NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Difference Between non primate and primates?
Start Learning for Free
Difference Between non primate and primates?
Most Upvoted Answer
Difference Between non primate and primates?
Community Answer
Difference Between non primate and primates?
Non-Primates vs. Primates
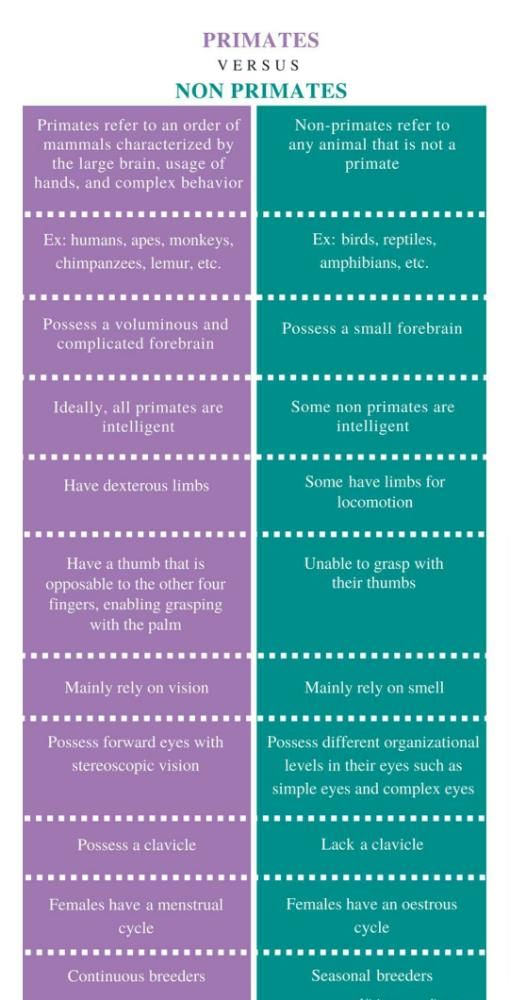
Primates and non-primates are two distinct groups of mammals with several key differences that set them apart. Let's explore these variations in detail:
Physical Characteristics:
- Primates typically have opposable thumbs, allowing for better grasping and manipulation of objects, while non-primates lack this feature.
- Non-primates often have claws or hooves for defense or locomotion, whereas primates have nails instead of claws.
Brain Structure and Function:
- Primates, including humans, have larger brains relative to their body size compared to non-primates. This increased brain size is associated with higher cognitive abilities.
- Non-primates generally have simpler brain structures and are less capable of complex problem-solving and social behaviors exhibited by primates.
Social Behavior:
- Primates are known for their complex social structures, forming tight-knit groups with intricate hierarchies and communication systems. Non-primates, on the other hand, often exhibit more solitary or less complex social behaviors.
- Primates engage in grooming, playing, and various forms of communication to maintain social bonds, while non-primates may have more limited social interactions.
Dietary Habits:
- Primates have diverse diets that can include fruits, leaves, insects, and even meat, depending on the species. Non-primates may have more specialized diets, such as herbivores that primarily consume plants.
- Some primates, like humans and chimpanzees, have omnivorous diets, allowing for a wider range of food sources compared to many non-primate species.
In conclusion, while both primates and non-primates are mammals, they exhibit distinct differences in physical characteristics, brain structure and function, social behavior, and dietary habits. These variations have contributed to the unique evolutionary paths and behaviors observed within each group.
Primates and non-primates are two distinct groups of mammals with several key differences that set them apart. Let's explore these variations in detail:
Physical Characteristics:
- Primates typically have opposable thumbs, allowing for better grasping and manipulation of objects, while non-primates lack this feature.
- Non-primates often have claws or hooves for defense or locomotion, whereas primates have nails instead of claws.
Brain Structure and Function:
- Primates, including humans, have larger brains relative to their body size compared to non-primates. This increased brain size is associated with higher cognitive abilities.
- Non-primates generally have simpler brain structures and are less capable of complex problem-solving and social behaviors exhibited by primates.
Social Behavior:
- Primates are known for their complex social structures, forming tight-knit groups with intricate hierarchies and communication systems. Non-primates, on the other hand, often exhibit more solitary or less complex social behaviors.
- Primates engage in grooming, playing, and various forms of communication to maintain social bonds, while non-primates may have more limited social interactions.
Dietary Habits:
- Primates have diverse diets that can include fruits, leaves, insects, and even meat, depending on the species. Non-primates may have more specialized diets, such as herbivores that primarily consume plants.
- Some primates, like humans and chimpanzees, have omnivorous diets, allowing for a wider range of food sources compared to many non-primate species.
In conclusion, while both primates and non-primates are mammals, they exhibit distinct differences in physical characteristics, brain structure and function, social behavior, and dietary habits. These variations have contributed to the unique evolutionary paths and behaviors observed within each group.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Question Description
Difference Between non primate and primates? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Difference Between non primate and primates? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Difference Between non primate and primates?.
Difference Between non primate and primates? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Difference Between non primate and primates? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Difference Between non primate and primates?.
Solutions for Difference Between non primate and primates? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Difference Between non primate and primates? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Difference Between non primate and primates?, a detailed solution for Difference Between non primate and primates? has been provided alongside types of Difference Between non primate and primates? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Difference Between non primate and primates? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















