All Exams >
UPSC >
Geography for UPSC CSE >
All Questions
All questions of Fundamentals of Physical Geography for UPSC CSE Exam
The radiations that heat earth’s atmosphere, comes from the- a)Sun
- b)Earth
- c)Ionosphere
- d)Sun and Earth
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The radiations that heat earth’s atmosphere, comes from the
a)
Sun
b)
Earth
c)
Ionosphere
d)
Sun and Earth
|
|
Asha Yadav answered |
The primary source of radiation that heats the Earth is the Sun. The Sun emits electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, ultraviolet radiation, and infrared radiation. As this radiation travels through space, it reaches the Earth's atmosphere and is absorbed, reflected, or scattered by various gases, particles, and surfaces.
The Earth's atmosphere also emits radiation, particularly in the form of infrared radiation, which is re-radiated back towards the Earth's surface. This process is known as the greenhouse effect, and it helps to trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere, making it possible for life to exist on the planet.
Other sources of radiation that contribute to the heating of the Earth include cosmic rays, which are high-energy particles that come from outer space and can penetrate the Earth's atmosphere, and radioactive decay, which generates heat within the Earth's core. However, these sources are much less significant than the Sun in terms of their contribution to the Earth's overall heat budget.
The Earth's atmosphere also emits radiation, particularly in the form of infrared radiation, which is re-radiated back towards the Earth's surface. This process is known as the greenhouse effect, and it helps to trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere, making it possible for life to exist on the planet.
Other sources of radiation that contribute to the heating of the Earth include cosmic rays, which are high-energy particles that come from outer space and can penetrate the Earth's atmosphere, and radioactive decay, which generates heat within the Earth's core. However, these sources are much less significant than the Sun in terms of their contribution to the Earth's overall heat budget.
The envelop of the air is called _________- a)Atmosphere
- b)Troposphere
- c)Stratosphere
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The envelop of the air is called _________
a)
Atmosphere
b)
Troposphere
c)
Stratosphere
d)
None
|
|
Chhavi Tripathi answered |
ATMOSPHERE is the correct answer.
The envelope of air around the earth is called ATMOSPHERE.
This is called atmosphere. The force of gravity holds this atmosphere near the earth.
I hope you got your answer
The envelope of air around the earth is called ATMOSPHERE.
This is called atmosphere. The force of gravity holds this atmosphere near the earth.
I hope you got your answer
Maximum insolation is received over the ____________- a)Equator
- b)Tropical areas
- c)Sub-tropical areas
- d)Poles
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Maximum insolation is received over the ____________
a)
Equator
b)
Tropical areas
c)
Sub-tropical areas
d)
Poles
|
|
Isha Ahuja answered |
Sub-tropical deserts receive maximum amount of insolation because cloudiness is the least there.
The continental drift theory was propounded by- a)Alfred Wegner.
- b)Aortelius.
- c)Hall and Danna.
- d)Abraham Ortelius.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The continental drift theory was propounded by
a)
Alfred Wegner.
b)
Aortelius.
c)
Hall and Danna.
d)
Abraham Ortelius.
|
|
Anisha Singh answered |
Alfred Wegener—a German meteorologist put forth a comprehensive argument in the form of “the continental drift theory” in 1912.
Which of the following gases absorbs ultra violet rays?- a)Carbon Dioxide
- b)Neon
- c)Ozone
- d)Nitrogen
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following gases absorbs ultra violet rays?
a)
Carbon Dioxide
b)
Neon
c)
Ozone
d)
Nitrogen

|
Vigith Viswam answered |
Ozone splits In to oxygen molecule and oxygen free radical. which is readily recombinable. Thus it's make cyclic process in presence of ultraviolet rays.
Subtropical highs are the areas between- a)30° N and 30° S.
- b)40° N and 40° S.
- c)45° N and 45° S.
- d)50° N and 50° S.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Subtropical highs are the areas between
a)
30° N and 30° S.
b)
40° N and 40° S.
c)
45° N and 45° S.
d)
50° N and 50° S.
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Subtropical highs are the areas between 30°N and 30° S. These are high pressure areas.
Igneous rocks are- a)primary rocks.
- b)secondary rocks.
- c)tertiary rocks.
- d)soft rocks.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Igneous rocks are
a)
primary rocks.
b)
secondary rocks.
c)
tertiary rocks.
d)
soft rocks.
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
The igneous rocks (Ignis – in Latin means ‘Fire’) are formed when magma cools and solidifies. As igneous rocks form out of magma and lava from the interior of the earth, they are known as primary rocks.
Growth in human population has increased the rate of- a)death per year.
- b)conservation of natural resources.
- c)research of new species.
- d)consumption of natural resources.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Growth in human population has increased the rate of
a)
death per year.
b)
conservation of natural resources.
c)
research of new species.
d)
consumption of natural resources.
|
|
Prasenjit Rane answered |
Since the last few decades, growth in human population has increased the rate of consumption of natural resources. It has accelerated the loss of species and habitation in different parts of the world.
The earth radiates energy to the atmosphere in:- a)Long wavelengths
- b)Radiation
- c)Insolation
- d)Short wavelengths
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The earth radiates energy to the atmosphere in:
a)
Long wavelengths
b)
Radiation
c)
Insolation
d)
Short wavelengths
|
|
Anshul Singh answered |
This energy heats up the atmosphere from below.
National parks and sanctuaries are established for the purpose of- a)hunting.
- b)conservation.
- c)recreation.
- d)pets.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
National parks and sanctuaries are established for the purpose of
a)
hunting.
b)
conservation.
c)
recreation.
d)
pets.
|
|
Mira Gupta answered |
National parks and sanctuaries are established for the purpose of conservation.
Increase in the volume of carbon dioxide for the past few decades is mainly due to- a)deforestation.
- b)climate change.
- c)atmospheric composition.
- d)burning of fossil fuels.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Increase in the volume of carbon dioxide for the past few decades is mainly due to
a)
deforestation.
b)
climate change.
c)
atmospheric composition.
d)
burning of fossil fuels.

|
Somasekhar Kamal answered |
The answer is D. Because,
1. Forests are the sinks for the carbon dioxide. Forests use CO2 in their growth. So, deforestation due to changes in land increases concentration of CO2.
2. The time taken for atmospheric CO2 to adjust to changes in sources to sinks is 20-50 yrs. It is rising at about 0.5 percent annually.
3. In atmosphere CO2 comprises only 0.04 percent.
All the above processes are causing the CO2 conc. to increase in atmosphere in small quantities. However,
4. The emission of CO2 comes mainly from fossil fuels combustion (oil, gas, coal). Which causes more and more pollution and led to global warming. (especially during to industrialization period).
Abiotic factors include- a)producers.
- b)consumers.
- c)decomposers.
- d)sunlight
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Abiotic factors include
a)
producers.
b)
consumers.
c)
decomposers.
d)
sunlight
|
|
Mansi Banerjee answered |
All ecosystems consist of abiotic and biotic factors. Abiotic factors include rainfall, temperature, sunlight, atmospheric humidity, soil conditions, inorganic substances. Biotic factors include the producers, consumers and decomposers.
The current of Indian Ocean is- a)the west wind drift.
- b)Labrador.
- c)California.
- d)Kuroshio.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The current of Indian Ocean is
a)
the west wind drift.
b)
Labrador.
c)
California.
d)
Kuroshio.
|
|
Kavya Khanna answered |
The current of Indian Ocean is the west wind drift.Its a cold current,which bring cold water into warm water areas.
Transformation of water vapours into water is called- a)evaporation.
- b)condensation.
- c)sublimation.
- d)saturation.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Transformation of water vapours into water is called
a)
evaporation.
b)
condensation.
c)
sublimation.
d)
saturation.
|
|
Sai Dey answered |
The transformation of water vapour into water is called condensation. It is caused by the loss of heat.
Which one of the following is not a minor relief feature in the oceans:- a)Seamount
- b)Atoll
- c)Oceanic Deep
- d)Guyot
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is not a minor relief feature in the oceans:
a)
Seamount
b)
Atoll
c)
Oceanic Deep
d)
Guyot
|
|
Hridoy Jain answered |
Oceanic deeps of submarine trenches:
Deep narrow steep sided depression is found along the abyssal plain.
The depth of these trenches may vary from 6,000 to 11,000 m. Example, Marina trenches is the deepest trench in Pacific Ocean.
Trenches are formed as a result of tectonic forces and normally occur along the marines of Pacific Ocean.
They occur at the base of the continental slopes and along the island area. Normally associated with volcanoes and strong earthquake.
There are 32 trenches in Pacific Ocean, 19 in Atlantic Ocean and just 6 in Indian Ocean.
In which one of the following cities, are the days the longest in Summar?
- a)Chandigarh.
- b)Hyderabad.
- c)Thiruvananthapuram.
- d)Nagpur.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In which one of the following cities, are the days the longest in Summar?
a)
Chandigarh.
b)
Hyderabad.
c)
Thiruvananthapuram.
d)
Nagpur.
|
|
Vijay Kumar answered |
In summer (March to September), in the northern hemisphere, as we move northwards, the length of the day increases. But in winter (September to March) the length of the night increases as we move northwards. since Chandigarh is northernmost among the options
When the water containing air becomes saturated, then- a)it will be calm.
- b)it will be windy above sea and rainy above land.
- c)it will start to rain.
- d)clouds will be formed.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When the water containing air becomes saturated, then
a)
it will be calm.
b)
it will be windy above sea and rainy above land.
c)
it will start to rain.
d)
clouds will be formed.
|
|
Kajal Singh answered |
The air becomes saturated when the capacity of containing moisture is full. At this point, air becomes incapable of holding any moisture. Condensation occurs and water vapour becomes liquid in the form of clouds.
In weathering ________- a)No motion of material takes place
- b)Materials move from one place to another
- c) The deposition of material takes place
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In weathering ________
a)
No motion of material takes place
b)
Materials move from one place to another
c)
The deposition of material takes place
d)
None of the above
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
Weathering is an in-situ or on-site process. Very little or no motion of materials takes place in weathering.
The expansion of the salt depends on- a)temperature.
- b)hails.
- c)atmospheric pressure.
- d)winds.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The expansion of the salt depends on
a)
temperature.
b)
hails.
c)
atmospheric pressure.
d)
winds.
|
|
Kabir Verma answered |
Salt expansion normally takes place in arid climates as strong heating causes strong evaporation; leading to its expansion. It is known as salt weathering.
Earth absorbs more
- a)humidity.
- b)heat.
- c)gases.
- d)water vapour.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Earth absorbs more
a)
humidity.
b)
heat.
c)
gases.
d)
water vapour.
|
|
Chhavi Tripathi answered |
The Earth is absorbing more energy ( heat ) from the Sun than it is emitting to space..... I hope you got your answer...
A freshwater ecosystem is- a)oceans.
- b)estuaries.
- c)coral reefs.
- d)marshes.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A freshwater ecosystem is
a)
oceans.
b)
estuaries.
c)
coral reefs.
d)
marshes.
|
|
Anand Mukherjee answered |
Aquatic ecosystems can be classed as marine and freshwater ecosystems. Marine ecosystem includes the oceans, coastal estuaries and coral reefs. Freshwater ecosystem includes lakes, ponds, streams, marshes and bogs.
If an air mass is fully lifted above the land surface, it is called:- a)Warm front
- b)Cold front
- c)Occluded front
- d)Anticyclones
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If an air mass is fully lifted above the land surface, it is called:
a)
Warm front
b)
Cold front
c)
Occluded front
d)
Anticyclones
|
|
Debolina Nair answered |
Occluded Front
An occluded front occurs when a faster-moving cold front catches up and overtakes a slower-moving warm front. As a result, the warm air mass is lifted above the land surface, creating an occluded front. Let's explore this concept in detail.
Understanding Fronts
- Fronts are the boundaries where different air masses meet. There are four main types of fronts: warm fronts, cold fronts, stationary fronts, and occluded fronts.
- Warm fronts occur when warm air advances and replaces cooler air. They are characterized by a gradual increase in temperature and the formation of clouds and precipitation.
- Cold fronts, on the other hand, occur when cold air advances and replaces warmer air. They are associated with rapidly changing weather conditions, such as thunderstorms and heavy rainfall.
- Stationary fronts occur when neither warm nor cold air masses advance. They result in prolonged periods of cloudy and rainy weather.
- Occluded fronts are formed when a cold front overtakes a warm front. They are characterized by the lifting of the warm air mass above the land surface.
Formation of an Occluded Front
- When a cold front catches up to a warm front, it begins to lift the warm air mass above the land surface.
- This lifting occurs because the cold air is denser and more stable, causing it to slide underneath the warm air.
- As the warm air is lifted, it cools and condenses, leading to the formation of clouds and precipitation.
- The occluded front is represented on weather maps by a purple line with alternating triangles and semi-circles pointing in the direction of the cold air mass.
Effects of an Occluded Front
- Occluded fronts often bring significant changes in weather conditions.
- The lifting of the warm air mass can result in the dissipation of the warm sector's energy, leading to a decrease in precipitation intensity.
- The occluded front may also have a combination of characteristics from both warm and cold fronts, such as cloud formations and precipitation.
- The weather associated with occluded fronts can vary, but it often includes a mix of rain, snow, or a combination of both.
In conclusion, if an air mass is fully lifted above the land surface, it is called an occluded front. This occurs when a faster-moving cold front overtakes and lifts a slower-moving warm front, resulting in changes in weather conditions.
An occluded front occurs when a faster-moving cold front catches up and overtakes a slower-moving warm front. As a result, the warm air mass is lifted above the land surface, creating an occluded front. Let's explore this concept in detail.
Understanding Fronts
- Fronts are the boundaries where different air masses meet. There are four main types of fronts: warm fronts, cold fronts, stationary fronts, and occluded fronts.
- Warm fronts occur when warm air advances and replaces cooler air. They are characterized by a gradual increase in temperature and the formation of clouds and precipitation.
- Cold fronts, on the other hand, occur when cold air advances and replaces warmer air. They are associated with rapidly changing weather conditions, such as thunderstorms and heavy rainfall.
- Stationary fronts occur when neither warm nor cold air masses advance. They result in prolonged periods of cloudy and rainy weather.
- Occluded fronts are formed when a cold front overtakes a warm front. They are characterized by the lifting of the warm air mass above the land surface.
Formation of an Occluded Front
- When a cold front catches up to a warm front, it begins to lift the warm air mass above the land surface.
- This lifting occurs because the cold air is denser and more stable, causing it to slide underneath the warm air.
- As the warm air is lifted, it cools and condenses, leading to the formation of clouds and precipitation.
- The occluded front is represented on weather maps by a purple line with alternating triangles and semi-circles pointing in the direction of the cold air mass.
Effects of an Occluded Front
- Occluded fronts often bring significant changes in weather conditions.
- The lifting of the warm air mass can result in the dissipation of the warm sector's energy, leading to a decrease in precipitation intensity.
- The occluded front may also have a combination of characteristics from both warm and cold fronts, such as cloud formations and precipitation.
- The weather associated with occluded fronts can vary, but it often includes a mix of rain, snow, or a combination of both.
In conclusion, if an air mass is fully lifted above the land surface, it is called an occluded front. This occurs when a faster-moving cold front overtakes and lifts a slower-moving warm front, resulting in changes in weather conditions.
Insolation refers to ________- a)Wind direction
- b)Solar radiation
- c)Precipitation
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Insolation refers to ________
a)
Wind direction
b)
Solar radiation
c)
Precipitation
d)
None
|
|
Ræjû Bhæï answered |
Solar radiation is radiant energy emitted by the sun from a nuclear fusion reaction that creates electromagnetic energy. The spectrum of solar radiation is close to that of a black body with a temperature of about 5800 K. About half of the radiation is in the visible short-wave part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
The Thermodynamics of the ocean are:- a)Currents
- b)Waves
- c)Tides
- d)Salinity
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The Thermodynamics of the ocean are:
a)
Currents
b)
Waves
c)
Tides
d)
Salinity
|
|
Rohit Datta answered |
Thermodynamics of the Ocean: Salinity
Salinity is a critical factor in the thermodynamics of the ocean as it affects the density, temperature, and movement of seawater. Salinity refers to the amount of salt or dissolved minerals in seawater, which is mainly composed of sodium chloride (NaCl) but also contains other elements like magnesium, calcium, and potassium.
How Salinity Affects Density
The density of seawater increases with higher salinity and decreases with lower salinity. This is because saltwater is denser than freshwater due to the added weight of dissolved salts. The density of seawater also increases with decreasing temperature, which is why colder water sinks below warmer water.
How Salinity Affects Temperature
Salinity also affects the temperature of seawater by influencing its heat capacity and thermal conductivity. Saltwater has a higher heat capacity than freshwater, which means it can absorb more heat energy without a significant increase in temperature. This makes it more resistant to temperature changes and helps to regulate the overall temperature of the ocean.
How Salinity Affects Movement
The movement of seawater is also affected by salinity due to its impact on density and temperature. Salinity differences between adjacent bodies of water create density gradients that drive currents and ocean circulation. These density gradients are particularly pronounced in areas where freshwater enters the ocean, such as at river mouths or near melting ice sheets.
Conclusion
In conclusion, salinity is a critical factor in the thermodynamics of the ocean, affecting its density, temperature, and movement. Understanding these complex interactions is crucial for predicting and managing the impacts of climate change on the ocean and its ecosystems.
Salinity is a critical factor in the thermodynamics of the ocean as it affects the density, temperature, and movement of seawater. Salinity refers to the amount of salt or dissolved minerals in seawater, which is mainly composed of sodium chloride (NaCl) but also contains other elements like magnesium, calcium, and potassium.
How Salinity Affects Density
The density of seawater increases with higher salinity and decreases with lower salinity. This is because saltwater is denser than freshwater due to the added weight of dissolved salts. The density of seawater also increases with decreasing temperature, which is why colder water sinks below warmer water.
How Salinity Affects Temperature
Salinity also affects the temperature of seawater by influencing its heat capacity and thermal conductivity. Saltwater has a higher heat capacity than freshwater, which means it can absorb more heat energy without a significant increase in temperature. This makes it more resistant to temperature changes and helps to regulate the overall temperature of the ocean.
How Salinity Affects Movement
The movement of seawater is also affected by salinity due to its impact on density and temperature. Salinity differences between adjacent bodies of water create density gradients that drive currents and ocean circulation. These density gradients are particularly pronounced in areas where freshwater enters the ocean, such as at river mouths or near melting ice sheets.
Conclusion
In conclusion, salinity is a critical factor in the thermodynamics of the ocean, affecting its density, temperature, and movement. Understanding these complex interactions is crucial for predicting and managing the impacts of climate change on the ocean and its ecosystems.
The percentage of species that are contained by Tropical rain forests are- a)10%
- b)40%
- c)50%
- d)60%
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The percentage of species that are contained by Tropical rain forests are
a)
10%
b)
40%
c)
50%
d)
60%
|
|
Hrishikesh Jain answered |
Tropical regions occupy about one-fourth of the total area of the earth
Horizontal distribution of pressure is studied by drawing- a)isotherms.
- b)isobars.
- c)isoheights.
- d)isochrones.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Horizontal distribution of pressure is studied by drawing
a)
isotherms.
b)
isobars.
c)
isoheights.
d)
isochrones.
|
|
Kavya Khanna answered |
Isobars are lines connecting places having equal pressure.
Which one of the following gases constitute the major portion of atmosphere?- a)Oxygen
- b)Nitrogen
- c)Argon
- d)Carbon dioxide
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following gases constitute the major portion of atmosphere?
a)
Oxygen
b)
Nitrogen
c)
Argon
d)
Carbon dioxide
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
The most abundant gas in our atmosphere is Nitrogen. It constitutes about 78% of our atmosphere.
Higher latitudes are not permanently frozen because of- a)Presence of warm and cold currents
- b)very less insolation
- c)redistribution of surplus heat energy pole wards from tropics
- d)Local aspects
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Higher latitudes are not permanently frozen because of
a)
Presence of warm and cold currents
b)
very less insolation
c)
redistribution of surplus heat energy pole wards from tropics
d)
Local aspects
|
|
Poonam Reddy answered |
There is a surplus of net radiation balance between 40 degrees north and south and the regions near the poles have a deficit. The surplus heat energy from the tropics is redistributed pole wards and as a result the tropics do not get progressively heated up due to the accumulation of excess heat or the high latitudes get permanently frozen due to excess deficit.
The heat energy absorbed by a known area in a fixed time is determined with the help of an instrument called- a)Psychrometer
- b)Pyrheliometer
- c)Thermometric well
- d)Any instrument
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The heat energy absorbed by a known area in a fixed time is determined with the help of an instrument called
a)
Psychrometer
b)
Pyrheliometer
c)
Thermometric well
d)
Any instrument
|
|
Ræjû Bhæï answered |
A pyrheliometer is an instrument for measurement of direct beam solar irradiance. Sunlight enters the instrument through a window and is directed onto a thermopile which converts heat to an electrical signal that can be recorded. The signal voltage is converted via a formula to measure watts per square metre.
Sea salt, pollen, ash, smoke, soot, fine soil, these all are associated with __________- a)Gases
- b)Dust particles
- c)Water vapours
- d)Meteors
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Sea salt, pollen, ash, smoke, soot, fine soil, these all are associated with __________
a)
Gases
b)
Dust particles
c)
Water vapours
d)
Meteors
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
All of these are dust particles, which are also present in the atmosphere.
A non-metallic mineral in the following minerals is- a)silver.
- b)copper.
- c)zinc.
- d)coal.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A non-metallic mineral in the following minerals is
a)
silver.
b)
copper.
c)
zinc.
d)
coal.
|
|
Anmol Banerjee answered |
Coal is used as a fossil fuel and is a non-metallic mineral with dull and non-reflective properties and it cannot be moulded in any form.
The current of Atlantic ocean is- a)west wind drift.
- b)Gulf stream.
- c)Equatorial counter current.
- d)Alaska current.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The current of Atlantic ocean is
a)
west wind drift.
b)
Gulf stream.
c)
Equatorial counter current.
d)
Alaska current.
|
|
Priyanka Chavan answered |
The current of Atlantic ocean is Gulf current.It is warm current which bring warm water into cold water areas.
The plate marked red colour in the world map is
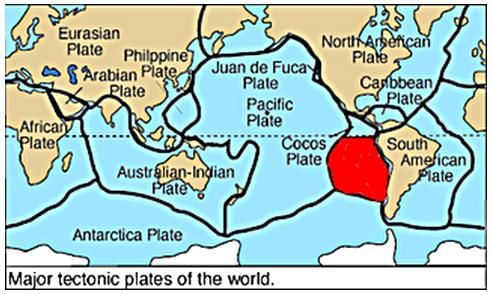
- a)Cocos plate.
- b)Nazca plate.
- c)Arabian plate.
- d)Philippine plate.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The plate marked red colour in the world map is


a)
Cocos plate.
b)
Nazca plate.
c)
Arabian plate.
d)
Philippine plate.
|
|
Alok Verma answered |
The Nazca Plate, named after the Nazca region of southern Peru, is an oceanic tectonic plate in the eastern Pacific Ocean basin off the west coast of South America.
The standard atmosphere is a unit of pressure defined as- a)101325 Pascal
- b)1325 Pascal
- c)10132 Pascal
- d)11325 Pascal
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The standard atmosphere is a unit of pressure defined as
a)
101325 Pascal
b)
1325 Pascal
c)
10132 Pascal
d)
11325 Pascal
|
|
Anjana Bose answered |
The standard atmosphere is a unit of pressure defined as 101325 Pascal (1.01325 bar), equivalent to 760 Millimeter of mercury (torr), 29.92 Inch of mercury and 14.696 Pounds per square inch.
What is Isotherm?- a)The line joining the places of equal temperature.
- b)The incoming short wave radiation.
- c)The line joining the places of equal pressure.
- d)None.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is Isotherm?
a)
The line joining the places of equal temperature.
b)
The incoming short wave radiation.
c)
The line joining the places of equal pressure.
d)
None.
|
|
Pooja Chakraborty answered |
Isotherms are the lines joining places of equal temperature.
Which of the following best describes incised or entrenched meanders?- a) They are formed primarily by lateral erosion in low-gradient streams.
- b) They develop over original gentle surfaces and can form deep gorges in hard rock areas.
- c) They are created by sediment deposition in floodplains.
- d) They are exclusively found in areas with significant tectonic activity.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following best describes incised or entrenched meanders?
a)
They are formed primarily by lateral erosion in low-gradient streams.
b)
They develop over original gentle surfaces and can form deep gorges in hard rock areas.
c)
They are created by sediment deposition in floodplains.
d)
They are exclusively found in areas with significant tectonic activity.

|
Crafty Classes answered |
Incised or entrenched meanders are formed as streams cut deeply into their valleys, often developing over original gentle surfaces. This process can lead to the formation of deep gorges and canyons, particularly in hard rock areas, as the streams experience significant vertical erosion. This contrasts with meanders in low-gradient streams, which typically develop through lateral erosion rather than vertical cutting. An interesting fact is that the presence of these entrenched meanders provides insights into the historical geological processes that shaped the landscape.
Which of the following organism have parasitic mode of nutrition?- a)Penicillium
- b)Plasmodium
- c)Paramecium
- d)Parrot
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following organism have parasitic mode of nutrition?
a)
Penicillium
b)
Plasmodium
c)
Paramecium
d)
Parrot
|
|
Deepika Reddy answered |
In parasitic nutrition organism derives its food from the body of another living organism called host without killing it. Parasitic mode of nutrition is observed in several fungi, bacteria, few plants like Cuscuta and some animals like Plasmodium and round worms. Plasmodium causes malarial disease.
The boundary in the given picture shows the
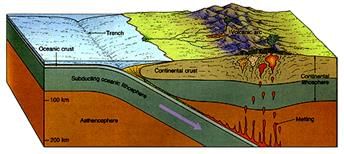
- a)divergent boundary.
- b)transform boundary.
- c)convergent boundary.
- d)oceanic boundary.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The boundary in the given picture shows the


a)
divergent boundary.
b)
transform boundary.
c)
convergent boundary.
d)
oceanic boundary.

|
Bharath Reddy Gundala answered |
When two plates collide (happens when move towards each other) only then subduction (one goes under another) happens which is why the case is convergent. Option C
Which of the following statement(s) is/are true-Statement I: Glaciers can cause significant erosion by plucking and abrasion, leading to the formation of U-shaped valleys.Statement II: U-shaped valleys are primarily formed by rivers eroding through soft, unconsolidated sediments.- a)Both Statement I and Statement II are true.
- b)Both Statement I and Statement II are false.
- c)Statement I is true, but Statement II is false.
- d)Statement I is false, but Statement II is true.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement(s) is/are true-
Statement I: Glaciers can cause significant erosion by plucking and abrasion, leading to the formation of U-shaped valleys.
Statement II: U-shaped valleys are primarily formed by rivers eroding through soft, unconsolidated sediments.
a)
Both Statement I and Statement II are true.
b)
Both Statement I and Statement II are false.
c)
Statement I is true, but Statement II is false.
d)
Statement I is false, but Statement II is true.
|
|
Soumya Bose answered |
Explanation of Statement I
- Glaciers are powerful agents of erosion. They cause significant landscape changes through two primary processes:
- Plucking: This occurs when a glacier freezes onto the rock, pulling pieces of it away as it moves.
- Abrasion: As glaciers slide over the landscape, they grind down surfaces, leading to erosion.
- The result of these processes is the formation of U-shaped valleys, characterized by their wide bases and steep sides, as opposed to the narrow V-shaped valleys formed by rivers.
Explanation of Statement II
- U-shaped valleys are not primarily formed by rivers. Instead:
- River Erosion: Rivers typically carve V-shaped valleys due to their flow dynamics, which is different from the glacial processes.
- Soft, Unconsolidated Sediments: While rivers can erode through these materials, the characteristic U-shape of valleys is a hallmark of glacial activity, not fluvial.
Conclusion
- Therefore, the statements can be evaluated as follows:
- Statement I is true because glaciers do cause significant erosion, leading to U-shaped valleys.
- Statement II is false as it misattributes the formation of U-shaped valleys to rivers instead of glaciers.
- The correct answer to the question is indeed option 'C': Statement I is true, but Statement II is false.
- Glaciers are powerful agents of erosion. They cause significant landscape changes through two primary processes:
- Plucking: This occurs when a glacier freezes onto the rock, pulling pieces of it away as it moves.
- Abrasion: As glaciers slide over the landscape, they grind down surfaces, leading to erosion.
- The result of these processes is the formation of U-shaped valleys, characterized by their wide bases and steep sides, as opposed to the narrow V-shaped valleys formed by rivers.
Explanation of Statement II
- U-shaped valleys are not primarily formed by rivers. Instead:
- River Erosion: Rivers typically carve V-shaped valleys due to their flow dynamics, which is different from the glacial processes.
- Soft, Unconsolidated Sediments: While rivers can erode through these materials, the characteristic U-shape of valleys is a hallmark of glacial activity, not fluvial.
Conclusion
- Therefore, the statements can be evaluated as follows:
- Statement I is true because glaciers do cause significant erosion, leading to U-shaped valleys.
- Statement II is false as it misattributes the formation of U-shaped valleys to rivers instead of glaciers.
- The correct answer to the question is indeed option 'C': Statement I is true, but Statement II is false.
Warm temperate climates extend from:- a)300 500 latitude
- b)40 50 latitude
- c)35 40 latitude
- d)450 50 latitude
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Warm temperate climates extend from:
a)
300 500 latitude
b)
40 50 latitude
c)
35 40 latitude
d)
450 50 latitude
|
|
Samridhi Chavan answered |
It is mainly on eastern and western margins of continents.
Arrange the following stages in the correct order of planet formation as described:
1: Condensation forms small-rounded objects around the core.
2: Gravitational forces create a core in the gas cloud.
3: Numerous small planetesimals accrete to form fewer, larger planetary bodies.
4: A rotating disc of gas and dust develops around this core.- a)2, 4, 1, 3
- b)2, 1, 4, 3
- c)1, 2, 3, 4
- d)4, 3, 2, 1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Arrange the following stages in the correct order of planet formation as described:
1: Condensation forms small-rounded objects around the core.
2: Gravitational forces create a core in the gas cloud.
3: Numerous small planetesimals accrete to form fewer, larger planetary bodies.
4: A rotating disc of gas and dust develops around this core.
1: Condensation forms small-rounded objects around the core.
2: Gravitational forces create a core in the gas cloud.
3: Numerous small planetesimals accrete to form fewer, larger planetary bodies.
4: A rotating disc of gas and dust develops around this core.
a)
2, 4, 1, 3
b)
2, 1, 4, 3
c)
1, 2, 3, 4
d)
4, 3, 2, 1

|
EduRev Humanities answered |
The correct sequence of events in the formation of planets based on the provided text is as follows:
Step 2: The formation process begins with gravitational forces creating a core within a gas cloud.
Step 4: Around this core, a rotating disc of gas and dust develops.
Step 1: As the gas cloud condenses, small-rounded objects form around the core, which through cohesion become planetesimals.
Step 3: These planetesimals undergo accretion, where numerous smaller bodies combine due to collisions and gravitational attraction to form fewer, larger bodies, eventually becoming planets.
Step 2: The formation process begins with gravitational forces creating a core within a gas cloud.
Step 4: Around this core, a rotating disc of gas and dust develops.
Step 1: As the gas cloud condenses, small-rounded objects form around the core, which through cohesion become planetesimals.
Step 3: These planetesimals undergo accretion, where numerous smaller bodies combine due to collisions and gravitational attraction to form fewer, larger bodies, eventually becoming planets.
With reference to the Tropical Savannah Region, consider the following statements:1. It is found to the north and south of tropical rainforest biomes.2. The largest expanses of savanna are in Africa, where much of the central part of the continent, for example, Kenya and Tanzania, consists of tropical grassland.3. Savanna grasslands can not be found in Brazil in South America.How many of the statements given above are correct?- a)Only one
- b)Only two
- c)All three
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
With reference to the Tropical Savannah Region, consider the following statements:
1. It is found to the north and south of tropical rainforest biomes.
2. The largest expanses of savanna are in Africa, where much of the central part of the continent, for example, Kenya and Tanzania, consists of tropical grassland.
3. Savanna grasslands can not be found in Brazil in South America.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
a)
Only one
b)
Only two
c)
All three
d)
None
|
|
Mainak Goyal answered |
Analysis of the Statements
The question evaluates three statements regarding the Tropical Savannah Region. Let's analyze them one by one.
Statement 1: It is found to the north and south of tropical rainforest biomes.
- This statement is correct. The Tropical Savannah is usually located at latitudes slightly above and below the equatorial regions where tropical rainforests are found. It typically lies at the edges of these rainforests.
Statement 2: The largest expanses of savanna are in Africa, where much of the central part of the continent, for example, Kenya and Tanzania, consists of tropical grassland.
- This statement is also correct. Africa is indeed home to some of the largest savanna regions, such as the Serengeti in Tanzania and the Maasai Mara in Kenya. These areas are characterized by extensive grasslands and scattered trees.
Statement 3: Savanna grasslands cannot be found in Brazil in South America.
- This statement is incorrect. While the most prominent savanna regions are in Africa, savanna grasslands can also be found in Brazil, particularly in the Cerrado region. The Cerrado is characterized by a mix of grasslands and sparse trees, fitting the savanna biome description.
Conclusion
- Therefore, two out of the three statements are correct. This leads to the conclusion that the correct answer is option 'B', as only Statements 1 and 2 are accurate.
The question evaluates three statements regarding the Tropical Savannah Region. Let's analyze them one by one.
Statement 1: It is found to the north and south of tropical rainforest biomes.
- This statement is correct. The Tropical Savannah is usually located at latitudes slightly above and below the equatorial regions where tropical rainforests are found. It typically lies at the edges of these rainforests.
Statement 2: The largest expanses of savanna are in Africa, where much of the central part of the continent, for example, Kenya and Tanzania, consists of tropical grassland.
- This statement is also correct. Africa is indeed home to some of the largest savanna regions, such as the Serengeti in Tanzania and the Maasai Mara in Kenya. These areas are characterized by extensive grasslands and scattered trees.
Statement 3: Savanna grasslands cannot be found in Brazil in South America.
- This statement is incorrect. While the most prominent savanna regions are in Africa, savanna grasslands can also be found in Brazil, particularly in the Cerrado region. The Cerrado is characterized by a mix of grasslands and sparse trees, fitting the savanna biome description.
Conclusion
- Therefore, two out of the three statements are correct. This leads to the conclusion that the correct answer is option 'B', as only Statements 1 and 2 are accurate.
The type of climate portrayed by Plateau Station, Antarctica is- a)Dw.
- b)ET.
- c)EF.
- d)Df.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The type of climate portrayed by Plateau Station, Antarctica is
a)
Dw.
b)
ET.
c)
EF.
d)
Df.
|
|
Gayatri Yadav answered |
The ice cap climate or ‘EF’ occurs in this region. It is the polar climate. Even in summer, the temperature is below freezing point. This area receives very little precipitation. The snow and ice gets accumulated and the mounting pressure causes deformation of the ice sheets and they break.
In the Western Australia, tropical cyclone is also known as- a)Hurricane.
- b)Typhoons.
- c)Monsoon.
- d)Willy-Willies
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the Western Australia, tropical cyclone is also known as
a)
Hurricane.
b)
Typhoons.
c)
Monsoon.
d)
Willy-Willies
|
|
Lakshmi Kulkarni answered |
Tropical cyclones are known as Cyclones in the Indian Ocean, Hurricanes in the Atlantic, Typhoons in the Western Pacific and South China Sea, and Willy-willies in the Western Australia.
The sun is vertically over head at noon on 21st June at- a)the equator.
- b)23.5 degree N.
- c)23.5 degree S.
- d)66.5 degree N.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The sun is vertically over head at noon on 21st June at
a)
the equator.
b)
23.5 degree N.
c)
23.5 degree S.
d)
66.5 degree N.
|
|
Jhanvi Joshi answered |
Explanation:
The position of the sun in the sky changes throughout the year due to the tilt of the Earth's axis. On 21st June, the sun is directly overhead at noon at a specific location on Earth.
Equator:
At the equator, the sun is overhead twice a year, during the equinoxes. On 21st June, the sun is not directly overhead at the equator, but rather it is at its northernmost point in the sky.
23.5 degree S:
At 23.5 degrees south latitude, the sun is directly overhead at noon on 21st December, during the southern hemisphere's summer solstice. On 21st June, the sun is at its southernmost point in the sky.
66.5 degree N:
At 66.5 degrees north latitude, the sun is directly overhead at noon on 21st June, during the northern hemisphere's summer solstice. This is the point located within the Arctic Circle.
23.5 degree N:
At 23.5 degrees north latitude, the sun is directly overhead at noon on 21st June, during the northern hemisphere's summer solstice. This is the Tropic of Cancer, and it is the correct answer to the question.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option B, 23.5 degree N, as this is the Tropic of Cancer, where the sun is directly overhead at noon on 21st June, during the northern hemisphere's summer solstice.
The position of the sun in the sky changes throughout the year due to the tilt of the Earth's axis. On 21st June, the sun is directly overhead at noon at a specific location on Earth.
Equator:
At the equator, the sun is overhead twice a year, during the equinoxes. On 21st June, the sun is not directly overhead at the equator, but rather it is at its northernmost point in the sky.
23.5 degree S:
At 23.5 degrees south latitude, the sun is directly overhead at noon on 21st December, during the southern hemisphere's summer solstice. On 21st June, the sun is at its southernmost point in the sky.
66.5 degree N:
At 66.5 degrees north latitude, the sun is directly overhead at noon on 21st June, during the northern hemisphere's summer solstice. This is the point located within the Arctic Circle.
23.5 degree N:
At 23.5 degrees north latitude, the sun is directly overhead at noon on 21st June, during the northern hemisphere's summer solstice. This is the Tropic of Cancer, and it is the correct answer to the question.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option B, 23.5 degree N, as this is the Tropic of Cancer, where the sun is directly overhead at noon on 21st June, during the northern hemisphere's summer solstice.
Chapter doubts & questions for Fundamentals of Physical Geography - Geography for UPSC CSE 2025 is part of UPSC CSE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the UPSC CSE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for UPSC CSE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Fundamentals of Physical Geography - Geography for UPSC CSE in English & Hindi are available as part of UPSC CSE exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for UPSC CSE Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily










