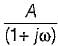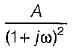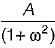All India Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Group
Two LTI systems in cascade form as shown in below figure-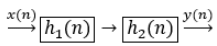 If h1(n) = 3nu(n) and h2(n) = 3δ(n) – 3δ(n – 1) and If x(n) = sin(n) then output will be
If h1(n) = 3nu(n) and h2(n) = 3δ(n) – 3δ(n – 1) and If x(n) = sin(n) then output will be- a)3cos(n-1)
- b)5sin(n/2)+3sin(n)
- c)2sin(n)+5cos(n)
- d)3sin(n)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Two LTI systems in cascade form as shown in below figure-
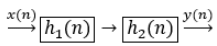
If h1(n) = 3nu(n) and h2(n) = 3δ(n) – 3δ(n – 1) and If x(n) = sin(n) then output will be
a)
3cos(n-1)
b)
5sin(n/2)+3sin(n)
c)
2sin(n)+5cos(n)
d)
3sin(n)

|
Cstoppers Instructors answered • yesterday |
Here two LTI systems are in cascaded form and the overall impulse response is-
h(n)=h2(n)*h1(n)=[ 3δ(n) – 3δ(n – 1)]* 3n u(n)
= 3n+1 u(n)- 3n+1 u(n-1)
= 3n+1 δ (n)
h(n)= 31 δ (n)
Since input is sin (n) hence output will be
h(n)*Sin (n)= 3δ (n)*sin(n)=3sin(n)
thus the band width gets reduced in a multi-stage amplifier.

|
Pooja Dasgupta
asked a question
|
A does half as much work as B in one third of the time taken by B. If together they take 20 days to finish the work then what will be the share of A if 1000 rupees is given for the whole work?- a)400
- b)500
- c)600
- d)700
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A does half as much work as B in one third of the time taken by B. If together they take 20 days to finish the work then what will be the share of A if 1000 rupees is given for the whole work?
a)
400
b)
500
c)
600
d)
700
e)
None of these

|
Mainak Verma
asked a question
|
Which changes were introduced in the classification of MSMEs in the Union Budget 2025?- a)Investment limits decreased for micro enterprises
- b)Investment and turnover limits for MSMEs were substantially increased
- c)Micro enterprises were excluded from government benefits
- d)All medium enterprises were eliminated
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Investment limits decreased for micro enterprises
b)
Investment and turnover limits for MSMEs were substantially increased
c)
Micro enterprises were excluded from government benefits
d)
All medium enterprises were eliminated

|
Sameer Yadav
asked a question
|
What is the primary focus of the active mobility initiative in India?- a)Promoting the use of electric vehicles
- b)Encouraging non-motorized transport like walking and cycling
- c)Banning all motorized vehicles
- d)Expanding public transport systems
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Promoting the use of electric vehicles
b)
Encouraging non-motorized transport like walking and cycling
c)
Banning all motorized vehicles
d)
Expanding public transport systems

|
Rithika Chakraborty
asked a question
|
What is the main challenge in India’s current health data governance?- a)Lack of global data sharing agreements
- b)Confusion between data as identity and data as property
- c)Excessive privatization of hospitals
- d)Outdated healthcare facilities
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Lack of global data sharing agreements
b)
Confusion between data as identity and data as property
c)
Excessive privatization of hospitals
d)
Outdated healthcare facilities

|
Arpita Pillai
asked a question
|
What was the NGT’s order regarding air horns on major roads?- a)Air horns must be used for all vehicles during the night
- b)The use of air horns is restricted on major roads at nighttime
- c)Air horns are banned at all times on major roads
- d)No restrictions were placed on air horns
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Air horns must be used for all vehicles during the night
b)
The use of air horns is restricted on major roads at nighttime
c)
Air horns are banned at all times on major roads
d)
No restrictions were placed on air horns

|
Aditya Ghoshal
asked a question
|
What recent shift has the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) made in its approach to internal security?- a)Moving from proactive reform to crisis management
- b)Moving from crisis management to proactive reform
- c)Reducing the security budget
- d)Focusing only on conflict zones
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Moving from proactive reform to crisis management
b)
Moving from crisis management to proactive reform
c)
Reducing the security budget
d)
Focusing only on conflict zones

|
Mainak Chakraborty
asked a question
|
Which article of the Indian Constitution grants the Governor the power to assent to, withhold assent from, or reserve bills for the President's consideration?- a)Article 143
- b)Article 200
- c)Article 201
- d)Article 142
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Article 143
b)
Article 200
c)
Article 201
d)
Article 142

|
Rutuja Das
asked a question
|
What is the primary aim of the Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU)?- a)To promote international cooperation and dialogue among national parliaments
- b)To control the economic policies of member countries
- c)To organize elections for global governance
- d)To regulate the trade laws of nations
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
To promote international cooperation and dialogue among national parliaments
b)
To control the economic policies of member countries
c)
To organize elections for global governance
d)
To regulate the trade laws of nations
|
|
Akshara Dasgupta
asked a question
|
What is the H5N1 strain of bird flu primarily known for?- a) It only affects human populations.
- b) It is highly contagious and can affect both birds and some mammals.
- c) It was first detected in Europe in 1995.
- d) It is harmless and does not spread easily.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the H5N1 strain of bird flu primarily known for?
a)
It only affects human populations.
b)
It is highly contagious and can affect both birds and some mammals.
c)
It was first detected in Europe in 1995.
d)
It is harmless and does not spread easily.

|
Simran Dasgupta
asked a question
|
What is the primary role of the Assam Rifles in northeastern India?- a) Providing disaster relief
- b) Conducting counterinsurgency operations
- c) Engaging in international peacekeeping missions
- d) Protecting cultural heritage sites
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the primary role of the Assam Rifles in northeastern India?
a)
Providing disaster relief
b)
Conducting counterinsurgency operations
c)
Engaging in international peacekeeping missions
d)
Protecting cultural heritage sites

|
Rakesh Kumar
asked a question
|
Consider the following statements regarding the Late Stone Age (Mesolithic Age):
Statement-I: Microliths were the characteristic tools of the Late Stone Age.
Statement-II: The Late Stone Age began during a warm and dry climate following the Ice Age.
Statement-III: The Belan Valley provides a sequential record of Palaeolithic, Mesolithic, and Neolithic phases.Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?- a)Both Statement-II and Statement-III are correct and both of them explain Statement-I.
- b)Both Statement-II and Statement-III are correct, but only one of them explains Statement-I.
- c)Only one of the Statements II and III is correct, and that explains Statement-I.
- d)Neither Statement-II nor Statement-III is correct.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements regarding the Late Stone Age (Mesolithic Age):
Statement-I: Microliths were the characteristic tools of the Late Stone Age.
Statement-II: The Late Stone Age began during a warm and dry climate following the Ice Age.
Statement-III: The Belan Valley provides a sequential record of Palaeolithic, Mesolithic, and Neolithic phases.
Statement-I: Microliths were the characteristic tools of the Late Stone Age.
Statement-II: The Late Stone Age began during a warm and dry climate following the Ice Age.
Statement-III: The Belan Valley provides a sequential record of Palaeolithic, Mesolithic, and Neolithic phases.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
a)
Both Statement-II and Statement-III are correct and both of them explain Statement-I.
b)
Both Statement-II and Statement-III are correct, but only one of them explains Statement-I.
c)
Only one of the Statements II and III is correct, and that explains Statement-I.
d)
Neither Statement-II nor Statement-III is correct.

|
Riya Ghosh
asked a question
|
Consider the following statements:1. Western Himalayas extend till west of River Kali whereas Eastern Himalayas extend from Kali to Brahmaputra river.
2. Western Himalayas have less biodiversity in comparison to the eastern Himalayas.
3. Altitude is higher in Western Himalayas than the Eastern Himalayas.Which of the above statements is/are correct concerning the comparison of Western Himalayas to Eastern Himalayas?- a)1 only
- b) 2 only
- c)2 and 3 only
- d)1 and 2 only
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
1. Western Himalayas extend till west of River Kali whereas Eastern Himalayas extend from Kali to Brahmaputra river.
2. Western Himalayas have less biodiversity in comparison to the eastern Himalayas.
3. Altitude is higher in Western Himalayas than the Eastern Himalayas.
2. Western Himalayas have less biodiversity in comparison to the eastern Himalayas.
3. Altitude is higher in Western Himalayas than the Eastern Himalayas.
Which of the above statements is/are correct concerning the comparison of Western Himalayas to Eastern Himalayas?
a)
1 only
b)
2 only
c)
2 and 3 only
d)
1 and 2 only

|
Rutuja Das
asked a question
|
Consider the following pairs:1. Mercury - Smallest and closest to the sun2. Jupiter - Second largest planet with 12 satellites3. Uranus - Orbits around the sun in a clockwise direction from east to west4. Neptune - Natural satellite is the moonHow many pairs given above are correctly matched?- a)Only one pair
- b)Only two pairs
- c)Only three pairs
- d)All four pairs
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following pairs:
1. Mercury - Smallest and closest to the sun
2. Jupiter - Second largest planet with 12 satellites
3. Uranus - Orbits around the sun in a clockwise direction from east to west
4. Neptune - Natural satellite is the moon
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
a)
Only one pair
b)
Only two pairs
c)
Only three pairs
d)
All four pairs
|
|
Harshit Thakkar
asked a question
|
What does the Technology and Innovation Report, 2025 emphasize regarding AI in developing nations?- a) The reduction of government involvement in technology sectors.
- b) The need for increased competition among tech companies.
- c) The necessity of focusing solely on economic growth.
- d) The importance of inclusive approaches to harness technological advancements.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What does the Technology and Innovation Report, 2025 emphasize regarding AI in developing nations?
a)
The reduction of government involvement in technology sectors.
b)
The need for increased competition among tech companies.
c)
The necessity of focusing solely on economic growth.
d)
The importance of inclusive approaches to harness technological advancements.
|
|
Mohit Agarwal
asked a question
|
What is a significant challenge facing India’s workforce in adapting to future job markets?- a) Overpopulation in urban centers.
- b) Skills mismatch and deficits in emerging technologies.
- c) Lack of job opportunities in rural areas.
- d) High unemployment rates among graduates.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is a significant challenge facing India’s workforce in adapting to future job markets?
a)
Overpopulation in urban centers.
b)
Skills mismatch and deficits in emerging technologies.
c)
Lack of job opportunities in rural areas.
d)
High unemployment rates among graduates.
|
|
Vedant Shukla
asked a question
|
Which of the following statements about the Maternity Benefit Amendment Act, 2017 is correct?- a) It mandates paid leave only after delivery.
- b) It entitles pregnant women to six months of paid leave before and after delivery.
- c) It applies to all organizations regardless of their size.
- d) It requires organizations with 50 or more employees to provide a crèche.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements about the Maternity Benefit Amendment Act, 2017 is correct?
a)
It mandates paid leave only after delivery.
b)
It entitles pregnant women to six months of paid leave before and after delivery.
c)
It applies to all organizations regardless of their size.
d)
It requires organizations with 50 or more employees to provide a crèche.
|
|
Siddharth Malhotra
asked a question
|
What has been a significant impact of the pink bollworm on India’s cotton production?- a) Development of new cotton cultivation techniques.
- b) Elimination of the need for genetically modified crops.
- c) Increased export of cotton fibers.
- d) A reduction of 25% in cotton production over a decade.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What has been a significant impact of the pink bollworm on India’s cotton production?
a)
Development of new cotton cultivation techniques.
b)
Elimination of the need for genetically modified crops.
c)
Increased export of cotton fibers.
d)
A reduction of 25% in cotton production over a decade.
|
|
Rajat Kapoor
asked a question
|
Why is the Bharatiya Vayuyan Adhiniyam, 2024 significant for India's aviation sector?- a) It increases the number of international flights.
- b) It introduces a new airline company.
- c) It completely deregulates the aviation market.
- d) It modernizes aviation regulations but lacks a strong arbitration mechanism.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Why is the Bharatiya Vayuyan Adhiniyam, 2024 significant for India's aviation sector?
a)
It increases the number of international flights.
b)
It introduces a new airline company.
c)
It completely deregulates the aviation market.
d)
It modernizes aviation regulations but lacks a strong arbitration mechanism.
|
|
Aryan Mathur
asked a question
|
What role does the Palna Scheme play in supporting working mothers?- a) It provides financial subsidies for childcare.
- b) It offers day-care facilities for children aged 6 months to 6 years.
- c) It arranges flexible work hours for mothers.
- d) It guarantees maternity leave for all working women.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What role does the Palna Scheme play in supporting working mothers?
a)
It provides financial subsidies for childcare.
b)
It offers day-care facilities for children aged 6 months to 6 years.
c)
It arranges flexible work hours for mothers.
d)
It guarantees maternity leave for all working women.
|
|
Charvi Reddy
asked a question
|
What is one of the primary objectives of the Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana (PMMY)?- a) To eliminate all forms of collateral requirements in banking.
- b) To provide loans exclusively to large corporations.
- c) To enhance financial accessibility for micro and small enterprises.
- d) To promote luxury goods manufacturing in India.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is one of the primary objectives of the Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana (PMMY)?
a)
To eliminate all forms of collateral requirements in banking.
b)
To provide loans exclusively to large corporations.
c)
To enhance financial accessibility for micro and small enterprises.
d)
To promote luxury goods manufacturing in India.
|
|
Gia Bhatia
asked a question
|
Which of the following best describes the function of CAPTCHA?- a) It provides a platform for online surveys.
- b) It distinguishes between human users and automated bots.
- c) It enhances website loading speed.
- d) It serves as a database for user information.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following best describes the function of CAPTCHA?
a)
It provides a platform for online surveys.
b)
It distinguishes between human users and automated bots.
c)
It enhances website loading speed.
d)
It serves as a database for user information.
|
|
Chaitanya Reddy
asked a question
|
What significant feature does INS Varsha include to enhance the operations of nuclear submarines?- a) Floating docks for immediate repairs.
- b) Enhanced surface combat systems.
- c) High-security underground facilities.
- d) A direct connection to international waters.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What significant feature does INS Varsha include to enhance the operations of nuclear submarines?
a)
Floating docks for immediate repairs.
b)
Enhanced surface combat systems.
c)
High-security underground facilities.
d)
A direct connection to international waters.
|
|
Xara Das
asked a question
|
What is the primary concern regarding the proposed linkage of Voter ID cards with Aadhaar numbers in India?- a) It simplifies the voting process significantly.
- b) It will enhance voter turnout.
- c) It raises issues related to electoral integrity and privacy.
- d) It aligns with international voting standards.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the primary concern regarding the proposed linkage of Voter ID cards with Aadhaar numbers in India?
a)
It simplifies the voting process significantly.
b)
It will enhance voter turnout.
c)
It raises issues related to electoral integrity and privacy.
d)
It aligns with international voting standards.

|
Maha Lakshmi
asked a question
|
Consider the following statements regarding the Palaeolithic Age:
Statement-I: Palaeolithic tools were made of rough stones used for hunting and food gathering.
Statement-II: Palaeolithic culture in India developed predominantly during the Pleistocene period.
Statement-III: Evidence of caves and rock shelters in the Belan Valley indicates their use as seasonal camps.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?- a)Both Statement-II and Statement-III are correct and both of them explain Statement-I.
- b)Both Statement-II and Statement-III are correct, but only one of them explains Statement-I.
- c)Only one of the Statements II and III is correct, and that explains Statement-I.
- d)Neither Statement-II nor Statement-III is correct.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements regarding the Palaeolithic Age:
Statement-I: Palaeolithic tools were made of rough stones used for hunting and food gathering.
Statement-II: Palaeolithic culture in India developed predominantly during the Pleistocene period.
Statement-III: Evidence of caves and rock shelters in the Belan Valley indicates their use as seasonal camps.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
Statement-I: Palaeolithic tools were made of rough stones used for hunting and food gathering.
Statement-II: Palaeolithic culture in India developed predominantly during the Pleistocene period.
Statement-III: Evidence of caves and rock shelters in the Belan Valley indicates their use as seasonal camps.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
a)
Both Statement-II and Statement-III are correct and both of them explain Statement-I.
b)
Both Statement-II and Statement-III are correct, but only one of them explains Statement-I.
c)
Only one of the Statements II and III is correct, and that explains Statement-I.
d)
Neither Statement-II nor Statement-III is correct.

|
Shreya Choudhary
asked a question
|
Looping on a K-map always results in the elimination of __________- a)Variables within the loop that appear only in their complemented form
- b)Variables that remain unchanged within the loop
- c)Variables within the loop that appear in both complemented and uncomplemented form
- d)Variables within the loop that appear only in their uncomplemented form
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Looping on a K-map always results in the elimination of __________
a)
Variables within the loop that appear only in their complemented form
b)
Variables that remain unchanged within the loop
c)
Variables within the loop that appear in both complemented and uncomplemented form
d)
Variables within the loop that appear only in their uncomplemented form

|
Dhruv Goyal
asked a question
|
We, at Comfort Stationers, have always been striving to provide stationery items that would make your work more enjoyable and less strenuous. Our latest innovations are a smooth-flow pen and gradual-friction paper. A combination of these two reduces strain on your fingers and allows faster writing the causes lesser fatigue. Therefore, replacement of your pen and paper with our innovative products reduces cost of clerical jobs. Which of the following, if true, would weaken the conclusion drawn in the above argument?- a)Those who are already using the above new products report greater difficulty in transition from new products to regular ones than from the regular ones to the new ones.
- b)The cost of manufacturing these new products is not more than the cost of manufacturing the regular ones and the new products last longer than the regular ones.
- c)The number of offices using the new products is increasing month by month.
- d)These products need to be purchased in huge lots and need to be stored in special conditions. The cost of procurement and strong is quite high.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
We, at Comfort Stationers, have always been striving to provide stationery items that would make your work more enjoyable and less strenuous. Our latest innovations are a smooth-flow pen and gradual-friction paper. A combination of these two reduces strain on your fingers and allows faster writing the causes lesser fatigue. Therefore, replacement of your pen and paper with our innovative products reduces cost of clerical jobs. Which of the following, if true, would weaken the conclusion drawn in the above argument?
a)
Those who are already using the above new products report greater difficulty in transition from new products to regular ones than from the regular ones to the new ones.
b)
The cost of manufacturing these new products is not more than the cost of manufacturing the regular ones and the new products last longer than the regular ones.
c)
The number of offices using the new products is increasing month by month.
d)
These products need to be purchased in huge lots and need to be stored in special conditions. The cost of procurement and strong is quite high.
|
|
Vaishnavi Saha
asked a question
|
Consider the following statements:
- The Harappan Civilization is older than the chalcolithic cultures found in the region.
- The area covered by the Harappan Civilization was approximately 1,299,600 square kilometers.
- The Harappan Civilization used metal money for trade.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- a)Only one
- b)Only two
- c)All three
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
- The Harappan Civilization is older than the chalcolithic cultures found in the region.
- The area covered by the Harappan Civilization was approximately 1,299,600 square kilometers.
- The Harappan Civilization used metal money for trade.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
a)
Only one
b)
Only two
c)
All three
d)
None

|
Dhruv Goyal
asked a question
|
Statement:
Cutting down of forests is a threat to the wild life. Most of the species of animals are on the verge of extinction.Courses of Action:
I. The species of animals, which are on the verge of extinction, must be protected by creating wild life sanctuaries which contain flora that defines the native habitat of the endangered animals.
II. To the maximum extent possible we should stop deforestation.
III. Growing urban forests to compensate for deforestation- a)Only II follows
- b)Only III follows
- c)Only I and II follow
- d)Only I and follows
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement:
Cutting down of forests is a threat to the wild life. Most of the species of animals are on the verge of extinction.
Cutting down of forests is a threat to the wild life. Most of the species of animals are on the verge of extinction.
Courses of Action:
I. The species of animals, which are on the verge of extinction, must be protected by creating wild life sanctuaries which contain flora that defines the native habitat of the endangered animals.
II. To the maximum extent possible we should stop deforestation.
III. Growing urban forests to compensate for deforestation
I. The species of animals, which are on the verge of extinction, must be protected by creating wild life sanctuaries which contain flora that defines the native habitat of the endangered animals.
II. To the maximum extent possible we should stop deforestation.
III. Growing urban forests to compensate for deforestation
a)
Only II follows
b)
Only III follows
c)
Only I and II follow
d)
Only I and follows

|
Tarun Khanna
asked a question
|
Consider the following statements:Statement-I:
In summer, the sun is overhead, and its sunrays fall almost vertically on the Earth, concentrating its heat on a small area. Temperature therefore rises, and summers are always warm.Statement-II:
In winters, the oblique rays of the sun come through the atmosphere less directly and have their heat absorbed by the atmosphere and water vapor. Sun rays fall obliquely and spread over a greater area, hence temperatures remain low.Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?- a)Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, but Statement-II does not explain Statement-I.
- b)Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect.
- c)Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I.
- d)Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement-II is correct.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
Statement-I:
In summer, the sun is overhead, and its sunrays fall almost vertically on the Earth, concentrating its heat on a small area. Temperature therefore rises, and summers are always warm.
In summer, the sun is overhead, and its sunrays fall almost vertically on the Earth, concentrating its heat on a small area. Temperature therefore rises, and summers are always warm.
Statement-II:
In winters, the oblique rays of the sun come through the atmosphere less directly and have their heat absorbed by the atmosphere and water vapor. Sun rays fall obliquely and spread over a greater area, hence temperatures remain low.
In winters, the oblique rays of the sun come through the atmosphere less directly and have their heat absorbed by the atmosphere and water vapor. Sun rays fall obliquely and spread over a greater area, hence temperatures remain low.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
a)
Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, but Statement-II does not explain Statement-I.
b)
Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect.
c)
Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I.
d)
Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement-II is correct.

