Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Exam > Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Questions > In IP packet has arrived with datagram of siz...
Start Learning for Free
In IP packet has arrived with datagram of size 700 bytes. The size of the IP header is 20 bytes. This packet will be forwarded on the link whose MTU is 185 bytes. The number of fragments that the IP datagram will be divided is ________.
Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
In IP packet has arrived with datagram of size 700 bytes. The size of ...
Maximum transmission unit = 185 bytes
Size of the IP header = 20 bytes
Number of fragments = 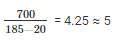
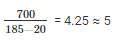
Most Upvoted Answer
In IP packet has arrived with datagram of size 700 bytes. The size of ...
IP Datagram Fragmentation
IP datagram fragmentation is the process of dividing a large IP datagram into smaller fragments to fit the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) of a network link. Each fragment is then reassembled at the destination to reconstruct the original datagram.
Given Information:
- Datagram size: 700 bytes
- IP header size: 20 bytes
- Link MTU: 185 bytes
Calculation:
To calculate the number of fragments required, we need to consider the following:
Total Datagram Size:
The total size of the IP datagram includes both the data and the IP header. So, the total datagram size is 700 + 20 = 720 bytes.
Fragmentation Offset:
Each fragment has a field called the Fragmentation Offset, which indicates the position of the fragment within the original datagram. The offset is measured in units of 8 bytes.
Maximum Data Length per Fragment:
To determine the maximum data length per fragment, we subtract the IP header size from the link MTU: 185 - 20 = 165 bytes.
Number of Fragments:
To calculate the number of fragments, we divide the total datagram size by the maximum data length per fragment and round up to the nearest whole number.
Number of fragments = ceil(total datagram size / maximum data length per fragment)
= ceil(720 / 165)
= 4.3636363636
≈ 5 (rounded up)
Therefore, the IP datagram will be divided into 5 fragments.
Note:
The last fragment may have less than the maximum data length if the remaining data is less than the maximum. In this case, the last fragment will contain the remaining data and the "More Fragments" flag will be set to 0 to indicate the end of the datagram.
IP datagram fragmentation is the process of dividing a large IP datagram into smaller fragments to fit the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) of a network link. Each fragment is then reassembled at the destination to reconstruct the original datagram.
Given Information:
- Datagram size: 700 bytes
- IP header size: 20 bytes
- Link MTU: 185 bytes
Calculation:
To calculate the number of fragments required, we need to consider the following:
Total Datagram Size:
The total size of the IP datagram includes both the data and the IP header. So, the total datagram size is 700 + 20 = 720 bytes.
Fragmentation Offset:
Each fragment has a field called the Fragmentation Offset, which indicates the position of the fragment within the original datagram. The offset is measured in units of 8 bytes.
Maximum Data Length per Fragment:
To determine the maximum data length per fragment, we subtract the IP header size from the link MTU: 185 - 20 = 165 bytes.
Number of Fragments:
To calculate the number of fragments, we divide the total datagram size by the maximum data length per fragment and round up to the nearest whole number.
Number of fragments = ceil(total datagram size / maximum data length per fragment)
= ceil(720 / 165)
= 4.3636363636
≈ 5 (rounded up)
Therefore, the IP datagram will be divided into 5 fragments.
Note:
The last fragment may have less than the maximum data length if the remaining data is less than the maximum. In this case, the last fragment will contain the remaining data and the "More Fragments" flag will be set to 0 to indicate the end of the datagram.

|
Explore Courses for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam
|

|
Similar Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Doubts
In IP packet has arrived with datagram of size 700 bytes. The size of the IP header is 20 bytes. This packet will be forwarded on the link whose MTU is 185 bytes. The number of fragments that the IP datagram will be divided is ________.Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
In IP packet has arrived with datagram of size 700 bytes. The size of the IP header is 20 bytes. This packet will be forwarded on the link whose MTU is 185 bytes. The number of fragments that the IP datagram will be divided is ________.Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) 2025 is part of Computer Science Engineering (CSE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam syllabus. Information about In IP packet has arrived with datagram of size 700 bytes. The size of the IP header is 20 bytes. This packet will be forwarded on the link whose MTU is 185 bytes. The number of fragments that the IP datagram will be divided is ________.Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In IP packet has arrived with datagram of size 700 bytes. The size of the IP header is 20 bytes. This packet will be forwarded on the link whose MTU is 185 bytes. The number of fragments that the IP datagram will be divided is ________.Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?.
In IP packet has arrived with datagram of size 700 bytes. The size of the IP header is 20 bytes. This packet will be forwarded on the link whose MTU is 185 bytes. The number of fragments that the IP datagram will be divided is ________.Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) 2025 is part of Computer Science Engineering (CSE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam syllabus. Information about In IP packet has arrived with datagram of size 700 bytes. The size of the IP header is 20 bytes. This packet will be forwarded on the link whose MTU is 185 bytes. The number of fragments that the IP datagram will be divided is ________.Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In IP packet has arrived with datagram of size 700 bytes. The size of the IP header is 20 bytes. This packet will be forwarded on the link whose MTU is 185 bytes. The number of fragments that the IP datagram will be divided is ________.Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for In IP packet has arrived with datagram of size 700 bytes. The size of the IP header is 20 bytes. This packet will be forwarded on the link whose MTU is 185 bytes. The number of fragments that the IP datagram will be divided is ________.Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Computer Science Engineering (CSE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In IP packet has arrived with datagram of size 700 bytes. The size of the IP header is 20 bytes. This packet will be forwarded on the link whose MTU is 185 bytes. The number of fragments that the IP datagram will be divided is ________.Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In IP packet has arrived with datagram of size 700 bytes. The size of the IP header is 20 bytes. This packet will be forwarded on the link whose MTU is 185 bytes. The number of fragments that the IP datagram will be divided is ________.Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for In IP packet has arrived with datagram of size 700 bytes. The size of the IP header is 20 bytes. This packet will be forwarded on the link whose MTU is 185 bytes. The number of fragments that the IP datagram will be divided is ________.Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of In IP packet has arrived with datagram of size 700 bytes. The size of the IP header is 20 bytes. This packet will be forwarded on the link whose MTU is 185 bytes. The number of fragments that the IP datagram will be divided is ________.Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In IP packet has arrived with datagram of size 700 bytes. The size of the IP header is 20 bytes. This packet will be forwarded on the link whose MTU is 185 bytes. The number of fragments that the IP datagram will be divided is ________.Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Computer Science Engineering (CSE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























