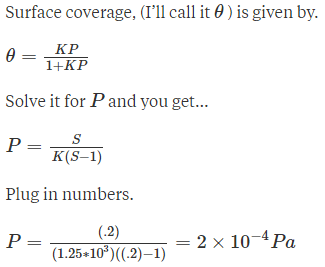All Exams >
Chemistry >
Physical Chemistry >
All Questions
All questions of Adsorption for Chemistry Exam
The correct statement(s) pertaining to the adsorption of a gas on a solid surface is (are):- a)Adsorption is always exothermic
- b)Physisorption may transform into chemisorption at high temperature
- c)Physisorption increases with increasing temperature but chemisorption decreases with increasing temperature
- d)Chemisorption is more exothermic than physisorption, however it is very slow due to higher energy of activation.
Correct answer is option 'A,B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct statement(s) pertaining to the adsorption of a gas on a solid surface is (are):
a)
Adsorption is always exothermic
b)
Physisorption may transform into chemisorption at high temperature
c)
Physisorption increases with increasing temperature but chemisorption decreases with increasing temperature
d)
Chemisorption is more exothermic than physisorption, however it is very slow due to higher energy of activation.
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
- When the gas adsorb surface energy decreases which appears in the form of heat i.e. exothermic.
- At high temperature gas molecules get activation energy required to form chemical bond and hence chemisorption is favored.
- As per le chatlier principle physiosorption being exothermic should decrease with temperature.
- Obviously reactions that require high activation energy are slow.
Hence A, B and D are correct.
Which statement is not correct:- a)Physical adsorption is due to van der Waal’s forces
- b)Physical adsorption decreases at high temperature and low pressure
- c)Physical adsorption is reversible
- d)Adsorption energy for a chemical adsorption is generally lesser than that of physical adsorption
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which statement is not correct:
a)
Physical adsorption is due to van der Waal’s forces
b)
Physical adsorption decreases at high temperature and low pressure
c)
Physical adsorption is reversible
d)
Adsorption energy for a chemical adsorption is generally lesser than that of physical adsorption
|
|
Pooja Choudhury answered |
- Physical adsorption is due to van der Waals forces which are weak forces,
- Physical adsorption decreases at high temperature and low pressure
- Physical adsorption is reversible
- Adsorption energy for chemical adsorption is generally more than that for physical adsorption. It is not lesser than that for physical adsorption.
Rate of physisorption increases with:- a)Decrease in temperature
- b)Increase in temperature
- c)Decrease in pressure
- d)Decrease in surface area.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Rate of physisorption increases with:
a)
Decrease in temperature
b)
Increase in temperature
c)
Decrease in pressure
d)
Decrease in surface area.

|
Shivam Sharma answered |
Adsorption is an exothermic process. Heat is releases whenever molecules are adsorbed on the surface.
So, rate of adsorption decreases whenever temperature is increases. This due to the fact that, when temperature is increases, the kinetic energy of adsorbed molecules gets increased and they overcome the electrostatic force of attraction by the adsorbent surface.
The Langmuir adsorption isotherm is deduced using the assumption:- a)The heat of adsorption varies with coverage
- b)The adsorbed molecules interact with each other
- c)The adsorption takes place in multi layer
- d)The adsorption sites are equivalent in their ability to adsorb the particles.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The Langmuir adsorption isotherm is deduced using the assumption:
a)
The heat of adsorption varies with coverage
b)
The adsorbed molecules interact with each other
c)
The adsorption takes place in multi layer
d)
The adsorption sites are equivalent in their ability to adsorb the particles.

|
Swara Dasgupta answered |
Langmuir adsorption isotherm is based on the assumption that every adsorption site is equivalent and that the ability of a particle to bind there is independent of wether nearly sites are occupied or not.
For adsorption of gas on solid surface, the plots of log x/m vs. log P is linear with a slope equal to:- a)K
- b)log K
- c)1/nK
- d)1/n ( n being interger)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
For adsorption of gas on solid surface, the plots of log x/m vs. log P is linear with a slope equal to:
a)
K
b)
log K
c)
1/nK
d)
1/n ( n being interger)

|
Kaavya Sengupta answered |
The empirical relation x/m = kp1/n put forward by Freundlich is known as Freundlich adsorption isotherm. Taking logarithm

Adsorption is accompanied with:- a)Decrease in entropy of system
- b)Decrease in enthalpy
- c)The value of ΔS. T is negative
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Adsorption is accompanied with:
a)
Decrease in entropy of system
b)
Decrease in enthalpy
c)
The value of ΔS. T is negative
d)
All of the above

|
Shivam Sharma answered |
Adsorption is accompanied by decrease in enthalpy (ΔH=−ve) and decrease in entropy (ΔS=−ve).
1 g of activated charcoal has a surface area 103 m3. If complete monolayer coverage is assumed, how much NH3 in cm3 at STP would be adsorbed on the surface of 25 g of the charcoal. Given diameter of NH3 molecule = 0.3 nm
Correct answer is '13.168'. Can you explain this answer?
1 g of activated charcoal has a surface area 103 m3. If complete monolayer coverage is assumed, how much NH3 in cm3 at STP would be adsorbed on the surface of 25 g of the charcoal. Given diameter of NH3 molecule = 0.3 nm

|
Anirban Kapoor answered |
Ans.

Method to Solve :

3g of activated charcoal was added to 50 ml of acetic acid solution (0.06 M) in a flask. After an hour it was filtered and the strength of filtrate was found to be 0.042 M. The amount of acetic acid adsorbed per gram of charcoal is
- a)42 mg
- b)18 mg
- c)54 mg
- d)36 mg
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
3g of activated charcoal was added to 50 ml of acetic acid solution (0.06 M) in a flask. After an hour it was filtered and the strength of filtrate was found to be 0.042 M. The amount of acetic acid adsorbed per gram of charcoal is
a)
42 mg
b)
18 mg
c)
54 mg
d)
36 mg
|
|
Vivek Khatri answered |
To find the amount of acetic acid adsorbed per gram of charcoal, we need to calculate the mass of acetic acid adsorbed by the activated charcoal and divide it by the mass of charcoal used.
The initial concentration of acetic acid is 0.06 M, and after adsorption, the final concentration is 0.042 M. The difference between the initial and final concentrations represents the amount of acetic acid adsorbed by the activated charcoal.
0.06 M - 0.042 M = 0.018 M
Now we need to find the mass of acetic acid (in grams) that was adsorbed by the activated charcoal. We can use the equation: molarity x volume = moles
0.018 M x 50 ml = 0.9 moles
Now, we can find mass of acetic acid adsorbed by mass = moles x molar mass
mass = 0.9 moles x 60 g/mol = 54 g
Now we need to divide the mass of acetic acid adsorbed by the mass of activated charcoal used:
54 g / 3 g = 18 g/g
Therefore, the amount of acetic acid adsorbed per gram of charcoal is 18 mg, So the correct answer is 2.
1 g of charcoal adsorbs 100 mL of 0.5 MCH3COOH to form a monolayer and thereby the molarity of CH3COOH reduces to 0.49. Calculate the surface area of charcoal adsorbed by each molecule of acetic acid. Surface area of charcoal = 3.01 × 102 m2/g.
- a)5 × 10–19
- b)3 × 10–19
- c)1 × 10–19
- d)7 × 10–19
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
1 g of charcoal adsorbs 100 mL of 0.5 MCH3COOH to form a monolayer and thereby the molarity of CH3COOH reduces to 0.49. Calculate the surface area of charcoal adsorbed by each molecule of acetic acid. Surface area of charcoal = 3.01 × 102 m2/g.
a)
5 × 10–19
b)
3 × 10–19
c)
1 × 10–19
d)
7 × 10–19

|
Isha Bose answered |

The conductivity of micelles is ___________- a)Higher than a colloidal solution
- b)Lower than a colloidal solution
- c)Equals to colloidal solution
- d)None of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The conductivity of micelles is ___________
a)
Higher than a colloidal solution
b)
Lower than a colloidal solution
c)
Equals to colloidal solution
d)
None of the mentioned
|
|
Vivek Khatri answered |
The conductivity of micelles is higher than the colloidal solution. And hence they can conduct more electric charges through them.
H2 gas was adsorbed on 1 g powdered copper surface forming monolayer of molecules. On desorption total H2 collected measured 1.36 cm3 at STP. Assuming volume of 1 molecule of H2 4.742 × 10–23 cm3, calculate specific area of copper powder- a)5.79 × 104
- b)3.79 × 104
- c)2.79 × 104
- d)6.79 × 104
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
H2 gas was adsorbed on 1 g powdered copper surface forming monolayer of molecules. On desorption total H2 collected measured 1.36 cm3 at STP. Assuming volume of 1 molecule of H2 4.742 × 10–23 cm3, calculate specific area of copper powder
a)
5.79 × 104
b)
3.79 × 104
c)
2.79 × 104
d)
6.79 × 104

|
Vaibhav Ghosh answered |
Ans.


Charcoal (1 g) of surface area 100 m2 per gram, adsorbs 60 mg of acetic from an aqueous solution at 25°C and 1 atmosphere pressure. The number of moles of acetic acid adsorbed per cm2 of charcoal surface is:
- a)10–2
- b)10–16
- c)10–15
- d)10–9
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Charcoal (1 g) of surface area 100 m2 per gram, adsorbs 60 mg of acetic from an aqueous solution at 25°C and 1 atmosphere pressure. The number of moles of acetic acid adsorbed per cm2 of charcoal surface is:
a)
10–2
b)
10–16
c)
10–15
d)
10–9

|
Aryan Choudhary answered |
°C. Calculate the amount of acetic acid adsorbed by 1 kg of charcoal at the same conditions.
To calculate the amount of acetic acid adsorbed by 1 kg of charcoal, we need to convert the given values to the same units.
1 kg of charcoal is equal to 1000 g.
The surface area of 1 g of charcoal is given as 100 m2 per gram.
Therefore, the surface area of 1000 g (1 kg) of charcoal is 1000 * 100 = 100,000 m2.
The amount of acetic acid adsorbed by 1 g of charcoal is given as 60 mg.
To find the amount of acetic acid adsorbed by 1 kg of charcoal, we multiply the amount adsorbed by 1 g by the mass of charcoal:
60 mg/g * 1000 g = 60,000 mg
To convert mg to grams, we divide by 1000:
60,000 mg / 1000 = 60 g
Therefore, 1 kg of charcoal at the same conditions will adsorb 60 g of acetic acid.
To calculate the amount of acetic acid adsorbed by 1 kg of charcoal, we need to convert the given values to the same units.
1 kg of charcoal is equal to 1000 g.
The surface area of 1 g of charcoal is given as 100 m2 per gram.
Therefore, the surface area of 1000 g (1 kg) of charcoal is 1000 * 100 = 100,000 m2.
The amount of acetic acid adsorbed by 1 g of charcoal is given as 60 mg.
To find the amount of acetic acid adsorbed by 1 kg of charcoal, we multiply the amount adsorbed by 1 g by the mass of charcoal:
60 mg/g * 1000 g = 60,000 mg
To convert mg to grams, we divide by 1000:
60,000 mg / 1000 = 60 g
Therefore, 1 kg of charcoal at the same conditions will adsorb 60 g of acetic acid.
True statement(s) about Langmuir isotherm is (are):- a)Valid for monolayer coverage
- b)All adsorption sites are equivalent
- c)There is dynamic equilibrium between free gas and adsorbed gas
- d)Adsorption probability is independent of occupancy at the neighbouring sites
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
True statement(s) about Langmuir isotherm is (are):
a)
Valid for monolayer coverage
b)
All adsorption sites are equivalent
c)
There is dynamic equilibrium between free gas and adsorbed gas
d)
Adsorption probability is independent of occupancy at the neighbouring sites

|
Bhavana Pillai answered |
Langmuir isotherm is a model that explains the adsorption phenomenon on a solid surface. It is named after Irving Langmuir, who proposed this model in 1916. The true statements about Langmuir isotherm are:
Valid for Monolayer Coverage:
Langmuir isotherm is valid for monolayer coverage, which means that it assumes that only one layer of gas molecules is adsorbed on the surface of the solid. This assumption is valid when the surface of the solid is homogeneous and the adsorption sites are equivalent.
All Adsorption Sites are Equivalent:
Langmuir isotherm assumes that all the adsorption sites on the surface of the solid are equivalent. It means that the probability of adsorption of gas molecules on any adsorption site is the same.
There is Dynamic Equilibrium between Free Gas and Adsorbed Gas:
Langmuir isotherm assumes that there is a dynamic equilibrium between the free gas molecules and the adsorbed gas molecules on the surface of the solid. At equilibrium, the rate of adsorption is equal to the rate of desorption.
Adsorption Probability is Independent of Occupancy at the Neighboring Sites:
Langmuir isotherm assumes that the probability of adsorption of gas molecules on a particular site is independent of the occupancy of the neighboring sites. It means that the adsorption probability is not affected by the presence or absence of adsorbed gas molecules on the neighboring sites.
In conclusion, Langmuir isotherm is a useful model to understand the adsorption phenomenon on a solid surface. It assumes that the adsorption sites are equivalent, there is a dynamic equilibrium between the free gas and the adsorbed gas, the probability of adsorption is independent of the neighboring sites, and it is valid for monolayer coverage.
Valid for Monolayer Coverage:
Langmuir isotherm is valid for monolayer coverage, which means that it assumes that only one layer of gas molecules is adsorbed on the surface of the solid. This assumption is valid when the surface of the solid is homogeneous and the adsorption sites are equivalent.
All Adsorption Sites are Equivalent:
Langmuir isotherm assumes that all the adsorption sites on the surface of the solid are equivalent. It means that the probability of adsorption of gas molecules on any adsorption site is the same.
There is Dynamic Equilibrium between Free Gas and Adsorbed Gas:
Langmuir isotherm assumes that there is a dynamic equilibrium between the free gas molecules and the adsorbed gas molecules on the surface of the solid. At equilibrium, the rate of adsorption is equal to the rate of desorption.
Adsorption Probability is Independent of Occupancy at the Neighboring Sites:
Langmuir isotherm assumes that the probability of adsorption of gas molecules on a particular site is independent of the occupancy of the neighboring sites. It means that the adsorption probability is not affected by the presence or absence of adsorbed gas molecules on the neighboring sites.
In conclusion, Langmuir isotherm is a useful model to understand the adsorption phenomenon on a solid surface. It assumes that the adsorption sites are equivalent, there is a dynamic equilibrium between the free gas and the adsorbed gas, the probability of adsorption is independent of the neighboring sites, and it is valid for monolayer coverage.
According to Langmuir adsorption isotherm the amount of gas adsorbed at very high pressure:- a)Reaches a constant limiting value
- b)Goes on increasing with pressure
- c)Goes on decreasing with pressure
- d)Increases first and decreases later with pressure
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
According to Langmuir adsorption isotherm the amount of gas adsorbed at very high pressure:
a)
Reaches a constant limiting value
b)
Goes on increasing with pressure
c)
Goes on decreasing with pressure
d)
Increases first and decreases later with pressure

|
Sagarika Patel answered |
According to langmuir Adsorption isotherm the amount of gas adsorbed at very high pressures reaches a constant limiting volume.
On the basis of data given below predict which of the following gases shows least adsorption on a definite amount of charcoal?

- a)CO2
- b)H2
- c)CH4
- d)SO2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
On the basis of data given below predict which of the following gases shows least adsorption on a definite amount of charcoal?


a)
CO2
b)
H2
c)
CH4
d)
SO2

|
Kiran Pillai answered |
The adsorption of gases on charcoal is influenced by several factors, including the nature of the gas molecules and the properties of the charcoal surface. In this case, we are given four gases: CO2, SO2, CH4, and H2, and we need to determine which gas shows the least adsorption on a definite amount of charcoal.
To predict the gas with the least adsorption, we can consider the following factors:
1. Molecular Size: The size of the gas molecules can affect their adsorption on the charcoal surface. Smaller molecules can penetrate the pores of the charcoal more easily, leading to stronger adsorption. Larger molecules may have difficulty accessing the charcoal surface and thus show weaker adsorption.
2. Polarity: The polarity of the gas molecules can also affect their adsorption. Polar molecules have dipole moments, which can interact with polar sites on the charcoal surface through dipole-dipole interactions. Nonpolar molecules, on the other hand, do not have dipole moments and may have weaker interactions with the charcoal surface.
Based on these factors, we can analyze the given gases:
a) CO2: Carbon dioxide is a relatively small molecule (linear with a molecular weight of 44 g/mol). It is also a polar molecule due to its linear geometry and the presence of polar carbon-oxygen bonds. CO2 can undergo dipole-dipole interactions with the charcoal surface, leading to moderate adsorption.
b) SO2: Sulfur dioxide is a larger molecule compared to CO2 (bent shape with a molecular weight of 64 g/mol). It is also a polar molecule due to the presence of polar sulfur-oxygen bonds. SO2 can undergo dipole-dipole interactions with the charcoal surface, similar to CO2. However, the larger size of SO2 may limit its access to the charcoal surface, resulting in weaker adsorption compared to CO2.
c) CH4: Methane is the smallest molecule among the given gases (tetrahedral shape with a molecular weight of 16 g/mol). It is a nonpolar molecule as it consists of only carbon-hydrogen bonds. Methane does not have a dipole moment and lacks the ability to form strong dipole-dipole interactions with the charcoal surface. Therefore, methane is expected to show weaker adsorption compared to CO2 and SO2.
d) H2: Hydrogen gas is the smallest molecule among the given gases (diatomic with a molecular weight of 2 g/mol). It is also a nonpolar molecule as it consists of two hydrogen atoms bonded together. Similar to methane, hydrogen gas lacks a dipole moment and strong dipole-dipole interactions with the charcoal surface. Therefore, hydrogen gas is expected to show weaker adsorption compared to CO2 and SO2.
Based on the analysis above, we can conclude that SO2 shows the least adsorption on a definite amount of charcoal among the given gases (CO2, SO2, CH4, and H2).
To predict the gas with the least adsorption, we can consider the following factors:
1. Molecular Size: The size of the gas molecules can affect their adsorption on the charcoal surface. Smaller molecules can penetrate the pores of the charcoal more easily, leading to stronger adsorption. Larger molecules may have difficulty accessing the charcoal surface and thus show weaker adsorption.
2. Polarity: The polarity of the gas molecules can also affect their adsorption. Polar molecules have dipole moments, which can interact with polar sites on the charcoal surface through dipole-dipole interactions. Nonpolar molecules, on the other hand, do not have dipole moments and may have weaker interactions with the charcoal surface.
Based on these factors, we can analyze the given gases:
a) CO2: Carbon dioxide is a relatively small molecule (linear with a molecular weight of 44 g/mol). It is also a polar molecule due to its linear geometry and the presence of polar carbon-oxygen bonds. CO2 can undergo dipole-dipole interactions with the charcoal surface, leading to moderate adsorption.
b) SO2: Sulfur dioxide is a larger molecule compared to CO2 (bent shape with a molecular weight of 64 g/mol). It is also a polar molecule due to the presence of polar sulfur-oxygen bonds. SO2 can undergo dipole-dipole interactions with the charcoal surface, similar to CO2. However, the larger size of SO2 may limit its access to the charcoal surface, resulting in weaker adsorption compared to CO2.
c) CH4: Methane is the smallest molecule among the given gases (tetrahedral shape with a molecular weight of 16 g/mol). It is a nonpolar molecule as it consists of only carbon-hydrogen bonds. Methane does not have a dipole moment and lacks the ability to form strong dipole-dipole interactions with the charcoal surface. Therefore, methane is expected to show weaker adsorption compared to CO2 and SO2.
d) H2: Hydrogen gas is the smallest molecule among the given gases (diatomic with a molecular weight of 2 g/mol). It is also a nonpolar molecule as it consists of two hydrogen atoms bonded together. Similar to methane, hydrogen gas lacks a dipole moment and strong dipole-dipole interactions with the charcoal surface. Therefore, hydrogen gas is expected to show weaker adsorption compared to CO2 and SO2.
Based on the analysis above, we can conclude that SO2 shows the least adsorption on a definite amount of charcoal among the given gases (CO2, SO2, CH4, and H2).
According to Freundlich adsorption isotherm, which of the following is correct?- a)xm ∝ p1
- b)xm ∝ p1/n
- c)xm ∝ p°
- d)All are correct of different ranges of pressure
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
According to Freundlich adsorption isotherm, which of the following is correct?
a)
xm ∝ p1
b)
xm ∝ p1/n
c)
xm ∝ p°
d)
All are correct of different ranges of pressure

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
- All are correct
- That is correct at low pressure,
- That is correct at moderate pressure and
- That is correct at high pressure (saturation pressure).
Which characteristic is not correct for physical adsorption:- a)Adsorption is spontaneous
- b)Both enthalpy and entropy change of adsorption are negative
- c)Adsorption on solid is reversible
- d)Adsorption increases with increase in temperature
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which characteristic is not correct for physical adsorption:
a)
Adsorption is spontaneous
b)
Both enthalpy and entropy change of adsorption are negative
c)
Adsorption on solid is reversible
d)
Adsorption increases with increase in temperature

|
Sagarika Patel answered |
During adsorption, there is always decrease in surface energy which appears as heat. Therefore adsorption always takes place with evolution of heat, i.e. it is an exothermic process and since the adsorption process is exothermic, the physical adsorption occurs readily at low temperature and decreases with increasing temperature. (Le Chatelier's principle).
Micelles behave as colloids only when?- a)Concentration is less than CMC
- b)Concentration is equal to CMC
- c)Concentration is greater than CMC
- d)They always behave as colloids
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Micelles behave as colloids only when?
a)
Concentration is less than CMC
b)
Concentration is equal to CMC
c)
Concentration is greater than CMC
d)
They always behave as colloids
|
|
Vivek Khatri answered |
Micelles behave as colloids only when its concentration is greater than CMC. The CMC is an important characteristic of a surfactant. Before reaching the CMC, the surface tension changes strongly with the concentration of the surfactant. After reaching the CMC, the surface tension remains relatively constant or changes with a lower slope.
Freundlich adsorption isotherm is given by the expression xm = k p1/n which of the following conclusions can be drawn from this expression.- a)When 1n = 0, the adsorption is independent of pressure.
- b)When 1n = 0, the adsorption is directly proportional to pressure.
- c)When n = 0, xm vs p graph is a line parallel to x-axis.
- d)When n = 0, plot of xm vs p is a curve.
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Freundlich adsorption isotherm is given by the expression xm = k p1/n which of the following conclusions can be drawn from this expression.
a)
When 1n = 0, the adsorption is independent of pressure.
b)
When 1n = 0, the adsorption is directly proportional to pressure.
c)
When n = 0, xm vs p graph is a line parallel to x-axis.
d)
When n = 0, plot of xm vs p is a curve.

