)3 x 109 m/s
- c)2 x 109 m/s
- d)2 x 1011 m/s
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Speed of light in vacuum is:
a)
3 x 108 m/s
b)
3 x 109 m/s
c)
2 x 109 m/s
d)
2 x 1011 m/s
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The speed of light in vacuum, commonly denoted c, is a universal physical constant important in many areas of physics. It's exact value is defined as 299 792 458 metres per second ( or approximately, 3*108 m/s)
A linear object is placed at a distance equal to focal length of a convex mirror. Its image is formed
- a)at infinite distance
- b)at the principal focus of mirror
- c)behind the mirror at a distance f/2
- d)in front of mirror at a distance f/2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A linear object is placed at a distance equal to focal length of a convex mirror. Its image is formed
a)
at infinite distance
b)
at the principal focus of mirror
c)
behind the mirror at a distance f/2
d)
in front of mirror at a distance f/2
|
|
Karthik murthy answered |
When a linear object is placed at a distance equal to focal length of a convex mirror then its virtual image is form ed behind the mirror at a distance f/2
As per sign convention u = - f and focal length o f convex mirror is + ve, hence from mirror formula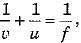 we have
we have
 or
or  or
or 
As per sign convention u = - f and focal length o f convex mirror is + ve, hence from mirror formula
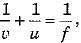 we have
we have  or
or  or
or 
f=R/2 is valid - a)for convex mirrors but not for concave mirrors
- b)for concave mirrors but not for convex mirrors
- c)for both convex and concave mirrors
- d)neither for convex mirrors nor for concave mirrors
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
f=R/2 is valid
a)
for convex mirrors but not for concave mirrors
b)
for concave mirrors but not for convex mirrors
c)
for both convex and concave mirrors
d)
neither for convex mirrors nor for concave mirrors
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
The relation f = R/2 is applicable only for mirrors. For lenses, you have to use the lens makers formula.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:A concave lens of 20 cm focal length forms an image 15 cm from the lens. What is the object distance?
- A:
60 cm
- B:
30 cm
- C:
-60 cm
- D:
-30 cm
The answer is c.
A concave lens of 20 cm focal length forms an image 15 cm from the lens. What is the object distance?
60 cm
30 cm
-60 cm
-30 cm
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
Focal length= -20(as it is concave lens)
v= -15 (as concave lens always forms virtual and erect image on left of lens)
Putting these values in lens formula,
1/ -20 - 1/u = 1/ -15
-1/ u= 1/-15 + 1/20
-1/u = -4+3/60
-1/u = -1/60
-u = -60
[u =60]
v= -15 (as concave lens always forms virtual and erect image on left of lens)
Putting these values in lens formula,
1/ -20 - 1/u = 1/ -15
-1/ u= 1/-15 + 1/20
-1/u = -4+3/60
-1/u = -1/60
-u = -60
[u =60]
Figure shows a ray of light as it travels from medium A to medium B. Refractive index of the medium B relative to medium A is
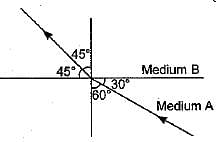
- a)

- b)

- c)
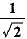
- d)√2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Figure shows a ray of light as it travels from medium A to medium B. Refractive index of the medium B relative to medium A is


a)

b)

c)
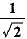
d)
√2
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Here, ∠i = 60°, ∠r = 45°
Using Snell’s law of refraction, refractive index of medium B with respect to medium A.

Using Snell’s law of refraction, refractive index of medium B with respect to medium A.

The lens which is used to correct myopia (shortsightedness) is- a)Both convex and concave
- b)Concave lens
- c)Converging lens
- d)Convex Lens
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The lens which is used to correct myopia (shortsightedness) is
a)
Both convex and concave
b)
Concave lens
c)
Converging lens
d)
Convex Lens
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Shortsightedness is corrected using a concave (curved inwards) lens which is placed in front of a myopic eye, moving the image back to the retina and making it clearer.
An object 2 cm high is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave mirror which produces an inverted image 4 cm high. Find the position of the image.
- a)-30 cm
- b)30 cm
- c)40 cm
- d)-40 cm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An object 2 cm high is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave mirror which produces an inverted image 4 cm high. Find the position of the image.
a)
-30 cm
b)
30 cm
c)
40 cm
d)
-40 cm
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The magnification produced by a concave mirror is given by the formula:
m = -v/u
where, m = magnification v = image distance u = object distance
From the problem, we have: u = -15 cm (since the object is placed in front of the mirror, the distance is negative) m = -4/2 = -2 (since the image is inverted and 4 cm high whereas the object is 2 cm high)
Substituting these values in the magnification formula, we get:
-2 = -v/(-15)
Simplifying, we get:
v = 30 cm
Therefore, the position of the image is 30 cm from the concave mirror.
If the magnification has a negative sign, the image formed by the concave mirror must be- a)Real and inverted
- b)Virtual and inverted
- c)Virtual and erect
- d)Real and erect
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If the magnification has a negative sign, the image formed by the concave mirror must be
a)
Real and inverted
b)
Virtual and inverted
c)
Virtual and erect
d)
Real and erect
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
We know that, if the magnification value is negative sign in the concave mirror, then the image will be real and inverted. Especially, when you come to concave mirror, the images are formed at the left of the mirror. So, it forms real and inverted.
A magnified real image is formed by a convex lens when the obiect is at:
- a)F
- b)Infinity
- c)2F
- d)Between F and 2F
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A magnified real image is formed by a convex lens when the obiect is at:
a)
F
b)
Infinity
c)
2F
d)
Between F and 2F
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
To get the real and magnified image for a convex lens, the object is placed in between F and 2F.
A ray of light AM is incident on a concave mirror as shown below. Then which of the following ray diagrams is correct for the reflected ray ?

- a)

- b)

- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A ray of light AM is incident on a concave mirror as shown below. Then which of the following ray diagrams is correct for the reflected ray ?


a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Naman pandey answered |
As the incident light ray is coming parallel to the principal axis of given concave mirror, the reflected ray must pass through the principal focus of mirror.
A lens has a power of +0.5 D. It is - a)a concave lens of focal length 5 m
- b)a convex lens of focal length 5 cm
- c)a convex lens of focal length 2 m
- d)a concave lens of focal length 2 m
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A lens has a power of +0.5 D. It is
a)
a concave lens of focal length 5 m
b)
a convex lens of focal length 5 cm
c)
a convex lens of focal length 2 m
d)
a concave lens of focal length 2 m
|
|
Sanya jain answered |
Given, power of the lens = 0.5 D.
We know that the power of the lens is given by the formula:
Power (P) = 1/f, where f is the focal length of the lens.
Therefore, we can write:
0.5 D = 1/f
Solving for f, we get:
f = 1/0.5 D
f = 2 m
Hence, the focal length of the lens is 2 m.
Therefore, the correct option is (c) a convex lens of focal length 2 m.
Explanation:
A convex lens has a positive power and can converge the light rays to a point. The focal length of a convex lens is positive. When the power of the lens is given, we can find the focal length of the lens using the formula P = 1/f. Here, the power is given as 0.5 D. On substituting the values, we get the focal length as 2 m. Hence, the lens is a convex lens of focal length 2 m.
We know that the power of the lens is given by the formula:
Power (P) = 1/f, where f is the focal length of the lens.
Therefore, we can write:
0.5 D = 1/f
Solving for f, we get:
f = 1/0.5 D
f = 2 m
Hence, the focal length of the lens is 2 m.
Therefore, the correct option is (c) a convex lens of focal length 2 m.
Explanation:
A convex lens has a positive power and can converge the light rays to a point. The focal length of a convex lens is positive. When the power of the lens is given, we can find the focal length of the lens using the formula P = 1/f. Here, the power is given as 0.5 D. On substituting the values, we get the focal length as 2 m. Hence, the lens is a convex lens of focal length 2 m.
A person of height 1.8 standing at the centre of a room having equal dimensions of 10 m wishesto see the full image of the back wall in the mirror fixed on the front wall. The minimum heightof the plane mirror needed for this purpose is - a)0.9 m
- b)1.8 m
- c)10/3 m
- d)10 m
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A person of height 1.8 standing at the centre of a room having equal dimensions of 10 m wishes
to see the full image of the back wall in the mirror fixed on the front wall. The minimum height
of the plane mirror needed for this purpose is
a)
0.9 m
b)
1.8 m
c)
10/3 m
d)
10 m
|
|
Vikas Kumar answered |
In this ray diagram h is the height of the man.
Form this ray diagram we can see that the minimum height of the plane mirror is 90 cm, so that the man can see his full image. ( which is equal to half of the height of the man)

