NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Classification of amino acid essential and no...
Start Learning for Free
Classification of amino acid essential and non essential?
Most Upvoted Answer
Classification of amino acid essential and non essential?
Community Answer
Classification of amino acid essential and non essential?
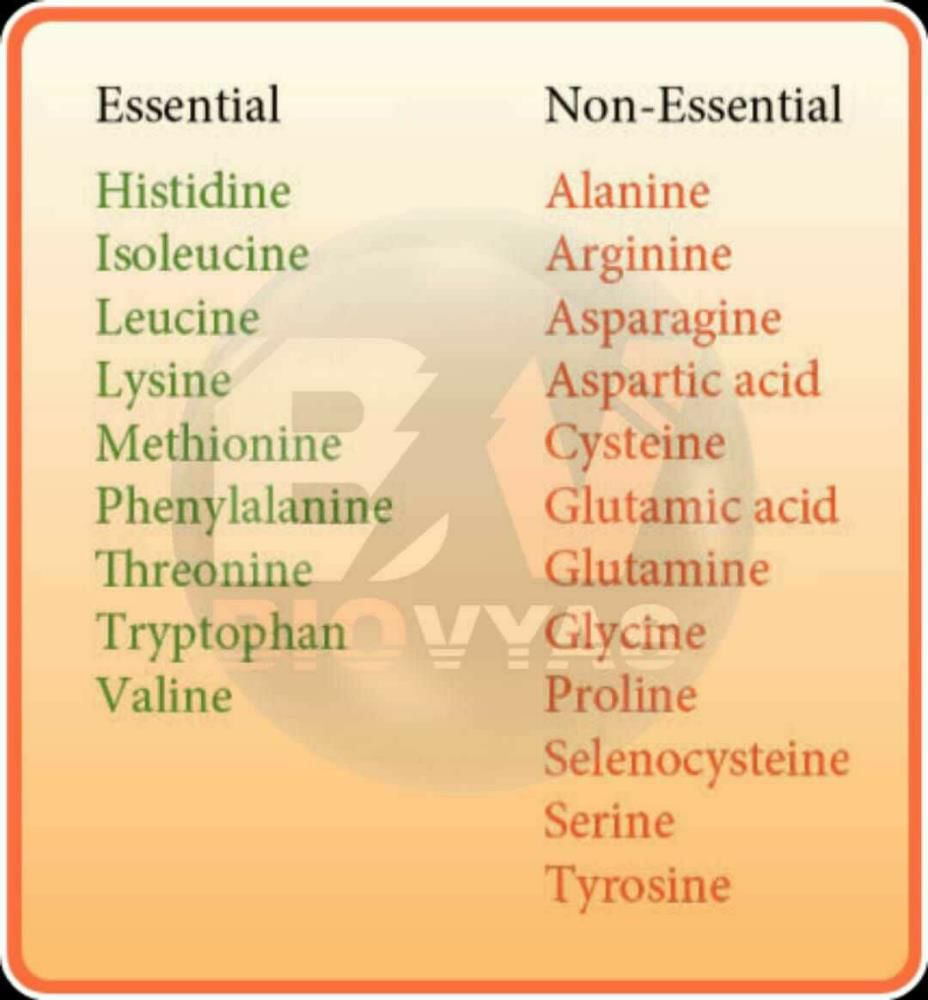
Essential and Non-essential Amino Acids
Essential Amino Acids
Essential amino acids are those that cannot be synthesized by the body and must be obtained through diet.
- There are 9 essential amino acids: histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine.
- These amino acids are crucial for various physiological functions such as protein synthesis, immune function, and neurotransmitter production.
- Foods rich in essential amino acids include meat, dairy products, eggs, and certain plant-based sources like quinoa and soy.
Non-essential Amino Acids
Non-essential amino acids are those that can be synthesized by the body and are not required to be obtained through diet.
- There are 11 non-essential amino acids: alanine, arginine, asparagine, aspartic acid, cysteine, glutamic acid, glutamine, glycine, proline, serine, and tyrosine.
- These amino acids play important roles in various bodily functions, such as energy production, hormone regulation, and collagen formation.
- Non-essential amino acids can be synthesized from other amino acids or through metabolic pathways within the body.
In conclusion, essential amino acids are crucial for overall health as they must be obtained through diet, while non-essential amino acids are still important for bodily functions but can be synthesized by the body. It is essential to consume a balanced diet containing both essential and non-essential amino acids to support optimal health and well-being.
Essential Amino Acids
Essential amino acids are those that cannot be synthesized by the body and must be obtained through diet.
- There are 9 essential amino acids: histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine.
- These amino acids are crucial for various physiological functions such as protein synthesis, immune function, and neurotransmitter production.
- Foods rich in essential amino acids include meat, dairy products, eggs, and certain plant-based sources like quinoa and soy.
Non-essential Amino Acids
Non-essential amino acids are those that can be synthesized by the body and are not required to be obtained through diet.
- There are 11 non-essential amino acids: alanine, arginine, asparagine, aspartic acid, cysteine, glutamic acid, glutamine, glycine, proline, serine, and tyrosine.
- These amino acids play important roles in various bodily functions, such as energy production, hormone regulation, and collagen formation.
- Non-essential amino acids can be synthesized from other amino acids or through metabolic pathways within the body.
In conclusion, essential amino acids are crucial for overall health as they must be obtained through diet, while non-essential amino acids are still important for bodily functions but can be synthesized by the body. It is essential to consume a balanced diet containing both essential and non-essential amino acids to support optimal health and well-being.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
Classification of amino acid essential and non essential?
Question Description
Classification of amino acid essential and non essential? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Classification of amino acid essential and non essential? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Classification of amino acid essential and non essential?.
Classification of amino acid essential and non essential? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Classification of amino acid essential and non essential? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Classification of amino acid essential and non essential?.
Solutions for Classification of amino acid essential and non essential? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Classification of amino acid essential and non essential? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Classification of amino acid essential and non essential?, a detailed solution for Classification of amino acid essential and non essential? has been provided alongside types of Classification of amino acid essential and non essential? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Classification of amino acid essential and non essential? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























