NEET Exam > NEET Questions > The inhibitor which does not resemble the sub...
Start Learning for Free
The inhibitor which does not resemble the substrate in structure and binds to the enzyme at site other than the active site is called
- a)Competitive inhibitor
- b)Non-competitive inhibitor
- c)Activator
- d)Substrate analogue
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
The inhibitor which does not resemble the substrate in structure and b...
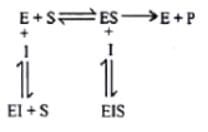
In non-competitve inhibition, the inhibitor binds at a site other than the active site ob the enzyme surface. This binding impairs the enzyme function. The inhibitor has no structural resemblance with the sunstrate. It does not interfere with the enzyme-substrate binding but the catalysis is prevented, possibly due to a distortion in the enzyme conformation. Non-competitive inhibition is usually irreversible because it cannot be overcome by increasing the substrate concentration. The inhibitor (l) generally binds with the enzyme as well as the ES complex. The overall relation in non.competitve inhibition is represented as :
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The inhibitor which does not resemble the substrate in structure and b...
Non-competitive inhibitor:
Non-competitive inhibitors are molecules that bind to an enzyme at a site other than the active site. They do not resemble the substrate in structure. These inhibitors inhibit enzyme activity by changing the shape of the enzyme, making it less effective in catalyzing the reaction.
Mechanism of action:
- Non-competitive inhibitors bind to the enzyme at an allosteric site, causing a conformational change in the enzyme.
- This conformational change may prevent the substrate from binding to the active site or inhibit the catalytic activity of the enzyme.
- Since non-competitive inhibitors do not compete with the substrate for the active site, increasing substrate concentration will not overcome their inhibitory effect.
Characteristics:
- Non-competitive inhibitors do not compete with the substrate for binding to the enzyme.
- They can bind to the enzyme-substrate complex as well as the free enzyme.
- The inhibition by non-competitive inhibitors is not easily reversible.
- These inhibitors are not affected by changes in substrate concentration.
Examples:
- Heavy metal ions like mercury and lead are examples of non-competitive inhibitors.
- Drugs like aspirin and certain antibiotics also act as non-competitive inhibitors of specific enzymes.
In conclusion, non-competitive inhibitors are molecules that bind to an enzyme at a site other than the active site, causing a conformational change that inhibits enzyme activity.
Non-competitive inhibitors are molecules that bind to an enzyme at a site other than the active site. They do not resemble the substrate in structure. These inhibitors inhibit enzyme activity by changing the shape of the enzyme, making it less effective in catalyzing the reaction.
Mechanism of action:
- Non-competitive inhibitors bind to the enzyme at an allosteric site, causing a conformational change in the enzyme.
- This conformational change may prevent the substrate from binding to the active site or inhibit the catalytic activity of the enzyme.
- Since non-competitive inhibitors do not compete with the substrate for the active site, increasing substrate concentration will not overcome their inhibitory effect.
Characteristics:
- Non-competitive inhibitors do not compete with the substrate for binding to the enzyme.
- They can bind to the enzyme-substrate complex as well as the free enzyme.
- The inhibition by non-competitive inhibitors is not easily reversible.
- These inhibitors are not affected by changes in substrate concentration.
Examples:
- Heavy metal ions like mercury and lead are examples of non-competitive inhibitors.
- Drugs like aspirin and certain antibiotics also act as non-competitive inhibitors of specific enzymes.
In conclusion, non-competitive inhibitors are molecules that bind to an enzyme at a site other than the active site, causing a conformational change that inhibits enzyme activity.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Question Description
The inhibitor which does not resemble the substrate in structure and binds to the enzyme at site other than the active site is calleda)Competitive inhibitorb)Non-competitive inhibitorc)Activatord)Substrate analogueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about The inhibitor which does not resemble the substrate in structure and binds to the enzyme at site other than the active site is calleda)Competitive inhibitorb)Non-competitive inhibitorc)Activatord)Substrate analogueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The inhibitor which does not resemble the substrate in structure and binds to the enzyme at site other than the active site is calleda)Competitive inhibitorb)Non-competitive inhibitorc)Activatord)Substrate analogueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
The inhibitor which does not resemble the substrate in structure and binds to the enzyme at site other than the active site is calleda)Competitive inhibitorb)Non-competitive inhibitorc)Activatord)Substrate analogueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about The inhibitor which does not resemble the substrate in structure and binds to the enzyme at site other than the active site is calleda)Competitive inhibitorb)Non-competitive inhibitorc)Activatord)Substrate analogueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The inhibitor which does not resemble the substrate in structure and binds to the enzyme at site other than the active site is calleda)Competitive inhibitorb)Non-competitive inhibitorc)Activatord)Substrate analogueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The inhibitor which does not resemble the substrate in structure and binds to the enzyme at site other than the active site is calleda)Competitive inhibitorb)Non-competitive inhibitorc)Activatord)Substrate analogueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The inhibitor which does not resemble the substrate in structure and binds to the enzyme at site other than the active site is calleda)Competitive inhibitorb)Non-competitive inhibitorc)Activatord)Substrate analogueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The inhibitor which does not resemble the substrate in structure and binds to the enzyme at site other than the active site is calleda)Competitive inhibitorb)Non-competitive inhibitorc)Activatord)Substrate analogueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The inhibitor which does not resemble the substrate in structure and binds to the enzyme at site other than the active site is calleda)Competitive inhibitorb)Non-competitive inhibitorc)Activatord)Substrate analogueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The inhibitor which does not resemble the substrate in structure and binds to the enzyme at site other than the active site is calleda)Competitive inhibitorb)Non-competitive inhibitorc)Activatord)Substrate analogueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The inhibitor which does not resemble the substrate in structure and binds to the enzyme at site other than the active site is calleda)Competitive inhibitorb)Non-competitive inhibitorc)Activatord)Substrate analogueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















