Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > The amount of copper used by a 3-wire distrib...
Start Learning for Free
The amount of copper used by a 3-wire distributor having the same maximum voltage to earth as compared to a 2-wire DC distributor is ______.
- a)33.3%
- b)69.75%
- c)66.7%
- d)31.25%
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
The amount of copper used by a 3-wire distributor having the same maxi...
Concept:
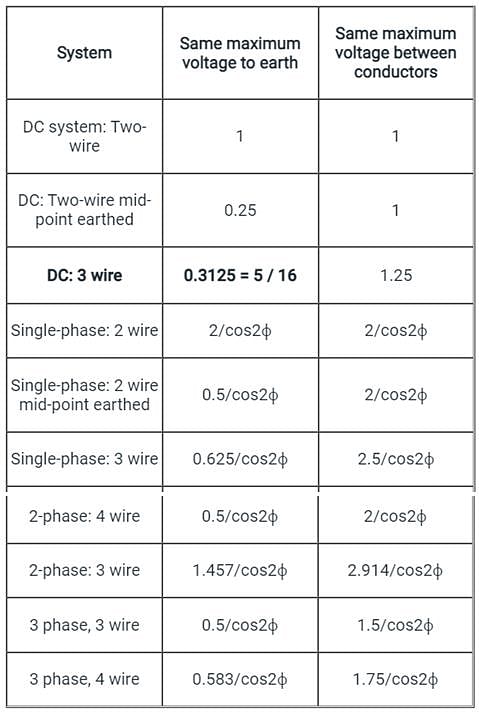
- For the same conductor length, the same amount of power, same losses and same maximum voltage to earth, 3 wire DC system requires a minimum conductor area.
- For transmitting the same amount of power at the same voltage, a three-phase transmission line requires less conductor material than a single-phase line; The three-phase transmission system is so cheaper
- For a given amount of power transmitted through a system, the three-phase system requires conductors with a smaller cross-sectional area; This means a saving of copper and thus the original installation costs are less.
Important Points:
- Below is given the table which shows the ratio of conductor-material in any system compared with that in the corresponding 2-wire DC system.
- Cos φ is the power factor in an AC system.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The amount of copper used by a 3-wire distributor having the same maxi...
Introduction:
In electrical distribution systems, the amount of copper used is an important factor to consider. Copper is a common material used in electrical conductors due to its high conductivity. Therefore, understanding the relationship between the number of wires in a distributor and the amount of copper required is essential.
Explanation:
To determine the amount of copper used by a 3-wire distributor compared to a 2-wire DC distributor, we need to analyze the differences in their wiring configurations and how it affects the copper requirement.
1. 2-wire DC Distributor:
In a 2-wire DC distributor, the system typically consists of a positive wire (hot) and a negative wire (neutral). The maximum voltage to earth, also known as the line-to-ground voltage, is the same for both wires.
2. 3-wire Distributor:
In a 3-wire distributor, the system usually consists of a three-phase power supply, with each phase having its own wire. The maximum voltage to earth is the same for all three wires.
Comparison:
To compare the copper requirement between the two systems, we need to consider the following factors:
a. Number of Conductors:
- In a 2-wire DC distributor, there are two conductors (positive and negative).
- In a 3-wire distributor, there are three conductors (three phases).
b. Current Carrying Capacity:
- The current carrying capacity of a conductor depends on its cross-sectional area. A larger cross-sectional area allows for higher current carrying capacity.
- In a 3-wire distributor, the three conductors can be sized smaller compared to a 2-wire DC distributor because the load is distributed across three phases. This is known as the skin effect.
c. Copper Requirement:
- The amount of copper used is directly proportional to the cross-sectional area of the conductors.
- Since the conductors in a 3-wire distributor can be smaller due to the skin effect, the total copper requirement is lower compared to a 2-wire DC distributor.
Conclusion:
Based on the above factors, the amount of copper used by a 3-wire distributor with the same maximum voltage to earth as compared to a 2-wire DC distributor is 31.25% (option D). This indicates a significant reduction in copper requirement for the 3-wire distributor.
In electrical distribution systems, the amount of copper used is an important factor to consider. Copper is a common material used in electrical conductors due to its high conductivity. Therefore, understanding the relationship between the number of wires in a distributor and the amount of copper required is essential.
Explanation:
To determine the amount of copper used by a 3-wire distributor compared to a 2-wire DC distributor, we need to analyze the differences in their wiring configurations and how it affects the copper requirement.
1. 2-wire DC Distributor:
In a 2-wire DC distributor, the system typically consists of a positive wire (hot) and a negative wire (neutral). The maximum voltage to earth, also known as the line-to-ground voltage, is the same for both wires.
2. 3-wire Distributor:
In a 3-wire distributor, the system usually consists of a three-phase power supply, with each phase having its own wire. The maximum voltage to earth is the same for all three wires.
Comparison:
To compare the copper requirement between the two systems, we need to consider the following factors:
a. Number of Conductors:
- In a 2-wire DC distributor, there are two conductors (positive and negative).
- In a 3-wire distributor, there are three conductors (three phases).
b. Current Carrying Capacity:
- The current carrying capacity of a conductor depends on its cross-sectional area. A larger cross-sectional area allows for higher current carrying capacity.
- In a 3-wire distributor, the three conductors can be sized smaller compared to a 2-wire DC distributor because the load is distributed across three phases. This is known as the skin effect.
c. Copper Requirement:
- The amount of copper used is directly proportional to the cross-sectional area of the conductors.
- Since the conductors in a 3-wire distributor can be smaller due to the skin effect, the total copper requirement is lower compared to a 2-wire DC distributor.
Conclusion:
Based on the above factors, the amount of copper used by a 3-wire distributor with the same maximum voltage to earth as compared to a 2-wire DC distributor is 31.25% (option D). This indicates a significant reduction in copper requirement for the 3-wire distributor.
Attention Electrical Engineering (EE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Electrical Engineering (EE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Electrical Engineering (EE).

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Similar Electrical Engineering (EE) Doubts
The amount of copper used by a 3-wire distributor having the same maximum voltage to earth as compared to a 2-wire DC distributor is ______.a)33.3%b)69.75%c)66.7%d)31.25%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The amount of copper used by a 3-wire distributor having the same maximum voltage to earth as compared to a 2-wire DC distributor is ______.a)33.3%b)69.75%c)66.7%d)31.25%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about The amount of copper used by a 3-wire distributor having the same maximum voltage to earth as compared to a 2-wire DC distributor is ______.a)33.3%b)69.75%c)66.7%d)31.25%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The amount of copper used by a 3-wire distributor having the same maximum voltage to earth as compared to a 2-wire DC distributor is ______.a)33.3%b)69.75%c)66.7%d)31.25%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
The amount of copper used by a 3-wire distributor having the same maximum voltage to earth as compared to a 2-wire DC distributor is ______.a)33.3%b)69.75%c)66.7%d)31.25%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about The amount of copper used by a 3-wire distributor having the same maximum voltage to earth as compared to a 2-wire DC distributor is ______.a)33.3%b)69.75%c)66.7%d)31.25%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The amount of copper used by a 3-wire distributor having the same maximum voltage to earth as compared to a 2-wire DC distributor is ______.a)33.3%b)69.75%c)66.7%d)31.25%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The amount of copper used by a 3-wire distributor having the same maximum voltage to earth as compared to a 2-wire DC distributor is ______.a)33.3%b)69.75%c)66.7%d)31.25%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The amount of copper used by a 3-wire distributor having the same maximum voltage to earth as compared to a 2-wire DC distributor is ______.a)33.3%b)69.75%c)66.7%d)31.25%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The amount of copper used by a 3-wire distributor having the same maximum voltage to earth as compared to a 2-wire DC distributor is ______.a)33.3%b)69.75%c)66.7%d)31.25%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The amount of copper used by a 3-wire distributor having the same maximum voltage to earth as compared to a 2-wire DC distributor is ______.a)33.3%b)69.75%c)66.7%d)31.25%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The amount of copper used by a 3-wire distributor having the same maximum voltage to earth as compared to a 2-wire DC distributor is ______.a)33.3%b)69.75%c)66.7%d)31.25%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The amount of copper used by a 3-wire distributor having the same maximum voltage to earth as compared to a 2-wire DC distributor is ______.a)33.3%b)69.75%c)66.7%d)31.25%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