|
Mainak Chakraborty
asked a question
|
Consider the following pairs:1. Winter Solstice: Day lasts for 6 months at the South Pole2. Equinoxes: Sun's rays are vertical at the Tropic of Cancer on 21 March and 21 September3. Summer Solstice: Sun's rays fall vertically at the Tropic of Capricorn on 21 June4. Seasonal Changes: Longer days in summer lead to higher temperaturesHow many pairs given above are correctly matched?- a)Only one pair
- b)Only two pairs
- c)Only three pairs
- d)All four pairs
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following pairs:
1. Winter Solstice: Day lasts for 6 months at the South Pole
2. Equinoxes: Sun's rays are vertical at the Tropic of Cancer on 21 March and 21 September
3. Summer Solstice: Sun's rays fall vertically at the Tropic of Capricorn on 21 June
4. Seasonal Changes: Longer days in summer lead to higher temperatures
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
a)
Only one pair
b)
Only two pairs
c)
Only three pairs
d)
All four pairs
|
|
Rahul Aggarwal
asked a question
|
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:During the economic boom of the Roaring Twenties, the traditional values of rural America were challenged by the Jazz Age. The average American was busy buying automobiles and household appliances, and speculating in the stock market, where big money could be made. Those appliances were bought on credit, however. Although businesses have made huge gains — 65 percent — from the mechanization of manufacturing, the average worker’s wages had only increased 8 percent.The imbalance between the rich and the poor, with 0.1 percent of society earning the same total income as 42 percent, combined with production of more and more goods and rising personal debt, could not be sustained. On Black Tuesday, October 29, 1929, the stock market crashed, triggering the Great Depression, the worst economic collapse in the history of the modern industrial world. It spread from the United States to the rest of the world, lasting from the end of 1929 until the early 1940s. With banks failing and businesses closing, more than 15 million Americans (one-quarter of the workforce) became unemployed.President Herbert Hoover, underestimating the seriousness of the crisis, called it ‘a passing incident in our national lives,’ and assured Americans that it would be over in 60 days. A strong believer in rugged individualism, Hoover did not think the federal government should offer relief to the poverty-stricken population. Focusing on a trickle-down economic program to help finance businesses and banks, Hoover met with resistance from business executives who preferred to lay off workers. Blamed by many for the Great Depression, Hoover was widely ridiculed: an empty pocket turned inside out was called a ‘Hoover flag;’ the decrepit shantytowns springing up around the country were called ‘Hoovervilles.’Franklin Delano Roosevelt, the rich governor from New York, offered Americans a New Deal, and was elected in a landslide victory in 1932. He took quick action to attack the Depression, declaring a four-day bank holiday, during which Congress passed the Emergency Banking Relief Act to stabilize the banking system. During the first 100 days of his administration, Roosevelt laid the groundwork for his New Deal remedies that would rescue the country from the depths of despair.The New Deal programs created a liberal political alliance of labor unions, blacks and other minorities, some farmers and others receiving government relief, and intellectuals. The hardship brought on by the Depression affected Americans deeply. Since the prevailing attitude of the 1920s was that success was earned, it followed that failure was deserved. The unemployment brought on by the Depression caused self-blame and self-doubt. Men were harder hit psychologically than women were. Since men were expected to provide for their families, it was humiliating to have to ask for assistance. Although some argued that women should not be given jobs when many men were unemployed, the percentage of women working increased slightly during the Depression. Traditionally female fields of teaching and social services grew under New Deal programs. Children took on more responsibilities, sometimes finding work when their parents could not. As a result of living through the Depression, some people developed habits of careful saving and frugality, others determined to create a comfortable life for themselves.African Americans suffered more than whites, since their jobs were often taken away from them and given to whites. In 1930, 50 percent of blacks were unemployed. However, Eleanor Roosevelt championed black rights, and New Deal programs prohibited discrimination. Discrimination continued in the South, however, as a result a large number of black voters switched from the Republican to the Democrat party during the Depression.The Great Depression and the New Deal changed forever the relationship between Americans and their government. Government involvement and responsibility in caring for the needy and regulating the economy came to be expected.Which of the following sections of the American society were most affected by the Great Depression?... more
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:
During the economic boom of the Roaring Twenties, the traditional values of rural America were challenged by the Jazz Age. The average American was busy buying automobiles and household appliances, and speculating in the stock market, where big money could be made. Those appliances were bought on credit, however. Although businesses have made huge gains — 65 percent — from the mechanization of manufacturing, the average worker’s wages had only increased 8 percent.
The imbalance between the rich and the poor, with 0.1 percent of society earning the same total income as 42 percent, combined with production of more and more goods and rising personal debt, could not be sustained. On Black Tuesday, October 29, 1929, the stock market crashed, triggering the Great Depression, the worst economic collapse in the history of the modern industrial world. It spread from the United States to the rest of the world, lasting from the end of 1929 until the early 1940s. With banks failing and businesses closing, more than 15 million Americans (one-quarter of the workforce) became unemployed.
President Herbert Hoover, underestimating the seriousness of the crisis, called it ‘a passing incident in our national lives,’ and assured Americans that it would be over in 60 days. A strong believer in rugged individualism, Hoover did not think the federal government should offer relief to the poverty-stricken population. Focusing on a trickle-down economic program to help finance businesses and banks, Hoover met with resistance from business executives who preferred to lay off workers. Blamed by many for the Great Depression, Hoover was widely ridiculed: an empty pocket turned inside out was called a ‘Hoover flag;’ the decrepit shantytowns springing up around the country were called ‘Hoovervilles.’
Franklin Delano Roosevelt, the rich governor from New York, offered Americans a New Deal, and was elected in a landslide victory in 1932. He took quick action to attack the Depression, declaring a four-day bank holiday, during which Congress passed the Emergency Banking Relief Act to stabilize the banking system. During the first 100 days of his administration, Roosevelt laid the groundwork for his New Deal remedies that would rescue the country from the depths of despair.
The New Deal programs created a liberal political alliance of labor unions, blacks and other minorities, some farmers and others receiving government relief, and intellectuals. The hardship brought on by the Depression affected Americans deeply. Since the prevailing attitude of the 1920s was that success was earned, it followed that failure was deserved. The unemployment brought on by the Depression caused self-blame and self-doubt. Men were harder hit psychologically than women were. Since men were expected to provide for their families, it was humiliating to have to ask for assistance. Although some argued that women should not be given jobs when many men were unemployed, the percentage of women working increased slightly during the Depression. Traditionally female fields of teaching and social services grew under New Deal programs. Children took on more responsibilities, sometimes finding work when their parents could not. As a result of living through the Depression, some people developed habits of careful saving and frugality, others determined to create a comfortable life for themselves.
African Americans suffered more than whites, since their jobs were often taken away from them and given to whites. In 1930, 50 percent of blacks were unemployed. However, Eleanor Roosevelt championed black rights, and New Deal programs prohibited discrimination. Discrimination continued in the South, however, as a result a large number of black voters switched from the Republican to the Democrat party during the Depression.
The Great Depression and the New Deal changed forever the relationship between Americans and their government. Government involvement and responsibility in caring for the needy and regulating the economy came to be expected.
Which of the following sections of the American society were most affected by the Great Depression?
|
|
Arnav Mathur
asked a question
|
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:During the economic boom of the Roaring Twenties, the traditional values of rural America were challenged by the Jazz Age. The average American was busy buying automobiles and household appliances, and speculating in the stock market, where big money could be made. Those appliances were bought on credit, however. Although businesses have made huge gains — 65 percent — from the mechanization of manufacturing, the average worker’s wages had only increased 8 percent.The imbalance between the rich and the poor, with 0.1 percent of society earning the same total income as 42 percent, combined with production of more and more goods and rising personal debt, could not be sustained. On Black Tuesday, October 29, 1929, the stock market crashed, triggering the Great Depression, the worst economic collapse in the history of the modern industrial world. It spread from the United States to the rest of the world, lasting from the end of 1929 until the early 1940s. With banks failing and businesses closing, more than 15 million Americans (one-quarter of the workforce) became unemployed.President Herbert Hoover, underestimating the seriousness of the crisis, called it ‘a passing incident in our national lives,’ and assured Americans that it would be over in 60 days. A strong believer in rugged individualism, Hoover did not think the federal government should offer relief to the poverty-stricken population. Focusing on a trickle-down economic program to help finance businesses and banks, Hoover met with resistance from business executives who preferred to lay off workers. Blamed by many for the Great Depression, Hoover was widely ridiculed: an empty pocket turned inside out was called a ‘Hoover flag;’ the decrepit shantytowns springing up around the country were called ‘Hoovervilles.’Franklin Delano Roosevelt, the rich governor from New York, offered Americans a New Deal, and was elected in a landslide victory in 1932. He took quick action to attack the Depression, declaring a four-day bank holiday, during which Congress passed the Emergency Banking Relief Act to stabilize the banking system. During the first 100 days of his administration, Roosevelt laid the groundwork for his New Deal remedies that would rescue the country from the depths of despair.The New Deal programs created a liberal political alliance of labor unions, blacks and other minorities, some farmers and others receiving government relief, and intellectuals. The hardship brought on by the Depression affected Americans deeply. Since the prevailing attitude of the 1920s was that success was earned, it followed that failure was deserved. The unemployment brought on by the Depression caused self-blame and self-doubt. Men were harder hit psychologically than women were. Since men were expected to provide for their families, it was humiliating to have to ask for assistance. Although some argued that women should not be given jobs when many men were unemployed, the percentage of women working increased slightly during the Depression. Traditionally female fields of teaching and social services grew under New Deal programs. Children took on more responsibilities, sometimes finding work when their parents could not. As a result of living through the Depression, some people developed habits of careful saving and frugality, others determined to create a comfortable life for themselves.African Americans suffered more than whites, since their jobs were often taken away from them and given to whites. In 1930, 50 percent of blacks were unemployed. However, Eleanor Roosevelt championed black rights, and New Deal programs prohibited discrimination. Discrimination continued in the South, however, as a result a large number of black voters switched from the Republican to the Democrat party during the Depression.The Great Depression and the New Deal changed forever the relationship between Americans and their government. Government involvement and responsibility in caring for the needy and regulating the economy came to be expected.What was the change in worker’s wages after mechanization of manufacturing?... more
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:
During the economic boom of the Roaring Twenties, the traditional values of rural America were challenged by the Jazz Age. The average American was busy buying automobiles and household appliances, and speculating in the stock market, where big money could be made. Those appliances were bought on credit, however. Although businesses have made huge gains — 65 percent — from the mechanization of manufacturing, the average worker’s wages had only increased 8 percent.
The imbalance between the rich and the poor, with 0.1 percent of society earning the same total income as 42 percent, combined with production of more and more goods and rising personal debt, could not be sustained. On Black Tuesday, October 29, 1929, the stock market crashed, triggering the Great Depression, the worst economic collapse in the history of the modern industrial world. It spread from the United States to the rest of the world, lasting from the end of 1929 until the early 1940s. With banks failing and businesses closing, more than 15 million Americans (one-quarter of the workforce) became unemployed.
President Herbert Hoover, underestimating the seriousness of the crisis, called it ‘a passing incident in our national lives,’ and assured Americans that it would be over in 60 days. A strong believer in rugged individualism, Hoover did not think the federal government should offer relief to the poverty-stricken population. Focusing on a trickle-down economic program to help finance businesses and banks, Hoover met with resistance from business executives who preferred to lay off workers. Blamed by many for the Great Depression, Hoover was widely ridiculed: an empty pocket turned inside out was called a ‘Hoover flag;’ the decrepit shantytowns springing up around the country were called ‘Hoovervilles.’
Franklin Delano Roosevelt, the rich governor from New York, offered Americans a New Deal, and was elected in a landslide victory in 1932. He took quick action to attack the Depression, declaring a four-day bank holiday, during which Congress passed the Emergency Banking Relief Act to stabilize the banking system. During the first 100 days of his administration, Roosevelt laid the groundwork for his New Deal remedies that would rescue the country from the depths of despair.
The New Deal programs created a liberal political alliance of labor unions, blacks and other minorities, some farmers and others receiving government relief, and intellectuals. The hardship brought on by the Depression affected Americans deeply. Since the prevailing attitude of the 1920s was that success was earned, it followed that failure was deserved. The unemployment brought on by the Depression caused self-blame and self-doubt. Men were harder hit psychologically than women were. Since men were expected to provide for their families, it was humiliating to have to ask for assistance. Although some argued that women should not be given jobs when many men were unemployed, the percentage of women working increased slightly during the Depression. Traditionally female fields of teaching and social services grew under New Deal programs. Children took on more responsibilities, sometimes finding work when their parents could not. As a result of living through the Depression, some people developed habits of careful saving and frugality, others determined to create a comfortable life for themselves.
African Americans suffered more than whites, since their jobs were often taken away from them and given to whites. In 1930, 50 percent of blacks were unemployed. However, Eleanor Roosevelt championed black rights, and New Deal programs prohibited discrimination. Discrimination continued in the South, however, as a result a large number of black voters switched from the Republican to the Democrat party during the Depression.
The Great Depression and the New Deal changed forever the relationship between Americans and their government. Government involvement and responsibility in caring for the needy and regulating the economy came to be expected.
What was the change in worker’s wages after mechanization of manufacturing?
|
|
Jatin Khanna
asked a question
|
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:In the decades following World War II, American business had undisputed control of the world economy, producing goods of such high quality and low cost that foreign corporations were unable to compete. But in the mid-1960s the United States began to lose its advantage and by the 1980s American corporations lagged behind the competition in many industries. In the computer chip industry, for example, American corporations had lost most of both domestic and foreign markets by the early 1980s. The first analysts to examine the decline of American business blamed the U.S. government. They argued that stringent governmental restrictions on the behaviour of American corporations, combined with the wholehearted support given to foreign firms by their governments, created and environment in which American products could not compete. Later analysts blamed predatory corporate raiders who bought corporations, not to make them more competitive in the face of foreign competition, but rather to sell off the most lucrative divisions for huge profits. Still later analysts blamed the American workforce, citing labour demands and poor productivity as the reasons American corporations have been unable to compete with Japanese and European firms. Finally, a few analysts even censured American consumers for their unpatriotic purchases of foreign goods. The blame actually lies with corporate management, which has made serious errors based on misconceptions about what it takes to be successful in the marketplace. These missteps involve labour costs, production choices, and growth strategies. Even though labour costs typically account for less than 15% of a product‘s total cost, management has been quick to blame the costs of workers‘ wages for driving up prices, making American goods uncompetitive. As a result of attempts to minimize the cost of wages, American corporations have had trouble recruiting and retaining skilled workers. The emphasis on cost minimization has also led to another blunder: an over-concentration on high technology products. Many foreign firms began by specializing in the mass production and sale of low technology products, gaining valuable experience and earning tremendous profits. Later, these corporations were able to break into high technology markets without much trouble; they simply applied their previous manufacturing experience and ample financial resources to the production of higher quality goods. American business has consistently ignored this very sensible approach. The recent rash of corporate mergers and acquisitions in the U.S. has not helped the situation either. While American firms have neglected long-range planning and production, preferring instead to reap fast profits through mergers and acquisitions, foreign firms have been quick to exploit opportunities to ensure their domination over future markets by investing in the streamlining and modernization of their facilities.Which of the following best encapsulates the primary reason for the decline of American business competitiveness according to the passage?... more
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:
In the decades following World War II, American business had undisputed control of the world economy, producing goods of such high quality and low cost that foreign corporations were unable to compete. But in the mid-1960s the United States began to lose its advantage and by the 1980s American corporations lagged behind the competition in many industries. In the computer chip industry, for example, American corporations had lost most of both domestic and foreign markets by the early 1980s. The first analysts to examine the decline of American business blamed the U.S. government. They argued that stringent governmental restrictions on the behaviour of American corporations, combined with the wholehearted support given to foreign firms by their governments, created and environment in which American products could not compete. Later analysts blamed predatory corporate raiders who bought corporations, not to make them more competitive in the face of foreign competition, but rather to sell off the most lucrative divisions for huge profits. Still later analysts blamed the American workforce, citing labour demands and poor productivity as the reasons American corporations have been unable to compete with Japanese and European firms. Finally, a few analysts even censured American consumers for their unpatriotic purchases of foreign goods. The blame actually lies with corporate management, which has made serious errors based on misconceptions about what it takes to be successful in the marketplace. These missteps involve labour costs, production choices, and growth strategies. Even though labour costs typically account for less than 15% of a product‘s total cost, management has been quick to blame the costs of workers‘ wages for driving up prices, making American goods uncompetitive. As a result of attempts to minimize the cost of wages, American corporations have had trouble recruiting and retaining skilled workers. The emphasis on cost minimization has also led to another blunder: an over-concentration on high technology products. Many foreign firms began by specializing in the mass production and sale of low technology products, gaining valuable experience and earning tremendous profits. Later, these corporations were able to break into high technology markets without much trouble; they simply applied their previous manufacturing experience and ample financial resources to the production of higher quality goods. American business has consistently ignored this very sensible approach. The recent rash of corporate mergers and acquisitions in the U.S. has not helped the situation either. While American firms have neglected long-range planning and production, preferring instead to reap fast profits through mergers and acquisitions, foreign firms have been quick to exploit opportunities to ensure their domination over future markets by investing in the streamlining and modernization of their facilities.
Which of the following best encapsulates the primary reason for the decline of American business competitiveness according to the passage?
|
|
Lucas Thompson
asked a question
|
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:In the decades following World War II, American business had undisputed control of the world economy, producing goods of such high quality and low cost that foreign corporations were unable to compete. But in the mid-1960s the United States began to lose its advantage and by the 1980s American corporations lagged behind the competition in many industries. In the computer chip industry, for example, American corporations had lost most of both domestic and foreign markets by the early 1980s.The first analysts to examine the decline of American business blamed the U.S. government. They argued that stringent governmental restrictions on the behaviour of American corporations, combined with the wholehearted support given to foreign firms by their governments, created and environment in which American products could not compete. Later analysts blamed predatory corporate raiders who bought corporations, not to make them more competitive in the face of foreign competition, but rather to sell off the most lucrative divisions for huge profits.Still later analysts blamed the American workforce, citing labour demands and poor productivity as the reasons American corporations have been unable to compete with Japanese and European firms. Finally, a few analysts even censured American consumers for their unpatriotic purchases of foreign goods. The blame actually lies with corporate management, which has made serious errors based on misconceptions about what it takes to be successful in the marketplace.These missteps involve labour costs, production choices, and growth strategies. Even though labour costs typically account for less than 15% of a product‘s total cost, management has been quick to blame the costs of workers‘ wages for driving up prices, making American goods uncompetitive. As a result of attempts to minimize the cost of wages, American corporations have had trouble recruiting and retaining skilled workers.The emphasis on cost minimization has also led to another blunder: an over-concentration on high technology products. Many foreign firms began by specializing in the mass production and sale of low technology products, gaining valuable experience and earning tremendous profits. Later, these corporations were able to break into high technology markets without much trouble; they simply applied their previous manufacturing experience and ample financial resources to the production of higher quality goods. American business has consistently ignored this very sensible approach.The recent rash of corporate mergers and acquisitions in the U.S. has not helped the situation either. While American firms have neglected long-range planning and production, preferring instead to reap fast profits through mergers and acquisitions, foreign firms have been quick to exploit opportunities to ensure their domination over future markets by investing in the streamlining and modernization of their facilities.Which of the following would most weaken the author‘s argument about the over-concentration on high technology products? ... more
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:
In the decades following World War II, American business had undisputed control of the world economy, producing goods of such high quality and low cost that foreign corporations were unable to compete. But in the mid-1960s the United States began to lose its advantage and by the 1980s American corporations lagged behind the competition in many industries. In the computer chip industry, for example, American corporations had lost most of both domestic and foreign markets by the early 1980s.
The first analysts to examine the decline of American business blamed the U.S. government. They argued that stringent governmental restrictions on the behaviour of American corporations, combined with the wholehearted support given to foreign firms by their governments, created and environment in which American products could not compete. Later analysts blamed predatory corporate raiders who bought corporations, not to make them more competitive in the face of foreign competition, but rather to sell off the most lucrative divisions for huge profits.
Still later analysts blamed the American workforce, citing labour demands and poor productivity as the reasons American corporations have been unable to compete with Japanese and European firms. Finally, a few analysts even censured American consumers for their unpatriotic purchases of foreign goods. The blame actually lies with corporate management, which has made serious errors based on misconceptions about what it takes to be successful in the marketplace.
These missteps involve labour costs, production choices, and growth strategies. Even though labour costs typically account for less than 15% of a product‘s total cost, management has been quick to blame the costs of workers‘ wages for driving up prices, making American goods uncompetitive. As a result of attempts to minimize the cost of wages, American corporations have had trouble recruiting and retaining skilled workers.
The emphasis on cost minimization has also led to another blunder: an over-concentration on high technology products. Many foreign firms began by specializing in the mass production and sale of low technology products, gaining valuable experience and earning tremendous profits. Later, these corporations were able to break into high technology markets without much trouble; they simply applied their previous manufacturing experience and ample financial resources to the production of higher quality goods. American business has consistently ignored this very sensible approach.
The recent rash of corporate mergers and acquisitions in the U.S. has not helped the situation either. While American firms have neglected long-range planning and production, preferring instead to reap fast profits through mergers and acquisitions, foreign firms have been quick to exploit opportunities to ensure their domination over future markets by investing in the streamlining and modernization of their facilities.
Which of the following would most weaken the author‘s argument about the over-concentration on high technology products?
|
|
Sanket Joshi
asked a question
|
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:In the decades following World War II, American business had undisputed control of the world economy, producing goods of such high quality and low cost that foreign corporations were unable to compete. But in the mid-1960s the United States began to lose its advantage and by the 1980s American corporations lagged behind the competition in many industries. In the computer chip industry, for example, American corporations had lost most of both domestic and foreign markets by the early 1980s.The first analysts to examine the decline of American business blamed the U.S. government. They argued that stringent governmental restrictions on the behaviour of American corporations, combined with the wholehearted support given to foreign firms by their governments, created and environment in which American products could not compete. Later analysts blamed predatory corporate raiders who bought corporations, not to make them more competitive in the face of foreign competition, but rather to sell off the most lucrative divisions for huge profits.Still later analysts blamed the American workforce, citing labour demands and poor productivity as the reasons American corporations have been unable to compete with Japanese and European firms. Finally, a few analysts even censured American consumers for their unpatriotic purchases of foreign goods. The blame actually lies with corporate management, which has made serious errors based on misconceptions about what it takes to be successful in the marketplace.These missteps involve labour costs, production choices, and growth strategies. Even though labour costs typically account for less than 15% of a product‘s total cost, management has been quick to blame the costs of workers‘ wages for driving up prices, making American goods uncompetitive. As a result of attempts to minimize the cost of wages, American corporations have had trouble recruiting and retaining skilled workers.The emphasis on cost minimization has also led to another blunder: an over-concentration on high technology products. Many foreign firms began by specializing in the mass production and sale of low technology products, gaining valuable experience and earning tremendous profits. Later, these corporations were able to break into high technology markets without much trouble; they simply applied their previous manufacturing experience and ample financial resources to the production of higher quality goods. American business has consistently ignored this very sensible approach.The recent rash of corporate mergers and acquisitions in the U.S. has not helped the situation either. While American firms have neglected long-range planning and production, preferring instead to reap fast profits through mergers and acquisitions, foreign firms have been quick to exploit opportunities to ensure their domination over future markets by investing in the streamlining and modernization of their facilities. With which of the following general statements would the author most likely NOT agree?... more
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:
In the decades following World War II, American business had undisputed control of the world economy, producing goods of such high quality and low cost that foreign corporations were unable to compete. But in the mid-1960s the United States began to lose its advantage and by the 1980s American corporations lagged behind the competition in many industries. In the computer chip industry, for example, American corporations had lost most of both domestic and foreign markets by the early 1980s.
The first analysts to examine the decline of American business blamed the U.S. government. They argued that stringent governmental restrictions on the behaviour of American corporations, combined with the wholehearted support given to foreign firms by their governments, created and environment in which American products could not compete. Later analysts blamed predatory corporate raiders who bought corporations, not to make them more competitive in the face of foreign competition, but rather to sell off the most lucrative divisions for huge profits.
Still later analysts blamed the American workforce, citing labour demands and poor productivity as the reasons American corporations have been unable to compete with Japanese and European firms. Finally, a few analysts even censured American consumers for their unpatriotic purchases of foreign goods. The blame actually lies with corporate management, which has made serious errors based on misconceptions about what it takes to be successful in the marketplace.
These missteps involve labour costs, production choices, and growth strategies. Even though labour costs typically account for less than 15% of a product‘s total cost, management has been quick to blame the costs of workers‘ wages for driving up prices, making American goods uncompetitive. As a result of attempts to minimize the cost of wages, American corporations have had trouble recruiting and retaining skilled workers.
The emphasis on cost minimization has also led to another blunder: an over-concentration on high technology products. Many foreign firms began by specializing in the mass production and sale of low technology products, gaining valuable experience and earning tremendous profits. Later, these corporations were able to break into high technology markets without much trouble; they simply applied their previous manufacturing experience and ample financial resources to the production of higher quality goods. American business has consistently ignored this very sensible approach.
The recent rash of corporate mergers and acquisitions in the U.S. has not helped the situation either. While American firms have neglected long-range planning and production, preferring instead to reap fast profits through mergers and acquisitions, foreign firms have been quick to exploit opportunities to ensure their domination over future markets by investing in the streamlining and modernization of their facilities.
With which of the following general statements would the author most likely NOT agree?
|
|
Rajiv Mehra
asked a question
|
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:In the decades following World War II, American business had undisputed control of the world economy, producing goods of such high quality and low cost that foreign corporations were unable to compete. But in the mid-1960s the United States began to lose its advantage and by the 1980s American corporations lagged behind the competition in many industries. In the computer chip industry, for example, American corporations had lost most of both domestic and foreign markets by the early 1980s.The first analysts to examine the decline of American business blamed the U.S. government. They argued that stringent governmental restrictions on the behaviour of American corporations, combined with the wholehearted support given to foreign firms by their governments, created and environment in which American products could not compete. Later analysts blamed predatory corporate raiders who bought corporations, not to make them more competitive in the face of foreign competition, but rather to sell off the most lucrative divisions for huge profits.Still later analysts blamed the American workforce, citing labour demands and poor productivity as the reasons American corporations have been unable to compete with Japanese and European firms. Finally, a few analysts even censured American consumers for their unpatriotic purchases of foreign goods. The blame actually lies with corporate management, which has made serious errors based on misconceptions about what it takes to be successful in the marketplace.These missteps involve labour costs, production choices, and growth strategies. Even though labour costs typically account for less than 15% of a product‘s total cost, management has been quick to blame the costs of workers‘ wages for driving up prices, making American goods uncompetitive. As a result of attempts to minimize the cost of wages, American corporations have had trouble recruiting and retaining skilled workers.The emphasis on cost minimization has also led to another blunder: an over-concentration on high technology products. Many foreign firms began by specializing in the mass production and sale of low technology products, gaining valuable experience and earning tremendous profits. Later, these corporations were able to break into high technology markets without much trouble; they simply applied their previous manufacturing experience and ample financial resources to the production of higher quality goods.American business has consistently ignored this very sensible approach. The recent rash of corporate mergers and acquisitions in the U.S. has not helped the situation either. While American firms have neglected long-range planning and production, preferring instead to reap fast profits through mergers and acquisitions, foreign firms have been quick to exploit opportunities to ensure their domination over future markets by investing in the streamlining and modernization of their facilities.The passage suggests that compared to Japanese workers, American workers are often considered: ... more
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:
In the decades following World War II, American business had undisputed control of the world economy, producing goods of such high quality and low cost that foreign corporations were unable to compete. But in the mid-1960s the United States began to lose its advantage and by the 1980s American corporations lagged behind the competition in many industries. In the computer chip industry, for example, American corporations had lost most of both domestic and foreign markets by the early 1980s.
The first analysts to examine the decline of American business blamed the U.S. government. They argued that stringent governmental restrictions on the behaviour of American corporations, combined with the wholehearted support given to foreign firms by their governments, created and environment in which American products could not compete. Later analysts blamed predatory corporate raiders who bought corporations, not to make them more competitive in the face of foreign competition, but rather to sell off the most lucrative divisions for huge profits.
Still later analysts blamed the American workforce, citing labour demands and poor productivity as the reasons American corporations have been unable to compete with Japanese and European firms. Finally, a few analysts even censured American consumers for their unpatriotic purchases of foreign goods. The blame actually lies with corporate management, which has made serious errors based on misconceptions about what it takes to be successful in the marketplace.
These missteps involve labour costs, production choices, and growth strategies. Even though labour costs typically account for less than 15% of a product‘s total cost, management has been quick to blame the costs of workers‘ wages for driving up prices, making American goods uncompetitive. As a result of attempts to minimize the cost of wages, American corporations have had trouble recruiting and retaining skilled workers.
The emphasis on cost minimization has also led to another blunder: an over-concentration on high technology products. Many foreign firms began by specializing in the mass production and sale of low technology products, gaining valuable experience and earning tremendous profits. Later, these corporations were able to break into high technology markets without much trouble; they simply applied their previous manufacturing experience and ample financial resources to the production of higher quality goods.
American business has consistently ignored this very sensible approach. The recent rash of corporate mergers and acquisitions in the U.S. has not helped the situation either. While American firms have neglected long-range planning and production, preferring instead to reap fast profits through mergers and acquisitions, foreign firms have been quick to exploit opportunities to ensure their domination over future markets by investing in the streamlining and modernization of their facilities.
The passage suggests that compared to Japanese workers, American workers are often considered:
|
|
Isabella Sanchez
asked a question
|
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:Suspicious as they are of American intentions, and bolstered by court rulings that seem to give them license to seek out and publish any and all government secrets, the media‘s distrust of our government, combined with their limited understanding of the world at large, damages our ability to design and conduct good policy in ways that the media rarely imagine.The leak through which sensitive information flows from the government to the press is detrimental to policy in so far as it almost completely precludes the possibility of serious discussion. The fear that anything they say, even in what is construed as a private forum, may appear in print, makes many people, whether our own government officials or the leaders of foreign countries, unwilling to speak their minds.Must we be content with the restriction of our leaders‘ policy discussions to a handful of people who trust each other, thus limiting the richness and variety of ideas that could be brought forward through a larger group because of the nearly endemic nature of this problem? It is vitally important for the leaders of the United States to know the real state of affairs internationally, and this can occur only if foreign leaders feel free to speak their minds to our diplomats.Until recently, it looked as if the media had convinced the public that journalists were more reliable than the government; however, this may be changing. With the passage of time, the media have lost lustre. They—having grown large and powerful—provoke the same public skepticism that other large institutions in the society do. A series of media scandals has contributed to this. Many Americans have concluded that the media are no more credible than the government, and public opinion surveys reflect much ambivalence about the press.While leaks are generally defended by media officials on the grounds of the public‘s ―right to know, in reality they are part of the Washington political power game, as well as part of the policy process. The "leaker" may be currying favour with the media, or maybe planting information to influence policy. In the first case, he is helping himself by enhancing the prestige of a journalist; in the second, he is using the media as a stage for his preferred policies. In either instance, it closes the circle: the leak begins with a political motive, is advanced by a politicized media, and continues because of politics. Although some of the journalists think they are doing the work, they are more often than not instruments of the process, not prime movers. The media must be held accountable for their activities, just like every other significant institution in our society, and the media must be forced to earn the public‘s trust.Based on the passage, when the media now challenge the actions of a public official, the public assumes that: ... more
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:
Suspicious as they are of American intentions, and bolstered by court rulings that seem to give them license to seek out and publish any and all government secrets, the media‘s distrust of our government, combined with their limited understanding of the world at large, damages our ability to design and conduct good policy in ways that the media rarely imagine.
The leak through which sensitive information flows from the government to the press is detrimental to policy in so far as it almost completely precludes the possibility of serious discussion. The fear that anything they say, even in what is construed as a private forum, may appear in print, makes many people, whether our own government officials or the leaders of foreign countries, unwilling to speak their minds.
Must we be content with the restriction of our leaders‘ policy discussions to a handful of people who trust each other, thus limiting the richness and variety of ideas that could be brought forward through a larger group because of the nearly endemic nature of this problem? It is vitally important for the leaders of the United States to know the real state of affairs internationally, and this can occur only if foreign leaders feel free to speak their minds to our diplomats.
Until recently, it looked as if the media had convinced the public that journalists were more reliable than the government; however, this may be changing. With the passage of time, the media have lost lustre. They—having grown large and powerful—provoke the same public skepticism that other large institutions in the society do. A series of media scandals has contributed to this. Many Americans have concluded that the media are no more credible than the government, and public opinion surveys reflect much ambivalence about the press.
While leaks are generally defended by media officials on the grounds of the public‘s ―right to know, in reality they are part of the Washington political power game, as well as part of the policy process. The "leaker" may be currying favour with the media, or maybe planting information to influence policy. In the first case, he is helping himself by enhancing the prestige of a journalist; in the second, he is using the media as a stage for his preferred policies. In either instance, it closes the circle: the leak begins with a political motive, is advanced by a politicized media, and continues because of politics. Although some of the journalists think they are doing the work, they are more often than not instruments of the process, not prime movers. The media must be held accountable for their activities, just like every other significant institution in our society, and the media must be forced to earn the public‘s trust.
Based on the passage, when the media now challenge the actions of a public official, the public assumes that:
|
|
Caleb Phillips
asked a question
|
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:Suspicious as they are of American intentions, and bolstered by court rulings that seem to give them license to seek out and publish any and all government secrets, the media‘s distrust of our government, combined with their limited understanding of the world at large, damages our ability to design and conduct good policy in ways that the media rarely imagine.The leak through which sensitive information flows from the government to the press is detrimental to policy in so far as it almost completely precludes the possibility of serious discussion. The fear that anything they say, even in what is construed as a private forum, may appear in print, makes many people, whether our own government officials or the leaders of foreign countries, unwilling to speak their minds.Must we be content with the restriction of our leaders‘ policy discussions to a handful of people who trust each other, thus limiting the richness and variety of ideas that could be brought forward through a larger group because of the nearly endemic nature of this problem? It is vitally important for the leaders of the United States to know the real state of affairs internationally, and this can occur only if foreign leaders feel free to speak their minds to our diplomats.Until recently, it looked as if the media had convinced the public that journalists were more reliable than the government; however, this may be changing. With the passage of time, the media have lost lustre. They—having grown large and powerful—provoke the same public skepticism that other large institutions in the society do. A series of media scandals has contributed to this. Many Americans have concluded that the media are no more credible than the government, and public opinion surveys reflect much ambivalence about the press.While leaks are generally defended by media officials on the grounds of the public‘s ―right to know, in reality they are part of the Washington political power game, as well as part of the policy process. The "leaker" may be currying favour with the media, or may be planting information to influence policy. In the first case, he is helping himself by enhancing the prestige of a journalist; in the second, he is using the media as a stage for his preferred policies. In either instance, it closes the circle: the leak begins with a political motive, is advanced by a politicized media, and continues because of politics. Although some of the journalists think they are doing the work, they are more often than not instruments of the process, not prime movers. The media must be held accountable for their activities, just like every other significant institution in our society, and the media must be forced to earn the public‘s trust. What is the main idea of the passage? ... more
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:
Suspicious as they are of American intentions, and bolstered by court rulings that seem to give them license to seek out and publish any and all government secrets, the media‘s distrust of our government, combined with their limited understanding of the world at large, damages our ability to design and conduct good policy in ways that the media rarely imagine.
The leak through which sensitive information flows from the government to the press is detrimental to policy in so far as it almost completely precludes the possibility of serious discussion. The fear that anything they say, even in what is construed as a private forum, may appear in print, makes many people, whether our own government officials or the leaders of foreign countries, unwilling to speak their minds.
Must we be content with the restriction of our leaders‘ policy discussions to a handful of people who trust each other, thus limiting the richness and variety of ideas that could be brought forward through a larger group because of the nearly endemic nature of this problem? It is vitally important for the leaders of the United States to know the real state of affairs internationally, and this can occur only if foreign leaders feel free to speak their minds to our diplomats.
Until recently, it looked as if the media had convinced the public that journalists were more reliable than the government; however, this may be changing. With the passage of time, the media have lost lustre. They—having grown large and powerful—provoke the same public skepticism that other large institutions in the society do. A series of media scandals has contributed to this. Many Americans have concluded that the media are no more credible than the government, and public opinion surveys reflect much ambivalence about the press.
While leaks are generally defended by media officials on the grounds of the public‘s ―right to know, in reality they are part of the Washington political power game, as well as part of the policy process. The "leaker" may be currying favour with the media, or may be planting information to influence policy. In the first case, he is helping himself by enhancing the prestige of a journalist; in the second, he is using the media as a stage for his preferred policies. In either instance, it closes the circle: the leak begins with a political motive, is advanced by a politicized media, and continues because of politics. Although some of the journalists think they are doing the work, they are more often than not instruments of the process, not prime movers. The media must be held accountable for their activities, just like every other significant institution in our society, and the media must be forced to earn the public‘s trust.
What is the main idea of the passage?
|
|
Kunal Kapoor
asked a question
|
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:Suspicious as they are of American intentions, and bolstered by court rulings that seem to give them license to seek out and publish any and all government secrets, the media‘s distrust of our government, combined with their limited understanding of the world at large, damages our ability to design and conduct good policy in ways that the media rarely imagine.The leak through which sensitive information flows from the government to the press is detrimental to policy in so far as it almost completely precludes the possibility of serious discussion. The fear that anything they say, even in what is construed as a private forum, may appear in print, makes many people, whether our own government officials or the leaders of foreign countries, unwilling to speak their minds.Must we be content with the restriction of our leaders‘ policy discussions to a handful of people who trust each other, thus limiting the richness and variety of ideas that could be brought forward through a larger group because of the nearly endemic nature of this problem? It is vitally important for the leaders of the United States to know the real state of affairs internationally, and this can occur only if foreign leaders feel free to speak their minds to our diplomats.Until recently, it looked as if the media had convinced the public that journalists were more reliable than the government; however, this may be changing. With the passage of time, the media have lost lustre. They—having grown large and powerful—provoke the same public skepticism that other large institutions in the society do. A series of media scandals has contributed to this. Many Americans have concluded that the media are no more credible than the government, and public opinion surveys reflect much ambivalence about the press.While leaks are generally defended by media officials on the grounds of the public‘s ―right to know, in reality they are part of the Washington political power game, as well as part of the policy process. The "leaker" may be currying favour with the media, or may be planting information to influence policy. In the first case, he is helping himself by enhancing the prestige of a journalist; in the second, he is using the media as a stage for his preferred policies. In either instance, it closes the circle: the leak begins with a political motive, is advanced by a politicized media, and continues because of politics. Although some of the journalists think they are doing the work, they are more often than not instruments of the process, not prime movers. The media must be held accountable for their activities, just like every other significant institution in our society, and the media must be forced to earn the public‘s trust. Implicit in the author‘s argument that leaks result in far more limited and unreliable policy discussions with foreign leaders is the idea that: ... more
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:
Suspicious as they are of American intentions, and bolstered by court rulings that seem to give them license to seek out and publish any and all government secrets, the media‘s distrust of our government, combined with their limited understanding of the world at large, damages our ability to design and conduct good policy in ways that the media rarely imagine.
The leak through which sensitive information flows from the government to the press is detrimental to policy in so far as it almost completely precludes the possibility of serious discussion. The fear that anything they say, even in what is construed as a private forum, may appear in print, makes many people, whether our own government officials or the leaders of foreign countries, unwilling to speak their minds.
Must we be content with the restriction of our leaders‘ policy discussions to a handful of people who trust each other, thus limiting the richness and variety of ideas that could be brought forward through a larger group because of the nearly endemic nature of this problem? It is vitally important for the leaders of the United States to know the real state of affairs internationally, and this can occur only if foreign leaders feel free to speak their minds to our diplomats.
Until recently, it looked as if the media had convinced the public that journalists were more reliable than the government; however, this may be changing. With the passage of time, the media have lost lustre. They—having grown large and powerful—provoke the same public skepticism that other large institutions in the society do. A series of media scandals has contributed to this. Many Americans have concluded that the media are no more credible than the government, and public opinion surveys reflect much ambivalence about the press.
While leaks are generally defended by media officials on the grounds of the public‘s ―right to know, in reality they are part of the Washington political power game, as well as part of the policy process. The "leaker" may be currying favour with the media, or may be planting information to influence policy. In the first case, he is helping himself by enhancing the prestige of a journalist; in the second, he is using the media as a stage for his preferred policies. In either instance, it closes the circle: the leak begins with a political motive, is advanced by a politicized media, and continues because of politics. Although some of the journalists think they are doing the work, they are more often than not instruments of the process, not prime movers. The media must be held accountable for their activities, just like every other significant institution in our society, and the media must be forced to earn the public‘s trust.
Implicit in the author‘s argument that leaks result in far more limited and unreliable policy discussions with foreign leaders is the idea that:
|
|
Gaurav Gupta
asked a question
|
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:Suspicious as they are of American intentions, and bolstered by court rulings that seem to give them license to seek out and publish any and all government secrets, the media‘s distrust of our government, combined with their limited understanding of the world at large, damages our ability to design and conduct good policy in ways that the media rarely imagine.The leak through which sensitive information flows from the government to the press is detrimental to policy in so far as it almost completely precludes the possibility of serious discussion. The fear that anything they say, even in what is construed as a private forum, may appear in print, makes many people, whether our own government officials or the leaders of foreign countries, unwilling to speak their minds.Must we be content with the restriction of our leaders‘ policy discussions to a handful of people who trust each other, thus limiting the richness and variety of ideas that could be brought forward through a larger group because of the nearly endemic nature of this problem? It is vitally important for the leaders of the United States to know the real state of affairs internationally, and this can occur only if foreign leaders feel free to speak their minds to our diplomats.Until recently, it looked as if the media had convinced the public that journalists were more reliable than the government; however, this may be changing. With the passage of time, the media have lost lustre. They—having grown large and powerful—provoke the same public skepticism that other large institutions in the society do. A series of media scandals has contributed to this. Many Americans have concluded that the media are no more credible than the government, and public opinion surveys reflect much ambivalence about the press.While leaks are generally defended by media officials on the grounds of the public‘s ―right to know,in reality they are part of the Washington political power game, as well as part of the policy process. The "leaker" may be currying favour with the media, or may be planting information to influence policy. In the first case, he is helping himself by enhancing the prestige of a journalist; in the second, he is using the media as a stage for his preferred policies. In either instance, it closes the circle: the leak begins with a political motive, is advanced by a politicized media, and continues because of politics. Although some of the journalists think they are doing the work, they are more often than not instruments of the process, not prime movers. The media must be held accountable for their activities, just like every other significant institution in our society, and the media must be forced to earn the public‘s trust.Based on the information in the passage, with which of the following statements would the author most likely disagree? ... more
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:
Suspicious as they are of American intentions, and bolstered by court rulings that seem to give them license to seek out and publish any and all government secrets, the media‘s distrust of our government, combined with their limited understanding of the world at large, damages our ability to design and conduct good policy in ways that the media rarely imagine.
The leak through which sensitive information flows from the government to the press is detrimental to policy in so far as it almost completely precludes the possibility of serious discussion. The fear that anything they say, even in what is construed as a private forum, may appear in print, makes many people, whether our own government officials or the leaders of foreign countries, unwilling to speak their minds.
Must we be content with the restriction of our leaders‘ policy discussions to a handful of people who trust each other, thus limiting the richness and variety of ideas that could be brought forward through a larger group because of the nearly endemic nature of this problem? It is vitally important for the leaders of the United States to know the real state of affairs internationally, and this can occur only if foreign leaders feel free to speak their minds to our diplomats.
Until recently, it looked as if the media had convinced the public that journalists were more reliable than the government; however, this may be changing. With the passage of time, the media have lost lustre. They—having grown large and powerful—provoke the same public skepticism that other large institutions in the society do. A series of media scandals has contributed to this. Many Americans have concluded that the media are no more credible than the government, and public opinion surveys reflect much ambivalence about the press.
While leaks are generally defended by media officials on the grounds of the public‘s ―right to know,in reality they are part of the Washington political power game, as well as part of the policy process. The "leaker" may be currying favour with the media, or may be planting information to influence policy. In the first case, he is helping himself by enhancing the prestige of a journalist; in the second, he is using the media as a stage for his preferred policies. In either instance, it closes the circle: the leak begins with a political motive, is advanced by a politicized media, and continues because of politics. Although some of the journalists think they are doing the work, they are more often than not instruments of the process, not prime movers. The media must be held accountable for their activities, just like every other significant institution in our society, and the media must be forced to earn the public‘s trust.
Based on the information in the passage, with which of the following statements would the author most likely disagree?
|
|
Gauri Krishnan
asked a question
|
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:Henry Varnum Poor, editor of American Railroad Journal, drew the important elements of the image of the railroad together in 1851, ―Look at the results of this material progress, the vigor, life, and executive energy that followed in its train, rapidly succeeded by wealth, the refinement and intellectual culture of a high civilization. All this is typified, in a degree, by a locomotive. The combination in its construction of nice art and scientific application of power, its speed surpassing that of our proudest courser, and its immense strength, are all characteristic of our age and tendencies. To us, like the telegraph, it is essential, it constitutes a part of our nature, is a condition of our being what we are.In the third decade of the nineteenth century, Americans began to define their character in light of the new railroads. They liked the idea that it took special people to foresee and capitalize on the promise of science. Railroad promoters, using the steam engine as a metaphor for what they thought Americans were and what they thought Americans were becoming, frequently discussed parallels between the locomotive and national character, pointing out that both possessed youth, power, speed, single-mindedness, and bright prospects.Poor was, of course, promoting acceptance of railroads and enticing his readers to open their pocketbooks. But his metaphors had their dark side. A locomotive was quite unlike anything Americans had ever seen. It was large, mysterious and dangerous; many thought that it was a monster waiting to devour the unwary. There was a suspicion that a country founded upon Jeffersonian agrarian principles had bought a ticket and boarded a train pulled by some iron monster into the dark recesses of an unknown future.To ease such public apprehensions, promoters, poets, editors, and writers alike adopted the notion that locomotives were really only ―iron horses,‖ an early metaphor that lingered because it made steam technology ordinary and understandable. Iron horse metaphors assuaged fears about inherent defects in the national character, prompting images of a more secure future, and made an alien technology less frightening, and even comforting and congenial.Essayist Ralph Waldo Emerson saw the locomotive as an agent of domestic harmony. He observed that ―the locomotive and the steamboat, like enormous shuttles, shoot every day across the thousand various threads of national descent and employment and bind them fast in one web,"adding ―an hourly assimilation goes forward, and there is no danger that local peculiarities and hostilities should be preserved. To us Americans, it seems to have fallen as a political aid. We could not else have held the vast North America together, which we now engage to do."Suppose that an early nineteenth-century American inventor had developed a device that made it easier to construct multi-story building. How would early nineteenth-century Americans be expected to react to this invention? ... more
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:
Henry Varnum Poor, editor of American Railroad Journal, drew the important elements of the image of the railroad together in 1851, ―Look at the results of this material progress, the vigor, life, and executive energy that followed in its train, rapidly succeeded by wealth, the refinement and intellectual culture of a high civilization. All this is typified, in a degree, by a locomotive. The combination in its construction of nice art and scientific application of power, its speed surpassing that of our proudest courser, and its immense strength, are all characteristic of our age and tendencies. To us, like the telegraph, it is essential, it constitutes a part of our nature, is a condition of our being what we are.
In the third decade of the nineteenth century, Americans began to define their character in light of the new railroads. They liked the idea that it took special people to foresee and capitalize on the promise of science. Railroad promoters, using the steam engine as a metaphor for what they thought Americans were and what they thought Americans were becoming, frequently discussed parallels between the locomotive and national character, pointing out that both possessed youth, power, speed, single-mindedness, and bright prospects.
Poor was, of course, promoting acceptance of railroads and enticing his readers to open their pocketbooks. But his metaphors had their dark side. A locomotive was quite unlike anything Americans had ever seen. It was large, mysterious and dangerous; many thought that it was a monster waiting to devour the unwary. There was a suspicion that a country founded upon Jeffersonian agrarian principles had bought a ticket and boarded a train pulled by some iron monster into the dark recesses of an unknown future.
To ease such public apprehensions, promoters, poets, editors, and writers alike adopted the notion that locomotives were really only ―iron horses,‖ an early metaphor that lingered because it made steam technology ordinary and understandable. Iron horse metaphors assuaged fears about inherent defects in the national character, prompting images of a more secure future, and made an alien technology less frightening, and even comforting and congenial.
Essayist Ralph Waldo Emerson saw the locomotive as an agent of domestic harmony. He observed that ―the locomotive and the steamboat, like enormous shuttles, shoot every day across the thousand various threads of national descent and employment and bind them fast in one web,"adding ―an hourly assimilation goes forward, and there is no danger that local peculiarities and hostilities should be preserved. To us Americans, it seems to have fallen as a political aid. We could not else have held the vast North America together, which we now engage to do."
Suppose that an early nineteenth-century American inventor had developed a device that made it easier to construct multi-story building. How would early nineteenth-century Americans be expected to react to this invention?
|
|
Camila Rodriguez
asked a question
|
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:Henry Varnum Poor, editor of American Railroad Journal, drew the important elements of the image of the railroad together in 1851, ―Look at the results of this material progress, the vigor, life, and executive energy that followed in its train, rapidly succeeded by wealth, the refinement and intellectual culture of a high civilization. All this is typified, in a degree, by a locomotive. The combination in its construction of nice art and scientific application of power, its speed surpassing that of our proudest courser, and its immense strength, are all characteristic of our age and tendencies. To us, like the telegraph, it is essential, it constitutes a part of our nature, is a condition of our being what we are.In the third decade of the nineteenth century, Americans began to define their character in light of the new railroads. They liked the idea that it took special people to foresee and capitalize on the promise of science. Railroad promoters, using the steam engine as a metaphor for what they thought Americans were and what they thought Americans were becoming, frequently discussed parallels between the locomotive and national character, pointing out that both possessed youth, power, speed, single-mindedness, and bright prospects.Poor was, of course, promoting acceptance of railroads and enticing his readers to open their pocketbooks. But his metaphors had their dark side. A locomotive was quite unlike anything Americans had ever seen. It was large, mysterious and dangerous; many thought that it was a monster waiting to devour the unwary. There was a suspicion that a country founded upon Jeffersonian agrarian principles had bought a ticket and boarded a train pulled by some iron monster into the dark recesses of an unknown future.To ease such public apprehensions, promoters, poets, editors, and writers alike adopted the notion that locomotives were really only ―iron horses,‖ an early metaphor that lingered because it made steam technology ordinary and understandable. Iron horse metaphors assuaged fears about inherent defects in the national character, prompting images of a more secure future, and made an alien technology less frightening, and even comforting and congenial.Essayist Ralph Waldo Emerson saw the locomotive as an agent of domestic harmony. He observed that ―the locomotive and the steamboat, like enormous shuttles, shoot every day across the thousand various threads of national descent and employment and bind them fast in one web,"adding ―an hourly assimilation goes forward, and there is no danger that local peculiarities and hostilities should be preserved. To us Americans, it seems to have fallen as a political aid. We could not else have held the vast North America together, which we now engage to do."According to the passage, which of the following is most likely to be true about Ralph Waldo Emerson‘s beliefs? ... more
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:
Henry Varnum Poor, editor of American Railroad Journal, drew the important elements of the image of the railroad together in 1851, ―Look at the results of this material progress, the vigor, life, and executive energy that followed in its train, rapidly succeeded by wealth, the refinement and intellectual culture of a high civilization. All this is typified, in a degree, by a locomotive. The combination in its construction of nice art and scientific application of power, its speed surpassing that of our proudest courser, and its immense strength, are all characteristic of our age and tendencies. To us, like the telegraph, it is essential, it constitutes a part of our nature, is a condition of our being what we are.
In the third decade of the nineteenth century, Americans began to define their character in light of the new railroads. They liked the idea that it took special people to foresee and capitalize on the promise of science. Railroad promoters, using the steam engine as a metaphor for what they thought Americans were and what they thought Americans were becoming, frequently discussed parallels between the locomotive and national character, pointing out that both possessed youth, power, speed, single-mindedness, and bright prospects.
Poor was, of course, promoting acceptance of railroads and enticing his readers to open their pocketbooks. But his metaphors had their dark side. A locomotive was quite unlike anything Americans had ever seen. It was large, mysterious and dangerous; many thought that it was a monster waiting to devour the unwary. There was a suspicion that a country founded upon Jeffersonian agrarian principles had bought a ticket and boarded a train pulled by some iron monster into the dark recesses of an unknown future.
To ease such public apprehensions, promoters, poets, editors, and writers alike adopted the notion that locomotives were really only ―iron horses,‖ an early metaphor that lingered because it made steam technology ordinary and understandable. Iron horse metaphors assuaged fears about inherent defects in the national character, prompting images of a more secure future, and made an alien technology less frightening, and even comforting and congenial.
Essayist Ralph Waldo Emerson saw the locomotive as an agent of domestic harmony. He observed that ―the locomotive and the steamboat, like enormous shuttles, shoot every day across the thousand various threads of national descent and employment and bind them fast in one web,"adding ―an hourly assimilation goes forward, and there is no danger that local peculiarities and hostilities should be preserved. To us Americans, it seems to have fallen as a political aid. We could not else have held the vast North America together, which we now engage to do."
According to the passage, which of the following is most likely to be true about Ralph Waldo Emerson‘s beliefs?
|
|
Gabriella Thompson
asked a question
|
