Chemistry Exam > Chemistry Questions > The pH of a solution made by adding 0.001 mol...
Start Learning for Free
The pH of a solution made by adding 0.001 mole of NaOH to 100cm3 of a solution which is 0.50 M in CH3COOH and 0.50 M in CH3COONa is _________________ (pkCH3cooH = 4.744) (Round off to two decimal places).
Correct answer is '4.76'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
The pH of a solution made by adding 0.001 mole of NaOH to 100cm3of a s...

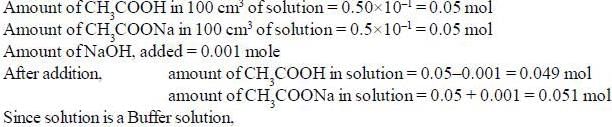
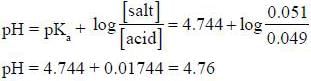
Most Upvoted Answer
The pH of a solution made by adding 0.001 mole of NaOH to 100cm3of a s...
Calculation of pH of the solution:
- The reaction between CH3COOH and NaOH can be represented as follows:
CH3COOH + NaOH → CH3COONa + H2O
- The initial concentration of CH3COOH is 0.50 M, and the concentration of CH3COONa is also 0.50 M as it is a salt of CH3COOH.
- Since NaOH is a strong base, it will completely react with CH3COOH to form CH3COONa and water.
- 0.001 mole of NaOH is added to the solution, which means 0.001 mole of CH3COOH will be neutralized.
- The final concentration of CH3COOH after neutralization will be 0.50 M - 0.001 M = 0.499 M.
Calculating the pH:
- The equilibrium constant expression for the dissociation of CH3COOH is Ka = [CH3COO-][H3O+]/[CH3COOH].
- Using the given pKa value of CH3COOH (4.744), we can calculate the Ka value as 10^(-4.744).
- Now, we can calculate the concentration of H3O+ ions using the Ka expression and the concentration of CH3COOH.
- Finally, pH is calculated using the formula pH = -log[H3O+].
Result:
- After the above calculations, the pH of the solution is found to be 4.76.
Therefore, the pH of the solution made by adding 0.001 mole of NaOH to 100cm3 of a solution which is 0.50 M in CH3COOH and 0.50 M in CH3COONa is 4.76.
- The reaction between CH3COOH and NaOH can be represented as follows:
CH3COOH + NaOH → CH3COONa + H2O
- The initial concentration of CH3COOH is 0.50 M, and the concentration of CH3COONa is also 0.50 M as it is a salt of CH3COOH.
- Since NaOH is a strong base, it will completely react with CH3COOH to form CH3COONa and water.
- 0.001 mole of NaOH is added to the solution, which means 0.001 mole of CH3COOH will be neutralized.
- The final concentration of CH3COOH after neutralization will be 0.50 M - 0.001 M = 0.499 M.
Calculating the pH:
- The equilibrium constant expression for the dissociation of CH3COOH is Ka = [CH3COO-][H3O+]/[CH3COOH].
- Using the given pKa value of CH3COOH (4.744), we can calculate the Ka value as 10^(-4.744).
- Now, we can calculate the concentration of H3O+ ions using the Ka expression and the concentration of CH3COOH.
- Finally, pH is calculated using the formula pH = -log[H3O+].
Result:
- After the above calculations, the pH of the solution is found to be 4.76.
Therefore, the pH of the solution made by adding 0.001 mole of NaOH to 100cm3 of a solution which is 0.50 M in CH3COOH and 0.50 M in CH3COONa is 4.76.

|
Explore Courses for Chemistry exam
|

|
Similar Chemistry Doubts
The pH of a solution made by adding 0.001 mole of NaOH to 100cm3of a solution which is 0.50 M in CH3COOH and 0.50 M in CH3COONa is _________________ (pkCH3cooH = 4.744) (Round off to two decimal places).Correct answer is '4.76'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The pH of a solution made by adding 0.001 mole of NaOH to 100cm3of a solution which is 0.50 M in CH3COOH and 0.50 M in CH3COONa is _________________ (pkCH3cooH = 4.744) (Round off to two decimal places).Correct answer is '4.76'. Can you explain this answer? for Chemistry 2024 is part of Chemistry preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Chemistry exam syllabus. Information about The pH of a solution made by adding 0.001 mole of NaOH to 100cm3of a solution which is 0.50 M in CH3COOH and 0.50 M in CH3COONa is _________________ (pkCH3cooH = 4.744) (Round off to two decimal places).Correct answer is '4.76'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Chemistry 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The pH of a solution made by adding 0.001 mole of NaOH to 100cm3of a solution which is 0.50 M in CH3COOH and 0.50 M in CH3COONa is _________________ (pkCH3cooH = 4.744) (Round off to two decimal places).Correct answer is '4.76'. Can you explain this answer?.
The pH of a solution made by adding 0.001 mole of NaOH to 100cm3of a solution which is 0.50 M in CH3COOH and 0.50 M in CH3COONa is _________________ (pkCH3cooH = 4.744) (Round off to two decimal places).Correct answer is '4.76'. Can you explain this answer? for Chemistry 2024 is part of Chemistry preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Chemistry exam syllabus. Information about The pH of a solution made by adding 0.001 mole of NaOH to 100cm3of a solution which is 0.50 M in CH3COOH and 0.50 M in CH3COONa is _________________ (pkCH3cooH = 4.744) (Round off to two decimal places).Correct answer is '4.76'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Chemistry 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The pH of a solution made by adding 0.001 mole of NaOH to 100cm3of a solution which is 0.50 M in CH3COOH and 0.50 M in CH3COONa is _________________ (pkCH3cooH = 4.744) (Round off to two decimal places).Correct answer is '4.76'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The pH of a solution made by adding 0.001 mole of NaOH to 100cm3of a solution which is 0.50 M in CH3COOH and 0.50 M in CH3COONa is _________________ (pkCH3cooH = 4.744) (Round off to two decimal places).Correct answer is '4.76'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Chemistry.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Chemistry Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The pH of a solution made by adding 0.001 mole of NaOH to 100cm3of a solution which is 0.50 M in CH3COOH and 0.50 M in CH3COONa is _________________ (pkCH3cooH = 4.744) (Round off to two decimal places).Correct answer is '4.76'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The pH of a solution made by adding 0.001 mole of NaOH to 100cm3of a solution which is 0.50 M in CH3COOH and 0.50 M in CH3COONa is _________________ (pkCH3cooH = 4.744) (Round off to two decimal places).Correct answer is '4.76'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The pH of a solution made by adding 0.001 mole of NaOH to 100cm3of a solution which is 0.50 M in CH3COOH and 0.50 M in CH3COONa is _________________ (pkCH3cooH = 4.744) (Round off to two decimal places).Correct answer is '4.76'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The pH of a solution made by adding 0.001 mole of NaOH to 100cm3of a solution which is 0.50 M in CH3COOH and 0.50 M in CH3COONa is _________________ (pkCH3cooH = 4.744) (Round off to two decimal places).Correct answer is '4.76'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The pH of a solution made by adding 0.001 mole of NaOH to 100cm3of a solution which is 0.50 M in CH3COOH and 0.50 M in CH3COONa is _________________ (pkCH3cooH = 4.744) (Round off to two decimal places).Correct answer is '4.76'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Chemistry tests.

|
Explore Courses for Chemistry exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















