NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Difference between bones and cartilage. Its a...
Start Learning for Free
Difference between bones and cartilage. Its all about to help you so don't answer please?
Most Upvoted Answer
Difference between bones and cartilage. Its all about to help you so d...
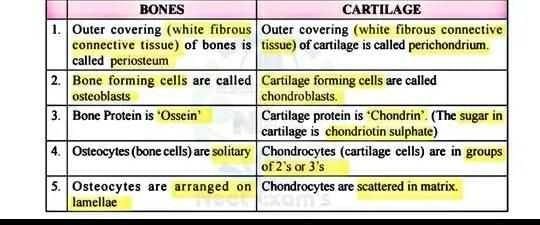
Community Answer
Difference between bones and cartilage. Its all about to help you so d...
Bones and Cartilage: Differences and Functions
Introduction:
Bones and cartilage are two important types of connective tissues found in the human body. While they share some similarities, they also have distinct differences in terms of structure and function.
Structure:
- Bones: Bones are hard, rigid, and dense connective tissues that form the skeletal system. They are made up of cells called osteocytes, as well as a matrix composed of collagen fibers and calcium salts. The compact bone forms the outer layer, while the spongy bone is found inside and contains marrow.
- Cartilage: Cartilage is a flexible and elastic connective tissue that is softer than bone. It consists of cells called chondrocytes and a matrix composed of collagen and proteoglycans. Cartilage lacks blood vessels and nerves, which gives it a smooth, rubber-like texture.
Function:
- Bones:
- Support: Bones provide a framework that supports the body and gives it shape.
- Protection: Bones protect vital organs such as the brain, heart, and lungs.
- Movement: Bones, along with muscles and joints, enable movement and locomotion.
- Blood Cell Formation: The bone marrow inside bones is responsible for the production of red and white blood cells.
- Mineral Storage: Bones store minerals such as calcium and phosphorus, which are essential for various bodily functions.
- Cartilage:
- Shock Absorption: Cartilage acts as a cushion between bones, reducing friction and impact during movements.
- Flexibility: Cartilage provides flexibility and elasticity to certain body structures, such as the ears and nose.
- Growth and Development: Cartilage plays a crucial role in the growth and development of long bones in children.
- Smooth Joint Movement: Cartilage covers the ends of bones in joints, allowing smooth and frictionless movement.
Key Differences:
- Structure: Bones are hard and rigid, while cartilage is flexible and elastic.
- Composition: Bones have a matrix of collagen fibers and calcium salts, while cartilage has a matrix of collagen and proteoglycans.
- Blood Supply: Bones have a rich blood supply, while cartilage lacks blood vessels.
- Nerve Supply: Bones are innervated, while cartilage is not.
- Regeneration: Bones have the ability to regenerate and heal more efficiently than cartilage.
Conclusion:
In summary, bones and cartilage are both important connective tissues in the human body. While bones provide support, protection, and movement, cartilage acts as a shock absorber and provides flexibility. Understanding their differences and functions helps us appreciate the intricate design of the human body.
Introduction:
Bones and cartilage are two important types of connective tissues found in the human body. While they share some similarities, they also have distinct differences in terms of structure and function.
Structure:
- Bones: Bones are hard, rigid, and dense connective tissues that form the skeletal system. They are made up of cells called osteocytes, as well as a matrix composed of collagen fibers and calcium salts. The compact bone forms the outer layer, while the spongy bone is found inside and contains marrow.
- Cartilage: Cartilage is a flexible and elastic connective tissue that is softer than bone. It consists of cells called chondrocytes and a matrix composed of collagen and proteoglycans. Cartilage lacks blood vessels and nerves, which gives it a smooth, rubber-like texture.
Function:
- Bones:
- Support: Bones provide a framework that supports the body and gives it shape.
- Protection: Bones protect vital organs such as the brain, heart, and lungs.
- Movement: Bones, along with muscles and joints, enable movement and locomotion.
- Blood Cell Formation: The bone marrow inside bones is responsible for the production of red and white blood cells.
- Mineral Storage: Bones store minerals such as calcium and phosphorus, which are essential for various bodily functions.
- Cartilage:
- Shock Absorption: Cartilage acts as a cushion between bones, reducing friction and impact during movements.
- Flexibility: Cartilage provides flexibility and elasticity to certain body structures, such as the ears and nose.
- Growth and Development: Cartilage plays a crucial role in the growth and development of long bones in children.
- Smooth Joint Movement: Cartilage covers the ends of bones in joints, allowing smooth and frictionless movement.
Key Differences:
- Structure: Bones are hard and rigid, while cartilage is flexible and elastic.
- Composition: Bones have a matrix of collagen fibers and calcium salts, while cartilage has a matrix of collagen and proteoglycans.
- Blood Supply: Bones have a rich blood supply, while cartilage lacks blood vessels.
- Nerve Supply: Bones are innervated, while cartilage is not.
- Regeneration: Bones have the ability to regenerate and heal more efficiently than cartilage.
Conclusion:
In summary, bones and cartilage are both important connective tissues in the human body. While bones provide support, protection, and movement, cartilage acts as a shock absorber and provides flexibility. Understanding their differences and functions helps us appreciate the intricate design of the human body.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
Difference between bones and cartilage. Its all about to help you so don't answer please?
Question Description
Difference between bones and cartilage. Its all about to help you so don't answer please? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Difference between bones and cartilage. Its all about to help you so don't answer please? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Difference between bones and cartilage. Its all about to help you so don't answer please?.
Difference between bones and cartilage. Its all about to help you so don't answer please? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Difference between bones and cartilage. Its all about to help you so don't answer please? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Difference between bones and cartilage. Its all about to help you so don't answer please?.
Solutions for Difference between bones and cartilage. Its all about to help you so don't answer please? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Difference between bones and cartilage. Its all about to help you so don't answer please? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Difference between bones and cartilage. Its all about to help you so don't answer please?, a detailed solution for Difference between bones and cartilage. Its all about to help you so don't answer please? has been provided alongside types of Difference between bones and cartilage. Its all about to help you so don't answer please? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Difference between bones and cartilage. Its all about to help you so don't answer please? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