A virtual, erect and magnified image of an object is to be produced with a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm. Object may be placed at a distance of- a)10 cm from the mirror
- b)15 cm from the mirror
- c)24 cm from the mirror
- d)48 cm from the mirror
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A virtual, erect and magnified image of an object is to be produced with a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm. Object may be placed at a distance of
a)
10 cm from the mirror
b)
15 cm from the mirror
c)
24 cm from the mirror
d)
48 cm from the mirror
|
|
Arun Sharma answered |
A concave mirror forms a virtual, erect and magnified image when an object is placed between pole and focus point of the mirror. As focal length of given concave mirror, hence object must be placed at a distance less than 12 cm i.e., u < 12 cm. Thus, the object may be placed at a distance of 10 cm from the mirror.
In case of a real and inverted image the magnification of a mirror is- a)positive and large
- b)negative
- c)positive and small
- d)negative and large
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In case of a real and inverted image the magnification of a mirror is
a)
positive and large
b)
negative
c)
positive and small
d)
negative and large
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
Magnification is negative for a real and inverted image formed by a mirror.
The minimum distance between an object and its real image in a convex lens is (f = focal length of the lens) - a)2.5 f
- b)2 f
- c)4 f
- d)f
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The minimum distance between an object and its real image in a convex lens is (f = focal length of the lens)
a)
2.5 f
b)
2 f
c)
4 f
d)
f
|
|
Arun Sharma answered |
Let the distance between the object and its real image formed by convex lens be d1.
Let the distance of the object from lens be x,so,the image distance from the lens is (d-x)
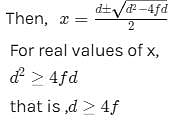
Let the distance of the object from lens be x,so,the image distance from the lens is (d-x)
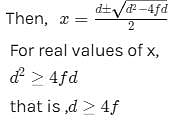
The minimum distance between an object and its real image in a convex lens is 4f.
hence,option C is correct.
.
hence,option C is correct.
.
An object is placed before a concave lens. The image formed- a)is always erect
- b)may be erect or inverted
- c)is always inverted
- d)is always real
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An object is placed before a concave lens. The image formed
a)
is always erect
b)
may be erect or inverted
c)
is always inverted
d)
is always real
|
|
Vivek Rana answered |
Because concave lens always produce an
Image which is always erect, diminished and virtual.
Image which is always erect, diminished and virtual.
No matter how far or close you stand from a mirror, your image is always virtual and erect. The mirror is- a)convex mirror
- b)plane mirror
- c)concave mirror
- d)either a convex or a plane mirror
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
No matter how far or close you stand from a mirror, your image is always virtual and erect. The mirror is
a)
convex mirror
b)
plane mirror
c)
concave mirror
d)
either a convex or a plane mirror
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Irrespective of the position of an object both convex mirror and plane mirror form virtual and erect images. Of course image formed by a plane mirror is of same size as the object but image formed by convex mirror is always diminished one.
Rays from sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that size of the image is exactly equal to the size of the object ?- a)30 cm in front of mirror
- b)15 cm in front of mirror
- c)Between 15 cm and 30 cm in front of mirror
- d)Less than 15 cm in front of mirror
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Rays from sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that size of the image is exactly equal to the size of the object ?
a)
30 cm in front of mirror
b)
15 cm in front of mirror
c)
Between 15 cm and 30 cm in front of mirror
d)
Less than 15 cm in front of mirror
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
As light rays from sun (u = ∞) converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror, hence focal length of concave mirror f = - 15 cm.
To form an image of exactly same size as that of an object, the object should be placed at the centre of curvature (u = R = 2f) of mirror. Hence, the object should be placed at 30 cm in front of mirror.
To form an image of exactly same size as that of an object, the object should be placed at the centre of curvature (u = R = 2f) of mirror. Hence, the object should be placed at 30 cm in front of mirror.
A point object is placed on the principal axis of a spherical mirror. The object-distance u is - a)definitely negative
- b)definitely positive
- c)positive if the object is to the left of the centre of curvature
- d)positive if the object is to the right of the centre of curvature
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A point object is placed on the principal axis of a spherical mirror. The object-distance u is
a)
definitely negative
b)
definitely positive
c)
positive if the object is to the left of the centre of curvature
d)
positive if the object is to the right of the centre of curvature
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
Option ( a) is the correct answer. As the object is always placed on the left side of the mirror and according to the sign convention, it has negative value for 'so axis.
Therefore, spherical mirrors have only one reflecting surface and it will be negative only.
Other names for myopia are- a)hyperopia and hypermetropia
- b)long-sightedness and hyperopia
- c)near-sightedness and presbyopia
- d)near-sightedness and short-sightedness
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Other names for myopia are
a)
hyperopia and hypermetropia
b)
long-sightedness and hyperopia
c)
near-sightedness and presbyopia
d)
near-sightedness and short-sightedness

