Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Questions > What is the difference between fragmentation ...
Start Learning for Free
What is the difference between fragmentation and multiple fission???
?Most Upvoted Answer
What is the difference between fragmentation and multiple fission??? R...
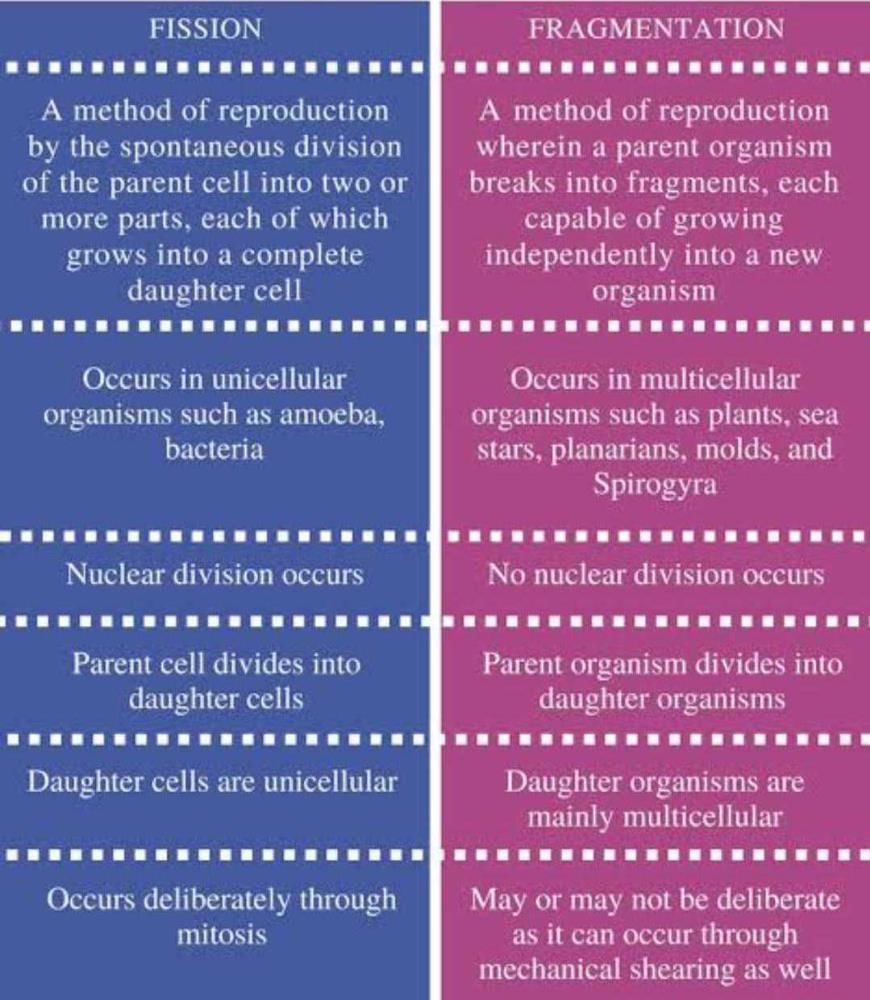
Community Answer
What is the difference between fragmentation and multiple fission??? R...
**Difference between Fragmentation and Multiple Fission**
Fragmentation and multiple fission are both methods of asexual reproduction used by different organisms. Let's understand the differences between the two:
**Fragmentation:**
1. Fragmentation is a form of asexual reproduction in which an organism breaks into several fragments, and each fragment grows into a complete organism.
2. It is commonly observed in multicellular organisms like fungi, algae, and some plants.
3. The process of fragmentation begins with the formation of small fragments due to the growth or splitting of the parent organism.
4. These fragments are capable of independent growth and development into new individuals.
5. Each fragment has the potential to regenerate missing parts and form a complete organism.
6. Fragmentation is often a response to environmental conditions, such as physical disturbances or nutrient availability.
7. Examples of organisms that reproduce through fragmentation include Spirogyra (a filamentous green alga) and yeast (a type of fungus).
**Multiple Fission:**
1. Multiple fission is a type of asexual reproduction in which an organism divides into several daughter cells simultaneously.
2. It is commonly observed in single-celled organisms like protists and some bacteria.
3. The process of multiple fission involves the division of the parent cell into multiple daughter cells, each of which is capable of independent growth and development.
4. The daughter cells are formed simultaneously and are genetically identical to each other and the parent cell.
5. Multiple fission is often triggered by favorable environmental conditions, such as an abundance of nutrients or suitable temperatures.
6. Examples of organisms that reproduce through multiple fission include Plasmodium (a parasite causing malaria) and Amoeba (a type of protist).
**Asexual Reproduction - Easy Explanation:**
Asexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction where offspring are produced without the involvement of gametes (reproductive cells) or the fusion of genetic material from two parents. It results in the production of genetically identical offspring, known as clones. Asexual reproduction is advantageous as it allows organisms to rapidly increase their population size and colonize new habitats.
In asexual reproduction, the parent organism directly gives rise to offspring without the need for specialized reproductive structures. Some common methods of asexual reproduction include binary fission (cell division), budding (outgrowth from the parent organism), vegetative propagation (formation of new plants from vegetative parts), and spore formation (production of specialized cells capable of growing into new individuals).
Asexual reproduction is commonly observed in both multicellular and unicellular organisms, providing them with the ability to rapidly reproduce and adapt to changing environments. However, it lacks the genetic diversity provided by sexual reproduction, limiting the potential for adaptation to new environmental challenges.
Fragmentation and multiple fission are both methods of asexual reproduction used by different organisms. Let's understand the differences between the two:
**Fragmentation:**
1. Fragmentation is a form of asexual reproduction in which an organism breaks into several fragments, and each fragment grows into a complete organism.
2. It is commonly observed in multicellular organisms like fungi, algae, and some plants.
3. The process of fragmentation begins with the formation of small fragments due to the growth or splitting of the parent organism.
4. These fragments are capable of independent growth and development into new individuals.
5. Each fragment has the potential to regenerate missing parts and form a complete organism.
6. Fragmentation is often a response to environmental conditions, such as physical disturbances or nutrient availability.
7. Examples of organisms that reproduce through fragmentation include Spirogyra (a filamentous green alga) and yeast (a type of fungus).
**Multiple Fission:**
1. Multiple fission is a type of asexual reproduction in which an organism divides into several daughter cells simultaneously.
2. It is commonly observed in single-celled organisms like protists and some bacteria.
3. The process of multiple fission involves the division of the parent cell into multiple daughter cells, each of which is capable of independent growth and development.
4. The daughter cells are formed simultaneously and are genetically identical to each other and the parent cell.
5. Multiple fission is often triggered by favorable environmental conditions, such as an abundance of nutrients or suitable temperatures.
6. Examples of organisms that reproduce through multiple fission include Plasmodium (a parasite causing malaria) and Amoeba (a type of protist).
**Asexual Reproduction - Easy Explanation:**
Asexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction where offspring are produced without the involvement of gametes (reproductive cells) or the fusion of genetic material from two parents. It results in the production of genetically identical offspring, known as clones. Asexual reproduction is advantageous as it allows organisms to rapidly increase their population size and colonize new habitats.
In asexual reproduction, the parent organism directly gives rise to offspring without the need for specialized reproductive structures. Some common methods of asexual reproduction include binary fission (cell division), budding (outgrowth from the parent organism), vegetative propagation (formation of new plants from vegetative parts), and spore formation (production of specialized cells capable of growing into new individuals).
Asexual reproduction is commonly observed in both multicellular and unicellular organisms, providing them with the ability to rapidly reproduce and adapt to changing environments. However, it lacks the genetic diversity provided by sexual reproduction, limiting the potential for adaptation to new environmental challenges.

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Question Description
What is the difference between fragmentation and multiple fission??? Related: Asexual Reproduction (Easy Explanation)? for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about What is the difference between fragmentation and multiple fission??? Related: Asexual Reproduction (Easy Explanation)? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is the difference between fragmentation and multiple fission??? Related: Asexual Reproduction (Easy Explanation)?.
What is the difference between fragmentation and multiple fission??? Related: Asexual Reproduction (Easy Explanation)? for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about What is the difference between fragmentation and multiple fission??? Related: Asexual Reproduction (Easy Explanation)? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is the difference between fragmentation and multiple fission??? Related: Asexual Reproduction (Easy Explanation)?.
Solutions for What is the difference between fragmentation and multiple fission??? Related: Asexual Reproduction (Easy Explanation)? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 10.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of What is the difference between fragmentation and multiple fission??? Related: Asexual Reproduction (Easy Explanation)? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
What is the difference between fragmentation and multiple fission??? Related: Asexual Reproduction (Easy Explanation)?, a detailed solution for What is the difference between fragmentation and multiple fission??? Related: Asexual Reproduction (Easy Explanation)? has been provided alongside types of What is the difference between fragmentation and multiple fission??? Related: Asexual Reproduction (Easy Explanation)? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice What is the difference between fragmentation and multiple fission??? Related: Asexual Reproduction (Easy Explanation)? tests, examples and also practice Class 10 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















