NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Explain current loop as a magnetic dipole?
Start Learning for Free
Explain current loop as a magnetic dipole?
Most Upvoted Answer
Explain current loop as a magnetic dipole?
Community Answer
Explain current loop as a magnetic dipole?
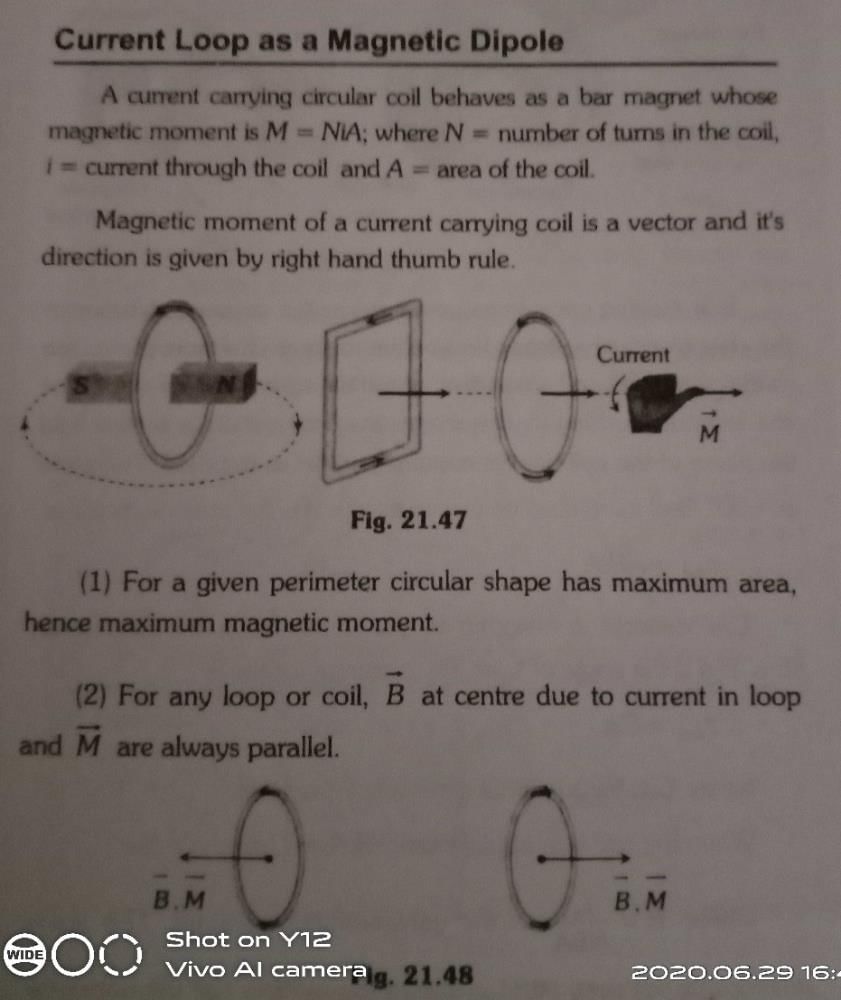
Current Loop as a Magnetic Dipole
A current loop refers to a closed conducting path through which an electric current flows. When a current flows through a loop, it generates a magnetic field around it. This can be explained by considering the current loop as a magnetic dipole.
Magnetic Dipole Moment
The magnetic dipole moment of a current loop is a measure of its strength and orientation. It is defined as the product of the current flowing through the loop and the area enclosed by the loop. Mathematically, the magnetic dipole moment (μ) is given by the equation:
μ = I * A
Where:
- μ is the magnetic dipole moment
- I is the current flowing through the loop
- A is the area enclosed by the loop
Magnetic Field Around a Current Loop
When a current flows through a loop, it generates a magnetic field in the surrounding space. The magnetic field lines form closed loops around the current-carrying loop. The direction of the magnetic field can be determined using the right-hand rule.
Right-Hand Rule
According to the right-hand rule, if you grasp the loop with your right hand such that your thumb points in the direction of the current, then the curl of your fingers will give the direction of the magnetic field lines.
Magnetic Field Strength
The strength of the magnetic field produced by a current loop depends on the magnitude of the current and the shape of the loop. The magnetic field strength (B) at a point on the axis of the loop is given by the equation:
B = (μ₀ * I * R²) / (2 * (R² + x²)^(3/2))
Where:
- B is the magnetic field strength
- μ₀ is the permeability of free space
- I is the current flowing through the loop
- R is the radius of the loop
- x is the distance from the center of the loop to the point on the axis
Applications
The concept of a current loop as a magnetic dipole has various applications, including:
- Electric motors: The interaction between the magnetic field of a current loop and an external magnetic field is utilized to generate rotational motion in electric motors.
- Magnetic compasses: The Earth's magnetic field aligns with the magnetic field of a current loop, making it useful in magnetic compasses for navigation.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): In medical imaging, strong magnetic fields created by current loops are used to generate detailed images of the internal structures of the body.
Conclusion
A current loop can be considered as a magnetic dipole due to the generation of a magnetic field around it. The magnetic dipole moment of the loop is determined by the current flowing through it and the area enclosed by the loop. Understanding the behavior of current loops as magnetic dipoles is essential in various applications, ranging from electric motors to medical imaging techniques like MRI.
A current loop refers to a closed conducting path through which an electric current flows. When a current flows through a loop, it generates a magnetic field around it. This can be explained by considering the current loop as a magnetic dipole.
Magnetic Dipole Moment
The magnetic dipole moment of a current loop is a measure of its strength and orientation. It is defined as the product of the current flowing through the loop and the area enclosed by the loop. Mathematically, the magnetic dipole moment (μ) is given by the equation:
μ = I * A
Where:
- μ is the magnetic dipole moment
- I is the current flowing through the loop
- A is the area enclosed by the loop
Magnetic Field Around a Current Loop
When a current flows through a loop, it generates a magnetic field in the surrounding space. The magnetic field lines form closed loops around the current-carrying loop. The direction of the magnetic field can be determined using the right-hand rule.
Right-Hand Rule
According to the right-hand rule, if you grasp the loop with your right hand such that your thumb points in the direction of the current, then the curl of your fingers will give the direction of the magnetic field lines.
Magnetic Field Strength
The strength of the magnetic field produced by a current loop depends on the magnitude of the current and the shape of the loop. The magnetic field strength (B) at a point on the axis of the loop is given by the equation:
B = (μ₀ * I * R²) / (2 * (R² + x²)^(3/2))
Where:
- B is the magnetic field strength
- μ₀ is the permeability of free space
- I is the current flowing through the loop
- R is the radius of the loop
- x is the distance from the center of the loop to the point on the axis
Applications
The concept of a current loop as a magnetic dipole has various applications, including:
- Electric motors: The interaction between the magnetic field of a current loop and an external magnetic field is utilized to generate rotational motion in electric motors.
- Magnetic compasses: The Earth's magnetic field aligns with the magnetic field of a current loop, making it useful in magnetic compasses for navigation.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): In medical imaging, strong magnetic fields created by current loops are used to generate detailed images of the internal structures of the body.
Conclusion
A current loop can be considered as a magnetic dipole due to the generation of a magnetic field around it. The magnetic dipole moment of the loop is determined by the current flowing through it and the area enclosed by the loop. Understanding the behavior of current loops as magnetic dipoles is essential in various applications, ranging from electric motors to medical imaging techniques like MRI.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Question Description
Explain current loop as a magnetic dipole? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Explain current loop as a magnetic dipole? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Explain current loop as a magnetic dipole?.
Explain current loop as a magnetic dipole? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Explain current loop as a magnetic dipole? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Explain current loop as a magnetic dipole?.
Solutions for Explain current loop as a magnetic dipole? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Explain current loop as a magnetic dipole? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Explain current loop as a magnetic dipole?, a detailed solution for Explain current loop as a magnetic dipole? has been provided alongside types of Explain current loop as a magnetic dipole? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Explain current loop as a magnetic dipole? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