|
Saxena Aastha answered |
Near-sightedness, short-sightedness is another name of myopia
The inability among the elderly to see nearby objects clearly because of the weakening of the ciliarymuscles is called - a)far-sightedness
- b)near-sightedness
- c)presbyopia
- d)astignatism
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The inability among the elderly to see nearby objects clearly because of the weakening of the ciliary
muscles is called
a)
far-sightedness
b)
near-sightedness
c)
presbyopia
d)
astignatism

|
Harini Senthil Kumar. answered |
Presbyopia..
## a person can't read comfortably and clearly.......
@causes ....
## weakness of ciliary muscle.....
## hardening of eye lens or elasticity...
$ Remedy.
##this defect can be corrected by using bifocal Lens which consists of both concave and convex lens......
## a person can't read comfortably and clearly.......
@causes ....
## weakness of ciliary muscle.....
## hardening of eye lens or elasticity...
$ Remedy.
##this defect can be corrected by using bifocal Lens which consists of both concave and convex lens......
A convex lens of focal length 12 cm produces a magnification of -1. The object should be placed at;- a)-12 cm
- b)-24 cm
- c)-48 cm
- d)-96 cm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A convex lens of focal length 12 cm produces a magnification of -1. The object should be placed at;
a)
-12 cm
b)
-24 cm
c)
-48 cm
d)
-96 cm
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
1/v - 1/u
1/f =-1/u - 1/u
1/f = - 2/u
u=-2f
u=-24 cm
1/f =-1/u - 1/u
1/f = - 2/u
u=-2f
u=-24 cm
The mirage is formed due to- a)reflection
- b)refraction
- c)total internal reflection
- d)dispersion
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The mirage is formed due to
a)
reflection
b)
refraction
c)
total internal reflection
d)
dispersion
|
|
Abhi answered |
Mirage is formed by total internal reflection in desents where due to heating of earth, refraction index of air near the surface of earth becomes lesser than above it.
An object is 9 cm from a magnifying lens and its image is formed 36 cm from the lens. Magnification of the lens is- a)4
- b)2
- c)0.25
- d)0.5
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An object is 9 cm from a magnifying lens and its image is formed 36 cm from the lens. Magnification of the lens is
a)
4
b)
2
c)
0.25
d)
0.5
|
|
Amit Kumar answered |
Magnification = the height of the image ÷ by the height of the object
M=36/9 =4
M=36/9 =4
A concave mirror is used to form an image of the sun on a white screen. If the lower half of the mirror is covered with a black paper, the effect on the image formed on the screen would be- a)to make the image less bright than before
- b)to make the lower half of the image disappear
- c)to prevent the image from being focussed
- d)to make the image smaller in size
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A concave mirror is used to form an image of the sun on a white screen. If the lower half of the mirror is covered with a black paper, the effect on the image formed on the screen would be
a)
to make the image less bright than before
b)
to make the lower half of the image disappear
c)
to prevent the image from being focussed
d)
to make the image smaller in size
|
|
Gourav khanna answered |
If lower half (or a part) of a mirror is covered with a black paper then complete image of the object will be formed as before. However, the image will be less bright now.
A full length image of a distant tall building can definitely be seen by using- a)a concave mirror
- b)a convex mirror
- c)a plane mirror
- d)both concave as well as convex mirrors
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A full length image of a distant tall building can definitely be seen by using
a)
a concave mirror
b)
a convex mirror
c)
a plane mirror
d)
both concave as well as convex mirrors