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:Henry Varnum Poor, editor of American Railroad Journal, drew the important elements of the image of the railroad together in 1851, ―Look at the results of this material progress, the vigor, life, and executive energy that followed in its train, rapidly succeeded by wealth, the refinement and intellectual culture of a high civilization. All this is typified, in a degree, by a locomotive. The combination in its construction of nice art and scientific application of power, its speed surpassing that of our proudest courser, and its immense strength, are all characteristic of our age and tendencies. To us, like the telegraph, it is essential, it constitutes a part of our nature, is a condition of our being what we are.In the third decade of the nineteenth century, Americans began to define their character in light of the new railroads. They liked the idea that it took special people to foresee and capitalize on the promise of science. Railroad promoters, using the steam engine as a metaphor for what they thought Americans were and what they thought Americans were becoming, frequently discussed parallels between the locomotive and national character, pointing out that both possessed youth, power, speed, single-mindedness, and bright prospects.Poor was, of course, promoting acceptance of railroads and enticing his readers to open their pocketbooks. But his metaphors had their dark side. A locomotive was quite unlike anything Americans had ever seen. It was large, mysterious and dangerous; many thought that it was a monster waiting to devour the unwary. There was a suspicion that a country founded upon Jeffersonian agrarian principles had bought a ticket and boarded a train pulled by some iron monster into the dark recesses of an unknown future.To ease such public apprehensions, promoters, poets, editors, and writers alike adopted the notion that locomotives were really only ―iron horses,‖ an early metaphor that lingered because it made steam technology ordinary and understandable. Iron horse metaphors assuaged fears about inherent defects in the national character, prompting images of a more secure future, and made an alien technology less frightening, and even comforting and congenial.Essayist Ralph Waldo Emerson saw the locomotive as an agent of domestic harmony. He observed that ―the locomotive and the steamboat, like enormous shuttles, shoot every day across the thousand various threads of national descent and employment and bind them fast in one web, "adding ―an hourly assimilation goes forward, and there is no danger that local peculiarities and hostilities should be preserved. To us Americans, it seems to have fallen as a political aid. We could not else have held the vast North America together, which we now engage to do"The passage is primarily concerned with which of the following? ... more
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:
Henry Varnum Poor, editor of American Railroad Journal, drew the important elements of the image of the railroad together in 1851, ―Look at the results of this material progress, the vigor, life, and executive energy that followed in its train, rapidly succeeded by wealth, the refinement and intellectual culture of a high civilization. All this is typified, in a degree, by a locomotive. The combination in its construction of nice art and scientific application of power, its speed surpassing that of our proudest courser, and its immense strength, are all characteristic of our age and tendencies. To us, like the telegraph, it is essential, it constitutes a part of our nature, is a condition of our being what we are.
In the third decade of the nineteenth century, Americans began to define their character in light of the new railroads. They liked the idea that it took special people to foresee and capitalize on the promise of science. Railroad promoters, using the steam engine as a metaphor for what they thought Americans were and what they thought Americans were becoming, frequently discussed parallels between the locomotive and national character, pointing out that both possessed youth, power, speed, single-mindedness, and bright prospects.
Poor was, of course, promoting acceptance of railroads and enticing his readers to open their pocketbooks. But his metaphors had their dark side. A locomotive was quite unlike anything Americans had ever seen. It was large, mysterious and dangerous; many thought that it was a monster waiting to devour the unwary. There was a suspicion that a country founded upon Jeffersonian agrarian principles had bought a ticket and boarded a train pulled by some iron monster into the dark recesses of an unknown future.
To ease such public apprehensions, promoters, poets, editors, and writers alike adopted the notion that locomotives were really only ―iron horses,‖ an early metaphor that lingered because it made steam technology ordinary and understandable. Iron horse metaphors assuaged fears about inherent defects in the national character, prompting images of a more secure future, and made an alien technology less frightening, and even comforting and congenial.
Essayist Ralph Waldo Emerson saw the locomotive as an agent of domestic harmony. He observed that ―the locomotive and the steamboat, like enormous shuttles, shoot every day across the thousand various threads of national descent and employment and bind them fast in one web, "adding ―an hourly assimilation goes forward, and there is no danger that local peculiarities and hostilities should be preserved. To us Americans, it seems to have fallen as a political aid. We could not else have held the vast North America together, which we now engage to do"
The passage is primarily concerned with which of the following?
|
|
Neha Datta
asked a question
|
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:Henry Varnum Poor, editor of American Railroad Journal, drew the important elements of the image of the railroad together in 1851, ―Look at the results of this material progress, the vigor, life, and executive energy that followed in its train, rapidly succeeded by wealth, the refinement and intellectual culture of a high civilization. All this is typified, in a degree, by a locomotive. The combination in its construction of nice art and scientific application of power, its speed surpassing that of our proudest courser, and its immense strength, are all characteristic of our age and tendencies. To us, like the telegraph, it is essential, it constitutes a part of our nature, is a condition of our being what we are.In the third decade of the nineteenth century, Americans began to define their character in light of the new railroads. They liked the idea that it took special people to foresee and capitalize on the promise of science. Railroad promoters, using the steam engine as a metaphor for what they thought Americans were and what they thought Americans were becoming, frequently discussed parallels between the locomotive and national character, pointing out that both possessed youth, power, speed, single-mindedness, and bright prospects.Poor was, of course, promoting acceptance of railroads and enticing his readers to open their pocketbooks. But his metaphors had their dark side. A locomotive was quite unlike anything Americans had ever seen. It was large, mysterious and dangerous; many thought that it was a monster waiting to devour the unwary. There was a suspicion that a country founded upon Jeffersonian agrarian principles had bought a ticket and boarded a train pulled by some iron monster into the dark recesses of an unknown future.To ease such public apprehensions, promoters, poets, editors, and writers alike adopted the notion that locomotives were really only ―iron horses, an early metaphor that lingered because it made steam technology ordinary and understandable. Iron horse metaphors assuaged fears about inherent defects in the national character, prompting images of a more secure future, and made an alien technology less frightening, and even comforting and congenial.Essayist Ralph Waldo Emerson saw the locomotive as an agent of domestic harmony. He observed that ―the locomotive and the steamboat, like enormous shuttles, shoot every day across the thousand various threads of national descent and employment and bind them fast in one web, adding ―an hourly assimilation goes forward, and there is no danger that local peculiarities and hostilities should be preserved. To us Americans, it seems to have fallen as a political aid. We could not else have held the vast North America together, which we now engage to do.Which of the following claims would the author of the passage most agree with? ... more
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:
Henry Varnum Poor, editor of American Railroad Journal, drew the important elements of the image of the railroad together in 1851, ―Look at the results of this material progress, the vigor, life, and executive energy that followed in its train, rapidly succeeded by wealth, the refinement and intellectual culture of a high civilization. All this is typified, in a degree, by a locomotive. The combination in its construction of nice art and scientific application of power, its speed surpassing that of our proudest courser, and its immense strength, are all characteristic of our age and tendencies. To us, like the telegraph, it is essential, it constitutes a part of our nature, is a condition of our being what we are.
In the third decade of the nineteenth century, Americans began to define their character in light of the new railroads. They liked the idea that it took special people to foresee and capitalize on the promise of science. Railroad promoters, using the steam engine as a metaphor for what they thought Americans were and what they thought Americans were becoming, frequently discussed parallels between the locomotive and national character, pointing out that both possessed youth, power, speed, single-mindedness, and bright prospects.
Poor was, of course, promoting acceptance of railroads and enticing his readers to open their pocketbooks. But his metaphors had their dark side. A locomotive was quite unlike anything Americans had ever seen. It was large, mysterious and dangerous; many thought that it was a monster waiting to devour the unwary. There was a suspicion that a country founded upon Jeffersonian agrarian principles had bought a ticket and boarded a train pulled by some iron monster into the dark recesses of an unknown future.
To ease such public apprehensions, promoters, poets, editors, and writers alike adopted the notion that locomotives were really only ―iron horses, an early metaphor that lingered because it made steam technology ordinary and understandable. Iron horse metaphors assuaged fears about inherent defects in the national character, prompting images of a more secure future, and made an alien technology less frightening, and even comforting and congenial.
Essayist Ralph Waldo Emerson saw the locomotive as an agent of domestic harmony. He observed that ―the locomotive and the steamboat, like enormous shuttles, shoot every day across the thousand various threads of national descent and employment and bind them fast in one web, adding ―an hourly assimilation goes forward, and there is no danger that local peculiarities and hostilities should be preserved. To us Americans, it seems to have fallen as a political aid. We could not else have held the vast North America together, which we now engage to do.
Which of the following claims would the author of the passage most agree with?
|
|
Oliver Hall
asked a question
|
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:Once surrounded and protected by vast wilderness, many of the national parks are adversely affected by activities outside their boundaries. The National Park Organic Act established the national park system and empowered the Secretary of the Interior to manage activities within the parks. Conditions outside park boundaries are not subject to regulation by the Park Service unless they involve the direct use of park resources.Several approaches to protecting the national parks from external degradation have been proposed, such as one focusing on enacting federal legislation granting the National Park Service broader powers over lands adjacent to the national parks. Legislation addressing external threats to the national parks twice passed the House of Representatives but died without action in the Senate. Also brought to the table as a possible remedy is giving the states bordering the parks a significant and meaningful role in developing federal park management policy.Because the livelihood of many citizens is linked to the management of national parks, local politicians often encourage state involvement in federal planning. But, state legislatures have not always addressed the fundamental policy issues of whether states should protect park wildlife.Timber harvesting, ranching and energy exploration compete with wildlife within the local ecosystem. Priorities among different land uses are not generally established by current legislation. Additionally, often no mechanism exists to coordinate planning by the state environmental regulatory agencies. These factors limit the impact of legislation aimed at protecting park wildlife and the larger park ecosystem.Even if these deficiencies can be overcome, state participation must be consistent with existing federal legislation. States lack jurisdiction within national parks themselves, and therefore state solutions cannot reach activities inside the parks, thus limiting state action to the land adjacent to the national parks. Under the supremacy clause, federal laws and regulations supersede state action if state law conflicts with federal legislation, if Congress precludes local regulation, or if federal regulation is so pervasive that no room remains for state control. Assuming that federal regulations leave open the possibility of state control, state participation in policy making must be harmonized with existing federal legislation.The residents of states bordering national parks are affected by park management policies. They in turn affect the success of those policies. This interrelationship must be considered in responding to the external threats problem. Local participation is necessary in deciding how to protect park wildlife. Local interests should not, however, dictate national policy, nor should they be used as a pretext to ignore the threats to park regions.According to the passage, which of the following developments is most likely if environmental cooperation between the federal government and state governments does not improve? ... more
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:
Once surrounded and protected by vast wilderness, many of the national parks are adversely affected by activities outside their boundaries. The National Park Organic Act established the national park system and empowered the Secretary of the Interior to manage activities within the parks. Conditions outside park boundaries are not subject to regulation by the Park Service unless they involve the direct use of park resources.
Several approaches to protecting the national parks from external degradation have been proposed, such as one focusing on enacting federal legislation granting the National Park Service broader powers over lands adjacent to the national parks. Legislation addressing external threats to the national parks twice passed the House of Representatives but died without action in the Senate. Also brought to the table as a possible remedy is giving the states bordering the parks a significant and meaningful role in developing federal park management policy.
Because the livelihood of many citizens is linked to the management of national parks, local politicians often encourage state involvement in federal planning. But, state legislatures have not always addressed the fundamental policy issues of whether states should protect park wildlife.
Timber harvesting, ranching and energy exploration compete with wildlife within the local ecosystem. Priorities among different land uses are not generally established by current legislation. Additionally, often no mechanism exists to coordinate planning by the state environmental regulatory agencies. These factors limit the impact of legislation aimed at protecting park wildlife and the larger park ecosystem.
Even if these deficiencies can be overcome, state participation must be consistent with existing federal legislation. States lack jurisdiction within national parks themselves, and therefore state solutions cannot reach activities inside the parks, thus limiting state action to the land adjacent to the national parks. Under the supremacy clause, federal laws and regulations supersede state action if state law conflicts with federal legislation, if Congress precludes local regulation, or if federal regulation is so pervasive that no room remains for state control. Assuming that federal regulations leave open the possibility of state control, state participation in policy making must be harmonized with existing federal legislation.
The residents of states bordering national parks are affected by park management policies. They in turn affect the success of those policies. This interrelationship must be considered in responding to the external threats problem. Local participation is necessary in deciding how to protect park wildlife. Local interests should not, however, dictate national policy, nor should they be used as a pretext to ignore the threats to park regions.
According to the passage, which of the following developments is most likely if environmental cooperation between the federal government and state governments does not improve?
|
|
Evelyn Wright
asked a question
|
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:Once surrounded and protected by vast wilderness, many of the national parks are adversely affected by activities outside their boundaries. The National Park Organic Act established the national park system and empowered the Secretary of the Interior to manage activities within the parks. Conditions outside park boundaries are not subject to regulation by the Park Service unless they involve the direct use of park resources.Several approaches to protecting the national parks from external degradation have been proposed, such as one focusing on enacting federal legislation granting the National Park Service broader powers over lands adjacent to the national parks. Legislation addressing external threats to the national parks twice passed the House of Representatives but died without action in the Senate. Also brought to the table as a possible remedy is giving the states bordering the parks a significant and meaningful role in developing federal park management policy.Because the livelihood of many citizens is linked to the management of national parks, local politicians often encourage state involvement in federal planning. But, state legislatures have not always addressed the fundamental policy issues of whether states should protect park wildlife.Timber harvesting, ranching and energy exploration compete with wildlife within the local ecosystem. Priorities among different land uses are not generally established by current legislation. Additionally, often no mechanism exists to coordinate planning by the state environmental regulatory agencies. These factors limit the impact of legislation aimed at protecting park wildlife and the larger park ecosystem.Even if these deficiencies can be overcome, state participation must be consistent with existing federal legislation. States lack jurisdiction within national parks themselves, and therefore state solutions cannot reach activities inside the parks, thus limiting state action to the land adjacent to the national parks. Under the supremacy clause, federal laws and regulations supersede state action if state law conflicts with federal legislation, if Congress precludes local regulation, or if federal regulation is so pervasive that no room remains for state control. Assuming that federal regulations leave open the possibility of state control, state participation in policy making must be harmonized with existing federal legislation.The residents of states bordering national parks are affected by park management policies. They in turn affect the success of those policies. This interrelationship must be considered in responding to the external threats problem. Local participation is necessary in deciding how to protect park wildlife. Local interests should not, however, dictate national policy, nor should they be used as a pretext to ignore the threats to park regions.In the context of the passage, the phrase external degradation (lines 8-9) refers to which of the following: ... more
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:
Once surrounded and protected by vast wilderness, many of the national parks are adversely affected by activities outside their boundaries. The National Park Organic Act established the national park system and empowered the Secretary of the Interior to manage activities within the parks. Conditions outside park boundaries are not subject to regulation by the Park Service unless they involve the direct use of park resources.
Several approaches to protecting the national parks from external degradation have been proposed, such as one focusing on enacting federal legislation granting the National Park Service broader powers over lands adjacent to the national parks. Legislation addressing external threats to the national parks twice passed the House of Representatives but died without action in the Senate. Also brought to the table as a possible remedy is giving the states bordering the parks a significant and meaningful role in developing federal park management policy.
Because the livelihood of many citizens is linked to the management of national parks, local politicians often encourage state involvement in federal planning. But, state legislatures have not always addressed the fundamental policy issues of whether states should protect park wildlife.
Timber harvesting, ranching and energy exploration compete with wildlife within the local ecosystem. Priorities among different land uses are not generally established by current legislation. Additionally, often no mechanism exists to coordinate planning by the state environmental regulatory agencies. These factors limit the impact of legislation aimed at protecting park wildlife and the larger park ecosystem.
Even if these deficiencies can be overcome, state participation must be consistent with existing federal legislation. States lack jurisdiction within national parks themselves, and therefore state solutions cannot reach activities inside the parks, thus limiting state action to the land adjacent to the national parks. Under the supremacy clause, federal laws and regulations supersede state action if state law conflicts with federal legislation, if Congress precludes local regulation, or if federal regulation is so pervasive that no room remains for state control. Assuming that federal regulations leave open the possibility of state control, state participation in policy making must be harmonized with existing federal legislation.
The residents of states bordering national parks are affected by park management policies. They in turn affect the success of those policies. This interrelationship must be considered in responding to the external threats problem. Local participation is necessary in deciding how to protect park wildlife. Local interests should not, however, dictate national policy, nor should they be used as a pretext to ignore the threats to park regions.
In the context of the passage, the phrase external degradation (lines 8-9) refers to which of the following:
|
|
Isha Kaur
asked a question
|
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:Once surrounded and protected by vast wilderness, many of the national parks are adversely affected by activities outside their boundaries. The National Park Organic Act established the national park system and empowered the Secretary of the Interior to manage activities within the parks. Conditions outside park boundaries are not subject to regulation by the Park Service unless they involve the direct use of park resources.Several approaches to protecting the national parks from external degradation have been proposed, such as one focusing on enacting federal legislation granting the National Park Service broader powers over lands adjacent to the national parks. Legislation addressing external threats to the national parks twice passed the House of Representatives but died without action in the Senate. Also brought to the table as a possible remedy is giving the states bordering the parks a significant and meaningful role in developing federal park management policy.Because the livelihood of many citizens is linked to the management of national parks, local politicians often encourage state involvement in federal planning. But, state legislatures have not always addressed the fundamental policy issues of whether states should protect park wildlife.Timber harvesting, ranching and energy exploration compete with wildlife within the local ecosystem. Priorities among different land uses are not generally established by current legislation. Additionally, often no mechanism exists to coordinate planning by the state environmental regulatory agencies. These factors limit the impact of legislation aimed at protecting park wildlife and the larger park ecosystem.Even if these deficiencies can be overcome, state participation must be consistent with existing federal legislation. States lack jurisdiction within national parks themselves, and therefore state solutions cannot reach activities inside the parks, thus limiting state action to the land adjacent to the national parks. Under the supremacy clause, federal laws and regulations supersede state action if state law conflicts with federal legislation, if Congress precludes local regulation, or if federal regulation is so pervasive that no room remains for state control. Assuming that federal regulations leave open the possibility of state control, state participation in policy making must be harmonized with existing federal legislation.The residents of states bordering national parks are affected by park management policies. They in turn affect the success of those policies. This interrelationship must be considered in responding to the external threats problem. Local participation is necessary in deciding how to protect park wildlife. Local interests should not, however, dictate national policy, nor should they be used as a pretext to ignore the threats to park regions.The passage provides support for which of the following assertions? ... more
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:
Once surrounded and protected by vast wilderness, many of the national parks are adversely affected by activities outside their boundaries. The National Park Organic Act established the national park system and empowered the Secretary of the Interior to manage activities within the parks. Conditions outside park boundaries are not subject to regulation by the Park Service unless they involve the direct use of park resources.
Several approaches to protecting the national parks from external degradation have been proposed, such as one focusing on enacting federal legislation granting the National Park Service broader powers over lands adjacent to the national parks. Legislation addressing external threats to the national parks twice passed the House of Representatives but died without action in the Senate. Also brought to the table as a possible remedy is giving the states bordering the parks a significant and meaningful role in developing federal park management policy.
Because the livelihood of many citizens is linked to the management of national parks, local politicians often encourage state involvement in federal planning. But, state legislatures have not always addressed the fundamental policy issues of whether states should protect park wildlife.
Timber harvesting, ranching and energy exploration compete with wildlife within the local ecosystem. Priorities among different land uses are not generally established by current legislation. Additionally, often no mechanism exists to coordinate planning by the state environmental regulatory agencies. These factors limit the impact of legislation aimed at protecting park wildlife and the larger park ecosystem.
Even if these deficiencies can be overcome, state participation must be consistent with existing federal legislation. States lack jurisdiction within national parks themselves, and therefore state solutions cannot reach activities inside the parks, thus limiting state action to the land adjacent to the national parks. Under the supremacy clause, federal laws and regulations supersede state action if state law conflicts with federal legislation, if Congress precludes local regulation, or if federal regulation is so pervasive that no room remains for state control. Assuming that federal regulations leave open the possibility of state control, state participation in policy making must be harmonized with existing federal legislation.
The residents of states bordering national parks are affected by park management policies. They in turn affect the success of those policies. This interrelationship must be considered in responding to the external threats problem. Local participation is necessary in deciding how to protect park wildlife. Local interests should not, however, dictate national policy, nor should they be used as a pretext to ignore the threats to park regions.
The passage provides support for which of the following assertions?
|
|
Maheshwar Shah
asked a question
|
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:Once surrounded and protected by vast wilderness, many of the national parks are adversely affected by activities outside their boundaries. The National Park Organic Act established the national park system and empowered the Secretary of the Interior to manage activities within the parks. Conditions outside park boundaries are not subject to regulation by the Park Service unless they involve the direct use of park resources.Several approaches to protecting the national parks from external degradation have been proposed, such as one focusing on enacting federal legislation granting the National Park Service broader powers over lands adjacent to the national parks. Legislation addressing external threats to the national parks twice passed the House of Representatives but died without action in the Senate. Also brought to the table as a possible remedy is giving the states bordering the parks a significant and meaningful role in developing federal park management policy.Because the livelihood of many citizens is linked to the management of national parks, local politicians often encourage state involvement in federal planning. But, state legislatures have not always addressed the fundamental policy issues of whether states should protect park wildlife.Timber harvesting, ranching and energy exploration compete with wildlife within the local ecosystem. Priorities among different land uses are not generally established by current legislation. Additionally, often no mechanism exists to coordinate planning by the state environmental regulatory agencies. These factors limit the impact of legislation aimed at protecting park wildlife and the larger park ecosystem.Even if these deficiencies can be overcome, state participation must be consistent with existing federal legislation. States lack jurisdiction within national parks themselves, and therefore state solutions cannot reach activities inside the parks, thus limiting state action to the land adjacent to the national parks. Under the supremacy clause, federal laws and regulations supersede state action if state law conflicts with federal legislation, if Congress precludes local regulation, or if federal regulation is so pervasive that no room remains for state control. Assuming that federal regulations leave open the possibility of state control, state participation in policy making must be harmonized with existing federal legislation.The residents of states bordering national parks are affected by park management policies. They in turn affect the success of those policies. This interrelationship must be considered in responding to the external threats problem. Local participation is necessary in deciding how to protect park wildlife. Local interests should not, however, dictate national policy, nor should they be used as a pretext to ignore the threats to park regions. What is the main purpose of the author in writing the passage? ... more
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the question given below:
Once surrounded and protected by vast wilderness, many of the national parks are adversely affected by activities outside their boundaries. The National Park Organic Act established the national park system and empowered the Secretary of the Interior to manage activities within the parks. Conditions outside park boundaries are not subject to regulation by the Park Service unless they involve the direct use of park resources.
Several approaches to protecting the national parks from external degradation have been proposed, such as one focusing on enacting federal legislation granting the National Park Service broader powers over lands adjacent to the national parks. Legislation addressing external threats to the national parks twice passed the House of Representatives but died without action in the Senate. Also brought to the table as a possible remedy is giving the states bordering the parks a significant and meaningful role in developing federal park management policy.
Because the livelihood of many citizens is linked to the management of national parks, local politicians often encourage state involvement in federal planning. But, state legislatures have not always addressed the fundamental policy issues of whether states should protect park wildlife.
Timber harvesting, ranching and energy exploration compete with wildlife within the local ecosystem. Priorities among different land uses are not generally established by current legislation. Additionally, often no mechanism exists to coordinate planning by the state environmental regulatory agencies. These factors limit the impact of legislation aimed at protecting park wildlife and the larger park ecosystem.
Even if these deficiencies can be overcome, state participation must be consistent with existing federal legislation. States lack jurisdiction within national parks themselves, and therefore state solutions cannot reach activities inside the parks, thus limiting state action to the land adjacent to the national parks. Under the supremacy clause, federal laws and regulations supersede state action if state law conflicts with federal legislation, if Congress precludes local regulation, or if federal regulation is so pervasive that no room remains for state control. Assuming that federal regulations leave open the possibility of state control, state participation in policy making must be harmonized with existing federal legislation.
The residents of states bordering national parks are affected by park management policies. They in turn affect the success of those policies. This interrelationship must be considered in responding to the external threats problem. Local participation is necessary in deciding how to protect park wildlife. Local interests should not, however, dictate national policy, nor should they be used as a pretext to ignore the threats to park regions.
What is the main purpose of the author in writing the passage?
|
|
Shaan Choudhary
asked a question
|
Which of the following best describes the role of the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) in India's digital economy?- a) A model for cash transactions
- b) A benchmark for global digital payment solutions
- c) A government initiative for traditional banking
- d) A platform for cryptocurrency exchange
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following best describes the role of the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) in India's digital economy?
a)
A model for cash transactions
b)
A benchmark for global digital payment solutions
c)
A government initiative for traditional banking
d)
A platform for cryptocurrency exchange
|
|
Sakshi Chauhan
asked a question
|
What is the main challenge faced by individuals attempting to access healthy diets globally?- a) Excessive availability of fast food
- b) Cultural dietary restrictions
- c) High costs of nutritious foods
- d) Lack of variety in food options
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the main challenge faced by individuals attempting to access healthy diets globally?
a)
Excessive availability of fast food
b)
Cultural dietary restrictions
c)
High costs of nutritious foods
d)
Lack of variety in food options
|
|
Hina Choudhary
asked a question
|
What is the primary goal of the Ottawa Convention?- a) To regulate the production of arms
- b) To eliminate the use of anti-personnel mines
- c) To establish a framework for international education
- d) To promote trade between nations
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the primary goal of the Ottawa Convention?
a)
To regulate the production of arms
b)
To eliminate the use of anti-personnel mines
c)
To establish a framework for international education
d)
To promote trade between nations
|
|
Falak Desai
asked a question
|
Which factor significantly affects the funding opportunities for deep tech start-ups in India?- a) Lack of governmental support
- b) Perception of high risk by investors
- c) High competition from global start-ups
- d) Overemphasis on consumer services
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which factor significantly affects the funding opportunities for deep tech start-ups in India?
a)
Lack of governmental support
b)
Perception of high risk by investors
c)
High competition from global start-ups
d)
Overemphasis on consumer services
|
|
Lekha Malhotra
asked a question
|
What major infrastructure improvement does the new Pamban Bridge provide over its predecessor?- a) Increased height for larger vessels
- b) Higher train speed capabilities
- c) Longer overall length
- d) Enhanced historical significance
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What major infrastructure improvement does the new Pamban Bridge provide over its predecessor?
a)
Increased height for larger vessels
b)
Higher train speed capabilities
c)
Longer overall length
d)
Enhanced historical significance
|
|
Tanya Chauhan
asked a question
|
What key area is highlighted as a significant gap in India's start-up priorities compared to those in China?- a) Social media applications
- b) Electric mobility and artificial intelligence
- c) E-commerce platforms
- d) Online delivery services
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What key area is highlighted as a significant gap in India's start-up priorities compared to those in China?
a)
Social media applications
b)
Electric mobility and artificial intelligence
c)
E-commerce platforms
d)
Online delivery services

|
Swarnzeet Singh
asked a question
|
Consider the following statements:Assertion (A): Volcanoes are not likely to be found in the regions of the earthquake.Reason (R): Earthquakes are induced by seismic activity; volcanoes do not require seismic activity.In the context of the above, which of these is correct? - a) A is correct, and R is an appropriate explanation of A.
- b) A is correct, but R is not an appropriate explanation of A.
- c) A is incorrect, but R is correct.
- d) Both A and R are incorrect.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
Assertion (A): Volcanoes are not likely to be found in the regions of the earthquake.
Reason (R): Earthquakes are induced by seismic activity; volcanoes do not require seismic activity.
In the context of the above, which of these is correct?
a)
A is correct, and R is an appropriate explanation of A.
b)
A is correct, but R is not an appropriate explanation of A.
c)
A is incorrect, but R is correct.
d)
Both A and R are incorrect.

|
Keerthi Spandana N
asked a question
|
Anil buys 12 toys and labels each with the same selling price. He sells 8 toys initially at 20% discount on the labeled price. Then he sells the remaining 4 toys at an additional 25% discount on the discounted price. Thus, he gets a total of Rs 2112, and makes a 10% profit. With no discounts, his percentage of profit would have been- a)55
- b)60
- c)54
- d)50
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Anil buys 12 toys and labels each with the same selling price. He sells 8 toys initially at 20% discount on the labeled price. Then he sells the remaining 4 toys at an additional 25% discount on the discounted price. Thus, he gets a total of Rs 2112, and makes a 10% profit. With no discounts, his percentage of profit would have been
a)
55
b)
60
c)
54
d)
50
|
|
Megha Sharma
asked a question
|
Parliamentary committee means a committee that: 1. Is appointed or elected by the Speaker / Chairman or nominated by the House2. Works under the direction of the Speaker / ChairmanWhich of these statements are correct?- a)1 Only
- b)2 Only
- c)Both 1 and 2
- d)Neither 1 nor 2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Parliamentary committee means a committee that:
1. Is appointed or elected by the Speaker / Chairman or nominated by the House
2. Works under the direction of the Speaker / Chairman
Which of these statements are correct?
a)
1 Only
b)
2 Only
c)
Both 1 and 2
d)
Neither 1 nor 2

|
J3rry
asked a question
|
Traders A and B buy two goods for Rs. 1000 and Rs. 2000 respectively. Trader A marks his goods up by x%, while trader B marks his goods up by 2x% and offers a discount of x%. If both make the same non-zero profit, find x.- a)25%
- b)12.5%
- c)37.5%
- d)40%
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Traders A and B buy two goods for Rs. 1000 and Rs. 2000 respectively. Trader A marks his goods up by x%, while trader B marks his goods up by 2x% and offers a discount of x%. If both make the same non-zero profit, find x.
a)
25%
b)
12.5%
c)
37.5%
d)
40%
|
|
Sanjana Gupta
asked a question
|
Instead of a metre scale, a cloth merchant uses a faulty 120 cm scale while buying, but uses a faulty 80 cm scale while selling the same cloth. If he offers a discount of 20%, what is his overall profit percentage?- a)25%
- b)20%
- c)40%
- d)15%
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Instead of a metre scale, a cloth merchant uses a faulty 120 cm scale while buying, but uses a faulty 80 cm scale while selling the same cloth. If he offers a discount of 20%, what is his overall profit percentage?
a)
25%
b)
20%
c)
40%
d)
15%
|
|
Wasima Thakur
asked a question
|
The passage below is accompanied by four questions. Based on the passage, choose the best answer for each question.Over the past four centuries liberalism has been so successful that it has driven all its opponents off the battlefield. Now it is disintegrating, destroyed by a mix of hubris and internal contradictions, according to Patrick Deneen, a professor of politics at the University of Notre Dame. . . . Equality of opportunity has produced a new meritocratic aristocracy that has all the aloofness of the old aristocracy with none of its sense of noblesse oblige. Democracy has degenerated into a theatre of the absurd. And technological advances are reducing ever more areas of work into meaningless drudgery. “The gap between liberalism’s claims about itself and the lived reality of the citizenry” is now so wide that “the lie can no longer be accepted,” Mr Deneen writes. What better proof of this than the vision of 1,000 private planes whisking their occupants to Davos to discuss the question of “creating a shared future in a fragmented world”? . . .Deneen does an impressive job of capturing the current mood of disillusionment, echoing leftwing complaints about rampant commercialism, right-wing complaints about narcissistic and bullying students, and general worries about atomisation and selfishness. But when he concludes that all this adds up to a failure of liberalism, is his argument convincing? . . . He argues that the essence of liberalism lies in freeing individuals from constraints. In fact, liberalism contains a wide range of intellectual traditions which provide different answers to the question of how to trade off the relative claims of rights and responsibilities, individual expression and social ties. . . . liberals experimented with a range of ideas from devolving power from the centre to creating national education systems.Mr Deneen’s fixation on the essence of liberalism leads to the second big problem of his book: his failure to recognise liberalism’s ability to reform itself and address its internal problems. The late 19th century saw America suffering from many of the problems that are reappearing today, including the creation of a business aristocracy, the rise of vast companies, the corruption of politics and the sense that society was dividing into winners and losers. But a wide variety of reformers, working within the liberal tradition, tackled these problems head on. Theodore Roosevelt took on the trusts. Progressives cleaned up government corruption. University reformers modernised academic syllabuses and built ladders of opportunity. Rather than dying, liberalism reformed itself.Mr Deneen is right to point out that the record of liberalism in recent years has been dismal. He is also right to assert that the world has much to learn from the premodern notions of liberty as self-mastery and self-denial. The biggest enemy of liberalism is not so much atomisation but old-fashioned greed, as members of the Davos elite pile their plates ever higher with perks and share options. But he is wrong to argue that the only way for people to liberate themselves from the contradictions of liberalism is “liberation from liberalism itself”. The best way to read “Why Liberalism Failed” is not as a funeral oration but as a call to action: up your game, or else.All of the following statements are evidence of the decline of liberalism today, EXCEPT:... more
The passage below is accompanied by four questions. Based on the passage, choose the best answer for each question.
Over the past four centuries liberalism has been so successful that it has driven all its opponents off the battlefield. Now it is disintegrating, destroyed by a mix of hubris and internal contradictions, according to Patrick Deneen, a professor of politics at the University of Notre Dame. . . . Equality of opportunity has produced a new meritocratic aristocracy that has all the aloofness of the old aristocracy with none of its sense of noblesse oblige. Democracy has degenerated into a theatre of the absurd. And technological advances are reducing ever more areas of work into meaningless drudgery. “The gap between liberalism’s claims about itself and the lived reality of the citizenry” is now so wide that “the lie can no longer be accepted,” Mr Deneen writes. What better proof of this than the vision of 1,000 private planes whisking their occupants to Davos to discuss the question of “creating a shared future in a fragmented world”? . . .
Deneen does an impressive job of capturing the current mood of disillusionment, echoing leftwing complaints about rampant commercialism, right-wing complaints about narcissistic and bullying students, and general worries about atomisation and selfishness. But when he concludes that all this adds up to a failure of liberalism, is his argument convincing? . . . He argues that the essence of liberalism lies in freeing individuals from constraints. In fact, liberalism contains a wide range of intellectual traditions which provide different answers to the question of how to trade off the relative claims of rights and responsibilities, individual expression and social ties. . . . liberals experimented with a range of ideas from devolving power from the centre to creating national education systems.
Mr Deneen’s fixation on the essence of liberalism leads to the second big problem of his book: his failure to recognise liberalism’s ability to reform itself and address its internal problems. The late 19th century saw America suffering from many of the problems that are reappearing today, including the creation of a business aristocracy, the rise of vast companies, the corruption of politics and the sense that society was dividing into winners and losers. But a wide variety of reformers, working within the liberal tradition, tackled these problems head on. Theodore Roosevelt took on the trusts. Progressives cleaned up government corruption. University reformers modernised academic syllabuses and built ladders of opportunity. Rather than dying, liberalism reformed itself.
Mr Deneen is right to point out that the record of liberalism in recent years has been dismal. He is also right to assert that the world has much to learn from the premodern notions of liberty as self-mastery and self-denial. The biggest enemy of liberalism is not so much atomisation but old-fashioned greed, as members of the Davos elite pile their plates ever higher with perks and share options. But he is wrong to argue that the only way for people to liberate themselves from the contradictions of liberalism is “liberation from liberalism itself”. The best way to read “Why Liberalism Failed” is not as a funeral oration but as a call to action: up your game, or else.
All of the following statements are evidence of the decline of liberalism today, EXCEPT:

|
Anuj Chakraborty
asked a question
|
What key feature distinguishes Vikramshila University from other ancient educational institutions?- a) Its establishment by the Gupta Empire
- b) Its location in the Himalayas
- c) Its focus on mathematics
- d) Its specialization in Tantric Buddhism and occult studies
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What key feature distinguishes Vikramshila University from other ancient educational institutions?
a)
Its establishment by the Gupta Empire
b)
Its location in the Himalayas
c)
Its focus on mathematics
d)
Its specialization in Tantric Buddhism and occult studies
|
|
Arnav Trivedi
asked a question
|
Which of the following is NOT a primary area of focus for the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA)?- a) Renewable Energy Development
- b) Trade and Investment Facilitation
- c) Disaster Risk Management
- d) Maritime Safety and Security
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is NOT a primary area of focus for the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA)?
a)
Renewable Energy Development
b)
Trade and Investment Facilitation
c)
Disaster Risk Management
d)
Maritime Safety and Security
|
|
Eesha Kapoor
asked a question
|
What was a notable outcome of the recent audit report by the Comptroller and Auditor General regarding Indian Railways?- a) Expansion of railway routes
- b) Increased passenger satisfaction
- c) Concerns about operational inefficiency
- d) A decrease in train accidents
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What was a notable outcome of the recent audit report by the Comptroller and Auditor General regarding Indian Railways?
a)
Expansion of railway routes
b)
Increased passenger satisfaction
c)
Concerns about operational inefficiency
d)
A decrease in train accidents
Fetching relevant content for you
Ask a doubt
Recommended Content
|
|
|
|
|




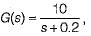 then the time constant of this system will be
then the time constant of this system will be
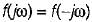
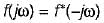
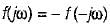
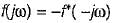
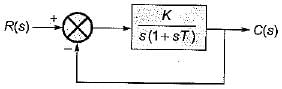

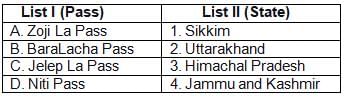
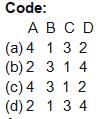

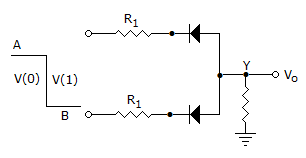






 When it is subjected to an input white noise process with a constant spectral dencity ‘A’ the spectral density of the output will be
When it is subjected to an input white noise process with a constant spectral dencity ‘A’ the spectral density of the output will be