Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Questions > What do you mean by exothermic and endothermi...
Start Learning for Free
What do you mean by exothermic and endothermic reaction ? give with examples.?
Most Upvoted Answer
What do you mean by exothermic and endothermic reaction ? give with ex...
- Exothermic reactions are the reactions in which heat is released during the process. In these type of reactions reactants are at higher energy as compared to products. Due to this products are more stable than the reactants.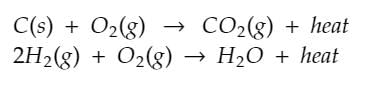
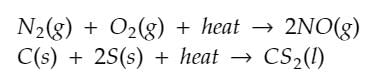
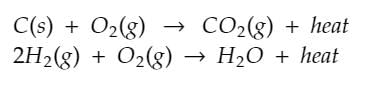
- Endothermic reactions are the reactions in which heat is absorbed during the process. In these type of reactions reactants are at lower energy as compared to products. Due to this products are less stable than the reactants.
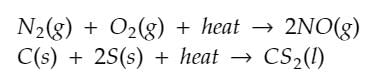
Community Answer
What do you mean by exothermic and endothermic reaction ? give with ex...
Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions:
Exothermic and endothermic reactions are two types of chemical reactions that involve the release or absorption of energy, respectively. These reactions can be better understood by exploring their definitions, examples, and explanations.
**Exothermic Reaction:**
An exothermic reaction is a chemical reaction that releases energy in the form of heat or light. In other words, the products of the reaction have less energy than the reactants, resulting in a net release of energy. This energy is often observed as an increase in temperature.
**Examples of Exothermic Reactions:**
1. Combustion: The reaction between a fuel and oxygen is highly exothermic. For example, the combustion of gasoline in a car engine releases energy in the form of heat and light.
2. Neutralization: When an acid reacts with a base, an exothermic reaction occurs. For instance, the reaction between hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide produces water and releases energy.
3. Oxidation: Oxidation reactions, such as the rusting of iron, are exothermic. Iron reacts with oxygen in the air, and this reaction releases heat.
**Explanation of Exothermic Reactions:**
In an exothermic reaction, the reactants have higher potential energy than the products. As the reaction proceeds, energy is released, leading to a decrease in the overall energy of the system. This energy is often observed as an increase in temperature. The reaction is spontaneous, meaning it occurs naturally without any external energy input.
**Endothermic Reaction:**
An endothermic reaction is a chemical reaction that absorbs energy from its surroundings. In this type of reaction, the products have higher energy than the reactants, resulting in a net absorption of energy.
**Examples of Endothermic Reactions:**
1. Photosynthesis: The process by which plants convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose and oxygen is an endothermic reaction. Energy from the sun is absorbed during this process.
2. Dissolution: When certain substances dissolve in water, they can absorb energy. For example, dissolving ammonium nitrate in water is an endothermic reaction that absorbs heat.
3. Cooking: Many cooking processes involve endothermic reactions. For instance, when you cook an egg, heat is absorbed from the surroundings to cook the egg.
**Explanation of Endothermic Reactions:**
In an endothermic reaction, the reactants have lower potential energy than the products. As the reaction proceeds, energy is absorbed from the surroundings, leading to an increase in the overall energy of the system. This energy is often observed as a decrease in temperature. The reaction is non-spontaneous and requires an external energy source to occur.
In summary, exothermic reactions release energy, while endothermic reactions absorb energy. These reactions play a crucial role in various chemical processes and have significant implications in fields such as energy production, cooking, and the environment.
Exothermic and endothermic reactions are two types of chemical reactions that involve the release or absorption of energy, respectively. These reactions can be better understood by exploring their definitions, examples, and explanations.
**Exothermic Reaction:**
An exothermic reaction is a chemical reaction that releases energy in the form of heat or light. In other words, the products of the reaction have less energy than the reactants, resulting in a net release of energy. This energy is often observed as an increase in temperature.
**Examples of Exothermic Reactions:**
1. Combustion: The reaction between a fuel and oxygen is highly exothermic. For example, the combustion of gasoline in a car engine releases energy in the form of heat and light.
2. Neutralization: When an acid reacts with a base, an exothermic reaction occurs. For instance, the reaction between hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide produces water and releases energy.
3. Oxidation: Oxidation reactions, such as the rusting of iron, are exothermic. Iron reacts with oxygen in the air, and this reaction releases heat.
**Explanation of Exothermic Reactions:**
In an exothermic reaction, the reactants have higher potential energy than the products. As the reaction proceeds, energy is released, leading to a decrease in the overall energy of the system. This energy is often observed as an increase in temperature. The reaction is spontaneous, meaning it occurs naturally without any external energy input.
**Endothermic Reaction:**
An endothermic reaction is a chemical reaction that absorbs energy from its surroundings. In this type of reaction, the products have higher energy than the reactants, resulting in a net absorption of energy.
**Examples of Endothermic Reactions:**
1. Photosynthesis: The process by which plants convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose and oxygen is an endothermic reaction. Energy from the sun is absorbed during this process.
2. Dissolution: When certain substances dissolve in water, they can absorb energy. For example, dissolving ammonium nitrate in water is an endothermic reaction that absorbs heat.
3. Cooking: Many cooking processes involve endothermic reactions. For instance, when you cook an egg, heat is absorbed from the surroundings to cook the egg.
**Explanation of Endothermic Reactions:**
In an endothermic reaction, the reactants have lower potential energy than the products. As the reaction proceeds, energy is absorbed from the surroundings, leading to an increase in the overall energy of the system. This energy is often observed as a decrease in temperature. The reaction is non-spontaneous and requires an external energy source to occur.
In summary, exothermic reactions release energy, while endothermic reactions absorb energy. These reactions play a crucial role in various chemical processes and have significant implications in fields such as energy production, cooking, and the environment.
Attention Class 10 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 10 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 10.

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Similar Class 10 Doubts
What do you mean by exothermic and endothermic reaction ? give with examples.?
Question Description
What do you mean by exothermic and endothermic reaction ? give with examples.? for Class 10 2024 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about What do you mean by exothermic and endothermic reaction ? give with examples.? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What do you mean by exothermic and endothermic reaction ? give with examples.?.
What do you mean by exothermic and endothermic reaction ? give with examples.? for Class 10 2024 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about What do you mean by exothermic and endothermic reaction ? give with examples.? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What do you mean by exothermic and endothermic reaction ? give with examples.?.
Solutions for What do you mean by exothermic and endothermic reaction ? give with examples.? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 10.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of What do you mean by exothermic and endothermic reaction ? give with examples.? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
What do you mean by exothermic and endothermic reaction ? give with examples.?, a detailed solution for What do you mean by exothermic and endothermic reaction ? give with examples.? has been provided alongside types of What do you mean by exothermic and endothermic reaction ? give with examples.? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice What do you mean by exothermic and endothermic reaction ? give with examples.? tests, examples and also practice Class 10 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























