All Exams >
NEET >
Biology Class 12 >
All Questions
All questions of Organisms and Population for NEET Exam
The birth and death rates of four counteries are given below. which one will have the least population growth rate?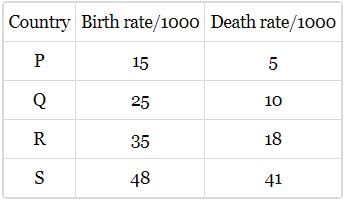
- a)P
- b)Q
- c)R
- d)S
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The birth and death rates of four counteries are given below. which one will have the least population growth rate?

a)
P
b)
Q
c)
R
d)
S

|
Top Rankers answered |
Growth rate = Birth rate - death rate
For country P, it is 10/1000. For country Q, It is 15/1000
For country R, it is 17/1000. For country S, It is 7/1000
Hence, country S has the least population growth rate
For country P, it is 10/1000. For country Q, It is 15/1000
For country R, it is 17/1000. For country S, It is 7/1000
Hence, country S has the least population growth rate
In a pond, last year there were 30 lotus plants. Through reproduction, 25 new lotus plants were added in one year while 8 plants died. The birth and death rates for the lotus population respectively are ___ and ____ individuals per lotus per year.- a)0.83 , 0.26
- b)0.26, 0.83
- c)0.25 , 0.80
- d)0.80, 0.25
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a pond, last year there were 30 lotus plants. Through reproduction, 25 new lotus plants were added in one year while 8 plants died. The birth and death rates for the lotus population respectively are ___ and ____ individuals per lotus per year.
a)
0.83 , 0.26
b)
0.26, 0.83
c)
0.25 , 0.80
d)
0.80, 0.25

|
Abha Dhamija answered |
Total number of plants (in the beginning ) = 30
New plants added by reproduction = 25
Birth rate (of a population)
New plants added by reproduction = 25
Birth rate (of a population)
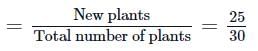
=0.83 individuals per lotus per year
Number of plants died =8
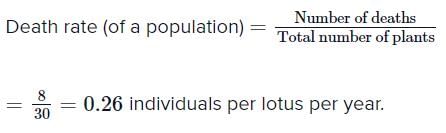
In a population per capita birth rate is 0.15 and per capita death rate is 0.08 during a unit time period. What is the value of r (intrinsic rate of natural increase) for the given population ?- a)0.023
- b)0.07
- c)0.05
- d)0.25
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a population per capita birth rate is 0.15 and per capita death rate is 0.08 during a unit time period. What is the value of r (intrinsic rate of natural increase) for the given population ?
a)
0.023
b)
0.07
c)
0.05
d)
0.25

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Intrinsic rate of natural increase (r)
= Birth rate − death rate
=0.15−0.08=0.07
If N population density at time t, then population density at time t+1 can be written asNt +1=Nt +[(A+B)−(C+D)]
Select the correct option for A, B, C and D in the above equation. - a)A can be mortality and B can be natality
- b)B can be immigration and C can be natality
- c)C can be mortality and D can be immigration
- d)A can be natality and D can be emigration
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If N population density at time t, then population density at time t+1 can be written as
Nt +1=Nt +[(A+B)−(C+D)]
Select the correct option for A, B, C and D in the above equation.
Select the correct option for A, B, C and D in the above equation.
a)
A can be mortality and B can be natality
b)
B can be immigration and C can be natality
c)
C can be mortality and D can be immigration
d)
A can be natality and D can be emigration
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
A and B are natality and immigration. They add to population density. C and D are mortality and emigration. They decrease population density.
Which of the following is not a factor that would limit the growth of a population ?- a)Food shortage
- b)Immigration
- c)Disease
- d)Famine
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a factor that would limit the growth of a population ?
a)
Food shortage
b)
Immigration
c)
Disease
d)
Famine
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Immigration is the permanent inward movement of some individuals coming from outside into an existing population. This increase population density and would not limit its growth.
_____ biomes are abundant in regions of hot and wet climate, while _____ biomes are found in hot and dry climate.- a)Desert, temperate
- b)Tropical, desert
- c)Tundra, savannah
- d)Desert, chapparal
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
_____ biomes are abundant in regions of hot and wet climate, while _____ biomes are found in hot and dry climate.
a)
Desert, temperate
b)
Tropical, desert
c)
Tundra, savannah
d)
Desert, chapparal
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
In tropical biome, the climate is warm with alternate wet dry periods. Rainfall is 90-160 cm. The climate in desert biome is hot and dry. The air, having little water vapour, is a poor insulator. The temperature rises considerably during the day and falls greatly at night because the ground radiates heat rapidly.
It can be said that some animals in their evolutionary development preferred to be conformers than regulators. Which of the following can be the best suited reason for it?- a)The metabolic reactions of these organisms can occur at a very wide range of temperature
- b)Maintaining homeostasis is an energetically expensive process
- c)The enzymes of these organisms are functional at high temperatures
- d)Both (b) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
It can be said that some animals in their evolutionary development preferred to be conformers than regulators. Which of the following can be the best suited reason for it?
a)
The metabolic reactions of these organisms can occur at a very wide range of temperature
b)
Maintaining homeostasis is an energetically expensive process
c)
The enzymes of these organisms are functional at high temperatures
d)
Both (b) and (c)
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Maintainig homeostasis, especially thermoregulation is energetically expensive for many organisms. During the course of evolution, the costs and benefits of maintaining a constant internal environment were taken into consideration and thus some species preferred to be conformers.
Which of the following is not an example of prey-predator relationship ?- a)Tiger eating a deer
- b)Plant Nepenthes trapping an insect
- c)Bacteria decomposing organic matter
- d)Crocodile killing a man
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not an example of prey-predator relationship ?
a)
Tiger eating a deer
b)
Plant Nepenthes trapping an insect
c)
Bacteria decomposing organic matter
d)
Crocodile killing a man
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Bacteria decompose the organic matter which is not really living. Hence, it cannot be considered as a prey predator relationship.
Choose the wrong statements
- a)Two species may not live in same habitat
- b)The more dissimilar the niches of two species the stronger is their competition between them
- c)No two species can occupy exactly the same niche in the same geographical area
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the wrong statements
a)
Two species may not live in same habitat
b)
The more dissimilar the niches of two species the stronger is their competition between them
c)
No two species can occupy exactly the same niche in the same geographical area
d)
All of these
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
According to the competitive exclusion principle, no two species can occupy exactly the same niche in exactly the same habitat at exactly the same time. Two species whose niches overlap may evolve by natural selection to have more distinct niches, resulting in resource partitioning.
So the correct answer is 'No two species can occupy exactly the same niche in the same geographical area.'
Exponential growth is observed in a population when- a)resources in the habitat are unlimited
- b)each species has the ability to realise its full innate potential
- c)both (a) and (b)
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Exponential growth is observed in a population when
a)
resources in the habitat are unlimited
b)
each species has the ability to realise its full innate potential
c)
both (a) and (b)
d)
none of these
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
When food and space for a population are unlimited, each species has the ability to realise fully its inherited potential to grow. Then the population grows in an exponential or geometric ratio.
Organisms may avoid stressful conditions by suspending their activities for sometime. If they do it to avoid high temperature it is called____ and if they do it to avoid low temperature then it is called_____ .- a)aestivation, migration
- b)migration, hibernation
- c)aestivation, hibernation
- d)hibernation, aestivation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Organisms may avoid stressful conditions by suspending their activities for sometime. If they do it to avoid high temperature it is called____ and if they do it to avoid low temperature then it is called_____ .
a)
aestivation, migration
b)
migration, hibernation
c)
aestivation, hibernation
d)
hibernation, aestivation
|
|
Mahesh Chaudhary answered |
Explanation:
Definition:
- Aestivation: Aestivation is a state of inactivity and dormancy in response to high temperatures and arid conditions.
- Hibernation: Hibernation is a state of inactivity and dormancy in response to low temperatures and limited food availability.
Characteristics:
- Aestivation: Organisms undergoing aestivation will reduce their metabolic rate, conserve energy, and wait for more favorable conditions.
- Hibernation: Organisms undergoing hibernation will lower their body temperature, slow down their heart rate, and enter a state of torpor to conserve energy.
Environmental Conditions:
- Aestivation: Aestivation is typically seen in animals living in hot and dry environments where water and food sources are scarce.
- Hibernation: Hibernation is common in animals living in cold climates where food is limited during the winter months.
Examples:
- Aestivation: Examples of animals that undergo aestivation include snails, earthworms, and certain amphibians during the dry season.
- Hibernation: Examples of animals that hibernate include bears, squirrels, and bats during the winter months.
In conclusion, organisms may adopt aestivation to avoid high temperatures and hibernation to avoid low temperatures as adaptive strategies to survive in challenging environmental conditions.
Definition:
- Aestivation: Aestivation is a state of inactivity and dormancy in response to high temperatures and arid conditions.
- Hibernation: Hibernation is a state of inactivity and dormancy in response to low temperatures and limited food availability.
Characteristics:
- Aestivation: Organisms undergoing aestivation will reduce their metabolic rate, conserve energy, and wait for more favorable conditions.
- Hibernation: Organisms undergoing hibernation will lower their body temperature, slow down their heart rate, and enter a state of torpor to conserve energy.
Environmental Conditions:
- Aestivation: Aestivation is typically seen in animals living in hot and dry environments where water and food sources are scarce.
- Hibernation: Hibernation is common in animals living in cold climates where food is limited during the winter months.
Examples:
- Aestivation: Examples of animals that undergo aestivation include snails, earthworms, and certain amphibians during the dry season.
- Hibernation: Examples of animals that hibernate include bears, squirrels, and bats during the winter months.
In conclusion, organisms may adopt aestivation to avoid high temperatures and hibernation to avoid low temperatures as adaptive strategies to survive in challenging environmental conditions.
A population with a larger proportion of older individuals than younger ones will likely to- a)grow larger and then decline
- b)continue to grow larger indefinitely
- c)grow smaller and may stabilize at a smaller population size
- d)not experience a change in population size.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A population with a larger proportion of older individuals than younger ones will likely to
a)
grow larger and then decline
b)
continue to grow larger indefinitely
c)
grow smaller and may stabilize at a smaller population size
d)
not experience a change in population size.
|
|
Anand Chaudhary answered |
Understanding Population Dynamics
A population with a larger proportion of older individuals is likely to face specific dynamics that influence its growth and stability.
Reasons for Option C: Grow Smaller and May Stabilize
- Higher Mortality Rates: Older individuals typically have shorter life expectancies, leading to increased mortality rates within this demographic. As these individuals age and pass away, the population will naturally decline.
- Lower Birth Rates: Populations with a higher proportion of older individuals often have lower birth rates, as older individuals are less likely to contribute to population growth. When fewer young individuals are born, the population's potential for growth diminishes.
- Age Structure Impact: The age structure of a population significantly influences its future growth. A population with more older individuals and fewer younger ones tends to transition towards stabilization or decline as the reproductive base shrinks.
- Potential for Stabilization: As the population decreases, it may reach a point of stabilization at a smaller size, given that the birth rates remain low and death rates may fluctuate based on health and environmental factors.
Conclusion
In summary, a population skewed towards older individuals is likely to experience a decline due to higher mortality and lower birth rates, potentially stabilizing at a smaller size. Hence, option C accurately reflects the expected demographic trends in such populations.
A population with a larger proportion of older individuals is likely to face specific dynamics that influence its growth and stability.
Reasons for Option C: Grow Smaller and May Stabilize
- Higher Mortality Rates: Older individuals typically have shorter life expectancies, leading to increased mortality rates within this demographic. As these individuals age and pass away, the population will naturally decline.
- Lower Birth Rates: Populations with a higher proportion of older individuals often have lower birth rates, as older individuals are less likely to contribute to population growth. When fewer young individuals are born, the population's potential for growth diminishes.
- Age Structure Impact: The age structure of a population significantly influences its future growth. A population with more older individuals and fewer younger ones tends to transition towards stabilization or decline as the reproductive base shrinks.
- Potential for Stabilization: As the population decreases, it may reach a point of stabilization at a smaller size, given that the birth rates remain low and death rates may fluctuate based on health and environmental factors.
Conclusion
In summary, a population skewed towards older individuals is likely to experience a decline due to higher mortality and lower birth rates, potentially stabilizing at a smaller size. Hence, option C accurately reflects the expected demographic trends in such populations.
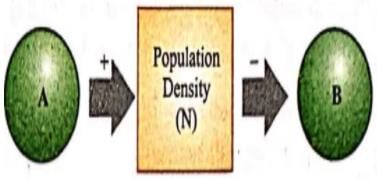
The density of a population in a given habitat during a given period, fluctuates due to changes in certain basic processes. On this basis, fill up boxes A and B in the given flow chart with correct option.
- a)A — Natality, B — Mortality
- b)A — Immigration , B — Emigration
- c)A — Natality, B — Immigration
- d)Both (a) and (b)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The density of a population in a given habitat during a given period, fluctuates due to changes in certain basic processes. On this basis, fill up boxes A and B in the given flow chart with correct option.

a)
A — Natality, B — Mortality
b)
A — Immigration , B — Emigration
c)
A — Natality, B — Immigration
d)
Both (a) and (b)
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
The population density in a given habitat and at a particular time period, fluctuates due to the changes in four basic processes given below:-
1. Natality- It refers to the number of births take place in a population during a given period.
2. Mortality- It refers to the number of deaths take place in a population during a given period.
3. Immigration- It refers to the number of individuals of the same species have migrated into the habitat from somewhere else during a particular time period.
4. Emigration- It refers to the number of individuals of the same species have migrated out of the habitat during a given time period.
Natality and immigration add to the population density whereas mortality and emigration decrease the population density.
Which of the following is not an example of using relative density to measure population density in a certain area ?- a)Counting pugmarks of tigers to find population density of tigers in a forest
- b)Counting the number of fishes caught in a trap to find population density of fishes in a lake
- c)Measuring biomass of bacterial culture to find out population density of bacteria in a petri dish
- d)Measuring biomass of phytoplanktons in 1cc water to find out population density of phytoplanktons in a lake
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not an example of using relative density to measure population density in a certain area ?
a)
Counting pugmarks of tigers to find population density of tigers in a forest
b)
Counting the number of fishes caught in a trap to find population density of fishes in a lake
c)
Measuring biomass of bacterial culture to find out population density of bacteria in a petri dish
d)
Measuring biomass of phytoplanktons in 1cc water to find out population density of phytoplanktons in a lake
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Sometimes, for certain ecological investigations, there is no need to know the absolute population densities. Relative densities serve the purpose equally well. In this case, population size is indirectly estimated without actually counting them. For example, the number of fishes caught per trap is good enough measure of its total population density in the lake. The tiger census in our National parks and tiger reserves is often based on pug marks (animal's foot print) and faecal pellets.
Total number of individuals of a species per unit area and per unit time is called:- a)Population size
- b)Population density
- c)Demography
- d)Population dynamics
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Total number of individuals of a species per unit area and per unit time is called:
a)
Population size
b)
Population density
c)
Demography
d)
Population dynamics
|
|
Chirag Unni answered |
Understanding Population Density
Population density is a crucial ecological concept that quantifies the number of individuals of a species within a specific area and timeframe.
Definition of Population Density
- Population density is defined as the total number of individuals of a species per unit area (e.g., per square kilometer) and per unit time (e.g., per year).
- It reflects how crowded a species is in a particular habitat, providing insight into resource availability, competition, and social structure.
Importance of Population Density
- Ecological Balance: Population density helps ecologists understand the balance within an ecosystem. High densities may indicate healthy breeding conditions, while low densities can signify environmental stress.
- Resource Management: Knowledge of population density is vital for wildlife management and conservation efforts, as it aids in assessing the sustainability of populations and the impact of human activities.
- Behavioral Insights: Studying population density allows researchers to examine social behaviors, territoriality, and interactions among species, which are influenced by how closely individuals are packed together.
Comparison with Other Terms
- Population Size: Refers only to the total number of individuals, without considering the area or time.
- Demography: Involves the statistical study of populations, including their structures and dynamics, but does not specifically focus on density.
- Population Dynamics: Encompasses the changes in population size and composition over time, influenced by birth rates, death rates, immigration, and emigration.
Understanding the concept of population density is essential for comprehending ecological relationships and managing biological resources effectively.
Population density is a crucial ecological concept that quantifies the number of individuals of a species within a specific area and timeframe.
Definition of Population Density
- Population density is defined as the total number of individuals of a species per unit area (e.g., per square kilometer) and per unit time (e.g., per year).
- It reflects how crowded a species is in a particular habitat, providing insight into resource availability, competition, and social structure.
Importance of Population Density
- Ecological Balance: Population density helps ecologists understand the balance within an ecosystem. High densities may indicate healthy breeding conditions, while low densities can signify environmental stress.
- Resource Management: Knowledge of population density is vital for wildlife management and conservation efforts, as it aids in assessing the sustainability of populations and the impact of human activities.
- Behavioral Insights: Studying population density allows researchers to examine social behaviors, territoriality, and interactions among species, which are influenced by how closely individuals are packed together.
Comparison with Other Terms
- Population Size: Refers only to the total number of individuals, without considering the area or time.
- Demography: Involves the statistical study of populations, including their structures and dynamics, but does not specifically focus on density.
- Population Dynamics: Encompasses the changes in population size and composition over time, influenced by birth rates, death rates, immigration, and emigration.
Understanding the concept of population density is essential for comprehending ecological relationships and managing biological resources effectively.
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Brood parasitism in birds is an example of parasitism in which the parasitic bird lays its eggs in the nest of its host and the host incubates them.
Statement 2: During the course of evolution, the eggs of the parasite bird have evolved to resemble the host's eggs in size and colour to reduce the chances of the host bird detecting the foreign eggs and removing them from the nest.
- a)Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect but statement 2 is not correct explanation of statement 1
- b)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1
- c)Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect
- d)Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Brood parasitism in birds is an example of parasitism in which the parasitic bird lays its eggs in the nest of its host and the host incubates them.
Statement 2: During the course of evolution, the eggs of the parasite bird have evolved to resemble the host's eggs in size and colour to reduce the chances of the host bird detecting the foreign eggs and removing them from the nest.
Statement 1: Brood parasitism in birds is an example of parasitism in which the parasitic bird lays its eggs in the nest of its host and the host incubates them.
Statement 2: During the course of evolution, the eggs of the parasite bird have evolved to resemble the host's eggs in size and colour to reduce the chances of the host bird detecting the foreign eggs and removing them from the nest.
a)
Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect but statement 2 is not correct explanation of statement 1
b)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1
c)
Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect
d)
Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
The correct option is:
2. Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1
Explanation:
- Statement 1 is correct: Brood parasitism in birds involves a parasitic bird laying its eggs in the nest of a host bird, and the host bird then incubates these eggs.
- Statement 2 is correct: During the course of evolution, the eggs of parasitic birds have evolved to resemble the host's eggs in size and color. This adaptation reduces the chances of the host bird detecting the foreign eggs and removing them from the nest.
Therefore, statement 2 provides the correct explanation for statement 1.
Which of the following equations correctly represents verhulst-Pearl logistic growth?- a)
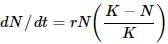
- b)
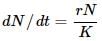
- c)
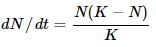
- d)
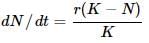
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following equations correctly represents verhulst-Pearl logistic growth?
a)
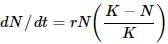
b)
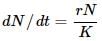
c)
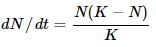
d)
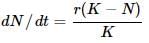

|
EduRev NEET answered |
S-shaped growth curve is also called Verhulst-Pearl logistic curve and is represented by the following equation :

where dN/dt= rate of change in population size, r= intrinsic rate of natural increase, N= population density, K= carrying capacity and 

What does the shape of the given age pyramids reflects about the growth status of the related population ?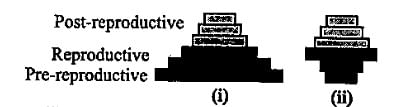
- a)(i) - Expanding (ii) - Stable
- b)(i) - Stable (ii) - Declining
- c)(i) - Expanding (ii) - Declining
- d)(i) - Declining (ii) - Stable
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What does the shape of the given age pyramids reflects about the growth status of the related population ?

a)
(i) - Expanding (ii) - Stable
b)
(i) - Stable (ii) - Declining
c)
(i) - Expanding (ii) - Declining
d)
(i) - Declining (ii) - Stable

|
Diwakar Singh answered |
Triangular age pyramid has high proportion of reproductive individuals, moderate number of reproductive individuals and fewer post-reproductive individuals. It represents young or rapidly growing population.
In urn-shaped age pyramid, the number of reproductive individuals is higher than the number of pre-reproductive individuals. It represents declining or diminishing population with negative growth
In bell-shaped age pyramid, the number of pre-reproductive and reproductive individuals is almost equal. Post reproductive individuals are comparatively fewer. It represents stable or stationary population where growth rate is nearly zero.
Many freshwater organisms cannot live for long in seawater because the surrounding water will be _____ to body cells and _____ may occur.- a)hypertonic, exosmosis
- b)hypertonic, endosmosis
- c)hypotonic, exosmosis
- d)hypotonic, endosmosis
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Many freshwater organisms cannot live for long in seawater because the surrounding water will be _____ to body cells and _____ may occur.
a)
hypertonic, exosmosis
b)
hypertonic, endosmosis
c)
hypotonic, exosmosis
d)
hypotonic, endosmosis
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
In sea water, the surrounding water is salty and hence is hypertonic to body cells. Thus, water will move from its higher concentration (in body) to its lower concentration (sea water) leading to exosmosis.Therefore, many fresh water animals can not live for long in sea water and vice varsa.
Read the following statements and select the incorrect ones.
(i) Homeostasis ensures constant osmotic concentration of cells.
(ii) The famous Keolado National Park (Bharatput) in Rajasthan hosts thousands of migratory birds coming from Siberia, in every winter.
(iii) 99% of animals and nearly all plants are regulators.
(iv) The conformers are able to maintain their body temperature inspite of changes in ambient temperature.- a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(ii) and (iii)
- c)(iii) and (iv)
- d)(i) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements and select the incorrect ones.
(i) Homeostasis ensures constant osmotic concentration of cells.
(ii) The famous Keolado National Park (Bharatput) in Rajasthan hosts thousands of migratory birds coming from Siberia, in every winter.
(iii) 99% of animals and nearly all plants are regulators.
(iv) The conformers are able to maintain their body temperature inspite of changes in ambient temperature.
(i) Homeostasis ensures constant osmotic concentration of cells.
(ii) The famous Keolado National Park (Bharatput) in Rajasthan hosts thousands of migratory birds coming from Siberia, in every winter.
(iii) 99% of animals and nearly all plants are regulators.
(iv) The conformers are able to maintain their body temperature inspite of changes in ambient temperature.
a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(ii) and (iii)
c)
(iii) and (iv)
d)
(i) and (iv)
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
About 99 percent of animals and nearly all plants do not have a mechanism to maintain a constant internal body environment. Their body temperature changes with the surrounding temperature. They are called conformers. They change their body temperature according to the ambient temperature.
Parameters related to age structure include- a)fecundity (birth rate)
- b)generation time
- c).Death rate
- d)all of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Parameters related to age structure include
a)
fecundity (birth rate)
b)
generation time
c)
.Death rate
d)
all of these
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
The age structure of a population is the percentage of individuals of different ages such as young, adult and old.
Age structure is shown by organisms in which individuals of more than one generation time are important related to it.
Age structure is shown by organisms in which individuals of more than one generation time are important related to it.
The plant-animal interactions often involve co-evolution of the mutualists so that- a)the mutually beneficial system could be safeguarded against 'cheaters'
- b)a given plant species can be pollinated only by its partner animal species and no other species
- c)the animal utilises plant not only for ovipositions but also to pollinate the plant
- d)all of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The plant-animal interactions often involve co-evolution of the mutualists so that
a)
the mutually beneficial system could be safeguarded against 'cheaters'
b)
a given plant species can be pollinated only by its partner animal species and no other species
c)
the animal utilises plant not only for ovipositions but also to pollinate the plant
d)
all of these
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Plant-animal interactions involve co-evolution of mutualists. This means, the evolution of the plant (e.g., flower) and the animal (e.g. pollinator species) are closely linked with one another.
Obligate parasites are those organisms which- a)obtain nutrition from dead, decaying organic matter only
- b)obtain nutrition from living organism only
- c)are essentially saporphytes but can also become parasites
- d)are essentially parasites but can also become saprophytes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Obligate parasites are those organisms which
a)
obtain nutrition from dead, decaying organic matter only
b)
obtain nutrition from living organism only
c)
are essentially saporphytes but can also become parasites
d)
are essentially parasites but can also become saprophytes
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Parasitism is a relationship between two living organisms of different species in which one organism called parasite obtains its food directly from another living organism called host. The parasite is usually smaller as compared to its host. It spends a part or whole of its life on or in the body of the host. Obligate parasites obtain their nutrition from living organisms only.
Which of the following algae are found in deepest ocean waters?- a)Red algae
- b)Yellow algae
- c)Green algae
- d)Brown algae
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following algae are found in deepest ocean waters?
a)
Red algae
b)
Yellow algae
c)
Green algae
d)
Brown algae
|
|
Pranitha Varma answered |
Red algae are found in deepest ocean waters
because it contains phycoerithrin pigment it can absorbs blue light which penetrates the most deep water for photosynthesis and appears Red because it reflects red light
so Red algae are found in deepest ocean waters
because it contains phycoerithrin pigment it can absorbs blue light which penetrates the most deep water for photosynthesis and appears Red because it reflects red light
so Red algae are found in deepest ocean waters
Very small animals are rarely found in polar regions because- a)smal animas have a larger surface area relative to their volume, so they lose body heat very fast when it is cold outside
- b)small animals have a smaller surface area relative to their volume, so they lose body heat very fast when it is cold outside
- c)small body volume makes internal heat production very difficult
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Very small animals are rarely found in polar regions because
a)
smal animas have a larger surface area relative to their volume, so they lose body heat very fast when it is cold outside
b)
small animals have a smaller surface area relative to their volume, so they lose body heat very fast when it is cold outside
c)
small body volume makes internal heat production very difficult
d)
none of these
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Temperature affects the absolute size of an animal and the relative proportions of various body parts. Birds and mammals attain greater body size in cold regions than in warm areas. But poikilotherms are smaller in cold region. This is Bergman's rule. This is true because small animals have little volume but larger surface area, so if they are in cold, they lose their body heat very fast. In cold climate, reduced surface area to volume ratio is ideal.
Which of the following problems does the frequent deep sea diver organisms like whales may face?- a)Compression of tissues surrounding air filled cavities
- b)High blood nitrogen levels
- c)Lack of oxygen
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following problems does the frequent deep sea diver organisms like whales may face?
a)
Compression of tissues surrounding air filled cavities
b)
High blood nitrogen levels
c)
Lack of oxygen
d)
All of these
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Diving to depth can result in mechanical distortion and tissue compression, especially in gas-filled spaces of the body. Absorption of nitrogen into blood can cause high blood nitrogen levels which can exert a narcotic effect. Lungs of the deep-diver cannot serve as a source of oxygen during the dive.
The population growth is generally described by the following equation:
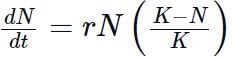
What does 'r' represent in the given equation ?- a)Population density at time 't'
- b)Intrinsic rate of natural increase
- c)Carrying capacity
- d)The base of natural logarithm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The population growth is generally described by the following equation:
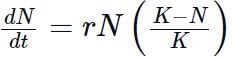
What does 'r' represent in the given equation ?
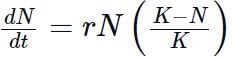
What does 'r' represent in the given equation ?
a)
Population density at time 't'
b)
Intrinsic rate of natural increase
c)
Carrying capacity
d)
The base of natural logarithm
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
A population growing in a habitat with limited resources shows initially a lag phase, followed by phases of increase and decrease and finally the population density reaches the carrying capacity. A plot of N in relation to time (t) results in a sigmoid curve. This type of population growth is called Verhulst- Pearl Logistic Growth as explained by the following equation:
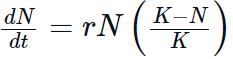
Where N = Population density at a time t;
r = Intrinsic rate of natural increase and;
K = Carrying capacity.
r = Intrinsic rate of natural increase and;
K = Carrying capacity.
Do humans exhibit any mutualistic relationships?- a)No humans form only parasitic relationships with other organisms
- b)No, humans are unable to form mutualistic relationships with other organisms
- c)Yes, between ourselves and the bacteria that make us ill
- d)Yes, between ourselves and the bacteria that live in our guts
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Do humans exhibit any mutualistic relationships?
a)
No humans form only parasitic relationships with other organisms
b)
No, humans are unable to form mutualistic relationships with other organisms
c)
Yes, between ourselves and the bacteria that make us ill
d)
Yes, between ourselves and the bacteria that live in our guts
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
In mutualism, both species are benefitted. Gut bacteria are dependent on us for food. They release certain enzymes which help us in digestion.
Human cells contain mitochondria, which are responsible for producing the energy needed by our cells. Remember that the ancestors of mitochondria may once have been free-living prokaryotes. If mitochondria were still considered to be seperate organisms within our cells, which of the following would best describe our relationship with them?- a)Parasitic
- b)Mutualistic
- c)Competitive
- d)Pathogenic
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Human cells contain mitochondria, which are responsible for producing the energy needed by our cells. Remember that the ancestors of mitochondria may once have been free-living prokaryotes. If mitochondria were still considered to be seperate organisms within our cells, which of the following would best describe our relationship with them?
a)
Parasitic
b)
Mutualistic
c)
Competitive
d)
Pathogenic
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
If mitochondria are still considered to be separate organisms, they would form mutualistic relationship with us. This is because they would get the resources from us and in turn produce energy for various activities of the body.
The prickly pear cactus became unusually abundant after its introduction in Australia, because it _________________.- a)had no coevolved herbivores
- b)formed new mycorrhizal association
- c)lost its thorns
- d)all of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The prickly pear cactus became unusually abundant after its introduction in Australia, because it _________________.
a)
had no coevolved herbivores
b)
formed new mycorrhizal association
c)
lost its thorns
d)
all of these
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Coevolution is caused by the selection pressures that each of the two species exerts on the other. Since there has been no coevolved herbivore with prickly pear cactus, it became abundant in Australia.
The interdependent evolution of flowering plants and pollinating insects together is known as- a)mutualism
- b)co-evolution
- c)commensalism
- d)co-operation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The interdependent evolution of flowering plants and pollinating insects together is known as
a)
mutualism
b)
co-evolution
c)
commensalism
d)
co-operation
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
The evolution of complementary adaptations in two species caused by the selection pressures that each exerts on the other is called co-evolution. It is common in symbiotic associations e.g., many insect-pollinated plants have evolved flowers whose shapes, colours, etc., make them attractive to particular insects, at the same time the pollinating insects have evolved sense organs and mouth parts specialised for quickly locating and extracting nectar from particular species of plants.
An inhabitant of Varanasi goes to Rohtang and experiences nausea, fatigue and heart palpitations. It is because- a)he is experiencing altitude sickness
- b)his RBC count is lower than required
- c)he is in an area of low atmospheric pressure
- d)all of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An inhabitant of Varanasi goes to Rohtang and experiences nausea, fatigue and heart palpitations. It is because
a)
he is experiencing altitude sickness
b)
his RBC count is lower than required
c)
he is in an area of low atmospheric pressure
d)
all of these
|
|
Charvi Rane answered |
Understanding Altitude Sickness
When an inhabitant from Varanasi travels to Rohtang, which is at a significantly higher altitude, they may experience various symptoms due to the change in environmental conditions. Here’s a breakdown of why the correct answer is option 'D' – all of these.
Altitude Sickness
- Definition: Altitude sickness, or acute mountain sickness (AMS), occurs due to reduced oxygen availability at high elevations.
- Symptoms: Common symptoms include nausea, fatigue, and heart palpitations, which the individual is experiencing.
RBC Count
- Importance of RBCs: Red blood cells (RBCs) carry oxygen throughout the body.
- Impact of Altitude: At higher altitudes, the thinner air can lead to lower oxygen levels, which may exacerbate symptoms if an individual's RBC count is not sufficient to meet oxygen demands.
Atmospheric Pressure
- Low Pressure Effects: Atmospheric pressure decreases with altitude, leading to reduced oxygen availability.
- Physiological Response: The body may react to this low pressure by increasing heart rate and causing fatigue and nausea as it struggles to obtain adequate oxygen.
Conclusion
In summary, the inhabitant's symptoms are a result of altitude sickness, potentially worsened by a lower RBC count and the effects of being in a low atmospheric pressure environment. Thus, all factors contribute to the experience of discomfort at high altitudes, confirming that option 'D' is indeed correct.
When an inhabitant from Varanasi travels to Rohtang, which is at a significantly higher altitude, they may experience various symptoms due to the change in environmental conditions. Here’s a breakdown of why the correct answer is option 'D' – all of these.
Altitude Sickness
- Definition: Altitude sickness, or acute mountain sickness (AMS), occurs due to reduced oxygen availability at high elevations.
- Symptoms: Common symptoms include nausea, fatigue, and heart palpitations, which the individual is experiencing.
RBC Count
- Importance of RBCs: Red blood cells (RBCs) carry oxygen throughout the body.
- Impact of Altitude: At higher altitudes, the thinner air can lead to lower oxygen levels, which may exacerbate symptoms if an individual's RBC count is not sufficient to meet oxygen demands.
Atmospheric Pressure
- Low Pressure Effects: Atmospheric pressure decreases with altitude, leading to reduced oxygen availability.
- Physiological Response: The body may react to this low pressure by increasing heart rate and causing fatigue and nausea as it struggles to obtain adequate oxygen.
Conclusion
In summary, the inhabitant's symptoms are a result of altitude sickness, potentially worsened by a lower RBC count and the effects of being in a low atmospheric pressure environment. Thus, all factors contribute to the experience of discomfort at high altitudes, confirming that option 'D' is indeed correct.
Which of the following statements is incorrect?- a)The flora of a place is heavily defined by availability and quality of water.
- b)The availability of light on land is closely linked with that of temperature since sun is the source for both.
- c)Topography does not affect biodiversity.
- d)Soil composition also affects the seepage of water into ground.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
a)
The flora of a place is heavily defined by availability and quality of water.
b)
The availability of light on land is closely linked with that of temperature since sun is the source for both.
c)
Topography does not affect biodiversity.
d)
Soil composition also affects the seepage of water into ground.
|
|
Kirti Khanna answered |
Topography does affect biodiversity.
Biodiversity refers to the variety of different species of plants, animals, and microorganisms found in a particular area. It is influenced by various factors including climate, geology, topography, and human activities. Each of these factors plays a crucial role in shaping the flora and fauna of a place.
Topography, which refers to the physical features of the land, has a significant impact on biodiversity. Here's why:
1. Habitat Diversity: Topography influences the formation of different habitats within an ecosystem. For example, mountains, valleys, rivers, and forests are all distinct habitats that support unique communities of organisms. The variation in elevation, slope, and landforms creates a range of microhabitats that offer different conditions for various species to thrive.
2. Microclimates: Topography affects the distribution of temperature, moisture, and sunlight, creating microclimates within a larger climate zone. These microclimates can support diverse species as they provide different environmental conditions. For instance, in mountainous regions, the temperature decreases with increasing altitude, leading to the formation of temperature gradients that support different plant and animal communities.
3. Water Availability: Topography determines the flow and availability of water in an area. It influences the formation of rivers, lakes, wetlands, and groundwater reservoirs. These water bodies provide vital resources for various organisms and contribute to the overall biodiversity of the region. The presence of water also affects the types of plants and animals that can survive in a particular area.
4. Fragmentation and Connectivity: Topography can lead to the fragmentation of habitats, isolating populations of species from each other. This fragmentation can reduce genetic diversity and limit the ability of organisms to disperse, resulting in lower overall biodiversity. On the other hand, topographical features such as corridors and connectivity between habitats can promote gene flow and enhance biodiversity by allowing species to move and interact with each other.
In summary, topography plays a crucial role in shaping biodiversity by creating diverse habitats, influencing microclimates, determining water availability, and affecting habitat connectivity. Therefore, the statement that topography does not affect biodiversity is incorrect.
Biodiversity refers to the variety of different species of plants, animals, and microorganisms found in a particular area. It is influenced by various factors including climate, geology, topography, and human activities. Each of these factors plays a crucial role in shaping the flora and fauna of a place.
Topography, which refers to the physical features of the land, has a significant impact on biodiversity. Here's why:
1. Habitat Diversity: Topography influences the formation of different habitats within an ecosystem. For example, mountains, valleys, rivers, and forests are all distinct habitats that support unique communities of organisms. The variation in elevation, slope, and landforms creates a range of microhabitats that offer different conditions for various species to thrive.
2. Microclimates: Topography affects the distribution of temperature, moisture, and sunlight, creating microclimates within a larger climate zone. These microclimates can support diverse species as they provide different environmental conditions. For instance, in mountainous regions, the temperature decreases with increasing altitude, leading to the formation of temperature gradients that support different plant and animal communities.
3. Water Availability: Topography determines the flow and availability of water in an area. It influences the formation of rivers, lakes, wetlands, and groundwater reservoirs. These water bodies provide vital resources for various organisms and contribute to the overall biodiversity of the region. The presence of water also affects the types of plants and animals that can survive in a particular area.
4. Fragmentation and Connectivity: Topography can lead to the fragmentation of habitats, isolating populations of species from each other. This fragmentation can reduce genetic diversity and limit the ability of organisms to disperse, resulting in lower overall biodiversity. On the other hand, topographical features such as corridors and connectivity between habitats can promote gene flow and enhance biodiversity by allowing species to move and interact with each other.
In summary, topography plays a crucial role in shaping biodiversity by creating diverse habitats, influencing microclimates, determining water availability, and affecting habitat connectivity. Therefore, the statement that topography does not affect biodiversity is incorrect.
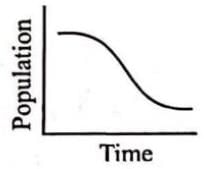
In a given population of 2000 individuals, 80 births and 125 deaths were reported over a given period of time. Which of the following graphs will correspond to it ?- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
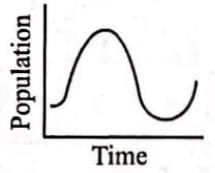
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a given population of 2000 individuals, 80 births and 125 deaths were reported over a given period of time. Which of the following graphs will correspond to it ?
a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Number of deaths is more than the number of births, showing a declining population.
In laboratory experiments, two species of the protist Paramecium (species 1 and 2) were grown alone and in the presence of the other species. The following graphs show growth of species 1 and species 2, both alone and when in mixed culture with the other species.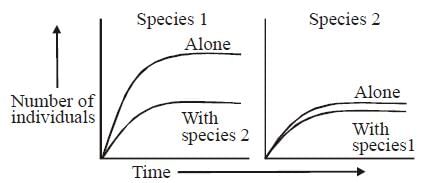 Which of the following conclusions can be drawn from the graphs ?
Which of the following conclusions can be drawn from the graphs ?- a)Competitive exclusion occurred in these experiments
- b)Both species are affected by interspecific competition but species 1 is affected less
- c)Both species are affected by interspecific competition but species 2 is affected less
- d)Both species are affected equally by interspecific competition
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In laboratory experiments, two species of the protist Paramecium (species 1 and 2) were grown alone and in the presence of the other species. The following graphs show growth of species 1 and species 2, both alone and when in mixed culture with the other species.

Which of the following conclusions can be drawn from the graphs ?
a)
Competitive exclusion occurred in these experiments
b)
Both species are affected by interspecific competition but species 1 is affected less
c)
Both species are affected by interspecific competition but species 2 is affected less
d)
Both species are affected equally by interspecific competition
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
When species 1 was kept with species 2, its number of individuals fell drastically while when species 2 was kept with species 1, its number of individuals was not much affected. Hence, both species are affected by inter-specific competition but species 2 is less affected.
Study the population growth curves (A and B) in the given graph and select the incorrect option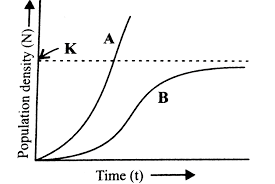
- a)Curve 'A' shows exponential growth, represented by equation dN/dt=rN
- b)Curve 'B' shows logistic growth, represented by equation
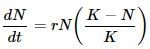
- c)Exponential growth curve is considered as more realistic than the logistic growth curve.
- d)Curve 'A' can also be represented by equation Nt=N0ert .
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the population growth curves (A and B) in the given graph and select the incorrect option

a)
Curve 'A' shows exponential growth, represented by equation dN/dt=rN
b)
Curve 'B' shows logistic growth, represented by equation
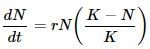
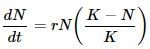
c)
Exponential growth curve is considered as more realistic than the logistic growth curve.
d)
Curve 'A' can also be represented by equation Nt=N0ert .
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Since resources of growth for most animal populations are finite and become limiting sooner or later, the logistic growth model is considered as more realistic.
Which of the following factors has a negative effect on the population growth rate ?- a)Emigration
- b)Immigration
- c)Natality
- d)Fecundity
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following factors has a negative effect on the population growth rate ?
a)
Emigration
b)
Immigration
c)
Natality
d)
Fecundity
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
migration is permanent outward movement of individuals from a population for settlement into a new area. If decreases the local population.
The maximum possible number of individuals that a habitat can support is called its- a)fecundity
- b)surviving ability
- c)carrying capacity
- d)biotic potential
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The maximum possible number of individuals that a habitat can support is called its
a)
fecundity
b)
surviving ability
c)
carrying capacity
d)
biotic potential
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
In nature, a given habitat has resources to support a certain number of individuals of a population, beyond which no further growth is possible. This limit is called as nature's carrying capacity (K) for that species in that habitat.
Organisms that can maintain a constant internal temperature are called as- a)homoiothermic
- b)poikilothermic
- c)oligothermic
- d)heterothermic
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Organisms that can maintain a constant internal temperature are called as
a)
homoiothermic
b)
poikilothermic
c)
oligothermic
d)
heterothermic
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Animals with constant body temperature are called homoiotherms. They have insulating coat to check the loss of body heat. This coat consists of hair in most mammals, blubber(subcutaneous fat) in whales and seals, and feathers in birds. Shivering warms up the body and perspiration cools down the body of these animals when required. These are also termed endotherms as they regulate their body temperature by physiological means and maintain more or less constant internal temperature. Poikilotherms are cold-blooded animals which are unable to regulate their body temperature which changes with change in temperature of environment e.g., fish, frog, lizards. They are also called as ectottherms.
Which of the following options exemplifies a behavioural means of homeostasis?- a)A man sweating profusely in a hot room
- b)A rhino covering itself in mud to keep cool
- c)A desert lizard basking in sun to increase its body temperature
- d)Both (b) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following options exemplifies a behavioural means of homeostasis?
a)
A man sweating profusely in a hot room
b)
A rhino covering itself in mud to keep cool
c)
A desert lizard basking in sun to increase its body temperature
d)
Both (b) and (c)
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Some organisms show behavioural adaptations to cope with variations in their environment. A rhino covering itself in mud to keep cool and desert lizard basking in sun to keep warm are examples of behavioural means of homeostasis. Desert lizards lack the physiological ability to deal with the high temperature, fairly constant by behavioural means. They enjoy in the sun and absorb heat when their body temperature drops below the comfort zone, but move into shade when the surrounding temperature starts increasing. Some species are capable of burrowing into the soil to hide and escape from too much heat.
The age structures of a population influences population growth because- a)younger females have more offsprings than do older females
- b)different ae groups have different reproductive capabilities
- c)more is the number of immature individuals, slower is the growth of population
- d)a shorter generation time results is slower population growth.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The age structures of a population influences population growth because
a)
younger females have more offsprings than do older females
b)
different ae groups have different reproductive capabilities
c)
more is the number of immature individuals, slower is the growth of population
d)
a shorter generation time results is slower population growth.
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Different age groups have different reproductive capabilities. Pre-reproductive individuals are the young individuals which will enter the reproductive age after some time. They are the potential source of increas in population. Reproductive individuals are the ones which are actually adding neq members to the population. Post-reproductive individuals are older individuals which no longer take part in reproduction.
A behavioural strategy of adaptation called echolocation is found in- a)bats
- b)butterfly
- c)praying mantis
- d)arctic tern
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A behavioural strategy of adaptation called echolocation is found in
a)
bats
b)
butterfly
c)
praying mantis
d)
arctic tern
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Bats are nocturnal flying mammals which do not employ eyesight for location of thir path, food, place of rest, etc. They produce high-frequency sound which produces echoes after striking various objects on the principle of sonar. Echoes are then analysed by the bats to know their path.
Which of the following an abiotic component?- a)Animals
- b)Plants
- c)Planktons
- d)Light
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following an abiotic component?
a)
Animals
b)
Plants
c)
Planktons
d)
Light

|
Bs Academy answered |
Among the following light is the odd one out since it is an abiotic factor. It is one of the limiting factors important for plant growth and development. It is an essential component required for photosynthesis and plant life.
What is the primary reason why very small animals are rarely found in polar regions?- a)They have a small surface area relative to their volume.
- b)They cannot regulate their internal environment over extreme conditions.
- c)They are better adapted to warm climates.
- d)They face no metabolic challenges in polar regions.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
They have a small surface area relative to their volume.
b)
They cannot regulate their internal environment over extreme conditions.
c)
They are better adapted to warm climates.
d)
They face no metabolic challenges in polar regions.

|
Lead Academy answered |
The correct answer is Option B. Small animals have a larger surface area relative to their volume, leading to rapid heat loss in cold conditions. They must expend a lot of energy to maintain body heat, making it challenging for them to survive in extreme cold, such as in polar regions.
Refer to the given table that summarises the interactions between two organisms (organisms 1 and organism 2). Identify the types of interaction (A,B and C) and select the correct answer.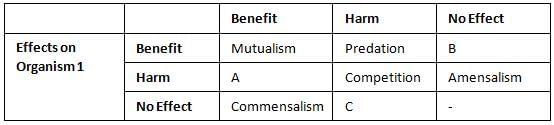 (i) A can be either predation or parasitism
(i) A can be either predation or parasitism
(ii) B can be either commensalism
(iii) C can be amensalism.
(iv) A can be amensalism, - a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(ii) and (iii)
- c)(ii) and (iv)
- d)(i) and (iii)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Refer to the given table that summarises the interactions between two organisms (organisms 1 and organism 2). Identify the types of interaction (A,B and C) and select the correct answer.

(i) A can be either predation or parasitism
(ii) B can be either commensalism
(iii) C can be amensalism.
(iv) A can be amensalism,
(ii) B can be either commensalism
(iii) C can be amensalism.
(iv) A can be amensalism,
a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(ii) and (iii)
c)
(ii) and (iv)
d)
(i) and (iii)
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
A can be either predation or parasitism since one species is harmed and the other is benefitted. B is commensalism since one species is benefitted and other has no effect on it. C can be amensalism since one species is harmed and the other has no effect on it.
Which type of interaction is being shown in the given figure ?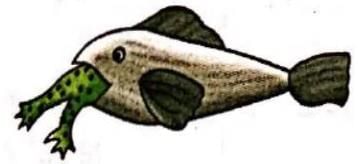
- a)Parasitism
- b)Commensalism
- c)Predation
- d)Amensalism
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which type of interaction is being shown in the given figure ?

a)
Parasitism
b)
Commensalism
c)
Predation
d)
Amensalism
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Predation is an interaction between members of two species in which members of one species capture, kill and eat up members of other species. The former are called predators and the latter are called preys.
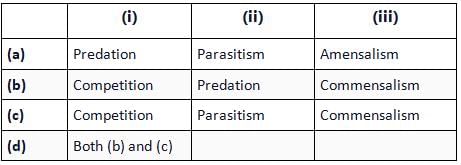
Refer to the given table. If '+' sign has been assigned for beneficial interaction, sign for detrimental interaction and '0' for neutral interaction, identify the type of interaction (i), (ii) and (iii) and select the correct option.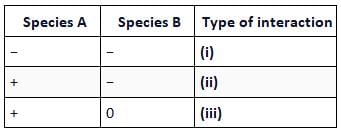
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Refer to the given table. If '+' sign has been assigned for beneficial interaction, sign for detrimental interaction and '0' for neutral interaction, identify the type of interaction (i), (ii) and (iii) and select the correct option.


a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
In competition, both species are harmed. In predation and parasitism, one species derives benefit and the other one is harmed. Commensalism is an interaction in which one species is benefitted and other one remains unaffected.
_____ is an attribute of the organism (morphological, physiological, behavioural) to survive and reproduce in its habitat.- a)Migration
- b)Hibernation
- c)Adaptation
- d)Homeostasis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
_____ is an attribute of the organism (morphological, physiological, behavioural) to survive and reproduce in its habitat.
a)
Migration
b)
Hibernation
c)
Adaptation
d)
Homeostasis
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
Adaptation is a quality of the organism (morphological physiological, behavioural) that enables it to survive and reproduce in its habitat. Adaptations allow organisms to live in different types of habitats. They develop due to natural selection of suitable variations appearing in living beings through mutations and recombinations.
Chapter doubts & questions for Organisms and Population - Biology Class 12 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Organisms and Population - Biology Class 12 in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup










