Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Questions > The muscles of the iris control thea)focal le...
Start Learning for Free
The muscles of the iris control the
- a)focal length of the eye-lens
- b)opening of the pupil
- c)shape of the crystalline lens
- d)optic nerve
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
The muscles of the iris control thea)focal length of the eye-lensb)ope...
The Laws of Reflection for Mirrors
- The laws of reflection apply to all mirrors, regardless of their shape.
- These laws state that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
- This means that the light rays that strike the mirror are reflected at the same angle.
- Whether the mirror is concave, convex, or plane, these laws will always hold true.
- Therefore, option B is correct as it includes all mirrors, not just a specific type.
- The laws of reflection apply to all mirrors, regardless of their shape.
- These laws state that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
- This means that the light rays that strike the mirror are reflected at the same angle.
- Whether the mirror is concave, convex, or plane, these laws will always hold true.
- Therefore, option B is correct as it includes all mirrors, not just a specific type.
Most Upvoted Answer
The muscles of the iris control thea)focal length of the eye-lensb)ope...
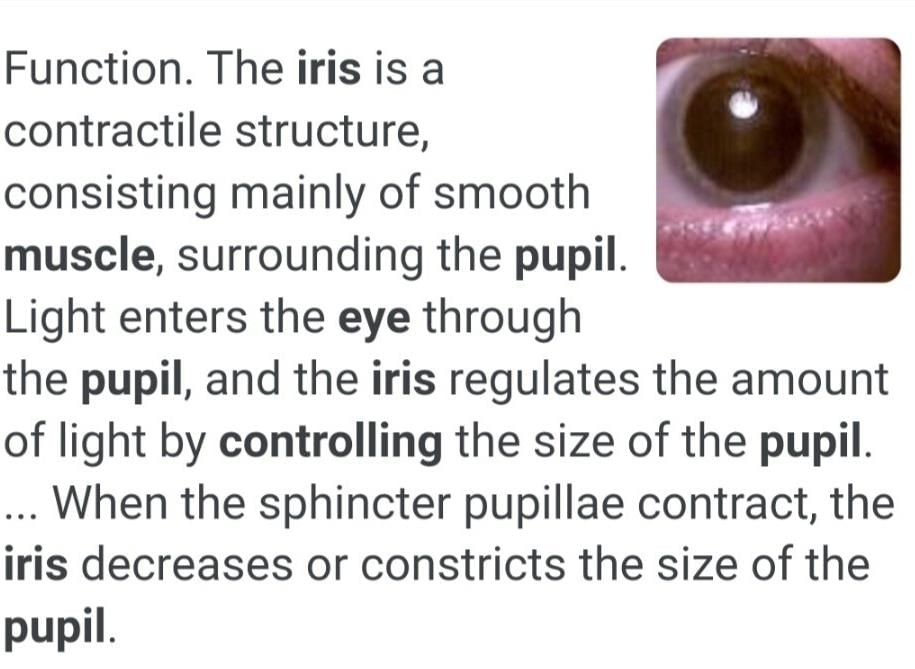
Function of Iris Muscles
The iris is the coloured part of the eye, and the muscles of the iris are responsible for controlling the size of the pupil. These muscles are known as the sphincter pupillae and the dilator pupillae. The sphincter pupillae muscles contract to constrict the pupil, while the dilator pupillae muscles contract to dilate the pupil.
Importance of Pupil Size
The size of the pupil is important for regulating the amount of light that enters the eye. When there is less light, the pupil dilates to allow more light in, and when there is more light, the pupil constricts to reduce the amount of light entering the eye. This helps to maintain clear vision and prevent damage to the retina.
Relation with Focal Length and Crystalline Lens
The iris muscles do not directly control the focal length of the eye-lens or the shape of the crystalline lens. The focal length of the eye-lens is determined by the curvature of the lens and the distance between the lens and the retina. The shape of the crystalline lens is controlled by the ciliary muscles, which are located behind the iris.
Relation with Optic Nerve
The optic nerve is responsible for transmitting visual information from the retina to the brain. The iris muscles do not play a direct role in the function of the optic nerve.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the muscles of the iris control the opening and size of the pupil, which is important for regulating the amount of light that enters the eye. They do not play a direct role in controlling the focal length of the eye-lens, the shape of the crystalline lens, or the function of the optic nerve.
The iris is the coloured part of the eye, and the muscles of the iris are responsible for controlling the size of the pupil. These muscles are known as the sphincter pupillae and the dilator pupillae. The sphincter pupillae muscles contract to constrict the pupil, while the dilator pupillae muscles contract to dilate the pupil.
Importance of Pupil Size
The size of the pupil is important for regulating the amount of light that enters the eye. When there is less light, the pupil dilates to allow more light in, and when there is more light, the pupil constricts to reduce the amount of light entering the eye. This helps to maintain clear vision and prevent damage to the retina.
Relation with Focal Length and Crystalline Lens
The iris muscles do not directly control the focal length of the eye-lens or the shape of the crystalline lens. The focal length of the eye-lens is determined by the curvature of the lens and the distance between the lens and the retina. The shape of the crystalline lens is controlled by the ciliary muscles, which are located behind the iris.
Relation with Optic Nerve
The optic nerve is responsible for transmitting visual information from the retina to the brain. The iris muscles do not play a direct role in the function of the optic nerve.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the muscles of the iris control the opening and size of the pupil, which is important for regulating the amount of light that enters the eye. They do not play a direct role in controlling the focal length of the eye-lens, the shape of the crystalline lens, or the function of the optic nerve.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The muscles of the iris control thea)focal length of the eye-lensb)ope...

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Question Description
The muscles of the iris control thea)focal length of the eye-lensb)opening of the pupilc)shape of the crystalline lensd)optic nerveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about The muscles of the iris control thea)focal length of the eye-lensb)opening of the pupilc)shape of the crystalline lensd)optic nerveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The muscles of the iris control thea)focal length of the eye-lensb)opening of the pupilc)shape of the crystalline lensd)optic nerveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
The muscles of the iris control thea)focal length of the eye-lensb)opening of the pupilc)shape of the crystalline lensd)optic nerveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about The muscles of the iris control thea)focal length of the eye-lensb)opening of the pupilc)shape of the crystalline lensd)optic nerveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The muscles of the iris control thea)focal length of the eye-lensb)opening of the pupilc)shape of the crystalline lensd)optic nerveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The muscles of the iris control thea)focal length of the eye-lensb)opening of the pupilc)shape of the crystalline lensd)optic nerveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 10.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The muscles of the iris control thea)focal length of the eye-lensb)opening of the pupilc)shape of the crystalline lensd)optic nerveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The muscles of the iris control thea)focal length of the eye-lensb)opening of the pupilc)shape of the crystalline lensd)optic nerveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The muscles of the iris control thea)focal length of the eye-lensb)opening of the pupilc)shape of the crystalline lensd)optic nerveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The muscles of the iris control thea)focal length of the eye-lensb)opening of the pupilc)shape of the crystalline lensd)optic nerveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The muscles of the iris control thea)focal length of the eye-lensb)opening of the pupilc)shape of the crystalline lensd)optic nerveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 10 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



















