NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Difference between dicot root and monocot roo...
Start Learning for Free
Difference between dicot root and monocot root__its all about to help you so don't answer please?
Most Upvoted Answer
Difference between dicot root and monocot root__its all about to help ...
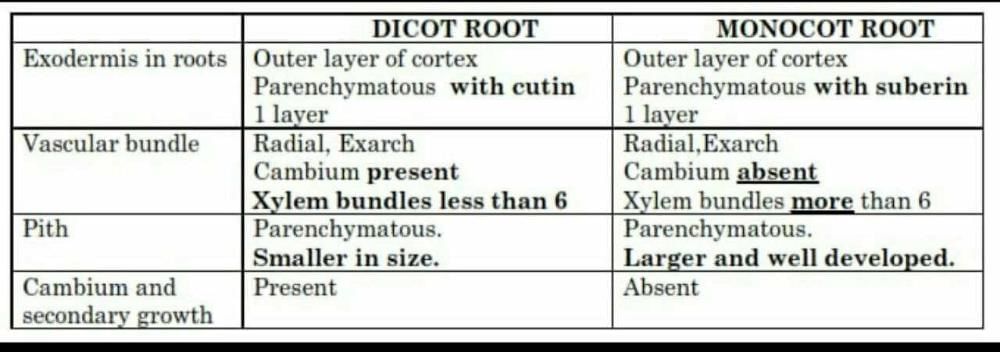
Community Answer
Difference between dicot root and monocot root__its all about to help ...
Difference between dicot root and monocot root:
1. Root Anatomy:
- Dicot Root: The dicot root consists of a taproot system with a primary root that grows vertically into the soil. It gives rise to numerous lateral roots or secondary roots. The primary root is thicker and longer than the lateral roots.
- Monocot Root: The monocot root has a fibrous root system without a distinct primary root. It consists of a cluster of thin and slender roots that arise from the base of the stem. These roots are more or less similar in size and thickness.
2. Root Cap:
- Dicot Root: In dicot roots, the root cap is well-developed and is composed of several layers of cells. It helps protect the growing tip of the root and aids in the penetration of the soil.
- Monocot Root: Monocot roots also possess a root cap, but it is relatively smaller and less prominent compared to dicot roots.
3. Vascular Tissue Arrangement:
- Dicot Root: The vascular tissue in dicot roots is organized in the form of a central vascular cylinder or stele. It consists of a solid core of xylem in the center, surrounded by a ring of phloem, and a layer of pericycle.
- Monocot Root: In monocot roots, the vascular tissue is scattered and not arranged in a distinct central cylinder. The xylem and phloem are distributed in a complex manner throughout the cortex.
4. Endodermis:
- Dicot Root: The endodermis in dicot roots consists of a single layer of tightly packed cells with a Casparian strip. The Casparian strip acts as a barrier to control the movement of water and minerals into the vascular tissue.
- Monocot Root: Monocot roots also possess an endodermis, but it lacks the Casparian strip. The cells of the endodermis are loosely arranged, allowing for a freer movement of substances.
5. Pith:
- Dicot Root: Some dicot roots may possess a pith, which is a central region of parenchyma cells located within the vascular cylinder. It provides storage and support to the root.
- Monocot Root: Monocot roots generally lack a pith and have a more compact arrangement of tissues in the center.
6. Growth Pattern:
- Dicot Root: Dicot roots exhibit both primary and secondary growth. The primary growth involves the elongation of the primary root, while secondary growth leads to the formation of lateral roots.
- Monocot Root: Monocot roots primarily undergo primary growth and do not exhibit significant secondary growth. The fibrous root system continually produces new roots from the base of the stem.
In conclusion, dicot and monocot roots differ in their anatomy, root cap, vascular tissue arrangement, endodermis structure, presence of pith, and growth patterns. Understanding these differences is essential to comprehend the unique characteristics and functions of each type of root.
1. Root Anatomy:
- Dicot Root: The dicot root consists of a taproot system with a primary root that grows vertically into the soil. It gives rise to numerous lateral roots or secondary roots. The primary root is thicker and longer than the lateral roots.
- Monocot Root: The monocot root has a fibrous root system without a distinct primary root. It consists of a cluster of thin and slender roots that arise from the base of the stem. These roots are more or less similar in size and thickness.
2. Root Cap:
- Dicot Root: In dicot roots, the root cap is well-developed and is composed of several layers of cells. It helps protect the growing tip of the root and aids in the penetration of the soil.
- Monocot Root: Monocot roots also possess a root cap, but it is relatively smaller and less prominent compared to dicot roots.
3. Vascular Tissue Arrangement:
- Dicot Root: The vascular tissue in dicot roots is organized in the form of a central vascular cylinder or stele. It consists of a solid core of xylem in the center, surrounded by a ring of phloem, and a layer of pericycle.
- Monocot Root: In monocot roots, the vascular tissue is scattered and not arranged in a distinct central cylinder. The xylem and phloem are distributed in a complex manner throughout the cortex.
4. Endodermis:
- Dicot Root: The endodermis in dicot roots consists of a single layer of tightly packed cells with a Casparian strip. The Casparian strip acts as a barrier to control the movement of water and minerals into the vascular tissue.
- Monocot Root: Monocot roots also possess an endodermis, but it lacks the Casparian strip. The cells of the endodermis are loosely arranged, allowing for a freer movement of substances.
5. Pith:
- Dicot Root: Some dicot roots may possess a pith, which is a central region of parenchyma cells located within the vascular cylinder. It provides storage and support to the root.
- Monocot Root: Monocot roots generally lack a pith and have a more compact arrangement of tissues in the center.
6. Growth Pattern:
- Dicot Root: Dicot roots exhibit both primary and secondary growth. The primary growth involves the elongation of the primary root, while secondary growth leads to the formation of lateral roots.
- Monocot Root: Monocot roots primarily undergo primary growth and do not exhibit significant secondary growth. The fibrous root system continually produces new roots from the base of the stem.
In conclusion, dicot and monocot roots differ in their anatomy, root cap, vascular tissue arrangement, endodermis structure, presence of pith, and growth patterns. Understanding these differences is essential to comprehend the unique characteristics and functions of each type of root.
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
Difference between dicot root and monocot root__its all about to help you so don't answer please?
Question Description
Difference between dicot root and monocot root__its all about to help you so don't answer please? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Difference between dicot root and monocot root__its all about to help you so don't answer please? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Difference between dicot root and monocot root__its all about to help you so don't answer please?.
Difference between dicot root and monocot root__its all about to help you so don't answer please? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Difference between dicot root and monocot root__its all about to help you so don't answer please? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Difference between dicot root and monocot root__its all about to help you so don't answer please?.
Solutions for Difference between dicot root and monocot root__its all about to help you so don't answer please? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Difference between dicot root and monocot root__its all about to help you so don't answer please? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Difference between dicot root and monocot root__its all about to help you so don't answer please?, a detailed solution for Difference between dicot root and monocot root__its all about to help you so don't answer please? has been provided alongside types of Difference between dicot root and monocot root__its all about to help you so don't answer please? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Difference between dicot root and monocot root__its all about to help you so don't answer please? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























