Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > A synchronous generator is feeding 250 MW to ...
Start Learning for Free
A synchronous generator is feeding 250 MW to a large 50 Hz network over a double circuit transmission line. The maximum steady state power that can be transmitted over the line with both circuits in operation is 500 MW and is 350 MW with any one of the circuits. A solid three phase fault occurring at the network end of one of the lines causes it to trip. Calculate the critical clearing angle in which the circuit breakers must trip so that synchronism is not lost.
- a)53°
- b)37°
- c)45°
- d)24°
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A synchronous generator is feeding 250 MW to a large 50 Hz network ove...
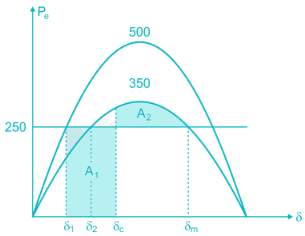
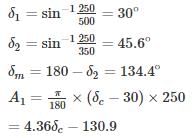
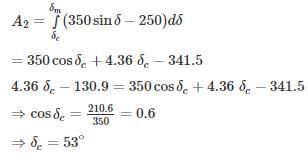
Most Upvoted Answer
A synchronous generator is feeding 250 MW to a large 50 Hz network ove...
Degrees
To calculate the critical clearing angle, we need to use the swing equation:
M(d^2δ/dt^2) + D(dδ/dt) = Pe - Ps
where:
M = generator inertia constant
D = damping coefficient
δ = rotor angle
Pe = electrical power input to the generator
Ps = electrical power output from the generator
Assuming no other generators or loads are affected by the fault, Ps will drop from 250 MW to 0 MW when one circuit trips. Therefore, we have:
M(d^2δ/dt^2) + D(dδ/dt) = Pe - 250
At the instant of fault clearing, the power input to the generator is still 250 MW, but the power output drops to zero. Therefore, the critical clearing angle occurs when the electrical power output reaches its minimum value, which is -350 MW (the maximum power that can be transmitted with one circuit). At this point, the swing equation becomes:
M(d^2δ/dt^2) + D(dδ/dt) = 250 - 350
M(d^2δ/dt^2) + D(dδ/dt) = -100
To solve for the critical clearing angle, we assume a solution of the form δ = A*cos(ωt + φ), where A is the amplitude, ω is the angular frequency, and φ is the phase angle. Substituting this into the swing equation, we get:
-Mω^2A*cos(ωt + φ) - DωA*sin(ωt + φ) = -100
Dividing both sides by A and rearranging, we get:
-Mω^2*cos(ωt + φ) - Dω*sin(ωt + φ) = -100/A
Since the left-hand side is a sinusoidal function, the maximum absolute value occurs when the argument is equal to ±π/2. Therefore, we choose the critical clearing angle to be the phase angle at which sin(φ) = -1 and cos(φ) = 0. This gives:
-Mω^2*cos(φ) - Dω*sin(φ) = -100/A
-Mω^2*0 - Dω*(-1) = -100/A
φ = arctan(Dω/100)
We can solve for ω using the formula for the natural frequency of a synchronous generator:
ω = 2πf/H
where f is the system frequency (50 Hz) and H is the generator's inertia constant (assume H = 4 seconds, typical for a large generator). This gives:
ω = 2π*50/4 = 31.4 rad/s
Substituting this into the expression for φ, we get:
φ = arctan(D*31.4/100)
To find D, we use the formula for the damping coefficient of a synchronous generator:
D = 2ξωnH
where ξ is the damping ratio (assume ξ = 0.1, typical for a large generator) and ωn is the undamped natural frequency (which we just calculated as 31.4 rad/s). This gives:
D = 2*0.1*31.4*4 = 25.1 Nm/(rad/s)
Substituting this into the expression for φ, we get:
φ = arct
To calculate the critical clearing angle, we need to use the swing equation:
M(d^2δ/dt^2) + D(dδ/dt) = Pe - Ps
where:
M = generator inertia constant
D = damping coefficient
δ = rotor angle
Pe = electrical power input to the generator
Ps = electrical power output from the generator
Assuming no other generators or loads are affected by the fault, Ps will drop from 250 MW to 0 MW when one circuit trips. Therefore, we have:
M(d^2δ/dt^2) + D(dδ/dt) = Pe - 250
At the instant of fault clearing, the power input to the generator is still 250 MW, but the power output drops to zero. Therefore, the critical clearing angle occurs when the electrical power output reaches its minimum value, which is -350 MW (the maximum power that can be transmitted with one circuit). At this point, the swing equation becomes:
M(d^2δ/dt^2) + D(dδ/dt) = 250 - 350
M(d^2δ/dt^2) + D(dδ/dt) = -100
To solve for the critical clearing angle, we assume a solution of the form δ = A*cos(ωt + φ), where A is the amplitude, ω is the angular frequency, and φ is the phase angle. Substituting this into the swing equation, we get:
-Mω^2A*cos(ωt + φ) - DωA*sin(ωt + φ) = -100
Dividing both sides by A and rearranging, we get:
-Mω^2*cos(ωt + φ) - Dω*sin(ωt + φ) = -100/A
Since the left-hand side is a sinusoidal function, the maximum absolute value occurs when the argument is equal to ±π/2. Therefore, we choose the critical clearing angle to be the phase angle at which sin(φ) = -1 and cos(φ) = 0. This gives:
-Mω^2*cos(φ) - Dω*sin(φ) = -100/A
-Mω^2*0 - Dω*(-1) = -100/A
φ = arctan(Dω/100)
We can solve for ω using the formula for the natural frequency of a synchronous generator:
ω = 2πf/H
where f is the system frequency (50 Hz) and H is the generator's inertia constant (assume H = 4 seconds, typical for a large generator). This gives:
ω = 2π*50/4 = 31.4 rad/s
Substituting this into the expression for φ, we get:
φ = arctan(D*31.4/100)
To find D, we use the formula for the damping coefficient of a synchronous generator:
D = 2ξωnH
where ξ is the damping ratio (assume ξ = 0.1, typical for a large generator) and ωn is the undamped natural frequency (which we just calculated as 31.4 rad/s). This gives:
D = 2*0.1*31.4*4 = 25.1 Nm/(rad/s)
Substituting this into the expression for φ, we get:
φ = arct
Attention Electrical Engineering (EE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Electrical Engineering (EE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Electrical Engineering (EE).

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Similar Electrical Engineering (EE) Doubts
A synchronous generator is feeding 250 MW to a large 50 Hz network over a double circuit transmission line. The maximum steady state power that can be transmitted over the line with both circuits in operation is 500 MW and is 350 MW with any one of the circuits. A solid three phase fault occurring at the network end of one of the lines causes it to trip. Calculate the critical clearing angle in which the circuit breakers must trip so that synchronism is not lost.a)53°b)37°c)45°d)24°Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A synchronous generator is feeding 250 MW to a large 50 Hz network over a double circuit transmission line. The maximum steady state power that can be transmitted over the line with both circuits in operation is 500 MW and is 350 MW with any one of the circuits. A solid three phase fault occurring at the network end of one of the lines causes it to trip. Calculate the critical clearing angle in which the circuit breakers must trip so that synchronism is not lost.a)53°b)37°c)45°d)24°Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about A synchronous generator is feeding 250 MW to a large 50 Hz network over a double circuit transmission line. The maximum steady state power that can be transmitted over the line with both circuits in operation is 500 MW and is 350 MW with any one of the circuits. A solid three phase fault occurring at the network end of one of the lines causes it to trip. Calculate the critical clearing angle in which the circuit breakers must trip so that synchronism is not lost.a)53°b)37°c)45°d)24°Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A synchronous generator is feeding 250 MW to a large 50 Hz network over a double circuit transmission line. The maximum steady state power that can be transmitted over the line with both circuits in operation is 500 MW and is 350 MW with any one of the circuits. A solid three phase fault occurring at the network end of one of the lines causes it to trip. Calculate the critical clearing angle in which the circuit breakers must trip so that synchronism is not lost.a)53°b)37°c)45°d)24°Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
A synchronous generator is feeding 250 MW to a large 50 Hz network over a double circuit transmission line. The maximum steady state power that can be transmitted over the line with both circuits in operation is 500 MW and is 350 MW with any one of the circuits. A solid three phase fault occurring at the network end of one of the lines causes it to trip. Calculate the critical clearing angle in which the circuit breakers must trip so that synchronism is not lost.a)53°b)37°c)45°d)24°Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about A synchronous generator is feeding 250 MW to a large 50 Hz network over a double circuit transmission line. The maximum steady state power that can be transmitted over the line with both circuits in operation is 500 MW and is 350 MW with any one of the circuits. A solid three phase fault occurring at the network end of one of the lines causes it to trip. Calculate the critical clearing angle in which the circuit breakers must trip so that synchronism is not lost.a)53°b)37°c)45°d)24°Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A synchronous generator is feeding 250 MW to a large 50 Hz network over a double circuit transmission line. The maximum steady state power that can be transmitted over the line with both circuits in operation is 500 MW and is 350 MW with any one of the circuits. A solid three phase fault occurring at the network end of one of the lines causes it to trip. Calculate the critical clearing angle in which the circuit breakers must trip so that synchronism is not lost.a)53°b)37°c)45°d)24°Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A synchronous generator is feeding 250 MW to a large 50 Hz network over a double circuit transmission line. The maximum steady state power that can be transmitted over the line with both circuits in operation is 500 MW and is 350 MW with any one of the circuits. A solid three phase fault occurring at the network end of one of the lines causes it to trip. Calculate the critical clearing angle in which the circuit breakers must trip so that synchronism is not lost.a)53°b)37°c)45°d)24°Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A synchronous generator is feeding 250 MW to a large 50 Hz network over a double circuit transmission line. The maximum steady state power that can be transmitted over the line with both circuits in operation is 500 MW and is 350 MW with any one of the circuits. A solid three phase fault occurring at the network end of one of the lines causes it to trip. Calculate the critical clearing angle in which the circuit breakers must trip so that synchronism is not lost.a)53°b)37°c)45°d)24°Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A synchronous generator is feeding 250 MW to a large 50 Hz network over a double circuit transmission line. The maximum steady state power that can be transmitted over the line with both circuits in operation is 500 MW and is 350 MW with any one of the circuits. A solid three phase fault occurring at the network end of one of the lines causes it to trip. Calculate the critical clearing angle in which the circuit breakers must trip so that synchronism is not lost.a)53°b)37°c)45°d)24°Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A synchronous generator is feeding 250 MW to a large 50 Hz network over a double circuit transmission line. The maximum steady state power that can be transmitted over the line with both circuits in operation is 500 MW and is 350 MW with any one of the circuits. A solid three phase fault occurring at the network end of one of the lines causes it to trip. Calculate the critical clearing angle in which the circuit breakers must trip so that synchronism is not lost.a)53°b)37°c)45°d)24°Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A synchronous generator is feeding 250 MW to a large 50 Hz network over a double circuit transmission line. The maximum steady state power that can be transmitted over the line with both circuits in operation is 500 MW and is 350 MW with any one of the circuits. A solid three phase fault occurring at the network end of one of the lines causes it to trip. Calculate the critical clearing angle in which the circuit breakers must trip so that synchronism is not lost.a)53°b)37°c)45°d)24°Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A synchronous generator is feeding 250 MW to a large 50 Hz network over a double circuit transmission line. The maximum steady state power that can be transmitted over the line with both circuits in operation is 500 MW and is 350 MW with any one of the circuits. A solid three phase fault occurring at the network end of one of the lines causes it to trip. Calculate the critical clearing angle in which the circuit breakers must trip so that synchronism is not lost.a)53°b)37°c)45°d)24°Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























