All Exams >
Grade 9 >
AP Biology >
All Questions
All questions of Unit 4: Cell Communication for Grade 9 Exam
What is the proper sequence in mitosis?- a)Anaphase, metaphase, telophase and prophase
- b)Telophase, anaphase, metaphase and prophase
- c)Metaphase, telophase, prophase and anaphase
- d)Prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the proper sequence in mitosis?
a)
Anaphase, metaphase, telophase and prophase
b)
Telophase, anaphase, metaphase and prophase
c)
Metaphase, telophase, prophase and anaphase
d)
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
Mitosis consists of four basic phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. These phases occur in this strict sequential order, and cytokinesis - the process of dividing the cell contents to make two new cells - starts in anaphase or telophase.
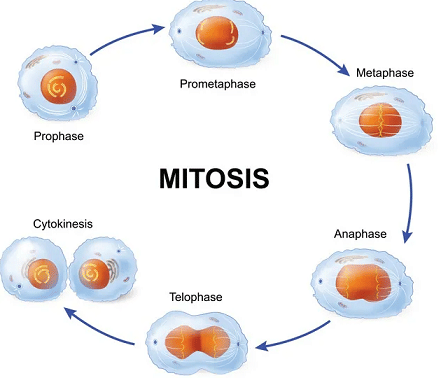
1. Prophase - During prophase, chromosomes get visible (chromatids), the centrioles migrate to the poles, nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear and spindle formation is seen. Prophase in mitosis is longer than any other phases of mitosis because the cell has to prepare for the actual division that takes place from early through late prophase.
2. Metaphase - During this, chromosomes lineup around the centre (Cells in metaphase have the chromosomes, which appear as long thin strands under the microscope).
3. Anaphase - here, chromatids separate and move to opposite poles by spindle fibers. This allows each daughter cell to have an identical copy of each of the original cell’s chromosomes.
4.Telophase - During this phase, chromosomes disappear (become chromatin), nuclear membrane reforms, nucleoli reappears, spindle disappears and centrioles duplicate.
The correct answer is option D.
How many mitotic divisions are needed for a single cell to make 128 cells?- a)7
- b)14
- c)28
- d)32
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
How many mitotic divisions are needed for a single cell to make 128 cells?
a)
7
b)
14
c)
28
d)
32
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Mitosis is a process of nuclear division in eukaryotic cells that occurs when a parent cell divides to produce two identical daughter cells.
Hence the process of the division will be:
► 1 cell gives 2 daughter cells (1st mitosis)
► 2 cells give 4 daughter cells (2nd mitosis)
► 4 cells give 8 daughter cells (3rd mitosis)
► 8 cells give 16 daughter cells (4th mitosis)
► 16 cells give 32 daughter cells (5th mitosis)
► 32 cells give 64 daughter cells (6th mitosis)
► 64 cells give 128 daughter cells (7th mitosis)
Hence the process of the division will be:
► 1 cell gives 2 daughter cells (1st mitosis)
► 2 cells give 4 daughter cells (2nd mitosis)
► 4 cells give 8 daughter cells (3rd mitosis)
► 8 cells give 16 daughter cells (4th mitosis)
► 16 cells give 32 daughter cells (5th mitosis)
► 32 cells give 64 daughter cells (6th mitosis)
► 64 cells give 128 daughter cells (7th mitosis)
Hence 7 mitotic divisions cell needed for a single cell to make 128 cells.
Sense of smell is by :a) olfactory lobeb) cerebellumc) cerebrumd) hypothalamusCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Deeksha answered |
Option c) olfactory lobe is responsible for sense of smell
Which stages of cell division do the figures A and B represent?
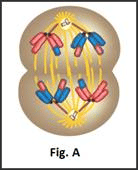
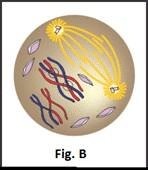
- a)A: Metaphase; B: Telophase
- b)A: Late anaphase; B: Prophase
- c)A: Telophase; B: Metaphase
- d)A: Prophase; B: Anaphase
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which stages of cell division do the figures A and B represent?




a)
A: Metaphase; B: Telophase
b)
A: Late anaphase; B: Prophase
c)
A: Telophase; B: Metaphase
d)
A: Prophase; B: Anaphase

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
- In Fig.A Chromatids are moving to opposite poles i.e Late anaphase.
- In Fig.B The duplicated DNA is compactly packed into chromosomes and spindle formation occurs i.e prophase.
Hence, the correct option is B.
NCERT Reference: Topic "Prophase” and “Anaphase” of chapter "Cell cycle and Cell division" of NCERT.
NCERT Reference: Topic "Prophase” and “Anaphase” of chapter "Cell cycle and Cell division" of NCERT.
A cell plate is laid during- a)Cytokinesis
- b)Karyokinesis
- c)Interphase
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A cell plate is laid during
a)
Cytokinesis
b)
Karyokinesis
c)
Interphase
d)
None of the above
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
- Cytokinesis is the part of the cell division process during which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell divides into two daughter cells.
- Cytoplasmic division begins during or after the late stages of nuclear division in mitosis and meiosis.
- During cytokinesis the spindle apparatus partitions and transports duplicated chromatids into the cytoplasm of the separating daughter cells. It thereby ensures that chromosome number and complement are maintained from one generation to the next and that, except in special cases, the daughter cells will be functional copies of the parent cell. After the completion of the telophase and cytokinesis, each daughter cell enters the interphase of the cell cycle.
Which of the phases of mitosis is the longest?- a)Telophase
- b)Prophase
- c)Anaphase
- d)Metaphase
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the phases of mitosis is the longest?
a)
Telophase
b)
Prophase
c)
Anaphase
d)
Metaphase
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Prophase and telophase are stages involved in mitosis or meiosis. During G2 phase division of centrioles, mitochondria and chloroplasts occurs.
In between two walls of adjacent cells are seen- a)Cell wall
- b)Cytoplasm
- c)Middle lamellae
- d)Plasma membrane
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In between two walls of adjacent cells are seen
a)
Cell wall
b)
Cytoplasm
c)
Middle lamellae
d)
Plasma membrane
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
The middle lamella serves as a cementing layer between the primary walls of adjacent cells.
The primary wall is the cellulose-containing layer laid down by cells that are dividing and growing.
The primary wall is the cellulose-containing layer laid down by cells that are dividing and growing.
Crossing over results the exchange of genetic material, which occurs between- a)Non-sister chromosomes
- b)Sister chromatids
- c)Non-homologous chromosome
- d)Homologous chromosomes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Crossing over results the exchange of genetic material, which occurs between
a)
Non-sister chromosomes
b)
Sister chromatids
c)
Non-homologous chromosome
d)
Homologous chromosomes
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Most organisms that undergo sexual reproduction contain two types of cells in their body – haploid and diploid cells. Diploid cells are seen in most parts of the body and contain two copies of every chromosome. Therefore, they contain two genes to determine the sequence of nearly every RNA or protein. Haploid cells are usually male or female gametes formed as a result of meiosis and are seen in sexual organs. They contain only one complete set of chromosomes and are designed to fuse with another haploid gamete to produce a diploid zygote – with one paternal and one maternal set of chromosomes. Though they code for the same genes, their DNA sequences can vary slightly from one another. For instance, the paternal chromosome may contain the genetic information to result in antigen A being present on red blood cells, while the maternal chromosome may code for antigen B. These two antigens are similar in function, but differ from each other marginally in their amino acid sequence.
M- phase in motosis undergoes which type of division?a)Cytokinesisb)Diakinesisc) Reductional divisiond)Equational divisionCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Mitosis is called equational division because during mitosis the cell divides equally into two identical daughter cells.
How many chromosomes are present in the each cell of the onion root tip?
- a)2 chromosomes
- b)3 chromosomes
- c)16 chromosomes
- d)4 chromosomes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How many chromosomes are present in the each cell of the onion root tip?
a)
2 chromosomes
b)
3 chromosomes
c)
16 chromosomes
d)
4 chromosomes
|
|
Rohit Jain answered |
The root tip cells of onion were used to test the potentially genotoxic effects of Alprazolam. The test was carried out according to Fiskesjö protocol (4, 11-12) with some modifications. Common onion (Allium cepa L.) has eight pairs of relatively large chromosomes (2n = 16) that allows for the easy detection of CAs.
Which part of the brain is affected first in a drunk person :[Bihar-2004]- a)Cerebrum
- b)Olfactory lobe
- c)Cerebellum
- d)Medulla oblongata
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which part of the brain is affected first in a drunk person :
[Bihar-2004]
a)
Cerebrum
b)
Olfactory lobe
c)
Cerebellum
d)
Medulla oblongata
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
When a person gets addicted to alcohol, many serious health problems can occur due to consumption of alcohol. The first part of brain to be affected first is Cerebellum. The will power and self control of the person gets reduced. Control over emotions and moral sense also gets reduced. Loss of muscle coordination also occurs as cerebellum is affected. As a result, speech becomes incoherent. Inflammation of axons also occur which causes neuritis.
In some lower plants and social insects, the haploid cells are divided by- a)Mitosis
- b)Cytokinesis
- c)Meiosis
- d)Karyokinesis
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In some lower plants and social insects, the haploid cells are divided by
a)
Mitosis
b)
Cytokinesis
c)
Meiosis
d)
Karyokinesis
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
Mitosis or the equational division is usually restricted to the diploid cells only. However, in some lower plants and in some social insects haploid cells also divide by mitosis. It is very essential to understand the significance of this division in the life of an organism. Are you aware of some examples where you have studied about haploid and diploid insects? Mitosis results in the production of diploid daughter cells with identical genetic complement usually. The growth of multicellular organisms is due to mitosis. Cell growth results in disturbing the ratio between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. It therefore becomes essential for the cell to divide to restore the nucleo-cytoplasmic ratio. A very significant contribution of mitosis is cell repair. The cells of the upper layer of the epidermis, cells of the lining of the gut, and blood cells are being constantly replaced. Mitotic divisions in the meristematic tissues – the apical and the lateral cambium, result in a continuous growth of plants throughout their life.
Voluntary activities of body are controlled by :-- a)Diencephalon
- b)Cerebrum
- c)Crura cerebri
- d)Cerebellum
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Voluntary activities of body are controlled by :-
a)
Diencephalon
b)
Cerebrum
c)
Crura cerebri
d)
Cerebellum

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
The cerebrum is the largest part of the forebrain. It is responsible for the integration of complex sensory and neural functions and the initiation and coordination of voluntary activity in the body. It has specific functional lobe which is controls speech, generates several responses to different stimulus.
So, the correct answer is option B.
So, the correct answer is option B.
Plants show mitotic divisions ina)Haploid cellsb)Haploid cells and diploid cellsc)Somatic cellsd)Diploid cellsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Mitosis is the type of cell division that ensures equal distribution of genetic material in daughter cells.
Mitosis can occur both in diploid and haploid cells. The main function of mitosis is to make copies of cells for growth and regeneration.
If a haploid cell undergoes mitosis, which is something certain types of plant and fungus do as part of their normal life cycles, the end result is two identical haploid cells (n→n),
Some plants and fungi have their bodies composed of haploid cell .
EXAMPLE: Gametophyte of Bryophyte plants. It is produced from mitotic cell division of spores, which are produced by meiosis in sporophytes.
If the corpus callosum is removed in mammalian brain then what will be affected :-- a)Coordination of Cerebrum
- b)Involuntary activity of brain
- c)Coordination of Cerebellum
- d)Behaviour and emotional disturbances
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If the corpus callosum is removed in mammalian brain then what will be affected :-
a)
Coordination of Cerebrum
b)
Involuntary activity of brain
c)
Coordination of Cerebellum
d)
Behaviour and emotional disturbances
|
|
Kadambala Hemalatha answered |
Option A is correct becose, corpus callosam is trancverce connection between two cerebral hemisphears.. it helps in coordination between the two cerebral hemisphears..
Area of most active vision in eye where sharp image is formed is called - a)Blind spot
- b)Yellow spot
- c)Lens
- d)Pupil
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Area of most active vision in eye where sharp image is formed is called
a)
Blind spot
b)
Yellow spot
c)
Lens
d)
Pupil
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
The yellow spot or macula is an oval yellow spot near the centre of the retina of the human eye. It has a size of 1.5 millimeters. It is specialized for seeing things with highest clearness or visual acuity. It is the area of best vision, where maximum amount of rod cells and cone cells are present.
In mitosis, the number of chromosome sets in daughter cells will be- a)Half of parent cells
- b)Double of parent cells
- c)Different from parent cells
- d)Same as in parent cells
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In mitosis, the number of chromosome sets in daughter cells will be
a)
Half of parent cells
b)
Double of parent cells
c)
Different from parent cells
d)
Same as in parent cells

|
Dilip Chaurasiya answered |
Same mitosis is also called equavational division becz. before and after mitosis ploidy is same..
The transition period between M-phase I and M-phase II in without DNA replication- a)Interstage
- b)Interkinesis
- c)Interphase
- d)Transition period
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The transition period between M-phase I and M-phase II in without DNA replication
a)
Interstage
b)
Interkinesis
c)
Interphase
d)
Transition period

|
Pallabi Reddy answered |
The transition period between M-phase of Meiosis I and M-phase II during which no replication of DNA occurs is called as interkinesis.
In mammals, the brain centre, which regulates body temperature is situated in :
[UP-CPMT 2001]
a)hypothalamusb)Olfactory lobec)Cerebellumd)Medulla oblongataCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Prasenjit Pillai answered |
The core temperature of a human is regulated and stabilized primarily by the hypothalamus, a region of the brain linking the endocrine system to the nervous system, and more specifically by the anterior hypothalamic nucleus and the adjacent preoptic area regions of the hypothalamus.
In meiosis, the daughter cells are not similar to the parent because of- a)Crossing over
- b)Synapsis
- c)Both 1 and 2 above
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In meiosis, the daughter cells are not similar to the parent because of
a)
Crossing over
b)
Synapsis
c)
Both 1 and 2 above
d)
None of the above
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Meiosis is basically an extended and complex version of mitosis. The term “Reductional division” gives this process the underlying definition, a sequence of events that results in reduction of the total number of chromosomes (from a diploid state of 46 to a haploid state of 23; in general, from ‘2n’ to ‘n’).
However, in the initial steps of meiosis, there is an eventful period wherein the previously duplicated chromosomes (in the S-Phase or Synthesis phase of cell cycle) exchange a part of their respective genetic material, a process termed as Recombination through crossing over (of the genetic material). The further steps are the same as in mitosis, but because of the exchange, the daughter chromosomes will have a different identity than their parents.
If cerebellum of man gets damaged, his movement become :-- a)Shaky & speech become defective
- b)Unbalanced, walk uncontrolled, defective speech & intention tremor
- c)Jerky & defective speech
- d)Jerky & walked uncontrolled
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If cerebellum of man gets damaged, his movement become :-
a)
Shaky & speech become defective
b)
Unbalanced, walk uncontrolled, defective speech & intention tremor
c)
Jerky & defective speech
d)
Jerky & walked uncontrolled
|
|
Pramod Bohara answered |
Cerebellum also called a small brain
coordinates muscular movements and maintains our body posture apart from this it is a main centre for skeletal muscles activities
So yes obviously the correct answer will be (B)
coordinates muscular movements and maintains our body posture apart from this it is a main centre for skeletal muscles activities
So yes obviously the correct answer will be (B)
At which stage of mitosis do chromatids separate and pass to different poles?- a)Anaphase
- b)Telophase
- c)Prophase
- d)Metaphase
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
At which stage of mitosis do chromatids separate and pass to different poles?
a)
Anaphase
b)
Telophase
c)
Prophase
d)
Metaphase
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Anaphase -The shortest stage of mitosis. The centromeres divide, and the sister chromatids of each chromosome are pulled apart - or 'disjoin' - and move to the opposite ends of the cell, pulled by spindle fibres attached to the kinetochore regions.
During which stage of prophase I the crossing over takes place?- a)Pachytene
- b)Leptotene
- c)Zygotene
- d)Diplotene
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
During which stage of prophase I the crossing over takes place?
a)
Pachytene
b)
Leptotene
c)
Zygotene
d)
Diplotene
|
|
Lakshmi Sarkar answered |
The crossing over takes place during the pachytene stage of prophase I of meiosis.
Explanation:
Prophase I is the first stage of meiosis I, which is further divided into five substages: leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene, and diakinesis. During the prophase I, homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material through a process known as crossing over. This results in the formation of recombinant chromosomes that carry a combination of genetic material from both parents.
The crossing over occurs during the pachytene stage, which is characterized by the following events:
1. Homologous chromosomes pair up: The homologous chromosomes come together and form a bivalent or a tetrad.
2. Synapsis: The paired homologous chromosomes undergo synapsis, which is the physical association of the homologs.
3. Crossing over: The chromatids of the homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material at specific sites known as chiasmata. This leads to the formation of recombinant chromosomes.
4. Formation of the synaptonemal complex: The synaptonemal complex holds the homologous chromosomes together and facilitates the exchange of genetic material.
5. Nuclear envelope breakdown: The nuclear envelope breaks down, and the spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes.
In conclusion, the crossing over takes place during the pachytene stage of prophase I of meiosis.
Explanation:
Prophase I is the first stage of meiosis I, which is further divided into five substages: leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene, and diakinesis. During the prophase I, homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material through a process known as crossing over. This results in the formation of recombinant chromosomes that carry a combination of genetic material from both parents.
The crossing over occurs during the pachytene stage, which is characterized by the following events:
1. Homologous chromosomes pair up: The homologous chromosomes come together and form a bivalent or a tetrad.
2. Synapsis: The paired homologous chromosomes undergo synapsis, which is the physical association of the homologs.
3. Crossing over: The chromatids of the homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material at specific sites known as chiasmata. This leads to the formation of recombinant chromosomes.
4. Formation of the synaptonemal complex: The synaptonemal complex holds the homologous chromosomes together and facilitates the exchange of genetic material.
5. Nuclear envelope breakdown: The nuclear envelope breaks down, and the spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes.
In conclusion, the crossing over takes place during the pachytene stage of prophase I of meiosis.
In the metaphase stage, the chromosomes are made up of- a)Two non-sister chromatids
- b)One sister and two non-sister chromatids
- c)Two sister chromatids
- d)One sister chromatid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the metaphase stage, the chromosomes are made up of
a)
Two non-sister chromatids
b)
One sister and two non-sister chromatids
c)
Two sister chromatids
d)
One sister chromatid

|
Abhijeet Goyal answered |
At metaphase stage, the chromosome is made up of two sister chromatids, which are held together by the centromere.
Which part of the brain regulates the body temperature, hunger and water balance :-- a)Hypothalamus
- b)Infundibulum
- c)Medulla oblongata
- d)Pons veroli
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which part of the brain regulates the body temperature, hunger and water balance :-
a)
Hypothalamus
b)
Infundibulum
c)
Medulla oblongata
d)
Pons veroli

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
The part of the brain that regulates body temperature, hunger, and water balance is the Hypothalamus. Here's why:
- Hypothalamus:
- Regulates body temperature by triggering mechanisms like sweating or shivering.
- Controls hunger by responding to hunger hormones and signals.
- Manages water balance by regulating thirst and controlling the release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH).
In summary, the hypothalamus plays a crucial role in maintaining internal balance (homeostasis) within the body, ensuring optimal functioning.
- Hypothalamus:
- Regulates body temperature by triggering mechanisms like sweating or shivering.
- Controls hunger by responding to hunger hormones and signals.
- Manages water balance by regulating thirst and controlling the release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH).
In summary, the hypothalamus plays a crucial role in maintaining internal balance (homeostasis) within the body, ensuring optimal functioning.
Pigmented layer in eye is called- a)Cornea
- b)Sclerotic
- c)Retina
- d)All
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Pigmented layer in eye is called
a)
Cornea
b)
Sclerotic
c)
Retina
d)
All
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The retina makes up the inner layer and occupies only the posterior two-third of the eye. The retina consists of several layers of cells, including the rods and cones, the sensory cells, that respond to light. The tips of the rods and cones are embedded in a pigmented layer of cells on the back of the retina. The pigment helps prevent light from scattering in the back of the eye.
In man nictitating membrane is- a)Absent
- b)Vestigeal
- c)Non-functional
- d)Functional
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In man nictitating membrane is
a)
Absent
b)
Vestigeal
c)
Non-functional
d)
Functional
|
|
T.ttttt answered |
Eye. The plica semilunaris is a small fold of tissue on the inside corner of the eye. It is the vestigial remnant of the nictitating membrane, an organ that is fully functional in some other species of mammals. Its associated muscles are also vestigial
In plant cells, the new cell wall begins by the- a)Cell plate
- b)Chromatid
- c)Cell cycle
- d)Centromere
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In plant cells, the new cell wall begins by the
a)
Cell plate
b)
Chromatid
c)
Cell cycle
d)
Centromere
|
|
Sounak Saini answered |
The correct answer is option 'A', the cell plate.
Plant cells have a unique feature called the cell wall, which provides support and protection to the cell. During cell division, a new cell wall is formed to separate the two daughter cells. This process is known as cytokinesis.
- Cell Division in Plant Cells:
1. Prophase: In the first stage of cell division, the nuclear membrane starts to disintegrate, and the chromosomes become visible. Each chromosome consists of two identical copies called chromatids, which are held together by a structure called the centromere.
2. Metaphase: The chromosomes align at the center of the cell, forming a metaphase plate. This alignment ensures that each daughter cell receives an equal number of chromosomes during division.
3. Anaphase: The chromatids separate and move towards opposite poles of the cell. This movement is facilitated by the spindle fibers, which attach to the centromere of each chromatid.
4. Telophase: As the chromatids reach the opposite poles, the nuclear membranes start to reform around them. At this stage, the cell begins to prepare for cytokinesis.
- Cytokinesis in Plant Cells:
In animal cells, cytokinesis occurs through a process called cleavage furrow formation, where a contractile ring pinches the cell membrane inwardly. However, plant cells have a rigid cell wall that cannot be constricted in the same way.
1. Cell Plate Formation: Instead of a cleavage furrow, plant cells form a structure called the cell plate during cytokinesis. The cell plate is made up of vesicles containing cell wall materials, such as cellulose and other polysaccharides.
2. Golgi Vesicles: Golgi vesicles containing cell wall materials accumulate at the center of the cell, between the two daughter nuclei.
3. Fusion of Vesicles: The Golgi vesicles fuse together, forming a continuous structure known as the cell plate. This structure gradually expands towards the periphery of the cell, eventually reaching the cell membrane.
4. Cell Wall Deposition: Enzymes are secreted into the cell plate, which catalyze the deposition of cellulose and other components of the cell wall. As the cell plate expands and fuses with the existing cell wall, it forms a new cell wall between the two daughter cells, separating them completely.
In conclusion, the new cell wall in plant cells begins to form through the process of cytokinesis, specifically through the formation and expansion of the cell plate. The Golgi vesicles fuse together to create the cell plate, which then undergoes cell wall deposition to form a new cell wall between the daughter cells.
Plant cells have a unique feature called the cell wall, which provides support and protection to the cell. During cell division, a new cell wall is formed to separate the two daughter cells. This process is known as cytokinesis.
- Cell Division in Plant Cells:
1. Prophase: In the first stage of cell division, the nuclear membrane starts to disintegrate, and the chromosomes become visible. Each chromosome consists of two identical copies called chromatids, which are held together by a structure called the centromere.
2. Metaphase: The chromosomes align at the center of the cell, forming a metaphase plate. This alignment ensures that each daughter cell receives an equal number of chromosomes during division.
3. Anaphase: The chromatids separate and move towards opposite poles of the cell. This movement is facilitated by the spindle fibers, which attach to the centromere of each chromatid.
4. Telophase: As the chromatids reach the opposite poles, the nuclear membranes start to reform around them. At this stage, the cell begins to prepare for cytokinesis.
- Cytokinesis in Plant Cells:
In animal cells, cytokinesis occurs through a process called cleavage furrow formation, where a contractile ring pinches the cell membrane inwardly. However, plant cells have a rigid cell wall that cannot be constricted in the same way.
1. Cell Plate Formation: Instead of a cleavage furrow, plant cells form a structure called the cell plate during cytokinesis. The cell plate is made up of vesicles containing cell wall materials, such as cellulose and other polysaccharides.
2. Golgi Vesicles: Golgi vesicles containing cell wall materials accumulate at the center of the cell, between the two daughter nuclei.
3. Fusion of Vesicles: The Golgi vesicles fuse together, forming a continuous structure known as the cell plate. This structure gradually expands towards the periphery of the cell, eventually reaching the cell membrane.
4. Cell Wall Deposition: Enzymes are secreted into the cell plate, which catalyze the deposition of cellulose and other components of the cell wall. As the cell plate expands and fuses with the existing cell wall, it forms a new cell wall between the two daughter cells, separating them completely.
In conclusion, the new cell wall in plant cells begins to form through the process of cytokinesis, specifically through the formation and expansion of the cell plate. The Golgi vesicles fuse together to create the cell plate, which then undergoes cell wall deposition to form a new cell wall between the daughter cells.
Cell growth results in disturbing the ratio between- a)Nucleus - chromosome ratio
- b)Cytoplasm-chromosome ratio
- c)Cytoplasm-spindle fibre ratio
- d)Nucleus-cytoplasm ratio
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Cell growth results in disturbing the ratio between
a)
Nucleus - chromosome ratio
b)
Cytoplasm-chromosome ratio
c)
Cytoplasm-spindle fibre ratio
d)
Nucleus-cytoplasm ratio
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Mitosis usually results in the production of diploid daughter cells with identical genetic complement.
The growth of multicellular organisms is due to mitosis.
Cell growth results in disturbing the ratio between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. It therefore becomes essential for the cell to divide to restore the nucleo-cytoplasmic ratio.
Crossing over may result in- a)Addition of genetic material
- b)Deletion of genetic material
- c)Exchange of genetic material
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Crossing over may result in
a)
Addition of genetic material
b)
Deletion of genetic material
c)
Exchange of genetic material
d)
All of the above
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Crossing over is the exchange of genes between two chromosomes, resulting in non-identical chromatids that comprise the genetic material of gametes. This process occurs during Prophase I of Meiosis, just prior to chromosome alignment and splitting of the cell.
Meiosis results in
- a)Production of gametes
- b)Reduction in Chromosome number
- c)Introduction of variation
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Meiosis results in
a)
Production of gametes
b)
Reduction in Chromosome number
c)
Introduction of variation
d)
All of the above
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
As previously mentioned, the first round of nuclear division that occurs during the formation of gametes is called meiosis I. It is also known as the reduction division because it results in cells that have half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Most of the involuntary action are controlled by :-- a)Medulla oblongata
- b)Cerebrum
- c)Cerebellum
- d)Diencephalon
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Most of the involuntary action are controlled by :-
a)
Medulla oblongata
b)
Cerebrum
c)
Cerebellum
d)
Diencephalon
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Involuntary actions are those action that controlled by medulla oblongata which is a part of the autonomous nervous system where as voluntary actions are controlled by the cerebellum. The medulla oblongata directly controls heartbeat, blood pressure, breathing and digestion. It is located in the hindbrain, anterior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped and contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor centers. Hence, the correct answer is option C.
In yeast the cell cycle is progressed through- a)60 minutes
- b)90 minutes
- c)20 minutes
- d)30 minutes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In yeast the cell cycle is progressed through
a)
60 minutes
b)
90 minutes
c)
20 minutes
d)
30 minutes

|
Aniket Chawla answered |
Yeast can progress through the cell cycle in only about 90 minutes.
Plant Cytokinesis differ from animals Cytokinesis in having- a)Midbody
- b)Microfilament
- c)Cell plate
- d)None of these
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Plant Cytokinesis differ from animals Cytokinesis in having
a)
Midbody
b)
Microfilament
c)
Cell plate
d)
None of these
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Plant cells divide by a cell plate that eventually becomes the cell wall whereas animal cells divide by a cleavage furrow.
The nuclear structures disappear during
a) Telophase
b) Metaphase
c) Anaphase
d) Prophase
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Subham Chavan answered |
The nuclear envelope and the nucleolus disappear and the spindle fibres start appearing. Metaphase is marked by the alignment of chromosomes at the equatorial plate.
The aperture controlling the light entering in eye is called - a)Iris
- b)Pupil
- c)Blind spot
- d)Sclerotic layer
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The aperture controlling the light entering in eye is called
a)
Iris
b)
Pupil
c)
Blind spot
d)
Sclerotic layer
|
|
Shalini... answered |
The pupil is a hole or aperture in the middle of the iris. Iris is the colored part of the eye that controls the amount of light entering the eye by adjusting the size of the pupil. The point of exit of optic nerve from eye forms a “blind spot” in the retina. The sclera is the white and opaque outer layer of the eyeball.
Lens and retina of vertebrate eye develop from - a)Mesoderm
- b)Ectoderm
- c) Endoderm
- d) Partly from ectoderm and partly from endoderm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Lens and retina of vertebrate eye develop from
a)
Mesoderm
b)
Ectoderm
c)
Endoderm
d)
Partly from ectoderm and partly from endoderm
|
|
Abdul Saleem4367 answered |
According to ncert ectoderm hi answer hoga Bhai...
Match List I and List II, and select the correct answer.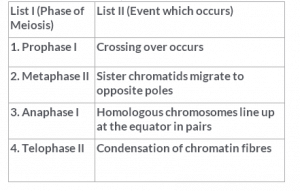
- a)1, 2 and 3 are correct.
- b)1 and 3 are correct.
- c)2 and 4 are correct.
- d)Only 1 is correct.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Match List I and List II, and select the correct answer.

a)
1, 2 and 3 are correct.
b)
1 and 3 are correct.
c)
2 and 4 are correct.
d)
Only 1 is correct.

|
Trisha Vashisht answered |
Correct Answer :- d
Explanation : Genetic variation comes from crossing over, which may occur during prophase I of meiosis.
In prophase I of meiosis, the replicated homologous pair of chromosomes comes together in the process called synapsis, and sections of the chromosomes are exchanged.
Cell division is initiated in plants by- a)Cytokinin
- b)Abscisic acid
- c)Gibberellin
- d)Auxin
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Cell division is initiated in plants by
a)
Cytokinin
b)
Abscisic acid
c)
Gibberellin
d)
Auxin
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
Mitosis is the mechanism by which the chromosome content of a somatic cell (haploid or diploid) is kept constant through successive cell divisions. The division of the cell is initiated by division of the nucleus i.e. Karyokinesis followed by division of cytoplasm i.e. Cytokinesis.
Division of nucleus without being followed by cytokinesis results into- a)Phargmoplast
- b)Polyploidy
- c)Uninucleate condition
- d)Multinucleate condition
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Division of nucleus without being followed by cytokinesis results into
a)
Phargmoplast
b)
Polyploidy
c)
Uninucleate condition
d)
Multinucleate condition

|
Aman Sharma answered |
The division of nucleus or karyokinesis without being followed by cytokinesis results into multinucleate condition.
In telophase I, which of the following event takes place?- a)Nuclear membrane disappear.
- b)Nucleolus disappears.
- c)Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear.
- d)Reoccurrence of nuclear membrane and nucleolus.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In telophase I, which of the following event takes place?
a)
Nuclear membrane disappear.
b)
Nucleolus disappears.
c)
Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear.
d)
Reoccurrence of nuclear membrane and nucleolus.
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
The nuclear membrane, also called the nuclear envelope, is a double membrane layer that separates the contents of the nucleus from the rest of the cell. It is found in both animal and plant cells. A cell has many jobs, such as building proteins, converting molecules into energy, and removing waste products. The nuclear envelope protects the cell’s genetic material from the chemical reactions that take place outside the nucleus. It also contains many proteins that are used in organizing DNA and regulating genes.
In animal cells, Cytokinesis takes place by furrow deepening centripetally and formation of two daughter cells. This method is known as- a)Phragmoplast
- b)Cleavage Cytokinesis
- c)Cell plate formation
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In animal cells, Cytokinesis takes place by furrow deepening centripetally and formation of two daughter cells. This method is known as
a)
Phragmoplast
b)
Cleavage Cytokinesis
c)
Cell plate formation
d)
None of these

|
Prakhar Maheshwari answered |
1)Microfilaments collect in the middle region of the cell below the cell membrane. The furrow deepens centripetally and cleaves the cell into two daughter cells. This method is called cleavage cytokinesis.
2)Cytokinesis in plants occurs by cell plate formation.
3)The phragmoplast is a plant cell specific structure that forms during late cytokinesis.
Hope it helps!!!!!
Centromere is required for- a)Transcription
- b)Cytoplasmic cleavage
- c)Movement of chromosomes towards poles
- d)Crossing over
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Centromere is required for
a)
Transcription
b)
Cytoplasmic cleavage
c)
Movement of chromosomes towards poles
d)
Crossing over

|
Aravind Saha answered |
The arms of chromosome are known as chromatids. These arms are held together at a point called the centromere (or primary constriction). Centromere occurs any where along the length of chromosome. During ceIl division spindle fibres are attached to centromere and help in the movement of chromosomes towards the poles.
Tear is a - a)Secretory fluid
- b)Excretory fluid
- c) Pure fluid
- d)Lymphatic fluid
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Tear is a
a)
Secretory fluid
b)
Excretory fluid
c)
Pure fluid
d)
Lymphatic fluid
|
|
Saumya Sarkar answered |
Tear is a Secretory Fluid
Explanation:
Tear is a fluid that is produced by the lacrimal gland, which is located in the upper outer portion of the eye socket. Tear is a secretory fluid that is made up of several components, including:
1. Water - Tears are mostly made up of water, which helps to keep the eye moist and lubricated.
2. Salt - Tears contain salt, which helps to keep the eye clean by killing bacteria and other harmful organisms.
3. Enzymes - Tears contain enzymes that help to break down bacteria and other harmful substances.
4. Proteins - Tears contain proteins that help to protect the eye and keep it healthy.
5. Mucus - Tears contain mucus, which helps to keep the eye's surface smooth and free of debris.
Functions of Tears:
Tears serve several important functions in the eye, including:
1. Lubrication - Tears help to keep the eye moist and lubricated, which helps to prevent dryness and irritation.
2. Protection - Tears help to protect the eye from bacteria, viruses, and other harmful substances.
3. Cleansing - Tears help to cleanse the eye by flushing out debris, dirt, and other particles.
4. Emotional expression - Tears can be produced in response to emotions such as sadness, joy, or frustration.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, tear is a secretory fluid that is produced by the lacrimal gland in the eye. It is made up of water, salt, enzymes, proteins, and mucus, and serves several important functions in the eye, including lubrication, protection, cleansing, and emotional expression.
Explanation:
Tear is a fluid that is produced by the lacrimal gland, which is located in the upper outer portion of the eye socket. Tear is a secretory fluid that is made up of several components, including:
1. Water - Tears are mostly made up of water, which helps to keep the eye moist and lubricated.
2. Salt - Tears contain salt, which helps to keep the eye clean by killing bacteria and other harmful organisms.
3. Enzymes - Tears contain enzymes that help to break down bacteria and other harmful substances.
4. Proteins - Tears contain proteins that help to protect the eye and keep it healthy.
5. Mucus - Tears contain mucus, which helps to keep the eye's surface smooth and free of debris.
Functions of Tears:
Tears serve several important functions in the eye, including:
1. Lubrication - Tears help to keep the eye moist and lubricated, which helps to prevent dryness and irritation.
2. Protection - Tears help to protect the eye from bacteria, viruses, and other harmful substances.
3. Cleansing - Tears help to cleanse the eye by flushing out debris, dirt, and other particles.
4. Emotional expression - Tears can be produced in response to emotions such as sadness, joy, or frustration.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, tear is a secretory fluid that is produced by the lacrimal gland in the eye. It is made up of water, salt, enzymes, proteins, and mucus, and serves several important functions in the eye, including lubrication, protection, cleansing, and emotional expression.
Nissl's granules are found in :[UTTARANCHAL-2005]- a)liver cells
- b)nerve cells
- c)kidney
- d)heart
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Nissl's granules are found in :
[UTTARANCHAL-2005]
a)
liver cells
b)
nerve cells
c)
kidney
d)
heart

|
Adit Raj answered |
Option B these are site proteins synthesis.. Rough endoplasmic reticulum(RER) are attached with ribosomesFound in nerve cells.
In diploid cells,each homologous chromosome consists of- a)Two sister chromatids
- b)A pair of maternal chromosomes
- c)A pair of paternal chromosomes
- d)Paternal and maternal chromosomes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In diploid cells,each homologous chromosome consists of
a)
Two sister chromatids
b)
A pair of maternal chromosomes
c)
A pair of paternal chromosomes
d)
Paternal and maternal chromosomes

|
Mahesh Saini answered |
In Diploid cells, each homologous chromosome consists of one paternal and one maternal chromosomethat fuse together during fertilization of gametes.
The common defect of eye which develops in old age is - a)Glaucoma
- b)Astigmatism
- c)Presbyopia
- d)Myopia
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The common defect of eye which develops in old age is
a)
Glaucoma
b)
Astigmatism
c)
Presbyopia
d)
Myopia
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Presbyopia occurs due to decrease in the power of accommodation of the eye usually because of ageing which causes gradual weakening of the ciliary muscles and diminishes flexibility of the eye lens.
Nissl’s granules are made up of: [Bihar-2004]
- a)RER bodies
- b)DNA
- c)carbohydrate
- d)Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Nissl’s granules are made up of: [Bihar-2004]
a)
RER bodies
b)
DNA
c)
carbohydrate
d)
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum

|
Anurag Yadav answered |
Nissl granules are made of ribosomes & endoplasmic reticulum found in Cyton and dendron & it'd primary function is protein synthesis.
Chapter doubts & questions for Unit 4: Cell Communication - AP Biology 2025 is part of Grade 9 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Grade 9 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Grade 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Unit 4: Cell Communication - AP Biology in English & Hindi are available as part of Grade 9 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Grade 9 Exam by signing up for free.
AP Biology
130 videos|198 docs|114 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily










