Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Questions > Draw a table to show the differences and simi...
Start Learning for Free
Draw a table to show the differences and similarities in the nation building process of france, germany and italy?
Most Upvoted Answer
Draw a table to show the differences and similarities in the nation bu...
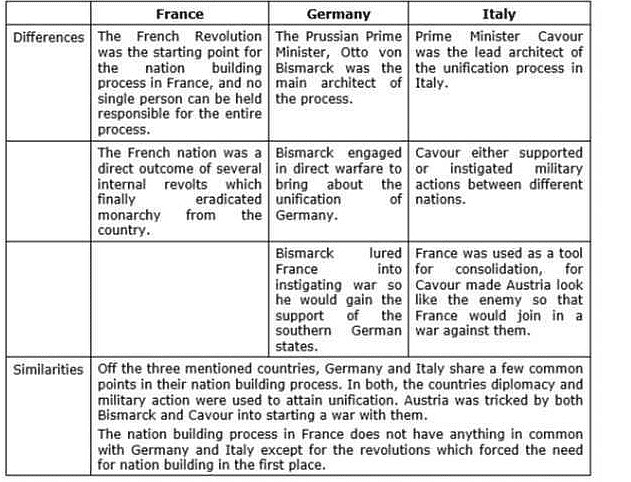
Community Answer
Draw a table to show the differences and similarities in the nation bu...
France:
- France underwent a nation-building process during the late 18th and 19th centuries, which was marked by significant political and social changes.
- The French Revolution (1789-1799) played a crucial role in shaping the nation. It led to the overthrow of the monarchy, the establishment of a republic, and the Reign of Terror.
- Napoleon Bonaparte emerged as a prominent figure during this period and further consolidated the French state. He introduced sweeping reforms, including the Napoleonic Code, which provided a standardized legal system.
- France experienced industrialization during the 19th century, which contributed to its economic growth and the consolidation of a national identity.
- The French nation-building process was characterized by a strong centralized state, the promotion of a French language and culture, and the assimilation of diverse regions into a unified nation.
Germany:
- Germany underwent a nation-building process during the 19th century, known as the "German unification." It was a complex and gradual process.
- The Congress of Vienna in 1815 laid the foundation for the German Confederation, a loose association of German states. However, it was largely dominated by Austria and Prussia.
- Otto von Bismarck, the Prime Minister of Prussia, played a pivotal role in German unification. He pursued a policy of "blood and iron" and successfully waged wars against Denmark, Austria, and France.
- The Franco-Prussian War of 1870-1871 resulted in the defeat of France and the proclamation of the German Empire in 1871. This marked the culmination of the nation-building process.
- Germany's nation-building process emphasized the role of Prussia and a strong militaristic state. Bismarck implemented policies to centralize power and promote German nationalism, including the Kulturkampf and the establishment of a unified legal system.
Italy:
- Italy underwent a nation-building process during the 19th century, known as the "Italian unification" or "Risorgimento." It was a complex and fragmented process due to regional divisions.
- Key figures such as Giuseppe Mazzini, Giuseppe Garibaldi, and Count Camillo di Cavour played significant roles in the unification movement.
- The Kingdom of Sardinia-Piedmont, led by Cavour, emerged as the driving force behind Italian unification. Through diplomatic alliances and military campaigns, Sardinia-Piedmont successfully annexed various regions.
- The Kingdom of Italy was proclaimed in 1861, although the process of unification was not fully completed until 1870 with the capture of Rome.
- Italy's nation-building process involved the consolidation of various states and regions, each with its own distinct cultural and linguistic identities. Efforts were made to promote a unified Italian language and culture.
In summary, France, Germany, and Italy underwent distinct nation-building processes during the 18th and 19th centuries. While France's process was marked by the French Revolution and a strong centralized state, Germany's process revolved around Prussian dominance and militarism. Italy's process involved the unification of various regions with distinct cultural identities. Despite their differences, all three nations sought to establish a unified state and promote a sense of national identity.
- France underwent a nation-building process during the late 18th and 19th centuries, which was marked by significant political and social changes.
- The French Revolution (1789-1799) played a crucial role in shaping the nation. It led to the overthrow of the monarchy, the establishment of a republic, and the Reign of Terror.
- Napoleon Bonaparte emerged as a prominent figure during this period and further consolidated the French state. He introduced sweeping reforms, including the Napoleonic Code, which provided a standardized legal system.
- France experienced industrialization during the 19th century, which contributed to its economic growth and the consolidation of a national identity.
- The French nation-building process was characterized by a strong centralized state, the promotion of a French language and culture, and the assimilation of diverse regions into a unified nation.
Germany:
- Germany underwent a nation-building process during the 19th century, known as the "German unification." It was a complex and gradual process.
- The Congress of Vienna in 1815 laid the foundation for the German Confederation, a loose association of German states. However, it was largely dominated by Austria and Prussia.
- Otto von Bismarck, the Prime Minister of Prussia, played a pivotal role in German unification. He pursued a policy of "blood and iron" and successfully waged wars against Denmark, Austria, and France.
- The Franco-Prussian War of 1870-1871 resulted in the defeat of France and the proclamation of the German Empire in 1871. This marked the culmination of the nation-building process.
- Germany's nation-building process emphasized the role of Prussia and a strong militaristic state. Bismarck implemented policies to centralize power and promote German nationalism, including the Kulturkampf and the establishment of a unified legal system.
Italy:
- Italy underwent a nation-building process during the 19th century, known as the "Italian unification" or "Risorgimento." It was a complex and fragmented process due to regional divisions.
- Key figures such as Giuseppe Mazzini, Giuseppe Garibaldi, and Count Camillo di Cavour played significant roles in the unification movement.
- The Kingdom of Sardinia-Piedmont, led by Cavour, emerged as the driving force behind Italian unification. Through diplomatic alliances and military campaigns, Sardinia-Piedmont successfully annexed various regions.
- The Kingdom of Italy was proclaimed in 1861, although the process of unification was not fully completed until 1870 with the capture of Rome.
- Italy's nation-building process involved the consolidation of various states and regions, each with its own distinct cultural and linguistic identities. Efforts were made to promote a unified Italian language and culture.
In summary, France, Germany, and Italy underwent distinct nation-building processes during the 18th and 19th centuries. While France's process was marked by the French Revolution and a strong centralized state, Germany's process revolved around Prussian dominance and militarism. Italy's process involved the unification of various regions with distinct cultural identities. Despite their differences, all three nations sought to establish a unified state and promote a sense of national identity.
Attention Class 9 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 9 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 9.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Similar Class 9 Doubts
Draw a table to show the differences and similarities in the nation building process of france, germany and italy?
Question Description
Draw a table to show the differences and similarities in the nation building process of france, germany and italy? for Class 9 2024 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about Draw a table to show the differences and similarities in the nation building process of france, germany and italy? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Draw a table to show the differences and similarities in the nation building process of france, germany and italy?.
Draw a table to show the differences and similarities in the nation building process of france, germany and italy? for Class 9 2024 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about Draw a table to show the differences and similarities in the nation building process of france, germany and italy? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Draw a table to show the differences and similarities in the nation building process of france, germany and italy?.
Solutions for Draw a table to show the differences and similarities in the nation building process of france, germany and italy? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 9.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Draw a table to show the differences and similarities in the nation building process of france, germany and italy? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Draw a table to show the differences and similarities in the nation building process of france, germany and italy?, a detailed solution for Draw a table to show the differences and similarities in the nation building process of france, germany and italy? has been provided alongside types of Draw a table to show the differences and similarities in the nation building process of france, germany and italy? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Draw a table to show the differences and similarities in the nation building process of france, germany and italy? tests, examples and also practice Class 9 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























