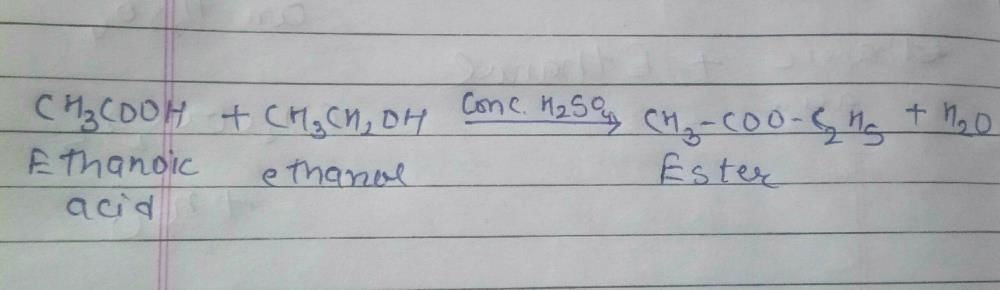All Exams >
Class 10 >
Science Class 10 >
All Questions
All questions of Carbon and its compounds for Class 10 Exam
In methane, the valency of carbon is:- a)four
- b)two
- c)one
- d)three
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In methane, the valency of carbon is:
a)
four
b)
two
c)
one
d)
three

|
Vp Classes answered |
Methane has its molecular formula CH4.
It is formed by one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms.
Hydrogen has its valency 1 and carbon being tetravalent needs four valence electrons to acquire noble gas configuration, where it shares its 4 electrons with four hydrogen atoms.
Therefore, the valency of carbon atom in Methane (CH4) is 4.
It is formed by one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms.
Hydrogen has its valency 1 and carbon being tetravalent needs four valence electrons to acquire noble gas configuration, where it shares its 4 electrons with four hydrogen atoms.
Therefore, the valency of carbon atom in Methane (CH4) is 4.
Which of the following is a non-polar molecule?- a)O2
- b)HF
- c)NH3
- d)H2O
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a non-polar molecule?
a)
O2
b)
HF
c)
NH3
d)
H2O
|
|
Pooja sengupta answered |
When 2 molecules of different electronegativity are bonded together covalently the bonding electron cloud is more attracted towards atom with higher electronegativity. ... So, the bond between 2 Oxygen atom is non-polar . Since, it is the only bonding in oxygen molecule Oxygen molecule is non-polar
Which of the following represents saponification reaction ?- a)
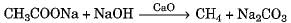
- b)
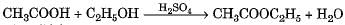
- c)
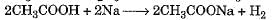
- d)
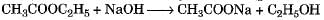
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following represents saponification reaction ?
a)
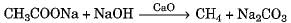
b)
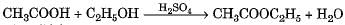
c)
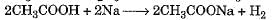
d)
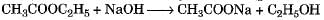
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
Hydrolysis of an ester with alkali is called saponification reaction.
The IUPAC name of CH3CHO is
- a)Ethanal
- b)Ethanol
- c)Methanol
- d)Acetone
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The IUPAC name of CH3CHO is
a)
Ethanal
b)
Ethanol
c)
Methanol
d)
Acetone
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
The IUPAC name of CH3CHO is Ethanal.
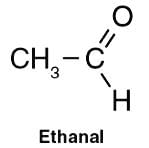
The IUPAC name for CH3CHO is Ethanal, also known as Acetaldehyde. It has 2 carbons, so the term “Eth” is used as prefix and it belongs to the aldehyde group, so the term “al” is used as suffix.

The IUPAC name for CH3CHO is Ethanal, also known as Acetaldehyde. It has 2 carbons, so the term “Eth” is used as prefix and it belongs to the aldehyde group, so the term “al” is used as suffix.
In conversion from ethanol to ethene, concentrated sulphuric acid is used as:
- a)Precipitating agent
- b)Oxidizing agent
- c)Dehydrating agent
- d)Reducing agent
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In conversion from ethanol to ethene, concentrated sulphuric acid is used as:
a)
Precipitating agent
b)
Oxidizing agent
c)
Dehydrating agent
d)
Reducing agent
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
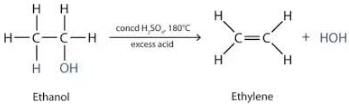
Sulphuric acid is used as a dehydrating agent because sulphuric acid has a great affinity for water. It readily removes elements of water from other compounds i.e, it acts as a dehydrating agent, it being a hygroscopic substance absorbs water from other substances without dissolving in it, so it is considered a good drying agent.

Which among the following are unsaturated hydrocarbons ?
(i) H3C -CH2-CH2-CH3
(ii) H3C -C = C-CH3
(iii) 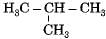
(iv) 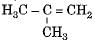
- a)(i) and (iii)
- b)(i) and (iii)
- c)(ii) and (iv)
- d)(iii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following are unsaturated hydrocarbons ?
(i) H3C -CH2-CH2-CH3
(ii) H3C -C = C-CH3
(iii)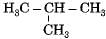
(iv)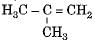
(i) H3C -CH2-CH2-CH3
(ii) H3C -C = C-CH3
(iii)
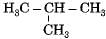
(iv)
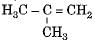
a)
(i) and (iii)
b)
(i) and (iii)
c)
(ii) and (iv)
d)
(iii) and (iv)
|
|
Arun Sharma answered |
Compounds of carbon and hydrogen containing double or triple bonds in the molecule are called unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Shared electron pair in covalent compound AB will be drawn:- a)On the top of A
- b)On the left side of A
- c)On the right side of B
- d)Between A and B
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Shared electron pair in covalent compound AB will be drawn:
a)
On the top of A
b)
On the left side of A
c)
On the right side of B
d)
Between A and B
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
Because the shared pair of electrons always stays in between two elements.
Most of covalent compounds are found in- a)solid state
- b)gaseous state
- c)liquid state
- d)both in liquid and gaseous state
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Most of covalent compounds are found in
a)
solid state
b)
gaseous state
c)
liquid state
d)
both in liquid and gaseous state
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Compounds having lesser number of carbon atoms are gases like CH4, C4H10 and some are liquids. Compounds having greater number of carbon atoms are solids.
Mineral acids are stronger acids than carboxylic acids because
(i) mineral acids are completely ionised.
(ii) carboxylic acids are completely ionised.
(iii) mineral acids are partially ionised.
(iv) carboxylic acids are partially ionised.- a)(i) and (iv)
- b)(ii) and (iii)
- c)(i) and (ii)
- d)(iii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Mineral acids are stronger acids than carboxylic acids because
(i) mineral acids are completely ionised.
(ii) carboxylic acids are completely ionised.
(iii) mineral acids are partially ionised.
(iv) carboxylic acids are partially ionised.
(i) mineral acids are completely ionised.
(ii) carboxylic acids are completely ionised.
(iii) mineral acids are partially ionised.
(iv) carboxylic acids are partially ionised.
a)
(i) and (iv)
b)
(ii) and (iii)
c)
(i) and (ii)
d)
(iii) and (iv)
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
It is well known that mineral acids are completely ionised while carboxylic acids are partially ionised
Ethanol, on heating at 443 K with cone H2S04 gives- a)CH2=CH2
- b)HC=CH
- c)CH4
- d)C2H6
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Ethanol, on heating at 443 K with cone H2S04 gives
a)
CH2=CH2
b)
HC=CH
c)
CH4
d)
C2H6
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
When ethanol is heated with concentrated sulphuric acid at 443 K, dehydration takes place and ethene is formed. In this reaction concentrated sulphuric acid acts as a dehydrating agent.
CH3-CH2-OH → (H2SO4 + heat) → CH2=CH2 + H2O
CH3-CH2-OH → (H2SO4 + heat) → CH2=CH2 + H2O
The name of the compound CH3 - CH2 - CHO is- a)Propanal
- b)Propanone
- c)Ethanol
- d)Ethanal
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The name of the compound CH3 - CH2 - CHO is
a)
Propanal
b)
Propanone
c)
Ethanol
d)
Ethanal
|
|
Vivek Rana answered |
It contains a total of three carbon atoms with an aldehyde group. Propane + al = propanal.
The blindness and death is caused by consuming adultrated liquor contains.- a)CH3OH
- b)CH3COOH
- c)CH3COCH3
- d)CH3CHO
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The blindness and death is caused by consuming adultrated liquor contains.
a)
CH3OH
b)
CH3COOH
c)
CH3COCH3
d)
CH3CHO
|
|
Swara bajaj answered |
Methanol causes blindness and even death.
The cooking gas used in our homes is mainly an:- a)Alkane
- b)Haloalkane
- c)Carboxylic acid
- d)Alkene
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The cooking gas used in our homes is mainly an:
a)
Alkane
b)
Haloalkane
c)
Carboxylic acid
d)
Alkene
|
|
Rahul Kapoor answered |
In organic chemistry, an alkane, or paraffin (a historical name that also has other meanings), is an acyclic saturated hydrocarbon. In other words, an alkane consists of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a tree structure in which all the carbon–carbon bonds are single. Alkanes have the general chemical formula CnH2n+2. The alkanes range in complexity from the simplest case of methane (CH4), where n = 1 (sometimes called the parent molecule), to arbitrarily large and complex molecules, like pentacontane (C50H102) or 6-ethyl-2-methyl-5-(1-methylethyl)octane, an isomer of tetradecane (C14H30)
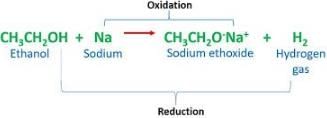
The bond which is formed by sharing of an electron pair between two atoms is known as:- a)Ionic bond
- b)Covalent bond
- c)Dative bond
- d)Metallic bond
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The bond which is formed by sharing of an electron pair between two atoms is known as:
a)
Ionic bond
b)
Covalent bond
c)
Dative bond
d)
Metallic bond
|
|
Rajiv Gupta answered |
A covalent bond, also called a molecular bond, is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs, and the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is known as covalent bonding.
While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside, it means that:- a)Fuel is burning completely.
- b)Fuel is wet.
- c)Food is not cooked completely.
- d)Fuel is not burning completely.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside, it means that:
a)
Fuel is burning completely.
b)
Fuel is wet.
c)
Food is not cooked completely.
d)
Fuel is not burning completely.

|
Shivangi Jasrotia answered |
Fuel is not burning completely because there is a lack of oxygen. Hence, incombustion is taking place over here.
The molecular formula of benzene is:- a)C6H6
- b)C6H10
- c)C6H12
- d)C6H8
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The molecular formula of benzene is:
a)
C6H6
b)
C6H10
c)
C6H12
d)
C6H8
|
|
Arun Sharma answered |
The chemical formula of benzene is C6H6, so it has six carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms.
Which of the following does not belong to the same homologous series ?- a)CH4
- b)C2H6
- c)C3H8
- d)C4H8
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following does not belong to the same homologous series ?
a)
CH4
b)
C2H6
c)
C3H8
d)
C4H8
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
Compounds (a), (b) and (c) are saturated hydrocarbons but compound (d) is unsaturated. Compounds of the same homologous series have the same general formula.
Which of the following will give a pleasant smell of ester when heated with ethyl alcohol and a small quantity of sulphuric acid?- a)CH3OH
- b)CH3CHO
- c)CH3COCH3
- d)CH3COOH
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following will give a pleasant smell of ester when heated with ethyl alcohol and a small quantity of sulphuric acid?
a)
CH3OH
b)
CH3CHO
c)
CH3COCH3
d)
CH3COOH
|
|
Neha Patel answered |
Carboxylic acids react with alcohols in presence of acid (catalyst) to produce sweet smelling compounds called esters.
Unsaturated carbon compounds on combustion give:- a)Yellow sooty flame
- b)Clean Blue flame
- c)Green flame
- d)Intense white flame
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Unsaturated carbon compounds on combustion give:
a)
Yellow sooty flame
b)
Clean Blue flame
c)
Green flame
d)
Intense white flame

|
Vp Classes answered |
Unsaturated hydrocarbons like ethyne also known as acetylene burn to produce a yellow sooty flame due to incomplete combustion in air.
The flame is sooty because the percentage of carbon is comparatively higher than that of alkanes and so does not get completely oxidized in air.
The oxidising agent used to convert alcohols into carboxylic acid is:- a)Conc. sulphuric acid
- b)Phosphorus trichloride
- c)Alkaline Potassium permanganate
- d)Sodium
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The oxidising agent used to convert alcohols into carboxylic acid is:
a)
Conc. sulphuric acid
b)
Phosphorus trichloride
c)
Alkaline Potassium permanganate
d)
Sodium
|
|
Praveenkumar Angadi answered |
Pottassium permanganate is a very strong oxidant able to react with many functional groups, such as secondary alcohols, 1,2-diols , aldehydes, alkenes, oxides, sulphides and thiols. Under controlled conditions potassium permanganate oxidizes primary alcohols into alcoholic acids very efficiently. I think you understand this.
The heteroatoms present in
CH3—CH2—O—CH2—CH2Cl are
(i) oxygen
(ii) carbon
(iii) hydrogen
(iv) chlorine- a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(ii) and (iii)
- c)(iii) and (iv)
- d)(i) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The heteroatoms present in
CH3—CH2—O—CH2—CH2Cl are
(i) oxygen
(ii) carbon
(iii) hydrogen
(iv) chlorine
CH3—CH2—O—CH2—CH2Cl are
(i) oxygen
(ii) carbon
(iii) hydrogen
(iv) chlorine
a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(ii) and (iii)
c)
(iii) and (iv)
d)
(i) and (iv)
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The atoms other than hydrogen and carbon are called heteroatoms.
CH2=CH2 + H2 → CH3-CH3 is an example of:- a)Substitution reaction
- b)Displacement reaction
- c)Elimination reaction
- d)Addition reaction
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
CH2=CH2 + H2 → CH3-CH3 is an example of:
a)
Substitution reaction
b)
Displacement reaction
c)
Elimination reaction
d)
Addition reaction
|
|
Apoorva Sharma answered |
Correct answer is option D because in this case Hydrogen is being added in the compound given and no elimination or substitution is done.
The alcoholic drinks contain- a)CH3OH
- b)CH3COOH
- c)CH3CH2OH
- d)CH3COOH3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The alcoholic drinks contain
a)
CH3OH
b)
CH3COOH
c)
CH3CH2OH
d)
CH3COOH3
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
CH3CH2OH is present in alcoholic drinks. It is known as ethanol which is prepared by fermentation of sugar (molasses).
Carbon forms four covalent bonds by sharing its four valence electrons with four univalent atoms, e.g., hydrogen. After the formation of four bonds, carbon attains the electronic configuration of- a)helium
- b)neon
- c)argon
- d)krypton
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Carbon forms four covalent bonds by sharing its four valence electrons with four univalent atoms, e.g., hydrogen. After the formation of four bonds, carbon attains the electronic configuration of
a)
helium
b)
neon
c)
argon
d)
krypton

|
Ritika Mishra answered |
Electronic configuration of carbon with atomic no. 6 = 2,4
The four valence electrons are involved in bonding with the four hydrogen atoms. Therefore after formation of four covalent bonds with hydrogen, atomic number of carbon in CH4 is 2+4+4 = 10, which is same as that of neon.
The four valence electrons are involved in bonding with the four hydrogen atoms. Therefore after formation of four covalent bonds with hydrogen, atomic number of carbon in CH4 is 2+4+4 = 10, which is same as that of neon.
The IUPAC name of CH3-O-C2H5 is- a)Methyl ethane
- b)Ethoxy ethane
- c)Methoxy ethane
- d)Ethyl ethane
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The IUPAC name of CH3-O-C2H5 is
a)
Methyl ethane
b)
Ethoxy ethane
c)
Methoxy ethane
d)
Ethyl ethane

|
Kds Coaching answered |
The compound CH3-O-C2H5 is an ether.
- The IUPAC name is based on identifying the groups attached to the oxygen atom.
- CH3 is the methoxy group.
- C2H5 is an ethyl group.
Therefore, the IUPAC name of the compound is methoxy ethane.
Aldehydes give carboxylic acids on:- a)Reduction
- b)Hydrolysis
- c)Hydrogenation
- d)Oxidation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Aldehydes give carboxylic acids on:
a)
Reduction
b)
Hydrolysis
c)
Hydrogenation
d)
Oxidation
|
|
Sheetal malhotra answered |
Understanding Aldehyde Oxidation
Aldehydes are organic compounds characterized by the presence of a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to at least one hydrogen atom. The oxidation of aldehydes leads to the formation of carboxylic acids, which is a key transformation in organic chemistry.
Oxidation Process
- Oxidizing Agents: Aldehydes can be oxidized by various agents such as potassium permanganate (KMnO4), dichromate (K2Cr2O7), or even atmospheric oxygen.
- Conversion: During oxidation, the hydrogen atom attached to the carbonyl carbon is removed, and an additional oxygen atom is added, resulting in the formation of a carboxylic acid (RCOOH).
Why Other Options Are Incorrect
- Reduction (Option A): This process involves the addition of hydrogen or removal of oxygen, which would convert aldehydes into primary alcohols, not acids.
- Hydrolysis (Option B): This is a reaction with water that typically affects esters or amides rather than aldehydes, and does not yield carboxylic acids directly.
- Hydrogenation (Option C): Involves the addition of hydrogen to a compound, reducing aldehydes to alcohols rather than oxidizing them to acids.
Conclusion
The correct pathway for converting aldehydes to carboxylic acids is through oxidation. This transformation is fundamental in organic synthesis and plays a significant role in various chemical reactions. Thus, option 'D' is the correct answer, highlighting the importance of understanding oxidation in organic chemistry.
Aldehydes are organic compounds characterized by the presence of a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to at least one hydrogen atom. The oxidation of aldehydes leads to the formation of carboxylic acids, which is a key transformation in organic chemistry.
Oxidation Process
- Oxidizing Agents: Aldehydes can be oxidized by various agents such as potassium permanganate (KMnO4), dichromate (K2Cr2O7), or even atmospheric oxygen.
- Conversion: During oxidation, the hydrogen atom attached to the carbonyl carbon is removed, and an additional oxygen atom is added, resulting in the formation of a carboxylic acid (RCOOH).
Why Other Options Are Incorrect
- Reduction (Option A): This process involves the addition of hydrogen or removal of oxygen, which would convert aldehydes into primary alcohols, not acids.
- Hydrolysis (Option B): This is a reaction with water that typically affects esters or amides rather than aldehydes, and does not yield carboxylic acids directly.
- Hydrogenation (Option C): Involves the addition of hydrogen to a compound, reducing aldehydes to alcohols rather than oxidizing them to acids.
Conclusion
The correct pathway for converting aldehydes to carboxylic acids is through oxidation. This transformation is fundamental in organic synthesis and plays a significant role in various chemical reactions. Thus, option 'D' is the correct answer, highlighting the importance of understanding oxidation in organic chemistry.
Carboxylic acids are:- a)Weak acids
- b)Strong acids
- c)Strong alkalis
- d)Weak alkalis
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Carboxylic acids are:
a)
Weak acids
b)
Strong acids
c)
Strong alkalis
d)
Weak alkalis
|
|
Rhea Reddy answered |
Carboxylic acid is a weak acid as it undergoes partial or incomplete dissociation in water.
The products obtained after the combustion of methane are:- a)Heat, water, carbon dioxide and light
- b)Carbon dioxide, water and heat
- c)Heat and light
- d)Water, carbon dioxide and light
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The products obtained after the combustion of methane are:
a)
Heat, water, carbon dioxide and light
b)
Carbon dioxide, water and heat
c)
Heat and light
d)
Water, carbon dioxide and light
|
|
Samarth Chakraborty answered |
Products obtained after the combustion of methane:
Methane is a hydrocarbon compound consisting of one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms (CH4). When methane undergoes combustion, it reacts with oxygen (O2) to produce various products.
1. Heat:
Combustion reactions are highly exothermic, meaning they release a large amount of heat energy. This is due to the breaking and forming of chemical bonds during the reaction. The combustion of methane results in the production of heat energy, which can be utilized for various applications.
2. Water:
One of the products obtained from the combustion of methane is water (H2O). The hydrogen atoms present in methane combine with the oxygen from the air to form water molecules. This is an important aspect of the combustion process as it contributes to the overall energy release.
3. Carbon Dioxide:
Another product formed during the combustion of methane is carbon dioxide (CO2). The carbon atom in methane combines with two oxygen atoms from the air to produce carbon dioxide. This is a greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change when released into the atmosphere.
4. Light:
During the combustion process, the release of heat energy is often accompanied by the emission of light. This light emission is typically seen as a flame when methane is burned in an open environment. The color and intensity of the flame can vary depending on the conditions of combustion.
Summary:
In summary, the products obtained after the combustion of methane are heat, water, carbon dioxide, and light. The combustion reaction involves the breaking of methane bonds and the formation of new bonds with oxygen. This process releases heat energy, produces water molecules, generates carbon dioxide, and emits light. These products have various applications and implications, making methane combustion an important process to understand in fields such as energy production and environmental science.
Methane is a hydrocarbon compound consisting of one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms (CH4). When methane undergoes combustion, it reacts with oxygen (O2) to produce various products.
1. Heat:
Combustion reactions are highly exothermic, meaning they release a large amount of heat energy. This is due to the breaking and forming of chemical bonds during the reaction. The combustion of methane results in the production of heat energy, which can be utilized for various applications.
2. Water:
One of the products obtained from the combustion of methane is water (H2O). The hydrogen atoms present in methane combine with the oxygen from the air to form water molecules. This is an important aspect of the combustion process as it contributes to the overall energy release.
3. Carbon Dioxide:
Another product formed during the combustion of methane is carbon dioxide (CO2). The carbon atom in methane combines with two oxygen atoms from the air to produce carbon dioxide. This is a greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change when released into the atmosphere.
4. Light:
During the combustion process, the release of heat energy is often accompanied by the emission of light. This light emission is typically seen as a flame when methane is burned in an open environment. The color and intensity of the flame can vary depending on the conditions of combustion.
Summary:
In summary, the products obtained after the combustion of methane are heat, water, carbon dioxide, and light. The combustion reaction involves the breaking of methane bonds and the formation of new bonds with oxygen. This process releases heat energy, produces water molecules, generates carbon dioxide, and emits light. These products have various applications and implications, making methane combustion an important process to understand in fields such as energy production and environmental science.
Vinegar is a solution of- a)50 % - 60 % acetic acid in alcohol
- b)5 % - 8 % acetic acid in alcohol
- c)5 % - 8 % acetic acid in water
- d)50 % - 60 % acetic acid in water
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Vinegar is a solution of
a)
50 % - 60 % acetic acid in alcohol
b)
5 % - 8 % acetic acid in alcohol
c)
5 % - 8 % acetic acid in water
d)
50 % - 60 % acetic acid in water
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Vinegar is a diluted solution of acetic acid in water. It’s composition is 5% - 8% of acetic acid in water.
IUPAC name of CH3COOH is:- a)Iso propanoic acid
- b)Methanoic acid
- c)Propanoic acid
- d)Ethanoic acid
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
IUPAC name of CH3COOH is:
a)
Iso propanoic acid
b)
Methanoic acid
c)
Propanoic acid
d)
Ethanoic acid
|
|
Vikas Kumar answered |
CH3COOH
2 carbon atoms.. so name has the word eth..
All single bonds so eth becames ethane
COOH - functional group carboxylic acid
So the 'e' at the end gets replaced with 'olic acid'
Ethanoic acid
The conversion of butene to butane in presence of nickel is an example of:- a)Oxidation reaction
- b)Substitution reaction
- c)Combustion reaction
- d)Addition Reaction
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The conversion of butene to butane in presence of nickel is an example of:
a)
Oxidation reaction
b)
Substitution reaction
c)
Combustion reaction
d)
Addition Reaction
|
|
Anjali Desai answered |
The reaction in which an element or molecule is added to unsaturated hydrocarbons is called addition reaction. In the above reaction unsaturated hydrocarbon is converted into saturated hydrocarbon.
Which of the following is not a straight chain hydrocarbon ?- a)
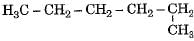
- b)H3C - CH2 - CH2 - CH2 - CH2 - CH3
- c)
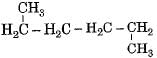
- d)
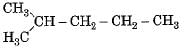
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a straight chain hydrocarbon ?
a)
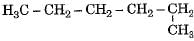
b)
H3C - CH2 - CH2 - CH2 - CH2 - CH3
c)
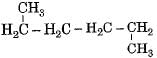
d)
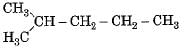
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Compounds (a), (b) and (c) can be written as straight chain compounds but compound (d) is really a branched chain compound
In the hydrogenation of vegetable oils, the unsaturated hydrocarbons generally add hydrogen in the presence of:- a)Copper
- b)Oxygen
- c)Nickel
- d)Sunlight
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the hydrogenation of vegetable oils, the unsaturated hydrocarbons generally add hydrogen in the presence of:
a)
Copper
b)
Oxygen
c)
Nickel
d)
Sunlight
|
|
Nisha Choudhury answered |
Addition of hydrogen across C-C double bonds is called hydrogenation. Unsaturated hydrocarbons add hydrogen in the presence of catalysts such as nickel/palladium to give saturated hydrocarbons. Vegetable oils used for cooking are long unsaturated hydrocarbons which are healthy.
The reaction in which oxidising agents supply nascent oxygen for oxidation of alcohols to their respective acids is known as:- a)Substitution reaction
- b)Combustion reaction
- c)Oxidation reaction
- d)Addition reaction
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The reaction in which oxidising agents supply nascent oxygen for oxidation of alcohols to their respective acids is known as:
a)
Substitution reaction
b)
Combustion reaction
c)
Oxidation reaction
d)
Addition reaction
|
|
Jay Gupta answered |
Oxidation is gain of oxygen.In this reaction oxygen is added to the reactant to form product.
How many carbon atoms is each carbon bonded to in diamond?- a)2
- b)3
- c)4
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How many carbon atoms is each carbon bonded to in diamond?
a)
2
b)
3
c)
4
d)
6

|
Kds Coaching answered |
In a diamond, each carbon atom is bonded to four other carbon atoms. This structure forms a strong and rigid lattice.
- This bonding results in a rigid 3D structure
- Each bond is a covalent bond, which contributes to diamond's extreme hardness.
Which of the following compounds has the suffix -al and is an example of an Aldehyde?- a)Propanol
- b)Propanal
- c)Propanoic acid
- d)Propanone
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following compounds has the suffix -al and is an example of an Aldehyde?
a)
Propanol
b)
Propanal
c)
Propanoic acid
d)
Propanone

|
Kds Coaching answered |
Propanal is an aldehyde, which uses the suffix "-al" as indicated in the table. Other options represent different types of compounds with different suffixes.
निम्नलिखित गद्यांशों को ध्यानपूर्वक पढ़कर नीचे दिए गए प्रश्नों के सही उत्तर विकल्पों में से चुनिएः
कुछ हुआ भी ऐसा ही। गली में ज्जोर का हल्ला उठा। लाला झाऊलाल जब तक दौडक़र नीचे उतरे तब तक एक भारी भीड़ आँगन में घुस आई। लाला झाऊलाल ने देखा कि इस भीड़ में प्रधान पात्र एक अंग्रे$ज है जो नखशिख से भीगा हुआ है और जो अपने एक पैर को हाथ से सहलाता हुआ दूसरे पैर पर नाच रहा है। उसी के पास अपराधी लोटे को भीगा हुआ देखकर लाला झाऊलाल जी ने .फौरन दो और दो जोडक़र स्थिति को समझ लिया।
प्रश्न:लोटे के लिए प्रयुक्त विशेषण कौन-सा है?- a)अपराधी
- b)भीगा हुआ
- c)प्रधन
- d)उसी के पास
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
निम्नलिखित गद्यांशों को ध्यानपूर्वक पढ़कर नीचे दिए गए प्रश्नों के सही उत्तर विकल्पों में से चुनिएः
कुछ हुआ भी ऐसा ही। गली में ज्जोर का हल्ला उठा। लाला झाऊलाल जब तक दौडक़र नीचे उतरे तब तक एक भारी भीड़ आँगन में घुस आई। लाला झाऊलाल ने देखा कि इस भीड़ में प्रधान पात्र एक अंग्रे$ज है जो नखशिख से भीगा हुआ है और जो अपने एक पैर को हाथ से सहलाता हुआ दूसरे पैर पर नाच रहा है। उसी के पास अपराधी लोटे को भीगा हुआ देखकर लाला झाऊलाल जी ने .फौरन दो और दो जोडक़र स्थिति को समझ लिया।
प्रश्न:लोटे के लिए प्रयुक्त विशेषण कौन-सा है?
कुछ हुआ भी ऐसा ही। गली में ज्जोर का हल्ला उठा। लाला झाऊलाल जब तक दौडक़र नीचे उतरे तब तक एक भारी भीड़ आँगन में घुस आई। लाला झाऊलाल ने देखा कि इस भीड़ में प्रधान पात्र एक अंग्रे$ज है जो नखशिख से भीगा हुआ है और जो अपने एक पैर को हाथ से सहलाता हुआ दूसरे पैर पर नाच रहा है। उसी के पास अपराधी लोटे को भीगा हुआ देखकर लाला झाऊलाल जी ने .फौरन दो और दो जोडक़र स्थिति को समझ लिया।
प्रश्न:लोटे के लिए प्रयुक्त विशेषण कौन-सा है?
a)
अपराधी
b)
भीगा हुआ
c)
प्रधन
d)
उसी के पास
|
|
Nitin Chavan answered |
Answer:
The correct answer is option 'A'.
Explanation:
Classification of Symbols
In the given symbol, there are four characters, i.e., $, ., :, and -. Each character has its own significance in the symbol. Let's classify these characters:
• $ - It is a symbol of currency, and its value is commonly known as a dollar.
• . - It is a decimal point that separates the whole number from the fractional part.
• : - It is a symbol of time, and it is used to separate hours from minutes.
• - - It is a hyphen, which is used to join two words or separate two parts of a word.
Interpretation of the Symbol
Using the above classification, we can interpret the given symbol as follows:
$ . : - It is a combination of currency, decimal point, time, and a hyphen. Therefore, it can be interpreted as follows:
• It represents an amount of money.
• The amount has a decimal value.
• The amount is related to time.
• The amount is connected with something else using a hyphen.
Options Explanation
a) This option is the correct answer because it represents the interpretation of the symbol as we have explained above.
b) This option is incorrect because it does not represent the interpretation of the symbol. The symbol does not represent a mathematical operation.
c) This option is incorrect because it does not represent the interpretation of the symbol. The symbol does not represent a unit of measurement.
d) This option is incorrect because it does not represent the interpretation of the symbol. The symbol does not represent a musical note.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the given symbol represents an amount of money with a decimal value that is related to time and connected with something else using a hyphen. The correct option is 'A'.
The correct answer is option 'A'.
Explanation:
Classification of Symbols
In the given symbol, there are four characters, i.e., $, ., :, and -. Each character has its own significance in the symbol. Let's classify these characters:
• $ - It is a symbol of currency, and its value is commonly known as a dollar.
• . - It is a decimal point that separates the whole number from the fractional part.
• : - It is a symbol of time, and it is used to separate hours from minutes.
• - - It is a hyphen, which is used to join two words or separate two parts of a word.
Interpretation of the Symbol
Using the above classification, we can interpret the given symbol as follows:
$ . : - It is a combination of currency, decimal point, time, and a hyphen. Therefore, it can be interpreted as follows:
• It represents an amount of money.
• The amount has a decimal value.
• The amount is related to time.
• The amount is connected with something else using a hyphen.
Options Explanation
a) This option is the correct answer because it represents the interpretation of the symbol as we have explained above.
b) This option is incorrect because it does not represent the interpretation of the symbol. The symbol does not represent a mathematical operation.
c) This option is incorrect because it does not represent the interpretation of the symbol. The symbol does not represent a unit of measurement.
d) This option is incorrect because it does not represent the interpretation of the symbol. The symbol does not represent a musical note.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the given symbol represents an amount of money with a decimal value that is related to time and connected with something else using a hyphen. The correct option is 'A'.
What distinguishes synthetic detergents from traditional soaps in terms of their cleansing action?
- a)Synthetic detergents are more environmentally friendly.
- b)Synthetic detergents do not interact with hard water minerals.
- c)Synthetic detergents do not form scum in hard water.
- d)Synthetic detergents create a stronger lather in soft water.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer??
What distinguishes synthetic detergents from traditional soaps in terms of their cleansing action?
a)
Synthetic detergents are more environmentally friendly.
b)
Synthetic detergents do not interact with hard water minerals.
c)
Synthetic detergents do not form scum in hard water.
d)
Synthetic detergents create a stronger lather in soft water.
|
|
Arun rawat answered |
Understanding Synthetic Detergents vs. Traditional Soaps
Synthetic detergents and traditional soaps serve the same primary function of cleaning, but they differ significantly in their chemical composition and interaction with water, especially hard water.
1. Interaction with Hard Water
- Traditional soaps are made from natural fats and oils, which react with minerals such as calcium and magnesium found in hard water.
- This reaction leads to the formation of insoluble compounds, commonly known as scum, which reduces the soap's effectiveness and leaves residues.
2. Properties of Synthetic Detergents
- Synthetic detergents, on the other hand, are formulated using petrochemical products and surfactants that do not react with hard water minerals.
- This means that they maintain their cleansing action even in hard water conditions.
3. Absence of Scum Formation
- One of the key advantages of synthetic detergents is that they do not form scum in hard water.
- This characteristic allows them to work effectively without leaving behind residues, making them more efficient for cleaning purposes.
4. Additional Benefits
- While synthetic detergents can create a stronger lather in soft water, their standout feature is their ability to perform optimally in hard water without scum formation.
- This makes them a preferred choice for many consumers, especially in regions with hard water.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 'C' because synthetic detergents do not form scum in hard water, ensuring a more effective and efficient cleaning process compared to traditional soaps.
Synthetic detergents and traditional soaps serve the same primary function of cleaning, but they differ significantly in their chemical composition and interaction with water, especially hard water.
1. Interaction with Hard Water
- Traditional soaps are made from natural fats and oils, which react with minerals such as calcium and magnesium found in hard water.
- This reaction leads to the formation of insoluble compounds, commonly known as scum, which reduces the soap's effectiveness and leaves residues.
2. Properties of Synthetic Detergents
- Synthetic detergents, on the other hand, are formulated using petrochemical products and surfactants that do not react with hard water minerals.
- This means that they maintain their cleansing action even in hard water conditions.
3. Absence of Scum Formation
- One of the key advantages of synthetic detergents is that they do not form scum in hard water.
- This characteristic allows them to work effectively without leaving behind residues, making them more efficient for cleaning purposes.
4. Additional Benefits
- While synthetic detergents can create a stronger lather in soft water, their standout feature is their ability to perform optimally in hard water without scum formation.
- This makes them a preferred choice for many consumers, especially in regions with hard water.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 'C' because synthetic detergents do not form scum in hard water, ensuring a more effective and efficient cleaning process compared to traditional soaps.
The first member of alkyne homologous series is- a)ethyne
- b)ethene
- c)propyne
- d)methane
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The first member of alkyne homologous series is
a)
ethyne
b)
ethene
c)
propyne
d)
methane

|
Athira Yadav answered |
Ethyne (C2H2) is the first member of alkyne homologous series.
Chapter doubts & questions for Carbon and its compounds - Science Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Carbon and its compounds - Science Class 10 in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 10 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup