All Exams >
Class 10 >
Science Class 10 >
All Questions
All questions of Life Processes for Class 10 Exam
Which part of alimentary canal receives bile from the liver ?- a)Stomach
- b)Small intestine
- c)Large intestine
- d)Oesophagus
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which part of alimentary canal receives bile from the liver ?
a)
Stomach
b)
Small intestine
c)
Large intestine
d)
Oesophagus
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
The small intestine is made up of duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. It receives the bile from the liver which helps in the breakdown of fats.
The common step between aerobic and anaerobic respiration takes place in :- a)cytoplasm
- b)mitochondria
- c)chloroplast
- d)golgi complex
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The common step between aerobic and anaerobic respiration takes place in :
a)
cytoplasm
b)
mitochondria
c)
chloroplast
d)
golgi complex
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Aerobic respiration first occurs in the cytoplasm and then in mitochondria, whereas Anaerobic respiration occurs in the cytoplasm itself.
Sometimes we get painful cramps in our leg muscles after running for a long time due to the accumulation of:- a)Lactic acid
- b)Carbon dioxide
- c)Hydrochloric acid
- d)Fat
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Sometimes we get painful cramps in our leg muscles after running for a long time due to the accumulation of:
a)
Lactic acid
b)
Carbon dioxide
c)
Hydrochloric acid
d)
Fat
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
- During heavy exercise, the demand for energy is high but the supply of oxygen to produce energy is limited. Therefore, anaerobic respiration takes place in the muscle cells to fulfil the demand for energy.
- This anaerobic breakdown of glucose leads to the formation of lactic acid in muscles.
- The accumulation of lactic acid in muscles leads to muscle cramps.
Thus option A is correct.
The vein which brings clean blood from the lungs into the heart is known as:- a)Superior vena cava
- b)Hepatic vein
- c)Pulmonary vein
- d)Pulmonary artery
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The vein which brings clean blood from the lungs into the heart is known as:
a)
Superior vena cava
b)
Hepatic vein
c)
Pulmonary vein
d)
Pulmonary artery
|
|
Arun Sharma answered |
The form of veins that transfer oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart is the pulmonary veins. The four major pulmonary veins, two from each of the lungs that flow into the left atrium of the heart, are the largest pulmonary veins.
Movement of food through the oesophagus is due to :
- a)Lubrication by saliva
- b)Alimentary Canal
- c)Diffusion
- d)Turgor pressure
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Movement of food through the oesophagus is due to :
a)
Lubrication by saliva
b)
Alimentary Canal
c)
Diffusion
d)
Turgor pressure
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
2. Alimentary Canal
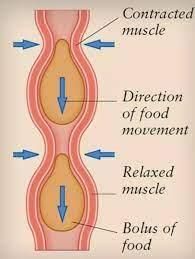
Explanation: The movement of food through the esophagus is primarily due to a process called peristalsis. Peristalsis is a series of wave-like muscle contractions that move food through the digestive tract, including the esophagus, which is a part of the alimentary canal. While lubrication by saliva helps in swallowing, the actual movement of food down the esophagus is due to the coordinated contractions of the muscles in the walls of the alimentary canal.
Oxygen liberated during photosynthesis comes from- a)water
- b)chlorophyll
- c)carbon dioxide
- d)glucose
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Oxygen liberated during photosynthesis comes from
a)
water
b)
chlorophyll
c)
carbon dioxide
d)
glucose
|
|
Arun Sharma answered |
Photosynthetic oxygen evolution occurs via the light-dependent oxidation of water. Free oxygen is generated as a by-product of this reaction and is released into the atmosphere.
Which is the first enzyme to mix with food in digestive tract ?- a)Pepsin
- b)Cellulose
- c)Amylase
- d)Trypsin
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the first enzyme to mix with food in digestive tract ?
a)
Pepsin
b)
Cellulose
c)
Amylase
d)
Trypsin
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
Salivary amylase, present in saliva, is the first digestive enzyme that gets mixed with food in the oral cavity during the process of mastication and bolus formation. The digestive enzyme salivary amylase hydrolyzes starch into maltose, malto-triose, dextrin and a small amount of glucose.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Haemoglobin is –
- A:
Vitamin
- B:
Skin pigment
- C:
Blood carrier
- D:
Respiratory pigment
The answer is D.
Haemoglobin is –
Vitamin
Skin pigment
Blood carrier
Respiratory pigment
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
the hemoglobin increases the oxygen carrying capacity of blood. In humans and most other vertebrates, the most common respiratory pigment is a protein called hemoglobin.
The filtration units of kidneys are called- a)ureter
- b)urethra
- c)neurons
- d)nephrons
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The filtration units of kidneys are called
a)
ureter
b)
urethra
c)
neurons
d)
nephrons
|
|
Aditya Shah answered |
Nephrons are the basic filtering units of a kidney each kidney poses a large number of nephrons approximately 1-1.5 million.
The main functions of a nephron are:
(i) Filtration
(ii) Ultrafiltration
(iii) Absorption
(iv) Reabsorption
(i) Filtration
(ii) Ultrafiltration
(iii) Absorption
(iv) Reabsorption
Can you explain the answer of this question below:The maximum affinity of haemoglobin is with –
- A:
Carbon monoxide
- B:
Carbondioxide
- C:
Oxygen
- D:
Ammonia
The answer is A.
The maximum affinity of haemoglobin is with –
Carbon monoxide
Carbondioxide
Oxygen
Ammonia
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
Hemoglobin in humans has a very high affinity for carbon monoxide, forming carboxyhemoglobin which is a very bright red in color. Carbon monoxide is thus problematic for humans because it has affinity higher than that of oxygen.
When air is blown from mouth into a test-tube containing lime water, the lime water turns milky due to the presence of- a)oxygen
- b)carbon dioxide
- c)nitrogen
- d)water vapour
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When air is blown from mouth into a test-tube containing lime water, the lime water turns milky due to the presence of
a)
oxygen
b)
carbon dioxide
c)
nitrogen
d)
water vapour
|
|
Arun Sharma answered |
The air we exhale contains CO2. When carbon dioxide is passed through lime water or Ca(OH)2 then it form calcium carbonate which is white in colour.
Sometimes we get painful cramps in our leg muscles after running for a long time due to the accumulation of:- a)Hydrochloric acid
- b)Fat
- c)Carbon dioxide
- d)Lactic acid
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Sometimes we get painful cramps in our leg muscles after running for a long time due to the accumulation of:
a)
Hydrochloric acid
b)
Fat
c)
Carbon dioxide
d)
Lactic acid
|
|
Avinash Patel answered |
The build-up of lactic acid in our muscles while running (less oxygen conditions) causes cramps.
The opening and closing of the stomatal pore depend upon:
- a)Oxygen
- b)Temperature
- c)Water in guard cells.
- d)Concentration of CO2 in stomata.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The opening and closing of the stomatal pore depend upon:
a)
Oxygen
b)
Temperature
c)
Water in guard cells.
d)
Concentration of CO2 in stomata.

|
Parth Basu answered |
- When a pair of guard cells surrounding a stoma receives the signal to open the stomatal pore, it is filled with water, thus changing the cell's shape and opening the pore.
- When guard cells receive a signal to close the stoma, this initiates a loss of water and causes them to shrink and the pore closes.
Thus, option C is correct.
Which of these is not a raw material for photosynthesis?- a) Carbon dioxide
- b)Water
- c)Oxygen
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of these is not a raw material for photosynthesis?
a)
Carbon dioxide
b)
Water
c)
Oxygen
d)
None of these
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
organism prepare their own food with the help of simple inorganic materials like CO2,H2O in sunlight with the help of chlorophyll. Thus, it doesn’t involve oxygen in the process.
Oxygen in lungs ultimately reaches –- a)Alveoli
- b)Trachea
- c)Bronchus
- d)Bronchioles
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Oxygen in lungs ultimately reaches –
a)
Alveoli
b)
Trachea
c)
Bronchus
d)
Bronchioles

|
Nk Classes answered |
The alveoli are the final branchings of the respiratory tree and act as the primary gas exchange units of the lung. Inhaled oxygen enters the lungs and reaches the alveoli.
The narrowest and most numberous tubes of lungs are termed as –- a)Bronchus
- b)Bronchioles
- c)Alveoli
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The narrowest and most numberous tubes of lungs are termed as –
a)
Bronchus
b)
Bronchioles
c)
Alveoli
d)
None of these
|
|
Vikas Kumar answered |
Bronchiole is a fine respiratory tube in the lungs of reptiles, birds and mammals. It is formed by the subdivision of a bronchus.
Plant can respire in :- a)Dark
- b)Light
- c)Both in light and dark
- d)Morning
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Plant can respire in :
a)
Dark
b)
Light
c)
Both in light and dark
d)
Morning
|
|
Arun Sharma answered |
Respiration is constitutive process that occurs in all tissues. Unlike photosynthesis that can happen only in the presence of sunlight, respiration in plant occurs all time. So, the answer is - both light and dark.
The transpiration organ in plant is- a)Epidermis
- b)Xylem
- c)Cortex
- d)Phloem
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The transpiration organ in plant is
a)
Epidermis
b)
Xylem
c)
Cortex
d)
Phloem
|
|
Damini nambiar answered |
**Transpiration Organ in Plants:**
The correct answer to the question is option 'A' - Epidermis.
**Explanation:**
The transpiration organ in plants is the epidermis. The epidermis is the outermost layer of cells covering the leaves, stems, and roots of plants. It serves as a protective barrier against mechanical injury, pathogens, and excessive water loss. It also plays a crucial role in the process of transpiration.
**Transpiration:**
Transpiration is the process by which plants lose water in the form of water vapor through the stomata, which are tiny openings present on the epidermis of leaves and stems. It is an essential process for plants as it helps in the absorption and transport of water and nutrients, cooling the plant, and maintaining turgidity.
**Role of Epidermis in Transpiration:**
The epidermis of leaves and stems contains specialized cells called guard cells, which surround and control the opening and closing of the stomata. When the plant needs to release excess water vapor, the guard cells open the stomata, allowing water to evaporate from the leaf surface. This process is known as transpiration.
**Structure of Epidermis:**
The epidermis is made up of tightly packed cells with a waxy layer called the cuticle on the outer surface. The cuticle helps in reducing water loss by acting as a waterproof barrier. However, the majority of transpiration occurs through the stomata.
**Importance of Transpiration:**
Transpiration is essential for several reasons:
1. Water and nutrient absorption: Transpiration creates a continuous flow of water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves, allowing plants to receive the necessary resources for growth and development.
2. Cooling effect: Transpiration helps in cooling the plant by releasing water vapor, similar to how sweating cools our bodies.
3. Maintaining turgidity: Transpiration maintains turgidity in plant cells, preventing wilting and maintaining the overall health and structure of the plant.
In conclusion, the epidermis of plants serves as the transpiration organ because it contains the stomata, which are responsible for the release of water vapor during the process of transpiration.
The correct answer to the question is option 'A' - Epidermis.
**Explanation:**
The transpiration organ in plants is the epidermis. The epidermis is the outermost layer of cells covering the leaves, stems, and roots of plants. It serves as a protective barrier against mechanical injury, pathogens, and excessive water loss. It also plays a crucial role in the process of transpiration.
**Transpiration:**
Transpiration is the process by which plants lose water in the form of water vapor through the stomata, which are tiny openings present on the epidermis of leaves and stems. It is an essential process for plants as it helps in the absorption and transport of water and nutrients, cooling the plant, and maintaining turgidity.
**Role of Epidermis in Transpiration:**
The epidermis of leaves and stems contains specialized cells called guard cells, which surround and control the opening and closing of the stomata. When the plant needs to release excess water vapor, the guard cells open the stomata, allowing water to evaporate from the leaf surface. This process is known as transpiration.
**Structure of Epidermis:**
The epidermis is made up of tightly packed cells with a waxy layer called the cuticle on the outer surface. The cuticle helps in reducing water loss by acting as a waterproof barrier. However, the majority of transpiration occurs through the stomata.
**Importance of Transpiration:**
Transpiration is essential for several reasons:
1. Water and nutrient absorption: Transpiration creates a continuous flow of water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves, allowing plants to receive the necessary resources for growth and development.
2. Cooling effect: Transpiration helps in cooling the plant by releasing water vapor, similar to how sweating cools our bodies.
3. Maintaining turgidity: Transpiration maintains turgidity in plant cells, preventing wilting and maintaining the overall health and structure of the plant.
In conclusion, the epidermis of plants serves as the transpiration organ because it contains the stomata, which are responsible for the release of water vapor during the process of transpiration.
Which of the following help in protecting the inner lining of the stomach from the harmful effect of hydrochloric acid?- a)Mucus
- b)Pepsin
- c)Trypsin
- d)Bile
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following help in protecting the inner lining of the stomach from the harmful effect of hydrochloric acid?
a)
Mucus
b)
Pepsin
c)
Trypsin
d)
Bile
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
Mucus is a viscous secretion that protects the inner lining of the stomach from the action of HCl.
Which part of the plant helps to absorb water and minerals from the soil?- a)Root hairs
- b)Roots
- c)Root cap
- d)Tap root
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which part of the plant helps to absorb water and minerals from the soil?
a)
Root hairs
b)
Roots
c)
Root cap
d)
Tap root
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
The root has further extensions which increase the surface area for absorption. These extensions are called root hair, which is present in all types of roots.
What is the primary function of the counter-current mechanism in the nephron?- a)To filter blood at the glomerulus
- b)To reabsorb glucose in the proximal tubule
- c)To concentrate urine by creating a concentration gradient in the medulla
- d)To transport urine from the kidney to the bladder
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
To filter blood at the glomerulus
b)
To reabsorb glucose in the proximal tubule
c)
To concentrate urine by creating a concentration gradient in the medulla
d)
To transport urine from the kidney to the bladder

|
Nk Classes answered |
The counter-current mechanism in the nephron primarily functions to concentrate urine by creating a concentration gradient in the medulla of the kidney. This gradient is established by the counter-current flow of fluids in the ascending and descending limbs of the loop of Henle, which facilitates the reabsorption of water and concentrates the urine.
Which statement accurately describes the process of hemodialysis?- a)It filters blood using a device that mimics kidney function.
- b)It stores excess water from the blood.
- c)It absorbs waste products directly from the urine.
- d)It reabsorbs glucose and amino acids into the blood.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
It filters blood using a device that mimics kidney function.
b)
It stores excess water from the blood.
c)
It absorbs waste products directly from the urine.
d)
It reabsorbs glucose and amino acids into the blood.

|
Nk Classes answered |
Hemodialysis is a medical procedure that uses an artificial device to mimic the filtering function of the kidneys. It helps remove waste products and excess fluids from the blood when the kidneys are not functioning properly.
What is the basic filtration unit in the kidneys called?- a)Alveoli
- b)Glomerulus
- c)Nephron
- d)Bowman's capsule
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the basic filtration unit in the kidneys called?
a)
Alveoli
b)
Glomerulus
c)
Nephron
d)
Bowman's capsule
|
|
Saptarshi Yadav answered |
Basic Filtration Unit in the Kidneys
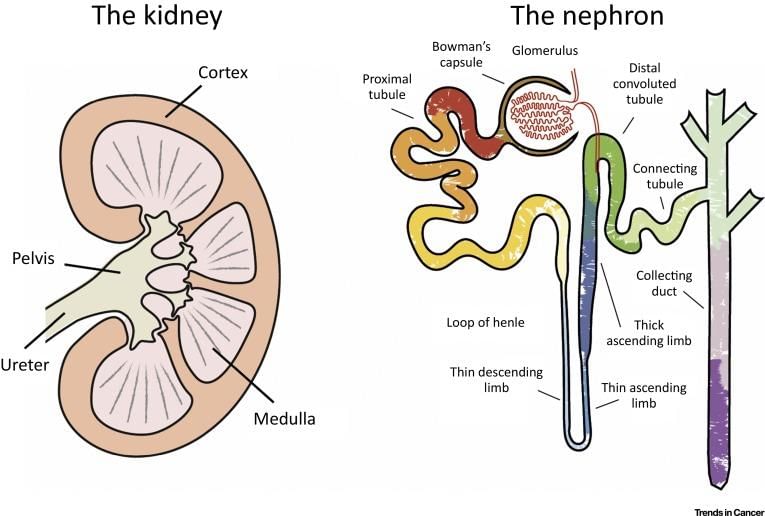
The correct answer is option 'C' - Nephron. The nephron is the fundamental structural and functional unit of the kidney responsible for filtering blood and forming urine.
Structure of Nephron
- Each kidney contains approximately one million nephrons.
- A nephron consists of two main parts:
- Renal Corpuscle: This includes the glomerulus and Bowman's capsule.
- Renal Tubule: This is divided into several segments - proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle, distal convoluted tubule, and collecting duct.
Function of Nephron
- Filtration: Blood enters through the glomerulus, where water, ions, and small molecules are filtered into Bowman's capsule.
- Reabsorption: Essential nutrients and water are reabsorbed back into the bloodstream from the renal tubule.
- Secretion: Waste products and excess substances are secreted into the tubule from the blood.
Importance of Nephrons
- Nephrons regulate the body's fluid balance, electrolyte levels, and waste removal.
- They play a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis, ensuring that the body functions optimally.
Conclusion
In summary, the nephron is the basic filtration unit of the kidneys, essential for the processes of filtration, reabsorption, and secretion, which together ensure proper kidney function and overall health.
The correct answer is option 'C' - Nephron. The nephron is the fundamental structural and functional unit of the kidney responsible for filtering blood and forming urine.
Structure of Nephron
- Each kidney contains approximately one million nephrons.
- A nephron consists of two main parts:
- Renal Corpuscle: This includes the glomerulus and Bowman's capsule.
- Renal Tubule: This is divided into several segments - proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle, distal convoluted tubule, and collecting duct.
Function of Nephron
- Filtration: Blood enters through the glomerulus, where water, ions, and small molecules are filtered into Bowman's capsule.
- Reabsorption: Essential nutrients and water are reabsorbed back into the bloodstream from the renal tubule.
- Secretion: Waste products and excess substances are secreted into the tubule from the blood.
Importance of Nephrons
- Nephrons regulate the body's fluid balance, electrolyte levels, and waste removal.
- They play a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis, ensuring that the body functions optimally.
Conclusion
In summary, the nephron is the basic filtration unit of the kidneys, essential for the processes of filtration, reabsorption, and secretion, which together ensure proper kidney function and overall health.
It is necessary to separate oxygenated blood from the deoxygenated blood in mammals- a)To maintain the body temperature
- b)To provide more oxygen to cells
- c)Both A and B
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
It is necessary to separate oxygenated blood from the deoxygenated blood in mammals
a)
To maintain the body temperature
b)
To provide more oxygen to cells
c)
Both A and B
d)
None of the above
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Oxygenated blood carries O2 to the various tissues, muscles, cells, et(c) from the lungs and heart, while deoxygenated blood carries CO2 from the organs to the lungs which is removed from the body. In birds and mammals, it is essential to keep the oxygenated blood separated from the deoxygenated blood In this way, only highly oxygenated blood is sent out to the body's tissues for far more efficient diffusion into the cells of the body, giving them more 'fuel' to run cellular respiration in the mitochondria, to make ATP molecules to run the reactions that allow them to maintain body temperature in addition to running all of their metabolic reactions of the body. If they were not separated, it would probably take much longer to perform simple activities and metabolism would be reduced as a consequence.
Which of the following is NOT a method used by plants for excretion?- a)Transpiration
- b)Storage in vacuoles
- c)Shedding of leaves
- d)Active transport into the atmosphere
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is NOT a method used by plants for excretion?
a)
Transpiration
b)
Storage in vacuoles
c)
Shedding of leaves
d)
Active transport into the atmosphere

|
EduRev Class 10 answered |
Plants do not actively transport waste into the atmosphere; they primarily use methods such as transpiration, storage in vacuoles, and shedding of leaves for excretion.
The enzymes pepsin and trypsin are secreted respectively by- a)Stomach and pancreas
- b)Salivary gland and stomach
- c)Liver and pancreas
- d)Liver and salivary gland
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The enzymes pepsin and trypsin are secreted respectively by
a)
Stomach and pancreas
b)
Salivary gland and stomach
c)
Liver and pancreas
d)
Liver and salivary gland
|
|
Avinash Patel answered |
Stomach secretes the enzyme pepsin and pancreas produces trypsin. Both of them break down protein.
What is the primary role of the ureters in the excretory system?- a)To filter blood
- b)To store urine
- c)To transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder
- d)To release urine from the body
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
To filter blood
b)
To store urine
c)
To transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder
d)
To release urine from the body

|
Kamna Science Academy answered |
The ureters are tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. They play a crucial role in transporting the urine formed in the kidneys to the bladder, where it is stored until it is eventually expelled from the body.
The form of energy used in respiration is –- a)Chemical energy
- b)Electrical energy
- c)Mechanical energy
- d)Radiant energy
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The form of energy used in respiration is –
a)
Chemical energy
b)
Electrical energy
c)
Mechanical energy
d)
Radiant energy
|
|
Vikas Kumar answered |
Cellular respiration is the process of breaking sugar into a form that the cell can use as energy. This happens in all forms of life. Cellular respiration takes in food and uses it to create ATP, a chemical which the cell uses for energy. Usually, this process uses oxygen, and is called aerobic respiration.
What are organisms that prepare their own food from inorganic substances called?- a)Heterotrophs
- b)Carnivores
- c)Autotrophs
- d)Omnivores
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What are organisms that prepare their own food from inorganic substances called?
a)
Heterotrophs
b)
Carnivores
c)
Autotrophs
d)
Omnivores
|
|
Shruti shukla answered |
Understanding Autotrophs
Organisms that prepare their own food from inorganic substances are classified as autotrophs. This process is essential for sustaining life on Earth and involves converting simple substances into complex organic compounds that can be used for energy.
Types of Organisms
- Heterotrophs:
- These organisms cannot synthesize their own food and rely on consuming other organisms (plants, animals, or organic matter) for energy.
- Examples include humans, animals, and many fungi.
- Carnivores:
- A subset of heterotrophs that specifically consume other animals for sustenance.
- Examples include lions and hawks.
- Omnivores:
- These organisms consume both plants and animals, making them flexible in their diet.
- Examples include humans, bears, and raccoons.
Characteristics of Autotrophs
- Self-sustaining:
- Autotrophs do not rely on other organisms for food. They can create their own nutrients through processes like photosynthesis or chemosynthesis.
- Photosynthesis:
- Most autotrophs, such as plants, use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. This process is vital for producing energy and organic material in ecosystems.
- Chemosynthesis:
- Some autotrophs, particularly certain bacteria, derive energy from inorganic molecules (like hydrogen sulfide), allowing them to produce food in environments without sunlight, such as deep-sea vents.
Importance of Autotrophs
- Autotrophs form the foundation of food chains and ecosystems. They provide energy and organic compounds for heterotrophs.
- They play a crucial role in oxygen production and carbon fixation, helping maintain ecological balance.
In summary, the correct answer to the question is option 'C' - autotrophs, as they are organisms capable of synthesizing their own food from inorganic substances.
Organisms that prepare their own food from inorganic substances are classified as autotrophs. This process is essential for sustaining life on Earth and involves converting simple substances into complex organic compounds that can be used for energy.
Types of Organisms
- Heterotrophs:
- These organisms cannot synthesize their own food and rely on consuming other organisms (plants, animals, or organic matter) for energy.
- Examples include humans, animals, and many fungi.
- Carnivores:
- A subset of heterotrophs that specifically consume other animals for sustenance.
- Examples include lions and hawks.
- Omnivores:
- These organisms consume both plants and animals, making them flexible in their diet.
- Examples include humans, bears, and raccoons.
Characteristics of Autotrophs
- Self-sustaining:
- Autotrophs do not rely on other organisms for food. They can create their own nutrients through processes like photosynthesis or chemosynthesis.
- Photosynthesis:
- Most autotrophs, such as plants, use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. This process is vital for producing energy and organic material in ecosystems.
- Chemosynthesis:
- Some autotrophs, particularly certain bacteria, derive energy from inorganic molecules (like hydrogen sulfide), allowing them to produce food in environments without sunlight, such as deep-sea vents.
Importance of Autotrophs
- Autotrophs form the foundation of food chains and ecosystems. They provide energy and organic compounds for heterotrophs.
- They play a crucial role in oxygen production and carbon fixation, helping maintain ecological balance.
In summary, the correct answer to the question is option 'C' - autotrophs, as they are organisms capable of synthesizing their own food from inorganic substances.
The enzymes contained in pancreatic juices help in the digestion of:- a)Fats and carbohydrates
- b)Proteins and fats
- c)Proteins and carbohydrates
- d)Proteins, fats, and carbohydrates
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The enzymes contained in pancreatic juices help in the digestion of:
a)
Fats and carbohydrates
b)
Proteins and fats
c)
Proteins and carbohydrates
d)
Proteins, fats, and carbohydrates
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
The pancreas contains all kinds of enzymes that can digest proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
What is the basic unit of filtration in the kidney that contains a cluster of capillaries?- a)Bowman’s capsule
- b)Glomerulus
- c)Ureter
- d)Collecting duct
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Bowman’s capsule
b)
Glomerulus
c)
Ureter
d)
Collecting duct

|
EduRev Class 10 answered |
The glomerulus is a network of capillaries within the nephron that performs the initial filtration of blood. It is surrounded by Bowman’s capsule, which collects the filtered urine. The glomerulus plays a crucial role in filtering waste products from the blood.
Why is it significant that the kidney’s filtration units, nephrons, are packed close together?- a)It aids in storing more urine
- b)It increases the efficiency of filtration
- c)It helps in producing more urea
- d)It allows for more glucose reabsorption
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Why is it significant that the kidney’s filtration units, nephrons, are packed close together?
a)
It aids in storing more urine
b)
It increases the efficiency of filtration
c)
It helps in producing more urea
d)
It allows for more glucose reabsorption
|
|
Rohit Patel answered |
Significance of Nephrons Packed Close Together
The close packing of nephrons in the kidneys plays a crucial role in enhancing the organ's ability to filter blood efficiently. Here are the key points explaining why this arrangement is significant:
1. Enhanced Filtration Efficiency
- The proximity of nephrons allows for a greater surface area for filtration.
- With more nephrons working simultaneously, the kidneys can process larger volumes of blood, effectively removing waste products and excess substances.
2. Concentrated Functionality
- Nephrons consist of glomeruli and tubules that work together to filter blood and reabsorb necessary substances.
- Close arrangement enables quick communication and cooperation between these components, leading to optimal performance.
3. Maximized Resource Utilization
- By packing nephrons together, the kidneys minimize the distance over which filtrate must travel, thus reducing the energy required for filtration and reabsorption processes.
- This efficiency is vital for maintaining homeostasis in the body, ensuring that crucial nutrients and electrolytes are preserved while waste is excreted.
4. Effective Waste Removal
- The design facilitates rapid filtration and concentration of urine by allowing multiple nephrons to contribute to the overall filtering process.
- This means toxins and waste products can be efficiently cleared from the bloodstream, maintaining the body's internal environment.
In summary, the close packing of nephrons significantly increases the efficiency of filtration in the kidneys, allowing for effective blood purification and waste removal, which is essential for overall health.
The close packing of nephrons in the kidneys plays a crucial role in enhancing the organ's ability to filter blood efficiently. Here are the key points explaining why this arrangement is significant:
1. Enhanced Filtration Efficiency
- The proximity of nephrons allows for a greater surface area for filtration.
- With more nephrons working simultaneously, the kidneys can process larger volumes of blood, effectively removing waste products and excess substances.
2. Concentrated Functionality
- Nephrons consist of glomeruli and tubules that work together to filter blood and reabsorb necessary substances.
- Close arrangement enables quick communication and cooperation between these components, leading to optimal performance.
3. Maximized Resource Utilization
- By packing nephrons together, the kidneys minimize the distance over which filtrate must travel, thus reducing the energy required for filtration and reabsorption processes.
- This efficiency is vital for maintaining homeostasis in the body, ensuring that crucial nutrients and electrolytes are preserved while waste is excreted.
4. Effective Waste Removal
- The design facilitates rapid filtration and concentration of urine by allowing multiple nephrons to contribute to the overall filtering process.
- This means toxins and waste products can be efficiently cleared from the bloodstream, maintaining the body's internal environment.
In summary, the close packing of nephrons significantly increases the efficiency of filtration in the kidneys, allowing for effective blood purification and waste removal, which is essential for overall health.
Which of the following structures in the kidney is responsible for the initial filtration of blood?- a)Ureter
- b)Urinary bladder
- c)Urethra
- d)Bowman's capsule
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following structures in the kidney is responsible for the initial filtration of blood?
a)
Ureter
b)
Urinary bladder
c)
Urethra
d)
Bowman's capsule
|
|
Urvashi dasgupta answered |
Introduction
The kidney is a vital organ in the human body responsible for filtering blood, eliminating waste, and maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance. Among its various structures, the Bowman's capsule plays a crucial role in the filtration process.
Bowman's Capsule: The Filtration Unit
- The Bowman's capsule is a cup-shaped structure that encases the glomerulus, a network of tiny blood vessels (capillaries).
- It is located in the nephron, the functional unit of the kidney, where blood filtration begins.
Filtration Process
- Blood Flow: Blood enters the kidney through the renal artery and reaches the glomerulus, where high pressure forces fluid and small solutes out of the blood.
- Filtration Barrier: The walls of the glomerulus and the Bowman's capsule form a selective barrier. This barrier allows water, ions, glucose, and small waste molecules to pass while retaining larger molecules like proteins and blood cells.
- Formation of Filtrate: The fluid that collects in the Bowman's capsule is called glomerular filtrate. This filtrate then moves into the renal tubules for further processing and reabsorption.
Other Structures Explained
- Ureter: A tube that carries urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
- Urinary Bladder: A storage organ for urine before it is expelled from the body.
- Urethra: The duct through which urine is discharged from the bladder.
Conclusion
In summary, the Bowman's capsule is the key structure in the kidney responsible for the initial filtration of blood. It initiates the process of waste removal, setting the stage for the kidneys' essential role in maintaining homeostasis.
The kidney is a vital organ in the human body responsible for filtering blood, eliminating waste, and maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance. Among its various structures, the Bowman's capsule plays a crucial role in the filtration process.
Bowman's Capsule: The Filtration Unit
- The Bowman's capsule is a cup-shaped structure that encases the glomerulus, a network of tiny blood vessels (capillaries).
- It is located in the nephron, the functional unit of the kidney, where blood filtration begins.
Filtration Process
- Blood Flow: Blood enters the kidney through the renal artery and reaches the glomerulus, where high pressure forces fluid and small solutes out of the blood.
- Filtration Barrier: The walls of the glomerulus and the Bowman's capsule form a selective barrier. This barrier allows water, ions, glucose, and small waste molecules to pass while retaining larger molecules like proteins and blood cells.
- Formation of Filtrate: The fluid that collects in the Bowman's capsule is called glomerular filtrate. This filtrate then moves into the renal tubules for further processing and reabsorption.
Other Structures Explained
- Ureter: A tube that carries urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
- Urinary Bladder: A storage organ for urine before it is expelled from the body.
- Urethra: The duct through which urine is discharged from the bladder.
Conclusion
In summary, the Bowman's capsule is the key structure in the kidney responsible for the initial filtration of blood. It initiates the process of waste removal, setting the stage for the kidneys' essential role in maintaining homeostasis.
Which waste product mentioned is directly associated with photosynthesis in plants?- a)Urea
- b)Uric acid
- c)Oxygen
- d)Carbon dioxide
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which waste product mentioned is directly associated with photosynthesis in plants?
a)
Urea
b)
Uric acid
c)
Oxygen
d)
Carbon dioxide
|
|
Manisha choudhary answered |
Photosynthesis and Oxygen Production
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose. This process relies on the presence of certain waste products and byproducts.
Oxygen Production
- During photosynthesis, plants take in carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere and water (H2O) from the soil.
- Through the process of photosynthesis, plants use the energy from sunlight to convert CO2 and H2O into glucose and oxygen (O2).
- The oxygen produced during photosynthesis is released into the atmosphere as a waste product.
Direct Association with Photosynthesis
- Oxygen is the waste product directly associated with photosynthesis in plants.
- It is a byproduct of the chemical reactions that occur during the process of photosynthesis.
- Oxygen is essential for the survival of most organisms on Earth, as it is used in cellular respiration to generate energy.
In conclusion, oxygen is the waste product directly associated with photosynthesis in plants. It is produced as a byproduct of the photosynthetic process and plays a crucial role in supporting life on Earth.
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose. This process relies on the presence of certain waste products and byproducts.
Oxygen Production
- During photosynthesis, plants take in carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere and water (H2O) from the soil.
- Through the process of photosynthesis, plants use the energy from sunlight to convert CO2 and H2O into glucose and oxygen (O2).
- The oxygen produced during photosynthesis is released into the atmosphere as a waste product.
Direct Association with Photosynthesis
- Oxygen is the waste product directly associated with photosynthesis in plants.
- It is a byproduct of the chemical reactions that occur during the process of photosynthesis.
- Oxygen is essential for the survival of most organisms on Earth, as it is used in cellular respiration to generate energy.
In conclusion, oxygen is the waste product directly associated with photosynthesis in plants. It is produced as a byproduct of the photosynthetic process and plays a crucial role in supporting life on Earth.
Exchange of gases in lung alveoli occurs through –- a)Active transport
- b)Osmosis
- c)Simple diffusion
- d)Passive transport
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Exchange of gases in lung alveoli occurs through –
a)
Active transport
b)
Osmosis
c)
Simple diffusion
d)
Passive transport

|
Ashok Pawar answered |
Because in alveoli( richly supplied with blood vessels), where oxygenated blood is present, is absorbed by haemoglobin, present in the RBC(Red Blood Cell). With the help of haemoglobin, the oxygenated blood is diffused in the whole body. Where on the other side, deoxygenated blood, which is present in the plasma, is reached to the alveoli and it absorbs by our lungs then finally the deoxygenated blood is exhaled by our nostrils. This is how alveoli helps for respiration with the help of diffusion in our lungs.
Which of the following statements about the breathing cycle is true?- a)The lungs are completely empty of air after exhalation.
- b)During the breathing cycle, air is taken in and let out, but the lungs always contain a residual volume of air.
- c)Residual volume refers to the air that is only present when the lungs are fully inflated.
- d)The residual volume of air prevents the absorption of oxygen.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements about the breathing cycle is true?
a)
The lungs are completely empty of air after exhalation.
b)
During the breathing cycle, air is taken in and let out, but the lungs always contain a residual volume of air.
c)
Residual volume refers to the air that is only present when the lungs are fully inflated.
d)
The residual volume of air prevents the absorption of oxygen.

|
Nk Classes answered |
Explanation of the Breathing Cycle:
- The lungs are never completely empty. After exhalation, a certain amount of air, known as residual volume, remains.
- This residual volume ensures that the lungs maintain structural integrity and continue to facilitate gas exchange.
- It is crucial for the lungs to always have some air to prevent collapse and to support the continual exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Which structure collects the filtrate in the kidneys?- a)Glomerulus
- b)Urethra
- c)Bowman's capsule
- d)Ureter
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which structure collects the filtrate in the kidneys?
a)
Glomerulus
b)
Urethra
c)
Bowman's capsule
d)
Ureter

|
Kamna Science Academy answered |
Bowman's capsule collects the filtrate from the glomerulus in the kidneys.
In anaerobic respiration –- a)O2 is given out
- b)CO2 is given out
- c)CO2 is taken in
- d)O2 is taken in
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In anaerobic respiration –
a)
O2 is given out
b)
CO2 is given out
c)
CO2 is taken in
d)
O2 is taken in
|
|
Esha nayar answered |
Understanding Anaerobic Respiration
Anaerobic respiration is a metabolic process that occurs in the absence of oxygen. It allows organisms to generate energy when oxygen is not available. This process is crucial for various organisms, especially in environments where oxygen levels are low.
Key Features of Anaerobic Respiration
- No Oxygen Utilization: Unlike aerobic respiration, anaerobic respiration does not use oxygen. As a result, oxygen is not taken in during this process.
- Production of Carbon Dioxide: One of the primary byproducts of anaerobic respiration is carbon dioxide (CO2). For example, in yeast, the process converts glucose into ethanol and carbon dioxide, which is why CO2 is released.
- Energy Yield: Anaerobic respiration produces less energy compared to aerobic respiration. While aerobic respiration yields about 36 ATP molecules from one glucose molecule, anaerobic respiration typically yields only 2 ATP molecules.
Examples of Anaerobic Respiration
- In Yeast: During fermentation, yeast converts sugars into alcohol and carbon dioxide. This is widely used in baking and brewing industries.
- In Muscle Cells: In humans, during intense exercise, muscle cells may rely on anaerobic respiration when oxygen levels are low, resulting in the production of lactic acid alongside carbon dioxide.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct answer to the question is option 'B' because, during anaerobic respiration, carbon dioxide is produced and released as a byproduct. Understanding this process is essential for appreciating how different organisms adapt to their environments and manage energy production.
Anaerobic respiration is a metabolic process that occurs in the absence of oxygen. It allows organisms to generate energy when oxygen is not available. This process is crucial for various organisms, especially in environments where oxygen levels are low.
Key Features of Anaerobic Respiration
- No Oxygen Utilization: Unlike aerobic respiration, anaerobic respiration does not use oxygen. As a result, oxygen is not taken in during this process.
- Production of Carbon Dioxide: One of the primary byproducts of anaerobic respiration is carbon dioxide (CO2). For example, in yeast, the process converts glucose into ethanol and carbon dioxide, which is why CO2 is released.
- Energy Yield: Anaerobic respiration produces less energy compared to aerobic respiration. While aerobic respiration yields about 36 ATP molecules from one glucose molecule, anaerobic respiration typically yields only 2 ATP molecules.
Examples of Anaerobic Respiration
- In Yeast: During fermentation, yeast converts sugars into alcohol and carbon dioxide. This is widely used in baking and brewing industries.
- In Muscle Cells: In humans, during intense exercise, muscle cells may rely on anaerobic respiration when oxygen levels are low, resulting in the production of lactic acid alongside carbon dioxide.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct answer to the question is option 'B' because, during anaerobic respiration, carbon dioxide is produced and released as a byproduct. Understanding this process is essential for appreciating how different organisms adapt to their environments and manage energy production.
The value of diastolic blood pressure is- a)120 mm Hg
- b)80 mm Hg
- c)120/80 mm Hg
- d)40 mm Hg
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The value of diastolic blood pressure is
a)
120 mm Hg
b)
80 mm Hg
c)
120/80 mm Hg
d)
40 mm Hg
|
|
Shalini Shalu..... answered |
A normal diastolic blood pressure is less than 80 mmHg... Thus , option B is right ans.
Which of the following statements about plant excretion is FALSE?- a)Plants excrete waste products into the soil
- b)Plants store waste products in cellular vacuoles
- c)Plants excrete urea and uric acid
- d)Plants can lose waste products through falling leaves
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements about plant excretion is FALSE?
a)
Plants excrete waste products into the soil
b)
Plants store waste products in cellular vacuoles
c)
Plants excrete urea and uric acid
d)
Plants can lose waste products through falling leaves

|
EduRev Class 10 answered |
Plants do not excrete urea and uric acid. These are nitrogenous wastes primarily excreted by animals. Plants handle waste products through vacuoles, fallen leaves, and excretion into the soil.
Which of the following statements is true about the energy released during respiration?- a)Anaerobic respiration releases more energy than aerobic respiration.
- b)Aerobic respiration releases more energy than anaerobic respiration.
- c)Both aerobic and anaerobic respiration release equal energy.
- d)No energy is released in either process.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is true about the energy released during respiration?
a)
Anaerobic respiration releases more energy than aerobic respiration.
b)
Aerobic respiration releases more energy than anaerobic respiration.
c)
Both aerobic and anaerobic respiration release equal energy.
d)
No energy is released in either process.

|
EduRev Class 10 answered |
Aerobic respiration releases more energy because glucose is completely broken down using oxygen.
In anaerobic respiration, glucose is only partially broken down, so less energy is released.
In anaerobic respiration, glucose is only partially broken down, so less energy is released.
Which among the following is NOT a function of the kidney- a)Elimination of urea and other nitrogenous wastes
- b)Maintenance of water balance
- c)Manufacture of antibodies
- d)Regulation of salt in the body E Formation of urine
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is NOT a function of the kidney
a)
Elimination of urea and other nitrogenous wastes
b)
Maintenance of water balance
c)
Manufacture of antibodies
d)
Regulation of salt in the body E Formation of urine
|
|
Jatya Arjilli answered |
As kidneys do not manufacture anti bodies.
hope this answer helps you out
hope this answer helps you out
Which structure in the human excretory system is responsible for storing urine until it is expelled from the body?- a)Kidney
- b)Ureter
- c)Urinary bladder
- d)Urethra
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which structure in the human excretory system is responsible for storing urine until it is expelled from the body?
a)
Kidney
b)
Ureter
c)
Urinary bladder
d)
Urethra
|
|
Rohit Patel answered |
Understanding the Human Excretory System
The human excretory system plays a crucial role in maintaining the body's internal balance by removing waste products and excess substances. Among its components, the urinary bladder is specifically responsible for storing urine until it is expelled from the body.
Key Structures of the Excretory System
- Kidney:
- The kidneys are vital organs that filter blood to produce urine. They remove waste and excess substances from the bloodstream.
- Ureter:
- The ureters are tubes that transport urine from each kidney to the urinary bladder. They do not store urine but are essential for its movement.
- Urinary Bladder:
- The urinary bladder is a muscular sac that temporarily holds urine. It can expand and contract, allowing it to accommodate varying volumes of urine. When the bladder is full, nerve signals prompt the urge to urinate, leading to the expulsion of urine.
- Urethra:
- The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. It plays a role in the final step of excretion but does not store urine.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct answer is option 'C', the urinary bladder, as it is specifically designed for storing urine until the body is ready to expel it. This organ's ability to stretch and hold urine is essential for the controlled release of waste, ensuring that excretion is managed effectively.
The human excretory system plays a crucial role in maintaining the body's internal balance by removing waste products and excess substances. Among its components, the urinary bladder is specifically responsible for storing urine until it is expelled from the body.
Key Structures of the Excretory System
- Kidney:
- The kidneys are vital organs that filter blood to produce urine. They remove waste and excess substances from the bloodstream.
- Ureter:
- The ureters are tubes that transport urine from each kidney to the urinary bladder. They do not store urine but are essential for its movement.
- Urinary Bladder:
- The urinary bladder is a muscular sac that temporarily holds urine. It can expand and contract, allowing it to accommodate varying volumes of urine. When the bladder is full, nerve signals prompt the urge to urinate, leading to the expulsion of urine.
- Urethra:
- The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. It plays a role in the final step of excretion but does not store urine.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct answer is option 'C', the urinary bladder, as it is specifically designed for storing urine until the body is ready to expel it. This organ's ability to stretch and hold urine is essential for the controlled release of waste, ensuring that excretion is managed effectively.
Arteries are best defined as the vessels which- a)Carry blood from one visceral organ to another visceral organ
- b)Supply blood to the different organs
- c)Break up into capillaries which reunite to form a vein
- d)Both B and C
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Arteries are best defined as the vessels which
a)
Carry blood from one visceral organ to another visceral organ
b)
Supply blood to the different organs
c)
Break up into capillaries which reunite to form a vein
d)
Both B and C
|
|
Rohit Sharma answered |
Arteries are the blood vessels which carry oxygenated blood from the heart to the organs. It breaks up into several branches of capillaries before entering the organs. These capillaries again reunite to form venules and ultimately veins which carry the deoxygenated blood towards the heart.
Choose the correct statement that describes arteries.- a)They have thick elastic walls, blood flows under high pressure; collect blood from different organs and bring it back to the heart.
- b)They have thin walls with valves inside, blood flows under low pressure and carries blood away from the heart to various organs of the body.
- c)They have thick elastic walls, blood flows under low pressure; carry blood from the heart to various organs of the body.
- d)They have thick elastic walls without valves inside, blood flows under high pressure and carries blood away from the heart to different parts of the body.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct statement that describes arteries.
a)
They have thick elastic walls, blood flows under high pressure; collect blood from different organs and bring it back to the heart.
b)
They have thin walls with valves inside, blood flows under low pressure and carries blood away from the heart to various organs of the body.
c)
They have thick elastic walls, blood flows under low pressure; carry blood from the heart to various organs of the body.
d)
They have thick elastic walls without valves inside, blood flows under high pressure and carries blood away from the heart to different parts of the body.
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Arteries are thick-walled blood vessels which pump blood at high pressure away from the heart. They do not have valves as their walls are highly muscular.
Assertion (A): The human excretory system is responsible for maintaining the right amount of water and ionic balance in the body.Reason (R): Kidneys perform osmoregulation in addition to filtering nitrogenous waste from the blood.- a)If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
- b)If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
- c)If Assertion is true but Reason is false
- d)If both Assertion and Reason are false
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): The human excretory system is responsible for maintaining the right amount of water and ionic balance in the body.
Reason (R): Kidneys perform osmoregulation in addition to filtering nitrogenous waste from the blood.
a)
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
b)
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
c)
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
d)
If both Assertion and Reason are false

|
EduRev Class 10 answered |
- Assertion: In this scenario, the Assertion is true as the kidneys do indeed play a vital role in osmoregulation, which involves maintaining the right balance of water and ions in the body.
- Reason: The Reason is also true since it correctly states that one of the main functions of the kidneys is osmoregulation along with filtering nitrogenous waste from the blood. Moreover, the Reason serves as a valid explanation for the Assertion, as the maintenance of water and ionic balance is directly linked to the osmoregulatory function of the kidneys.
- Hence, Option A is the correct answer.
Where organ helps in expelling urine out from the body?- a)Kidneys
- b)Ureters
- c)Urethra
- d)Urinary Bladder
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Where organ helps in expelling urine out from the body?
a)
Kidneys
b)
Ureters
c)
Urethra
d)
Urinary Bladder
|
|
Pragya shah answered |
Understanding the Urinary System
The urinary system plays a crucial role in maintaining the body's fluid balance and expelling waste. Each organ within this system has a specific function.
Key Organs Involved
- Kidneys:
- Function to filter blood, removing waste products and excess substances.
- Produce urine, which contains these waste products.
- Ureters:
- Tubes that transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
- They do not help in expelling urine but are essential for its movement.
- Urinary Bladder:
- A muscular sac that stores urine until it is ready to be expelled.
- It contracts to push urine into the urethra during urination.
- Urethra:
- The duct through which urine exits the body.
- Plays a direct role in the expulsion of urine.
Why Option 'C' is Correct
The correct answer is option 'C', the urethra, as it is the organ responsible for expelling urine from the body. Here’s how it works:
- The urinary bladder fills with urine and stretches.
- When it reaches a certain level, nerve signals prompt the bladder to contract.
- This contraction forces urine into the urethra.
- The urethra then opens, allowing urine to exit the body.
Conclusion
While other organs are vital for urine production and transportation, the urethra is the final pathway through which urine is expelled from the body, making it the correct answer to the question. Understanding these functions helps clarify the role of each organ in the urinary system.
The urinary system plays a crucial role in maintaining the body's fluid balance and expelling waste. Each organ within this system has a specific function.
Key Organs Involved
- Kidneys:
- Function to filter blood, removing waste products and excess substances.
- Produce urine, which contains these waste products.
- Ureters:
- Tubes that transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
- They do not help in expelling urine but are essential for its movement.
- Urinary Bladder:
- A muscular sac that stores urine until it is ready to be expelled.
- It contracts to push urine into the urethra during urination.
- Urethra:
- The duct through which urine exits the body.
- Plays a direct role in the expulsion of urine.
Why Option 'C' is Correct
The correct answer is option 'C', the urethra, as it is the organ responsible for expelling urine from the body. Here’s how it works:
- The urinary bladder fills with urine and stretches.
- When it reaches a certain level, nerve signals prompt the bladder to contract.
- This contraction forces urine into the urethra.
- The urethra then opens, allowing urine to exit the body.
Conclusion
While other organs are vital for urine production and transportation, the urethra is the final pathway through which urine is expelled from the body, making it the correct answer to the question. Understanding these functions helps clarify the role of each organ in the urinary system.
Raw materials required in the autotrophic mode of nutrition involves:i. Carbon dioxide and waterii. Chlorophylliii. Nitrogeniv. Sunlight- a)(i), (ii) and (iii)
- b)(i) and (ii)
- c)(i), (ii) and (iv)
- d)All (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Raw materials required in the autotrophic mode of nutrition involves:
i. Carbon dioxide and water
ii. Chlorophyll
iii. Nitrogen
iv. Sunlight
a)
(i), (ii) and (iii)
b)
(i) and (ii)
c)
(i), (ii) and (iv)
d)
All (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)

|
EduRev Class 10 answered |
The correct answer is:
c) (i), (ii) and (iv)
c) (i), (ii) and (iv)
Explanation:
In autotrophic mode of nutrition (like in green plants), organisms prepare their own food using simple substances from the surroundings through photosynthesis.
The main raw materials required are:
- (i) Carbon dioxide – from the atmosphere and Water – from the soil
- (ii) Chlorophyll – as the pigment necessary to capture sunlight
- (iv) Sunlight – as the energy source
Note:
Chlorophyll is not a "raw material" but a requirement for photosynthesis.
Nitrogen (iii) is essential for growth and protein synthesis, but not directly involved in the photosynthesis process.
Hence, option (c) is the most appropriate.
The manufactured food in a green plant moves from the leaves to other parts through________.- a)Xylem
- b)Phloem
- c)Cortex
- d)Pith
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The manufactured food in a green plant moves from the leaves to other parts through________.
a)
Xylem
b)
Phloem
c)
Cortex
d)
Pith
|
|
Meera Rana answered |
The sugars, synthesized in leaves (as a result of photosynthesis) are translocated downwards, upwards, and laterally to storage organs mainly through phloem. These sugars are translocated in the form of sucrose.
What does the milky appearance of lime water in the fermentation experiment indicate?
- a)Presence of oxygen in the solution
- b)Formation of a new chemical compound
- c)Release of carbon dioxide
- d)Increase in temperature of the solution
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer??
What does the milky appearance of lime water in the fermentation experiment indicate?
a)
Presence of oxygen in the solution
b)
Formation of a new chemical compound
c)
Release of carbon dioxide
d)
Increase in temperature of the solution
|
|
Shantala nair answered |
Understanding Lime Water in Fermentation
In the fermentation experiment, the milky appearance of lime water is a significant observation. This phenomenon is primarily due to the release of carbon dioxide during the fermentation process. Here’s a detailed explanation:
What is Lime Water?
- Lime water is a dilute solution of calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2).
- It is clear and colorless when undisturbed.
What Happens During Fermentation?
- Fermentation is a metabolic process where sugars are converted into alcohol or acids by microorganisms like yeast.
- During this process, carbon dioxide (CO2) is produced as a byproduct.
Formation of Calcium Carbonate
- When carbon dioxide is bubbled through lime water, it reacts with calcium hydroxide, forming calcium carbonate (CaCO3).
- The chemical reaction can be summarized as follows:
- Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 (precipitate) + H2O
Indication of Carbon Dioxide Release
- The formation of calcium carbonate is what causes the milky appearance of the lime water.
- The precipitate makes the solution appear cloudy or milky, indicating that carbon dioxide is present in the solution.
Conclusion: Why Option 'C' is Correct
- The milky appearance signifies the release of carbon dioxide during fermentation, confirming option 'C' as the correct answer.
- Thus, the observation serves as a practical indicator of the fermentation process occurring, validating the metabolic activity of the microorganisms involved.
In the fermentation experiment, the milky appearance of lime water is a significant observation. This phenomenon is primarily due to the release of carbon dioxide during the fermentation process. Here’s a detailed explanation:
What is Lime Water?
- Lime water is a dilute solution of calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2).
- It is clear and colorless when undisturbed.
What Happens During Fermentation?
- Fermentation is a metabolic process where sugars are converted into alcohol or acids by microorganisms like yeast.
- During this process, carbon dioxide (CO2) is produced as a byproduct.
Formation of Calcium Carbonate
- When carbon dioxide is bubbled through lime water, it reacts with calcium hydroxide, forming calcium carbonate (CaCO3).
- The chemical reaction can be summarized as follows:
- Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 (precipitate) + H2O
Indication of Carbon Dioxide Release
- The formation of calcium carbonate is what causes the milky appearance of the lime water.
- The precipitate makes the solution appear cloudy or milky, indicating that carbon dioxide is present in the solution.
Conclusion: Why Option 'C' is Correct
- The milky appearance signifies the release of carbon dioxide during fermentation, confirming option 'C' as the correct answer.
- Thus, the observation serves as a practical indicator of the fermentation process occurring, validating the metabolic activity of the microorganisms involved.
Chapter doubts & questions for Life Processes - Science Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Life Processes - Science Class 10 in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 10 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









