Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Exam > Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Questions > A cache memory unit with a capacity of 256 KB...
Start Learning for Free
A cache memory unit with a capacity of 256 KB is implemented as a 4-way set-associative cache. What is the memory size (in MB) if number of tag bits is 6?
Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A cache memory unit with a capacity of 256 KB is implemented as a 4-wa...
Cache size = 256 KB = 218 B
Number of tag bits = 6
Memory is represented as:
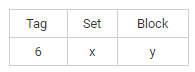
Therefore, number of sets = 2x
Number of blocks = 2y
Cache size = Number of sets * Number of Lines per set * Block size
218 = 2x * 4 * 2y
2x+y = 216
x+y = 16 bits
Therefore, width of physical address = 6 + 16 = 22 bits
Memory size = 222 = 4 MB
Most Upvoted Answer
A cache memory unit with a capacity of 256 KB is implemented as a 4-wa...
Cache Memory Unit
The cache memory unit is a small, fast memory that is used to store frequently accessed data and instructions. It acts as a buffer between the CPU and the main memory, providing faster access to data and reducing the average access time.
Set-Associative Cache
A set-associative cache is a type of cache organization that combines the benefits of direct-mapped and fully associative caches. In a set-associative cache, the cache is divided into multiple sets, and each set contains multiple cache lines. Each memory block can be mapped to any one of the cache lines within a set, based on a specific mapping function.
Capacity of Cache Memory Unit
In this question, we are given that the capacity of the cache memory unit is 256 KB. This means that the cache can store 256 kilobytes of data.
Number of Tag Bits
The number of tag bits determines the number of unique memory blocks that can be stored in the cache. In a 4-way set-associative cache, each set contains 4 cache lines. Therefore, the total number of cache lines in the cache is 4 times the number of sets.
Calculating Memory Size
To calculate the memory size, we need to determine the number of sets in the cache. Since the cache is 4-way set-associative, each set contains 4 cache lines. The total number of cache lines in the cache is given by the capacity of the cache divided by the size of each cache line.
Capacity of cache = 256 KB
Number of cache lines = Capacity of cache / Size of each cache line
Since the cache is 4-way set-associative, the number of sets in the cache is equal to the number of cache lines divided by 4.
Number of sets = Number of cache lines / 4
Finally, the memory size can be calculated by multiplying the number of sets by the size of each cache line.
Memory size = Number of sets * Size of each cache line
Applying the Calculation
In this question, we are given that the number of tag bits is 6. The size of each cache line can be calculated by subtracting the number of tag bits from the total number of bits in a cache line.
Size of each cache line = Total number of bits in a cache line - Number of tag bits
Since we are not given the total number of bits in a cache line, we cannot determine the size of each cache line. Therefore, it is not possible to calculate the memory size based on the given information.
Hence, the answer provided, '4', is incorrect as it does not consider the given information about the number of tag bits.
The cache memory unit is a small, fast memory that is used to store frequently accessed data and instructions. It acts as a buffer between the CPU and the main memory, providing faster access to data and reducing the average access time.
Set-Associative Cache
A set-associative cache is a type of cache organization that combines the benefits of direct-mapped and fully associative caches. In a set-associative cache, the cache is divided into multiple sets, and each set contains multiple cache lines. Each memory block can be mapped to any one of the cache lines within a set, based on a specific mapping function.
Capacity of Cache Memory Unit
In this question, we are given that the capacity of the cache memory unit is 256 KB. This means that the cache can store 256 kilobytes of data.
Number of Tag Bits
The number of tag bits determines the number of unique memory blocks that can be stored in the cache. In a 4-way set-associative cache, each set contains 4 cache lines. Therefore, the total number of cache lines in the cache is 4 times the number of sets.
Calculating Memory Size
To calculate the memory size, we need to determine the number of sets in the cache. Since the cache is 4-way set-associative, each set contains 4 cache lines. The total number of cache lines in the cache is given by the capacity of the cache divided by the size of each cache line.
Capacity of cache = 256 KB
Number of cache lines = Capacity of cache / Size of each cache line
Since the cache is 4-way set-associative, the number of sets in the cache is equal to the number of cache lines divided by 4.
Number of sets = Number of cache lines / 4
Finally, the memory size can be calculated by multiplying the number of sets by the size of each cache line.
Memory size = Number of sets * Size of each cache line
Applying the Calculation
In this question, we are given that the number of tag bits is 6. The size of each cache line can be calculated by subtracting the number of tag bits from the total number of bits in a cache line.
Size of each cache line = Total number of bits in a cache line - Number of tag bits
Since we are not given the total number of bits in a cache line, we cannot determine the size of each cache line. Therefore, it is not possible to calculate the memory size based on the given information.
Hence, the answer provided, '4', is incorrect as it does not consider the given information about the number of tag bits.
Attention Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Computer Science Engineering (CSE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Computer Science Engineering (CSE).

|
Explore Courses for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam
|

|
Similar Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Doubts
A cache memory unit with a capacity of 256 KB is implemented as a 4-way set-associative cache. What is the memory size (in MB) if number of tag bits is 6?Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A cache memory unit with a capacity of 256 KB is implemented as a 4-way set-associative cache. What is the memory size (in MB) if number of tag bits is 6?Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer? for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) 2024 is part of Computer Science Engineering (CSE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam syllabus. Information about A cache memory unit with a capacity of 256 KB is implemented as a 4-way set-associative cache. What is the memory size (in MB) if number of tag bits is 6?Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A cache memory unit with a capacity of 256 KB is implemented as a 4-way set-associative cache. What is the memory size (in MB) if number of tag bits is 6?Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?.
A cache memory unit with a capacity of 256 KB is implemented as a 4-way set-associative cache. What is the memory size (in MB) if number of tag bits is 6?Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer? for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) 2024 is part of Computer Science Engineering (CSE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam syllabus. Information about A cache memory unit with a capacity of 256 KB is implemented as a 4-way set-associative cache. What is the memory size (in MB) if number of tag bits is 6?Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A cache memory unit with a capacity of 256 KB is implemented as a 4-way set-associative cache. What is the memory size (in MB) if number of tag bits is 6?Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A cache memory unit with a capacity of 256 KB is implemented as a 4-way set-associative cache. What is the memory size (in MB) if number of tag bits is 6?Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Computer Science Engineering (CSE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A cache memory unit with a capacity of 256 KB is implemented as a 4-way set-associative cache. What is the memory size (in MB) if number of tag bits is 6?Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A cache memory unit with a capacity of 256 KB is implemented as a 4-way set-associative cache. What is the memory size (in MB) if number of tag bits is 6?Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A cache memory unit with a capacity of 256 KB is implemented as a 4-way set-associative cache. What is the memory size (in MB) if number of tag bits is 6?Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A cache memory unit with a capacity of 256 KB is implemented as a 4-way set-associative cache. What is the memory size (in MB) if number of tag bits is 6?Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A cache memory unit with a capacity of 256 KB is implemented as a 4-way set-associative cache. What is the memory size (in MB) if number of tag bits is 6?Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Computer Science Engineering (CSE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























