All Exams >
A Level >
Biology A-Level >
All Questions
All questions of Immunity for A Level Exam
The chemical test that is used for diagnosis of typhoid is:- a)ESR-Test
- b)PCR-Test
- c)Widal-Test
- d)ELISA-Test
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The chemical test that is used for diagnosis of typhoid is:
a)
ESR-Test
b)
PCR-Test
c)
Widal-Test
d)
ELISA-Test

|
Jeeshan Ahmed answered |
The Widal test is one method that may be used to help make a presumptive diagnosis of enteric fever, also known as typhoid fever.The test was based on demonstrating the presence of agglutinin (antibody) in the serum of an infected patient, against the H (flagellar) and O (somatic) antigens ofSalmonella typhi.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The chemical test that is used for diagnosis of typhoid is:- a)ESR-Test
- b)PCR-Test
- c)Widal-Test
- d)ELISA-Test
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The chemical test that is used for diagnosis of typhoid is:
a)
ESR-Test
b)
PCR-Test
c)
Widal-Test
d)
ELISA-Test

|
Dilip answered |
Its given in 12th NCERT.... widal test for typhoid
Can you explain the answer of this question below:The disease chikunguniya is transmitted by- A:Cockroach
- B:Aedes mosquitoes
- C:House flies
- D:Female Anopheles
The answer is b.
The disease chikunguniya is transmitted by
A:
Cockroach
B:
Aedes mosquitoes
C:
House flies
D:
Female Anopheles
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
When a mosquito feeds on an infected person, the mosquito can become infected and can bite and infect others. The Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes transmit chikungunya. They also transmit dengue fever, another disease caused by a virus.
The organisms which cause diseases in plants and animals are called:- a)Worms
- b)Pathogens
- c)Vectors
- d)Insects
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The organisms which cause diseases in plants and animals are called:
a)
Worms
b)
Pathogens
c)
Vectors
d)
Insects
|
|
Anshu Banerjee answered |
Pathogens
Pathogens are organisms that cause diseases in plants and animals. They include viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites. These microorganisms can infect the host organism and cause harm by disrupting normal physiological processes. Pathogens can cause a wide range of symptoms, from mild to severe, and can even be fatal in some cases.
Types of Pathogens
There are several types of pathogens that can cause diseases in plants and animals:
1. Bacteria: These are single-celled microorganisms that can cause a variety of diseases, from mild infections to severe illnesses. Some examples of bacterial diseases include tuberculosis, strep throat, and food poisoning.
2. Viruses: These are tiny, infectious agents that can cause diseases in animals and humans. They can infect cells and disrupt normal cellular functions. Some examples of viral diseases include the flu, HIV, and the common cold.
3. Fungi: These are multicellular organisms that can cause diseases in plants and animals. They can infect tissues and cause damage to the host organism. Some examples of fungal diseases include athlete's foot, ringworm, and candidiasis.
4. Parasites: These are organisms that live on or inside the host organism and can cause harm. They can be single-celled or multicellular. Some examples of parasitic diseases include malaria, giardiasis, and tapeworm infections.
Effects of Pathogens on Plants and Animals
Pathogens can have a variety of effects on plants and animals. In plants, they can cause wilting, yellowing, and stunted growth. They can also cause lesions, cankers, and other types of damage to the plant tissues. In animals, they can cause a wide range of symptoms, from mild to severe. Some examples of animal diseases caused by pathogens include:
1. Lyme disease: This is a bacterial disease that is transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected tick. It can cause fever, fatigue, and a characteristic bull's-eye rash.
2. Anthrax: This is a bacterial disease that can affect both animals and humans. It can cause fever, chills, and other symptoms, and can be fatal in some cases.
3. Rabies: This is a viral disease that affects the nervous system. It can be transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected animal and can be fatal if left untreated.
Prevention and Treatment
Preventing the spread of pathogens is important in controlling diseases in plants and animals. Some strategies for preventing the spread of pathogens include:
1. Quarantining infected individuals or plants to prevent the spread of the disease.
2. Disinfecting surfaces and equipment to kill pathogens.
3. Vaccinating individuals or plants to prevent infection.
4. Implementing good hygiene practices, such as washing hands and keeping living spaces clean.
Treatment of diseases caused by pathogens can vary depending on the type of pathogen and the severity of the disease. Some treatments include:
1. Antibiotics for bacterial infections.
2. Antiviral medications for viral infections.
3. Antifungal medications for fungal infections.
4. Parasiticides for parasitic infections.
Conclusion
Pathogens are organisms that can cause diseases in plants and animals. They can have a wide range of effects on their hosts, from mild to severe. Preventing the spread of pathogens is important in controlling diseases, and treatment can vary depending on the type of pathogen and the severity of the disease.
Pathogens are organisms that cause diseases in plants and animals. They include viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites. These microorganisms can infect the host organism and cause harm by disrupting normal physiological processes. Pathogens can cause a wide range of symptoms, from mild to severe, and can even be fatal in some cases.
Types of Pathogens
There are several types of pathogens that can cause diseases in plants and animals:
1. Bacteria: These are single-celled microorganisms that can cause a variety of diseases, from mild infections to severe illnesses. Some examples of bacterial diseases include tuberculosis, strep throat, and food poisoning.
2. Viruses: These are tiny, infectious agents that can cause diseases in animals and humans. They can infect cells and disrupt normal cellular functions. Some examples of viral diseases include the flu, HIV, and the common cold.
3. Fungi: These are multicellular organisms that can cause diseases in plants and animals. They can infect tissues and cause damage to the host organism. Some examples of fungal diseases include athlete's foot, ringworm, and candidiasis.
4. Parasites: These are organisms that live on or inside the host organism and can cause harm. They can be single-celled or multicellular. Some examples of parasitic diseases include malaria, giardiasis, and tapeworm infections.
Effects of Pathogens on Plants and Animals
Pathogens can have a variety of effects on plants and animals. In plants, they can cause wilting, yellowing, and stunted growth. They can also cause lesions, cankers, and other types of damage to the plant tissues. In animals, they can cause a wide range of symptoms, from mild to severe. Some examples of animal diseases caused by pathogens include:
1. Lyme disease: This is a bacterial disease that is transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected tick. It can cause fever, fatigue, and a characteristic bull's-eye rash.
2. Anthrax: This is a bacterial disease that can affect both animals and humans. It can cause fever, chills, and other symptoms, and can be fatal in some cases.
3. Rabies: This is a viral disease that affects the nervous system. It can be transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected animal and can be fatal if left untreated.
Prevention and Treatment
Preventing the spread of pathogens is important in controlling diseases in plants and animals. Some strategies for preventing the spread of pathogens include:
1. Quarantining infected individuals or plants to prevent the spread of the disease.
2. Disinfecting surfaces and equipment to kill pathogens.
3. Vaccinating individuals or plants to prevent infection.
4. Implementing good hygiene practices, such as washing hands and keeping living spaces clean.
Treatment of diseases caused by pathogens can vary depending on the type of pathogen and the severity of the disease. Some treatments include:
1. Antibiotics for bacterial infections.
2. Antiviral medications for viral infections.
3. Antifungal medications for fungal infections.
4. Parasiticides for parasitic infections.
Conclusion
Pathogens are organisms that can cause diseases in plants and animals. They can have a wide range of effects on their hosts, from mild to severe. Preventing the spread of pathogens is important in controlling diseases, and treatment can vary depending on the type of pathogen and the severity of the disease.
The disease causing microorganisms are called?- a)Microbes
- b)Fungi
- c)Allotropes
- d)Pathogen
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The disease causing microorganisms are called?
a)
Microbes
b)
Fungi
c)
Allotropes
d)
Pathogen
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Most microbes belong to four major groups: bacteria, viruses, protozoa or fungi. (To find out more, see the “Bacteria/Viruses/Protozoa” fact sheets). Disease-causing microbes can also be called pathogens, germs or bugs and are responsible for causing infectious diseases.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Antigenic determinant sites bind to which portion of an antibody molecule?
(1) Light chain
(2) Heavy chain
(3) Intermediate chains
(4) Plasma cells- A:1 and 2 are correct
- B:2 and 4 are correct
- C:1, 2, 3 are correct
- D:1 and 3 are correct
The answer is a.
Antigenic determinant sites bind to which portion of an antibody molecule?
(1) Light chain
(2) Heavy chain
(3) Intermediate chains
(4) Plasma cells
(1) Light chain
(2) Heavy chain
(3) Intermediate chains
(4) Plasma cells
A:
1 and 2 are correct
B:
2 and 4 are correct
C:
1, 2, 3 are correct
D:
1 and 3 are correct

|
Aiims New Delhi answered |
Light and heavy chainas u know formula of antibody H2L2😀😀😀😀💯💯💯👍👍👍
The sporozoites that cause infection, when a female Anopheles mosquito bites a person, are stored in
- a)Liver of person
- b)RBCs of mosquito
- c)Salivary glands of mosquito
- d)Intestine of person
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The sporozoites that cause infection, when a female Anopheles mosquito bites a person, are stored in
a)
Liver of person
b)
RBCs of mosquito
c)
Salivary glands of mosquito
d)
Intestine of person
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
- Sporozoites enter the female Anopheles mosquito when they bite an infected person where these sporozoite fertilise and multiply in the stomach wall of the female Anopheles and stored in the salivary gland of mosquito till it is again transferred to the human body by a mosquito bite.
- After entering the human body the sporozoites reach the liver cells, where they multiply. This is followed by their attack on red blood cells resulting in their rupture. The ruptured RBCs release a toxin called haemozoin, which is responsible for high recurring fever, chills and shivering.
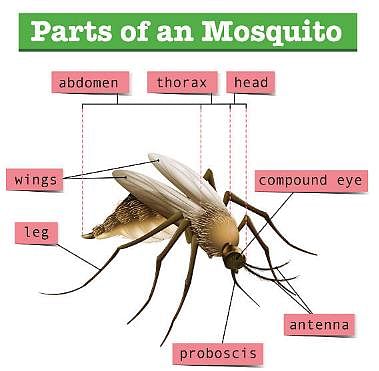
- Mosquito Anatomy:
Formation of antibodies within our body is called:- a)Innate immunity
- b)Acquired immunity
- c)Passive immunity
- d)Active immunity
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Formation of antibodies within our body is called:
a)
Innate immunity
b)
Acquired immunity
c)
Passive immunity
d)
Active immunity
|
|
Shalini Basu answered |
The combination of antibodies and complement promotes rapid clearing of pathogens. The production of antibodies by plasma cells in response to an antigen is called active immunity and describes the host's active response of theimmune system to an infection or to a vaccination.
Antibodies are produced by:- a)T-cells
- b)B-cells
- c)Monocytes
- d)Phagocytes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Antibodies are produced by:
a)
T-cells
b)
B-cells
c)
Monocytes
d)
Phagocytes
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
Antibodies are produced by specialized white blood cells called B lymphocytes (or B cells). When an antigen binds to the B-cell surface, it stimulates the B cell to divide and mature into a group of identical cells called a clone.
Where memory cells are formed?- a)Monocytes
- b)Neutrophils
- c)Eosinophil
- d)Lymphocytes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Where memory cells are formed?
a)
Monocytes
b)
Neutrophils
c)
Eosinophil
d)
Lymphocytes
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
B lymphocytes are the cells of the immune system that make antibodies to invading pathogens like viruses. They form memory cells that remember the same pathogen for faster antibody production in future infections.
Immuno-deficiency syndrome could develop due to- a)Defective liver
- b)AIDS virus
- c)Defective thymus
- d)Weak immune system
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Immuno-deficiency syndrome could develop due to
a)
Defective liver
b)
AIDS virus
c)
Defective thymus
d)
Weak immune system
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immune deficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).Following initial infection, a person may not notice any symptoms or may experience a brief period of influenza-like illness. Typically, this is followed by a prolonged period with no symptoms. As the infection progresses, it interferes more with the immune system, increasing the risk of developing common infections such as tuberculosis, as well as other opportunistic infections, and tumors that rarely affect people who have working immune systems.[5] These late symptoms of infection are referred to as acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).This stage is often also associated with unintended weight loss.
Both sickle cell anaemia and Huntington’s chorea are:- a)Congenital diseases
- b)Viral diseases
- c)Bacterial diseases
- d)Pollution-related diseases
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Both sickle cell anaemia and Huntington’s chorea are:
a)
Congenital diseases
b)
Viral diseases
c)
Bacterial diseases
d)
Pollution-related diseases
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Both sickle cell anaemia and Huntington's chorea are congenital genetic disorders. Sickle cell anaemia was first opened by James Herrick (1904). In this disease the patient's haemoglobin level reduced to half of the normal and the RBCs become sickle shaped. A single mutation in a gene can cause sickle cell anaemia.
Huntington's chorea is caused by autosomal mutation which is dominant. The gene is present on chromosome number 4.
Marijuana, hashish, charas and ganga are group of drugs collectively called?- a)Cannabinoids
- b)Opioids
- c)Coke
- d)Crack
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Marijuana, hashish, charas and ganga are group of drugs collectively called?
a)
Cannabinoids
b)
Opioids
c)
Coke
d)
Crack
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Marijuana, hashish, charas, and ganja contain chemicals called cannabinoids. They are generally, taken as inhalation or oral ingestion to effects cardiovascular system of the body.
Where will you look for the sporozoites of the malarial parasite?- a)Saliva of infected female Anopheles mosquito
- b)Spleen of infected humans
- c)Salivary glands of freshly moulted female Anopheles mosquito
- d)Red blood corpuscles of human suffering from malaria
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Where will you look for the sporozoites of the malarial parasite?
a)
Saliva of infected female Anopheles mosquito
b)
Spleen of infected humans
c)
Salivary glands of freshly moulted female Anopheles mosquito
d)
Red blood corpuscles of human suffering from malaria
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Sporozoite is the infective stage of the malarial parasite. They are present in the saliva of infected female anopheles mosquito.
HIV is a member of group of viruses called:- a)Retro viruses
- b)Gemini viruses
- c)Lysogenic viruses
- d)Bacteriophages
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
HIV is a member of group of viruses called:
a)
Retro viruses
b)
Gemini viruses
c)
Lysogenic viruses
d)
Bacteriophages
|
|
Kadambala Hemalatha answered |
HIV is belong's to members of retro viruses..
The function of IgE is- a)Protection from inhaled/ingested pathogens
- b)Mediate in allergic response
- c)Activation of B-cells
- d)Stimulation of complement system, passive immunity to foetus
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The function of IgE is
a)
Protection from inhaled/ingested pathogens
b)
Mediate in allergic response
c)
Activation of B-cells
d)
Stimulation of complement system, passive immunity to foetus
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
The function of IgE antibody as mediators in allergic reactions of Type I is explained by their ability to interact both with antigen and with receptor molecules on the membrane of blood basophils and tissue mast cells. However, it is not understood how the interaction of an allergen with cell-bound IgE antibody will induce basophil (mast) cells to release a great number of biologically active substances of which some will be further discussed at this meeting, nor is it known what role the IgE-mast cell system plays in the development and control of a normal immune response.
Which one of the following acts as a physiological barrier to the entry of microorganisms in human body?- a)Monocytes
- b)Epithelium of Urogenital tract
- c)Tears
- d)Skin
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following acts as a physiological barrier to the entry of microorganisms in human body?
a)
Monocytes
b)
Epithelium of Urogenital tract
c)
Tears
d)
Skin
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
- Physiological barriers to the entry of microorganisms into the human body are tears in the eyes, saliva in the mouth and HCl in the stomach.
- The enzymes lysozymes are found in tears and saliva and inhibit the synthesis of peptidoglycan present in the cell wall of microorganisms especially eubacteria.
- Disease-causing microorganism enters through different routes into the body. The physiological barrier prevents their entry. Tears act as a physiological barrier for entry of pathogen.
Japanese encephalitis is transmitted by- a)Tse tse fly
- b)Sand fly
- c)Housefly
- d)Mosquito
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Japanese encephalitis is transmitted by
a)
Tse tse fly
b)
Sand fly
c)
Housefly
d)
Mosquito
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Japanese encephalitis (JE) virus, a flavivirus, is closely related to West Nile and St. Louis encephalitis viruses. JE virus is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected Culex species mosquitoes, particularly Culex tritaeniorhynchus.
The virus is maintained in a cycle between mosquitoes and vertebrate hosts, primarily pigs and wading birds. Humans are incidental or dead-end hosts, because they usually do not develop high enough concentrations of JE virus in their bloodstreams to infect feeding mosquitoes.
JE virus transmission occurs primarily in rural agricultural areas, often associated with rice production and flooding irrigation. In some areas of Asia, these conditions can occur near urban centers.
In temperate areas of Asia, JE virus transmission is seasonal. Human disease usually peaks in the summer and fall. In the subtropics and tropics, transmission can occur year-round, often with a peak during the rainy season.
Which of the following is the unit of immune system?- a)Chondrocyte
- b)Erythrocyte
- c)Lymphocyte
- d)Parasite
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the unit of immune system?
a)
Chondrocyte
b)
Erythrocyte
c)
Lymphocyte
d)
Parasite

|
Pankaj Banerjee answered |
Lymphocytes are one of several different types of white blood cells. Lymphocytes are of two types B cells and T cells. When a macrophage engulfs organisms, B cells (humoral immunity) release antibodies which cause the destruction of bacteria. The T cells (cell-mediated immunity) destroy the infectious organisms by killing the body cells that are affected. Hence lymphocytes is a unit of the immune system.
So, the correct answer is 'Lymphocytes'.
Which one of the following is a matching pair of a drug and its category?- a)Heroin – psychotropic
- b)Benzodiazepines – pain killer
- c)Lysergic acid dimethyl amide – narcotic
- d)Amphetamines – stimulant
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is a matching pair of a drug and its category?
a)
Heroin – psychotropic
b)
Benzodiazepines – pain killer
c)
Lysergic acid dimethyl amide – narcotic
d)
Amphetamines – stimulant

|
Shivani Rane answered |
Amphetamines is kind of drug which is used as stimulant. It is a strong CNS stimulant that is used in the treatment of ADHD. Lysergic acid dimethyl amide is not a narcotic and heroin is not a psychotropic agent.
Anti venom against snake poison contains:- a)Antigens
- b)Enzymes
- c)Antigen-antibody complexes
- d)Antibodies
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Anti venom against snake poison contains:
a)
Antigens
b)
Enzymes
c)
Antigen-antibody complexes
d)
Antibodies
|
|
Madhavan Ghosh answered |
Anti venom against snake poison contains antibodies.
Explanation:
Anti venom is a serum that is used to treat snake bites. It contains antibodies that are specifically produced to neutralize the venom of a particular snake species. The antibodies are produced by injecting a small amount of the snake venom into an animal, usually a horse, and then collecting the blood serum from the animal after a certain period of time. This serum contains the antibodies that have been produced in response to the venom.
The antibodies in the anti venom work by binding to the venom molecules and neutralizing their toxic effects. This prevents the venom from causing damage to the body and allows the body's own immune system to clear the venom from the bloodstream.
It is important to note that anti venom is specific to the species of snake that produced the venom. This means that anti venom for one species of snake will not be effective against the venom of another species. It is also important to administer anti venom as soon as possible after a snake bite, as the venom can rapidly spread through the body and cause severe damage if left untreated.
Explanation:
Anti venom is a serum that is used to treat snake bites. It contains antibodies that are specifically produced to neutralize the venom of a particular snake species. The antibodies are produced by injecting a small amount of the snake venom into an animal, usually a horse, and then collecting the blood serum from the animal after a certain period of time. This serum contains the antibodies that have been produced in response to the venom.
The antibodies in the anti venom work by binding to the venom molecules and neutralizing their toxic effects. This prevents the venom from causing damage to the body and allows the body's own immune system to clear the venom from the bloodstream.
It is important to note that anti venom is specific to the species of snake that produced the venom. This means that anti venom for one species of snake will not be effective against the venom of another species. It is also important to administer anti venom as soon as possible after a snake bite, as the venom can rapidly spread through the body and cause severe damage if left untreated.
The primary and secondary immune response are carried out with the help of two special types of lymphocytes present in our blood called?- a)B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes
- b)Lymphocytes and monocytes
- c)T-lymphocytes and A-lymphocytes
- d)B-lymphocytes and M-lymphocytes
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The primary and secondary immune response are carried out with the help of two special types of lymphocytes present in our blood called?
a)
B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes
b)
Lymphocytes and monocytes
c)
T-lymphocytes and A-lymphocytes
d)
B-lymphocytes and M-lymphocytes
|
|
Anaswara Rajput answered |
The primary immune response can be described as the first response of our body system to a newly introduced foreign agent, while the secondary immune response is defined as an intensified immune response to this previously exposed antigen. The primary and secondary immune response is carried out by following two types of lymphocytes;
1)B-Lymphocytes: responsible for the production of antibodies in our blood. the type of antibodies is IgA. IgD, IgE, IgG, IgM.
2)T-Lymphocytes: These are mediators cell-mediated immunity.
So, the correct answer is 'Option A
1)B-Lymphocytes: responsible for the production of antibodies in our blood. the type of antibodies is IgA. IgD, IgE, IgG, IgM.
2)T-Lymphocytes: These are mediators cell-mediated immunity.
So, the correct answer is 'Option A
Goitre can occur as a consequence of all the following except:- a)Pituitary Adenoma
- b)Iodine deficiency
- c)Grave’s disease
- d)Excessive intake of exogenous thyroxin
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Goitre can occur as a consequence of all the following except:
a)
Pituitary Adenoma
b)
Iodine deficiency
c)
Grave’s disease
d)
Excessive intake of exogenous thyroxin

|
Rajesh Datta answered |
Goitre is a deficiency disease that occurs due to less secretion of hormone thyroxin. Less or no secretion of this hormone may occurs due to iodine deficiency, pituitary adenoma ad Grave’s disease.
Which one is matched with LSD?- a)Bacteria
- b)Protozoan
- c)Fungi
- d)Virus
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is matched with LSD?
a)
Bacteria
b)
Protozoan
c)
Fungi
d)
Virus
|
|
Smruti Sucharita answered |
LSD obtained from fungi ..claviceps purpurea...
HIV is classified as a retrovirus because its genetic information is carried in- a)DNA instead of RNA
- b)RNA instead of DNA
- c)DNA
- d)Protein coat
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
HIV is classified as a retrovirus because its genetic information is carried in
a)
DNA instead of RNA
b)
RNA instead of DNA
c)
DNA
d)
Protein coat
|
|
Shivani Mishra answered |
HIV is classified as a retrovirus because its genetic information is carried in RNA instead of DNA.
Explanation:
1. Retroviruses: Retroviruses are a family of RNA viruses that have the unique ability to convert their RNA genome into DNA inside the host cell. This reverse transcription process is carried out by the enzyme reverse transcriptase, which is encoded by the retroviral genome itself.
2. Genetic information: Genetic information in living organisms is typically stored in the form of DNA. However, retroviruses, including HIV, store their genetic information in the form of RNA.
3. RNA genome: HIV has a single-stranded RNA genome, which carries the necessary genetic information for the virus to replicate and produce new copies of itself.
4. Reverse transcription: When HIV infects a host cell, it uses its RNA genome as a template to synthesize a complementary DNA strand. This process is called reverse transcription. The viral enzyme reverse transcriptase catalyzes the synthesis of DNA from the viral RNA template.
5. Integration into host DNA: After the reverse transcription, the newly synthesized DNA molecule, known as the viral DNA or proviral DNA, is integrated into the host cell's DNA. This integration allows the viral genetic material to become a permanent part of the host cell's genome.
6. Transcription and translation: Once integrated, the viral DNA is transcribed and translated by the host cell's machinery, leading to the production of new viral proteins and eventually the assembly of new viral particles.
7. Replication cycle: The replication cycle of HIV involves reverse transcription, integration, transcription, translation, and assembly. This unique characteristic of retroviruses, including HIV, is why they are classified as retroviruses.
In conclusion, HIV is classified as a retrovirus because it carries its genetic information in the form of RNA, which undergoes reverse transcription to convert it into DNA inside the host cell. This DNA is then integrated into the host cell's genome and used to produce new viral particles.
Explanation:
1. Retroviruses: Retroviruses are a family of RNA viruses that have the unique ability to convert their RNA genome into DNA inside the host cell. This reverse transcription process is carried out by the enzyme reverse transcriptase, which is encoded by the retroviral genome itself.
2. Genetic information: Genetic information in living organisms is typically stored in the form of DNA. However, retroviruses, including HIV, store their genetic information in the form of RNA.
3. RNA genome: HIV has a single-stranded RNA genome, which carries the necessary genetic information for the virus to replicate and produce new copies of itself.
4. Reverse transcription: When HIV infects a host cell, it uses its RNA genome as a template to synthesize a complementary DNA strand. This process is called reverse transcription. The viral enzyme reverse transcriptase catalyzes the synthesis of DNA from the viral RNA template.
5. Integration into host DNA: After the reverse transcription, the newly synthesized DNA molecule, known as the viral DNA or proviral DNA, is integrated into the host cell's DNA. This integration allows the viral genetic material to become a permanent part of the host cell's genome.
6. Transcription and translation: Once integrated, the viral DNA is transcribed and translated by the host cell's machinery, leading to the production of new viral proteins and eventually the assembly of new viral particles.
7. Replication cycle: The replication cycle of HIV involves reverse transcription, integration, transcription, translation, and assembly. This unique characteristic of retroviruses, including HIV, is why they are classified as retroviruses.
In conclusion, HIV is classified as a retrovirus because it carries its genetic information in the form of RNA, which undergoes reverse transcription to convert it into DNA inside the host cell. This DNA is then integrated into the host cell's genome and used to produce new viral particles.
The first antibiotic was discovered by___?- a)Louis Pasteur
- b)Koch
- c)R. Fleminng
- d)A. Fleming
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The first antibiotic was discovered by___?
a)
Louis Pasteur
b)
Koch
c)
R. Fleminng
d)
A. Fleming
|
|
Ashish Dasgupta answered |
Antibiotics and their discovery:
Antibiotics are a class of drugs that destroy or inhibit the growth of bacteria. They have revolutionized the field of medicine and have saved countless lives since their discovery. The first antibiotic was discovered by Alexander Fleming in 1928.
Alexander Fleming and his discovery:
Alexander Fleming was a Scottish biologist and pharmacologist who is credited with the discovery of the first antibiotic. In 1928, while working at St. Mary's Hospital in London, Fleming noticed that a mold called Penicillium notatum had contaminated one of his Petri dishes. He observed that the bacteria growing on the dish were actively killed by the mold, while the surrounding area remained free of bacteria.
Fleming's experiment was a breakthrough in the field of medicine, as it was the first time that anyone had demonstrated the ability of a substance to kill bacteria. He named the substance produced by the mold "penicillin" and began investigating its properties.
Further research and development:
Fleming's discovery of penicillin was a major breakthrough, but it was not until the 1940s that penicillin was mass-produced and began to be used widely as an antibiotic. Researchers Howard Florey and Ernst Chain at the University of Oxford developed methods for producing and purifying penicillin, and in 1942, the drug was used to successfully treat a British police officer who had been infected with a life-threatening bacterial infection.
Since then, the development of antibiotics has continued, with many new drugs being discovered and developed. Today, antibiotics are widely used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, and they have had a profound impact on human health and medicine.
Antibiotics are a class of drugs that destroy or inhibit the growth of bacteria. They have revolutionized the field of medicine and have saved countless lives since their discovery. The first antibiotic was discovered by Alexander Fleming in 1928.
Alexander Fleming and his discovery:
Alexander Fleming was a Scottish biologist and pharmacologist who is credited with the discovery of the first antibiotic. In 1928, while working at St. Mary's Hospital in London, Fleming noticed that a mold called Penicillium notatum had contaminated one of his Petri dishes. He observed that the bacteria growing on the dish were actively killed by the mold, while the surrounding area remained free of bacteria.
Fleming's experiment was a breakthrough in the field of medicine, as it was the first time that anyone had demonstrated the ability of a substance to kill bacteria. He named the substance produced by the mold "penicillin" and began investigating its properties.
Further research and development:
Fleming's discovery of penicillin was a major breakthrough, but it was not until the 1940s that penicillin was mass-produced and began to be used widely as an antibiotic. Researchers Howard Florey and Ernst Chain at the University of Oxford developed methods for producing and purifying penicillin, and in 1942, the drug was used to successfully treat a British police officer who had been infected with a life-threatening bacterial infection.
Since then, the development of antibiotics has continued, with many new drugs being discovered and developed. Today, antibiotics are widely used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, and they have had a profound impact on human health and medicine.
The antibody which can cross placental barrier is- a)IgA
- b)IgE
- c)IgM
- d)IgG
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The antibody which can cross placental barrier is
a)
IgA
b)
IgE
c)
IgM
d)
IgG

|
Yash answered |
IgG immunoglobin me sabse jyada 80% paye jate h . ye sbse chote imuno globin hote h kyuki enme paratopes kevel 2 hote h upr se ye monovalant hote h. chote size ke karan ye placenta ko cross kr jate h
Addiction is a psychological attachment to certain effects such as euphoria and temporary feeling of well-being is associated with- a)Sweet and pizza
- b)Drugs and alcohols
- c)Sedative and painkiller
- d)Love and coitus
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Addiction is a psychological attachment to certain effects such as euphoria and temporary feeling of well-being is associated with
a)
Sweet and pizza
b)
Drugs and alcohols
c)
Sedative and painkiller
d)
Love and coitus
|
|
Dhruba Sharma answered |
Addiction is a psychological attachment to certain effects such as euphoria and temporary feeling of well-being is associated with drugs and alcohols. These drive people to take them even these are not needed.
Development of vaccine is difficult for AIDS because HIV gene- a)Integrates into large number of host genes
- b)Undergoes mutation at rapid
- c)Undergoes reverse transcriptase
- d)Integrates its genome into that of helper T cells
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Development of vaccine is difficult for AIDS because HIV gene
a)
Integrates into large number of host genes
b)
Undergoes mutation at rapid
c)
Undergoes reverse transcriptase
d)
Integrates its genome into that of helper T cells
|
|
Kekan Dp answered |
It damage our immunity system from which any bacteria or virus can affect on us it's difficult to choose one tablet
Human Immunodeficiency Virus causes aids by attacking a type of white blood cell called- a)CD4
- b)CD3
- c)CD8
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Human Immunodeficiency Virus causes aids by attacking a type of white blood cell called
a)
CD4
b)
CD3
c)
CD8
d)
None of these
|
|
Bhaskar Ala answered |
"HIV " Attacks CD4 cells (T- helper, T- cells) .. this cells plays important role in immune system..
A tumor enclosed within a capsule is termed- a)Malignant
- b)Basophils
- c)Benign
- d)Metastasis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A tumor enclosed within a capsule is termed
a)
Malignant
b)
Basophils
c)
Benign
d)
Metastasis
|
|
Wahid Khan answered |
A tumor enclosed within a capsule is called benign tumor. Benign tumors normally remain confined to their original location and do not spread to other parts of the body and cause little damage.
Which property is not exhibited by a disease-causing pathogen?- a)Invasiveness
- b)Toxigenicity
- c)Virulence
- d)Co-operation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which property is not exhibited by a disease-causing pathogen?
a)
Invasiveness
b)
Toxigenicity
c)
Virulence
d)
Co-operation
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
A. Invasiveness of a pathogen is its ability to gain entry into a host and grow.
B. Toxigenicity is the power of a pathogen to form toxins capable of damaging host cells.
C. Virulence is the ability of a pathogen to produce disease.
D. Co-operation is a property not exhibited by a pathogen.
Hence, the correct answer is option D: Co-operation
Motile zygote of Plasmodium occurs in__________.- a)Human RBCs
- b)Human liver
- c)Salivary glands of Anopheles
- d)Gut of female Anopheles
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Motile zygote of Plasmodium occurs in__________.
a)
Human RBCs
b)
Human liver
c)
Salivary glands of Anopheles
d)
Gut of female Anopheles
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
Gut of female Anopheles
When female Anopheles, sucks the blood of an infected person, the gametocytes of plasmodium are picked up by the mosquito. Now sexual reproduction of Plasmodium occurs inside mosquito. The outer envelope of gametocyte is dissolved and its contents are liberated into the cavity of gut. These content undergo gametogony, i.e., formation of microgametes and macroagamete. The nuclei of both fuse and a synkaryon or zygote is formed. This zygote is motionless and spherical for sometime and vermiform very soon. Now, it is called vermicule or ookinete. Ookinete pierces the stomach wall and forms a cyst(oocyst) on its outer surface which has about 1000 sporozoites. The latter pass into salivary glands of the mosquito.
Anti-venom is used for the treatment of snake bite. The treatment of snake bite by anti-venom is an example of- a)Artificially acquired active immunity
- b)Specific natural immunity
- c)Naturally acquired passive immunity
- d)Artificially acquired passive immunity
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Anti-venom is used for the treatment of snake bite. The treatment of snake bite by anti-venom is an example of
a)
Artificially acquired active immunity
b)
Specific natural immunity
c)
Naturally acquired passive immunity
d)
Artificially acquired passive immunity
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
The treatment of snake bite by anit-venom is an example of artificial acquired passive immunity. Anti-venom neutralize the effect of venom in the body.
AIDS is caused by Human immuno deficiency virus (HIV) which is a member of group of virus called?- a)Mono virus
- b)Retro virus
- c)Miso virus
- d)Micro virus
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
AIDS is caused by Human immuno deficiency virus (HIV) which is a member of group of virus called?
a)
Mono virus
b)
Retro virus
c)
Miso virus
d)
Micro virus

|
Ishani Patel answered |
AIDS is caused by the Human immunodeficiency virus of a member of the group of virus called retrovirus. It is a type of RNA virus that inserts a copy of its genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell.
World AIDS Day was observed on which day?- a)30th November
- b)1st December
- c)2nd December
- d)3rd December
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
World AIDS Day was observed on which day?
a)
30th November
b)
1st December
c)
2nd December
d)
3rd December
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
On October 27, 1988, the UN General Assembly officially recognized that the World Health Organization declared December 1, 1988, to be World AIDS Day. World AIDS Day has also been observed on this date each year since then.
Cervical cancer can be caused by- a)Chlamydia sp.
- b)Human papilloma virus
- c)Herpes simplex virus
- d)Salmonella sp.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Cervical cancer can be caused by
a)
Chlamydia sp.
b)
Human papilloma virus
c)
Herpes simplex virus
d)
Salmonella sp.
|
|
Nandini Sharma answered |
Causes of Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that occurs in the cells of the cervix, which is the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. The most common cause of cervical cancer is an infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV).
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
HPV is a sexually transmitted infection that can cause changes in the cells of the cervix, which can lead to cancer. There are many different types of HPV, but some types are more likely to cause cancer than others. HPV is very common, and most people who are sexually active will contract the virus at some point in their lives. However, most people who contract HPV will not develop cervical cancer.
Other Risk Factors
In addition to HPV, there are other risk factors that can increase a woman's risk of developing cervical cancer. These include:
- Smoking
- Having a weakened immune system
- Having a history of sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
- Having multiple sexual partners
- Having sex at a young age
- Having a family history of cervical cancer
Prevention
The best way to prevent cervical cancer is to get vaccinated against HPV. The HPV vaccine is recommended for girls and boys between the ages of 11 and 12, although it can be given to people up to age 26. The vaccine is most effective when given before a person becomes sexually active.
Regular cervical cancer screening is also important for early detection of the disease. The Pap test, also known as a Pap smear, is a screening test that can detect abnormal cells in the cervix before they become cancerous. The American Cancer Society recommends that women begin getting Pap tests at age 21 and continue getting them every three years until age 29. After age 30, women can switch to getting a Pap test and an HPV test every five years. Women with certain risk factors may need to be screened more frequently.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cervical cancer is most commonly caused by an infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). Other risk factors, such as smoking and having a weakened immune system, can also increase a woman's risk of developing cervical cancer. Prevention measures, such as getting vaccinated against HPV and getting regular cervical cancer screening, can help reduce the risk of developing the disease.
Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that occurs in the cells of the cervix, which is the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. The most common cause of cervical cancer is an infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV).
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
HPV is a sexually transmitted infection that can cause changes in the cells of the cervix, which can lead to cancer. There are many different types of HPV, but some types are more likely to cause cancer than others. HPV is very common, and most people who are sexually active will contract the virus at some point in their lives. However, most people who contract HPV will not develop cervical cancer.
Other Risk Factors
In addition to HPV, there are other risk factors that can increase a woman's risk of developing cervical cancer. These include:
- Smoking
- Having a weakened immune system
- Having a history of sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
- Having multiple sexual partners
- Having sex at a young age
- Having a family history of cervical cancer
Prevention
The best way to prevent cervical cancer is to get vaccinated against HPV. The HPV vaccine is recommended for girls and boys between the ages of 11 and 12, although it can be given to people up to age 26. The vaccine is most effective when given before a person becomes sexually active.
Regular cervical cancer screening is also important for early detection of the disease. The Pap test, also known as a Pap smear, is a screening test that can detect abnormal cells in the cervix before they become cancerous. The American Cancer Society recommends that women begin getting Pap tests at age 21 and continue getting them every three years until age 29. After age 30, women can switch to getting a Pap test and an HPV test every five years. Women with certain risk factors may need to be screened more frequently.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cervical cancer is most commonly caused by an infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). Other risk factors, such as smoking and having a weakened immune system, can also increase a woman's risk of developing cervical cancer. Prevention measures, such as getting vaccinated against HPV and getting regular cervical cancer screening, can help reduce the risk of developing the disease.
Heroin is commonly called smack is chemically:- a)Diacetylchloride
- b)Diacetylmorphine
- c)Dichlordiethyl acetone
- d)Cocaine
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Heroin is commonly called smack is chemically:
a)
Diacetylchloride
b)
Diacetylmorphine
c)
Dichlordiethyl acetone
d)
Cocaine
|
|
Wahid Khan answered |
Heroine or smack is chemically ,diacetylmorphine which is a white, odourless, bitter crystalline compound.
Who discovered the technique of preparing vaccine from attenuated pathogen and in which year?- a)Edward Jenner, 1796
- b)Louis Pasteur, 1879
- c)Robert Downey, 1856
- d)Von Behring, 1950
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Who discovered the technique of preparing vaccine from attenuated pathogen and in which year?
a)
Edward Jenner, 1796
b)
Louis Pasteur, 1879
c)
Robert Downey, 1856
d)
Von Behring, 1950
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Louis Pasteur discovered the technique of preparing vaccine from an attenuated pathogen in 1879. This was the first true vaccine consisting of weakened micro-organisms against the disease chicken cholera.
Which of the following is a pair of viral diseases?- a)Ringworm, AIDS
- b)Dysentery, Common Cold
- c)Common Cold, AIDS
- d)Typhoid, Tuberculosis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a pair of viral diseases?
a)
Ringworm, AIDS
b)
Dysentery, Common Cold
c)
Common Cold, AIDS
d)
Typhoid, Tuberculosis
|
|
Muskan Sethi answered |
Ringworm - fungal infection
AIDS- HIV virus
Common cold - Rhino Virus
typhoid - Salmonella typhi ( bacteria)
tuberculosis - mycobacterium tuberculosis ( bacteria)
dysentery - it is of two types bacterial and amoebic
therefore the viral diseases are AIDS and Common cold
The drug which binds to specific opioid receptors present in our central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract is:- a)Smack
- b)Opioids
- c)Cannabinoids
- d)Heroine
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The drug which binds to specific opioid receptors present in our central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract is:
a)
Smack
b)
Opioids
c)
Cannabinoids
d)
Heroine
|
|
Maitri Tiwari answered |
Opioids are drugs that act on the central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract by binding to specific opioid receptors. These receptors are present in various parts of the body, including the brain, spinal cord, and digestive tract.
Mechanism of Action:
When opioids bind to the receptors, they activate a series of chemical reactions that lead to pain relief, sedation, and a sense of euphoria. Opioids work by mimicking the body's natural pain-relieving chemicals, such as endorphins.
Types of Opioids:
There are several types of opioids, including natural, semi-synthetic, and synthetic opioids. Examples of natural opioids include morphine and codeine, while semi-synthetic opioids include oxycodone and hydrocodone. Synthetic opioids include fentanyl and tramadol.
Medical Uses:
Opioids are commonly used in medical settings to treat pain, such as after surgery or for chronic pain conditions. They may also be used to treat coughing and diarrhea.
Risks and Side Effects:
However, opioids can be highly addictive and can lead to dependence, tolerance, and overdose. They can also cause a range of side effects, including drowsiness, constipation, nausea, and respiratory depression.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, opioids are a class of drugs that bind to specific opioid receptors in the central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract. They are commonly used to treat pain, but can also be highly addictive and have a range of side effects. It is important to use opioids only as prescribed and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Mechanism of Action:
When opioids bind to the receptors, they activate a series of chemical reactions that lead to pain relief, sedation, and a sense of euphoria. Opioids work by mimicking the body's natural pain-relieving chemicals, such as endorphins.
Types of Opioids:
There are several types of opioids, including natural, semi-synthetic, and synthetic opioids. Examples of natural opioids include morphine and codeine, while semi-synthetic opioids include oxycodone and hydrocodone. Synthetic opioids include fentanyl and tramadol.
Medical Uses:
Opioids are commonly used in medical settings to treat pain, such as after surgery or for chronic pain conditions. They may also be used to treat coughing and diarrhea.
Risks and Side Effects:
However, opioids can be highly addictive and can lead to dependence, tolerance, and overdose. They can also cause a range of side effects, including drowsiness, constipation, nausea, and respiratory depression.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, opioids are a class of drugs that bind to specific opioid receptors in the central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract. They are commonly used to treat pain, but can also be highly addictive and have a range of side effects. It is important to use opioids only as prescribed and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
AIDS day is________.- a)May 1
- b)December 1
- c)June 1
- d)December 20
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
AIDS day is________.
a)
May 1
b)
December 1
c)
June 1
d)
December 20
|
|
Dorri answered |
Since 1988, 1st December is celebrated as International AIDS day to raise awareness about it's spread.
HIV originated from CHIMPANZEES to Humans cross, in Democratic Republic of CONGO (known currently). Chimps who carried SIV(closely related to HIV) were being hunted & then eaten by people living there in 1920s.
Cancer cells are more damaged by radiations while others are not because cancer cells are
a) Undergoing rapid divisions
b) Different in nature
c) Starved
d) None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Tapsee Choudhary answered |
Always undifferentiated , quickly dividing and metabolically more active cells be sensitive for radiations... and cancer cells undergo rapid division and and more active metabolically.....
so they can damaged easily by radiations....
so they can damaged easily by radiations....
Alzheimer disease in humans is associated with the deficiency of______.- a)Glutamic acid
- b)Dopamine
- c)Acetylcholine
- d)Gamma amnobutyric acid(GABA)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Alzheimer disease in humans is associated with the deficiency of______.
a)
Glutamic acid
b)
Dopamine
c)
Acetylcholine
d)
Gamma amnobutyric acid(GABA)

|
Abhiram Nair answered |
Alzheimer disease is a neurological disorder in which the death of brain cells causes memory loss and cognitive decline. It is caused in human due to deficiency of acetylcholine.
Withdrawal syndrome like anxiety, shakiness, nausea and sweating due to- a)If regular dose of drug or alcohol is taken for long time
- b)If excessive dose of drug or alcohol is taken
- c)If regular dose of drug or alcohol is abruptly discontinued
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Withdrawal syndrome like anxiety, shakiness, nausea and sweating due to
a)
If regular dose of drug or alcohol is taken for long time
b)
If excessive dose of drug or alcohol is taken
c)
If regular dose of drug or alcohol is abruptly discontinued
d)
All of the above

|
Kaviya Lakshmi answered |
If a person who is having heavy dose of alcohol or drug suddenly stop or cut back on its consumption, it is called as alcohol or drug withdrawal. Mild withdrawal syndrome includes anxiety, shakiness, headache, nausea, vomiting, insomnia, sweating. The severe syndrome includes hallucination, seizures.
Sickle cell anemia has not been eliminated from the African population because- a)It is controlled by recessive genes
- b)It is not a fatal disease
- c)It is controlled by dominant genes
- d)It provides immunity against malaria
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Sickle cell anemia has not been eliminated from the African population because
a)
It is controlled by recessive genes
b)
It is not a fatal disease
c)
It is controlled by dominant genes
d)
It provides immunity against malaria
|
|
Rahul answered |
Sickle cell anaemia is an autosomal recessive disorder. Sickle cell anaemia is due to the substitution of glutamic acid by valine at the 6th position of the beta-globin chain of haemoglobin. The gene mutation gives protection against malaria in the carriers.
Assertion: A person who has received a cut and is bleeding needs to be given anti-tetanus treatment.
Reason: Anti-tetanus injection provides immunity by producing antibodies for tetanus.
- a)Both Assertion and Reason are false
- b)Both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion
- c)Assertion is true statement but reason is false
- d)Both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion: A person who has received a cut and is bleeding needs to be given anti-tetanus treatment.
Reason: Anti-tetanus injection provides immunity by producing antibodies for tetanus.
a)
Both Assertion and Reason are false
b)
Both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion
c)
Assertion is true statement but reason is false
d)
Both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion

|
Ayush Choudhury answered |
If a person has received a cut and is bleeding needs to be given anti-tetanus treatment. Anti-tetanus injection contains preformed antibodies to initiate quick response.
Carcinoma refers to- a)Malignant tumors of the connective tissue
- b)Malignant tumors of the colon
- c)Malignant tumors of the skin or mucous membrane
- d)Benign tumors of the connective tissue
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Carcinoma refers to
a)
Malignant tumors of the connective tissue
b)
Malignant tumors of the colon
c)
Malignant tumors of the skin or mucous membrane
d)
Benign tumors of the connective tissue
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Carcinoma refers to a malignant neoplasm of epithelial origin or cancer of the internal or external lining of the body. Carcinomas, malignancies of epithelial tissue, account for 80 to 90 percent of all cancer cases. Epithelial tissue is found throughout the body.
Chapter doubts & questions for Immunity - Biology A-Level 2024 is part of A Level exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the A Level exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for A Level 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Immunity - Biology A-Level in English & Hindi are available as part of A Level exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for A Level Exam by signing up for free.
Biology A-Level
280 videos|166 docs|147 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









