Physics Exam > Physics Questions > A npn transistor circuit has∝ = 0.985. I...
Start Learning for Free
A npn transistor circuit has ∝ = 0.985. If IC = 2mA then the value of lB (in mA) is?
Correct answer is '0.03'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
A npn transistor circuit has∝ = 0.985. If IC= 2mAthen the value o...
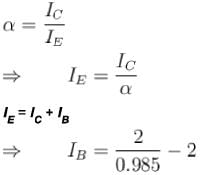
= 0.03 mA
The correct answer is: 0.03
Most Upvoted Answer
A npn transistor circuit has∝ = 0.985. If IC= 2mAthen the value o...
Three layers of semiconductor material: a layer of p-type material sandwiched between two layers of n-type material. The p-type material is doped with impurities that create an excess of positively charged holes, while the n-type material is doped with impurities that create an excess of negatively charged electrons. This configuration allows the transistor to function as a switch or amplifier.
In a typical npn transistor circuit, the emitter is connected to the negative terminal of the power supply, the base is connected to the control signal, and the collector is connected to the load or output. When a small current flows into the base, it controls a much larger current flowing between the collector and emitter.
The npn transistor operates in three different modes: cutoff, active, and saturation. In cutoff mode, there is no current flowing between the collector and emitter because the base-emitter junction is not forward biased. In active mode, the base-emitter junction is forward biased, allowing a small current to flow from the base to the emitter, resulting in a larger current flowing between the collector and emitter. In saturation mode, the base-emitter junction is heavily forward biased, allowing a large current to flow from the base to the emitter, resulting in maximum current flow between the collector and emitter.
The npn transistor can be used in various applications, such as amplifiers, switches, oscillators, and voltage regulators. It is commonly used in electronic devices and circuits to control and amplify electrical signals.
In a typical npn transistor circuit, the emitter is connected to the negative terminal of the power supply, the base is connected to the control signal, and the collector is connected to the load or output. When a small current flows into the base, it controls a much larger current flowing between the collector and emitter.
The npn transistor operates in three different modes: cutoff, active, and saturation. In cutoff mode, there is no current flowing between the collector and emitter because the base-emitter junction is not forward biased. In active mode, the base-emitter junction is forward biased, allowing a small current to flow from the base to the emitter, resulting in a larger current flowing between the collector and emitter. In saturation mode, the base-emitter junction is heavily forward biased, allowing a large current to flow from the base to the emitter, resulting in maximum current flow between the collector and emitter.
The npn transistor can be used in various applications, such as amplifiers, switches, oscillators, and voltage regulators. It is commonly used in electronic devices and circuits to control and amplify electrical signals.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
A npn transistor circuit has∝ = 0.985. If IC= 2mAthen the value o...
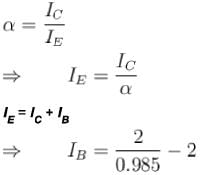
= 0.03 mA
The correct answer is: 0.03

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Question Description
A npn transistor circuit has∝ = 0.985. If IC= 2mAthen the value of lB (in mA)is?Correct answer is '0.03'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2025 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about A npn transistor circuit has∝ = 0.985. If IC= 2mAthen the value of lB (in mA)is?Correct answer is '0.03'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A npn transistor circuit has∝ = 0.985. If IC= 2mAthen the value of lB (in mA)is?Correct answer is '0.03'. Can you explain this answer?.
A npn transistor circuit has∝ = 0.985. If IC= 2mAthen the value of lB (in mA)is?Correct answer is '0.03'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2025 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about A npn transistor circuit has∝ = 0.985. If IC= 2mAthen the value of lB (in mA)is?Correct answer is '0.03'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A npn transistor circuit has∝ = 0.985. If IC= 2mAthen the value of lB (in mA)is?Correct answer is '0.03'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A npn transistor circuit has∝ = 0.985. If IC= 2mAthen the value of lB (in mA)is?Correct answer is '0.03'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Physics.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Physics Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A npn transistor circuit has∝ = 0.985. If IC= 2mAthen the value of lB (in mA)is?Correct answer is '0.03'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A npn transistor circuit has∝ = 0.985. If IC= 2mAthen the value of lB (in mA)is?Correct answer is '0.03'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A npn transistor circuit has∝ = 0.985. If IC= 2mAthen the value of lB (in mA)is?Correct answer is '0.03'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A npn transistor circuit has∝ = 0.985. If IC= 2mAthen the value of lB (in mA)is?Correct answer is '0.03'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A npn transistor circuit has∝ = 0.985. If IC= 2mAthen the value of lB (in mA)is?Correct answer is '0.03'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Physics tests.

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