|
Abhiram Gupta answered |
We know that a convex mirror forms a virtual and smaller image irrespective of position of the object. So, a full length image of a distant tall building can definitely be seen by using a convex mirror.
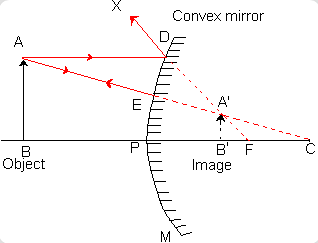
An object of size 2.0 cm is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave mirror. The distanceof the object from the mirror equals the radius of curvature. The size of the image will be - a)0.5 cm
- b)1.5 cm
- c)1.0cm
- d)2.0 cm
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An object of size 2.0 cm is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave mirror. The distance
of the object from the mirror equals the radius of curvature. The size of the image will be
a)
0.5 cm
b)
1.5 cm
c)
1.0cm
d)
2.0 cm
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
The size of the image will be 2.0 cm.
V=U(given)
m=-v/u
m= - 1
m=h`/h
-1=h`/2
h`=-2
h=2cm
V=U(given)
m=-v/u
m= - 1
m=h`/h
-1=h`/2
h`=-2
h=2cm
The angle of incidence is the angle between- a)the incident ray and the surface of the mirror
- b)the reflected ray and the surface of the mirror
- c)the normal to the surface and the incident ray
- d)the normal to the surface and the reflected ray
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The angle of incidence is the angle between
a)
the incident ray and the surface of the mirror
b)
the reflected ray and the surface of the mirror
c)
the normal to the surface and the incident ray
d)
the normal to the surface and the reflected ray
|
|
Hitakshi 💞💞 answered |
The angle between the incident ray and the normal is called as angle of incidence and it is generally denoted by i. The angle between the normal and the reflected ray is called as angle of reflection and it is generally denoted by r.
A ray of light is reflected by the pole of a concave mirror at an angle of 80o. The angle of incidence will be
- a)80º
- b)180º
- c)0º
- d)50º
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A ray of light is reflected by the pole of a concave mirror at an angle of 80o. The angle of incidence will be
a)
80º
b)
180º
c)
0º
d)
50º
|
|
Ashiii answered |
Angle of Reflection = Angle of Incidence
Angle of Reflection = 80॰
⁂ Angle of Incidence = 80॰
..v@.**
The angle of incidence of any light ray passing through the centre of curvature of a spherical mirror is- a)0°
- b)45°
- c)90°
- d)60°
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The angle of incidence of any light ray passing through the centre of curvature of a spherical mirror is
a)
0°
b)
45°
c)
90°
d)
60°
|
|
Chirag raman answered |
The angle of incidence of any light ray passing through the centre of curvature of a spherical mirror is 0°, because a line joining centre of curvature to any point on the mirror is a normal drawn at that point of the mirror.
In a convex lens, where is the image formed, when an object is placed at 2F ?- a)Between F and 2F
- b)At focus (F)
- c)At 2F on the other side
- d)At 2F on the same side
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a convex lens, where is the image formed, when an object is placed at 2F ?
a)
Between F and 2F
b)
At focus (F)
c)
At 2F on the other side
d)
At 2F on the same side
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
At the 2F point, the object distance equals the image distance and the object height equals the image height. As the object distance approaches one focal length, the image distance and image height approaches infinity.
If a lens has a focal length, F = +12 cm, then it is a- a)Can be convex or concave
- b)Convex lens
- c)Diverging lens
- d)Concave lens
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If a lens has a focal length, F = +12 cm, then it is a
a)
Can be convex or concave
b)
Convex lens
c)
Diverging lens
d)
Concave lens
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
The focal length of convex lens is always positive. Image obtained can be either real or virtual.
Which lens always forms diminished and erect image ?
- a)Convex lens
- b)Concave lens
- c)Converging lens
- d)Both convex and concave
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which lens always forms diminished and erect image ?
a)
Convex lens
b)
Concave lens
c)
Converging lens
d)
Both convex and concave
|
|
Harshali Chavan answered |
Ans is concave lens because of following
1 it's diverging alwags forms virtual image
2 it's same as convex mirror
3 and also always erect n diminished
1 it's diverging alwags forms virtual image
2 it's same as convex mirror
3 and also always erect n diminished
The muscles of the iris control the- a)focal length of the eye-lens
- b)opening of the pupil
- c)shape of the crystalline lens
- d)optic nerve
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The muscles of the iris control the
a)
focal length of the eye-lens
b)
opening of the pupil
c)
shape of the crystalline lens
d)
optic nerve
|
|
Sahil Mehta answered |
Function of Iris Muscles
The iris is the coloured part of the eye, and the muscles of the iris are responsible for controlling the size of the pupil. These muscles are known as the sphincter pupillae and the dilator pupillae. The sphincter pupillae muscles contract to constrict the pupil, while the dilator pupillae muscles contract to dilate the pupil.
Importance of Pupil Size
The size of the pupil is important for regulating the amount of light that enters the eye. When there is less light, the pupil dilates to allow more light in, and when there is more light, the pupil constricts to reduce the amount of light entering the eye. This helps to maintain clear vision and prevent damage to the retina.
Relation with Focal Length and Crystalline Lens
The iris muscles do not directly control the focal length of the eye-lens or the shape of the crystalline lens. The focal length of the eye-lens is determined by the curvature of the lens and the distance between the lens and the retina. The shape of the crystalline lens is controlled by the ciliary muscles, which are located behind the iris.
Relation with Optic Nerve
The optic nerve is responsible for transmitting visual information from the retina to the brain. The iris muscles do not play a direct role in the function of the optic nerve.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the muscles of the iris control the opening and size of the pupil, which is important for regulating the amount of light that enters the eye. They do not play a direct role in controlling the focal length of the eye-lens, the shape of the crystalline lens, or the function of the optic nerve.
The iris is the coloured part of the eye, and the muscles of the iris are responsible for controlling the size of the pupil. These muscles are known as the sphincter pupillae and the dilator pupillae. The sphincter pupillae muscles contract to constrict the pupil, while the dilator pupillae muscles contract to dilate the pupil.
Importance of Pupil Size
The size of the pupil is important for regulating the amount of light that enters the eye. When there is less light, the pupil dilates to allow more light in, and when there is more light, the pupil constricts to reduce the amount of light entering the eye. This helps to maintain clear vision and prevent damage to the retina.
Relation with Focal Length and Crystalline Lens
The iris muscles do not directly control the focal length of the eye-lens or the shape of the crystalline lens. The focal length of the eye-lens is determined by the curvature of the lens and the distance between the lens and the retina. The shape of the crystalline lens is controlled by the ciliary muscles, which are located behind the iris.
Relation with Optic Nerve
The optic nerve is responsible for transmitting visual information from the retina to the brain. The iris muscles do not play a direct role in the function of the optic nerve.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the muscles of the iris control the opening and size of the pupil, which is important for regulating the amount of light that enters the eye. They do not play a direct role in controlling the focal length of the eye-lens, the shape of the crystalline lens, or the function of the optic nerve.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Light travels faster in substance X as compared to substance Y, then refractive index is greater for
- A:
Can’t tell with the information provided
- B:
Substance-Y
- C:
Refractive index for both is same
- D:
Substance-X
The answer is b.
Light travels faster in substance X as compared to substance Y, then refractive index is greater for
Can’t tell with the information provided
Substance-Y
Refractive index for both is same
Substance-X
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
As the refractive index increases, the velocity of light decreases.
The unit of linear magnification is- a)Dioptre
- b)Metre
- c)Metre per second
- d)It is unitless
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The unit of linear magnification is
a)
Dioptre
b)
Metre
c)
Metre per second
d)
It is unitless
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Magnification is thr ratio of size of image to size of object and since it is a ratio of tel similar quantities hence it is unitless.
An object 4 cm tall is placed in front of a convex lens. It produces an image 3 cm tall. What is the magnification of the lens ?
- a)1.33
- b)12
- c)0.75
- d)11
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An object 4 cm tall is placed in front of a convex lens. It produces an image 3 cm tall. What is the magnification of the lens ?
a)
1.33
b)
12
c)
0.75
d)
11
|
|
Rohit Sharma answered |
We know, height of the object is 4 cm h1, height of the image is 3 cm, h2.
So we have, m = h2/h1
=> m = 3/4
=> m = 0.75
Therefore, magnification of the lens is 0.75
So we have, m = h2/h1
=> m = 3/4
=> m = 0.75
Therefore, magnification of the lens is 0.75
A glass prism has refractive index 1.5 and the refracting angle 90° If a ray falls on it at an angleof incidence of 30°, then the angle of emergence will be - a)60°
- b)45°
- c)30°
- d)the ray will not emerge at all
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A glass prism has refractive index 1.5 and the refracting angle 90° If a ray falls on it at an angle
of incidence of 30°, then the angle of emergence will be
a)
60°
b)
45°
c)
30°
d)
the ray will not emerge at all
|
|
Rohit Sharma answered |
We have, ( 1.5-1) *90
= 0.5 *90 ⇒ 45°
Now, 45-30+90°
⇒ 105°
Angle of emergence has inclination with second surface.
⇒ 90 - 105
⇒ -15
This shows that light ray will not emerge out of the prism.
= 0.5 *90 ⇒ 45°
Now, 45-30+90°
⇒ 105°
Angle of emergence has inclination with second surface.
⇒ 90 - 105
⇒ -15
This shows that light ray will not emerge out of the prism.
An object is placed before a convex lens. The image formed- a)is always real
- b)may be real or virtual
- c)is always virtual
- d)is always erect
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An object is placed before a convex lens. The image formed
a)
is always real
b)
may be real or virtual
c)
is always virtual
d)
is always erect
|
|
Radhika bajaj answered |
Explanation:
When an object is placed before a convex lens, the image formed can either be real or virtual depending on the position of the object with respect to the lens. This is because the convex lens has the ability to converge the light rays that pass through it.
Real Image:
A real image is formed when the light rays converge at a point on the other side of the lens. This type of image can be projected onto a screen and is always inverted. For a real image to be formed, the object must be placed beyond the focal point of the lens.
Virtual Image:
A virtual image is formed when the light rays appear to be coming from a point on the same side of the lens as the object. This type of image cannot be projected onto a screen and is always upright. For a virtual image to be formed, the object must be placed between the lens and its focal point.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the image formed by a convex lens can be either real or virtual depending on the position of the object with respect to the lens. Hence, option B is the correct answer.
When an object is placed before a convex lens, the image formed can either be real or virtual depending on the position of the object with respect to the lens. This is because the convex lens has the ability to converge the light rays that pass through it.
Real Image:
A real image is formed when the light rays converge at a point on the other side of the lens. This type of image can be projected onto a screen and is always inverted. For a real image to be formed, the object must be placed beyond the focal point of the lens.
Virtual Image:
A virtual image is formed when the light rays appear to be coming from a point on the same side of the lens as the object. This type of image cannot be projected onto a screen and is always upright. For a virtual image to be formed, the object must be placed between the lens and its focal point.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the image formed by a convex lens can be either real or virtual depending on the position of the object with respect to the lens. Hence, option B is the correct answer.
Refractive index of glass w.r.t. air is 3/2. What is the refractie index of air w.r.t glass ?- a)2/3
- b)1
- c)Zero
- d)(3/2)2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Refractive index of glass w.r.t. air is 3/2. What is the refractie index of air w.r.t glass ?
a)
2/3
b)
1
c)
Zero
d)
(3/2)2
|
|
Zara Khan answered |
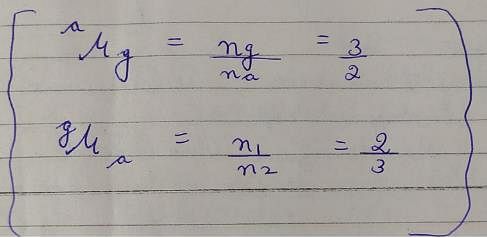
If refractive index of glass w.r.t air is 3/2 , then refractive index of air w. r. t glass will be it's reciprocal ie. ⅔ ..
Where should an object be placed in front of convex lens so as to obtain the image formed on slide projector?- a)At 2 F1
- b)At F1
- c)Between F1 and 2 F1
- d)Beyond F1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Where should an object be placed in front of convex lens so as to obtain the image formed on slide projector?
a)
At 2 F1
b)
At F1
c)
Between F1 and 2 F1
d)
Beyond F1
|
|
Nisha Choudhury answered |
An object should be placed between F1 and 2 F1 so as to obtain the image formation used in slide projector. This is because, the image has to be enlarged and has to form at a little larger distance from the projector.
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens to get a real image of the size of the object ?- a)At infinity
- b)At twice the focal length
- c)Between the optical centre of the lens and its principal focus.
- d)At the principal focus of the lens
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens to get a real image of the size of the object ?
a)
At infinity
b)
At twice the focal length
c)
Between the optical centre of the lens and its principal focus.
d)
At the principal focus of the lens
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
At twice the focal length the image formed by convex lens is real and of the same size as object.
A ray of light is incident on a concave mirror. If it is parallel to the principal axis, the reflected ray will- a)pass through the focus
- b)pass through the centre of curvature
- c)pass through the pole
- d)retrace its path
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A ray of light is incident on a concave mirror. If it is parallel to the principal axis, the reflected ray will
a)
pass through the focus
b)
pass through the centre of curvature
c)
pass through the pole
d)
retrace its path
|
|
Diana Nair answered |
A ray of light which is parallel to the principle axis after reflection will pass through the focus of a concave mirror.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) or Practice Quiz with solutions of Chapter - "Ray Optics" of Class 10 Science, the questions are available for practice
Q. A mirror forms a virtual image of a real object.
- A:
It must be a convex mirror.
- B:
It must be a concave mirror.
- C:
It must be a plane mirror.
- D:
It may be any of the mirrors mentioned above.
The answer is D.
MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) or Practice Quiz with solutions of Chapter - "Ray Optics" of Class 10 Science, the questions are available for practice
Q. A mirror forms a virtual image of a real object.
It must be a convex mirror.
It must be a concave mirror.
It must be a plane mirror.
It may be any of the mirrors mentioned above.
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The image in a plane mirror forms virtual and erect image and appears to be as far behind the mirror as the object is in front of the mirror. A diverging lens or a convex mirror forms a virtual image.A virtual image is produced by a concave mirror when the object is placed inside the focal length of the mirror.
The path of a ray of light coming from air passing through a rectangular glass slab traced by four students are shown as A, B, C and D in figure. Which one of them is correct?


