All Exams >
NEET >
4 Months Preparation for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Molecular Basis of Inheritance for NEET Exam
Which of the following steps in transcription is catalysed by RNA polymerase?
- a)Initiation
- b)Elongation
- c)Termination
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following steps in transcription is catalysed by RNA polymerase?
a)
Initiation
b)
Elongation
c)
Termination
d)
All of the above
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
RNA polymerase moves along the template strand, synthesising an mRNA molecule. In prokaryotes RNA polymerase is a holoenzyme consisting of a number of subunits, including a sigma factor (transcription factor) that recognises the promoter. In eukaryotes there are three RNA polymerases: I, II and III. The process includes a proofreading mechanism.
The strand of DNA that forms mRNA is called?
- a)Lagging strand
- b)Coding strand
- c)Antisense strand
- d)Template strand
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The strand of DNA that forms mRNA is called?
a)
Lagging strand
b)
Coding strand
c)
Antisense strand
d)
Template strand
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
The strand of DNA that forms mRNA is called the template strand or the antisense strand. During transcription, the DNA molecule unwinds, and one of the strands (the template strand) is used as a template to synthesize a complementary RNA molecule, which is called messenger RNA (mRNA). The other strand of DNA, which is not used as a template during transcription, is called the coding strand or the sense strand because it has the same sequence as the mRNA molecule (except for the presence of thymine instead of uracil).
Transformation was discovered by: [2014]- a)Meselson and Stahl
- b)Hershey and Chase
- c)Griffith
- d)Watson and Crick
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Transformation was discovered by: [2014]
a)
Meselson and Stahl
b)
Hershey and Chase
c)
Griffith
d)
Watson and Crick

|
Yash Saha answered |
(c) Frederick Griffith (in 1928), a British Medical officer described the phenomenon of bacterial transformation. He carried out experiment with Streptococcus pneumoniae (bacterium causing pneumonia) which is used to infect mice. By using S Strain (heat killed) and R strain (live) it was concluded that R strain has been transformed by some material of S strain which makes R strain virulent and enable to synthesize smooth polysachharide.
Which one of the following is wrongly matched? [2014]- a)Transcription – Writing information from DNA to tRNA.
- b)Translation – Using information in mRNA to make protein
- c)Repressor protein – Binds to operator to stop enzyme synthesis.
- d)Operon – Structural genes, operator and promoter
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is wrongly matched? [2014]
a)
Transcription – Writing information from DNA to tRNA.
b)
Translation – Using information in mRNA to make protein
c)
Repressor protein – Binds to operator to stop enzyme synthesis.
d)
Operon – Structural genes, operator and promoter

