NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Michaelis Menten Constant(Km)is equal toa)The...
Start Learning for Free
Michaelis Menten Constant (Km) is equal to
- a)The rate of reaction
- b)The rate of enzymatic activity
- c)Substrate concentration at which the reaction attains half of its maximum velocity
- d)Substrate concentration at which the rate of reaction is maximum
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Michaelis Menten Constant(Km)is equal toa)The rate of reactionb)The ra...
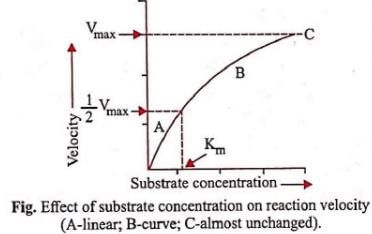
Km or the Michaelis-Menten constant is defined as the substrate concentration (expressed in moles/l) at which half-maximum velocity in an enzyme catalysed reaction is achieved. It indicates that half of the enzyme molecules (i.e. 50%) are bound with the substrate molecules when the substrate concentration equals the Km value. It was given by Leonor Michaelis and Maud Menten (1913). Km value is a characteristic feature of a given enzyme. It is a representative for measuring the strength of ES complex. A low Km value indicates a strong affinity between enzyme and substrate, whereas a high Km value reflects a weak affinity between them. For majority of enzymes, the Km values are in the range of 10−5 to 10−2 moles.

Most Upvoted Answer
Michaelis Menten Constant(Km)is equal toa)The rate of reactionb)The ra...
Substrate concentration at which the reaction attains half of its maximum velocity
The Michaelis-Menten constant (Km) is a parameter used in enzyme kinetics to describe the affinity of an enzyme for its substrate. It is defined as the substrate concentration at which the reaction rate is half of its maximum velocity.
Enzyme Kinetics
Enzyme kinetics is the study of the rates at which enzymes catalyze chemical reactions. It involves the measurement of reaction rates under different conditions, including varying substrate concentrations.
Michaelis-Menten Equation
The Michaelis-Menten equation is a mathematical model that describes the relationship between the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction and the substrate concentration. It is given by the equation:
v = (Vmax * [S]) / (Km + [S])
Where:
- v is the reaction rate or velocity
- Vmax is the maximum velocity of the reaction
- [S] is the substrate concentration
- Km is the Michaelis-Menten constant
Interpreting Km
The Michaelis-Menten constant (Km) is a measure of the affinity of the enzyme for its substrate. It represents the substrate concentration at which the reaction rate is half of its maximum velocity.
When the substrate concentration is below Km, the rate of the reaction is relatively slow because there is not enough substrate available to saturate the enzyme. As the substrate concentration increases and approaches Km, the rate of the reaction increases.
Once the substrate concentration exceeds Km, the rate of the reaction reaches its maximum velocity (Vmax). At this point, the enzyme is saturated with substrate and all active sites are occupied. Further increases in substrate concentration will not increase the rate of the reaction.
Therefore, the correct answer is option C: Km represents the substrate concentration at which the reaction attains half of its maximum velocity.
The Michaelis-Menten constant (Km) is a parameter used in enzyme kinetics to describe the affinity of an enzyme for its substrate. It is defined as the substrate concentration at which the reaction rate is half of its maximum velocity.
Enzyme Kinetics
Enzyme kinetics is the study of the rates at which enzymes catalyze chemical reactions. It involves the measurement of reaction rates under different conditions, including varying substrate concentrations.
Michaelis-Menten Equation
The Michaelis-Menten equation is a mathematical model that describes the relationship between the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction and the substrate concentration. It is given by the equation:
v = (Vmax * [S]) / (Km + [S])
Where:
- v is the reaction rate or velocity
- Vmax is the maximum velocity of the reaction
- [S] is the substrate concentration
- Km is the Michaelis-Menten constant
Interpreting Km
The Michaelis-Menten constant (Km) is a measure of the affinity of the enzyme for its substrate. It represents the substrate concentration at which the reaction rate is half of its maximum velocity.
When the substrate concentration is below Km, the rate of the reaction is relatively slow because there is not enough substrate available to saturate the enzyme. As the substrate concentration increases and approaches Km, the rate of the reaction increases.
Once the substrate concentration exceeds Km, the rate of the reaction reaches its maximum velocity (Vmax). At this point, the enzyme is saturated with substrate and all active sites are occupied. Further increases in substrate concentration will not increase the rate of the reaction.
Therefore, the correct answer is option C: Km represents the substrate concentration at which the reaction attains half of its maximum velocity.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Question Description
Michaelis Menten Constant(Km)is equal toa)The rate of reactionb)The rate of enzymatic activityc)Substrate concentration at which the reaction attains half of its maximum velocityd)Substrate concentration at which the rate of reaction is maximumCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Michaelis Menten Constant(Km)is equal toa)The rate of reactionb)The rate of enzymatic activityc)Substrate concentration at which the reaction attains half of its maximum velocityd)Substrate concentration at which the rate of reaction is maximumCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Michaelis Menten Constant(Km)is equal toa)The rate of reactionb)The rate of enzymatic activityc)Substrate concentration at which the reaction attains half of its maximum velocityd)Substrate concentration at which the rate of reaction is maximumCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Michaelis Menten Constant(Km)is equal toa)The rate of reactionb)The rate of enzymatic activityc)Substrate concentration at which the reaction attains half of its maximum velocityd)Substrate concentration at which the rate of reaction is maximumCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Michaelis Menten Constant(Km)is equal toa)The rate of reactionb)The rate of enzymatic activityc)Substrate concentration at which the reaction attains half of its maximum velocityd)Substrate concentration at which the rate of reaction is maximumCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Michaelis Menten Constant(Km)is equal toa)The rate of reactionb)The rate of enzymatic activityc)Substrate concentration at which the reaction attains half of its maximum velocityd)Substrate concentration at which the rate of reaction is maximumCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Michaelis Menten Constant(Km)is equal toa)The rate of reactionb)The rate of enzymatic activityc)Substrate concentration at which the reaction attains half of its maximum velocityd)Substrate concentration at which the rate of reaction is maximumCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Michaelis Menten Constant(Km)is equal toa)The rate of reactionb)The rate of enzymatic activityc)Substrate concentration at which the reaction attains half of its maximum velocityd)Substrate concentration at which the rate of reaction is maximumCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Michaelis Menten Constant(Km)is equal toa)The rate of reactionb)The rate of enzymatic activityc)Substrate concentration at which the reaction attains half of its maximum velocityd)Substrate concentration at which the rate of reaction is maximumCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Michaelis Menten Constant(Km)is equal toa)The rate of reactionb)The rate of enzymatic activityc)Substrate concentration at which the reaction attains half of its maximum velocityd)Substrate concentration at which the rate of reaction is maximumCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Michaelis Menten Constant(Km)is equal toa)The rate of reactionb)The rate of enzymatic activityc)Substrate concentration at which the reaction attains half of its maximum velocityd)Substrate concentration at which the rate of reaction is maximumCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Michaelis Menten Constant(Km)is equal toa)The rate of reactionb)The rate of enzymatic activityc)Substrate concentration at which the reaction attains half of its maximum velocityd)Substrate concentration at which the rate of reaction is maximumCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























