NEET Exam > NEET Questions > A concave mirror of focal length f1 is placed...
Start Learning for Free
A concave mirror of focal length f1 is placed at a distance of d from a convex lens of focal length f2. A beam of light coming from infinity and falling on this convex lens - concave mirror combination returns to infinity. The distance d must equal
- a)f1 + f2
- b)−f1 + f2
- c)2f1 + f2
- d)−2f1 + f2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
A concave mirror of focal length f1 is placed at a distance of d from ...
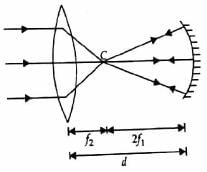
∴ d = 2f1 + f2
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
A concave mirror of focal length f1 is placed at a distance of d from ...
2f1f2/(f1+f2)c)2f1f2/(f2-f1)d)2f1f2/(f1-f2)
The correct answer is b) 2f1f2/(f1+f2).
Explanation:
Let the incident ray of light coming from infinity be parallel to the principal axis of the convex lens. This ray will pass through the focal point of the convex lens and become convergent. Let the point where this ray converges be denoted as A.
Now, this converging ray will fall on the concave mirror. As the mirror is concave, it will diverge the ray of light. Let the point where this diverging ray appears to come from be denoted as B.
This diverging ray will again fall on the convex lens. As the lens is convex, it will converge the ray of light. Let the point where this converging ray appears to come from be denoted as C.
From the given information, we know that the ray of light leaving the convex lens - concave mirror combination is parallel to the principal axis. This means that the converging ray from the convex lens and the diverging ray from the concave mirror must meet at a point on the principal axis that is at infinity.
From the ray diagram, we can see that the distance between the concave mirror and the convex lens is equal to the distance between point B and point C. Let this distance be denoted as x.
Using the mirror formula for the concave mirror and the lens formula for the convex lens, we can write:
1/f1 = 1/v - 1/u1 (for the concave mirror)
1/f2 = 1/u2 + 1/v' (for the convex lens)
where u1 is the distance of point A from the concave mirror, v is the distance of point B from the concave mirror, u2 is the distance of point B from the convex lens, and v' is the distance of point C from the convex lens.
As the ray of light leaving the convex lens - concave mirror combination is parallel to the principal axis, we can write:
v' = -u2
Substituting this value of v' in the lens formula, we get:
1/f2 = 1/u2 - 1/u2
1/f2 = 0
This means that the focal length of the convex lens is infinity. As the convex lens is a converging lens, this implies that the lens must be a plano-convex lens, with the flat side facing the concave mirror.
Substituting this value of f2 in the mirror formula, we get:
1/f1 = 1/v - 1/u1
1/f1 = -1/u1
f1 = -u1
As the concave mirror is a diverging mirror, the focal length of the mirror is negative. Substituting this value of f1 in the lens formula, we get:
1/f2 = 1/u2 - 1/(-u1)
1/f2 = 1/u2 + 1/u1
Substituting the value of v' = -u2, we get:
1/f2 = 1/u1 - 1/v'
1/f2 = 1/u1 + 1/(-u2)
1/f2 = (u2-u1
The correct answer is b) 2f1f2/(f1+f2).
Explanation:
Let the incident ray of light coming from infinity be parallel to the principal axis of the convex lens. This ray will pass through the focal point of the convex lens and become convergent. Let the point where this ray converges be denoted as A.
Now, this converging ray will fall on the concave mirror. As the mirror is concave, it will diverge the ray of light. Let the point where this diverging ray appears to come from be denoted as B.
This diverging ray will again fall on the convex lens. As the lens is convex, it will converge the ray of light. Let the point where this converging ray appears to come from be denoted as C.
From the given information, we know that the ray of light leaving the convex lens - concave mirror combination is parallel to the principal axis. This means that the converging ray from the convex lens and the diverging ray from the concave mirror must meet at a point on the principal axis that is at infinity.
From the ray diagram, we can see that the distance between the concave mirror and the convex lens is equal to the distance between point B and point C. Let this distance be denoted as x.
Using the mirror formula for the concave mirror and the lens formula for the convex lens, we can write:
1/f1 = 1/v - 1/u1 (for the concave mirror)
1/f2 = 1/u2 + 1/v' (for the convex lens)
where u1 is the distance of point A from the concave mirror, v is the distance of point B from the concave mirror, u2 is the distance of point B from the convex lens, and v' is the distance of point C from the convex lens.
As the ray of light leaving the convex lens - concave mirror combination is parallel to the principal axis, we can write:
v' = -u2
Substituting this value of v' in the lens formula, we get:
1/f2 = 1/u2 - 1/u2
1/f2 = 0
This means that the focal length of the convex lens is infinity. As the convex lens is a converging lens, this implies that the lens must be a plano-convex lens, with the flat side facing the concave mirror.
Substituting this value of f2 in the mirror formula, we get:
1/f1 = 1/v - 1/u1
1/f1 = -1/u1
f1 = -u1
As the concave mirror is a diverging mirror, the focal length of the mirror is negative. Substituting this value of f1 in the lens formula, we get:
1/f2 = 1/u2 - 1/(-u1)
1/f2 = 1/u2 + 1/u1
Substituting the value of v' = -u2, we get:
1/f2 = 1/u1 - 1/v'
1/f2 = 1/u1 + 1/(-u2)
1/f2 = (u2-u1

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Question Description
A concave mirror of focal length f1 is placed at a distance of d from a convex lens of focal length f2. A beam of light coming from infinity and falling on this convex lens - concave mirror combination returns to infinity. The distance d must equala)f1+ f2b)−f1+ f2c)2f1 + f2d)−2f1 + f2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about A concave mirror of focal length f1 is placed at a distance of d from a convex lens of focal length f2. A beam of light coming from infinity and falling on this convex lens - concave mirror combination returns to infinity. The distance d must equala)f1+ f2b)−f1+ f2c)2f1 + f2d)−2f1 + f2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A concave mirror of focal length f1 is placed at a distance of d from a convex lens of focal length f2. A beam of light coming from infinity and falling on this convex lens - concave mirror combination returns to infinity. The distance d must equala)f1+ f2b)−f1+ f2c)2f1 + f2d)−2f1 + f2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
A concave mirror of focal length f1 is placed at a distance of d from a convex lens of focal length f2. A beam of light coming from infinity and falling on this convex lens - concave mirror combination returns to infinity. The distance d must equala)f1+ f2b)−f1+ f2c)2f1 + f2d)−2f1 + f2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about A concave mirror of focal length f1 is placed at a distance of d from a convex lens of focal length f2. A beam of light coming from infinity and falling on this convex lens - concave mirror combination returns to infinity. The distance d must equala)f1+ f2b)−f1+ f2c)2f1 + f2d)−2f1 + f2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A concave mirror of focal length f1 is placed at a distance of d from a convex lens of focal length f2. A beam of light coming from infinity and falling on this convex lens - concave mirror combination returns to infinity. The distance d must equala)f1+ f2b)−f1+ f2c)2f1 + f2d)−2f1 + f2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A concave mirror of focal length f1 is placed at a distance of d from a convex lens of focal length f2. A beam of light coming from infinity and falling on this convex lens - concave mirror combination returns to infinity. The distance d must equala)f1+ f2b)−f1+ f2c)2f1 + f2d)−2f1 + f2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A concave mirror of focal length f1 is placed at a distance of d from a convex lens of focal length f2. A beam of light coming from infinity and falling on this convex lens - concave mirror combination returns to infinity. The distance d must equala)f1+ f2b)−f1+ f2c)2f1 + f2d)−2f1 + f2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A concave mirror of focal length f1 is placed at a distance of d from a convex lens of focal length f2. A beam of light coming from infinity and falling on this convex lens - concave mirror combination returns to infinity. The distance d must equala)f1+ f2b)−f1+ f2c)2f1 + f2d)−2f1 + f2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A concave mirror of focal length f1 is placed at a distance of d from a convex lens of focal length f2. A beam of light coming from infinity and falling on this convex lens - concave mirror combination returns to infinity. The distance d must equala)f1+ f2b)−f1+ f2c)2f1 + f2d)−2f1 + f2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A concave mirror of focal length f1 is placed at a distance of d from a convex lens of focal length f2. A beam of light coming from infinity and falling on this convex lens - concave mirror combination returns to infinity. The distance d must equala)f1+ f2b)−f1+ f2c)2f1 + f2d)−2f1 + f2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A concave mirror of focal length f1 is placed at a distance of d from a convex lens of focal length f2. A beam of light coming from infinity and falling on this convex lens - concave mirror combination returns to infinity. The distance d must equala)f1+ f2b)−f1+ f2c)2f1 + f2d)−2f1 + f2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