|
Aman Sharma answered |
(a) Process of copying genetic information from DNA to RNA is called transcription. At a time only one DNA strand is being transcribed into RNA. The strand of DNA with polarity 3' → 5' act as template strand and the DNA strand with polarity 5' → 3' act as coding strand.
Removal of the introns and joining of the exons in a defined order in a transcription unit is called- a)Capping
- b)Transformation
- c)Tailing
- d)Splicing
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Removal of the introns and joining of the exons in a defined order in a transcription unit is called
a)
Capping
b)
Transformation
c)
Tailing
d)
Splicing
|
|
Avantika Gupta answered |
Splicing is the process of removing introns and joining exons in a defined order in a transcription unit. This process takes place in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and is mediated by a complex called the spliceosome.
Explanation:
• Transcription is the process of synthesizing RNA from a DNA template. During transcription, the entire DNA sequence is transcribed into RNA, including both the introns and exons.
• Introns are non-coding sequences within a gene, while exons are the coding sequences that specify the amino acid sequence of a protein. Introns need to be removed from the RNA sequence before translation can occur.
• Splicing is the process of removing introns and joining exons in a defined order, resulting in a mature messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule that can be translated into a protein.
• The splicing process is mediated by the spliceosome, a complex that consists of small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) and proteins. The snRNAs base-pair with the intron sequences, while the proteins catalyze the chemical reactions that remove the introns and join the exons.
• Splicing is essential for the proper expression of genes, as it allows for the creation of multiple protein variants from a single gene by alternative splicing. Mutations that affect splicing can lead to a variety of diseases, including cancer and genetic disorders.
In conclusion, splicing is the process of removing introns and joining exons in a defined order in a transcription unit, and it is essential for the proper expression of genes.
Explanation:
• Transcription is the process of synthesizing RNA from a DNA template. During transcription, the entire DNA sequence is transcribed into RNA, including both the introns and exons.
• Introns are non-coding sequences within a gene, while exons are the coding sequences that specify the amino acid sequence of a protein. Introns need to be removed from the RNA sequence before translation can occur.
• Splicing is the process of removing introns and joining exons in a defined order, resulting in a mature messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule that can be translated into a protein.
• The splicing process is mediated by the spliceosome, a complex that consists of small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) and proteins. The snRNAs base-pair with the intron sequences, while the proteins catalyze the chemical reactions that remove the introns and join the exons.
• Splicing is essential for the proper expression of genes, as it allows for the creation of multiple protein variants from a single gene by alternative splicing. Mutations that affect splicing can lead to a variety of diseases, including cancer and genetic disorders.
In conclusion, splicing is the process of removing introns and joining exons in a defined order in a transcription unit, and it is essential for the proper expression of genes.
DNA contains nucleobases, sugar and phosphate. Removal of which among these from a DNA sample will not significantly affect the length of DNA?- a)Nucleobases
- b)Sugar
- c)Phosphate
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
DNA contains nucleobases, sugar and phosphate. Removal of which among these from a DNA sample will not significantly affect the length of DNA?
a)
Nucleobases
b)
Sugar
c)
Phosphate
d)
None of the above
|
|
Shreya Singh answered |
Nucleobases, also known as nitrogenous bases are nitrogen-containing biological compounds that form nucleosides, which in turn are components of nucleotides, with all of these monomersconstituting the basic building blocks of nucleic acids. The ability of nucleobases to form base pairs and to stack one upon another leads directly to long-chain helical structures such as ribonucleic acid (RNA) and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)....
The amino acid attaches to the tRNA at its- a)5′ end
- b)Anticodon site
- c)3′ end
- d)DHU loop
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The amino acid attaches to the tRNA at its
a)
5′ end
b)
Anticodon site
c)
3′ end
d)
DHU loop
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
TRNA with an attached amino acid is said to be "charged". The enzyme that attaches the amino acid to the 3'-OH is called an aminoacyl tRNA synthetase (aaRS). There is a specific tRNA for each amino acid, 20 in all. Similarly, there is a specific aaRS for each tRNA.
Protein synthesis occurs over- a)Cytoplasm
- b)Ribosomes
- c)Amino acids
- d)Mitochondria
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Protein synthesis occurs over
a)
Cytoplasm
b)
Ribosomes
c)
Amino acids
d)
Mitochondria
|
|
Sathvika Tadri answered |
Ribosomes are site of protein synthesis and are known as protein factory
During transcription, the DNA site at which RNA polymerase binds is called- a)Enhancer
- b)Receptor
- c)Promoter
- d)Regulator
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During transcription, the DNA site at which RNA polymerase binds is called
a)
Enhancer
b)
Receptor
c)
Promoter
d)
Regulator
|
|
Prashanth Chatterjee answered |
The site at which RNA polymerase binds during transcription is called the promoter. It is a specific region of DNA that is recognized by RNA polymerase, which then initiates the process of transcription. The promoter is located upstream of the transcriptional start site and contains specific DNA sequences that are recognized by RNA polymerase and other transcription factors.
The promoter plays a crucial role in regulating gene expression, as different promoters can activate or repress transcription depending on the cellular context. The strength of the promoter can also affect the rate of transcription, with stronger promoters resulting in higher levels of mRNA production.
There are different types of promoters, including constitutive promoters, which are active in all cells, and inducible promoters, which are activated in response to specific signals or conditions. The sequence and structure of the promoter can vary depending on the gene being transcribed and the organism in which it is expressed.
In summary, the promoter is a critical element in the process of transcription, serving as the site at which RNA polymerase binds and initiating the production of mRNA from DNA. It plays a crucial role in regulating gene expression and can vary in strength and specificity depending on the cellular context and the gene being transcribed.
The promoter plays a crucial role in regulating gene expression, as different promoters can activate or repress transcription depending on the cellular context. The strength of the promoter can also affect the rate of transcription, with stronger promoters resulting in higher levels of mRNA production.
There are different types of promoters, including constitutive promoters, which are active in all cells, and inducible promoters, which are activated in response to specific signals or conditions. The sequence and structure of the promoter can vary depending on the gene being transcribed and the organism in which it is expressed.
In summary, the promoter is a critical element in the process of transcription, serving as the site at which RNA polymerase binds and initiating the production of mRNA from DNA. It plays a crucial role in regulating gene expression and can vary in strength and specificity depending on the cellular context and the gene being transcribed.
The portion of DNA which contains information for an entire polypeptide is called- a)Operon
- b)Recon
- c)Muton
- d)Cistron
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The portion of DNA which contains information for an entire polypeptide is called
a)
Operon
b)
Recon
c)
Muton
d)
Cistron
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
Cistron is a nucleotide sequence responsible for the synthesis of a polypeptide sequence of a functional protein.
The word cistron is used to emphasize that genes exhibit a specific behavior in a cis-trans test, distinct positions (or loci) within a genome are cistronic.
Repressor proteins are coded for by ______ genes.- a)Promoter
- b)Structural
- c)Regulator
- d)Operator
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Repressor proteins are coded for by ______ genes.
a)
Promoter
b)
Structural
c)
Regulator
d)
Operator
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Regulator genes codes for repressor proteins during translation of DNA into protein via mRNA.
Commonly used vectors for human genome sequencing are: [2014]- a)T-DNA
- b)BAC and YAC
- c)Expression Vectors
- d)T/A Cloning Vectors
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Commonly used vectors for human genome sequencing are: [2014]
a)
T-DNA
b)
BAC and YAC
c)
Expression Vectors
d)
T/A Cloning Vectors

|
Anirudh Datta answered |
(b) Human genome sequencing is a process that determines the complete DNA sequence of an organism's genome at a single time. This requires sequencing all of an organism's chromosomal DNA as well as DNA contained in the mitochondria and, for plants, in the chloroplast. Commonly used vectors for human genome sequencing are BAC (Bacterial artificial chromosomes) and YAC (Yeast artificial chromosomes).
An abnormal human baby with 'XXX' sex chromosomes was born due to- a)formation of abnormal sperms in the father
- b)formation of abnormal ova in the mother
- c)fusion of two ova and one sperm
- d)fusion of two sperms and one ovum
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An abnormal human baby with 'XXX' sex chromosomes was born due to
a)
formation of abnormal sperms in the father
b)
formation of abnormal ova in the mother
c)
fusion of two ova and one sperm
d)
fusion of two sperms and one ovum

|
Mrinalini Bajaj answered |
Alleles are different molecular forms of a gene, representing altemate forms of a given character.
Height of a pea plant-T for tallness and t for dwarfness.
T and t are altemate forms for given character of height.
Heterozygotes and homozygotes refers to inheritance of two different and similar travels for a character respectively.
The coding segment of DNA isa)Mutonb)Repliconc)Intrond)CodonCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Exon: The coding sequences or expressed sequences are defined as exon. Exons are said to be those sequences that appear in mature or processed RNA.
A complex of ribosomes attached to a single strand of RNA is known as [2016]- a)Polysome
- b)Polymer
- c)Polypeptide
- d)Okazaki fragment
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A complex of ribosomes attached to a single strand of RNA is known as [2016]
a)
Polysome
b)
Polymer
c)
Polypeptide
d)
Okazaki fragment

|
Dipika Das answered |
(a) A polysome or polyribosome is a complex of an mRNA molecule and two or more ribosomes, which is formed during the active translation process. They were initially named as ergosomes in 1963. However, further research by Jonathan Warner and Alex Rich characterized polysome.
Out of 64 codons, the number of codons with GGG is- a)4
- b)1
- c)2
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Out of 64 codons, the number of codons with GGG is
a)
4
b)
1
c)
2
d)
6
|
|
Sankar Banerjee answered |
GGG code is present only 1 tym nd the amino acid produced by GGG is glycine.
A pleiotropic gene: [2015 RS]- a)is a gene evolved during Pliocene.
- b)controls a trait only in combination with another gene
- c)controls multiple traits in an individual.
- d)is expressed only in primitive plants
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A pleiotropic gene: [2015 RS]
a)
is a gene evolved during Pliocene.
b)
controls a trait only in combination with another gene
c)
controls multiple traits in an individual.
d)
is expressed only in primitive plants
|
|
Hitakshi 💞💞 answered |
The ability of a gene to have multiple phenotypic effects because it influences a number of characters simultaneously is known as pleiotropy. The gene having a multiple phenotypic effect because of its ability to control expression of two or more characters is called pleiotropic gene. In human beings pleiotropy is exhibited by syndromes called sickle cell anaemia and phenylketonuria.
Some amino acids are coded by more than one codon; hence, the code is- a)Unambiguous
- b)Universal
- c)Degenerate
- d)Initiator
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Some amino acids are coded by more than one codon; hence, the code is
a)
Unambiguous
b)
Universal
c)
Degenerate
d)
Initiator
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
The genetic code is degenerate: Some amino acids are encoded by more than one codon, inasmuch as there are 64 possible base triplets and only 20 amino acids. In fact, 61 of the 64 possible triplets specify particular amino acids and 3 triplets (called stop codons) designate the termination of translation. Thus, for most amino acids, there is more than one code word.
DNA has genetic properties was revealed for the first time by- a)Chargaff
- b)Griffith
- c)Avery
- d)Wilkins
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
DNA has genetic properties was revealed for the first time by
a)
Chargaff
b)
Griffith
c)
Avery
d)
Wilkins
|
|
Pooja Choudhury answered |
The discovery that DNA has genetic properties was first revealed by Oswald Avery and his team of scientists in 1944. Avery was a molecular biologist who worked at the Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research in New York City.
Experiment
Avery and his team conducted a series of experiments to determine whether DNA was the genetic material responsible for the transformation of bacteria. They used two strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae, one that was virulent (able to cause disease) and one that was non-virulent. The virulent strain had a capsule made of a complex sugar that protected it from the immune system, while the non-virulent strain lacked this capsule and was easily destroyed by the immune system.
Results
Avery and his team extracted various biochemical components from the virulent strain of bacteria, including proteins, lipids, RNA, and DNA. They then mixed each of these components with the non-virulent strain to see if they could induce transformation. Only the DNA extract was able to transform the non-virulent strain into a virulent one, proving that DNA was the genetic material responsible for the transformation.
Conclusion
Avery's discovery was groundbreaking because it showed that DNA, which was previously thought to be a simple molecule with no biological significance, was in fact the carrier of genetic information. This discovery paved the way for the development of the field of molecular biology and our current understanding of genetics.
Experiment
Avery and his team conducted a series of experiments to determine whether DNA was the genetic material responsible for the transformation of bacteria. They used two strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae, one that was virulent (able to cause disease) and one that was non-virulent. The virulent strain had a capsule made of a complex sugar that protected it from the immune system, while the non-virulent strain lacked this capsule and was easily destroyed by the immune system.
Results
Avery and his team extracted various biochemical components from the virulent strain of bacteria, including proteins, lipids, RNA, and DNA. They then mixed each of these components with the non-virulent strain to see if they could induce transformation. Only the DNA extract was able to transform the non-virulent strain into a virulent one, proving that DNA was the genetic material responsible for the transformation.
Conclusion
Avery's discovery was groundbreaking because it showed that DNA, which was previously thought to be a simple molecule with no biological significance, was in fact the carrier of genetic information. This discovery paved the way for the development of the field of molecular biology and our current understanding of genetics.
Which of the following important biochemical reactions in living systems is catalyzed by a ribozyme?
a)Formation of peptide bondb)Repair of DNAc)Electron transfer chaind)Organization of MTOC during cell divisonCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
In prokaryotes (bacteria) the 23srRNA of the larger subunit of ribosome is the enzyme ribozyme that catalyzes peptide bond formation.
Hence, the correct option is A.
NCERT Reference: Page no. 115 of topic “6.7 TRANSLATION” of chapter 6.
NCERT Reference: Page no. 115 of topic “6.7 TRANSLATION” of chapter 6.
The chromosomes in which centromere is situated close to one end are: [2015 RS]- a)Acrocentric
- b)Telocentric
- c)Sub-metacentric
- d)Metacentric
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The chromosomes in which centromere is situated close to one end are: [2015 RS]
a)
Acrocentric
b)
Telocentric
c)
Sub-metacentric
d)
Metacentric

|
Aman Sharma answered |
(a) In acrocentric chromosomes, one arm is very short but another is long.
Match column with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.
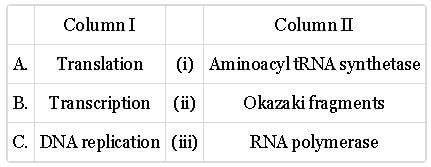
- a)A-(i), B-(i), C-(iii)
- b)A-(i), B-(iii), C-(ii)
- c)A-(iii), B-(i), C-(ii)
- d)A-(ii), B-(iii), C-(i)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Match column with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.


a)
A-(i), B-(i), C-(iii)
b)
A-(i), B-(iii), C-(ii)
c)
A-(iii), B-(i), C-(ii)
d)
A-(ii), B-(iii), C-(i)

|
Lead Academy answered |
DNA Replication: DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes an identical copy of its DNA. It occurs during the cell cycle to ensure that each daughter cell receives a complete set of genetic instructions. DNA replication is a highly accurate process in which the DNA double helix is unwound, and each strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a complementary strand.
Transcription: Transcription is the process by which a segment of DNA is used as a template to synthesize a complementary RNA molecule. It is the first step in the central dogma of molecular biology, which describes how genetic information is used to produce proteins. In transcription, an enzyme called RNA polymerase reads the DNA template and assembles a single-stranded RNA molecule, known as messenger RNA (mRNA), by matching RNA nucleotides to the DNA template.
Translation: Translation is the process in which the information contained in an mRNA molecule is used to synthesize a protein. This process occurs at ribosomes, cellular structures that serve as the protein-manufacturing factories. During translation, the mRNA is read in sets of three nucleotides called codons. Each codon corresponds to a specific amino acid, the building blocks of proteins.
In sea urchin DNA, which is double stranded, 17% of the bases were shown to be cytosine. The percentages of the other three bases expected to be present in this DNA are :- [2015 RS]- a)G 17%, A 16.5%, T 32.5%
- b)G 17%, A 33%, T 33%
- c)G 8.5%, A 50%, T 24.5%
- d)G 34%, A 24.5%, T 24.5%
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In sea urchin DNA, which is double stranded, 17% of the bases were shown to be cytosine. The percentages of the other three bases expected to be present in this DNA are :- [2015 RS]
a)
G 17%, A 16.5%, T 32.5%
b)
G 17%, A 33%, T 33%
c)
G 8.5%, A 50%, T 24.5%
d)
G 34%, A 24.5%, T 24.5%

|
Diya Datta answered |
(b) Chargaff's rule states that A = T and G º C. The molar amount of adenine = molar amount of thymine. The molar amount of guanine = molar amount of cytosine. Hence, G is 17%, so, C = 17% A = 33%, so, T = 33%
Why are UGA, UAG and UAA called termination codons?- a)They terminate anticodons
- b)They are presenting at the beginning of mRNA
- c)They indicate initiation of translation
- d)They do not specify any amino acid
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Why are UGA, UAG and UAA called termination codons?
a)
They terminate anticodons
b)
They are presenting at the beginning of mRNA
c)
They indicate initiation of translation
d)
They do not specify any amino acid
|
|
Supriya Senapati answered |
Since The stop codons are UAA, UAG, and UGA. They encode no amino acid. The ribosome pauses and falls off the mRNA.
According to Chargaff’s rule, which one is correct?- a)[A] + [T] = [G] + [C]
- b)[A] + [C] = [G] + [T]
- c)[A] + [G] = [T] + [C]
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
According to Chargaff’s rule, which one is correct?
a)
[A] + [T] = [G] + [C]
b)
[A] + [C] = [G] + [T]
c)
[A] + [G] = [T] + [C]
d)
All of these
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
According to Chargaff’s rule in all cellular DNA, regardless of the species, number of adenosine residues is equal to the number of thymidine residues which means that A = T and the number of guanosine residues is equal to the number of cytidine residues; G = C . Hence, that the sum of the purine residues equals the sum of the pyrimidine residues; i.e., A + G = T + C.
Which of the following is not required for any of the techniques of DNA fingerprinting available at present ? [2016]- a)Polymerase chain reaction
- b)Zinc finger analysis
- c)Restriction enzymes
- d)DNA-DNA hybridization
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not required for any of the techniques of DNA fingerprinting available at present ? [2016]
a)
Polymerase chain reaction
b)
Zinc finger analysis
c)
Restriction enzymes
d)
DNA-DNA hybridization

|
Pooja Choudhary answered |
(b) Zinc-finger analysis is used for protein analysis. The zinc finger proteins are a super family of proteins involved in numerous activities of plant growth and development.
Which chromosome of human genome contains least number of genes?- a)Chromosome 12
- b)Chromosome X
- c)Chromosome Y
- d)Chromosome 1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which chromosome of human genome contains least number of genes?
a)
Chromosome 12
b)
Chromosome X
c)
Chromosome Y
d)
Chromosome 1
|
|
Afifa Aaliya answered |
Chromosomes are thread like structures of DNA and proteins that carry genetic information of organisms in the form of genes. The human chromosomes with least number of genes is Your chromosome.
Option " C " is correct answer.
Option " C " is correct answer.
DNA is made of two chains that twist about one another in the shape of a _______.- a)Broken ladder
- b)Straight ladder
- c)Straight spiral
- d)Double helix
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
DNA is made of two chains that twist about one another in the shape of a _______.
a)
Broken ladder
b)
Straight ladder
c)
Straight spiral
d)
Double helix
|
|
Ananya Duney answered |
They are twist in a right handed double helical way therefore it's called double helix DNA which was given by Watson and crick
"hope it'll help"
"hope it'll help"
Whose experiments cracked the DNA and discovered unequivocally that a genetic code is a triplet?- a)Nirenberg and Matthaei
- b)Hershey and Chase
- c)Beadle and Tatum
- d)Morgan and Sturtevant
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Whose experiments cracked the DNA and discovered unequivocally that a genetic code is a triplet?
a)
Nirenberg and Matthaei
b)
Hershey and Chase
c)
Beadle and Tatum
d)
Morgan and Sturtevant
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
The existence of a triplet code was simply an assumption till 1961 when Nirenberg and Methaei proved its existence by experiment. They were able to synthesise artificial mRNA, which contained only one nitrogenous base, ie, uracil. This synthetic poly-U sequence was then placed in a cell-free system containing protein synthesizing enzymes (extracted from bacterium E. coil) and 20 amino acids together with necessary ATP. During the process, a small polypeptide molecule was produced, which was formed by the linking of phenylalanine. This issuggested that UUU is code for phenylalanine. Nirenberg got Nobel Prize for his contributions.
Codon is made up of- a)Single nucleotide
- b)Four nucleotides
- c)three nucleotides
- d)two nucleotides
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Codon is made up of
a)
Single nucleotide
b)
Four nucleotides
c)
three nucleotides
d)
two nucleotides
|
|
Gopikas S answered |
Codons are found in mRNA.A sequence of three nucleotides in messenger RNA makes a codon for an amino acid. A codon is a sequence of three adjacent nucleotides constituting the genetic code that determines the insertion of a specific amino acid in a polypeptide chain during protein synthesis or the signal to stop protein synthesis. A codon is defined by the initial nucleotide from which translation starts.
Which one of the following also acts as a catalyst in a bacterial cell ?[2011]- a)5 sr RNA
- b)sn RNA
- c)hn RNA
- d)23 sr RNA
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following also acts as a catalyst in a bacterial cell ?
[2011]
a)
5 sr RNA
b)
sn RNA
c)
hn RNA
d)
23 sr RNA

|
Abhishek Choudhary answered |
23sr RNA acts as a catalyst in a bacterial cell.
The following code codes for which of the amino acid respectively?
AUG and GUG- a)Phenylalanine, tyrosine
- b)Methionine, valine
- c)Methionine, alanine
- d)Lysine, valine
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The following code codes for which of the amino acid respectively?
AUG and GUG
AUG and GUG
a)
Phenylalanine, tyrosine
b)
Methionine, valine
c)
Methionine, alanine
d)
Lysine, valine
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Three base triplets form a codon that codes for an amino acid. Thus AUG codes for methionine and GUG codes for Valine. AUG and GUG are both initiating codons for translation.
The code AUG stands for- a)Aniline
- b)Methionine
- c)Glycine
- d)N-formyl methionine
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The code AUG stands for
a)
Aniline
b)
Methionine
c)
Glycine
d)
N-formyl methionine
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
The genetic code consists of 64 triplets of nucleotides. These triplets are called codons.With three exceptions, each codon encodes for one of the 20 amino acids used in the synthesis of proteins. That produces some redundancy in the code: most of the amino acids being encoded by more than one codon.
One codon, AUG serves two related functions:
1. it signals the start of translation
2. it codes for the incorporation of the amino acid methionine (Met) into the growing polypeptide chain
What is called Griffith effect?- a)DNA transcription
- b)RNA translation
- c)Bacterial transduction
- d)Bacterial transformation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is called Griffith effect?
a)
DNA transcription
b)
RNA translation
c)
Bacterial transduction
d)
Bacterial transformation
|
|
Mathi Mathi answered |
Bacteria can take up forigen DNA in a process called transformation. It occurs after restriction digest and ligation and transfers newly made plasmid to bacteria.
Bacteria with a plasmid are antibiotic resistant, and each will form a colony.
Bacteria with a plasmid are antibiotic resistant, and each will form a colony.
Which one of the following pairs of nitrogenous bases of nucleic acids, is wrongly matched with the category mentioned against it?[2008]- a)Thymine, Uracil - Pyrimidines
- b)Uracil, Cytosine - Pyrimidines
- c)Guanine, Adenine - Purines
- d)Adenine, Thymine - Purines
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following pairs of nitrogenous bases of nucleic acids, is wrongly matched with the category mentioned against it?
[2008]
a)
Thymine, Uracil - Pyrimidines
b)
Uracil, Cytosine - Pyrimidines
c)
Guanine, Adenine - Purines
d)
Adenine, Thymine - Purines

|
Lekshmi Banerjee answered |
Purine is an organic nitrogenous base sparingly soluble in water, that gives rise to a group of biologically important derivatives, notably adenine and guanine, which occur in nucleotides and nucleic acids (DNA and RNA).
By which bonds the purine & pyrimidine pairs of Complementary Strands of DNA held together?- a)N – bonds
- b)H – bonds
- c)O - bonds
- d)C - bonds
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
By which bonds the purine & pyrimidine pairs of Complementary Strands of DNA held together?
a)
N – bonds
b)
H – bonds
c)
O - bonds
d)
C - bonds
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
In complementary strands of DNA, purines and pyrimidine are held together by Hydrogen bond (H-bond). Adenine and Thymine have double hydrogen bond and cytosine and guanine are held by triple hydrogen bond.
RNA polymerase is only capable of catalyzing the process of- a)Elongation
- b)Initiation
- c)Termination
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
RNA polymerase is only capable of catalyzing the process of
a)
Elongation
b)
Initiation
c)
Termination
d)
All of the above

|
Arnav Iyer answered |
During protein synthesis, elongation of peptide chain is catalyzed by the enzyme RNA polymerase. Elongation continuous until a non-sense or stop codon is reached.
Which one of the following is not applicable to RNA? [2015 RS]- a)5' phosphoryl and 3' hydroxyl ends
- b)Heterocyclic nitrogenous bases
- c)Chargaff's rule
- d)Complementary base pairing
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is not applicable to RNA? [2015 RS]
a)
5' phosphoryl and 3' hydroxyl ends
b)
Heterocyclic nitrogenous bases
c)
Chargaff's rule
d)
Complementary base pairing

|
Priyanka Iyer answered |
(c) Chargaff's rule is not applicable to RNA
A man with blood group 'A' marries a woman with blood group 'B'. What are all the possible blood groups of their offsprings ? [2015 RS]- a)A,B and AB only
- b)A,B,AB and O
- c)O only
- d)A and B only
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A man with blood group 'A' marries a woman with blood group 'B'. What are all the possible blood groups of their offsprings ? [2015 RS]
a)
A,B and AB only
b)
A,B,AB and O
c)
O only
d)
A and B only

|
Shruti Chauhan answered |
(b) Possible × Possible genotype genotype of man with blood of woman with group A blood group B I A IA, IA IO × IB IB, IB IO If the genotype is I A IO × IB IO The possibility of resultant blood group may be A, B, AB and O.
The structure in chromatin seen as 'beads-on' string' when viewed under electron microscope are called- a)nucleotides
- b)nuclesides
- c)histone octamer
- d)nucleosomes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The structure in chromatin seen as 'beads-on' string' when viewed under electron microscope are called
a)
nucleotides
b)
nuclesides
c)
histone octamer
d)
nucleosomes
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
Nucleosomes constitute the repeating unit of a structure in nucleus called chromatin, thread-like stained (coloured) bodies seen in nucleus. The nucleosomes in chromatin are seen as 'beads-on-string' structure when viewed under electron microscope.
Removal of introns and joining the exons in a defined order in a transcription unit is called:[2009]- a)tailing
- b)transformation
- c)capping
- d)splicing
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Removal of introns and joining the exons in a defined order in a transcription unit is called:
[2009]
a)
tailing
b)
transformation
c)
capping
d)
splicing

|
Ayush Choudhury answered |
Splicing is the removal of introns and joining the exons in a defined order in a transcription unit. In molecular biology, splicing is a modification of RNA after transcription, in which introns are removed and exons are joined.
Who among the following scientists had no contribution in the development of the double helix model for the structure of DNA?- a)Meselson and Stahl
- b)Rosalind Franklin
- c)Erwin Chargaff
- d)Maurice Wilkins
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Who among the following scientists had no contribution in the development of the double helix model for the structure of DNA?
a)
Meselson and Stahl
b)
Rosalind Franklin
c)
Erwin Chargaff
d)
Maurice Wilkins

|
Dilip Chaurasiya answered |
Meselson and Stahl prove experimentally semi conservation of DNA replication not say but structure of DNA.
PCR and restriction fragment length polymorphism are methods for- a)Genetic fingerprinting
- b)Genetic transformation
- c)DNA sequencing
- d)Study of enzymes
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
PCR and restriction fragment length polymorphism are methods for
a)
Genetic fingerprinting
b)
Genetic transformation
c)
DNA sequencing
d)
Study of enzymes
|
|
Janhavi Menon answered |
Genetic Fingerprinting
Genetic fingerprinting or DNA fingerprinting is a technique used to identify individuals based on their unique DNA profiles. PCR and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) are two commonly used methods for genetic fingerprinting.
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
PCR is a powerful technique used to amplify a specific DNA sequence. It involves a series of repeated cycles of denaturation, annealing, and extension, resulting in the exponential amplification of a specific DNA fragment. PCR is used in genetic fingerprinting to amplify DNA from a sample, such as blood or tissue, and create multiple copies of a specific DNA fragment for analysis.
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP)
RFLP is a technique used to identify variations in DNA sequences between individuals. It involves the use of restriction enzymes to cut DNA at specific sites, resulting in fragments of different sizes. The resulting fragments are separated by gel electrophoresis and visualized using a staining agent. The pattern of fragment sizes is unique to each individual and can be used to identify them.
Applications of Genetic Fingerprinting
Genetic fingerprinting has a wide range of applications, including:
- Forensic investigations: DNA evidence can be used to identify suspects or victims in criminal investigations.
- Paternity testing: DNA analysis can be used to determine biological relationships, such as paternity or maternity.
- Medical diagnosis: Genetic fingerprinting can be used to diagnose genetic diseases and identify carriers of genetic mutations.
- Evolutionary studies: Genetic fingerprinting can be used to study the evolutionary relationships between different species.
Conclusion
PCR and RFLP are two powerful techniques used in genetic fingerprinting. These techniques have revolutionized the field of forensic science and have a wide range of applications in medicine, biology, and genetics.
Genetic fingerprinting or DNA fingerprinting is a technique used to identify individuals based on their unique DNA profiles. PCR and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) are two commonly used methods for genetic fingerprinting.
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
PCR is a powerful technique used to amplify a specific DNA sequence. It involves a series of repeated cycles of denaturation, annealing, and extension, resulting in the exponential amplification of a specific DNA fragment. PCR is used in genetic fingerprinting to amplify DNA from a sample, such as blood or tissue, and create multiple copies of a specific DNA fragment for analysis.
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP)
RFLP is a technique used to identify variations in DNA sequences between individuals. It involves the use of restriction enzymes to cut DNA at specific sites, resulting in fragments of different sizes. The resulting fragments are separated by gel electrophoresis and visualized using a staining agent. The pattern of fragment sizes is unique to each individual and can be used to identify them.
Applications of Genetic Fingerprinting
Genetic fingerprinting has a wide range of applications, including:
- Forensic investigations: DNA evidence can be used to identify suspects or victims in criminal investigations.
- Paternity testing: DNA analysis can be used to determine biological relationships, such as paternity or maternity.
- Medical diagnosis: Genetic fingerprinting can be used to diagnose genetic diseases and identify carriers of genetic mutations.
- Evolutionary studies: Genetic fingerprinting can be used to study the evolutionary relationships between different species.
Conclusion
PCR and RFLP are two powerful techniques used in genetic fingerprinting. These techniques have revolutionized the field of forensic science and have a wide range of applications in medicine, biology, and genetics.
Multiple alleles are present : [2015 RS]- a)At different loci on the same chromosome
- b)At the same locus of the chromosome
- c)On non-sister chromatids
- d)On different chromosomes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Multiple alleles are present : [2015 RS]
a)
At different loci on the same chromosome
b)
At the same locus of the chromosome
c)
On non-sister chromatids
d)
On different chromosomes

|
Krish Patel answered |
(b) All alleles of a gene are situated on the same loci of chromosome in organisms.
Genetic information is carried out by long chain molecule made up of- a)Nucleotides
- b)Enzymes
- c)Histone proteins
- d)Amino acids
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Genetic information is carried out by long chain molecule made up of
a)
Nucleotides
b)
Enzymes
c)
Histone proteins
d)
Amino acids
|
|
Aarya Khanna answered |
Genetic information is carried out by DNA and RNA. Both DNA and RNA are called genetic material, made up of long chain of nucleotide having-nitrogenous base, sugar and phosphate ions.
The hybridization of probes having radioactive isotopes with various sequence of nitrogen bases with ssVNTR is called?- a)Eastern blotting
- b)Southern blotting
- c)Western blotting
- d)Northern blotting
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The hybridization of probes having radioactive isotopes with various sequence of nitrogen bases with ssVNTR is called?
a)
Eastern blotting
b)
Southern blotting
c)
Western blotting
d)
Northern blotting
|
|
Ankita Raj answered |
The hybridization of probes having radioactive isotopes with various sequence of nitrogen bases with ssVNTR is called southern blotting. Southern blotting is a laboratory technique used to detect a specific DNA sequence in a blood or tissue sample. A restriction enzyme is used to cut a sample of DNA into fragments that are separated using gel electrophoresis. The DNA fragments are transferred out of the gel to the surface of a membrane. The membrane is exposed to a DNA probe labeled with a radioactive or chemical tag. If the probe binds to the membrane, then the probe sequence is present in the sample. Hence, the correct answer is option 'B'.
A typical nucleosome contains- a)100 bp of DNA helix
- b)400 bp of DNA helix
- c)200 bp of DNA helix
- d)300 bp of DNA helix
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A typical nucleosome contains
a)
100 bp of DNA helix
b)
400 bp of DNA helix
c)
200 bp of DNA helix
d)
300 bp of DNA helix
|
|
Suresh Kumar answered |
A typical nucleosome contains 200 bp of DNA double helix wrapped(2 turns) around a core of histone octamer having two copies of each of four types of histone proteins ..H2A,H2B,H3,&H4.....H1 histone molecule lies outside the nucleosome core & seals the two turns of DNA by binding at the point where DNA enters and leaves the core..
Gene regulation governing lactose operon of E.coli that involves the lac I gene product is : [2015 RS]- a)Negative and inducible because repressor protein prevents transcription
- b)Negative and repressible because repressor protein prevents transcription
- c)Feedback inhibition because excess of bgalactosidase can switch off trascription
- d)Positive and inducible because it can be induced by lactose
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Gene regulation governing lactose operon of E.coli that involves the lac I gene product is : [2015 RS]
a)
Negative and inducible because repressor protein prevents transcription
b)
Negative and repressible because repressor protein prevents transcription
c)
Feedback inhibition because excess of bgalactosidase can switch off trascription
d)
Positive and inducible because it can be induced by lactose
|
|
Raza Great answered |
In negative inducible operons, a regulatory repressor protein is normally bound to the operator, which prevents the transcription of the genes in the operon. If an inducer molecule is present, it binds to the repressor and changes its conformation so that it is unable to bind to the operator. This allows for expression of the operon. The lac operon is a negatively controlled inducible operon, where the inducer molecule is allolactose
The movement of a gene from one linkage group to another is called : [2015 RS]- a)Duplication
- b)Translocation
- c)Crossing over
- d)Inversion
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The movement of a gene from one linkage group to another is called : [2015 RS]
a)
Duplication
b)
Translocation
c)
Crossing over
d)
Inversion

|
Harshitha Dey answered |
(b) In translocation, the movement of a gene takes place from one linkage group to another between non-homologous chromosomes.
Chapter doubts & questions for Molecular Basis of Inheritance - 4 Months Preparation for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Molecular Basis of Inheritance - 4 Months Preparation for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily