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
(a) and (c) are correct, when n = 0.
∴ xm vs p graph is line parallel to x-axis.
when 1n = 0, xm is independent of pressure at high pressure.
∴ xm vs p graph is line parallel to x-axis.
when 1n = 0, xm is independent of pressure at high pressure.
The protective power of lyophilic colloidal sol is expressed in terms of- a)coagulation value
- b)gold number
- c)CMC (Critical Micelle Concentration)
- d)oxidation numbers
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The protective power of lyophilic colloidal sol is expressed in terms of
a)
coagulation value
b)
gold number
c)
CMC (Critical Micelle Concentration)
d)
oxidation numbers

|
Aditi Basak answered |
Protective Power of Lyophilic Colloidal Sol
The protective power of lyophilic colloidal sol refers to its ability to protect colloidal particles from coagulation or aggregation. When a colloidal sol is formed, the particles are dispersed and stabilized in a medium. However, these particles have a tendency to aggregate due to attractive forces between them. The protective power of a lyophilic colloidal sol helps to prevent or minimize this aggregation, thus maintaining the stability of the sol.
Gold Number
The protective power of lyophilic colloidal sol is quantitatively expressed in terms of the Gold Number. The Gold Number is a measure of the amount of an electrolyte required to cause coagulation or aggregation of a given volume of a lyophilic colloidal sol. It is named after Thomas Thomson Gold, who first introduced this concept.
Principle of Gold Number
The principle behind the Gold Number is based on the fact that the addition of an electrolyte to a colloidal sol neutralizes the charge on the colloidal particles. When the charge is neutralized, the repulsive forces between the particles decrease, leading to their aggregation. The Gold Number represents the minimum amount of electrolyte required to cause coagulation under specific conditions.
Determination of Gold Number
To determine the Gold Number, a series of solutions with different concentrations of an electrolyte are prepared. A fixed volume of the colloidal sol is added to each solution, and the mixture is observed for coagulation. The Gold Number is the minimum concentration of the electrolyte that causes coagulation.
Significance of Gold Number
The Gold Number provides a quantitative measure of the protective power of a lyophilic colloidal sol. Higher Gold Numbers indicate greater protective power, as a larger amount of electrolyte is required to cause coagulation. Therefore, a higher Gold Number implies greater stability of the colloidal sol.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the protective power of lyophilic colloidal sol is expressed in terms of the Gold Number. The Gold Number represents the minimum concentration of an electrolyte required to cause coagulation of a given volume of the colloidal sol. It serves as a quantitative measure of the stability of the colloidal sol, with higher Gold Numbers indicating greater protective power.
The protective power of lyophilic colloidal sol refers to its ability to protect colloidal particles from coagulation or aggregation. When a colloidal sol is formed, the particles are dispersed and stabilized in a medium. However, these particles have a tendency to aggregate due to attractive forces between them. The protective power of a lyophilic colloidal sol helps to prevent or minimize this aggregation, thus maintaining the stability of the sol.
Gold Number
The protective power of lyophilic colloidal sol is quantitatively expressed in terms of the Gold Number. The Gold Number is a measure of the amount of an electrolyte required to cause coagulation or aggregation of a given volume of a lyophilic colloidal sol. It is named after Thomas Thomson Gold, who first introduced this concept.
Principle of Gold Number
The principle behind the Gold Number is based on the fact that the addition of an electrolyte to a colloidal sol neutralizes the charge on the colloidal particles. When the charge is neutralized, the repulsive forces between the particles decrease, leading to their aggregation. The Gold Number represents the minimum amount of electrolyte required to cause coagulation under specific conditions.
Determination of Gold Number
To determine the Gold Number, a series of solutions with different concentrations of an electrolyte are prepared. A fixed volume of the colloidal sol is added to each solution, and the mixture is observed for coagulation. The Gold Number is the minimum concentration of the electrolyte that causes coagulation.
Significance of Gold Number
The Gold Number provides a quantitative measure of the protective power of a lyophilic colloidal sol. Higher Gold Numbers indicate greater protective power, as a larger amount of electrolyte is required to cause coagulation. Therefore, a higher Gold Number implies greater stability of the colloidal sol.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the protective power of lyophilic colloidal sol is expressed in terms of the Gold Number. The Gold Number represents the minimum concentration of an electrolyte required to cause coagulation of a given volume of the colloidal sol. It serves as a quantitative measure of the stability of the colloidal sol, with higher Gold Numbers indicating greater protective power.
After placing 9 g of charcoal in a one litre vessel containing gas at 300 K, the pressure of the gas decreases by 40% of the original pressure equal to 700 milli bar. Calculate the volume of gas at 1 bar and 273.15 K adsorbed per g of charcoal. Density of charcoal sample is 1.5 g cm–3.
Correct answer is '2840'. Can you explain this answer?
After placing 9 g of charcoal in a one litre vessel containing gas at 300 K, the pressure of the gas decreases by 40% of the original pressure equal to 700 milli bar. Calculate the volume of gas at 1 bar and 273.15 K adsorbed per g of charcoal. Density of charcoal sample is 1.5 g cm–3.
|
|
Subho Sutradhar answered |
It comes out 2805
Adsorption of ethanoic acid on wood charcoal follows Freundlich isotherm. Calculate the mass of ethanoic acid adsorbed by 500 g of wood charcoal at 300 K form 3 litre of 0.65 M ethanol solution. The value of constant k = 0.16 and n = 2.35. Also report the molarity of left ethanol in solution.
Correct answer is '17'. Can you explain this answer?
Adsorption of ethanoic acid on wood charcoal follows Freundlich isotherm. Calculate the mass of ethanoic acid adsorbed by 500 g of wood charcoal at 300 K form 3 litre of 0.65 M ethanol solution. The value of constant k = 0.16 and n = 2.35. Also report the molarity of left ethanol in solution.

|
Komal Mavi answered |
THE ANSWER GIVEN IN THE ANSWER KEY IS NOT 17 BUT .17 KINDLY RECHECK FIRST .
Acc to Freundlich adsorption isotherm,
x/m = k.c^1/n
x/500 = 0.16 (0.65)^1/2.35
On solving,
*x = 66.6g*
Initially, we had 3L of 0.65 M ethanol solution
i.e. 0.65 × 3 mol = 1.95 mol = 1.95 ×46 g = 89.7 g of ethanol
Therefore, after adsorption, mass of ethanol in solution = 89.7 g - 66.6 g
= 23.1 g
= 23.1/46 mol = 0.502 mol of ethanol
Molarity of left ethanol solution. = 0.502 mol/ 3L
= 0.167 mol/L
Hope it helps :)
Adsorption of methane follows the Langmuir adsorption isotherm at 90K. If p = 1.896cm3g-1bar-1 and b = 0.146bar-1. Calculate the value of θ.- a)0.116 bar
- b)0.514 bar
- c)0.214 bar
- d)0.216 bar
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Adsorption of methane follows the Langmuir adsorption isotherm at 90K. If p = 1.896cm3g-1bar-1 and b = 0.146bar-1. Calculate the value of θ.
a)
0.116 bar
b)
0.514 bar
c)
0.214 bar
d)
0.216 bar

|
Jaya Sen answered |
Given data
p = 1.896cm3g-1 bar-1
b = 0.146 bar-1
p = 1.896cm3g-1 bar-1
b = 0.146 bar-1
Substitute in the corresponding equation
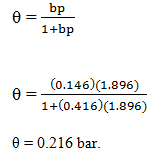
The coagulation values in millimoles per litre of the electrolyte for the coagulation of As2S3 sol are given
I. NaCl (52)
II. BaCl2 (0.69)
III. MgSO4 (0.22)
The correct order of coagulating power is- a)I > II > III
- b)II > I > III
- c)III > II > I
- d)III > I > II
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The coagulation values in millimoles per litre of the electrolyte for the coagulation of As2S3 sol are given
I. NaCl (52)
II. BaCl2 (0.69)
III. MgSO4 (0.22)
The correct order of coagulating power is
I. NaCl (52)
II. BaCl2 (0.69)
III. MgSO4 (0.22)
The correct order of coagulating power is
a)
I > II > III
b)
II > I > III
c)
III > II > I
d)
III > I > II
|
|
Vivek Khatri answered |
∵ Lesser the coagulation value, more is coagulating power meaning it is inversely proportional.
20% surface sites have absorbed N2. On heating N2 gas is evolved from sites and were collected at 0.001 atm and 298 K in a container of volume 2.46 cm3. Density of surface sites is 6.023 × 1014 cm–2 and surface area is 1000 cm2. Find out the number of surface sites occupied per molecule of N2.
Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?
20% surface sites have absorbed N2. On heating N2 gas is evolved from sites and were collected at 0.001 atm and 298 K in a container of volume 2.46 cm3. Density of surface sites is 6.023 × 1014 cm–2 and surface area is 1000 cm2. Find out the number of surface sites occupied per molecule of N2.

|
Mrinalini Sen answered |
No. of surface sites = 6.023*10^14 * 1000
occupied sites = 20/100 * 6.023 * 10^14 * 1000 = 6.022/5*10^17
no. of moles of N2 = 0.001 * 0.00246 / 0.0821 * 298 = 10^-7
no. of molecules = 10^-7 * 6.022*10^23 = 6.022 * 10^16
so no. of surface sites per molecule of N2 = (6.022*10^17/5)/(6.022*10^16) = 2
The transition of ions to micelle is ___________- a)Reversible
- b)Irreversible
- c)All of the mentioned
- d)None of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The transition of ions to micelle is ___________
a)
Reversible
b)
Irreversible
c)
All of the mentioned
d)
None of the mentioned
|
|
Vivek Khatri answered |
The transition of ions to micelle is a reversible process. In the micelle formation, the water insoluble tails are directed towards the centre, and the water soluble heads are on the surface in contact with water.
The number of stearate ions required to form a micelle of colloidal size is ___________- a)50
- b)60
- c)70
- d)80
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of stearate ions required to form a micelle of colloidal size is ___________
a)
50
b)
60
c)
70
d)
80
|
|
Vivek Khatri answered |
About 70 stearate ions aggregate to form a micelle of colloidal size.
The correct ascending order of adsorption of the following gases on the same mass of charcoal at same temperature and pressure is- a)CH4 < H2 < SO2
- b)H2 < CH4 < SO2
- c)SO2 < CH4 < H2
- d)H2 < SO2 < CH4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct ascending order of adsorption of the following gases on the same mass of charcoal at same temperature and pressure is
a)
CH4 < H2 < SO2
b)
H2 < CH4 < SO2
c)
SO2 < CH4 < H2
d)
H2 < SO2 < CH4
|
|
Vivek Khatri answered |
The extent of adsorption increases with increase in polarity and molar mass so the correct option is b.
3 g of activated charcoal was added to 50 mL of acetic acid solution (0.06 N) in a flask. After an hour it was filtered and the strength of the filtrate was found to be 0.042 N. The amount of acetic acid adsorbed (per gram of charcoal) is:- a)18 gm
- b)36 gm
- c)42 gm
- d)54 gm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
3 g of activated charcoal was added to 50 mL of acetic acid solution (0.06 N) in a flask. After an hour it was filtered and the strength of the filtrate was found to be 0.042 N. The amount of acetic acid adsorbed (per gram of charcoal) is:
a)
18 gm
b)
36 gm
c)
42 gm
d)
54 gm

|
Rahul Chatterjee answered |
The initial strength of acetic acid = 0.06N
Final strength = 0.042 N
Volume given = 50 mL
there Initial m moles of CH3COOH
= 0.06 x 50 = 3
Final m moles of CH3COOH
= 0.042 x 50 = 21
therefore, m moles of CH3COOH absorbed
= 3-2.1
= 0.9 m mol
Hence, mass of CH3COOH absorbed per gram of charcoal
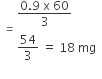
When O2 is adsorbed on a metallic surface, electron transfer occurs from the metal to O2. The true statement(s) regarding this adsorption is(are):- a)O2 is physisorbed
- b)Heat is released
- c)Occupancy of
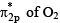 is increased
is increased - d)Bond length of O2 is increased
Correct answer is option 'B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
When O2 is adsorbed on a metallic surface, electron transfer occurs from the metal to O2. The true statement(s) regarding this adsorption is(are):
a)
O2 is physisorbed
b)
Heat is released
c)
Occupancy of 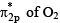 is increased
is increased
d)
Bond length of O2 is increased
|
|
Bittoo Jangra answered |
B) when oxygen absorb electron then energy released in form of heat.
c) acc. to M.O.T , last electrons of O2 are in pi* so after absorbing electrons, e- increase in pi*.
d) when e- increase in pi* orbital, bond order of O2 decrease so bond length of O2 increase.
c) acc. to M.O.T , last electrons of O2 are in pi* so after absorbing electrons, e- increase in pi*.
d) when e- increase in pi* orbital, bond order of O2 decrease so bond length of O2 increase.
Surface area available for adsorption per g of catalyst is called:
- a) Molar surface area
- b) Specific surface area
- c) Normal surface area
- d) Equivalent surface area.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Surface area available for adsorption per g of catalyst is called:
a)
Molar surface areab)
Specific surface areac)
Normal surface aread)
Equivalent surface area.|
|
Pooja Choudhury answered |
Surface area available for adsorption per gram of catalyst is called specific surface area.
Specific surface area is important to measure to evaluate the activity and adsorption capacity of materials. (e.g. catalysis and adsorbent).
Specific surface area is important to measure to evaluate the activity and adsorption capacity of materials. (e.g. catalysis and adsorbent).
The specific surface area is increased as the particle size becomes small. The specific surface area is also increased if the particle has pores. The surface activity and adsorption volume are changed according to the specific surface area.
Physical adsorption of a gaseous species may change to chemical adsorption with ___________.- a)decrease in temperature
- b)increase in temperature
- c)increase in surface area of adsorbent
- d)decrease in surface area of adsorbent
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Physical adsorption of a gaseous species may change to chemical adsorption with ___________.
a)
decrease in temperature
b)
increase in temperature
c)
increase in surface area of adsorbent
d)
decrease in surface area of adsorbent

|
Edurev.iitjam answered |
At high temperature, covalent bonds will be seen forming as activation energy will be provided.
Gold sol can be prepared by- a)Hydrolysis of AUCl3
- b)Oxidation of Gold by aqua-regia
- c)Peptization
- d)Reduction of AUCl3 with HCHO solution.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Gold sol can be prepared by
a)
Hydrolysis of AUCl3
b)
Oxidation of Gold by aqua-regia
c)
Peptization
d)
Reduction of AUCl3 with HCHO solution.

|
Soumya Sengupta answered |
Reduction of AUCl3 with HCHO solution
AUCl3 can be reduced to Gold sol by using formaldehyde (HCHO) solution. This process involves the following steps:
Preparation of AUCl3 solution:
- Firstly, a solution of AUCl3 is prepared by dissolving gold trichloride in water.
Reduction with HCHO solution:
- Formaldehyde (HCHO) solution is then added to the AUCl3 solution under controlled conditions.
- The reduction of AUCl3 by formaldehyde leads to the formation of Gold sol.
- This reaction involves the transfer of electrons from formaldehyde to AUCl3, resulting in the reduction of gold ions to form Gold sol.
Characteristics of Gold sol:
- Gold sol is a colloidal solution of gold nanoparticles dispersed in a solvent.
- It exhibits unique optical properties due to the presence of nanoparticles, such as the red color observed in solutions of Gold sol.
Applications of Gold sol:
- Gold sol finds applications in various fields, including catalysis, electronics, and medicine.
- It is used in the preparation of nanomaterials and as a catalyst in organic synthesis reactions.
In conclusion, the reduction of AUCl3 with HCHO solution is an effective method for the preparation of Gold sol, which has diverse applications in different industries.
The stability of lyophobic sols is due to- a)adsorption of covalent molecules on the colloid
- b)the size of the particles
- c)the charge on particles
- d)Tyndall effect.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The stability of lyophobic sols is due to
a)
adsorption of covalent molecules on the colloid
b)
the size of the particles
c)
the charge on particles
d)
Tyndall effect.

|
Anagha Bajaj answered |
The stability of lyophobic sols is due to the charge on particles.
Explanation:
Lyophobic sols are colloidal sols in which the dispersed phase (colloidal particles) has little or no affinity for the dispersion medium. This means that the particles are not easily dispersed in the medium and tend to aggregate or settle quickly. However, the stability of lyophobic sols is achieved by introducing charges on the particles.
The charge on particles in lyophobic sols is usually achieved through the process of adsorption. When a lyophobic sol is prepared, the dispersion medium is treated with a suitable electrolyte. This electrolyte dissociates into positive and negative ions, and these ions get adsorbed on the surface of the particles. The adsorption of these ions imparts a charge to the particles, creating a stable colloidal system.
The charge on particles plays a crucial role in stabilizing lyophobic sols. Here's why:
1. Electrostatic Repulsion: The like-charged particles repel each other due to electrostatic forces. This repulsion prevents the particles from coming close together and aggregating. As a result, the sol remains stable and the particles stay dispersed.
2. Steric Stabilization: In addition to electrostatic repulsion, charged particles may also have adsorbed layers of molecules or ions that create a physical barrier around the particle. This is known as steric stabilization. The adsorbed layers prevent the particles from approaching each other closely, further enhancing the stability of the sol.
3. Prevention of Coagulation: The charge on particles hinders the process of coagulation or flocculation. Coagulation occurs when colloidal particles come together to form larger aggregates. The charged particles repel each other, making it difficult for coagulation to occur.
4. Redispersion: If the sol undergoes slight flocculation or settles, it can be easily redispersed by gentle shaking or stirring. The charged particles will disperse again due to repulsion forces.
In summary, the stability of lyophobic sols is primarily due to the charge on particles. This charge creates repulsion forces that prevent aggregation and coagulation of particles, thus maintaining the sol's stability.
Explanation:
Lyophobic sols are colloidal sols in which the dispersed phase (colloidal particles) has little or no affinity for the dispersion medium. This means that the particles are not easily dispersed in the medium and tend to aggregate or settle quickly. However, the stability of lyophobic sols is achieved by introducing charges on the particles.
The charge on particles in lyophobic sols is usually achieved through the process of adsorption. When a lyophobic sol is prepared, the dispersion medium is treated with a suitable electrolyte. This electrolyte dissociates into positive and negative ions, and these ions get adsorbed on the surface of the particles. The adsorption of these ions imparts a charge to the particles, creating a stable colloidal system.
The charge on particles plays a crucial role in stabilizing lyophobic sols. Here's why:
1. Electrostatic Repulsion: The like-charged particles repel each other due to electrostatic forces. This repulsion prevents the particles from coming close together and aggregating. As a result, the sol remains stable and the particles stay dispersed.
2. Steric Stabilization: In addition to electrostatic repulsion, charged particles may also have adsorbed layers of molecules or ions that create a physical barrier around the particle. This is known as steric stabilization. The adsorbed layers prevent the particles from approaching each other closely, further enhancing the stability of the sol.
3. Prevention of Coagulation: The charge on particles hinders the process of coagulation or flocculation. Coagulation occurs when colloidal particles come together to form larger aggregates. The charged particles repel each other, making it difficult for coagulation to occur.
4. Redispersion: If the sol undergoes slight flocculation or settles, it can be easily redispersed by gentle shaking or stirring. The charged particles will disperse again due to repulsion forces.
In summary, the stability of lyophobic sols is primarily due to the charge on particles. This charge creates repulsion forces that prevent aggregation and coagulation of particles, thus maintaining the sol's stability.
The mole of gases NH3, CO2 and H2 adsorbed by 1 g charcoal at 300 K and 1 atm pressure shows the order:
- a)CO2 > H2 > NH3
- b)NH3 > CO2 > H2
- c)H2 > CO2 > NH3
- d)CO2 > NH3 > H2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The mole of gases NH3, CO2 and H2 adsorbed by 1 g charcoal at 300 K and 1 atm pressure shows the order:
a)
CO2 > H2 > NH3
b)
NH3 > CO2 > H2
c)
H2 > CO2 > NH3
d)
CO2 > NH3 > H2

|
Shivani Mehta answered |
The order of adsorption of gases NH3, CO2 and H2 by 1 g charcoal at 300 K and 1 atm pressure is given by option 'B', i.e., NH3, CO2, H2.
Explanation:
Adsorption is the process of accumulation of molecules of a substance on the surface of another substance. In this case, the gases NH3, CO2, and H2 are adsorbed by 1 g charcoal at 300 K and 1 atm pressure. The order of adsorption is determined by the force of attraction between the gas molecules and the charcoal surface.
NH3 has the highest order of adsorption because it has the highest dipole moment among the three gases. The dipole moment of NH3 allows it to form hydrogen bonds with the polar surface of charcoal, which results in a stronger force of attraction between NH3 and charcoal.
CO2 has the second-highest order of adsorption because it is a polar molecule and can form weak van der Waals forces with the surface of charcoal.
H2 has the lowest order of adsorption because it is non-polar and cannot form any significant interaction with the surface of charcoal.
Therefore, the order of adsorption of gases NH3, CO2, and H2 by 1 g charcoal at 300 K and 1 atm pressure is NH3 > CO2 > H2, which is given by option 'B'.
Explanation:
Adsorption is the process of accumulation of molecules of a substance on the surface of another substance. In this case, the gases NH3, CO2, and H2 are adsorbed by 1 g charcoal at 300 K and 1 atm pressure. The order of adsorption is determined by the force of attraction between the gas molecules and the charcoal surface.
NH3 has the highest order of adsorption because it has the highest dipole moment among the three gases. The dipole moment of NH3 allows it to form hydrogen bonds with the polar surface of charcoal, which results in a stronger force of attraction between NH3 and charcoal.
CO2 has the second-highest order of adsorption because it is a polar molecule and can form weak van der Waals forces with the surface of charcoal.
H2 has the lowest order of adsorption because it is non-polar and cannot form any significant interaction with the surface of charcoal.
Therefore, the order of adsorption of gases NH3, CO2, and H2 by 1 g charcoal at 300 K and 1 atm pressure is NH3 > CO2 > H2, which is given by option 'B'.
The given graphs/data I, II, III and IV represent general trends observed for different physisorption and chemisorption process under mild conditions of temperature and pressure. Which of the following choice(s) about I, II III and IV is (are) correct: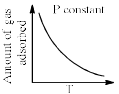
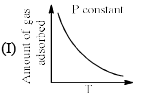
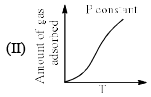
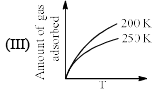
- a)I is physisorption and II is chemisorption
- b)I is physisorption and III is chemisorption
- c)IV is chemisorption and II is physisorption
- d)IV is chemisorption and III is physisorption
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
The given graphs/data I, II, III and IV represent general trends observed for different physisorption and chemisorption process under mild conditions of temperature and pressure. Which of the following choice(s) about I, II III and IV is (are) correct:
a)
I is physisorption and II is chemisorption
b)
I is physisorption and III is chemisorption
c)
IV is chemisorption and II is physisorption
d)
IV is chemisorption and III is physisorption

|
Surajit Samui answered |
Admin is contradicting his/her own answer. In option a (II) is Chemisorption , now in option C (II) is Physisorption .How is this possible ?? a,d option should be correct.
Which statements are correct:- a)Physical adsorption is multi-layer, non-directional and non-specific
- b)Chemical adsorption is due to valence of atoms
- c)Physical adsorption is due to valence of atoms
- d)Chemical adsorption is more stronger than physical adsorption
Correct answer is option 'A,B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which statements are correct:
a)
Physical adsorption is multi-layer, non-directional and non-specific
b)
Chemical adsorption is due to valence of atoms
c)
Physical adsorption is due to valence of atoms
d)
Chemical adsorption is more stronger than physical adsorption

|
Anisha Banerjee answered |
Physical adsorption is the process by which a substance adheres to the surface of another substance through weak intermolecular forces. Chemical adsorption, on the other hand, involves the formation of chemical bonds between the adsorbate and the adsorbent. Let's analyze each statement to determine their accuracy.
a) Physical adsorption is multi-layer, non-directional, and non-specific
- Multi-layer: Physical adsorption can occur in multiple layers, meaning that the adsorbate molecules can stack on top of each other on the surface of the adsorbent. This is due to the weak van der Waals forces that are involved in physical adsorption.
- Non-directional: The forces involved in physical adsorption are non-directional, meaning that they act equally in all directions. This lack of directionality allows the adsorbate molecules to be easily removed from the surface of the adsorbent.
- Non-specific: Physical adsorption is a non-specific process, meaning that it does not depend on the specific chemical properties of the adsorbate or the adsorbent. Any molecule that can interact with the surface through weak intermolecular forces can undergo physical adsorption.
b) Chemical adsorption is due to valence of atoms
- Chemical adsorption involves the formation of chemical bonds between the adsorbate and the adsorbent. These bonds are typically formed through the sharing or transfer of valence electrons between the atoms of the adsorbate and the adsorbent. Therefore, it is correct to say that chemical adsorption is due to the valence of atoms.
c) Physical adsorption is due to valence of atoms
- This statement is incorrect. Physical adsorption is not due to the valence of atoms. Instead, it is primarily governed by weak intermolecular forces such as van der Waals forces, dipole-dipole interactions, and hydrogen bonding. These forces arise from temporary fluctuations in electron distribution within molecules and do not involve the sharing or transfer of valence electrons.
d) Chemical adsorption is stronger than physical adsorption
- This statement is correct. Chemical adsorption is generally stronger than physical adsorption due to the formation of chemical bonds. Chemical bonds are typically stronger than intermolecular forces, resulting in a stronger adsorbate-adsorbent interaction. Chemical adsorption is often more difficult to reverse or remove compared to physical adsorption.
In summary, the correct statements are a) Physical adsorption is multi-layer, non-directional, and non-specific, b) Chemical adsorption is due to the valence of atoms, and d) Chemical adsorption is stronger than physical adsorption.
a) Physical adsorption is multi-layer, non-directional, and non-specific
- Multi-layer: Physical adsorption can occur in multiple layers, meaning that the adsorbate molecules can stack on top of each other on the surface of the adsorbent. This is due to the weak van der Waals forces that are involved in physical adsorption.
- Non-directional: The forces involved in physical adsorption are non-directional, meaning that they act equally in all directions. This lack of directionality allows the adsorbate molecules to be easily removed from the surface of the adsorbent.
- Non-specific: Physical adsorption is a non-specific process, meaning that it does not depend on the specific chemical properties of the adsorbate or the adsorbent. Any molecule that can interact with the surface through weak intermolecular forces can undergo physical adsorption.
b) Chemical adsorption is due to valence of atoms
- Chemical adsorption involves the formation of chemical bonds between the adsorbate and the adsorbent. These bonds are typically formed through the sharing or transfer of valence electrons between the atoms of the adsorbate and the adsorbent. Therefore, it is correct to say that chemical adsorption is due to the valence of atoms.
c) Physical adsorption is due to valence of atoms
- This statement is incorrect. Physical adsorption is not due to the valence of atoms. Instead, it is primarily governed by weak intermolecular forces such as van der Waals forces, dipole-dipole interactions, and hydrogen bonding. These forces arise from temporary fluctuations in electron distribution within molecules and do not involve the sharing or transfer of valence electrons.
d) Chemical adsorption is stronger than physical adsorption
- This statement is correct. Chemical adsorption is generally stronger than physical adsorption due to the formation of chemical bonds. Chemical bonds are typically stronger than intermolecular forces, resulting in a stronger adsorbate-adsorbent interaction. Chemical adsorption is often more difficult to reverse or remove compared to physical adsorption.
In summary, the correct statements are a) Physical adsorption is multi-layer, non-directional, and non-specific, b) Chemical adsorption is due to the valence of atoms, and d) Chemical adsorption is stronger than physical adsorption.
Variation of x/m vs. P are plotted for a gas at different temperature as shown below. The correct order of temperature is:
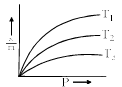
- a)T1 > T2 > T3
- b)T3 > T2 > T1
- c)T2 > T1 > T3
- d)T2 > T3 > T1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Variation of x/m vs. P are plotted for a gas at different temperature as shown below. The correct order of temperature is:
a)
T1 > T2 > T3
b)
T3 > T2 > T1
c)
T2 > T1 > T3
d)
T2 > T3 > T1

|
Asf Institute answered |
The correct order of temperature is T3>T2>T1.
Temperature is inversely proportional to rate of adsorption. Higher is the temperature, lower is the adsorption.
Temperature is inversely proportional to rate of adsorption. Higher is the temperature, lower is the adsorption.
Collodion is 4% solution of which one of the following in alcohol-ether mixture.- a)Nitroglycerin
- b)Cellulose acetate
- c)Glycol dinitrate
- d)Nitrocellulose
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Collodion is 4% solution of which one of the following in alcohol-ether mixture.
a)
Nitroglycerin
b)
Cellulose acetate
c)
Glycol dinitrate
d)
Nitrocellulose

|
Pragati Sharma answered |
**Collodion:**
Collodion is a liquid preparation that is mainly used in medicine and photography. It is a solution of nitrocellulose in a mixture of alcohol and ether. When applied to the skin, collodion forms a flexible film that can be used for wound dressings or as a protective covering.
**Composition:**
Collodion is composed of a 4% solution of a specific substance in an alcohol-ether mixture. The correct answer is option D, nitrocellulose. Nitrocellulose is a highly flammable compound that is produced by nitrating cellulose with a mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid. It is commonly used in the production of explosives, lacquers, and films.
**Explanation:**
Nitrocellulose is the correct answer because it is the main ingredient in collodion. When nitrocellulose is dissolved in an alcohol-ether mixture, it forms a solution that can be easily applied to the skin. The alcohol and ether in the mixture help to dissolve the nitrocellulose and create a liquid solution.
When the collodion is applied to the skin, the alcohol and ether quickly evaporate, leaving behind a thin film of nitrocellulose. This film provides a protective barrier and helps to seal wounds. It can also be used as a base for applying medications or other substances to the skin.
**Other Options:**
The other options, nitroglycerin, cellulose acetate, and glycol dinitrate, are not correct answers because they are not commonly used in the preparation of collodion.
- Nitroglycerin: Nitroglycerin is a highly explosive compound that is used in the production of dynamite and as a medication for heart conditions. It is not commonly used in the preparation of collodion.
- Cellulose acetate: Cellulose acetate is a derivative of cellulose that is used in the production of films, fibers, and coatings. While it is similar to nitrocellulose, it is not commonly used in the preparation of collodion.
- Glycol dinitrate: Glycol dinitrate is an explosive compound that is used as a stabilizer in the production of dynamite. It is not commonly used in the preparation of collodion.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D, nitrocellulose.
Collodion is a liquid preparation that is mainly used in medicine and photography. It is a solution of nitrocellulose in a mixture of alcohol and ether. When applied to the skin, collodion forms a flexible film that can be used for wound dressings or as a protective covering.
**Composition:**
Collodion is composed of a 4% solution of a specific substance in an alcohol-ether mixture. The correct answer is option D, nitrocellulose. Nitrocellulose is a highly flammable compound that is produced by nitrating cellulose with a mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid. It is commonly used in the production of explosives, lacquers, and films.
**Explanation:**
Nitrocellulose is the correct answer because it is the main ingredient in collodion. When nitrocellulose is dissolved in an alcohol-ether mixture, it forms a solution that can be easily applied to the skin. The alcohol and ether in the mixture help to dissolve the nitrocellulose and create a liquid solution.
When the collodion is applied to the skin, the alcohol and ether quickly evaporate, leaving behind a thin film of nitrocellulose. This film provides a protective barrier and helps to seal wounds. It can also be used as a base for applying medications or other substances to the skin.
**Other Options:**
The other options, nitroglycerin, cellulose acetate, and glycol dinitrate, are not correct answers because they are not commonly used in the preparation of collodion.
- Nitroglycerin: Nitroglycerin is a highly explosive compound that is used in the production of dynamite and as a medication for heart conditions. It is not commonly used in the preparation of collodion.
- Cellulose acetate: Cellulose acetate is a derivative of cellulose that is used in the production of films, fibers, and coatings. While it is similar to nitrocellulose, it is not commonly used in the preparation of collodion.
- Glycol dinitrate: Glycol dinitrate is an explosive compound that is used as a stabilizer in the production of dynamite. It is not commonly used in the preparation of collodion.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D, nitrocellulose.
During the adsorption of gas on the surface of solid, which of the following is true?- a)ΔG < 0, ΔH > 0, ΔS < 0
- b)ΔG > 0, ΔH < 0, ΔS < 0
- c)ΔG < 0, ΔH < 0, ΔS < 0
- d)ΔG < 0, ΔH < 0, ΔS > 0
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During the adsorption of gas on the surface of solid, which of the following is true?
a)
ΔG < 0, ΔH > 0, ΔS < 0
b)
ΔG > 0, ΔH < 0, ΔS < 0
c)
ΔG < 0, ΔH < 0, ΔS < 0
d)
ΔG < 0, ΔH < 0, ΔS > 0
|
|
Vivek Khatri answered |
ΔG < 0 means process is spontaneous because adsorption is exothermic in nature, ΔH = negative and entropy is decreasing, i.e., ΔS will come out as negative.
The amount of gas adsorbed on a solid surface - a)Increases with increase in the temperature
- b)Increases with decrease in the temperature
- c)Independent on temperature
- d)Cannot say
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The amount of gas adsorbed on a solid surface
a)
Increases with increase in the temperature
b)
Increases with decrease in the temperature
c)
Independent on temperature
d)
Cannot say

|
Shilpa Datta answered |
Effect of Temperature on Gas Adsorption:
Factors affecting gas adsorption on a solid surface include temperature. Let's discuss how temperature influences the amount of gas adsorbed.
Effect of Temperature on Gas Adsorption:
- Increases with decrease in the temperature:
When the temperature decreases, the kinetic energy of gas molecules decreases, leading to a greater tendency for them to be adsorbed on the solid surface. This is due to the fact that at lower temperatures, the gas molecules have less energy to overcome the attractive forces of the solid surface, resulting in more adsorption.
- Decreases with increase in the temperature:
Conversely, when the temperature increases, the kinetic energy of gas molecules increases. This causes the gas molecules to have more energy to escape the attractive forces of the solid surface, leading to a decrease in the amount of gas adsorbed.
Therefore, the correct answer to the question is that the amount of gas adsorbed on a solid surface increases with a decrease in temperature.
Factors affecting gas adsorption on a solid surface include temperature. Let's discuss how temperature influences the amount of gas adsorbed.
Effect of Temperature on Gas Adsorption:
- Increases with decrease in the temperature:
When the temperature decreases, the kinetic energy of gas molecules decreases, leading to a greater tendency for them to be adsorbed on the solid surface. This is due to the fact that at lower temperatures, the gas molecules have less energy to overcome the attractive forces of the solid surface, resulting in more adsorption.
- Decreases with increase in the temperature:
Conversely, when the temperature increases, the kinetic energy of gas molecules increases. This causes the gas molecules to have more energy to escape the attractive forces of the solid surface, leading to a decrease in the amount of gas adsorbed.
Therefore, the correct answer to the question is that the amount of gas adsorbed on a solid surface increases with a decrease in temperature.
The formation of micelles takes place only above- a)Inversion temperature
- b)Boyle’s temperature
- c)Critical temperature
- d)Kraft temperature
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The formation of micelles takes place only above
a)
Inversion temperature
b)
Boyle’s temperature
c)
Critical temperature
d)
Kraft temperature
|
|
Vivek Khatri answered |
The temperature above which micelles formation takes place is called Kraft temperature.
The best coagulant for the precipitation of Fe(OH)3 sol is- a)Na2HPO3
- b)NaNO3
- c)Na3PO4
- d)Na2SO4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The best coagulant for the precipitation of Fe(OH)3 sol is
a)
Na2HPO3
b)
NaNO3
c)
Na3PO4
d)
Na2SO4
|
|
Vivek Khatri answered |
PO3−4 works in most effective way for positively charged Fe(OH)3sol due to higher charge.
Which part of the stearate ion is hydrophilic in nature?- a)Tail
- b)Hydrocarbon chain
- c)Head
- d)None of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which part of the stearate ion is hydrophilic in nature?
a)
Tail
b)
Hydrocarbon chain
c)
Head
d)
None of the mentioned

|
Rohan Desai answered |
Hydrophilic nature of Stearate ion:
Stearate ion is a negatively charged ion and is derived from stearic acid. It has a long hydrocarbon chain with a carboxylate group (-COO-) at the end. The hydrocarbon chain is nonpolar and hydrophobic in nature, whereas the carboxylate group is polar and hydrophilic in nature.
The hydrophilic nature of the stearate ion is due to the carboxylate group, which is made up of a carbonyl group (-C=O) and a hydroxyl group (-OH), both of which are polar in nature. The carbonyl group is electron-withdrawing, which causes the oxygen atom to become slightly negative, and the carbon atom to become slightly positive. Similarly, the hydroxyl group is electron-donating, which causes the oxygen atom to become slightly negative, and the hydrogen atom to become slightly positive.
The polar nature of the carboxylate group makes it attracted to water molecules, and thus, hydrophilic in nature. This allows the stearate ion to dissolve in water and form a stable solution.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the head of the stearate ion, which is the carboxylate group, is hydrophilic in nature due to its polar nature.
Stearate ion is a negatively charged ion and is derived from stearic acid. It has a long hydrocarbon chain with a carboxylate group (-COO-) at the end. The hydrocarbon chain is nonpolar and hydrophobic in nature, whereas the carboxylate group is polar and hydrophilic in nature.
The hydrophilic nature of the stearate ion is due to the carboxylate group, which is made up of a carbonyl group (-C=O) and a hydroxyl group (-OH), both of which are polar in nature. The carbonyl group is electron-withdrawing, which causes the oxygen atom to become slightly negative, and the carbon atom to become slightly positive. Similarly, the hydroxyl group is electron-donating, which causes the oxygen atom to become slightly negative, and the hydrogen atom to become slightly positive.
The polar nature of the carboxylate group makes it attracted to water molecules, and thus, hydrophilic in nature. This allows the stearate ion to dissolve in water and form a stable solution.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the head of the stearate ion, which is the carboxylate group, is hydrophilic in nature due to its polar nature.
Adsorption of a gas on solid metal surface is spontaneous and exothermic, then:- a)H increases
- b)S increases
- c)G increases
- d)S decreases
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Adsorption of a gas on solid metal surface is spontaneous and exothermic, then:
a)
H increases
b)
S increases
c)
G increases
d)
S decreases

|
Shivam Sharma answered |
For spontaneous absorption ΔG is negative as well as the degree of randomness of gas molecules
decreases thereby ΔS also negative. That’s why T.ΔS is –ve
∴ ΔH = ΔG + T.ΔS
Thereby ΔH is –ve
1 g of activated charcoal has a surface area 103 m3. If complete monolayer coverage is assumed and effective surface area of NH3 molecule is 0.129 cm2, how much NH3 in cm3 at STP could be adsorbed on 25 g of charcoal.
Correct answer is between '0.322,0.323'. Can you explain this answer?
1 g of activated charcoal has a surface area 103 m3. If complete monolayer coverage is assumed and effective surface area of NH3 molecule is 0.129 cm2, how much NH3 in cm3 at STP could be adsorbed on 25 g of charcoal.

|
Aashna Shah answered |

Chapter doubts & questions for Adsorption - Physical Chemistry 2025 is part of Chemistry exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Chemistry exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Chemistry 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Adsorption - Physical Chemistry in English & Hindi are available as part of Chemistry exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Chemistry Exam by signing up for free.
Physical Chemistry
90 videos|144 docs|67 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup