All Exams >
Humanities/Arts >
Political Science CUET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of The End of Bipolarity for Humanities/Arts Exam
Who took over as the only nuclear state of the post-soviet space?- a)Uzbekistan
- b)Ukraine
- c)Russia
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Who took over as the only nuclear state of the post-soviet space?
a)
Uzbekistan
b)
Ukraine
c)
Russia
d)
None
|
|
Pushkar Singh answered |
Russia.. there are many reson to become successor USSR
When did the socialist revolution take place in Russia?- a)1914
- b)1917
- c)1913
- d)1920
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When did the socialist revolution take place in Russia?
a)
1914
b)
1917
c)
1913
d)
1920
|
|
Soumya Bose answered |
The Socialist Revolution in Russia took place in 1917.
Background
- In 1914, Russia had entered World War I on the side of the Allies.
- The war brought about economic hardship, food shortages, and military casualties.
- These issues led to discontent among the Russian people and created an environment ripe for revolution.
February Revolution
- In February 1917, a series of protests and strikes broke out in Petrograd (now St. Petersburg), the capital of Russia.
- The protests were mainly led by workers and soldiers who were demanding better working conditions, higher wages, and an end to the war.
- The protests quickly spread throughout the city and eventually led to the overthrow of Tsar Nicholas II, who had been ruling Russia since 1894.
Provisional Government
- Following the Tsar's abdication, a Provisional Government was established to rule Russia until a new government could be formed.
- However, the Provisional Government was weak and ineffective, and it failed to address the main concerns of the Russian people.
October Revolution
- In October 1917, the Bolshevik Party, led by Vladimir Lenin, seized power from the Provisional Government in a coup d'état known as the October Revolution.
- The Bolsheviks established a new government based on Marxist principles, which became known as the Soviet Union.
- The October Revolution marked the beginning of the socialist revolution in Russia and led to significant changes in the country's political, social, and economic structures.
Conclusion
The Socialist Revolution in Russia took place in 1917, following a period of discontent and unrest among the Russian people. The February Revolution led to the overthrow of Tsar Nicholas II and the establishment of a weak Provisional Government. The October Revolution, led by the Bolshevik Party, marked the beginning of a new era in Russian history and the establishment of the Soviet Union.
Background
- In 1914, Russia had entered World War I on the side of the Allies.
- The war brought about economic hardship, food shortages, and military casualties.
- These issues led to discontent among the Russian people and created an environment ripe for revolution.
February Revolution
- In February 1917, a series of protests and strikes broke out in Petrograd (now St. Petersburg), the capital of Russia.
- The protests were mainly led by workers and soldiers who were demanding better working conditions, higher wages, and an end to the war.
- The protests quickly spread throughout the city and eventually led to the overthrow of Tsar Nicholas II, who had been ruling Russia since 1894.
Provisional Government
- Following the Tsar's abdication, a Provisional Government was established to rule Russia until a new government could be formed.
- However, the Provisional Government was weak and ineffective, and it failed to address the main concerns of the Russian people.
October Revolution
- In October 1917, the Bolshevik Party, led by Vladimir Lenin, seized power from the Provisional Government in a coup d'état known as the October Revolution.
- The Bolsheviks established a new government based on Marxist principles, which became known as the Soviet Union.
- The October Revolution marked the beginning of the socialist revolution in Russia and led to significant changes in the country's political, social, and economic structures.
Conclusion
The Socialist Revolution in Russia took place in 1917, following a period of discontent and unrest among the Russian people. The February Revolution led to the overthrow of Tsar Nicholas II and the establishment of a weak Provisional Government. The October Revolution, led by the Bolshevik Party, marked the beginning of a new era in Russian history and the establishment of the Soviet Union.
Study the cartoon given below and answer the following questions: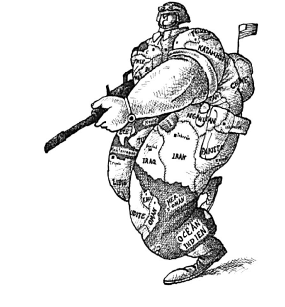 Q. Why have the names of so many countries been written on the uniform of the soldier?
Q. Why have the names of so many countries been written on the uniform of the soldier?- a)It symbolizes the union of these countries.
- b)It symbolizes the colonization of these countries by USA.
- c)USA has invaded these countries.
- d)None of the above.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the cartoon given below and answer the following questions:

Q. Why have the names of so many countries been written on the uniform of the soldier?
a)
It symbolizes the union of these countries.
b)
It symbolizes the colonization of these countries by USA.
c)
USA has invaded these countries.
d)
None of the above.

|
Trisha Vashisht answered |
(i) The United States of America is represented by this mighty soldier.
(ii) On 19 March 2003, the US launched its invasion of Iraq under the code name “Operation Iraqui Freedom”. More than forty other countries joined in the US-led invasion. The names of these countries have been written on this soldier’s uniform.
(iii) This cartoon shows that America is all powerful and can go to any extent to serve its interests. It attacked Iraq even after the UN refused to give its mandate to the invasion.
The Russian Revolution in 1917 was led by- a)Joseph Stalin.
- b)Nikita Khrushchev.
- c)Mikhail Gorbachev.
- d)Vladimir Ilyich Lenin.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The Russian Revolution in 1917 was led by
a)
Joseph Stalin.
b)
Nikita Khrushchev.
c)
Mikhail Gorbachev.
d)
Vladimir Ilyich Lenin.
|
|
Priyanka Chavan answered |
Vladimir Ilyich Lenin, the leader of Bolshevik Communist Party, led the Revolution of 1917. He was the founder head of the USSR.
The Chechens are- a)Bhuddhist group.
- b)Christain ethnic group.
- c)Jewish ethnic group.
- d)Muslim ethinic group.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The Chechens are
a)
Bhuddhist group.
b)
Christain ethnic group.
c)
Jewish ethnic group.
d)
Muslim ethinic group.
|
|
Kunal Verma answered |
The Chechens are a largely Muslim ethnic group that has lived for centuries in the mountainous Caucasus region.
Which was the first Soviet Republic to declare its independence from Soviet Russia?- a)Lithuania.
- b)Moldova.
- c)Armenia.
- d)Georgia.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which was the first Soviet Republic to declare its independence from Soviet Russia?
a)
Lithuania.
b)
Moldova.
c)
Armenia.
d)
Georgia.
|
|
Rohit Goyal answered |
In March 1990, Lithuania became the first of the 15 Soviet republics to declare its independence.
the cartoon given below and answer the following questions: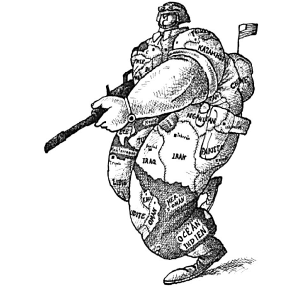 Q. Which country is represented by this mighty soldier?
Q. Which country is represented by this mighty soldier?- a)Russia
- b)China
- c)USA
- d)Canada
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
the cartoon given below and answer the following questions:

Q. Which country is represented by this mighty soldier?
a)
Russia
b)
China
c)
USA
d)
Canada
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
The United States of America is represented by this mighty soldier.
How many broad kinds of enduring changes resulted from the collapse of the second world of the soviet union?- a)Two
- b)Three
- c)Five
- d)Four
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How many broad kinds of enduring changes resulted from the collapse of the second world of the soviet union?
a)
Two
b)
Three
c)
Five
d)
Four
|
|
Anugya Dixit answered |
When second world of the soviet union was collapsed it resulted three broad kinds of enduring changes.
Read the following excerpt and answer the questions that follow:
The Soviet Union had become stagnant in an administrative and political sense as well. The Communist Party that had ruled the Soviet Union for over 70 years was not accountable to the people. Ordinary people were alienated by slow and stifling administration, rampant corruption, the inability of the system to correct mistakes it had made, the unwillingness to allow more openness in government, and the centralisation of authority in a vast land. Worse still, the party bureaucrats gained more privileges than ordinary citizens. People did not identify with the system and with the rulers, and the government increasingly lost popular backing. Gorbachev’s reforms promised to deal with these problems. Gorbachev promised to reform the economy, catch up with the West, and loosen the administrative system. All this might not have led to the collapse of the Soviet Union but for another development that surprised most observers and indeed many insiders. The rise of nationalism and the desire for sovereignty within various republics including Russia and the Baltic Republics (Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania), Ukraine, Georgia, and others proved to be the final and most immediate cause for the disintegration of the USSR.Q. What was the final and most immediate cause for the disintegration of Soviet Union?- a)The rise of nationalism and the desire for sovereignty within various republics including Russia and the Baltic Republics, Ukraine, Georgia, and others.
- b)The rise of extremism and the desire for privatization within various republics including Russia and the Baltic Republics, Ukraine, Georgia, and others.
- c)The rise of capitalism and the desire for democratic government within various republics including Russia and the Baltic Republics, Ukraine, Georgia, and others.
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following excerpt and answer the questions that follow:
The Soviet Union had become stagnant in an administrative and political sense as well. The Communist Party that had ruled the Soviet Union for over 70 years was not accountable to the people. Ordinary people were alienated by slow and stifling administration, rampant corruption, the inability of the system to correct mistakes it had made, the unwillingness to allow more openness in government, and the centralisation of authority in a vast land. Worse still, the party bureaucrats gained more privileges than ordinary citizens. People did not identify with the system and with the rulers, and the government increasingly lost popular backing. Gorbachev’s reforms promised to deal with these problems. Gorbachev promised to reform the economy, catch up with the West, and loosen the administrative system. All this might not have led to the collapse of the Soviet Union but for another development that surprised most observers and indeed many insiders. The rise of nationalism and the desire for sovereignty within various republics including Russia and the Baltic Republics (Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania), Ukraine, Georgia, and others proved to be the final and most immediate cause for the disintegration of the USSR.
The Soviet Union had become stagnant in an administrative and political sense as well. The Communist Party that had ruled the Soviet Union for over 70 years was not accountable to the people. Ordinary people were alienated by slow and stifling administration, rampant corruption, the inability of the system to correct mistakes it had made, the unwillingness to allow more openness in government, and the centralisation of authority in a vast land. Worse still, the party bureaucrats gained more privileges than ordinary citizens. People did not identify with the system and with the rulers, and the government increasingly lost popular backing. Gorbachev’s reforms promised to deal with these problems. Gorbachev promised to reform the economy, catch up with the West, and loosen the administrative system. All this might not have led to the collapse of the Soviet Union but for another development that surprised most observers and indeed many insiders. The rise of nationalism and the desire for sovereignty within various republics including Russia and the Baltic Republics (Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania), Ukraine, Georgia, and others proved to be the final and most immediate cause for the disintegration of the USSR.
Q. What was the final and most immediate cause for the disintegration of Soviet Union?
a)
The rise of nationalism and the desire for sovereignty within various republics including Russia and the Baltic Republics, Ukraine, Georgia, and others.
b)
The rise of extremism and the desire for privatization within various republics including Russia and the Baltic Republics, Ukraine, Georgia, and others.
c)
The rise of capitalism and the desire for democratic government within various republics including Russia and the Baltic Republics, Ukraine, Georgia, and others.
d)
All of the above
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
The rise of nationalism and the desire for sovereignty within various republics including Russia and the Baltic Republic (Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania), Ukraine, Georgia and others proved to be the most immediate cause for disintegration of the USSR.
When did the Soviet Union collapse?- a)1989
- b)1990
- c)1991
- d)1992
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When did the Soviet Union collapse?
a)
1989
b)
1990
c)
1991
d)
1992
|
|
Anmol Rane answered |
In December 1991, Second World the Soviet Union collapsed.
The USSR came into being after the Socialist Revolution in Russia in the year- a)1915.
- b)1916.
- c)1917.
- d)1918.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The USSR came into being after the Socialist Revolution in Russia in the year
a)
1915.
b)
1916.
c)
1917.
d)
1918.
|
|
Milan Das answered |
The revolution was inspired by the ideals of socialism, as opposed to capitalism and the need for an egalitarian society.
Who promised to reform the economy, catch up with the west, and loosen the administrative system?- a)Yeltsin
- b)Khosrove
- c)Collier
- d)Gorbachev
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Who promised to reform the economy, catch up with the west, and loosen the administrative system?
a)
Yeltsin
b)
Khosrove
c)
Collier
d)
Gorbachev
|
|
Pj Commerce Academy answered |
Who promised to reform the economy, catch up with the west, and loosen the administrative system?
Answer: d. Gorbachev
- Background: Mikhail Gorbachev was a Soviet politician who served as the General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1985 until 1991.
- Economic Reform: Gorbachev promised to reform the Soviet economy through policies such as perestroika, which aimed to restructure and modernize the economy.
- Catching up with the West: Gorbachev recognized the need for the Soviet Union to catch up with Western countries in terms of technology, productivity, and living standards.
- Loosening Administrative System: Gorbachev also implemented policies like glasnost, which aimed to increase transparency and openness in the political system, loosening the strict control of the Communist Party.
Overall, Gorbachev's promises to reform the economy, catch up with the West, and loosen the administrative system were part of his efforts to modernize the Soviet Union and address its economic and political challenges.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Q. Assertion: Shock Therapy was the transitional form from authoritarian socialist system to a democratic capitalist system in Russia, Central Asia and East Europe under the influence of the World Bank and IMF.Reason: The model of transition in Russia, Central Asia and east Europe that was influenced by the World Bank and the IMF came to be known as ‘Shock therapy’.- a)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- b)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- c)(A) is true, but (R) is false.
- d)(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Q. Assertion: Shock Therapy was the transitional form from authoritarian socialist system to a democratic capitalist system in Russia, Central Asia and East Europe under the influence of the World Bank and IMF.
Reason: The model of transition in Russia, Central Asia and east Europe that was influenced by the World Bank and the IMF came to be known as ‘Shock therapy’.
a)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c)
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
d)
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
|
|
Arjun Singhania answered |
Assertion (A) is a statement about the role of Shock Therapy in the transition from authoritarian socialist systems to democratic capitalist systems in Russia, Central Asia, and Eastern Europe. Reason (R) is a statement about the origin of the term "Shock Therapy" and how it relates to this transition process.
Both (A) and (R) are true statements. Assertion (A) accurately describes the role of Shock Therapy in the transition process, and Reason (R) accurately explains the origin of the term and how it is related to this process. Therefore, the correct choice is (a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Q. Assertion: Gorbachev did nothing to save the disintegration of soviet system.Reason: These developments were accompanied by a rapidly escalating crisis within the USSR that hastened its disintegration.- a)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- b)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- c)(A) is true, but (R) is false.
- d)(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Q. Assertion: Gorbachev did nothing to save the disintegration of soviet system.
Reason: These developments were accompanied by a rapidly escalating crisis within the USSR that hastened its disintegration.
a)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c)
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
d)
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
|
|
Arun Yadav answered |
Gorbachev passed many reforms to revitalize the disintegrating Soviet system. But the bureaucrats never supported the reforms. Moreover, corruption and distrust of the people contributed in the decline of USSR.
Read the following excerpt and answer the questions that follow:
Economist Jeffrey Sachs is widely associated with shock therapy. He developed a plan of shock therapy for post-communist Poland in 1990, for post-communist Russia in 1992, and several other countries, including Bolivia and Chile. Bolivia, in particular, in 1985, had success as a result of shock therapy in ending a period of hyperinflation.Poland also initially seemed to benefit from shock therapy as inflation was controlled, but it saw a sharp rise in unemployment that peaked at 16.9%. Sachs did not like the term shock therapy, which he said was coined by the media and made the reform process sound more painful than it was.In Russia, neo- liberal shock therapy did not produce favourable outcomes. Shock therapy was applied swiftly and on a large scale, as opposed to how it was applied in other nations. Almost all of Russia’s industries were undervalued and sold to private individuals and companies, with most acquired by a few Russian oligarchs.With limited government intervention, most industries disappeared. The Russian currency declined, causing high inflation and the erosion of most citizens’ savings. Unemployment increased drastically, and government subsidies were removed, further pushing Russian families into poverty.Q. What happened in Poland after the initial success of the shock therapy?- a)Rise in the commodity prices
- b)Economy declines
- c)Rise in the unemployment rate
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following excerpt and answer the questions that follow:
Economist Jeffrey Sachs is widely associated with shock therapy. He developed a plan of shock therapy for post-communist Poland in 1990, for post-communist Russia in 1992, and several other countries, including Bolivia and Chile. Bolivia, in particular, in 1985, had success as a result of shock therapy in ending a period of hyperinflation.
Economist Jeffrey Sachs is widely associated with shock therapy. He developed a plan of shock therapy for post-communist Poland in 1990, for post-communist Russia in 1992, and several other countries, including Bolivia and Chile. Bolivia, in particular, in 1985, had success as a result of shock therapy in ending a period of hyperinflation.
Poland also initially seemed to benefit from shock therapy as inflation was controlled, but it saw a sharp rise in unemployment that peaked at 16.9%. Sachs did not like the term shock therapy, which he said was coined by the media and made the reform process sound more painful than it was.
In Russia, neo- liberal shock therapy did not produce favourable outcomes. Shock therapy was applied swiftly and on a large scale, as opposed to how it was applied in other nations. Almost all of Russia’s industries were undervalued and sold to private individuals and companies, with most acquired by a few Russian oligarchs.
With limited government intervention, most industries disappeared. The Russian currency declined, causing high inflation and the erosion of most citizens’ savings. Unemployment increased drastically, and government subsidies were removed, further pushing Russian families into poverty.
Q. What happened in Poland after the initial success of the shock therapy?
a)
Rise in the commodity prices
b)
Economy declines
c)
Rise in the unemployment rate
d)
All of the above
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Poland has been cited by some[according to whom] as an example of the successful use of shock therapy, though this is disputed. When economic liberalism came to this nation, the government took Sachs' advice and immediately withdrew regulations, price controls and subsidies to state-owned industries. However, with respect to the privatization of the state sector (which may or may not be considered as part of shock therapy depending on the definition being used) the change was much more gradualist.
Read the following excerpt and answer the questions that follow:
A coup took place in 1991 that was encouraged by Communist Party hard-liners. The people had tasted freedom by then and did not want the oldstyle rule of the Communist Party. Boris Yeltsin emerged as a national hero in opposing this coup. The Russian Republic, where Yeltsin won a popular election, began to shake off centralised control. Power began to shift from the Soviet centre to the republics, especially in the more Europeanised part of the Soviet Union, which saw themselves as sovereign states. The Central Asian republics did not ask for independence and wanted to remain with the Soviet Federation. In December 1991, under the leadership of Yeltsin, Russia, Ukraine and Belarus, three major republics of the USSR, declared that the Soviet Union was disbanded. The Communist Party of the Soviet Union was banned. Capitalism and democracy were adopted as the bases for the post-Soviet republics. The declaration on the disintegration of the USSR and the formation of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) came as a surprise to the other republics, especially to the Central Asian ones. The exclusion of these republics was an issue that was quickly solved by making them founding members of the CIS. Russia was now accepted as the successor state of the Soviet Union. It inherited the Soviet seat in the UN Security Council. Russia accepted all the international treaties and commitments of the Soviet Union. It took over as the only nuclear state of the post-Soviet space and carried out some nuclear disarmament measures with the US. The old Soviet Union was thus dead and buried.Q. Which country became the successor state of the Soviet Union?- a)Belarus
- b)Ukraine
- c)Central Asian Republics
- d)Russia
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following excerpt and answer the questions that follow:
A coup took place in 1991 that was encouraged by Communist Party hard-liners. The people had tasted freedom by then and did not want the oldstyle rule of the Communist Party. Boris Yeltsin emerged as a national hero in opposing this coup. The Russian Republic, where Yeltsin won a popular election, began to shake off centralised control. Power began to shift from the Soviet centre to the republics, especially in the more Europeanised part of the Soviet Union, which saw themselves as sovereign states. The Central Asian republics did not ask for independence and wanted to remain with the Soviet Federation. In December 1991, under the leadership of Yeltsin, Russia, Ukraine and Belarus, three major republics of the USSR, declared that the Soviet Union was disbanded. The Communist Party of the Soviet Union was banned. Capitalism and democracy were adopted as the bases for the post-Soviet republics. The declaration on the disintegration of the USSR and the formation of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) came as a surprise to the other republics, especially to the Central Asian ones. The exclusion of these republics was an issue that was quickly solved by making them founding members of the CIS. Russia was now accepted as the successor state of the Soviet Union. It inherited the Soviet seat in the UN Security Council. Russia accepted all the international treaties and commitments of the Soviet Union. It took over as the only nuclear state of the post-Soviet space and carried out some nuclear disarmament measures with the US. The old Soviet Union was thus dead and buried.
A coup took place in 1991 that was encouraged by Communist Party hard-liners. The people had tasted freedom by then and did not want the oldstyle rule of the Communist Party. Boris Yeltsin emerged as a national hero in opposing this coup. The Russian Republic, where Yeltsin won a popular election, began to shake off centralised control. Power began to shift from the Soviet centre to the republics, especially in the more Europeanised part of the Soviet Union, which saw themselves as sovereign states. The Central Asian republics did not ask for independence and wanted to remain with the Soviet Federation. In December 1991, under the leadership of Yeltsin, Russia, Ukraine and Belarus, three major republics of the USSR, declared that the Soviet Union was disbanded. The Communist Party of the Soviet Union was banned. Capitalism and democracy were adopted as the bases for the post-Soviet republics. The declaration on the disintegration of the USSR and the formation of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) came as a surprise to the other republics, especially to the Central Asian ones. The exclusion of these republics was an issue that was quickly solved by making them founding members of the CIS. Russia was now accepted as the successor state of the Soviet Union. It inherited the Soviet seat in the UN Security Council. Russia accepted all the international treaties and commitments of the Soviet Union. It took over as the only nuclear state of the post-Soviet space and carried out some nuclear disarmament measures with the US. The old Soviet Union was thus dead and buried.
Q. Which country became the successor state of the Soviet Union?
a)
Belarus
b)
Ukraine
c)
Central Asian Republics
d)
Russia
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
With the dissolution of the USSR in 1991, the United States considered the Russian Federation as the successor state of the USSR.
Read the following excerpt and answer the questions that follow:
The Soviet Union had become stagnant in an administrative and political sense as well. The Communist Party that had ruled the Soviet Union for over 70 years was not accountable to the people. Ordinary people were alienated by slow and stifling administration, rampant corruption, the inability of the system to correct mistakes it had made, the unwillingness to allow more openness in government, and the centralisation of authority in a vast land. Worse still, the party bureaucrats gained more privileges than ordinary citizens. People did not identify with the system and with the rulers, and the government increasingly lost popular backing. Gorbachev’s reforms promised to deal with these problems. Gorbachev promised to reform the economy, catch up with the West, and loosen the administrative system. All this might not have led to the collapse of the Soviet Union but for another development that surprised most observers and indeed many insiders. The rise of nationalism and the desire for sovereignty within various republics including Russia and the Baltic Republics (Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania), Ukraine, Georgia, and others proved to be the final and most immediate cause for the disintegration of the USSR.Q. What led to the collapse of the Soviet System?- a)Because of its failure in World War Two
- b)Because people did not identify with the system
- c)Because of its extreme bureaucratic nature
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following excerpt and answer the questions that follow:
The Soviet Union had become stagnant in an administrative and political sense as well. The Communist Party that had ruled the Soviet Union for over 70 years was not accountable to the people. Ordinary people were alienated by slow and stifling administration, rampant corruption, the inability of the system to correct mistakes it had made, the unwillingness to allow more openness in government, and the centralisation of authority in a vast land. Worse still, the party bureaucrats gained more privileges than ordinary citizens. People did not identify with the system and with the rulers, and the government increasingly lost popular backing. Gorbachev’s reforms promised to deal with these problems. Gorbachev promised to reform the economy, catch up with the West, and loosen the administrative system. All this might not have led to the collapse of the Soviet Union but for another development that surprised most observers and indeed many insiders. The rise of nationalism and the desire for sovereignty within various republics including Russia and the Baltic Republics (Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania), Ukraine, Georgia, and others proved to be the final and most immediate cause for the disintegration of the USSR.
The Soviet Union had become stagnant in an administrative and political sense as well. The Communist Party that had ruled the Soviet Union for over 70 years was not accountable to the people. Ordinary people were alienated by slow and stifling administration, rampant corruption, the inability of the system to correct mistakes it had made, the unwillingness to allow more openness in government, and the centralisation of authority in a vast land. Worse still, the party bureaucrats gained more privileges than ordinary citizens. People did not identify with the system and with the rulers, and the government increasingly lost popular backing. Gorbachev’s reforms promised to deal with these problems. Gorbachev promised to reform the economy, catch up with the West, and loosen the administrative system. All this might not have led to the collapse of the Soviet Union but for another development that surprised most observers and indeed many insiders. The rise of nationalism and the desire for sovereignty within various republics including Russia and the Baltic Republics (Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania), Ukraine, Georgia, and others proved to be the final and most immediate cause for the disintegration of the USSR.
Q. What led to the collapse of the Soviet System?
a)
Because of its failure in World War Two
b)
Because people did not identify with the system
c)
Because of its extreme bureaucratic nature
d)
All of the above
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
The Soviet system became so weak and Soviet economy stagnant due to the following reasons
(i) The Soviet economy used much of its resources in maintaining nuclear and military arsenals.
(ii) Ordinary citizens became more knowledgeable about the economic advancement of the West and backwardness of Soviet system.
Which of the following statements about the Soviet political system is incorrect- a)The Communist Party controlled all institutions
- b)Democracy and political opposition were allowed
- c)The economy was state-controlled and planned
- d)The Soviet Union had a one-party system
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements about the Soviet political system is incorrect
a)
The Communist Party controlled all institutions
b)
Democracy and political opposition were allowed
c)
The economy was state-controlled and planned
d)
The Soviet Union had a one-party system

|
K.L Institute answered |
The Soviet political system had several defining characteristics:
- The Communist Party had control over all institutions, ensuring a unified direction according to its policies.
- There was a one-party system, meaning no other political parties were allowed to compete for power.
- The economy was state-controlled and planned, with the government making all major economic decisions.
- Democracy and political opposition were not allowed, contrary to the principles of a democratic political system.
Therefore, Correct Answer- Option B
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Q. Assertion: Cold War had a great cost on the economy of the country.Reason: In the arms race, the Soviet Union managed to match the US from time to time.- a)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- b)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- c)(A) is true, but (R) is false.
- d)(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Q. Assertion: Cold War had a great cost on the economy of the country.
Reason: In the arms race, the Soviet Union managed to match the US from time to time.
a)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c)
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
d)
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Though Soviet Union was giving a tough rivalry to US in Cold War, it had economic consequences. But, Russia was not weaker in any sense than US in the Cold War era.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Q. Assertion: After the Second World War, the east European countries that the Soviet Army had liberated from the fascist forces came under the control of the USSR.
Reason: The Soviet System, however, became very bureaucratic and authoritarian, making life very difficult for its citizens.- a)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- b)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- c)(A) is true, but (R) is false.
- d)(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Q. Assertion: After the Second World War, the east European countries that the Soviet Army had liberated from the fascist forces came under the control of the USSR.
Reason: The Soviet System, however, became very bureaucratic and authoritarian, making life very difficult for its citizens.
Reason: The Soviet System, however, became very bureaucratic and authoritarian, making life very difficult for its citizens.
a)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c)
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
d)
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
USSR emerged as two of the most powerful blocs. Many countries after Second World War adopted Soviet system. Russia was in control of this bloc.
Who emerged as a national hero in opposing the coup?- a)Mikhail Gorbachev
- b)Kenedy
- c)Ambedkar
- d)Boris Yeltsin
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Who emerged as a national hero in opposing the coup?
a)
Mikhail Gorbachev
b)
Kenedy
c)
Ambedkar
d)
Boris Yeltsin
|
|
Shruti Joshi answered |
Boris Yeltsin emerged as a national hero in opposing the coup in the Soviet Union.
Background:
• In August 1991, a group of Soviet hardliners attempted a coup to remove Soviet President Mikhail Gorbachev from power.
• The coup was led by Communist Party officials who were opposed to Gorbachev's reforms and wanted to restore the Soviet Union to its former state.
• The coup failed due to mass protests and resistance from the public, including Boris Yeltsin, who was the President of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic at the time.
Boris Yeltsin's Role:
• Yeltsin was a vocal critic of the coup from the beginning and was instrumental in organizing and leading the resistance against it.
• He addressed the crowds gathered in Moscow, calling for a general strike and urging the military to join the resistance.
• Yeltsin also climbed onto a tank outside the Russian White House, the seat of the Russian government, to address the crowds and show his defiance against the coup leaders.
• His bravery and leadership during the coup earned him widespread admiration and support from the public, and he emerged as a national hero.
Aftermath:
• The coup ultimately failed, and Gorbachev was restored to power.
• However, the coup's failure was a turning point in the collapse of the Soviet Union, as it revealed the deep divisions within the Communist Party and the military.
• Yeltsin's role in opposing the coup helped to elevate his profile and boost his political career, leading to his election as the first President of the Russian Federation in 1991.
• Yeltsin's opposition to the coup also paved the way for the eventual dissolution of the Soviet Union and the emergence of Russia as an independent state.
Background:
• In August 1991, a group of Soviet hardliners attempted a coup to remove Soviet President Mikhail Gorbachev from power.
• The coup was led by Communist Party officials who were opposed to Gorbachev's reforms and wanted to restore the Soviet Union to its former state.
• The coup failed due to mass protests and resistance from the public, including Boris Yeltsin, who was the President of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic at the time.
Boris Yeltsin's Role:
• Yeltsin was a vocal critic of the coup from the beginning and was instrumental in organizing and leading the resistance against it.
• He addressed the crowds gathered in Moscow, calling for a general strike and urging the military to join the resistance.
• Yeltsin also climbed onto a tank outside the Russian White House, the seat of the Russian government, to address the crowds and show his defiance against the coup leaders.
• His bravery and leadership during the coup earned him widespread admiration and support from the public, and he emerged as a national hero.
Aftermath:
• The coup ultimately failed, and Gorbachev was restored to power.
• However, the coup's failure was a turning point in the collapse of the Soviet Union, as it revealed the deep divisions within the Communist Party and the military.
• Yeltsin's role in opposing the coup helped to elevate his profile and boost his political career, leading to his election as the first President of the Russian Federation in 1991.
• Yeltsin's opposition to the coup also paved the way for the eventual dissolution of the Soviet Union and the emergence of Russia as an independent state.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Q. Assertion: Development was now envisaged through more trade, and thus a sudden and complete switch to free trade was considered essential.
Reason: Shock therapy also involved a drastic change in the external orientation of these economies.- a)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- b)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- c)(A) is true, but (R) is false.
- d)(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Q. Assertion: Development was now envisaged through more trade, and thus a sudden and complete switch to free trade was considered essential.
Reason: Shock therapy also involved a drastic change in the external orientation of these economies.
Reason: Shock therapy also involved a drastic change in the external orientation of these economies.
a)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c)
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
d)
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
They needed a change in all the aspects of the post-soviet nations. Hence, Shock Therapy demanded the changes which in turn anticipated a united contribution of the nations.
Read the following excerpt and answer the questions that follow:
Economist Jeffrey Sachs is widely associated with shock therapy. He developed a plan of shock therapy for post-communist Poland in 1990, for post-communist Russia in 1992, and several other countries, including Bolivia and Chile. Bolivia, in particular, in 1985, had success as a result of shock therapy in ending a period of hyperinflation.Poland also initially seemed to benefit from shock therapy as inflation was controlled, but it saw a sharp rise in unemployment that peaked at 16.9%. Sachs did not like the term shock therapy, which he said was coined by the media and made the reform process sound more painful than it was.In Russia, neo- liberal shock therapy did not produce favourable outcomes. Shock therapy was applied swiftly and on a large scale, as opposed to how it was applied in other nations. Almost all of Russia’s industries were undervalued and sold to private individuals and companies, with most acquired by a few Russian oligarchs.With limited government intervention, most industries disappeared. The Russian currency declined, causing high inflation and the erosion of most citizens’ savings. Unemployment increased drastically, and government subsidies were removed, further pushing Russian families into poverty.Q. Which country benefited with the Shock therapy in 1985?- a)Bolivia
- b)Poland
- c)Ukraine
- d)Russia
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following excerpt and answer the questions that follow:
Economist Jeffrey Sachs is widely associated with shock therapy. He developed a plan of shock therapy for post-communist Poland in 1990, for post-communist Russia in 1992, and several other countries, including Bolivia and Chile. Bolivia, in particular, in 1985, had success as a result of shock therapy in ending a period of hyperinflation.
Economist Jeffrey Sachs is widely associated with shock therapy. He developed a plan of shock therapy for post-communist Poland in 1990, for post-communist Russia in 1992, and several other countries, including Bolivia and Chile. Bolivia, in particular, in 1985, had success as a result of shock therapy in ending a period of hyperinflation.
Poland also initially seemed to benefit from shock therapy as inflation was controlled, but it saw a sharp rise in unemployment that peaked at 16.9%. Sachs did not like the term shock therapy, which he said was coined by the media and made the reform process sound more painful than it was.
In Russia, neo- liberal shock therapy did not produce favourable outcomes. Shock therapy was applied swiftly and on a large scale, as opposed to how it was applied in other nations. Almost all of Russia’s industries were undervalued and sold to private individuals and companies, with most acquired by a few Russian oligarchs.
With limited government intervention, most industries disappeared. The Russian currency declined, causing high inflation and the erosion of most citizens’ savings. Unemployment increased drastically, and government subsidies were removed, further pushing Russian families into poverty.
Q. Which country benefited with the Shock therapy in 1985?
a)
Bolivia
b)
Poland
c)
Ukraine
d)
Russia
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Bolivia, in particular, in 1985, had success as a result of shock therapy in ending a period of hyperinflation. Poland also initially seemed to benefit from shock therapy as inflation was controlled, but it saw a sharp rise in unemployment that peaked at 16.9%.
Read the following excerpt and answer the questions that follow:
Economist Jeffrey Sachs is widely associated with shock therapy. He developed a plan of shock therapy for post-communist Poland in 1990, for post-communist Russia in 1992, and several other countries, including Bolivia and Chile. Bolivia, in particular, in 1985, had success as a result of shock therapy in ending a period of hyperinflation.Poland also initially seemed to benefit from shock therapy as inflation was controlled, but it saw a sharp rise in unemployment that peaked at 16.9%. Sachs did not like the term shock therapy, which he said was coined by the media and made the reform process sound more painful than it was.In Russia, neo- liberal shock therapy did not produce favourable outcomes. Shock therapy was applied swiftly and on a large scale, as opposed to how it was applied in other nations. Almost all of Russia’s industries were undervalued and sold to private individuals and companies, with most acquired by a few Russian oligarchs.With limited government intervention, most industries disappeared. The Russian currency declined, causing high inflation and the erosion of most citizens’ savings. Unemployment increased drastically, and government subsidies were removed, further pushing Russian families into poverty.Q. What was the aftermath of the shock therapy in Russia?- a)Rise in the economy and in currency value.
- b)Decline in the unemployment rate and boosting economy.
- c)Improvement in people’s income and life style
- d)Decline in the currency, increasing unemployment, high inflation and decrease in people’s incomes.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following excerpt and answer the questions that follow:
Economist Jeffrey Sachs is widely associated with shock therapy. He developed a plan of shock therapy for post-communist Poland in 1990, for post-communist Russia in 1992, and several other countries, including Bolivia and Chile. Bolivia, in particular, in 1985, had success as a result of shock therapy in ending a period of hyperinflation.
Economist Jeffrey Sachs is widely associated with shock therapy. He developed a plan of shock therapy for post-communist Poland in 1990, for post-communist Russia in 1992, and several other countries, including Bolivia and Chile. Bolivia, in particular, in 1985, had success as a result of shock therapy in ending a period of hyperinflation.
Poland also initially seemed to benefit from shock therapy as inflation was controlled, but it saw a sharp rise in unemployment that peaked at 16.9%. Sachs did not like the term shock therapy, which he said was coined by the media and made the reform process sound more painful than it was.
In Russia, neo- liberal shock therapy did not produce favourable outcomes. Shock therapy was applied swiftly and on a large scale, as opposed to how it was applied in other nations. Almost all of Russia’s industries were undervalued and sold to private individuals and companies, with most acquired by a few Russian oligarchs.
With limited government intervention, most industries disappeared. The Russian currency declined, causing high inflation and the erosion of most citizens’ savings. Unemployment increased drastically, and government subsidies were removed, further pushing Russian families into poverty.
Q. What was the aftermath of the shock therapy in Russia?
a)
Rise in the economy and in currency value.
b)
Decline in the unemployment rate and boosting economy.
c)
Improvement in people’s income and life style
d)
Decline in the currency, increasing unemployment, high inflation and decrease in people’s incomes.
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
In Russia, the state-controlled industrial sector lost 90% of its industries. The industries were sold to private individuals and companies.
Read the following cartoon and answer the following questions: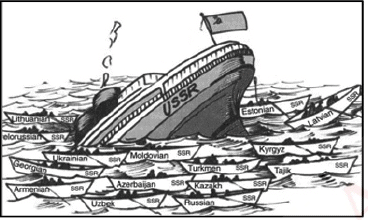 Q. How many countries did the Soviet Union disintegrate?
Q. How many countries did the Soviet Union disintegrate?- a)15
- b)14
- c)13
- d)18
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following cartoon and answer the following questions:

Q. How many countries did the Soviet Union disintegrate?
a)
15
b)
14
c)
13
d)
18
|
|
Ojasvi Mehta answered |
This disintegration emerged in many new countries dividing the Soviet Union into 15 independent countries alongwith their own aspirations and choices.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Q. Assertion: The hydrocarbon resources have brought an enormous prosperity to these countries. KReason: The Central Asian Republics are areas with vast hydrocarbon resources.- a)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- b)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- c)(A) is true, but (R) is false.
- d)(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Q. Assertion: The hydrocarbon resources have brought an enormous prosperity to these countries. K
Reason: The Central Asian Republics are areas with vast hydrocarbon resources.
a)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c)
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
d)
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
After the Soviet breakup, Central Asia has gained importance for several States because of its geographical location and abundance of hydrocarbon reserves. These hydrocarbon reserves are located mainly in three countries: Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Q. Assertion: Each state from this bloc was now linked directly to the West and not to each other in the region.Reason: The transition also involved a breakup of the existing trade alliances among the countries of the Soviet bloc.- a)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- b)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- c)(A) is true, but (R) is false.
- d)(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Q. Assertion: Each state from this bloc was now linked directly to the West and not to each other in the region.
Reason: The transition also involved a breakup of the existing trade alliances among the countries of the Soviet bloc.
a)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c)
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
d)
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
This was the real situation of the post-soviet countries. On the one hand, there was a new hope, but on the other, a painstaking task to apply the changes which had possibilities of bringing hard times.
What party had ruled the soviet union for over 70 years?- a)Fascist
- b)Socialist
- c)Democrat
- d)Communist
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What party had ruled the soviet union for over 70 years?
a)
Fascist
b)
Socialist
c)
Democrat
d)
Communist
|
|
Mainak Goyal answered |
Overview of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union was a socialist state that existed from 1922 until its dissolution in 1991. The Communist Party was the ruling political party throughout this entire period.
Key Points about the Communist Party’s Rule
Conclusion
The Communist Party's dominance in the Soviet Union for over 70 years shaped not only the nation but also had lasting impacts on global politics and the ideological landscape of the 20th century.
The Soviet Union was a socialist state that existed from 1922 until its dissolution in 1991. The Communist Party was the ruling political party throughout this entire period.
Key Points about the Communist Party’s Rule
- Ideological Foundation: The Communist Party was built on Marxist-Leninist ideology, which advocated for a classless society and the abolition of private property.
- Single-Party System: The Soviet Union was a single-party state, meaning that no other political parties were allowed to operate, consolidating power within the Communist Party.
- Leadership and Governance: The party led all aspects of governance, from economic planning to social policies, which were aimed at achieving a communist society.
- Historical Context: The party came to power following the Russian Revolution in 1917, overthrowing the provisional government and establishing a communist regime.
- Duration of Rule: The Communist Party maintained control for over 70 years, influencing global politics, economics, and social structures during that time.
- End of the Era: The dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991 marked the end of the Communist Party's rule, leading to the emergence of multiple independent nations.
Conclusion
The Communist Party's dominance in the Soviet Union for over 70 years shaped not only the nation but also had lasting impacts on global politics and the ideological landscape of the 20th century.
Read the following cartoon and answer the following questions: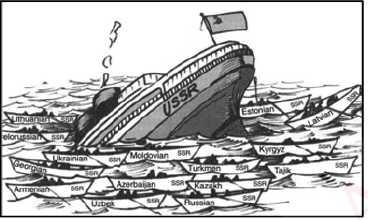 Q. What event officially marked the end of communism in the Soviet Union?
Q. What event officially marked the end of communism in the Soviet Union?- a)End of Cuban Missile Crisis
- b)Rise of New World Order
- c)The failed August Coup
- d)Rise in US economy
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following cartoon and answer the following questions:

Q. What event officially marked the end of communism in the Soviet Union?
a)
End of Cuban Missile Crisis
b)
Rise of New World Order
c)
The failed August Coup
d)
Rise in US economy
|
|
Arun Yadav answered |
Last, in the Soviet Union, the failed August Coup in 1991 led to the end of the Communist party in USSR. All of these events led to the end of communism and the making of a democratic Russia.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Q. Assertion: The Shock Therapy brought success which was not anticipated at all.Reason: Each of these countries was required to make a total shift to a capitalist economy, which meant rooting out completely any structures evolved during the Soviet period.- a)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- b)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- c)(A) is true, but (R) is false.
- d)(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Q. Assertion: The Shock Therapy brought success which was not anticipated at all.
Reason: Each of these countries was required to make a total shift to a capitalist economy, which meant rooting out completely any structures evolved during the Soviet period.
a)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c)
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
d)
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
Shock Therapy affected trade and commerce of Russia. The value of Ruble, the Russian currency, declined and inflation rose at a very high rate and it lost all savings of people.
Shock therapy involved a drastic change in the ...................... orientation of the economies.- a)external
- b)internal
- c)both (a) and (b)
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Shock therapy involved a drastic change in the ...................... orientation of the economies.
a)
external
b)
internal
c)
both (a) and (b)
d)
None of the above
|
|
Pranab Patel answered |
Understanding Shock Therapy
Shock therapy is an economic strategy used primarily in transitioning economies, particularly after the fall of communism in Eastern Europe. It entails rapid and comprehensive reforms aimed at shifting an economy from a centrally planned system to a market-oriented one.
Focus on External Orientation
- Definition: External orientation relates to how an economy interacts with the global market, including trade policies, foreign investment, and international economic relations.
- Market Integration: Shock therapy emphasizes integrating the economy into the global market by removing trade barriers and encouraging foreign direct investment. This is crucial for countries seeking to stimulate growth and increase competitiveness.
Why Option 'A' is Correct
- External Changes: The drastic changes implemented in shock therapy predominantly focus on external factors, such as:
- Liberalization of trade
- Deregulation of prices
- Opening markets to foreign competition
- Impact on the Economy: These external changes aim to attract foreign capital, improve export performance, and enhance overall economic growth. By doing so, countries can stabilize their economies more rapidly than through gradual reforms.
Contrast with Internal Orientation
- Internal Orientation: Internal changes usually involve structural reforms related to domestic policies, such as labor laws and social safety nets. While these are important, shock therapy's immediate goal is to reposition the economy externally.
- Example: Countries like Poland and Russia adopted shock therapy to quickly shift their economies towards market-based systems, focusing on external trade and investment as a primary strategy.
In summary, shock therapy primarily focuses on the external orientation of economies to facilitate rapid transition and integration into the global market, making option 'A' the correct choice.
Shock therapy is an economic strategy used primarily in transitioning economies, particularly after the fall of communism in Eastern Europe. It entails rapid and comprehensive reforms aimed at shifting an economy from a centrally planned system to a market-oriented one.
Focus on External Orientation
- Definition: External orientation relates to how an economy interacts with the global market, including trade policies, foreign investment, and international economic relations.
- Market Integration: Shock therapy emphasizes integrating the economy into the global market by removing trade barriers and encouraging foreign direct investment. This is crucial for countries seeking to stimulate growth and increase competitiveness.
Why Option 'A' is Correct
- External Changes: The drastic changes implemented in shock therapy predominantly focus on external factors, such as:
- Liberalization of trade
- Deregulation of prices
- Opening markets to foreign competition
- Impact on the Economy: These external changes aim to attract foreign capital, improve export performance, and enhance overall economic growth. By doing so, countries can stabilize their economies more rapidly than through gradual reforms.
Contrast with Internal Orientation
- Internal Orientation: Internal changes usually involve structural reforms related to domestic policies, such as labor laws and social safety nets. While these are important, shock therapy's immediate goal is to reposition the economy externally.
- Example: Countries like Poland and Russia adopted shock therapy to quickly shift their economies towards market-based systems, focusing on external trade and investment as a primary strategy.
In summary, shock therapy primarily focuses on the external orientation of economies to facilitate rapid transition and integration into the global market, making option 'A' the correct choice.
Read the following excerpt and answer the questions that follow:
A coup took place in 1991 that was encouraged by Communist Party hard-liners. The people had tasted freedom by then and did not want the old style rule of the Communist Party. Boris Yeltsin emerged as a national hero in opposing this coup. The Russian Republic, where Yeltsin won a popular election, began to shake off centralised control. Power began to shift from the Soviet centre to the republics, especially in the more Europeanised part of the Soviet Union, which saw themselves as sovereign states. The Central Asian republics did not ask for independence and wanted to remain with the Soviet Federation. In December 1991, under the leadership of Yeltsin, Russia, Ukraine and Belarus, three major republics of the USSR, declared that the Soviet Union was disbanded. The Communist Party of the Soviet Union was banned. Capitalism and democracy were adopted as the bases for the post-Soviet republics. The declaration on the disintegration of the USSR and the formation of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) came as a surprise to the other republics, especially to the Central Asian ones. The exclusion of these republics was an issue that was quickly solved by making them founding members of the CIS. Russia was now accepted as the successor state of the Soviet Union. It inherited the Soviet seat in the UN Security Council. Russia accepted all the international treaties and commitments of the Soviet Union. It took over as the only nuclear state of the post-Soviet space and carried out some nuclear disarmament measures with the US. The old Soviet Union was thus dead and buried.Q. Who opposed the coup of 1991?- a)Mikhail Gorbachev
- b)Post-Soviet republics
- c)Communist party
- d)Boris Yeltsin
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following excerpt and answer the questions that follow:
A coup took place in 1991 that was encouraged by Communist Party hard-liners. The people had tasted freedom by then and did not want the old style rule of the Communist Party. Boris Yeltsin emerged as a national hero in opposing this coup. The Russian Republic, where Yeltsin won a popular election, began to shake off centralised control. Power began to shift from the Soviet centre to the republics, especially in the more Europeanised part of the Soviet Union, which saw themselves as sovereign states. The Central Asian republics did not ask for independence and wanted to remain with the Soviet Federation. In December 1991, under the leadership of Yeltsin, Russia, Ukraine and Belarus, three major republics of the USSR, declared that the Soviet Union was disbanded. The Communist Party of the Soviet Union was banned. Capitalism and democracy were adopted as the bases for the post-Soviet republics. The declaration on the disintegration of the USSR and the formation of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) came as a surprise to the other republics, especially to the Central Asian ones. The exclusion of these republics was an issue that was quickly solved by making them founding members of the CIS. Russia was now accepted as the successor state of the Soviet Union. It inherited the Soviet seat in the UN Security Council. Russia accepted all the international treaties and commitments of the Soviet Union. It took over as the only nuclear state of the post-Soviet space and carried out some nuclear disarmament measures with the US. The old Soviet Union was thus dead and buried.
A coup took place in 1991 that was encouraged by Communist Party hard-liners. The people had tasted freedom by then and did not want the old style rule of the Communist Party. Boris Yeltsin emerged as a national hero in opposing this coup. The Russian Republic, where Yeltsin won a popular election, began to shake off centralised control. Power began to shift from the Soviet centre to the republics, especially in the more Europeanised part of the Soviet Union, which saw themselves as sovereign states. The Central Asian republics did not ask for independence and wanted to remain with the Soviet Federation. In December 1991, under the leadership of Yeltsin, Russia, Ukraine and Belarus, three major republics of the USSR, declared that the Soviet Union was disbanded. The Communist Party of the Soviet Union was banned. Capitalism and democracy were adopted as the bases for the post-Soviet republics. The declaration on the disintegration of the USSR and the formation of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) came as a surprise to the other republics, especially to the Central Asian ones. The exclusion of these republics was an issue that was quickly solved by making them founding members of the CIS. Russia was now accepted as the successor state of the Soviet Union. It inherited the Soviet seat in the UN Security Council. Russia accepted all the international treaties and commitments of the Soviet Union. It took over as the only nuclear state of the post-Soviet space and carried out some nuclear disarmament measures with the US. The old Soviet Union was thus dead and buried.
Q. Who opposed the coup of 1991?
a)
Mikhail Gorbachev
b)
Post-Soviet republics
c)
Communist party
d)
Boris Yeltsin
|
|
Jyoti Das answered |
Opposition to the coup of 1991
The individual who opposed the coup of 1991 was Boris Yeltsin. Here is an explanation of why he stood against the coup:
- Popular support: Boris Yeltsin emerged as a national hero due to his opposition to the coup. The people of Russia had already experienced a taste of freedom and did not want to return to the old style rule of the Communist Party. Yeltsin's stance resonated with the populace and garnered significant support.
- Shift in power: Yeltsin's opposition to the coup marked a significant shift in power dynamics within the Soviet Union. The Russian Republic, where Yeltsin had won a popular election, began to shake off centralised control. Power started to move away from the Soviet centre towards the republics, particularly those in the more Europeanised regions.
- Role in the disintegration of the USSR: Under Yeltsin's leadership, Russia, along with Ukraine and Belarus, declared the disbandment of the Soviet Union in December 1991. This declaration marked the end of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union and paved the way for the adoption of capitalism and democracy in the post-Soviet republics.
- Successor state: Russia was widely accepted as the successor state of the Soviet Union. It inherited the Soviet seat in the UN Security Council and took on all the international treaties and commitments of the former USSR. Additionally, Russia became the sole nuclear state in the post-Soviet space and engaged in nuclear disarmament measures with the United States.
The individual who opposed the coup of 1991 was Boris Yeltsin. Here is an explanation of why he stood against the coup:
- Popular support: Boris Yeltsin emerged as a national hero due to his opposition to the coup. The people of Russia had already experienced a taste of freedom and did not want to return to the old style rule of the Communist Party. Yeltsin's stance resonated with the populace and garnered significant support.
- Shift in power: Yeltsin's opposition to the coup marked a significant shift in power dynamics within the Soviet Union. The Russian Republic, where Yeltsin had won a popular election, began to shake off centralised control. Power started to move away from the Soviet centre towards the republics, particularly those in the more Europeanised regions.
- Role in the disintegration of the USSR: Under Yeltsin's leadership, Russia, along with Ukraine and Belarus, declared the disbandment of the Soviet Union in December 1991. This declaration marked the end of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union and paved the way for the adoption of capitalism and democracy in the post-Soviet republics.
- Successor state: Russia was widely accepted as the successor state of the Soviet Union. It inherited the Soviet seat in the UN Security Council and took on all the international treaties and commitments of the former USSR. Additionally, Russia became the sole nuclear state in the post-Soviet space and engaged in nuclear disarmament measures with the United States.
Read the following excerpt and answer the questions that follow:
Economist Jeffrey Sachs is widely associated with shock therapy. He developed a plan of shock therapy for post-communist Poland in 1990, for post-communist Russia in 1992, and several other countries, including Bolivia and Chile. Bolivia, in particular, in 1985, had success as a result of shock therapy in ending a period of hyperinflation.Poland also initially seemed to benefit from shock therapy as inflation was controlled, but it saw a sharp rise in unemployment that peaked at 16.9%. Sachs did not like the term shock therapy, which he said was coined by the media and made the reform process sound more painful than it was.In Russia, neo- liberal shock therapy did not produce favourable outcomes. Shock therapy was applied swiftly and on a large scale, as opposed to how it was applied in other nations. Almost all of Russia’s industries were undervalued and sold to private individuals and companies, with most acquired by a few Russian oligarchs.With limited government intervention, most industries disappeared. The Russian currency declined, causing high inflation and the erosion of most citizens’ savings. Unemployment increased drastically, and government subsidies were removed, further pushing Russian families into poverty.Q. Who developed the plan of the Shock therapy for the post-communist Poland?- a)Mikhail Gorbachev
- b)Jeffery Sachs
- c)Both of them
- d)None of them
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following excerpt and answer the questions that follow:
Economist Jeffrey Sachs is widely associated with shock therapy. He developed a plan of shock therapy for post-communist Poland in 1990, for post-communist Russia in 1992, and several other countries, including Bolivia and Chile. Bolivia, in particular, in 1985, had success as a result of shock therapy in ending a period of hyperinflation.
Economist Jeffrey Sachs is widely associated with shock therapy. He developed a plan of shock therapy for post-communist Poland in 1990, for post-communist Russia in 1992, and several other countries, including Bolivia and Chile. Bolivia, in particular, in 1985, had success as a result of shock therapy in ending a period of hyperinflation.
Poland also initially seemed to benefit from shock therapy as inflation was controlled, but it saw a sharp rise in unemployment that peaked at 16.9%. Sachs did not like the term shock therapy, which he said was coined by the media and made the reform process sound more painful than it was.
In Russia, neo- liberal shock therapy did not produce favourable outcomes. Shock therapy was applied swiftly and on a large scale, as opposed to how it was applied in other nations. Almost all of Russia’s industries were undervalued and sold to private individuals and companies, with most acquired by a few Russian oligarchs.
With limited government intervention, most industries disappeared. The Russian currency declined, causing high inflation and the erosion of most citizens’ savings. Unemployment increased drastically, and government subsidies were removed, further pushing Russian families into poverty.
Q. Who developed the plan of the Shock therapy for the post-communist Poland?
a)
Mikhail Gorbachev
b)
Jeffery Sachs
c)
Both of them
d)
None of them
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Jeffrey Sachs is widely associated with shock therapy. He developed a plan of shock therapy for post-communist Poland in 1990.
Read the following excerpt and answer the questions that follow:
The Soviet Union had become stagnant in an administrative and political sense as well. The Communist Party that had ruled the Soviet Union for over 70 years was not accountable to the people. Ordinary people were alienated by slow and stifling administration, rampant corruption, the inability of the system to correct mistakes it had made, the unwillingness to allow more openness in government, and the centralisation of authority in a vast land. Worse still, the party bureaucrats gained more privileges than ordinary citizens. People did not identify with the system and with the rulers, and the government increasingly lost popular backing. Gorbachev’s reforms promised to deal with these problems. Gorbachev promised to reform the economy, catch up with the West, and loosen the administrative system. All this might not have led to the collapse of the Soviet Union but for another development that surprised most observers and indeed many insiders. The rise of nationalism and the desire for sovereignty within various republics including Russia and the Baltic Republics (Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania), Ukraine, Georgia, and others proved to be the final and most immediate cause for the disintegration of the USSR.Q. Gorbachev promised to…- a)Back the people in war and international tensions.
- b)Provide employment and pensions to elder citizens.
- c)To defeat west and become the sole super power.
- d)To reform the economy, catch up with the West, and loosen the administrative system.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following excerpt and answer the questions that follow:
The Soviet Union had become stagnant in an administrative and political sense as well. The Communist Party that had ruled the Soviet Union for over 70 years was not accountable to the people. Ordinary people were alienated by slow and stifling administration, rampant corruption, the inability of the system to correct mistakes it had made, the unwillingness to allow more openness in government, and the centralisation of authority in a vast land. Worse still, the party bureaucrats gained more privileges than ordinary citizens. People did not identify with the system and with the rulers, and the government increasingly lost popular backing. Gorbachev’s reforms promised to deal with these problems. Gorbachev promised to reform the economy, catch up with the West, and loosen the administrative system. All this might not have led to the collapse of the Soviet Union but for another development that surprised most observers and indeed many insiders. The rise of nationalism and the desire for sovereignty within various republics including Russia and the Baltic Republics (Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania), Ukraine, Georgia, and others proved to be the final and most immediate cause for the disintegration of the USSR.
The Soviet Union had become stagnant in an administrative and political sense as well. The Communist Party that had ruled the Soviet Union for over 70 years was not accountable to the people. Ordinary people were alienated by slow and stifling administration, rampant corruption, the inability of the system to correct mistakes it had made, the unwillingness to allow more openness in government, and the centralisation of authority in a vast land. Worse still, the party bureaucrats gained more privileges than ordinary citizens. People did not identify with the system and with the rulers, and the government increasingly lost popular backing. Gorbachev’s reforms promised to deal with these problems. Gorbachev promised to reform the economy, catch up with the West, and loosen the administrative system. All this might not have led to the collapse of the Soviet Union but for another development that surprised most observers and indeed many insiders. The rise of nationalism and the desire for sovereignty within various republics including Russia and the Baltic Republics (Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania), Ukraine, Georgia, and others proved to be the final and most immediate cause for the disintegration of the USSR.
Q. Gorbachev promised to…
a)
Back the people in war and international tensions.
b)
Provide employment and pensions to elder citizens.
c)
To defeat west and become the sole super power.
d)
To reform the economy, catch up with the West, and loosen the administrative system.
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Gorbachev’s decision to allow elections with a multi-party system and create a presidency for the Soviet Union began a slow process of democratization that eventually destabilized Communist control and contributed to the collapse of the Soviet Union.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Q. Assertion: Most of the former Soviet Republics are prone to conflicts, and many have had civil wars and insurgencies.Reason: In Russia, two republics, Chechnya and Dagestan, have had violent secessionist movements.- a)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- b)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- c)(A) is true, but (R) is false.
- d)(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Q. Assertion: Most of the former Soviet Republics are prone to conflicts, and many have had civil wars and insurgencies.
Reason: In Russia, two republics, Chechnya and Dagestan, have had violent secessionist movements.
a)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c)
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
d)
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
After the disintegration of soviet system, many of the soviet republics witnessed violent secessionist movements. Chechnya and Dagestan were two of them.
Which of the following statements about the Soviet Union's political system is correct?- a)The Communist Party allowed multiple political parties to exist.
- b)The political system was open and democratic.
- c)The Communist Party of the Soviet Union had tight control over all institutions.
- d)The Soviet Union was governed by a coalition of political parties.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements about the Soviet Union's political system is correct?
a)
The Communist Party allowed multiple political parties to exist.
b)
The political system was open and democratic.
c)
The Communist Party of the Soviet Union had tight control over all institutions.
d)
The Soviet Union was governed by a coalition of political parties.
|
|
Sreemoyee Kaur answered |
Overview of the Soviet Union's Political System
The political structure of the Soviet Union was characterized by a single-party system dominated by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU). This system ensured that the party maintained strict control over the state and society.
Control by the Communist Party
- The CPSU was the only legal political party, effectively eliminating any political pluralism.
- All political institutions, including the government, armed forces, and media, were under the direct influence of the Communist Party.
- The party's decisions dictated laws and policies, ensuring a top-down governance structure.
Suppression of Opposition
- Any form of dissent or opposition to the CPSU was met with repression, including imprisonment and exile of political opponents.
- Political competition was non-existent, as the party systematically dismantled any potential rival groups or parties.
Lack of Democratic Processes
- Elections in the Soviet Union were held, but they were largely ceremonial and lacked genuine competition.
- The outcomes were predetermined, and candidates were typically members of the Communist Party who were approved by the party leadership.
Conclusion
In summary, option 'C' is correct because the Communist Party of the Soviet Union maintained tight control over all institutions, ensuring that no independent political entities could threaten its authority. This structure created an environment where political freedom was severely restricted, contrasting with democratic norms observed in multi-party systems.
The political structure of the Soviet Union was characterized by a single-party system dominated by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU). This system ensured that the party maintained strict control over the state and society.
Control by the Communist Party
- The CPSU was the only legal political party, effectively eliminating any political pluralism.
- All political institutions, including the government, armed forces, and media, were under the direct influence of the Communist Party.
- The party's decisions dictated laws and policies, ensuring a top-down governance structure.
Suppression of Opposition
- Any form of dissent or opposition to the CPSU was met with repression, including imprisonment and exile of political opponents.
- Political competition was non-existent, as the party systematically dismantled any potential rival groups or parties.
Lack of Democratic Processes
- Elections in the Soviet Union were held, but they were largely ceremonial and lacked genuine competition.
- The outcomes were predetermined, and candidates were typically members of the Communist Party who were approved by the party leadership.
Conclusion
In summary, option 'C' is correct because the Communist Party of the Soviet Union maintained tight control over all institutions, ensuring that no independent political entities could threaten its authority. This structure created an environment where political freedom was severely restricted, contrasting with democratic norms observed in multi-party systems.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Q. Assertion: Reforms were necessary to keep the USSR abreast of the information and technological revolutions taking place in the West.
Reason: Mikhail Gorbachev, who had become General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union in 1985, sought to reform this system.- a)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- b)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- c)(A) is true, but (R) is false.
- d)(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Q. Assertion: Reforms were necessary to keep the USSR abreast of the information and technological revolutions taking place in the West.
Reason: Mikhail Gorbachev, who had become General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union in 1985, sought to reform this system.
Reason: Mikhail Gorbachev, who had become General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union in 1985, sought to reform this system.
a)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c)
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
d)
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
|
|
Arun Yadav answered |
Gorbachev put his best efforts to save the Soviet system. But, with growing unrest in its various constituent republics developing into an incessant political and legislative conflict between the republics and the central government brought an end to soviet system.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Q. Assertion: The Russian Republic, where Yeltsin won a popular election, began to shake off centralized control.Reason: A coup took place in 1991 that was encouraged by Communist Party hard-liners.- a)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- b)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- c)(A) is true, but (R) is false.
- d)(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Q. Assertion: The Russian Republic, where Yeltsin won a popular election, began to shake off centralized control.
Reason: A coup took place in 1991 that was encouraged by Communist Party hard-liners.
a)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c)
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
d)
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
The 1991 Soviet coup d’état attempt, also known as the August Coup, was a failed attempt made by Communist leaders of the Soviet Union to take control of the country from Mikhail Gorbachev, who was Soviet President and General Secretary of the party.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Q. Assertion: Gorbachev’s decision to normalize relations with the West and democratize and reform the Soviet Union had some other effects that neither he nor anyone else intended or anticipated.Reason: People supported Gorbachev in his every decision he has taken.- a)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- b)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- c)(A) is true, but (R) is false.
- d)(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Q. Assertion: Gorbachev’s decision to normalize relations with the West and democratize and reform the Soviet Union had some other effects that neither he nor anyone else intended or anticipated.
Reason: People supported Gorbachev in his every decision he has taken.
a)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c)
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
d)
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Soviet economy was under great pressure and burden. What added to the problem was its corrupt governance and unrest among people.
The collapse of Eastern Europe in ______ and USSR in ______ lead to emergence of the transitory economies.- a)1989, 1991
- b)1988, 1995
- c)1997, 1991
- d)1980, 1987
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The collapse of Eastern Europe in ______ and USSR in ______ lead to emergence of the transitory economies.
a)
1989, 1991
b)
1988, 1995
c)
1997, 1991
d)
1980, 1987
|
|
Ankit Shah answered |
Background:
The collapse of Eastern Europe in 1989 and the USSR in 1991 marked the end of the Cold War era and the emergence of transitory economies in the region. This period brought significant political, social, and economic changes that had a profound impact on the countries involved.
Impact on Eastern Europe (1989):
- The fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989 symbolized the end of communist rule in Eastern Europe.
- Countries like Poland, Hungary, Czechoslovakia, and East Germany transitioned to market economies and adopted democratic political systems.
Impact on USSR (1991):
- The dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991 led to the emergence of independent states such as Russia, Ukraine, Belarus, and the Baltic countries.
- These newly independent states faced the challenge of transitioning from a centrally planned economy to a market-oriented economy.
Emergence of Transitory Economies:
- The collapse of Eastern Europe and the USSR created a vacuum that needed to be filled with new economic systems.
- The transitory economies in the region underwent a period of transition characterized by privatization, deregulation, and liberalization of markets.
- These countries faced challenges such as high inflation, unemployment, and social instability during the transition process.
Conclusion:
The collapse of Eastern Europe in 1989 and the USSR in 1991 paved the way for the emergence of transitory economies in the region. This period of transition brought about significant changes and challenges as countries moved from central planning to market-oriented systems.
The collapse of Eastern Europe in 1989 and the USSR in 1991 marked the end of the Cold War era and the emergence of transitory economies in the region. This period brought significant political, social, and economic changes that had a profound impact on the countries involved.
Impact on Eastern Europe (1989):
- The fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989 symbolized the end of communist rule in Eastern Europe.
- Countries like Poland, Hungary, Czechoslovakia, and East Germany transitioned to market economies and adopted democratic political systems.
Impact on USSR (1991):
- The dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991 led to the emergence of independent states such as Russia, Ukraine, Belarus, and the Baltic countries.
- These newly independent states faced the challenge of transitioning from a centrally planned economy to a market-oriented economy.
Emergence of Transitory Economies:
- The collapse of Eastern Europe and the USSR created a vacuum that needed to be filled with new economic systems.
- The transitory economies in the region underwent a period of transition characterized by privatization, deregulation, and liberalization of markets.
- These countries faced challenges such as high inflation, unemployment, and social instability during the transition process.
Conclusion:
The collapse of Eastern Europe in 1989 and the USSR in 1991 paved the way for the emergence of transitory economies in the region. This period of transition brought about significant changes and challenges as countries moved from central planning to market-oriented systems.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Q. Assertion: In Georgia, the demand for independence has come from two provinces, resulting in a Civil War.Reason: In Central Asia, Tajikistan witnessed a Civil War that went on for ten years till 2001.- a)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- b)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- c)(A) is true, but (R) is false.
- d)(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Q. Assertion: In Georgia, the demand for independence has come from two provinces, resulting in a Civil War.
Reason: In Central Asia, Tajikistan witnessed a Civil War that went on for ten years till 2001.
a)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c)
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
d)
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Post cold war era was not free of the uproars. Former soviet republics witnessed violent conflicts over many issues. Many new countries were born after the disintegration of Soviet Union. But, their inception was not free from bloodshed.
The Russian Revolution in 1917 was led by- a)Joseph Stalin.
- b)Vladimir Ilyich Lenin
- c)Nikita Khrushchev.
- d)Mikhail Gorbachev.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The Russian Revolution in 1917 was led by
a)
Joseph Stalin.
b)
Vladimir Ilyich Lenin
c)
Nikita Khrushchev.
d)
Mikhail Gorbachev.
|
|
Arun Yadav answered |
On November 6 and 7, 1917 (or October 24 and 25 on the Julian calendar, which is why the event is often referred to as the October Revolution), leftist revolutionaries led by Bolshevik Party leader Vladimir Lenin launched a nearly bloodless coup d'état against the Duma's provisional government.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Q. Assertion: The exclusion of these republics was an issue that was quickly solved by making them founding members of the CIS.Reason: The declaration on the disintegration of the USSR and the formation of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) came as a surprise to the other republics, especially to the Central Asian ones.- a)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- b)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- c)(A) is true, but (R) is false.
- d)(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Q. Assertion: The exclusion of these republics was an issue that was quickly solved by making them founding members of the CIS.
Reason: The declaration on the disintegration of the USSR and the formation of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) came as a surprise to the other republics, especially to the Central Asian ones.
a)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c)
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
d)
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
In the end, the Russian Federation became the successor state for the Soviet Union, which meant that it took responsibility for weapons control and disposal, for outstanding debt, but also for the Soviet seat on the UN Security Council.
Read the following excerpt and answer the questions that follow:
A coup took place in 1991 that was encouraged by Communist Party hard-liners. The people had tasted freedom by then and did not want the oldstyle rule of the Communist Party. Boris Yeltsin emerged as a national hero in opposing this coup. The Russian Republic, where Yeltsin won a popular election, began to shake off centralised control. Power began to shift from the Soviet centre to the republics, especially in the more Europeanised part of the Soviet Union, which saw themselves as sovereign states. The Central Asian republics did not ask for independence and wanted to remain with the Soviet Federation. In December 1991, under the leadership of Yeltsin, Russia, Ukraine and Belarus, three major republics of the USSR, declared that the Soviet Union was disbanded. The Communist Party of the Soviet Union was banned. Capitalism and democracy were adopted as the bases for the post-Soviet republics. The declaration on the disintegration of the USSR and the formation of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) came as a surprise to the other republics, especially to the Central Asian ones. The exclusion of these republics was an issue that was quickly solved by making them founding members of the CIS. Russia was now accepted as the successor state of the Soviet Union. It inherited the Soviet seat in the UN Security Council. Russia accepted all the international treaties and commitments of the Soviet Union. It took over as the only nuclear state of the post-Soviet space and carried out some nuclear disarmament measures with the US. The old Soviet Union was thus dead and buried.Q. Which type of government was adopted by the post-soviet countries?- a)Socialist
- b)Capitalist and Democratic
- c)Communist Democratic
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following excerpt and answer the questions that follow:
A coup took place in 1991 that was encouraged by Communist Party hard-liners. The people had tasted freedom by then and did not want the oldstyle rule of the Communist Party. Boris Yeltsin emerged as a national hero in opposing this coup. The Russian Republic, where Yeltsin won a popular election, began to shake off centralised control. Power began to shift from the Soviet centre to the republics, especially in the more Europeanised part of the Soviet Union, which saw themselves as sovereign states. The Central Asian republics did not ask for independence and wanted to remain with the Soviet Federation. In December 1991, under the leadership of Yeltsin, Russia, Ukraine and Belarus, three major republics of the USSR, declared that the Soviet Union was disbanded. The Communist Party of the Soviet Union was banned. Capitalism and democracy were adopted as the bases for the post-Soviet republics. The declaration on the disintegration of the USSR and the formation of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) came as a surprise to the other republics, especially to the Central Asian ones. The exclusion of these republics was an issue that was quickly solved by making them founding members of the CIS. Russia was now accepted as the successor state of the Soviet Union. It inherited the Soviet seat in the UN Security Council. Russia accepted all the international treaties and commitments of the Soviet Union. It took over as the only nuclear state of the post-Soviet space and carried out some nuclear disarmament measures with the US. The old Soviet Union was thus dead and buried.
A coup took place in 1991 that was encouraged by Communist Party hard-liners. The people had tasted freedom by then and did not want the oldstyle rule of the Communist Party. Boris Yeltsin emerged as a national hero in opposing this coup. The Russian Republic, where Yeltsin won a popular election, began to shake off centralised control. Power began to shift from the Soviet centre to the republics, especially in the more Europeanised part of the Soviet Union, which saw themselves as sovereign states. The Central Asian republics did not ask for independence and wanted to remain with the Soviet Federation. In December 1991, under the leadership of Yeltsin, Russia, Ukraine and Belarus, three major republics of the USSR, declared that the Soviet Union was disbanded. The Communist Party of the Soviet Union was banned. Capitalism and democracy were adopted as the bases for the post-Soviet republics. The declaration on the disintegration of the USSR and the formation of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) came as a surprise to the other republics, especially to the Central Asian ones. The exclusion of these republics was an issue that was quickly solved by making them founding members of the CIS. Russia was now accepted as the successor state of the Soviet Union. It inherited the Soviet seat in the UN Security Council. Russia accepted all the international treaties and commitments of the Soviet Union. It took over as the only nuclear state of the post-Soviet space and carried out some nuclear disarmament measures with the US. The old Soviet Union was thus dead and buried.
Q. Which type of government was adopted by the post-soviet countries?
a)
Socialist
b)
Capitalist and Democratic
c)
Communist Democratic
d)
None of the above

|
Manmeet Sekhon answered |
After the coup of 1991 which leds to disintegration of USSR in 1991 there is a end of bipolar world and all new 15 republics adopted new govt of capitalist and democratic as per USA system!.after that there is a end of ussr and its ideology!
The most severe conflict took place in the Balkan republics of…- a)Bulgaria
- b)Greece
- c)Yugoslavia
- d)Macedonia
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The most severe conflict took place in the Balkan republics of…
a)
Bulgaria
b)
Greece
c)
Yugoslavia
d)
Macedonia
|
|
Nitin Chakraborty answered |
The most severe conflict took place in the Balkan republics of Yugoslavia. After 1991, it broke apart with several provinces like Croatia, Slovenia and Bosnia and Herzegovina declaring independence.
Who controlled the economy in the soviet system?- a)Federal
- b)Government
- c)State
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Who controlled the economy in the soviet system?
a)
Federal
b)
Government
c)
State
d)
None
|
|
Ujwal Kulkarni answered |
In the Soviet system, the economy was controlled by the state. This means that the government had complete control over all aspects of the economy, including production, distribution, and pricing. The Soviet Union was a command economy, which meant that the state planned and directed economic activity through a series of five-year plans.
Control over the economy was exercised through a centralized planning system, which was overseen by the Communist Party. The State Planning Committee (Gosplan) was responsible for creating and implementing the five-year plans, which set production targets for each industry and region of the country. The government also controlled the prices of goods and services, and allocated resources according to the priorities set out in the plans.
Under the Soviet system, private ownership of the means of production was abolished, and all enterprises were owned and operated by the state. This included everything from large industrial factories to small retail shops. The state also controlled the distribution of goods and services, including food, clothing, and housing.
Overall, the Soviet system was designed to create a centrally planned, socialist economy that was focused on meeting the needs of the people rather than maximizing profits for private individuals or corporations. While this system was successful in achieving some of its goals, such as rapid industrialization and improving access to education and healthcare, it also led to inefficiencies, shortages, and other economic problems.
Control over the economy was exercised through a centralized planning system, which was overseen by the Communist Party. The State Planning Committee (Gosplan) was responsible for creating and implementing the five-year plans, which set production targets for each industry and region of the country. The government also controlled the prices of goods and services, and allocated resources according to the priorities set out in the plans.
Under the Soviet system, private ownership of the means of production was abolished, and all enterprises were owned and operated by the state. This included everything from large industrial factories to small retail shops. The state also controlled the distribution of goods and services, including food, clothing, and housing.
Overall, the Soviet system was designed to create a centrally planned, socialist economy that was focused on meeting the needs of the people rather than maximizing profits for private individuals or corporations. While this system was successful in achieving some of its goals, such as rapid industrialization and improving access to education and healthcare, it also led to inefficiencies, shortages, and other economic problems.
Read the following excerpt and answer the questions that follow:
The Soviet Union had become stagnant in an administrative and political sense as well. The Communist Party that had ruled the Soviet Union for over 70 years was not accountable to the people. Ordinary people were alienated by slow and stifling administration, rampant corruption, the inability of the system to correct mistakes it had made, the unwillingness to allow more openness in government, and the centralisation of authority in a vast land. Worse still, the party bureaucrats gained more privileges than ordinary citizens. People did not identify with the system and with the rulers, and the government increasingly lost popular backing. Gorbachev’s reforms promised to deal with these problems. Gorbachev promised to reform the economy, catch up with the West, and loosen the administrative system. All this might not have led to the collapse of the Soviet Union but for another development that surprised most observers and indeed many insiders. The rise of nationalism and the desire for sovereignty within various republics including Russia and the Baltic Republics (Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania), Ukraine, Georgia, and others proved to be the final and most immediate cause for the disintegration of the USSR.Q. How long has the communist party been ruling the Soviet Union?- a)For sixty eight years
- b)For seventy years
- c)For 82 years
- d)For fifty years
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following excerpt and answer the questions that follow:
The Soviet Union had become stagnant in an administrative and political sense as well. The Communist Party that had ruled the Soviet Union for over 70 years was not accountable to the people. Ordinary people were alienated by slow and stifling administration, rampant corruption, the inability of the system to correct mistakes it had made, the unwillingness to allow more openness in government, and the centralisation of authority in a vast land. Worse still, the party bureaucrats gained more privileges than ordinary citizens. People did not identify with the system and with the rulers, and the government increasingly lost popular backing. Gorbachev’s reforms promised to deal with these problems. Gorbachev promised to reform the economy, catch up with the West, and loosen the administrative system. All this might not have led to the collapse of the Soviet Union but for another development that surprised most observers and indeed many insiders. The rise of nationalism and the desire for sovereignty within various republics including Russia and the Baltic Republics (Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania), Ukraine, Georgia, and others proved to be the final and most immediate cause for the disintegration of the USSR.
The Soviet Union had become stagnant in an administrative and political sense as well. The Communist Party that had ruled the Soviet Union for over 70 years was not accountable to the people. Ordinary people were alienated by slow and stifling administration, rampant corruption, the inability of the system to correct mistakes it had made, the unwillingness to allow more openness in government, and the centralisation of authority in a vast land. Worse still, the party bureaucrats gained more privileges than ordinary citizens. People did not identify with the system and with the rulers, and the government increasingly lost popular backing. Gorbachev’s reforms promised to deal with these problems. Gorbachev promised to reform the economy, catch up with the West, and loosen the administrative system. All this might not have led to the collapse of the Soviet Union but for another development that surprised most observers and indeed many insiders. The rise of nationalism and the desire for sovereignty within various republics including Russia and the Baltic Republics (Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania), Ukraine, Georgia, and others proved to be the final and most immediate cause for the disintegration of the USSR.
Q. How long has the communist party been ruling the Soviet Union?
a)
For sixty eight years
b)
For seventy years
c)
For 82 years
d)
For fifty years
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
The Soviet Union collapsed in 1991, the Communist Party had been in power for a little more than 70 years. Similarly, the Institutional Revolutionary Party (PRI) ruled in Mexico from its founding in 1929 until its defeat in the 2000 elections—71 years.
Chapter doubts & questions for The End of Bipolarity - Political Science CUET Preparation 2025 is part of Humanities/Arts exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Humanities/Arts exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Humanities/Arts 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of The End of Bipolarity - Political Science CUET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of Humanities/Arts exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Humanities/Arts Exam by signing up for free.
Political Science CUET Preparation
32 videos|39 docs|62 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily












