UPSC Exam > UPSC Questions > Consider the following statements:1. The dur...
Start Learning for Free
Consider the following statements:
1. The duration of the monsoon decreases from southern India to northern India.
2. The amount of annual rainfall in the northern plains of India decreases from east to west.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- a)1 only
- b)2 only
- c)Both 1 and 2
- d)Neither 1 nor 2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Consider the following statements:1. The duration of the monsoon decr...
The correct answer is Both 1 and 2.
View all questions of this test
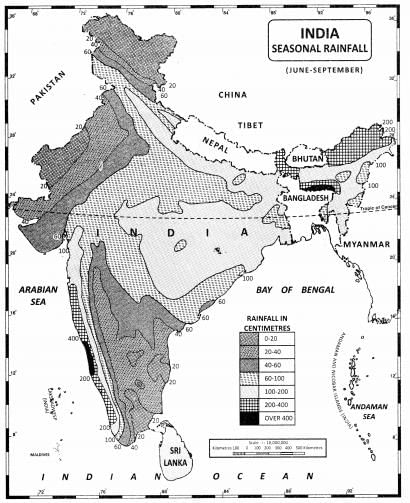
Key-Points Distribution of Rainfall in India- Areas of Medium Rainfall- Areas of Low Rainfall- Areas of Inadequate Rainfall-
- Duration of the monsoon in India-
- The Southern part of India, being near to the sea, gets rainfall early and for a longer duration than in the northern part.
- As rain-bearing winds cross western ghats humidity decreases and so does rainfall in the northern part of India.
- The Southern part of India receives rainfall from the southwest monsoon and the retreating southwest monsoon (northeast monsoon). Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- The monsoon rainfall has a declining trend with increasing distance from the sea. Kolkata receives 119 cm during the southwest monsoon period, Patna 105 cm, Allahabad 76 cm and Delhi 56 cm. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- The average annual rainfall in India is about 125 cm, but it has great spatial variations.
- Areas of High Rainfall-
- The highest rainfall occurs along the west coast, on the Western Ghats, as well as in the sub-Himalayan areas in the northeast and the hills of Meghalaya. Here the rainfall exceeds 200 cm.
- In some parts of Khasi and Jaintia hills, the rainfall exceeds 1,000 cm.
- In the Brahmaputra valley and the adjoining hills, the rainfall is less than 200 cm.
- Rainfall between 100-200 cm is received in the southern parts of Gujarat, east Tamil Nadu, northeastern Peninsula covering Odisha, Jharkhand, Bihar, eastern Madhya Pradesh, northern Ganga plain along the sub-Himalayas and the Cachar Valley and Manipur.
- Western Uttar Pradesh, Delhi, Haryana, Punjab, Jammu and Kashmir, eastern Rajasthan, Gujarat and Deccan Plateau receives rainfall between 50-100 cm.
- Parts of the Peninsula, especially in Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka and Maharashtra, Ladakh and most of western Rajasthan receive rainfall below 50 cm.
Most Upvoted Answer
Consider the following statements:1. The duration of the monsoon decr...
Statement 1: The duration of the monsoon decreases from southern India to northern India.
The monsoon is a seasonal wind pattern that brings heavy rainfall to the Indian subcontinent. It is characterized by the southwest monsoon (June to September) and the northeast monsoon (October to December).
In southern India, the southwest monsoon arrives in early June and lasts until September, bringing a significant amount of rainfall to the region. However, as we move towards northern India, the duration of the monsoon gradually decreases. In northern India, the monsoon arrives later, usually in July, and lasts for a shorter period, generally until September or early October. This means that the southern parts of India experience a longer duration of monsoon compared to the northern parts.
Therefore, Statement 1 is correct.
Statement 2: The amount of annual rainfall in the northern plains of India decreases from east to west.
The northern plains of India are a vast fertile region that stretches from the foothills of the Himalayas in the north to the Deccan Plateau in the south. These plains are watered by various rivers, including the Ganga, Yamuna, and their tributaries.
The distribution of rainfall in the northern plains is influenced by the geography and the prevailing wind patterns. The eastern parts of the northern plains, which are closer to the Bay of Bengal, receive more rainfall due to the moisture-laden winds from the Bay. As we move towards the western parts, which are farther away from the Bay, the amount of rainfall gradually decreases.
Therefore, Statement 2 is correct.
Conclusion: Both Statement 1 and Statement 2 are correct.
The monsoon duration decreases from southern India to northern India, and the amount of annual rainfall in the northern plains of India decreases from east to west. These are important geographical features of the Indian subcontinent and have significant implications for agriculture, water resources, and overall climate patterns in the region.
The monsoon is a seasonal wind pattern that brings heavy rainfall to the Indian subcontinent. It is characterized by the southwest monsoon (June to September) and the northeast monsoon (October to December).
In southern India, the southwest monsoon arrives in early June and lasts until September, bringing a significant amount of rainfall to the region. However, as we move towards northern India, the duration of the monsoon gradually decreases. In northern India, the monsoon arrives later, usually in July, and lasts for a shorter period, generally until September or early October. This means that the southern parts of India experience a longer duration of monsoon compared to the northern parts.
Therefore, Statement 1 is correct.
Statement 2: The amount of annual rainfall in the northern plains of India decreases from east to west.
The northern plains of India are a vast fertile region that stretches from the foothills of the Himalayas in the north to the Deccan Plateau in the south. These plains are watered by various rivers, including the Ganga, Yamuna, and their tributaries.
The distribution of rainfall in the northern plains is influenced by the geography and the prevailing wind patterns. The eastern parts of the northern plains, which are closer to the Bay of Bengal, receive more rainfall due to the moisture-laden winds from the Bay. As we move towards the western parts, which are farther away from the Bay, the amount of rainfall gradually decreases.
Therefore, Statement 2 is correct.
Conclusion: Both Statement 1 and Statement 2 are correct.
The monsoon duration decreases from southern India to northern India, and the amount of annual rainfall in the northern plains of India decreases from east to west. These are important geographical features of the Indian subcontinent and have significant implications for agriculture, water resources, and overall climate patterns in the region.

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
Question Description
Consider the following statements:1. The duration of the monsoon decreases from southern India to northern India.2. The amount of annual rainfall in the northern plains of India decreases from east to west.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?a)1 onlyb)2 onlyc)Both 1 and 2d)Neither 1 nor 2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for UPSC 2025 is part of UPSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the UPSC exam syllabus. Information about Consider the following statements:1. The duration of the monsoon decreases from southern India to northern India.2. The amount of annual rainfall in the northern plains of India decreases from east to west.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?a)1 onlyb)2 onlyc)Both 1 and 2d)Neither 1 nor 2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for UPSC 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Consider the following statements:1. The duration of the monsoon decreases from southern India to northern India.2. The amount of annual rainfall in the northern plains of India decreases from east to west.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?a)1 onlyb)2 onlyc)Both 1 and 2d)Neither 1 nor 2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Consider the following statements:1. The duration of the monsoon decreases from southern India to northern India.2. The amount of annual rainfall in the northern plains of India decreases from east to west.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?a)1 onlyb)2 onlyc)Both 1 and 2d)Neither 1 nor 2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for UPSC 2025 is part of UPSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the UPSC exam syllabus. Information about Consider the following statements:1. The duration of the monsoon decreases from southern India to northern India.2. The amount of annual rainfall in the northern plains of India decreases from east to west.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?a)1 onlyb)2 onlyc)Both 1 and 2d)Neither 1 nor 2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for UPSC 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Consider the following statements:1. The duration of the monsoon decreases from southern India to northern India.2. The amount of annual rainfall in the northern plains of India decreases from east to west.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?a)1 onlyb)2 onlyc)Both 1 and 2d)Neither 1 nor 2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Consider the following statements:1. The duration of the monsoon decreases from southern India to northern India.2. The amount of annual rainfall in the northern plains of India decreases from east to west.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?a)1 onlyb)2 onlyc)Both 1 and 2d)Neither 1 nor 2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for UPSC.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for UPSC Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Consider the following statements:1. The duration of the monsoon decreases from southern India to northern India.2. The amount of annual rainfall in the northern plains of India decreases from east to west.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?a)1 onlyb)2 onlyc)Both 1 and 2d)Neither 1 nor 2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Consider the following statements:1. The duration of the monsoon decreases from southern India to northern India.2. The amount of annual rainfall in the northern plains of India decreases from east to west.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?a)1 onlyb)2 onlyc)Both 1 and 2d)Neither 1 nor 2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Consider the following statements:1. The duration of the monsoon decreases from southern India to northern India.2. The amount of annual rainfall in the northern plains of India decreases from east to west.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?a)1 onlyb)2 onlyc)Both 1 and 2d)Neither 1 nor 2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Consider the following statements:1. The duration of the monsoon decreases from southern India to northern India.2. The amount of annual rainfall in the northern plains of India decreases from east to west.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?a)1 onlyb)2 onlyc)Both 1 and 2d)Neither 1 nor 2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Consider the following statements:1. The duration of the monsoon decreases from southern India to northern India.2. The amount of annual rainfall in the northern plains of India decreases from east to west.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?a)1 onlyb)2 onlyc)Both 1 and 2d)Neither 1 nor 2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice UPSC tests.

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