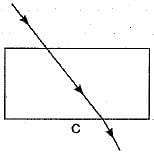

- a)A
- b)B
- c)C
- d)D
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The path of a ray of light coming from air passing through a rectangular glass slab traced by four students are shown as A, B, C and D in figure. Which one of them is correct?








a)
A
b)
B
c)
C
d)
D
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
When a light ray is incident oblikely on one face of rectangular glass slab, the emergent ray will be parallel to the incident ray and shifted sideward slightly.
In which of the following, the image of an object placed at infinity will be highly diminished and point sized ?- a)Concave mirror only
- b)Convex mirror only
- c)Convex lens only
- d)All types of mirrors and lenses
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following, the image of an object placed at infinity will be highly diminished and point sized ?
a)
Concave mirror only
b)
Convex mirror only
c)
Convex lens only
d)
All types of mirrors and lenses
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
When an object is placed at infinity, a parallel beam of light is incident on the mirror/lens. For all types of mirrors and lenses the beam will get focussed at the principal focus of mirror/lens and a highly diminished, point size image is formed there.
Chapter doubts & questions for Light and Reflection - Science for Grade 10 2024 is part of Grade 10 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Grade 10 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Grade 10 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Light and Reflection - Science for Grade 10 in English & Hindi are available as part of Grade 10 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Grade 10 Exam by signing up for free.
Science for Grade 10
9 videos|49 docs|3 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup











