NEET Exam > NEET Questions > The plant hormone used to destroy weeds in a ...
Start Learning for Free
The plant hormone used to destroy weeds in a field is: [2021]
- a)2, 4-D
- b)IBA
- c)IAA
- d)NAA
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
The plant hormone used to destroy weeds in a field is: [2021]a)2, 4-D...
2, 4-D, widely used to kill dicotyledonous weeds, does not affect mature monocotyledonous plants.
They help to initiate rooting in stem cuttings, an application widely used for plant propagation. Auxins promote flowering e.g. in pineapples. They help to prevent fruit and leaf drop at early stages but promote the abscission of older mature leaves and fruits.
In most higher plants, the growing apical bud inhibits the growth of the lateral (axillary) buds, a phenomenon called apical dominance. Removal of shoot tips (decapitation) usually results in the growth of lateral buds (Figure 15.11). It is widely applied in tea plantations, hedge-making. Can you explain why?
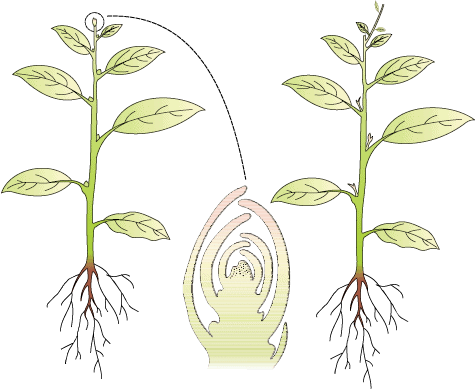
In most higher plants, the growing apical bud inhibits the growth of the lateral (axillary) buds, a phenomenon called apical dominance. Removal of shoot tips (decapitation) usually results in the growth of lateral buds (Figure 15.11). It is widely applied in tea plantations, hedge-making. Can you explain why?

Most Upvoted Answer
The plant hormone used to destroy weeds in a field is: [2021]a)2, 4-D...
2, 4-D as a Plant Hormone for Weed Control
Definition:
2, 4-D (2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid) is a synthetic plant hormone that is widely used as a selective herbicide to control broadleaf weeds in fields.
Mechanism of Action:
- 2, 4-D mimics the natural plant hormone auxin, which regulates plant growth and development.
- When applied to weeds, 2, 4-D disrupts the normal growth patterns by causing uncontrolled cell division and growth, ultimately leading to the death of the weed.
Selective Herbicide:
- One of the key advantages of 2, 4-D is its selectivity towards broadleaf weeds while being relatively safe for grasses.
- This selectivity allows farmers to target specific weeds without harming their crops.
Application:
- 2, 4-D is commonly used in agriculture, forestry, and residential settings to control weeds in fields, pastures, lawns, and gardens.
- It is available in various formulations such as liquid sprays, granules, and pellets for different application methods.
Environmental Considerations:
- While 2, 4-D is effective in weed control, there are concerns about its potential environmental impact, including runoff into water sources and non-target plant damage.
- Proper application techniques and adherence to safety guidelines are essential to minimize these risks.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, 2, 4-D is a plant hormone that acts as a potent herbicide for weed control in agricultural settings. Its selective nature, mode of action, and application versatility make it a valuable tool for farmers in managing weed infestations effectively. However, proper usage and environmental considerations are crucial to ensure its sustainable use in weed management practices.
Definition:
2, 4-D (2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid) is a synthetic plant hormone that is widely used as a selective herbicide to control broadleaf weeds in fields.
Mechanism of Action:
- 2, 4-D mimics the natural plant hormone auxin, which regulates plant growth and development.
- When applied to weeds, 2, 4-D disrupts the normal growth patterns by causing uncontrolled cell division and growth, ultimately leading to the death of the weed.
Selective Herbicide:
- One of the key advantages of 2, 4-D is its selectivity towards broadleaf weeds while being relatively safe for grasses.
- This selectivity allows farmers to target specific weeds without harming their crops.
Application:
- 2, 4-D is commonly used in agriculture, forestry, and residential settings to control weeds in fields, pastures, lawns, and gardens.
- It is available in various formulations such as liquid sprays, granules, and pellets for different application methods.
Environmental Considerations:
- While 2, 4-D is effective in weed control, there are concerns about its potential environmental impact, including runoff into water sources and non-target plant damage.
- Proper application techniques and adherence to safety guidelines are essential to minimize these risks.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, 2, 4-D is a plant hormone that acts as a potent herbicide for weed control in agricultural settings. Its selective nature, mode of action, and application versatility make it a valuable tool for farmers in managing weed infestations effectively. However, proper usage and environmental considerations are crucial to ensure its sustainable use in weed management practices.
Free Test
| FREE | Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The plant hormone used to destroy weeds in a field is: [2021]a)2, 4-D...
2, 4-D as a Plant Hormone for Weed Control
What is 2, 4-D?
2, 4-D (2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid) is a synthetic auxin plant hormone that is widely used as a herbicide to control broadleaf weeds in fields.
Mechanism of Action
- 2, 4-D acts by mimicking the natural auxin hormone in plants, causing uncontrolled growth and eventually leading to the death of the weed.
- It disrupts the normal growth patterns of plants, causing them to exhibit symptoms such as uncontrolled cell division, lack of apical dominance, and abnormal growth.
Application of 2, 4-D
- 2, 4-D is commonly used in agriculture to control weeds in crops such as corn, soybeans, and wheat.
- It is applied in the form of herbicides that are sprayed directly onto the leaves of weeds, where it is absorbed and translocated throughout the plant.
Benefits of Using 2, 4-D
- 2, 4-D is effective in controlling a wide range of broadleaf weeds, making it a versatile herbicide for farmers.
- It is relatively inexpensive and has a long history of safe use when applied according to label instructions.
Concerns and Precautions
- Despite its effectiveness, there are concerns about the potential environmental impacts of 2, 4-D, including runoff into water sources and non-target plant damage.
- It is important for farmers and applicators to follow proper application guidelines to minimize these risks.
In conclusion, 2, 4-D is a widely used plant hormone herbicide that effectively controls weeds in agricultural fields. Its ability to mimic natural auxin hormones makes it a powerful tool for farmers seeking to manage weed populations and improve crop yields.
What is 2, 4-D?
2, 4-D (2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid) is a synthetic auxin plant hormone that is widely used as a herbicide to control broadleaf weeds in fields.
Mechanism of Action
- 2, 4-D acts by mimicking the natural auxin hormone in plants, causing uncontrolled growth and eventually leading to the death of the weed.
- It disrupts the normal growth patterns of plants, causing them to exhibit symptoms such as uncontrolled cell division, lack of apical dominance, and abnormal growth.
Application of 2, 4-D
- 2, 4-D is commonly used in agriculture to control weeds in crops such as corn, soybeans, and wheat.
- It is applied in the form of herbicides that are sprayed directly onto the leaves of weeds, where it is absorbed and translocated throughout the plant.
Benefits of Using 2, 4-D
- 2, 4-D is effective in controlling a wide range of broadleaf weeds, making it a versatile herbicide for farmers.
- It is relatively inexpensive and has a long history of safe use when applied according to label instructions.
Concerns and Precautions
- Despite its effectiveness, there are concerns about the potential environmental impacts of 2, 4-D, including runoff into water sources and non-target plant damage.
- It is important for farmers and applicators to follow proper application guidelines to minimize these risks.
In conclusion, 2, 4-D is a widely used plant hormone herbicide that effectively controls weeds in agricultural fields. Its ability to mimic natural auxin hormones makes it a powerful tool for farmers seeking to manage weed populations and improve crop yields.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Question Description
The plant hormone used to destroy weeds in a field is: [2021]a)2, 4-Db)IBAc)IAAd)NAACorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about The plant hormone used to destroy weeds in a field is: [2021]a)2, 4-Db)IBAc)IAAd)NAACorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The plant hormone used to destroy weeds in a field is: [2021]a)2, 4-Db)IBAc)IAAd)NAACorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
The plant hormone used to destroy weeds in a field is: [2021]a)2, 4-Db)IBAc)IAAd)NAACorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about The plant hormone used to destroy weeds in a field is: [2021]a)2, 4-Db)IBAc)IAAd)NAACorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The plant hormone used to destroy weeds in a field is: [2021]a)2, 4-Db)IBAc)IAAd)NAACorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The plant hormone used to destroy weeds in a field is: [2021]a)2, 4-Db)IBAc)IAAd)NAACorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The plant hormone used to destroy weeds in a field is: [2021]a)2, 4-Db)IBAc)IAAd)NAACorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The plant hormone used to destroy weeds in a field is: [2021]a)2, 4-Db)IBAc)IAAd)NAACorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The plant hormone used to destroy weeds in a field is: [2021]a)2, 4-Db)IBAc)IAAd)NAACorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The plant hormone used to destroy weeds in a field is: [2021]a)2, 4-Db)IBAc)IAAd)NAACorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The plant hormone used to destroy weeds in a field is: [2021]a)2, 4-Db)IBAc)IAAd)NAACorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























