Chemical Engineering Exam > Chemical Engineering Questions > Solar radiation of falls on a grey opaque su...
Start Learning for Free
Solar radiation of falls on a grey opaque surface at steady state. The surface has a temperature of and emissivity of 0.8. Find radiosity from the surface?
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Solar radiation of falls on a grey opaque surface at steady state. Th...
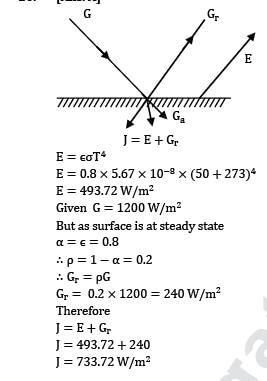
J = E+Gr
E = εσT4
E = 0.8 x 5.67 x 10-8 x (50 + 273)4
E = 493.72 W/m2
Given G = 1200 W/m2
But as surface is at steady state
α = ε = 0.8
∴ ρ = 1 -α = 0.2
∴ Gr = ρG
Gr = 0.2 x 1200 = 240 W/m2
Therefore
J = E+Gr
J = 493.72 + 240
J = 733.72 W/m2
Most Upvoted Answer
Solar radiation of falls on a grey opaque surface at steady state. Th...
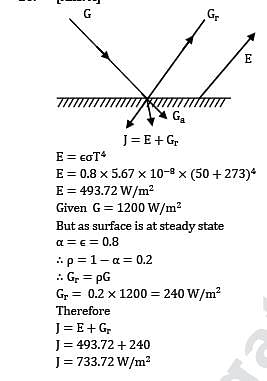
J = E+Gr
E = εσT4
E = 0.8 x 5.67 x 10-8 x (50 + 273)4
E = 493.72 W/m2
Given G = 1200 W/m2
But as surface is at steady state
α = ε = 0.8
∴ ρ = 1 -α = 0.2
∴ Gr = ρG
Gr = 0.2 x 1200 = 240 W/m2
Therefore
J = E+Gr
J = 493.72 + 240
J = 733.72 W/m2
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Solar radiation of falls on a grey opaque surface at steady state. Th...
Understanding the Problem
In this scenario, we are examining a grey opaque surface receiving solar radiation at steady state. The surface has a defined temperature and an emissivity of 0.8. Our goal is to determine the radiosity of this surface.
Key Concepts
- Radiosity (J): This is the total energy leaving a surface per unit area, which includes both emitted and reflected energy.
- Emissivity (ε): This is a measure of how effectively a surface emits thermal radiation relative to a perfect black body. For this case, ε is given as 0.8.
Formulating the Radiosity
The formula for radiosity can be expressed as:
J = ε * σ * T^4 + (1 - ε) * G
Where:
- J = Radiosity
- ε = Emissivity of the surface (0.8)
- σ = Stefan-Boltzmann constant (approximately 5.67 x 10^-8 W/m²K⁴)
- T = Temperature of the surface in Kelvin
- G = Irradiation or solar radiation incident on the surface
Calculating the Components
1. Emitted Radiation: This is calculated using the emissivity and the temperature of the surface.
2. Reflected Radiation: This is determined by the proportion of solar radiation that is not absorbed due to emissivity.
Final Calculation
To find the final value of radiosity, simply plug in the values for temperature, emissivity, and solar radiation into the formula. The final output will yield the radiosity of the grey opaque surface.
Conclusion
In summary, the total radiosity J combines both emitted and reflected components, accounting for the surface's emissivity. By understanding the contribution from both thermal emission and solar radiation absorption, one can accurately determine the radiosity from the surface in question.
In this scenario, we are examining a grey opaque surface receiving solar radiation at steady state. The surface has a defined temperature and an emissivity of 0.8. Our goal is to determine the radiosity of this surface.
Key Concepts
- Radiosity (J): This is the total energy leaving a surface per unit area, which includes both emitted and reflected energy.
- Emissivity (ε): This is a measure of how effectively a surface emits thermal radiation relative to a perfect black body. For this case, ε is given as 0.8.
Formulating the Radiosity
The formula for radiosity can be expressed as:
J = ε * σ * T^4 + (1 - ε) * G
Where:
- J = Radiosity
- ε = Emissivity of the surface (0.8)
- σ = Stefan-Boltzmann constant (approximately 5.67 x 10^-8 W/m²K⁴)
- T = Temperature of the surface in Kelvin
- G = Irradiation or solar radiation incident on the surface
Calculating the Components
1. Emitted Radiation: This is calculated using the emissivity and the temperature of the surface.
2. Reflected Radiation: This is determined by the proportion of solar radiation that is not absorbed due to emissivity.
Final Calculation
To find the final value of radiosity, simply plug in the values for temperature, emissivity, and solar radiation into the formula. The final output will yield the radiosity of the grey opaque surface.
Conclusion
In summary, the total radiosity J combines both emitted and reflected components, accounting for the surface's emissivity. By understanding the contribution from both thermal emission and solar radiation absorption, one can accurately determine the radiosity from the surface in question.

|
Explore Courses for Chemical Engineering exam
|

|
Similar Chemical Engineering Doubts
Solar radiation of falls on a grey opaque surface at steady state. The surface has a temperature of and emissivity of 0.8. Find radiosity from the surface?Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Solar radiation of falls on a grey opaque surface at steady state. The surface has a temperature of and emissivity of 0.8. Find radiosity from the surface?Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Chemical Engineering 2024 is part of Chemical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Chemical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about Solar radiation of falls on a grey opaque surface at steady state. The surface has a temperature of and emissivity of 0.8. Find radiosity from the surface?Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Chemical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Solar radiation of falls on a grey opaque surface at steady state. The surface has a temperature of and emissivity of 0.8. Find radiosity from the surface?Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solar radiation of falls on a grey opaque surface at steady state. The surface has a temperature of and emissivity of 0.8. Find radiosity from the surface?Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Chemical Engineering 2024 is part of Chemical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Chemical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about Solar radiation of falls on a grey opaque surface at steady state. The surface has a temperature of and emissivity of 0.8. Find radiosity from the surface?Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Chemical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Solar radiation of falls on a grey opaque surface at steady state. The surface has a temperature of and emissivity of 0.8. Find radiosity from the surface?Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Solar radiation of falls on a grey opaque surface at steady state. The surface has a temperature of and emissivity of 0.8. Find radiosity from the surface?Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Chemical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Chemical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Solar radiation of falls on a grey opaque surface at steady state. The surface has a temperature of and emissivity of 0.8. Find radiosity from the surface?Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Solar radiation of falls on a grey opaque surface at steady state. The surface has a temperature of and emissivity of 0.8. Find radiosity from the surface?Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Solar radiation of falls on a grey opaque surface at steady state. The surface has a temperature of and emissivity of 0.8. Find radiosity from the surface?Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Solar radiation of falls on a grey opaque surface at steady state. The surface has a temperature of and emissivity of 0.8. Find radiosity from the surface?Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Solar radiation of falls on a grey opaque surface at steady state. The surface has a temperature of and emissivity of 0.8. Find radiosity from the surface?Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Chemical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Chemical Engineering exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















