NEET Exam > NEET Questions > The presence of carbon in an organic compound...
Start Learning for Free
The presence of carbon in an organic compound can be shown by
- a)Heating the compound with sodium
- b)Heating the compound with cupric oxide
- c)Heating the compound on bunsen flame
- d)Heating the compound with magnesium.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
The presence of carbon in an organic compound can be shown bya)Heating...
Compound when heated with CuO reduces CuO to Cu and oxidises C to CO2 which turns lime water milky.
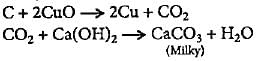
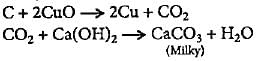
Most Upvoted Answer
The presence of carbon in an organic compound can be shown bya)Heating...
Explanation:
The presence of carbon in an organic compound can be shown by heating the compound with cupric oxide (CuO). This is known as the copper oxide test or the combustion of organic compounds.
Procedure:
1. Take a small amount of the organic compound in a test tube.
2. Add a small amount of cupric oxide (CuO) to the test tube.
3. Mix the compound and cupric oxide thoroughly.
4. Heat the mixture strongly using a Bunsen burner flame.
5. Observe the changes that occur during the heating process.
Observations:
1. Initially, the organic compound and cupric oxide appear as separate solids.
2. As the mixture is heated, the organic compound undergoes combustion and produces carbon dioxide gas (CO2).
3. The carbon dioxide gas can be identified by passing it through lime water (calcium hydroxide solution), which turns milky due to the formation of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) precipitate.
4. The cupric oxide is reduced to metallic copper (Cu) during the combustion process.
Explanation:
Organic compounds are compounds that contain carbon atoms bonded to other elements such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and halogens. Carbon is a unique element that forms the backbone of organic molecules due to its ability to form stable covalent bonds with other atoms.
When an organic compound is heated with cupric oxide (CuO), the carbon in the compound undergoes combustion. Combustion is a chemical reaction in which a substance reacts with oxygen to produce heat, light, and new products. In the case of organic compounds, the carbon atoms combine with oxygen from the cupric oxide to form carbon dioxide gas (CO2). This reaction is exothermic, meaning it releases energy in the form of heat and light.
The production of carbon dioxide gas is a characteristic reaction of organic compounds that contain carbon. By observing the formation of carbon dioxide gas and its reaction with lime water to form a white precipitate of calcium carbonate, we can confirm the presence of carbon in the organic compound.
In contrast, the other options mentioned in the question (heating the compound with sodium, heating the compound on a Bunsen flame, and heating the compound with magnesium) are not specific tests for the presence of carbon in organic compounds. These reactions may have other purposes or may not produce a specific reaction that confirms the presence of carbon. Therefore, option B (heating the compound with cupric oxide) is the correct answer.
The presence of carbon in an organic compound can be shown by heating the compound with cupric oxide (CuO). This is known as the copper oxide test or the combustion of organic compounds.
Procedure:
1. Take a small amount of the organic compound in a test tube.
2. Add a small amount of cupric oxide (CuO) to the test tube.
3. Mix the compound and cupric oxide thoroughly.
4. Heat the mixture strongly using a Bunsen burner flame.
5. Observe the changes that occur during the heating process.
Observations:
1. Initially, the organic compound and cupric oxide appear as separate solids.
2. As the mixture is heated, the organic compound undergoes combustion and produces carbon dioxide gas (CO2).
3. The carbon dioxide gas can be identified by passing it through lime water (calcium hydroxide solution), which turns milky due to the formation of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) precipitate.
4. The cupric oxide is reduced to metallic copper (Cu) during the combustion process.
Explanation:
Organic compounds are compounds that contain carbon atoms bonded to other elements such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and halogens. Carbon is a unique element that forms the backbone of organic molecules due to its ability to form stable covalent bonds with other atoms.
When an organic compound is heated with cupric oxide (CuO), the carbon in the compound undergoes combustion. Combustion is a chemical reaction in which a substance reacts with oxygen to produce heat, light, and new products. In the case of organic compounds, the carbon atoms combine with oxygen from the cupric oxide to form carbon dioxide gas (CO2). This reaction is exothermic, meaning it releases energy in the form of heat and light.
The production of carbon dioxide gas is a characteristic reaction of organic compounds that contain carbon. By observing the formation of carbon dioxide gas and its reaction with lime water to form a white precipitate of calcium carbonate, we can confirm the presence of carbon in the organic compound.
In contrast, the other options mentioned in the question (heating the compound with sodium, heating the compound on a Bunsen flame, and heating the compound with magnesium) are not specific tests for the presence of carbon in organic compounds. These reactions may have other purposes or may not produce a specific reaction that confirms the presence of carbon. Therefore, option B (heating the compound with cupric oxide) is the correct answer.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Question Description
The presence of carbon in an organic compound can be shown bya)Heating the compound with sodiumb)Heating the compound with cupric oxidec)Heating the compound on bunsen flamed)Heating the compound with magnesium.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about The presence of carbon in an organic compound can be shown bya)Heating the compound with sodiumb)Heating the compound with cupric oxidec)Heating the compound on bunsen flamed)Heating the compound with magnesium.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The presence of carbon in an organic compound can be shown bya)Heating the compound with sodiumb)Heating the compound with cupric oxidec)Heating the compound on bunsen flamed)Heating the compound with magnesium.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
The presence of carbon in an organic compound can be shown bya)Heating the compound with sodiumb)Heating the compound with cupric oxidec)Heating the compound on bunsen flamed)Heating the compound with magnesium.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about The presence of carbon in an organic compound can be shown bya)Heating the compound with sodiumb)Heating the compound with cupric oxidec)Heating the compound on bunsen flamed)Heating the compound with magnesium.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The presence of carbon in an organic compound can be shown bya)Heating the compound with sodiumb)Heating the compound with cupric oxidec)Heating the compound on bunsen flamed)Heating the compound with magnesium.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The presence of carbon in an organic compound can be shown bya)Heating the compound with sodiumb)Heating the compound with cupric oxidec)Heating the compound on bunsen flamed)Heating the compound with magnesium.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The presence of carbon in an organic compound can be shown bya)Heating the compound with sodiumb)Heating the compound with cupric oxidec)Heating the compound on bunsen flamed)Heating the compound with magnesium.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The presence of carbon in an organic compound can be shown bya)Heating the compound with sodiumb)Heating the compound with cupric oxidec)Heating the compound on bunsen flamed)Heating the compound with magnesium.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The presence of carbon in an organic compound can be shown bya)Heating the compound with sodiumb)Heating the compound with cupric oxidec)Heating the compound on bunsen flamed)Heating the compound with magnesium.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The presence of carbon in an organic compound can be shown bya)Heating the compound with sodiumb)Heating the compound with cupric oxidec)Heating the compound on bunsen flamed)Heating the compound with magnesium.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The presence of carbon in an organic compound can be shown bya)Heating the compound with sodiumb)Heating the compound with cupric oxidec)Heating the compound on bunsen flamed)Heating the compound with magnesium.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















