Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > In a Schering bridge, the dial of the variabl...
Start Learning for Free
In a Schering bridge, the dial of the variable capacitor is calibrated directly in terms of the dissipation factor of the unknown arm. At 50 Hz frequency, the value of the dissipation factor of the unknown capacitor was found to be D. What would be the value of the dissipation factor at 60 Hz
- a)6 D
- b)1 / 6 D
- c)5 / 6 D
- d)6 / 5 D
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
In a Schering bridge, the dial of the variable capacitor is calibrated...
Concept:
Schering bridge:
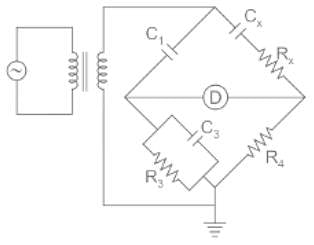
At bridge balance condition,


At bridge balance condition,

⇒ R4Cx (1 + jωR3C3) = R3C1 (1 + jω Cx Rx)
By comparing both sides

Dissipation factor = ωCxRx = ωR3C3 = 2πf R3C3

Dissipation factor = ωCxRx = ωR3C3 = 2πf R3C3
Dissipation factor α frequency(f) --------(1)
Calculation:
Given:
Dissipation factor D at frequency 50Hz
Let Dissipation factor x at frequency 60Hz
From equation 1:
f1/f2 = D/z
x = 6/5 D
f1/f2 = D/z
x = 6/5 D
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
In a Schering bridge, the dial of the variable capacitor is calibrated...
Dissipation Factor in Schering Bridge
The dissipation factor (D) of a capacitor is a measure of its efficiency, representing the ratio of the resistive power loss to the reactive power stored. The Schering bridge is commonly used to measure the dissipation factor at various frequencies.
Frequency Dependence of Dissipation Factor
- The dissipation factor varies with frequency.
- A higher frequency typically results in a lower dissipation factor due to reduced resistive losses in the capacitor.
Given Conditions
- At 50 Hz, the dissipation factor of the unknown capacitor is D.
- We need to determine the dissipation factor at 60 Hz.
Calculating the New Dissipation Factor
- The relationship between the dissipation factor and frequency can be approximated as:
\[ D_{60} = D_{50} \times \left( \frac{f_{50}}{f_{60}} \right) \]
- Substituting the known frequencies:
\[ D_{60} = D \times \left( \frac{50}{60} \right) \]
Final Calculation
- Rearranging gives:
\[ D_{60} = D \times \frac{5}{6} \]
Conclusion
- The dissipation factor at 60 Hz is \( \frac{5}{6} D \).
- Therefore, the correct answer is option **D: \(\frac{6}{5} D\)**.
This indicates that as frequency increases from 50 Hz to 60 Hz, the dissipation factor decreases, confirming the inverse relationship with frequency changes in capacitive elements.
The dissipation factor (D) of a capacitor is a measure of its efficiency, representing the ratio of the resistive power loss to the reactive power stored. The Schering bridge is commonly used to measure the dissipation factor at various frequencies.
Frequency Dependence of Dissipation Factor
- The dissipation factor varies with frequency.
- A higher frequency typically results in a lower dissipation factor due to reduced resistive losses in the capacitor.
Given Conditions
- At 50 Hz, the dissipation factor of the unknown capacitor is D.
- We need to determine the dissipation factor at 60 Hz.
Calculating the New Dissipation Factor
- The relationship between the dissipation factor and frequency can be approximated as:
\[ D_{60} = D_{50} \times \left( \frac{f_{50}}{f_{60}} \right) \]
- Substituting the known frequencies:
\[ D_{60} = D \times \left( \frac{50}{60} \right) \]
Final Calculation
- Rearranging gives:
\[ D_{60} = D \times \frac{5}{6} \]
Conclusion
- The dissipation factor at 60 Hz is \( \frac{5}{6} D \).
- Therefore, the correct answer is option **D: \(\frac{6}{5} D\)**.
This indicates that as frequency increases from 50 Hz to 60 Hz, the dissipation factor decreases, confirming the inverse relationship with frequency changes in capacitive elements.
Attention Electrical Engineering (EE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Electrical Engineering (EE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Electrical Engineering (EE).

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Similar Electrical Engineering (EE) Doubts
In a Schering bridge, the dial of the variable capacitor is calibrated directly in terms of the dissipation factor of the unknown arm. At 50 Hz frequency, the value of the dissipation factor of the unknown capacitor was found to be D. What would be the value of the dissipation factor at 60 Hza)6 Db)1 / 6 Dc)5 / 6 Dd)6 / 5 DCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
In a Schering bridge, the dial of the variable capacitor is calibrated directly in terms of the dissipation factor of the unknown arm. At 50 Hz frequency, the value of the dissipation factor of the unknown capacitor was found to be D. What would be the value of the dissipation factor at 60 Hza)6 Db)1 / 6 Dc)5 / 6 Dd)6 / 5 DCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about In a Schering bridge, the dial of the variable capacitor is calibrated directly in terms of the dissipation factor of the unknown arm. At 50 Hz frequency, the value of the dissipation factor of the unknown capacitor was found to be D. What would be the value of the dissipation factor at 60 Hza)6 Db)1 / 6 Dc)5 / 6 Dd)6 / 5 DCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In a Schering bridge, the dial of the variable capacitor is calibrated directly in terms of the dissipation factor of the unknown arm. At 50 Hz frequency, the value of the dissipation factor of the unknown capacitor was found to be D. What would be the value of the dissipation factor at 60 Hza)6 Db)1 / 6 Dc)5 / 6 Dd)6 / 5 DCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
In a Schering bridge, the dial of the variable capacitor is calibrated directly in terms of the dissipation factor of the unknown arm. At 50 Hz frequency, the value of the dissipation factor of the unknown capacitor was found to be D. What would be the value of the dissipation factor at 60 Hza)6 Db)1 / 6 Dc)5 / 6 Dd)6 / 5 DCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about In a Schering bridge, the dial of the variable capacitor is calibrated directly in terms of the dissipation factor of the unknown arm. At 50 Hz frequency, the value of the dissipation factor of the unknown capacitor was found to be D. What would be the value of the dissipation factor at 60 Hza)6 Db)1 / 6 Dc)5 / 6 Dd)6 / 5 DCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In a Schering bridge, the dial of the variable capacitor is calibrated directly in terms of the dissipation factor of the unknown arm. At 50 Hz frequency, the value of the dissipation factor of the unknown capacitor was found to be D. What would be the value of the dissipation factor at 60 Hza)6 Db)1 / 6 Dc)5 / 6 Dd)6 / 5 DCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for In a Schering bridge, the dial of the variable capacitor is calibrated directly in terms of the dissipation factor of the unknown arm. At 50 Hz frequency, the value of the dissipation factor of the unknown capacitor was found to be D. What would be the value of the dissipation factor at 60 Hza)6 Db)1 / 6 Dc)5 / 6 Dd)6 / 5 DCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In a Schering bridge, the dial of the variable capacitor is calibrated directly in terms of the dissipation factor of the unknown arm. At 50 Hz frequency, the value of the dissipation factor of the unknown capacitor was found to be D. What would be the value of the dissipation factor at 60 Hza)6 Db)1 / 6 Dc)5 / 6 Dd)6 / 5 DCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In a Schering bridge, the dial of the variable capacitor is calibrated directly in terms of the dissipation factor of the unknown arm. At 50 Hz frequency, the value of the dissipation factor of the unknown capacitor was found to be D. What would be the value of the dissipation factor at 60 Hza)6 Db)1 / 6 Dc)5 / 6 Dd)6 / 5 DCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for In a Schering bridge, the dial of the variable capacitor is calibrated directly in terms of the dissipation factor of the unknown arm. At 50 Hz frequency, the value of the dissipation factor of the unknown capacitor was found to be D. What would be the value of the dissipation factor at 60 Hza)6 Db)1 / 6 Dc)5 / 6 Dd)6 / 5 DCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of In a Schering bridge, the dial of the variable capacitor is calibrated directly in terms of the dissipation factor of the unknown arm. At 50 Hz frequency, the value of the dissipation factor of the unknown capacitor was found to be D. What would be the value of the dissipation factor at 60 Hza)6 Db)1 / 6 Dc)5 / 6 Dd)6 / 5 DCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In a Schering bridge, the dial of the variable capacitor is calibrated directly in terms of the dissipation factor of the unknown arm. At 50 Hz frequency, the value of the dissipation factor of the unknown capacitor was found to be D. What would be the value of the dissipation factor at 60 Hza)6 Db)1 / 6 Dc)5 / 6 Dd)6 / 5 DCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























